IB BIOLOGY B4.2 Ecological Niches
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Habitat abiotic factors
made up of non-living factors
Habitat biotic factors
other living organisms
Niche
a unique role that a species plays in its community, including habitat and activities
Obligate anaerobes
poisoned by oxygen (e.g. lives in soil, deep water, animal intestines) (the og prokaryotes)
obligate aerobes
require oxygen
What's hypoxia?
the reduction of O2 (oxygen)
What's anoxia?
The absence of O2 (oxygen)
Facultative anaerobes
Capable of anaerobic and aerobic respiration
Fundamental niche:
Fundamental niche: the potential of a species based on adaptations and tolerance limits.
Realized niche
Realized niche: actual extent of a species when in competition with another species
Autotrophs
Make their own food from inorganic substances
Heterotrophs
Must eat or absorb other organisms or their by-products for nutrition.
Holozoic nutrition
Ingestion, internal digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.
Mixotroph
can make their own food or ingest another organism for it.
Competitive exclusion principle
No two species in a community can occupy the same niche (one will die out and give way for other or both population numbers will decrease).
Saprotrophic nutrition
Decomposers. Secrete digestive enzymes and absorb the products of digestion
Archaea
One of the three domains of life. Obtain energy for ATP production through: 1) Photosynthesis, 2) chemosynthesis, 3) Heterotrophic nutrition.
Chemoautotroph
Energy created using chemical reactions and not the sun - chemosynthesis
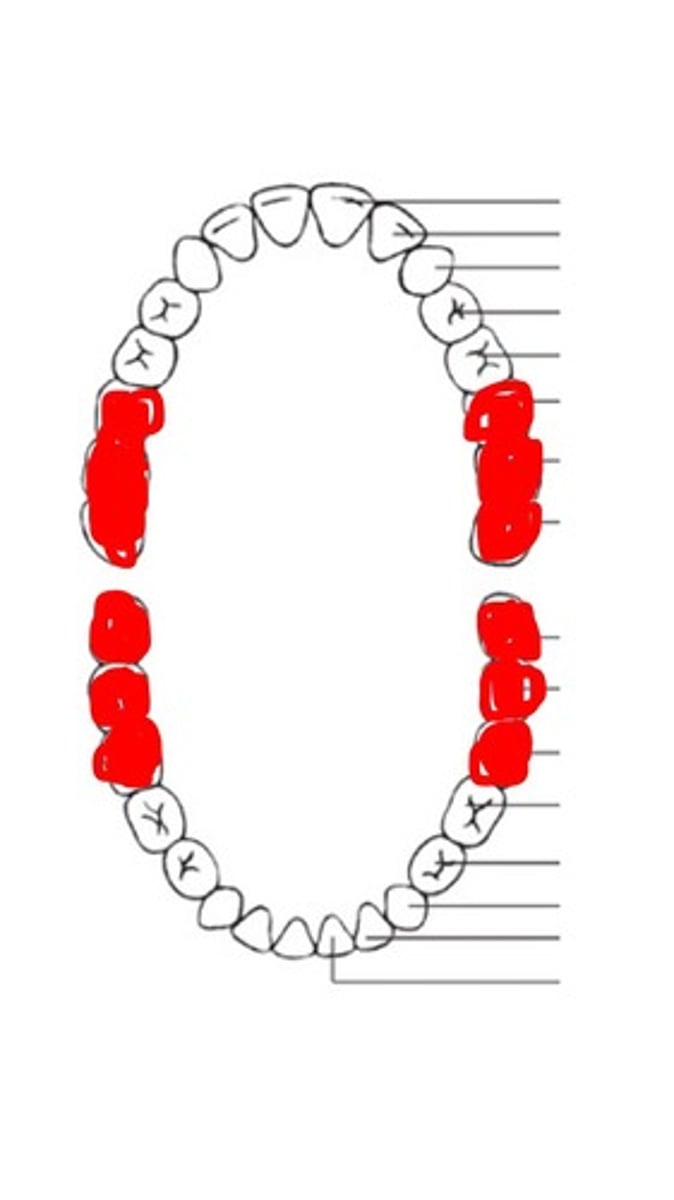
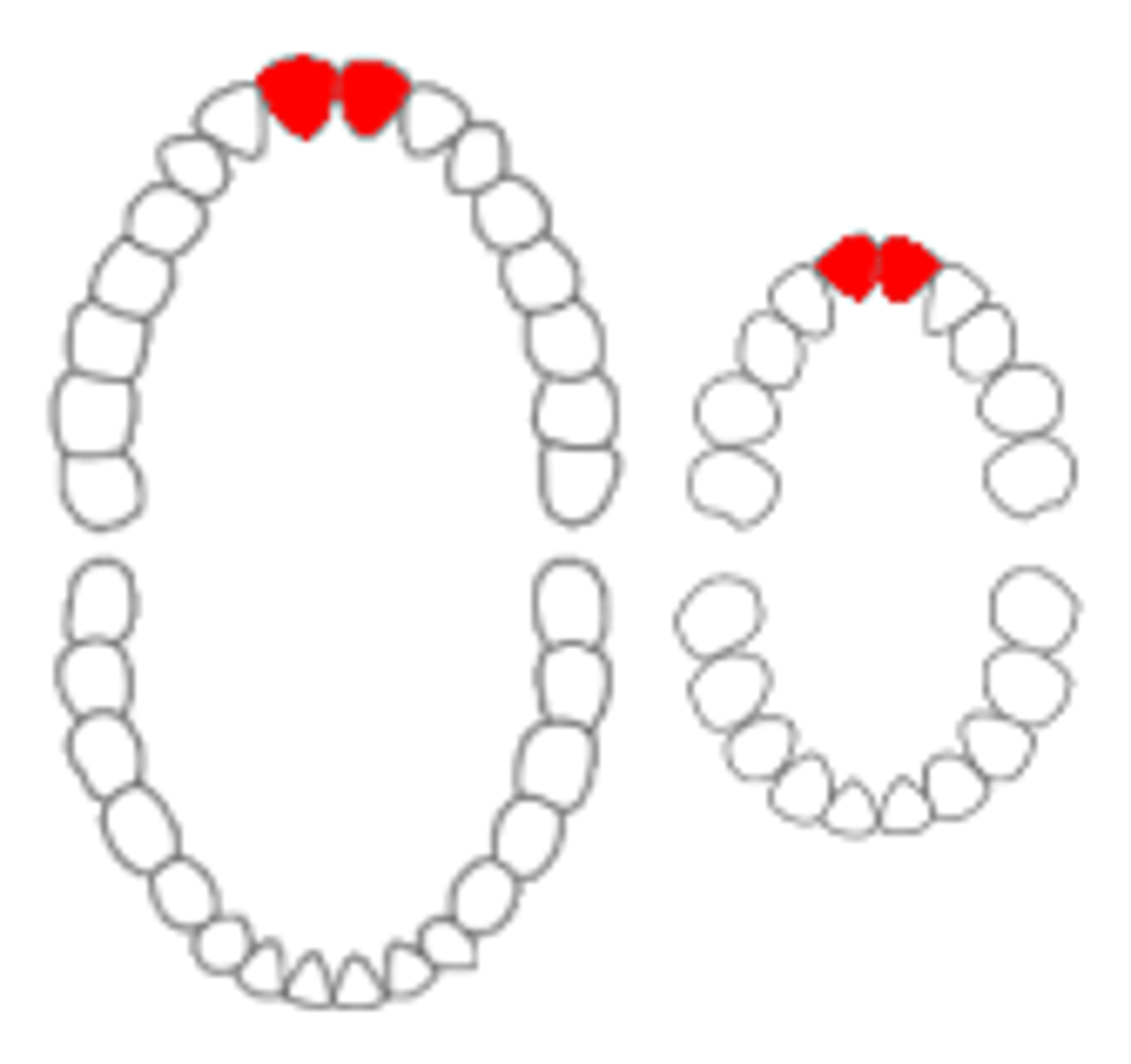
Incisors are for
cutting off bite-sized pieces of food
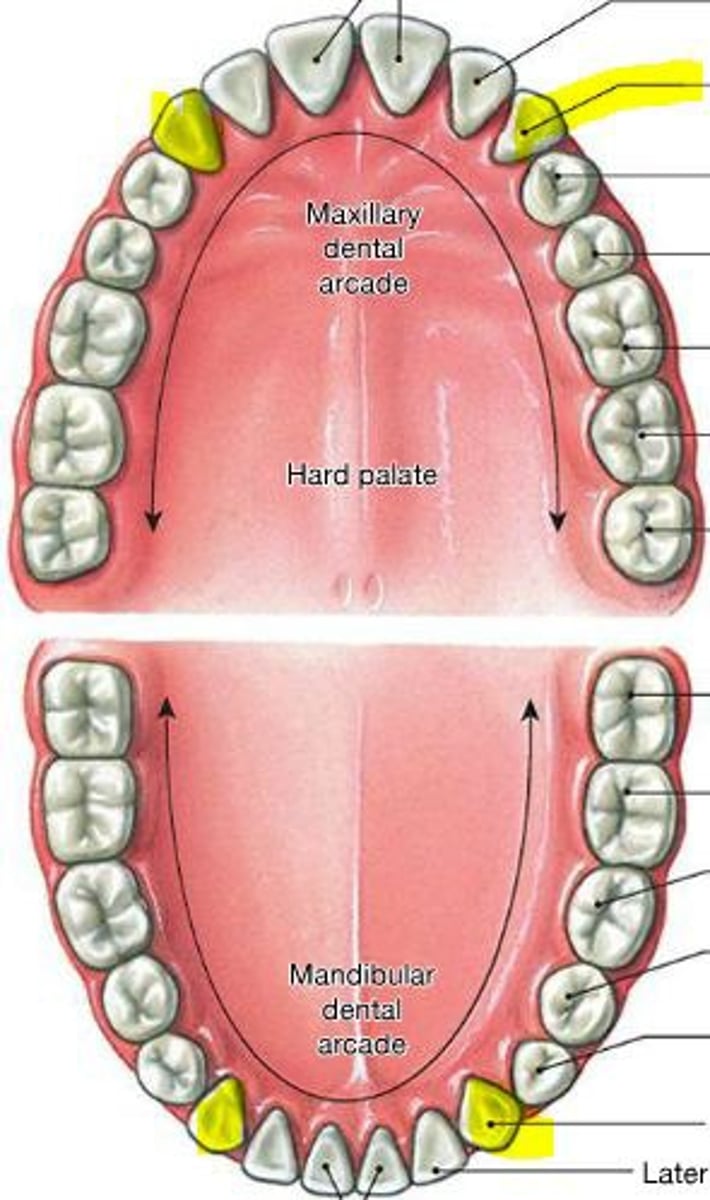
Canines are for
ripping meat and tougher foods. Are sharper
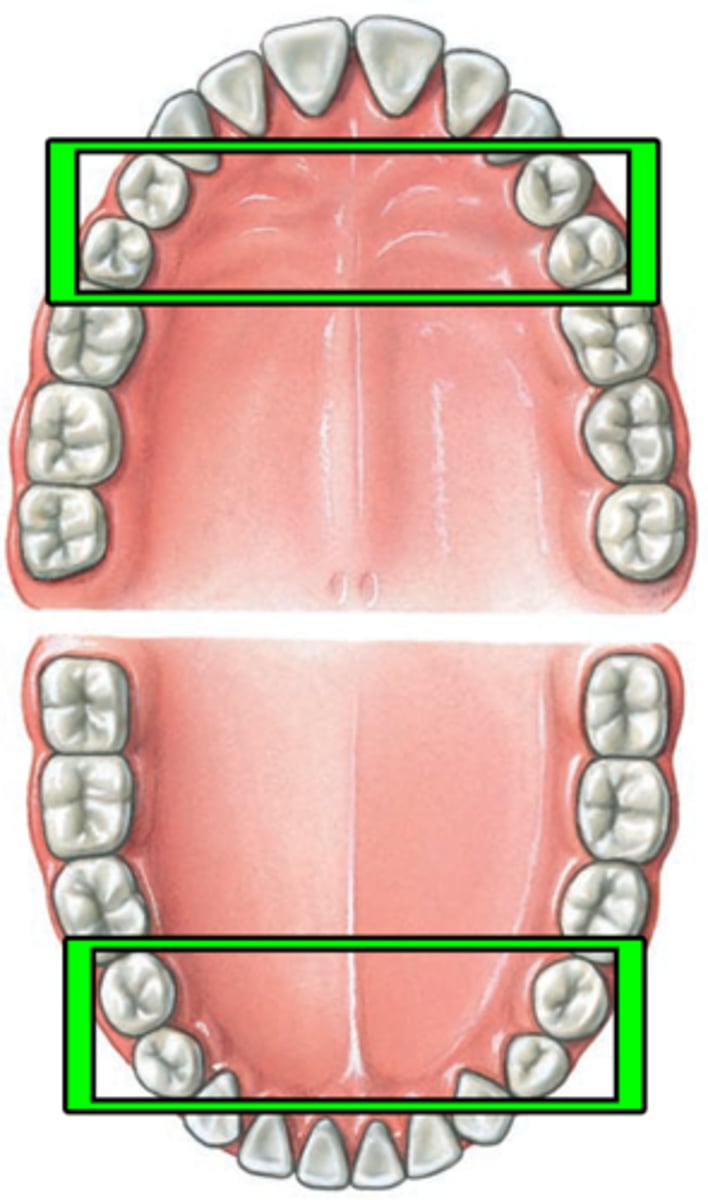
Premolars
For crushing up/slicing food
Molars are for
grinding food