Ch3 Sex Determination
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Sex Determination is two things?
Chromosomal and genetic
Sex determination involves what processes that produce the male and female characteristics of a species?
Genetic and biological processes
What is considered chromosomal sex?
The presence of chromosomes characteristics of each sex and is determined at the moment of fertilizaiton
What is phenotypic sex?
Is the internal and external morphology of each sex, and results from differences in gene expression
In mammalian sex determination what type of mammals have X and Y chromosomes?
Placental mammals
In mammals: males are ?
XY (normal), XXY or XYY
In mammals females are?
XX (normal), XO or XXX
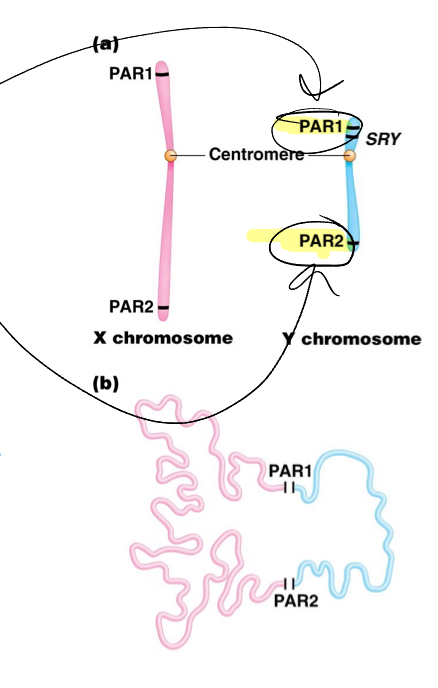
What are the two small regions of Homology that exist between X and Y chromosomes?
Pseudoautosomal regions? (PAR1 and PAR2)
The pseudoautosomal regions (PAR1 and PAR 2) allows what pairing between the X and Y at meiosis?
Homologous pairing
There is evidence that what occurs within the PAR1 and PAR2 regions? During meiosis
Crossing over
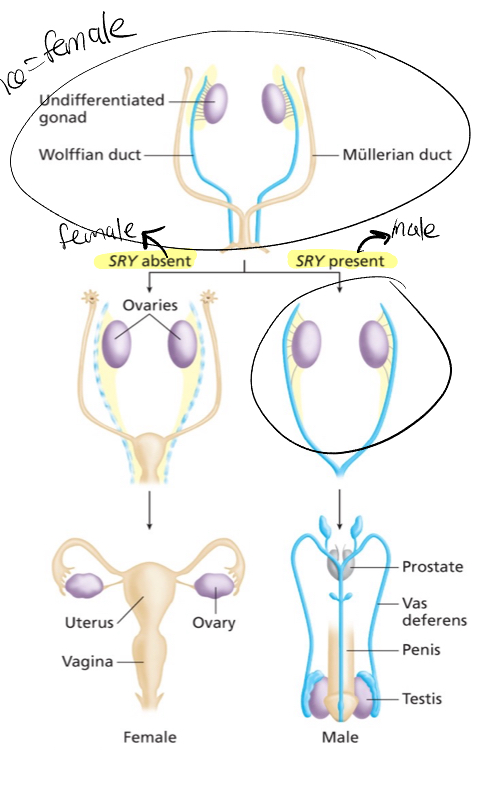
Early mammalian embryos have clusters of tissue called what? That can develop into?
Undifferentiated gonads, ovaries or testes
Sex determination depends on the presence of a sense of a single gene? Called? And found where?
SRY, found on the Y chromsome
SRY is a BLANK needed for male specific gene expression
Transcription factor
Expression of SRY intimates what type of development of undifferentiated gonads
Testicular development
The absence of SRY expression allows the BLANK to develop
Default female state
A different system called the BLANK is used by birds, some reptiles, some fish, butterflies and moths
Z/W system
In the Z/W system- what do females vs males have chromsome wise?
Females- two different sex chromosome (ZW)
Males- two sex chromosomes that are the same (ZZ)
Sex Chromsomes of the platypus consist of how many pairs of sex chromosomes and what do females vs males have
5 pairs of sex chromosomes
Females- 5 XX pairs
Males- 5 XY pairs
Sex Determination in Drosophila
Females have?
Males have?
Females- two X chromosomes, XXY or XX (normal)
Males- one X chromosome, XO, XYY, or XY (normal)
The dosage of the x chromosome in drosophila determines what?
The outcome of a sex determination gene regulation cascade
In drosophila what determines the gender based on the number of X chromosomes to sets of autosomes
And what is the male to female ratio?
The X/A ratio (X autosome ratio)
Males- X/A ratio of 0.5
Females- X/A ratio of 1.0
In organisms with sex chromosomes, there is BLANK between the copy number of genes on the sex chromosomes any mechanism that compensates for the differences in number of copies of genes between males and female is called BLANK
Gender imbalance
Dosage compensation
How many different mechanisms of dosage compensation are there?
Four
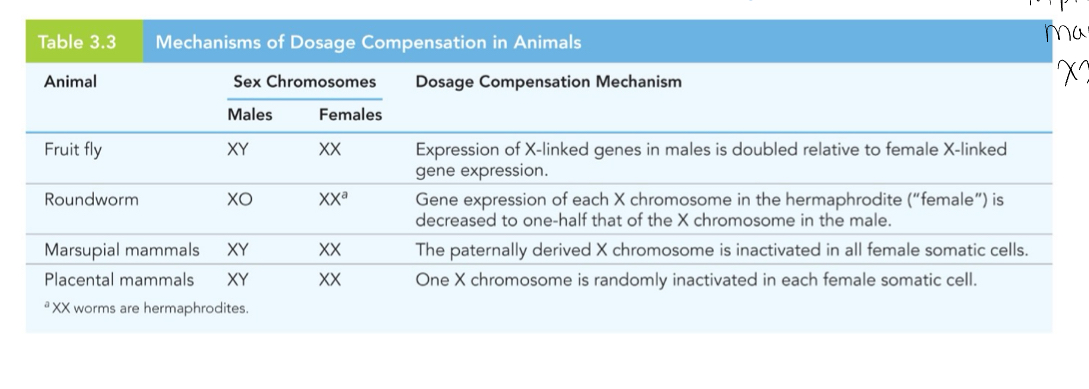
Early in mammalian development of the two BLANK in each female somatic cell is BLANK
X chromosomes, randomly inactivated
The random X inactivation hypothesis is also called the BLANK, after who and year?
Lyon hypothesis, Mary Lyon 1962
What is the name of the inactive X chromosome visible near nuclear wall first visualized by? And year?
Barr Body, Murray Barr 1949
What are female mammals considered?
Mosaics
Once inactivation has occurred in a cell, it is BLANK in all descendants of that cell
Permanent
Some female mammals are mosaics of two populations of cells one expresses BLANK and the other expresses BLANK
Maternal X and paternal X
Alleles of both chromosomes are expressed approximately BLANK over the whole organism
Equally
Calico and Tortoiseshell cats are BLANK mosaic
Visibly
In cats, the BLANK carriers a gene responsible for BLANK
X chromosome
Coat color
In such cats BLANK specifies a BLANK color, the other a bLANK color
One allele, black, yellow
Random X Inactivation in BLANK leads to a pattern of orange and black patches that is unique to each individual
Heterozygous females
Random X inactivation requires an X-linked gene called?
Xist (X-inactivation-specific-transcript)
Xist produces BLANK that spread it and cover (or paint) the chromosome to be inactivated
Large RNA molecules
Xist can only act on the chromosome from which it is being BLANK
Transcribed (not the homolog)
Some genes on the inactive X escape X inactivation
Humans Sex-linked transmission follows?
Distinct patterns
In X linked recessive inheritance females homozygous for the recessive allele or BLANK for it display the recessive phenotype
Males hemizygous
Can you describe hemizygous?
A diploid organism is hemizygous when only one copy is present the cell or organism is called a hemizygote, hemizygosity is also observed when one copy of a gene is deleted or int he heterogametic sex when a gene is located on a sex chromosome
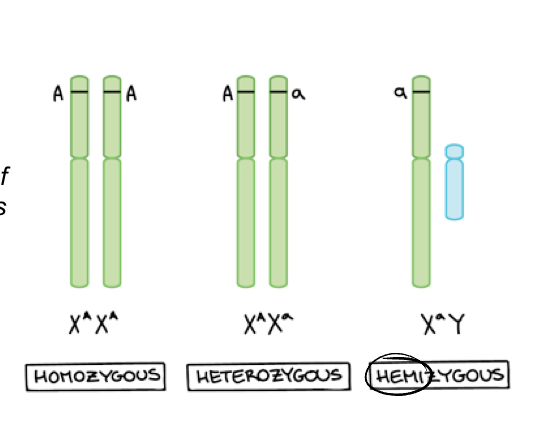
What display any allele on t heir single X whether the allele is recessive or dominant in females?
Hemizygous males
In BLANK traits heterozygous females and males hemizygous for the dominant allele express the dominant phenotype
X-linked dominant
A hallmark of recessive X-linked inheritance is the expression of the trait much more often in BLANK than BLANK
Males, females

The Features of X-linked Recessive Inheritance
Many more males than females have the trait due to BLANK
Hemizygosity
A recessive male mated to a homozygous dominant female produces all offspring with the dominant phenotypes and all BLANK are carriers
Female offspring
Mating of recessive males with carrier females give BLANK and BLANK of both sexes
Half dominant, and half recessive offspring
Mating of homozygous recessive females with dominant males produce all?
Dominant (carrier) female offspring and all recessive male offspring
Hemophilia A is a BLANK recessive trait?
X-linked
Hemophilia A is caused by a mutation in the BLANK gene on the X chromosome
Factor VIII
In Hemophilia A the mutant allele produces a?
Nonfunctional blood-clotting protein
A de-novo (newly occurring) mutation is thought to have been passed from?
Queen Victoria of England to some of her offspring
X-Linked Dominant Traits
Heterozygous females mated to wild type males transmit the dormant allele to half their progeny of each sex- dominant males mated to homozygous females pass the trait to all their daughters and none of their sons
The trait appears with relatively BLANK
Equal frequency in males and females
What is a rare X-linked dominant disorder?
Congenital Hypertrichosis (CGH)
What does CGH lead to?
A large increase in the number of hair follicles on the body, and males and females have more body hair than normal
Y-linked traits are transmitted in a?
Exclusively male-to-male pattern
In mammals there are fewer than BLANK on the Y chromosome, many play roles in sex determination or development
Genes on the human Y chromosome BLANK have a copy on the X chromosome
50
Do not