Systems Path Section 5 - The heart pg 100-end
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
reaction to group A beta hemolytic strep exotoxin (1-4 days after strep throat)
scarlet fever
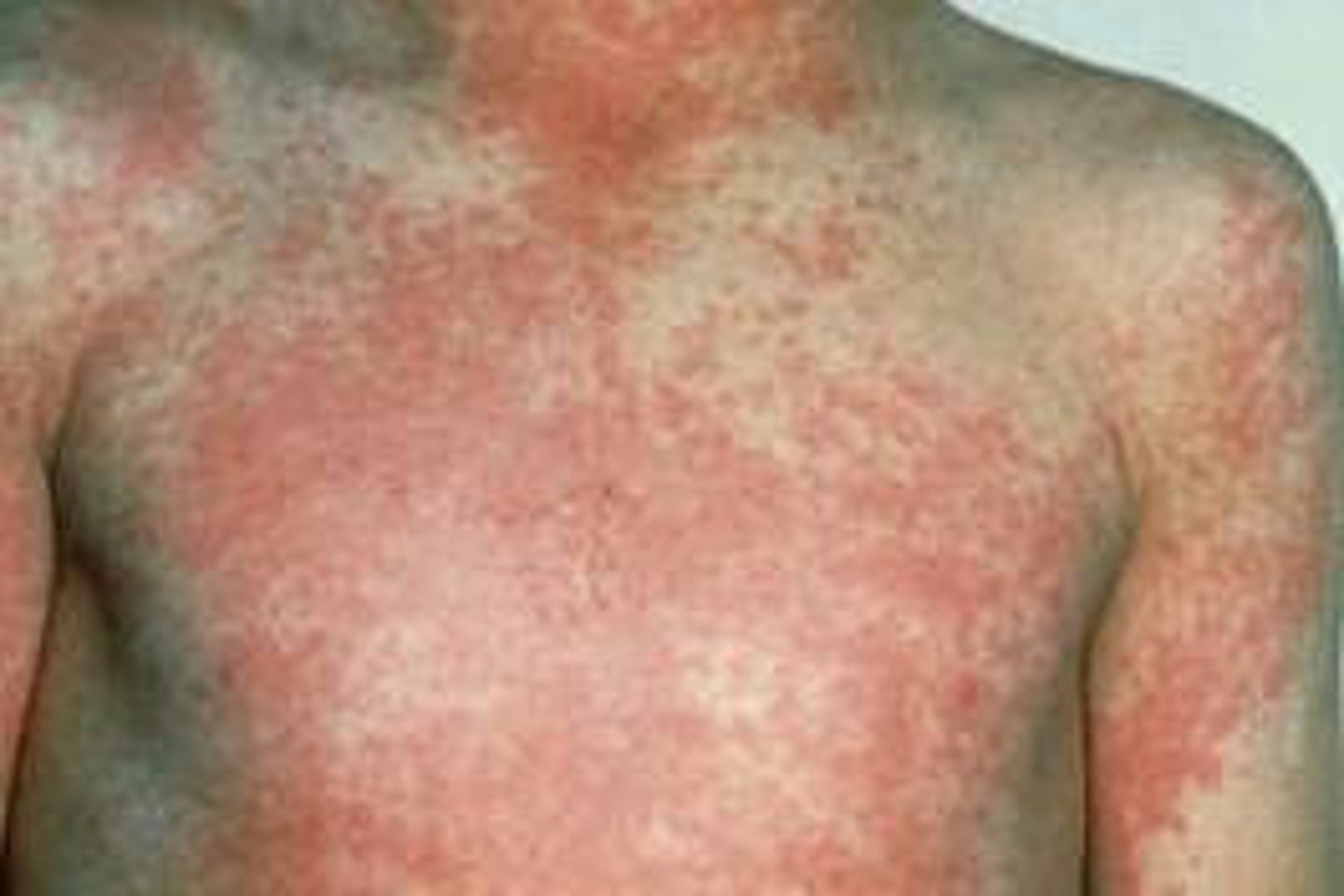
who is most likely to get scarlet fever
children
symptoms/signs of scarlet fever
sandpaper rash, circumpolar pallor, strawberry tongue,
complications of scarlet fever may result in...
septicemia and RF
MC bacterial infection of inner layer of heart and valves (MC left) causing flu-like symptoms producing lethal arrhythmia, renal failure, vegetations on valves and heart destruction
infective endocarditis
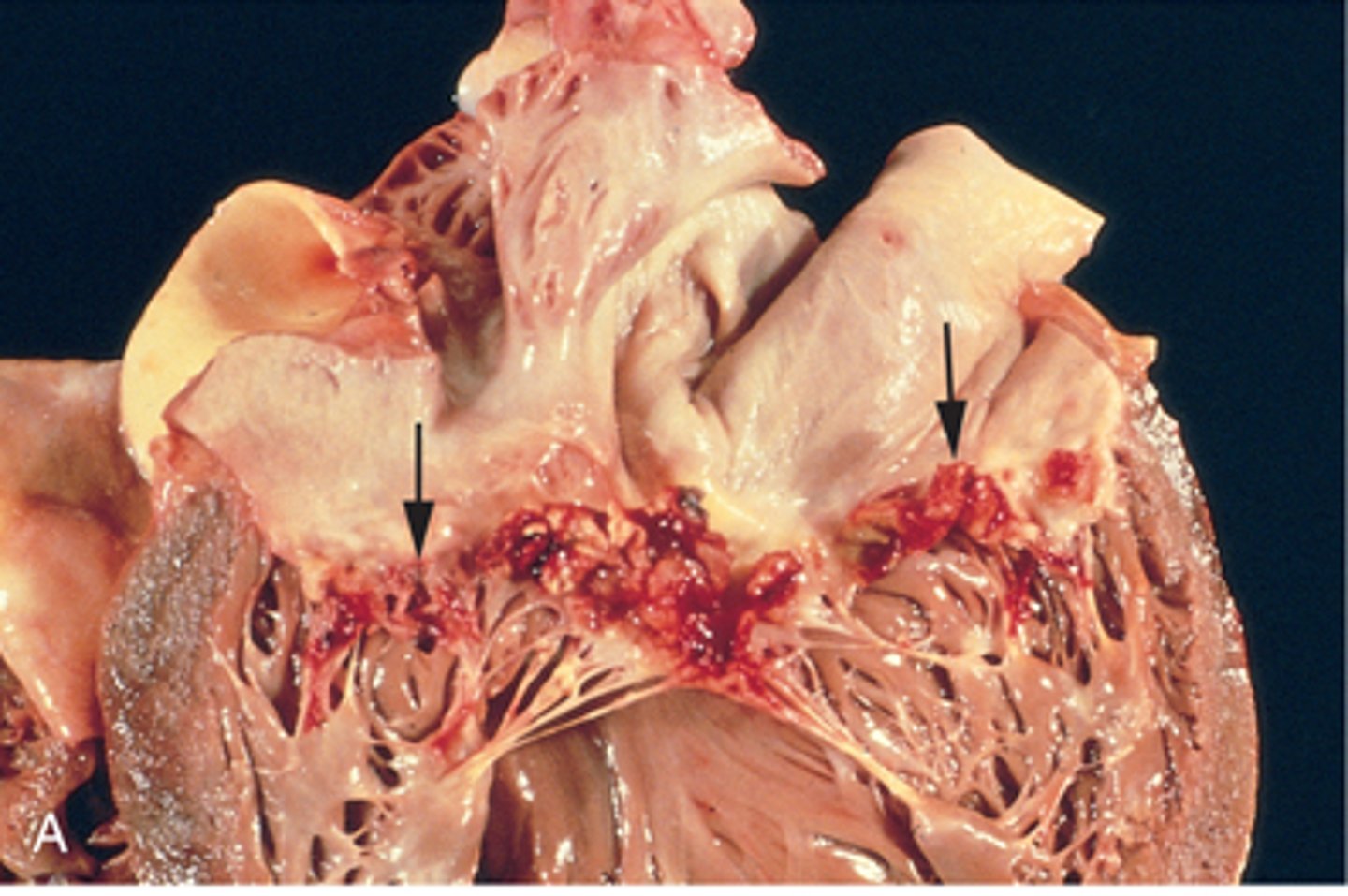
what type of infective endocarditis is destructive, difficult to treat, affects normal tissue and is caused by virulent staph. aureus
acute
what type of infective endocarditis is easy to treat, has low virulence, affects damaged tissue and is caused by low-virulence strep. viridans
subacute
who is more likely to get infective endocarditis?
this with prosthetic valve
possible sources of infection for infective endocarditis
skin infection, dental procedures, surgery
viral (MC) inflammation of heart wall
myocarditis
viral causes of myocarditis
covid, coxsackievirus A & B, HIV, CMV, influenza
non-viral causes of myocarditis
SLE, chagas disease, Lyme disease, toxoplasmosis
complications associated with myocarditis
arrhythmia and dilated heart wall
who/why may someone get myocarditis
viral infection by unknown agent
inflammation of pericardium (MC viral) causing "atypical chest pain"
pericarditis
Primary pericarditis
viral (MC), bacterial fungal
secondary pericarditis
MI, surgery, irradiation, RF, SLE, CA
Beck's triad for cardiac tamponade
low BP, JVD (distended neck veins), muffled heart sounds
how does someone get pericarditis?
inflammation leads to fibrosis and restriction within pericardium (potentially leading to edema and fibrosis/constriction)
MC prosthetic cardiac valve
mechanical
20% of infective endocarditis cases are caused by what?
prosthetic cardiac valve infection
disease of heart + muscle + disease
cardiomyopathy
types of cardiomyopathies
dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive
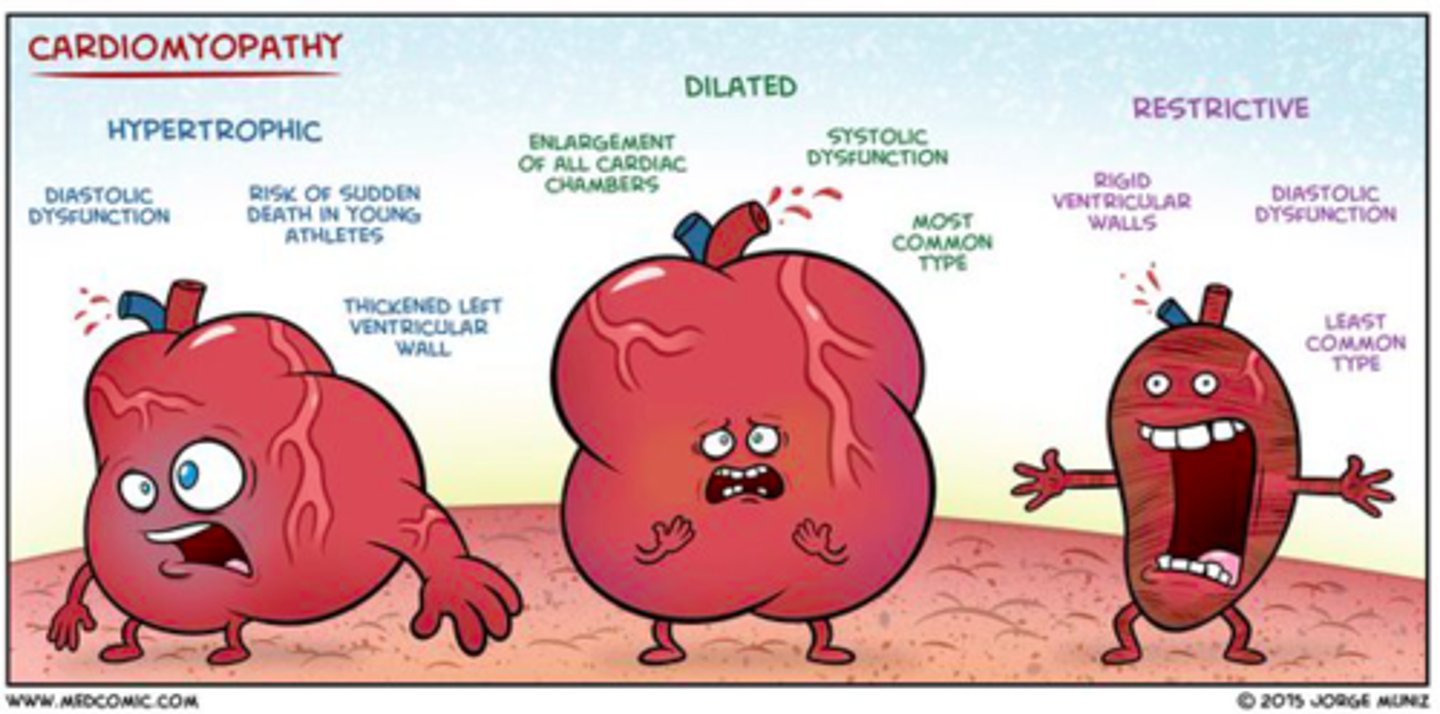
what accounts for 90% of all cardiomyopathies causing dilation of all chambers and progressive systolic dysfunction (dyspnea and fatigue)
dilated cardiomyopathy
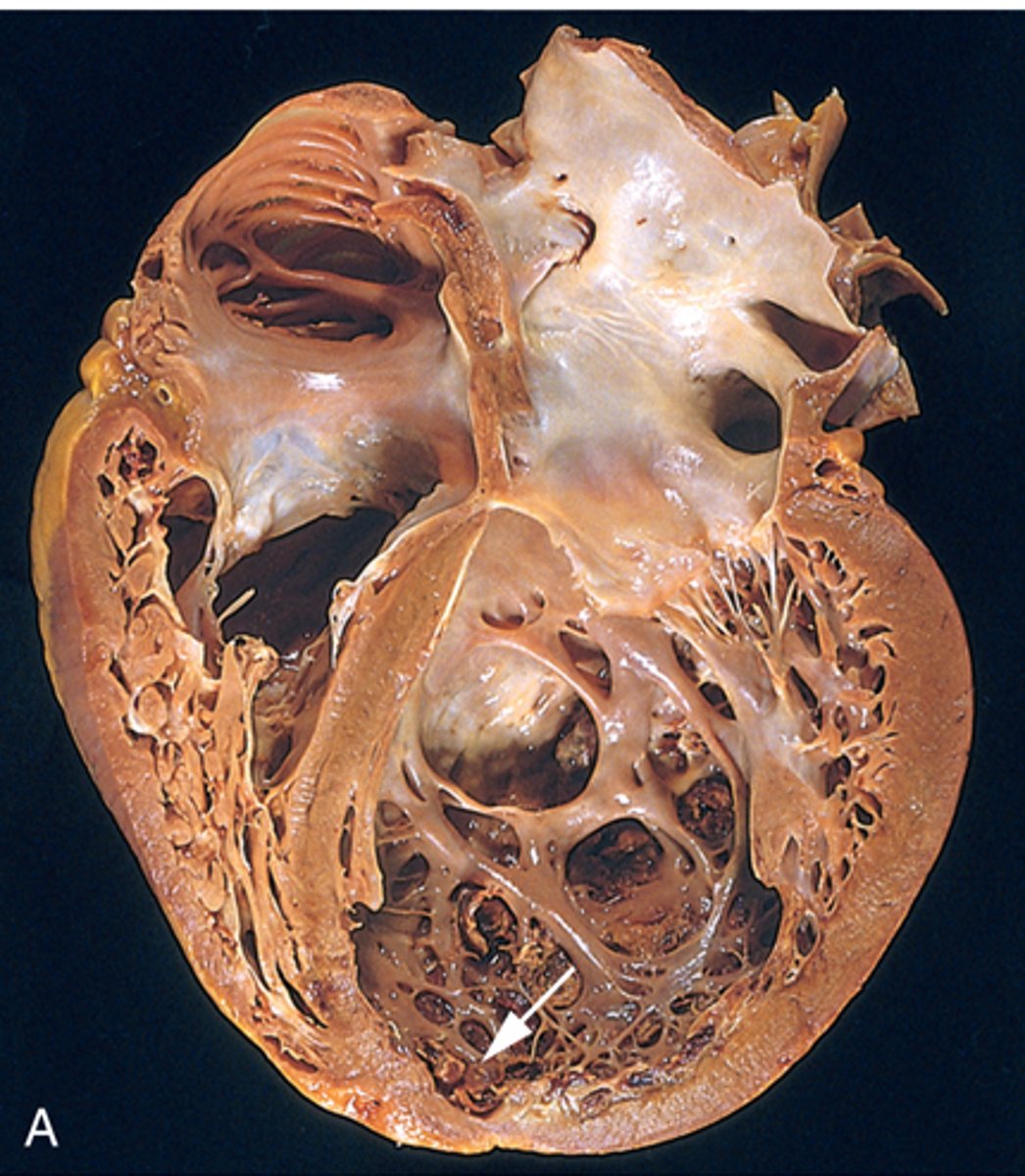
risks associated with dilated cardiomyopathy
genetics, CHF, viral infections, toxins, hemochromatosis, decreased thiamine
who is most likely to get dilated cardiomyopathy
20-50
genetic (MC B-myosin) hypercontractile sarcomeres leading to increased asymmetrical left ventricular hypertrophy and decreased cardiac output MC after puberty
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
signs and symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
hypertrophy, murmur, interstitial fibrosis, elongated L ventricle, dyspnea
asymmetrical septal hypertrophy is associated with which type of cardiomyopathy?
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
least common type of cardiomyopathy leading to diastolic dysfunction (failure of ventricles to fill) leading to decreased output, dyspnea, and fatigue
restrictive cardiomyopathy
how does someone get restrictive cardiomyopathy
stiffening and fibrosis of heart walls
who gets restrictive cardiomyopathy
MC in those with African ancestry
risk associated with developing restrictive cardiomyopathy
history of amyloidosis and heart damage due to irradiation/parasitic infection
cardiac neoplasms in adults
myxoma (MC), fibroma, lipoma
cardiac neoplasm in children
rhabdomyoma
what is a rhabdomyoma associated with?
Tuberous sclerosis
what is the MC cardiac neoplasm in adults which is benign, found in atria (MC left) and can be large
myxoma
how does someone get a myxoma?
mobile mass (wrecking ball) that can interfere with/damage valves (MC mitral)
characteristic of a myxoma
gelatinous appearance
risks associated with cardiac transplants
transplant rejection and allograft arteriopathy (stenosis of coronary arteries)
after 5 years, 90% of transplants have evidence of _________
ateriopathy