Chap 8 - Social Influence, Socialization, and Organizational Culture
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Information dependence
Reliance on others for information about how to think, feel and act
Social information processing theory
Information from others is used to interpret events and develop expectations about appropriate and acceptable attitudes and behaviours
Effect dependence
Reliance on others due tot heir capacity to provide rewards and punishment
Compliance
Conformity to a social norm prompted by the desire to acquire rewards or avoid punishment
Identification
Conformity to a social norm prompted by perceptions that those who promote the norm are attractive or similar to oneself
Internalization
Conformity to a social norm prompted by true acceptance of the beliefs, values, and attitudes that underlie the norm
Socialization
The process by which people learn the attitudes, knowledge, and behaviours that are necessary for a person to function in a group or organization
Uncertainty reduction theory
Newcomers are motivated to reduce their uncertainty so that the work environment becomes more predictable and understandable
Sensemaking
Constructing meaning and interpreting events in the organization
Person organization fit
The match between an employee’s personal values and the values of an organization
Person group fit
The match between an employee’s values and the values of the employee’s work group
Organizational identification
The extent to which individuals define themselves in terms of the organization and what it is perceived to represent
Stages of socialization
Anticipatory socialization
Encounter
Role management
Anticipatory socialization
Can occur before a person becomes a member of a particular organization
Sometimes it is a formal process of skill and attitude acquisition (ex: attending university)
Other times it is acquired informally, through summer jobs or watching the portrayal of organizational life in tv
Encounter
A new recruit, armed with some expectations about organizational life, encounters dat ti dat reality of this life
Formal aspects include orientation programs and rotation through various parts of the organization
Informal aspects include getting to know an understand the style and personality of one’s boss and coworkers
Role management
New member’s attention shifts to fine tuning and actively managing their new role in the organization
Following some conformity to group norms, the new recruit might now be in a position to modify the role to better serve the organization
This requires forming connections outside the immediate work group
Newcomer also needs to balance organizational roles and non work roles
Unmet expetations
When there is a difference between initial expectations and actual experiences on the job
Reality shcok
When the reality of a new job and organization is inconsistent with and does not meet one’s exceptions
Psychological contract
Beliefs held by employees regarding the reciprocal obligations and promises between them and their organization
Psychological contract breach
Employee perceptions that their organization has failed to fulfill one or more of its promises or obligations int he psychological contract
Socialization resources theory
Providing newcomers with resources throughout the organizational socialization process to facilitate their adjustment and a successful socialization
Realistic job previews
The provision of a balanced, realistic picture of the positive and negative aspects of a job to applicants
Self selection
Job applicants who are not a good match for the job and have low PJ and PO fit perceptions withdraw from the application process
Employee orientation programs
Programs designed to introduce new employees to their job, to the people they will be working with, and to the organization
Realistic orientation programs for entry stress (ROPES)
An orientation program that is designed to teach newcomers coping techniques to manage workplace stressors
Socialization tactics
The manner in which organizations structure the early work experiences of newcomers and employees who are in transition from one role to another
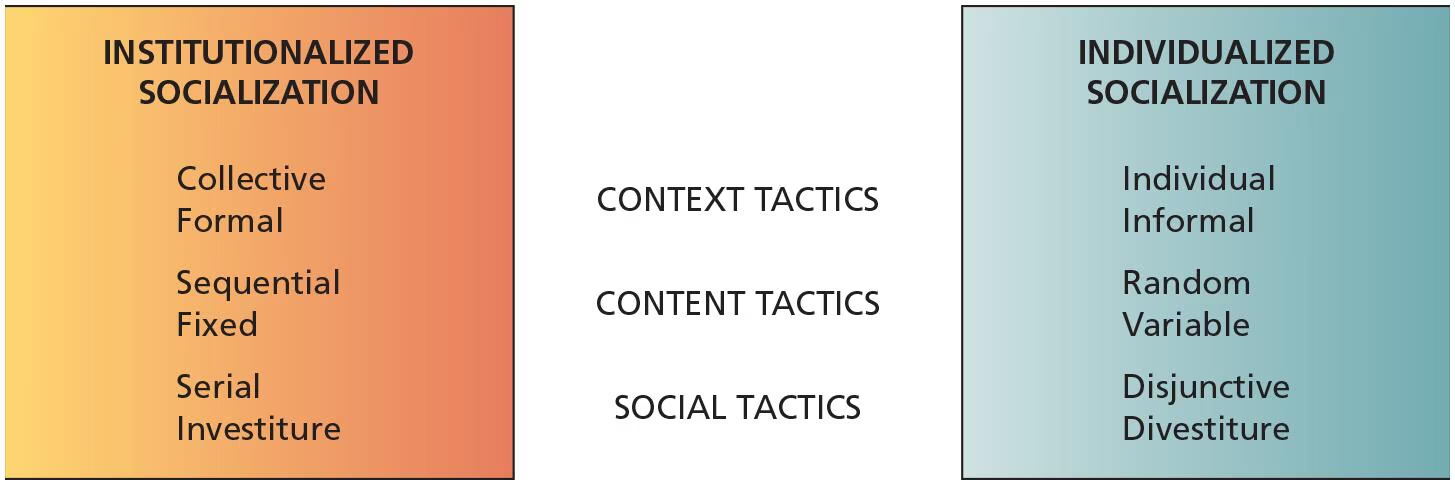
Collective vs individual tactics
Collective tactic consists of a number of new members being socialized as a group, going through the same experiences, and facing the same challenges
Individual tactic consists of socialization experiences that are tailor made for each new member
Formal vs informal tactics
Formal tactics involve segregating newcomers from regular organizational members and providing them with formal learning experiences during the period of socialization
Informal tactics do not distinguish a newcomer from more experienced members and rely more on informal and on the job learning
Sequential vs random tactics
Sequential tactic involves a fixed sequence of steps or stages leading to the assumption of the role
Random tactic there is an ambiguous or changing sequence
Serial vs disjunctive tactics
Serial tactic refers to a process in which newcomers are socialized by experienced members of the organization
The disjunctive tactic refers to a socialization process where role models and experienced organization members do not groom the members or “show them the ropes”
Investiture vs divestiture tactics
Divestiture (debasement) tactics involve putting new members through a series of experiences that are designed to humble them and strip away some of their initial self confidence and change their attitudes and beliefs
Investiture tactic affirms the incoming identity and attributes of new hires rather than denying them and stripping them away
Mentor
An experienced or more senior person in the organization who provides a junior person with guidance and special attention, such as giving advice and creating opportunities for assistance, especially during the early stages of the junior person’s career
Formal mentoring programs
Organization sponsored programs in which seasoned employees are recruited as mentors and matches with proteges
Developmental networks
Groups of people who take an active interest in a protege’s (pupil) career and take actions toward advancing it by providing developmental assistance
Proactive socialization
The process in which newcomers play an active role in their own socialization through the use of proactive socialization behaviours
Feedback seeking
Requesting information about how one is performing one’s tasks and role
Information seeking
Requesting information about one’s job, role, group, and organization
What are some proactive socialization behaviours?
Feedback seeking
Information seeking
General socializing
Relationship building
Positive framing
Boss relationship building
Networking
Job change negotiation
Organizational culture
The shared beliefs, values, and assumptions that exist in an organization
Subcultures
Smaller cultures that develop within a larger organizational culture and are based on differences in training, occupation, or departmental goals
Strong culture
An organizational culture with intense and pervasive beliefs, values, and assumptions
What are some assets of strong cultures
Coordination
Conflict resolution
Financial success
Liabilities of strong cultures
Resistance to change
Culture clash
Pathology
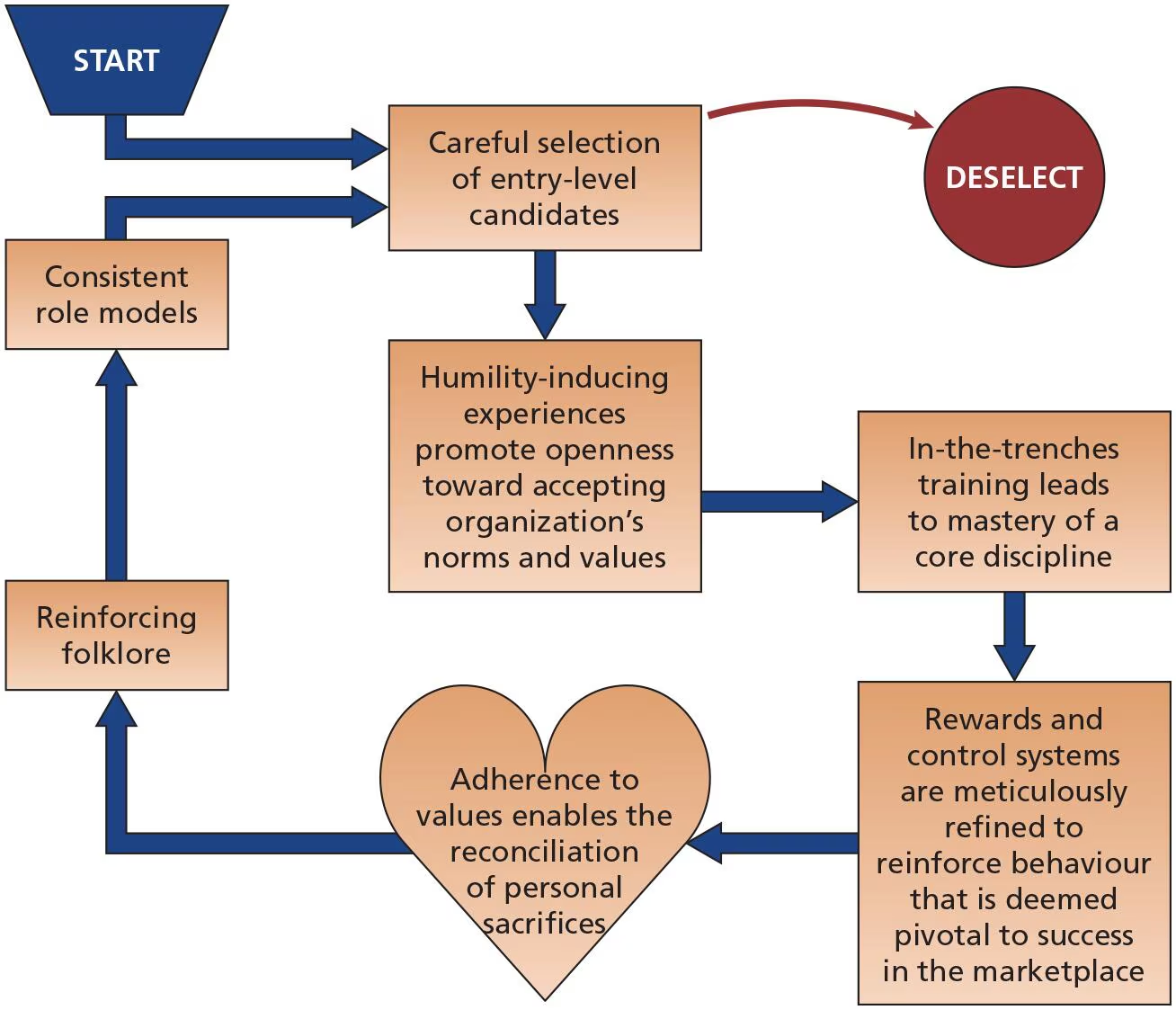
How are cultures built and maintained?
The founder’s role
Socialization
What are the socialization steps in strong cultures?
Selecting employees
Debasement
Training “in the trenches”
Reward and promotion
Exposure to core culture
Organizational folklore
Role models
Symbols
An object, act, event, quality or relation that serves as a vehicle for conveying meaning, usually by representing something
Rites
Elaborate, dramatic, planned activities that consolidate various forms of cultural expression into one event, which is carried out through social interactions for the benefit of an audience
Rituals
Standardized, detailed sets of techniques, actions, and behaviours that are performed in recognition of some event or accomplishment
Ceremonial
A system of several rites connected with a single occasion or event
Rite of passage
A rite that facilitates the transition into new social roles
Story
A narrative based on true events that are often a combination of truth and fiction