PSK4U - Unit 2 Review
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Skeletal System
The human skeleton consists of 206 bones (on average). Babies are born with about 305 bones but these fuse together over time (ie. skull, spine...). In utero, bones begin as cartilage and ossify (become harder) as the child gets older.
Function of Bones (x5)
Support - A stiff structure for soft tissues like muscles and organs
Movement - Bones provide the leverage for muscles to produce movement
Protection - Helps prevent soft tissue injury. Bone fractures are more easily (and better) repaired
Blood Production - Bone marrow produces blood cells (red, white, and platelets
Mineral Storage - Required minerals such as calcium and phosphorus are kept in bone for later use
Bone Composition (x2)
Collagen - Collagen is a series of rope-like fibers that provide a base network. This gives bone its flexibility
Apatite - Apatite is a collection of minerals (mainly phosphorus and calcium) that covers the collagen. This gives bone its strength
Collagen
Collagen is a series of rope-like fibers that provide a base network. This gives bone its flexibility
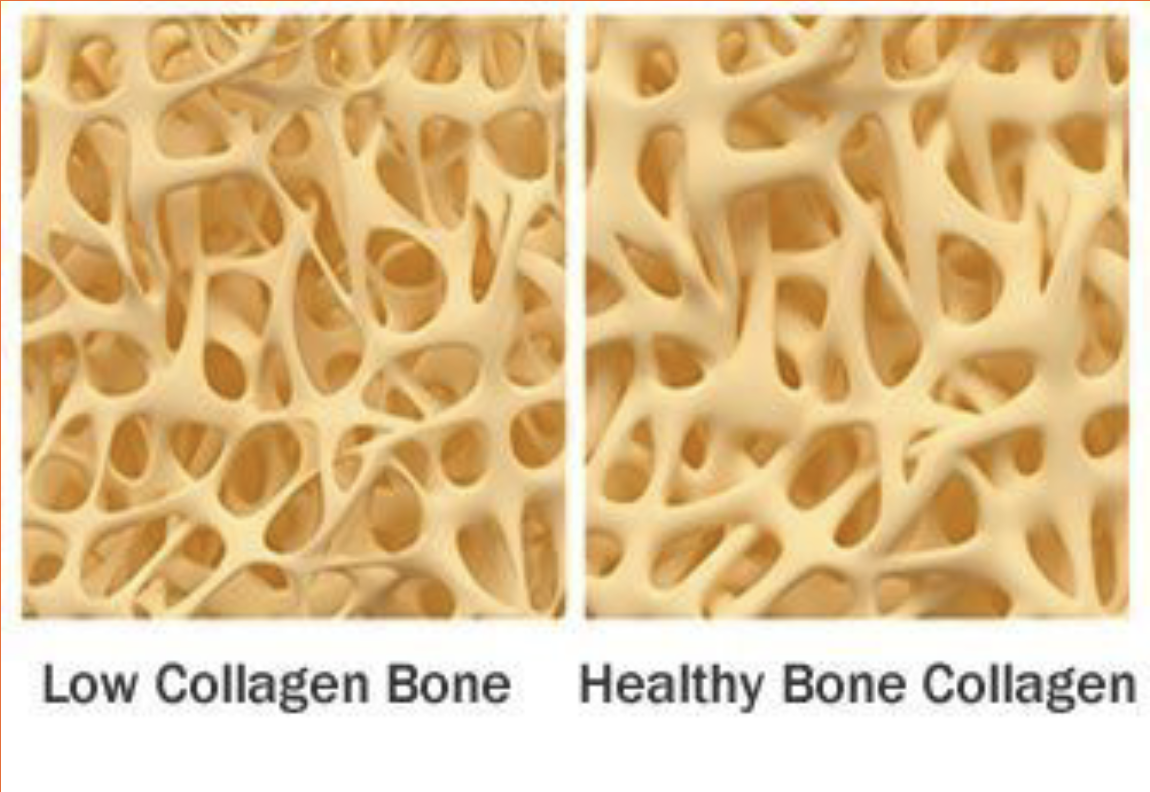
Apatite
Apatite is a collection of minerals (mainly phosphorus and calcium) that covers the collagen. This gives bone its strength
Bone Remodeling
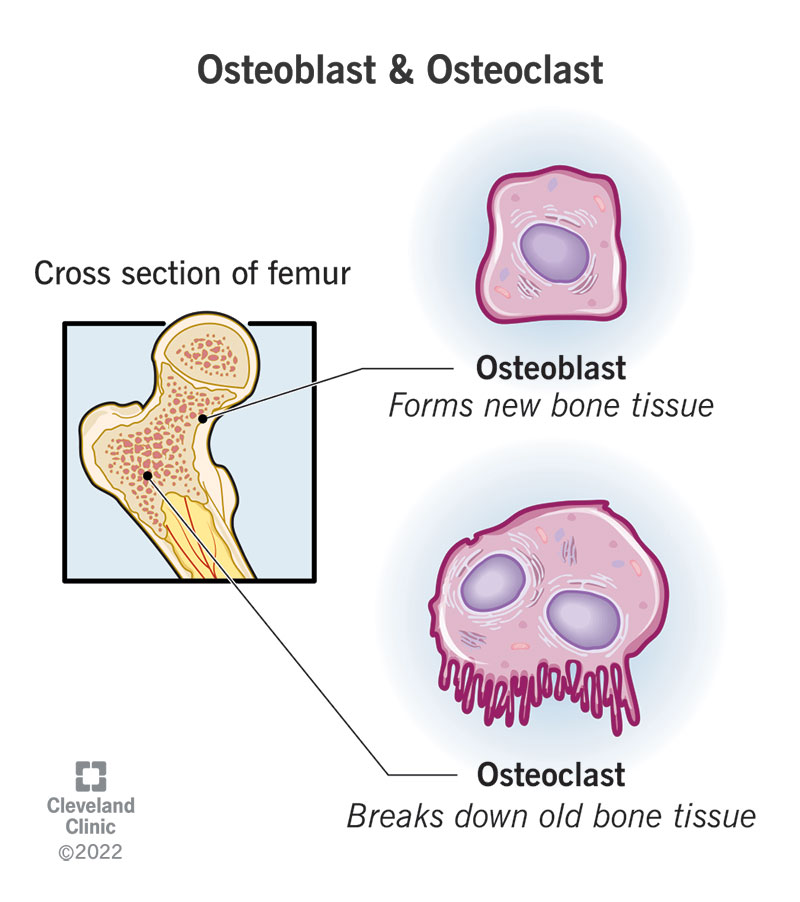
Bone are not only strong and flexible, they can also repair themselves. The periosteum is a connective tissue that covers bone and contains two important cells that continuously repair and upgrade bone. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts are cells that lay down new bone material where damage or weakness is sensed.
Children have layers of osteoblasts in the shape of plates at the ends of their bones. These are called “growth plates”.
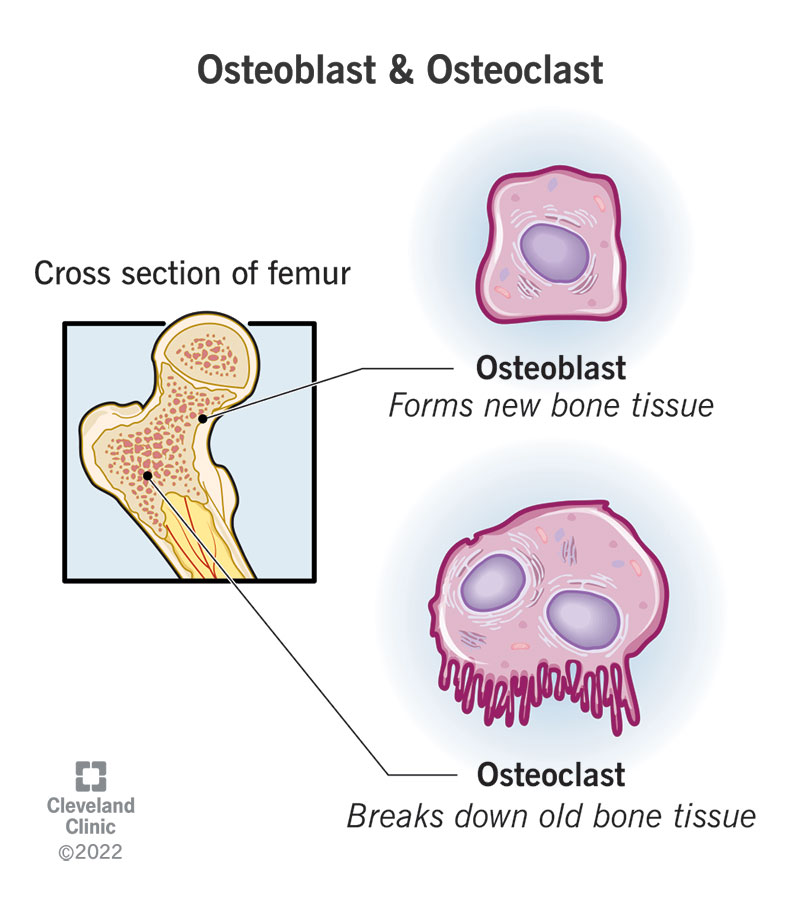
Osteoclasts
Osteoclasts are cells that break down bone material for the purposes of proper shaping or mineral needs.
Use for fracture or when minerals are needed in the blood stream.
Bone Modeling
Bones that are regularly subjected to weight-bearing physical activity tend to become denser and more mineralized than bones that are inactive.
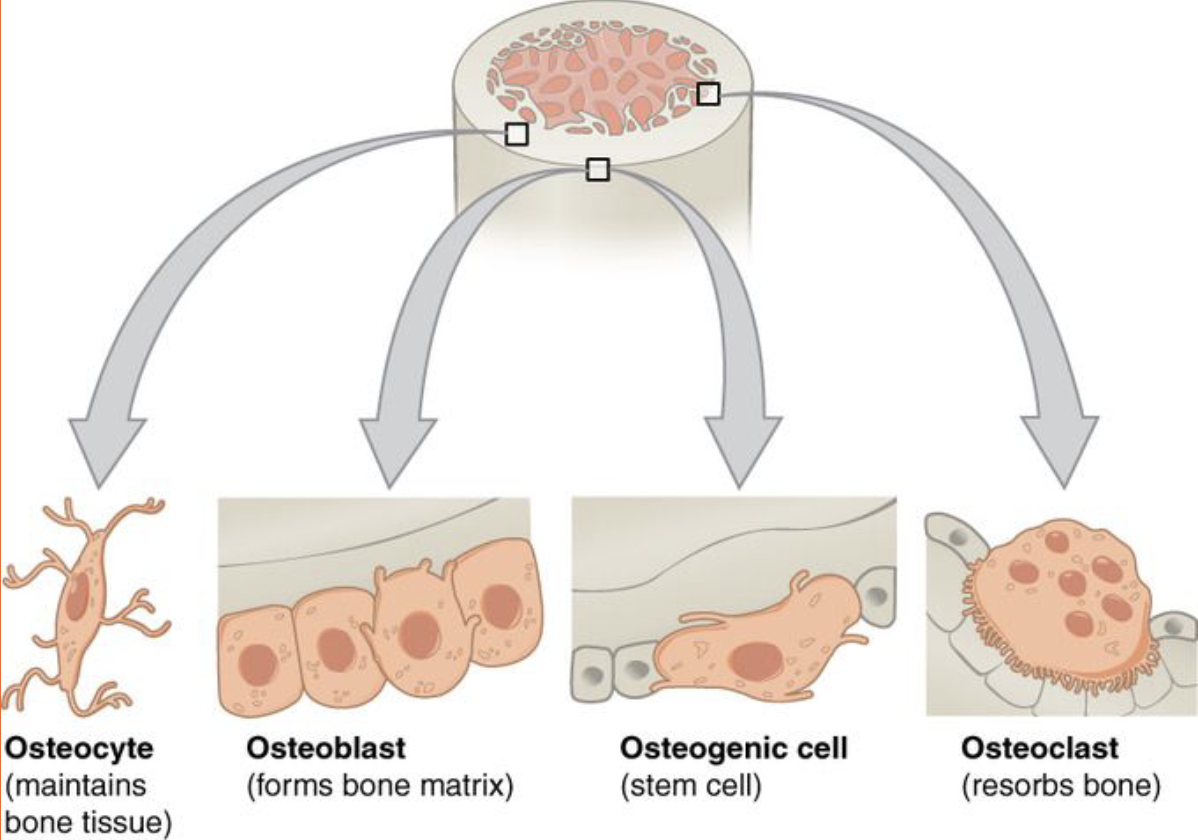
Osteocytes
Osteocytes (used up osteoblasts) are embedded in the bone tissue to become the ‘sensors’ for stress on bones and signal increased or decreased osteoblast activity.
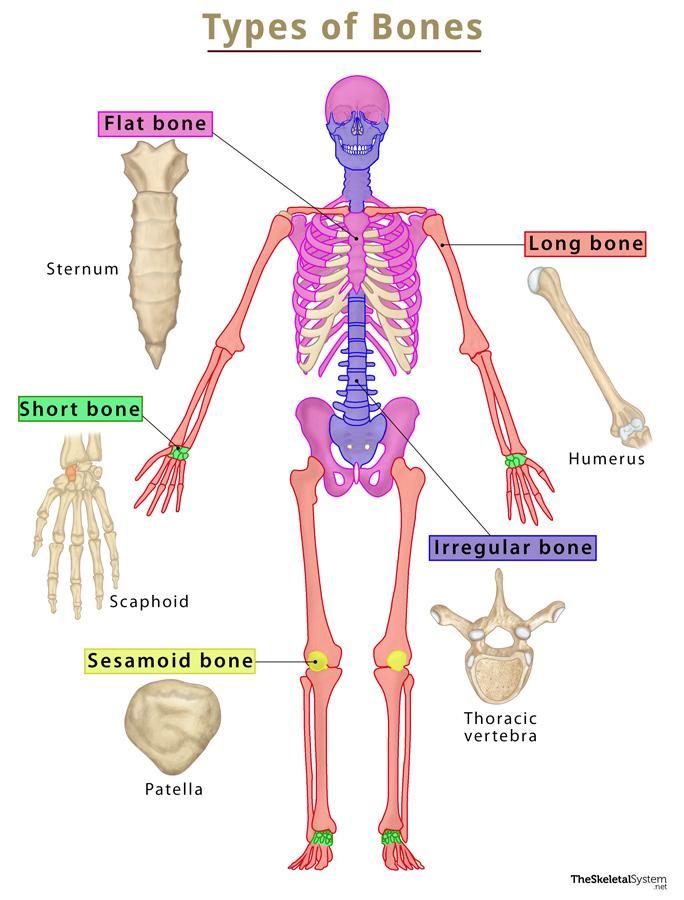
Types of Bones (x5)
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular, Sesamoid
Long Bone
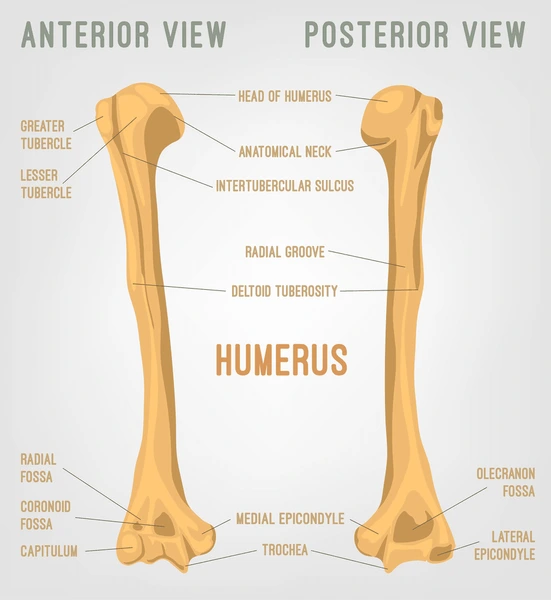
Bones whose length significantly exceed their diameter (ie. femur, humerus). They contain both spongy and compact bone.
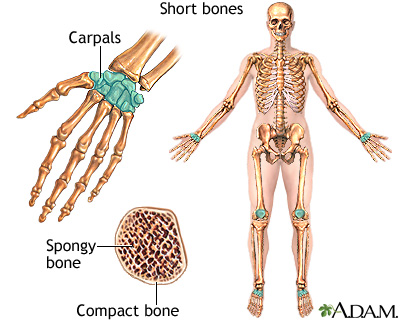
Short Bone
Bones that are small and often square in shape (ie. carpals, tarsals). They consist mainly of spongy bone. These are often "load-bearing" bones.
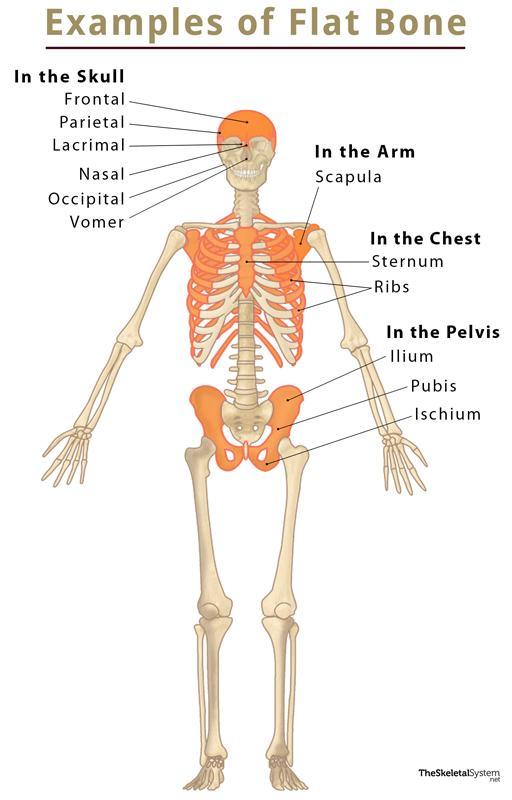
Flat Bone
Bones that are thin, wide and often in areas protecting vital organs (ie. skull, ribcage).
They also produce more blood cells than other bone types.
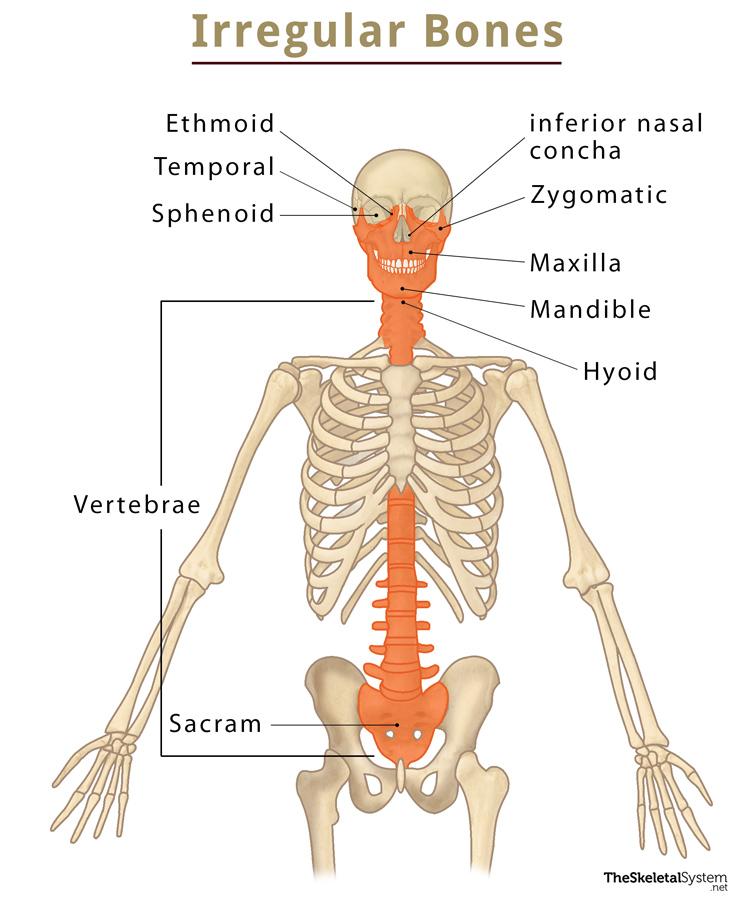
Irregular Bone
Bones that have odd shapes or patterns (ie. vertebrae or sacrum).
Sesamoid Bone
Bones that are small and wrapped in tendon material (ie. patella).

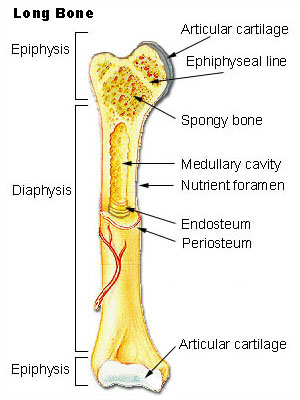
Anatomy of a Long Bone
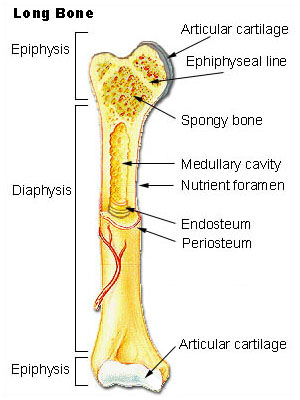
Cartilage
This type of cartilage is referred to as articulating cartilage as it protects the points of articulation (where two bones meet).It allows for smoother movement at joints.
Periosteum
Thin layer of connective tissue that covers bone. Contains cells for bone re-modelling and is the connecting point for tendons and ligaments.

Medullary Cavity
Hollow part of bone shaft where bone marrow produces blood cells.
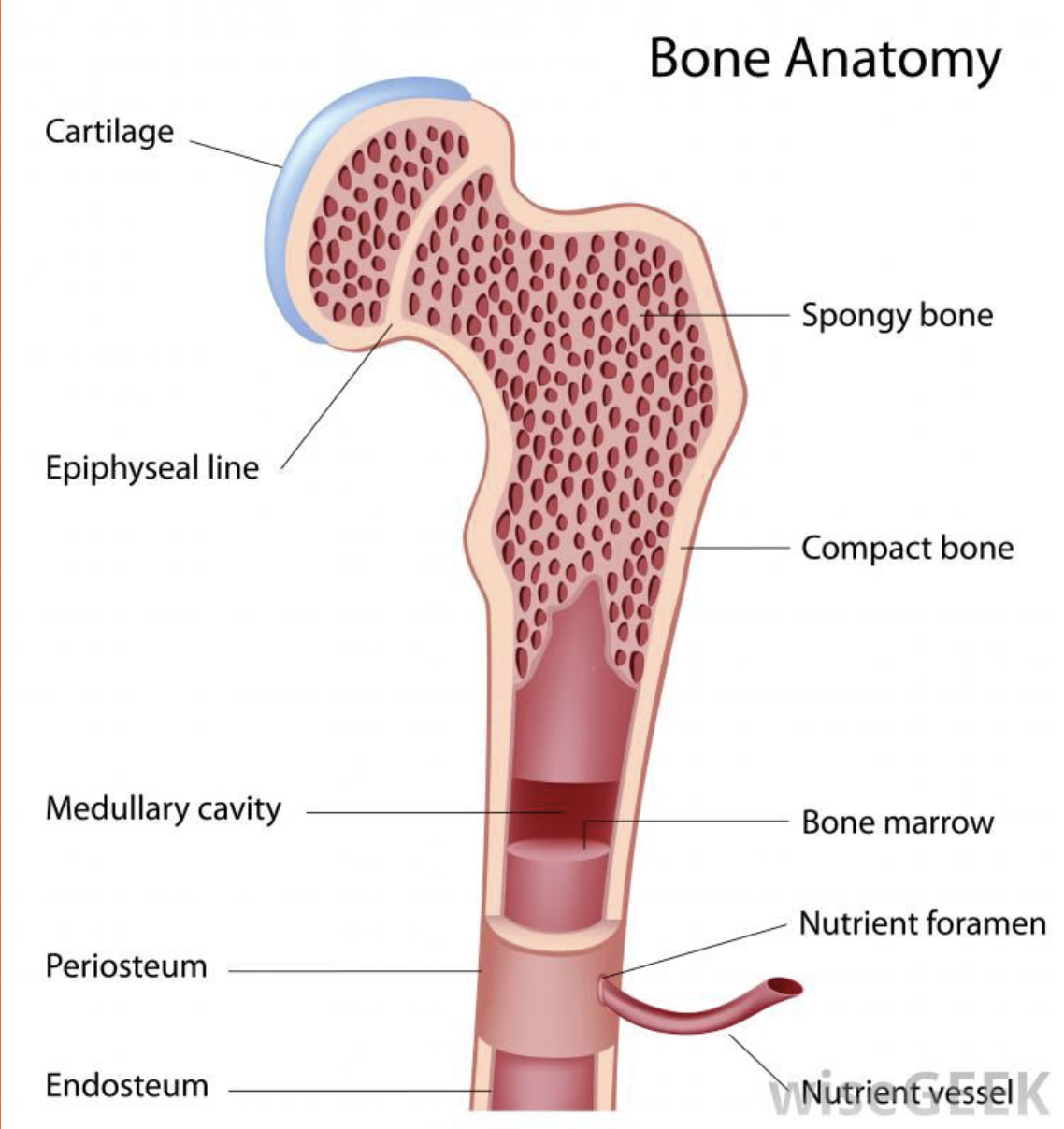
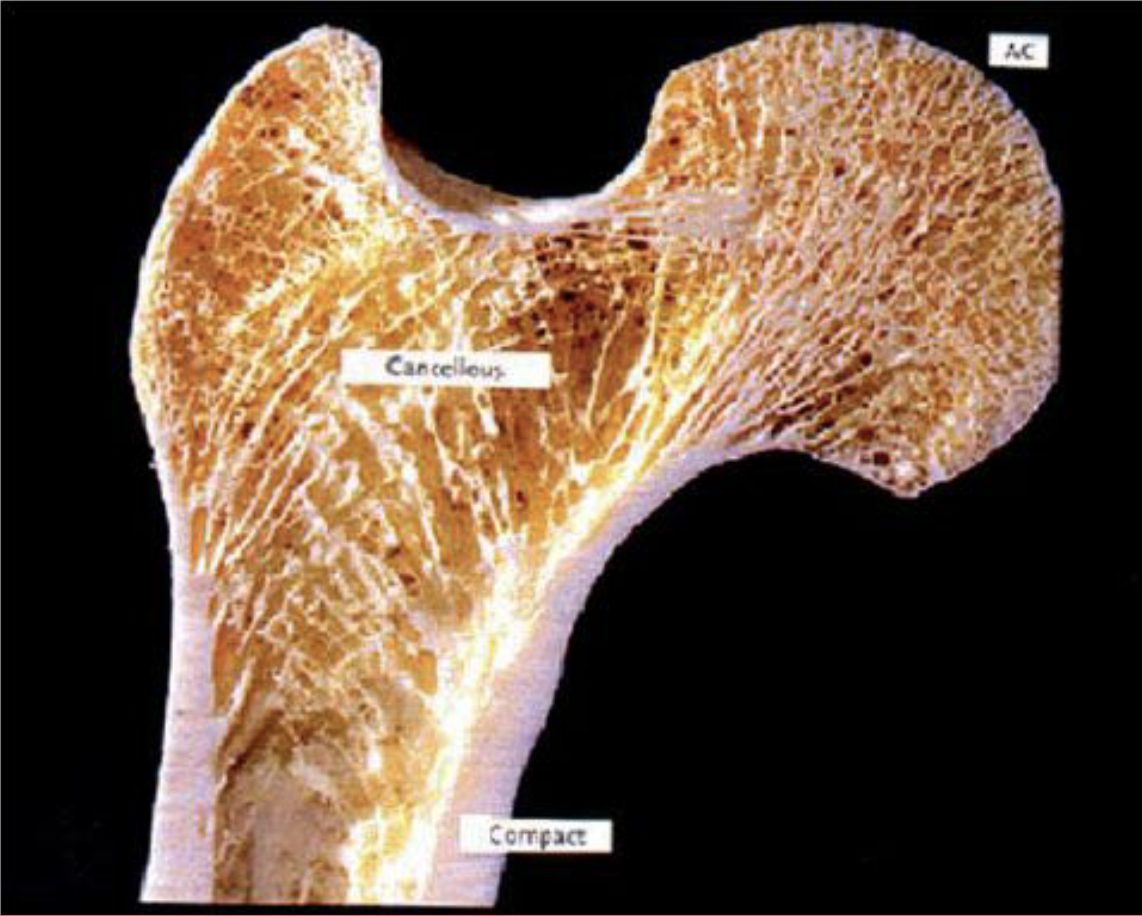
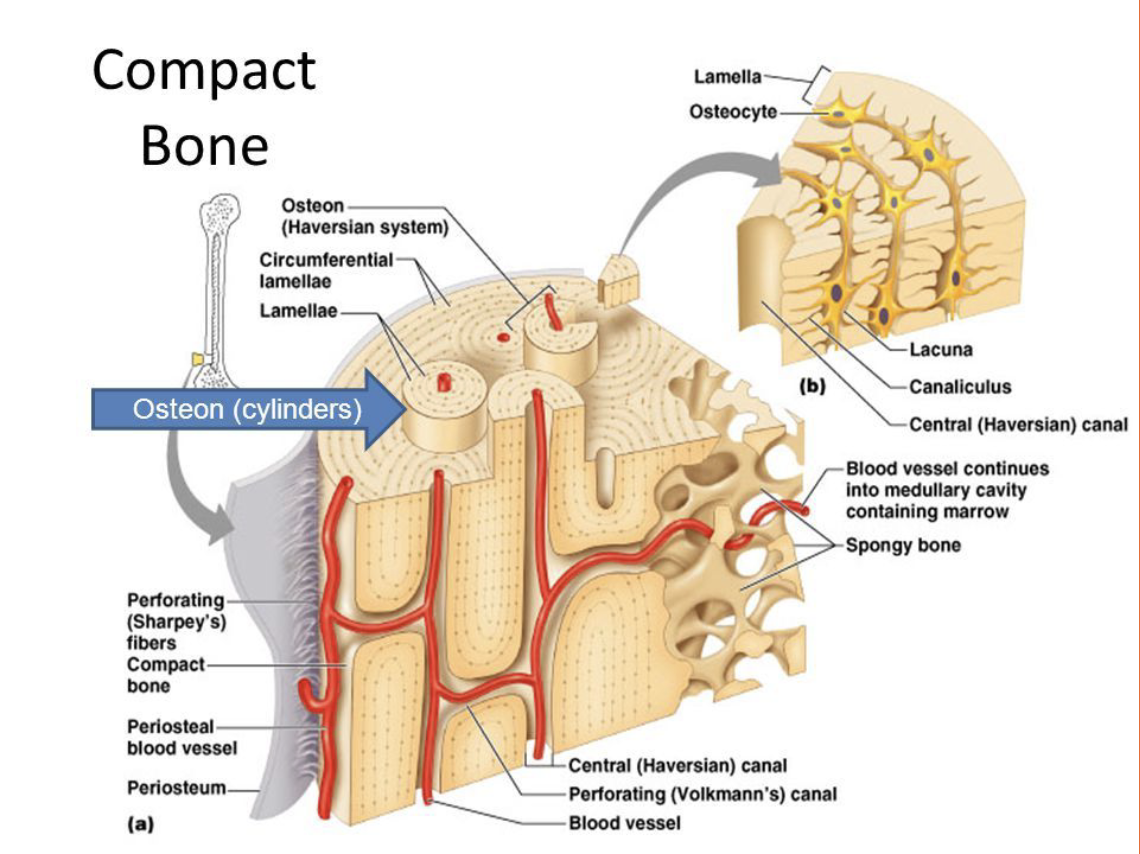
Compact Bone
Dense, rigid bone usually on bone shaft (diaphysis)
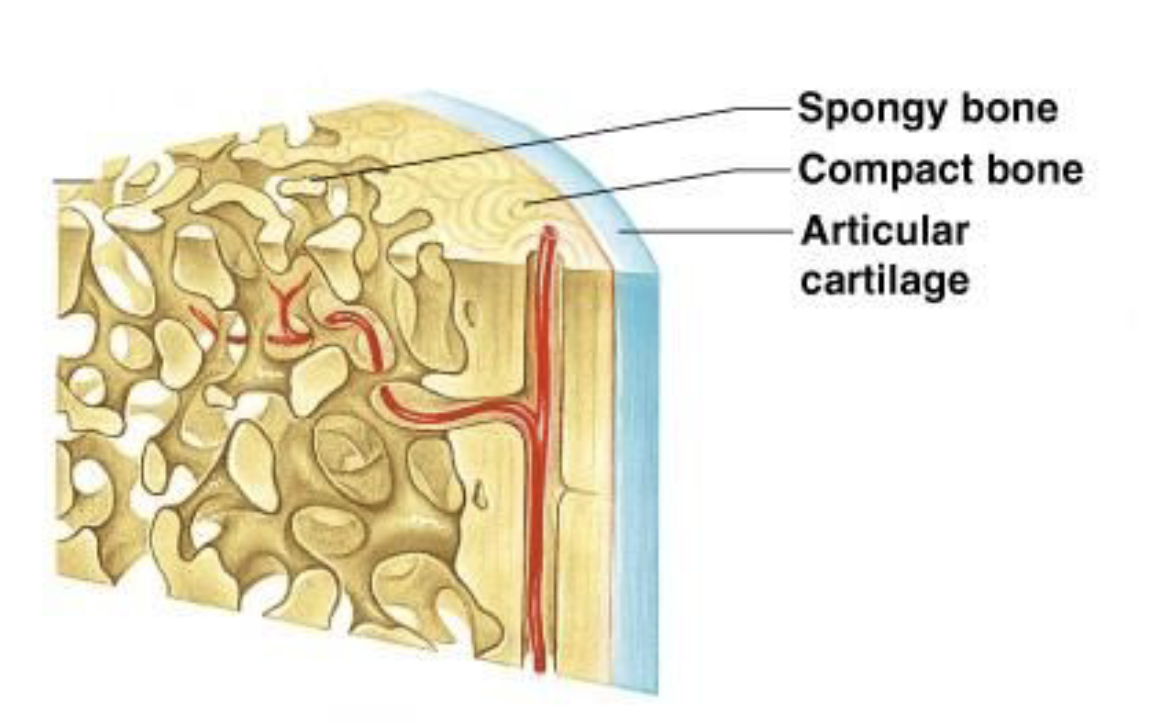
Spongy Bone
Compressive, flexible bone usually on bone ends (epiphysis). The trabeculae running throughout gives the bone its load-bearing capability and 'spongy' look.
Epiphyseal Plates
Site where most bone growth occurs. Contains a higher concentration of osteoblasts.
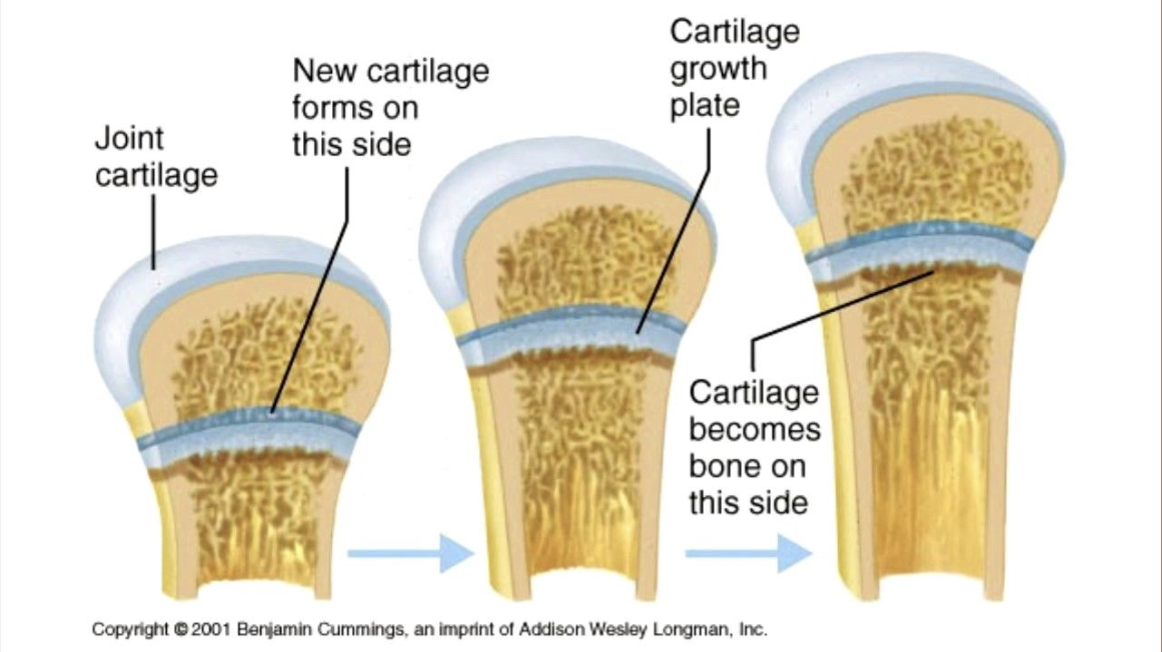
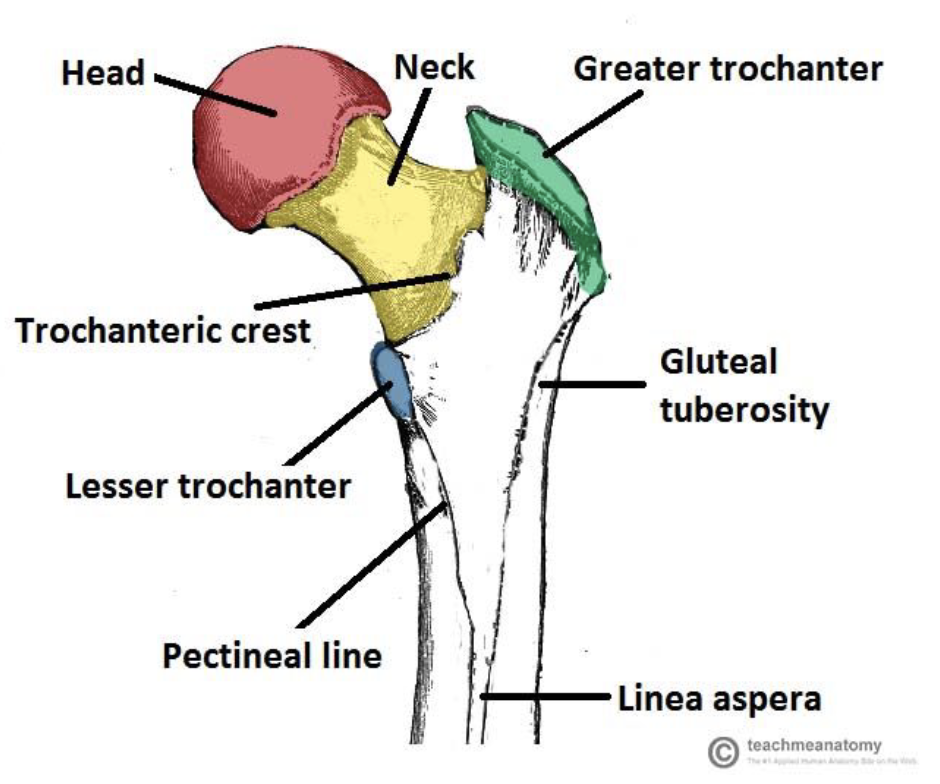
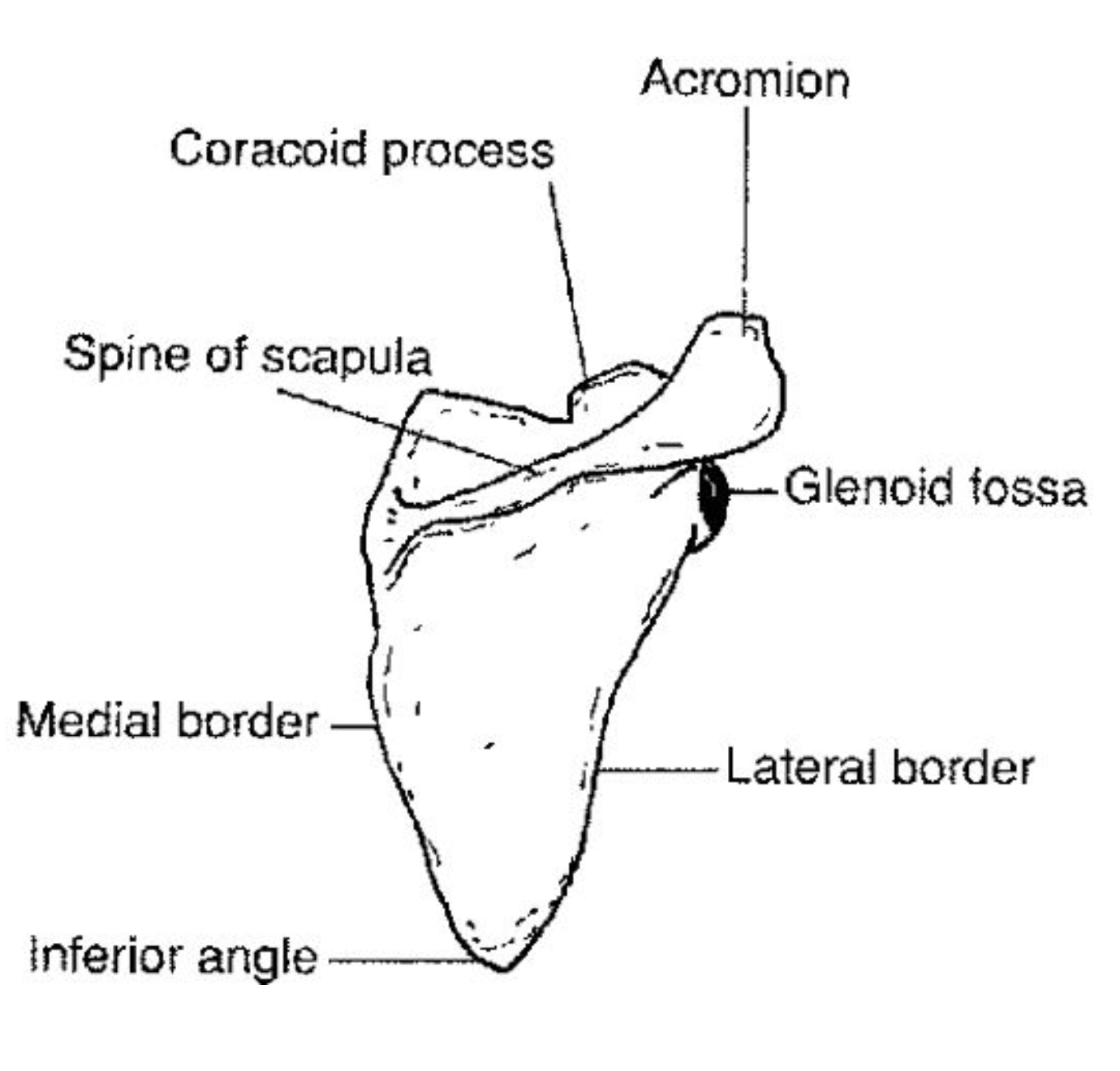
Bone Landmarks
Bones often have prominent features called landmarks. These may be ridges, grooves, depressions, or other surface markers on a bone. These can be a point of attachment or allow space for other systems.
Names of landmarks include crest, spine, tuberosity, condyle, fossa…
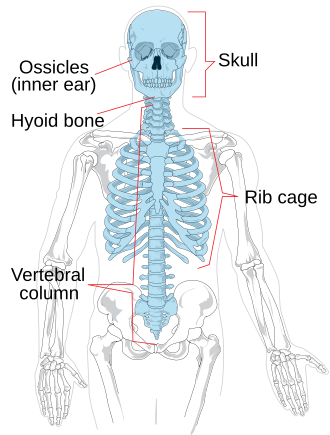
Types of Skeleton (x2)
The human skeleton is broken down into two main parts:
Axial Skeleton - This includes the skull, ribcage, and vertebral column (spine).
Appendicular Skeleton - This includes all the bones articulating with the arms and legs.

Axial Skeleton consists of:
Skull, Vertebra, Ribs, and Sternum
Skull is formed by 2 sets of bones:
Cranial and Facial
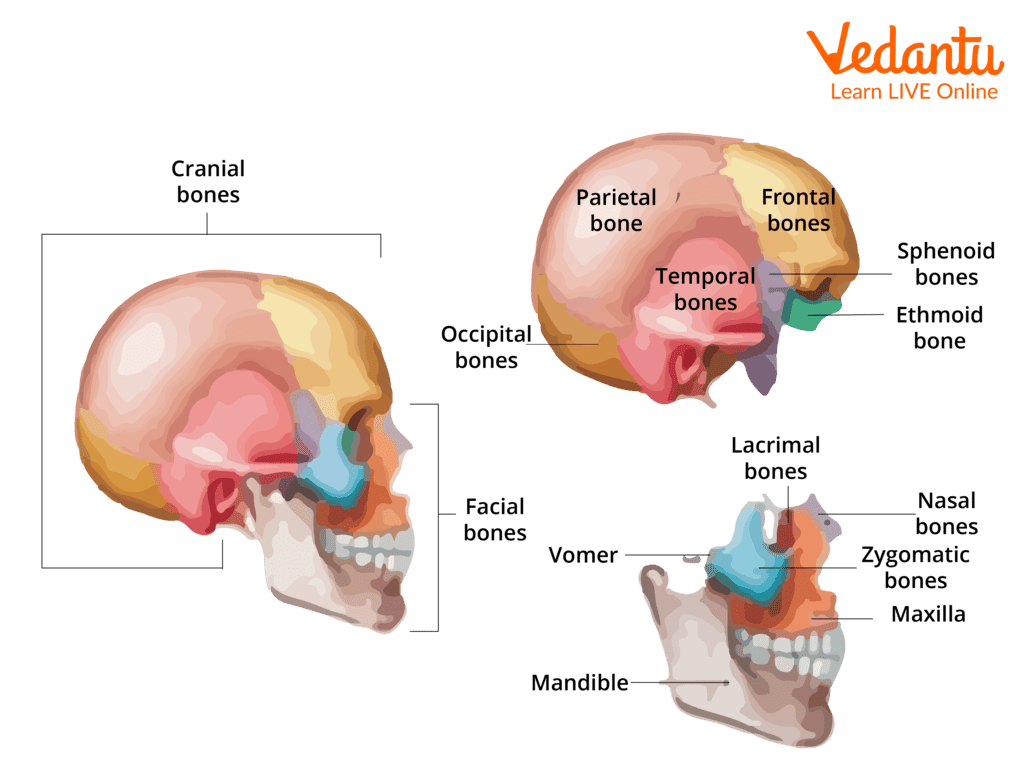
Cranial Bones (x8):
Ethmoid (1), Sphenoid (1), Frontal (1), Parietal (2), Temporal (2), Occipital (1)
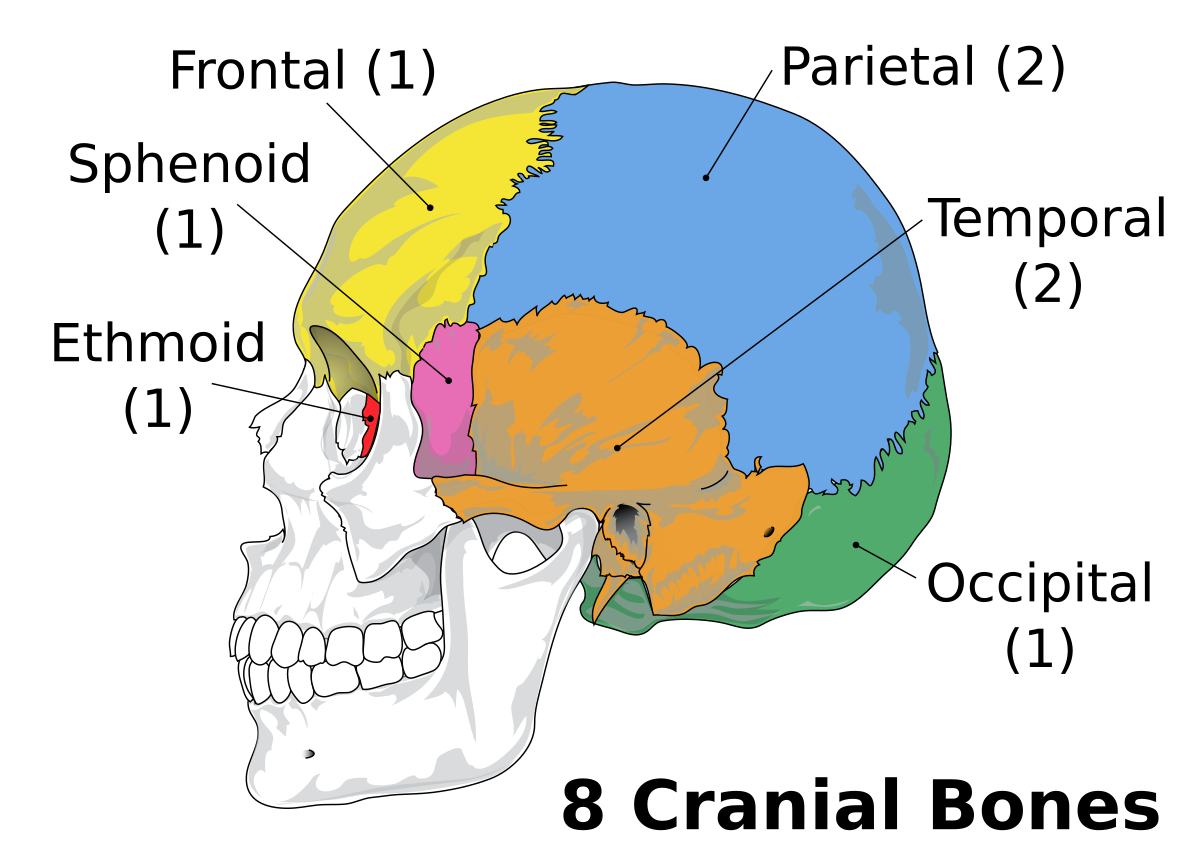
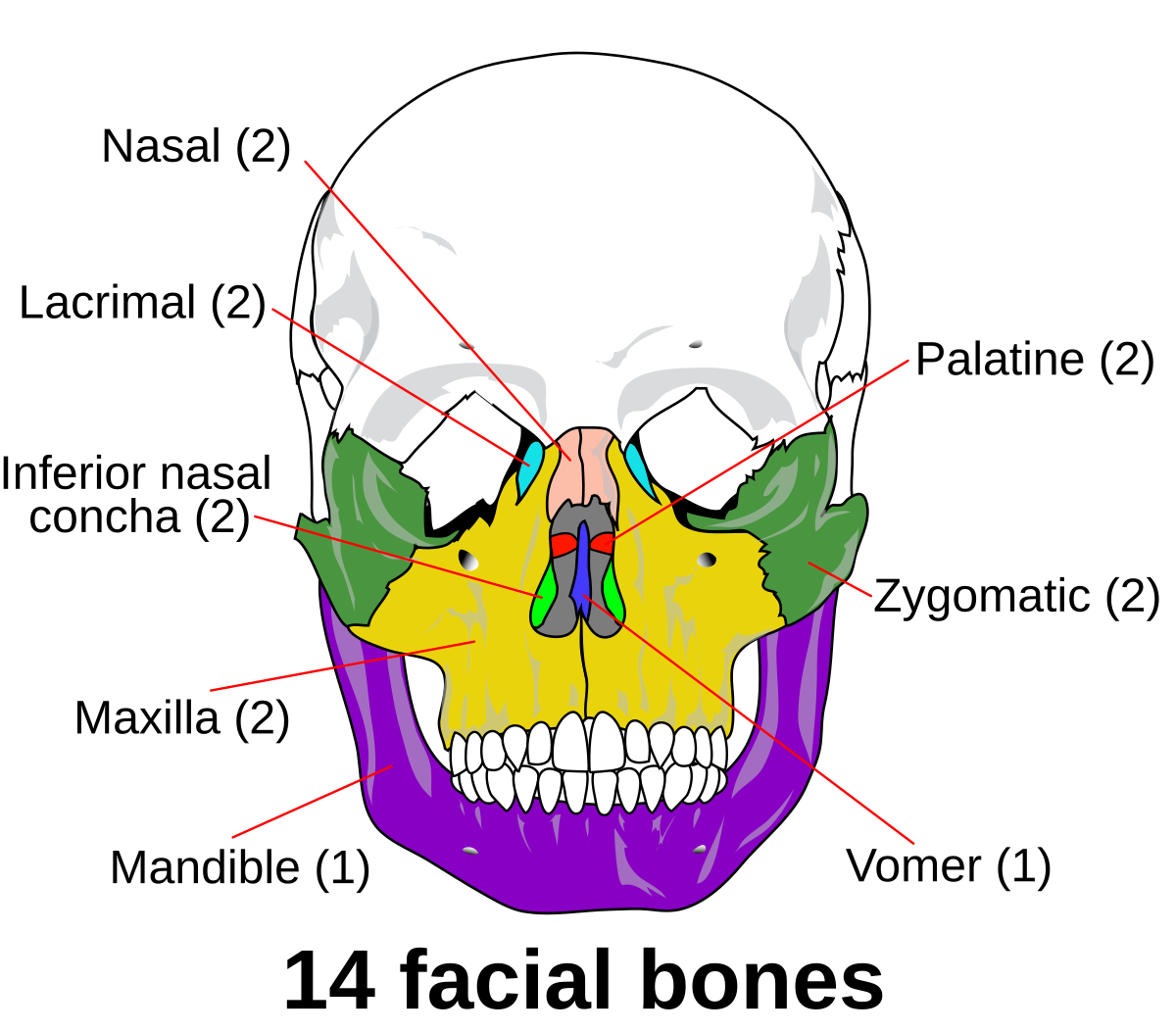
Facial Bones (x14):
Vomer (1), Zygomatic (2), Palatine (2), Nasal (4), Lacrimal (2), Maxilla (2), Mandible (1)
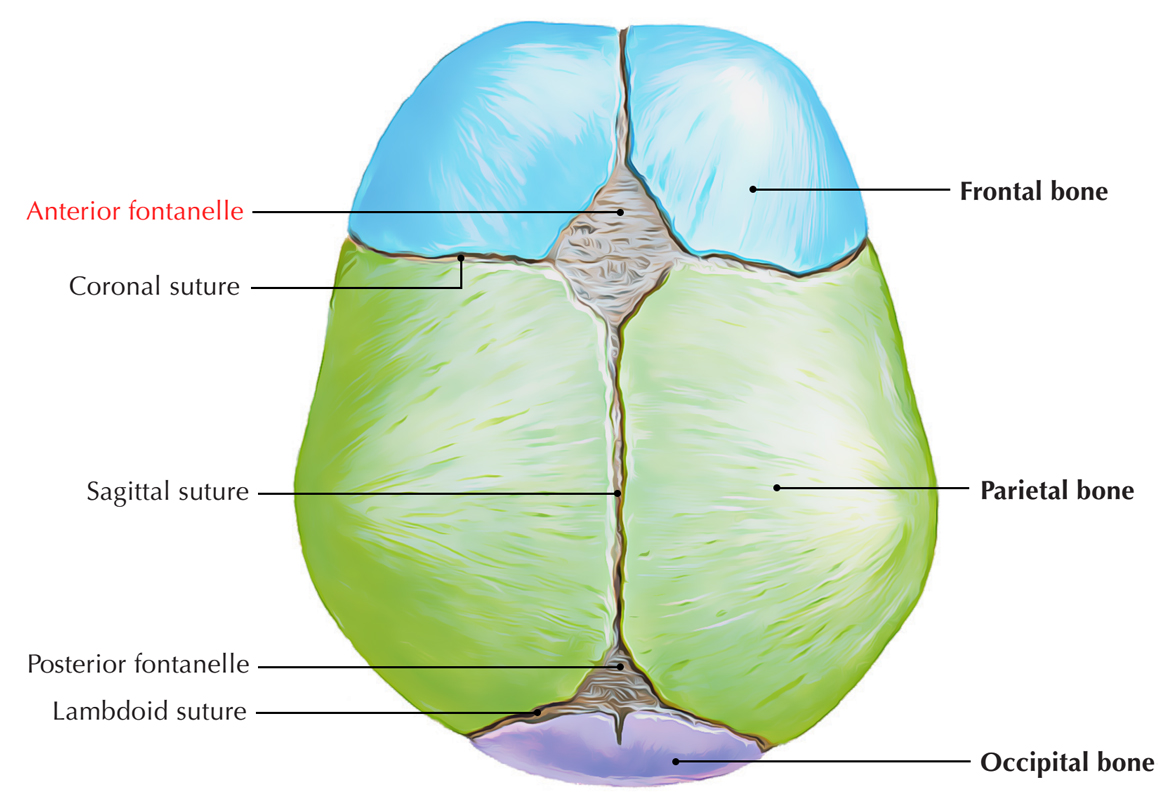
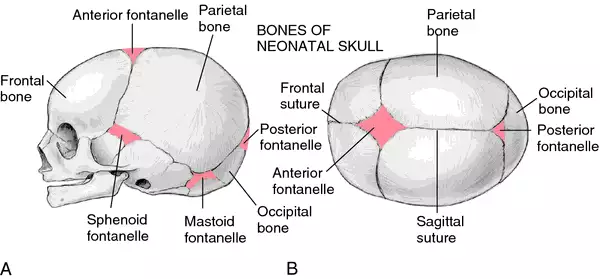
Fontanelle
Membrane filled spaces between bones on infant skulls
Anterior fontanelle closes after about 18 months
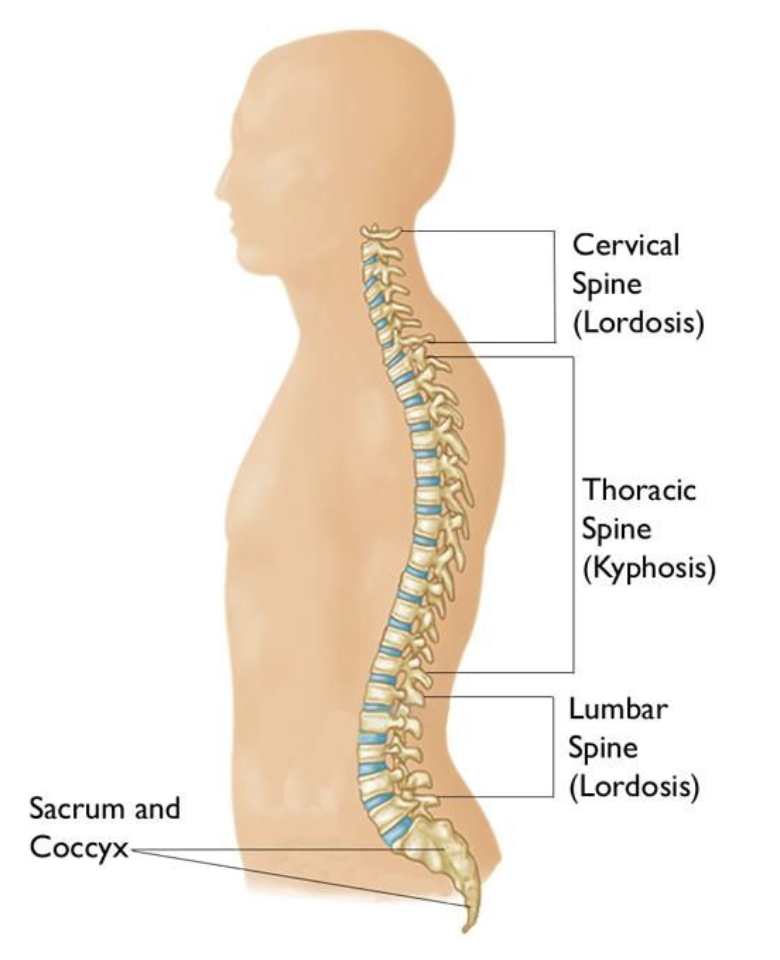
Spine consists of:
Cervical Vertebrae (7), Atlas (C1), Axis (C2), Thoracic Vertebrae (12), Lumbar Vertebrae (5), Sacrum (1) (5 fused), Coccyx (1) (3-5 fused)
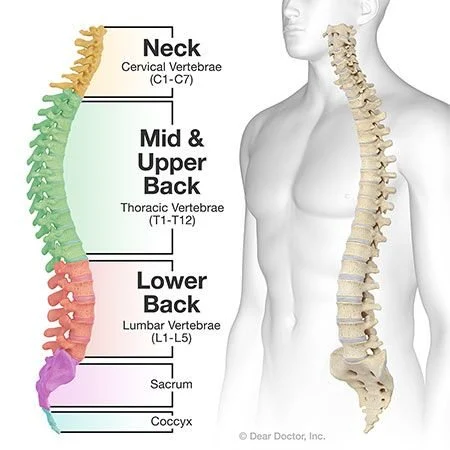
Vertebrae (The Spine)
Born with 33 vertebrae, but those at bottom of spine fuse together to form the sacrum and coccyx
Adult backbone consist of 26 separate vertebrae
Each vertebrae is separated by an “intervertebral disk”
Intervertebral disks prevent bones from grinding against each other and provides cushion to absorb shock when we move
Excluding the sacrum and coccyx
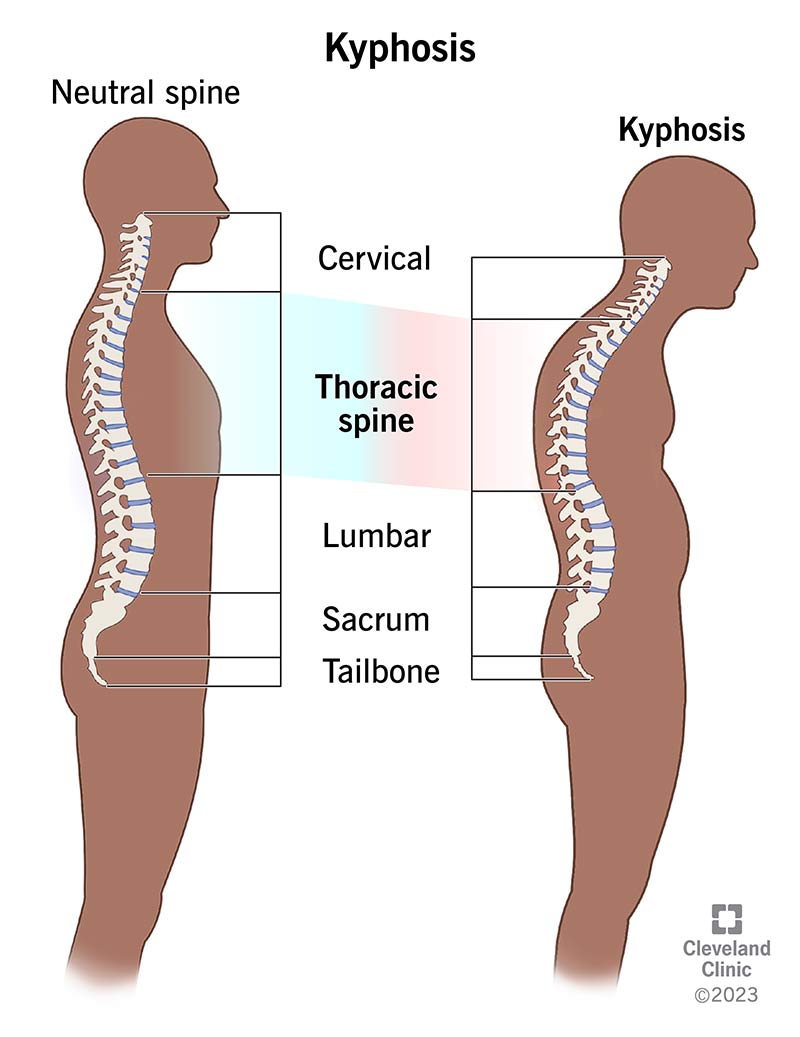
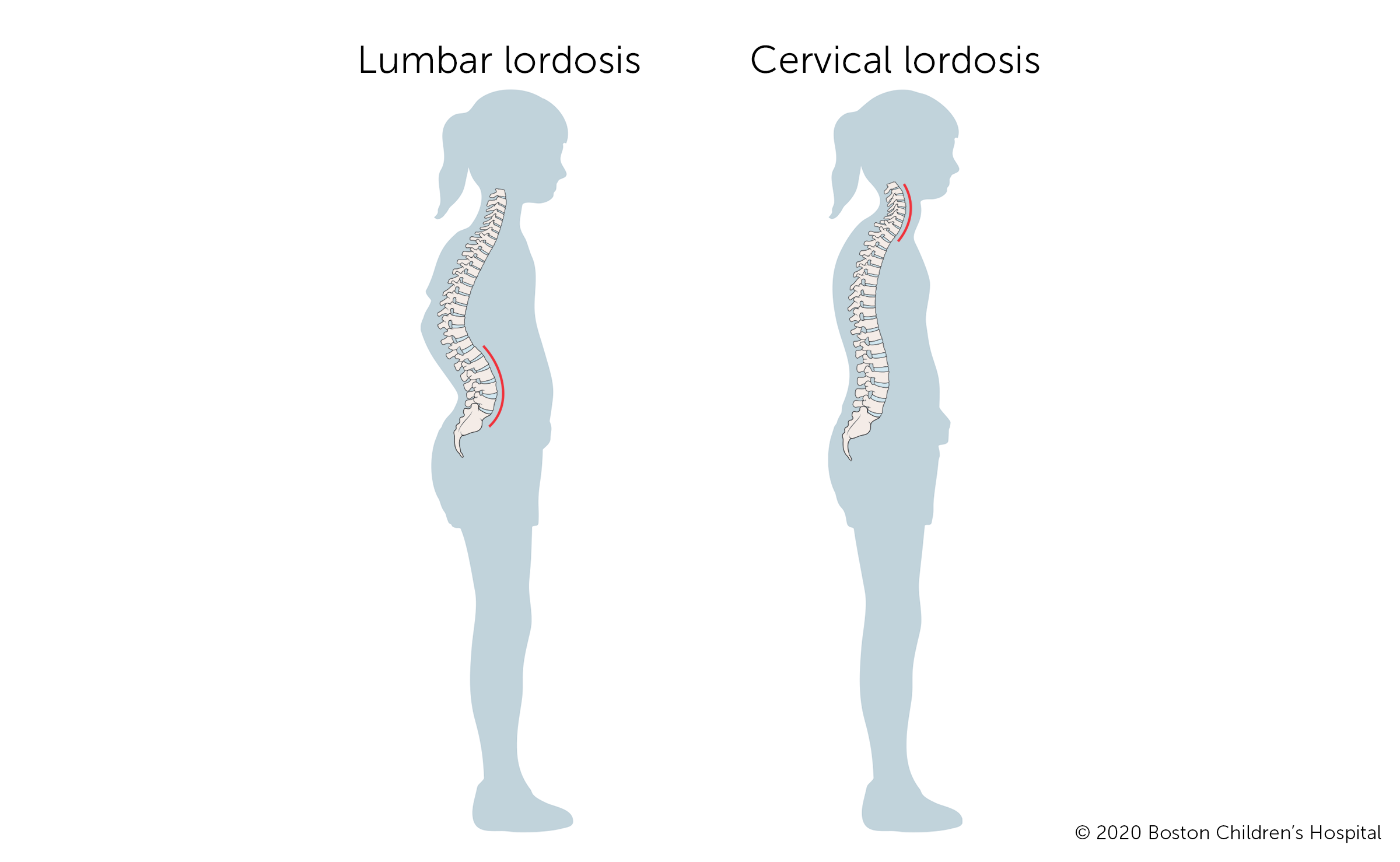
Spine has curves to help absorb shock
cervical curve = lordotic,
thoracic curve = kyphotic,
lumbar curve = lordotic
sacrum and coccyx = kyphotic
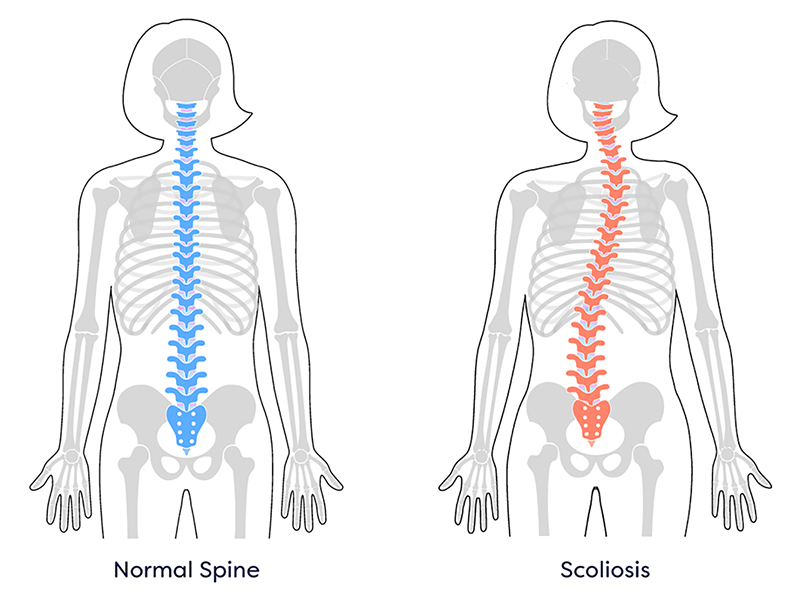
Scoliosis
Kyphosis
Lordosis
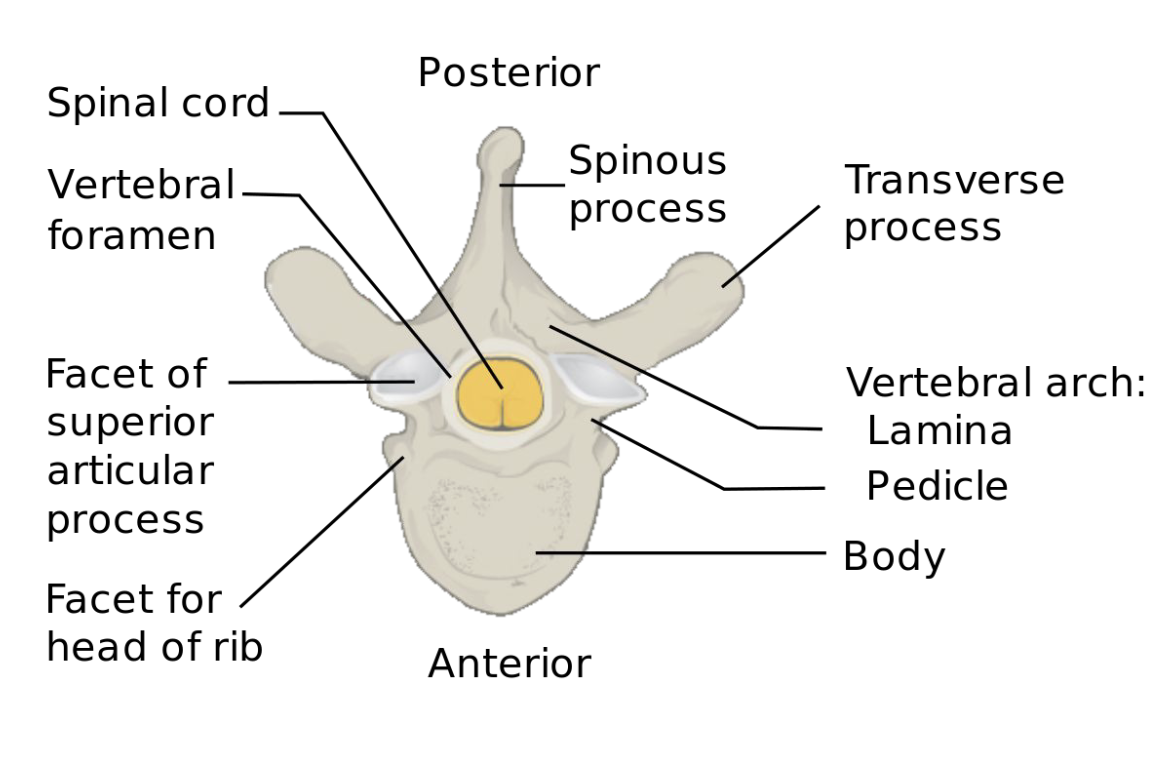
Vertebrae
Vertebrae (except top 2) have a thick body to bear weight and two lamina that join and form a ring = vertebral arch
Ring opening is called vertebral foramen = where spinal cord passes through
Vertebra have processes that act as anchors for muscle attachment, shields to protect spinal cord
Cervical Vertebrae (7)
Smallest and lightest
C1-C7
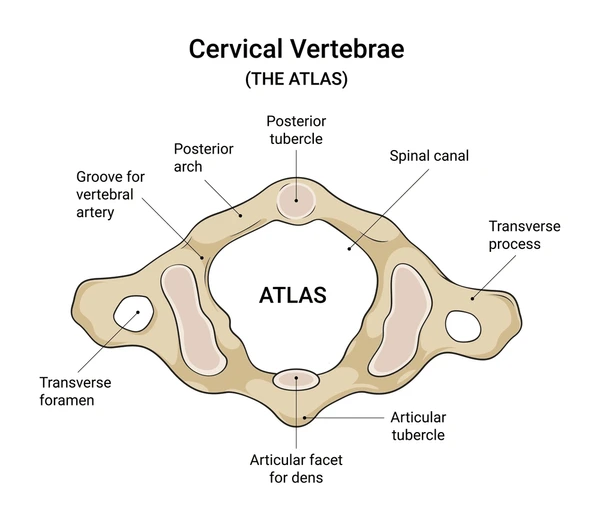
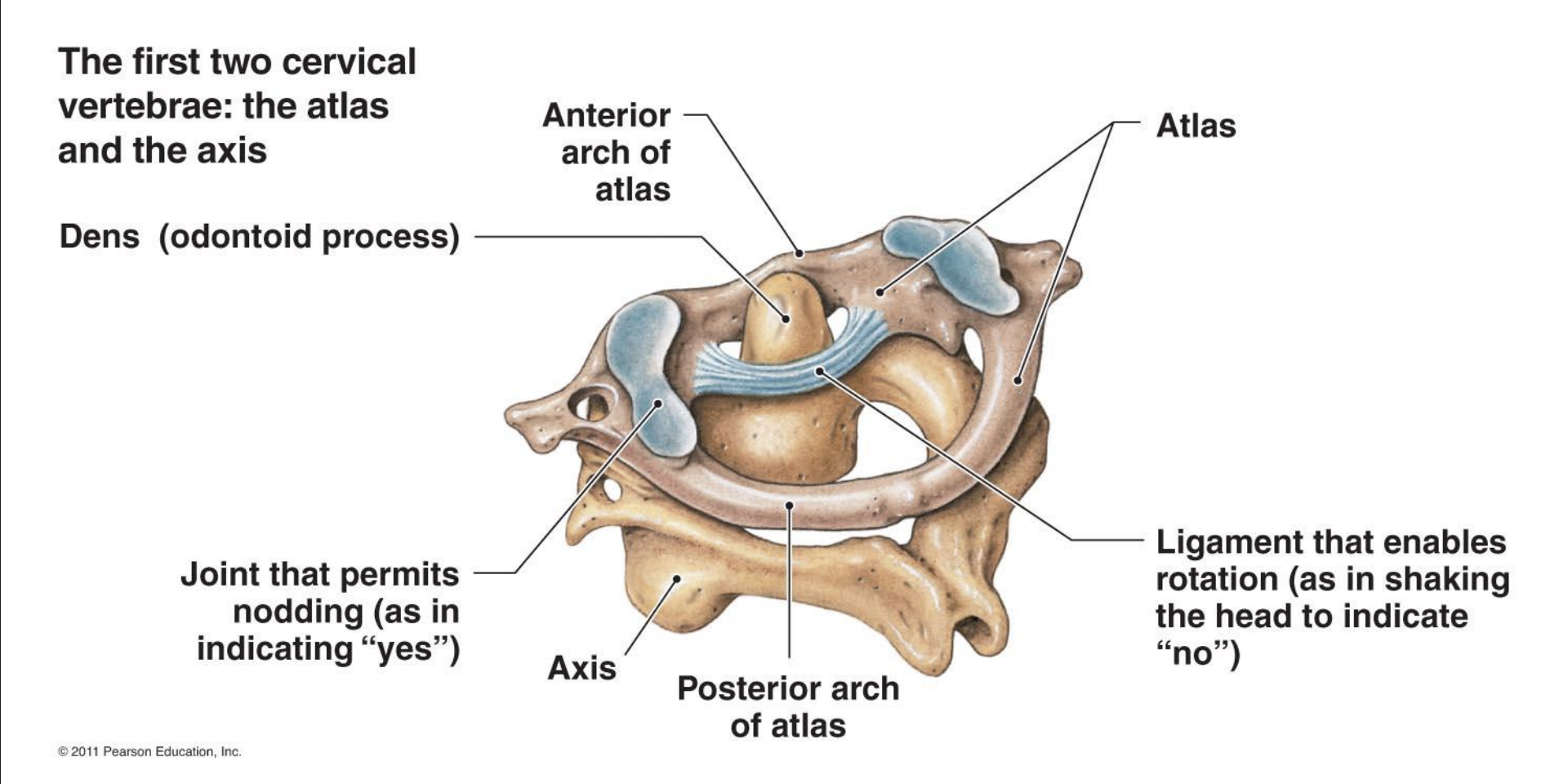
Atlas (C1)
Atlas has no body
Superior surface of its transverse processes contain large depressions that receive occipital condyles of skull
Yes!
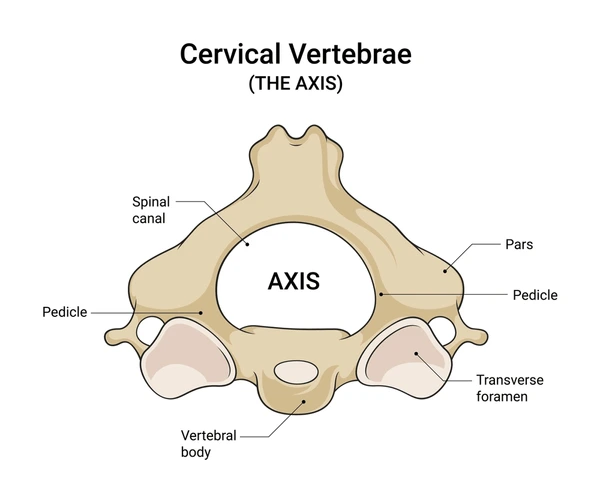
Axis (C2)
Axis (C2) acts as pivot for rotation of Atlas and skull
No!
Atlas and Axis
Thoracic Vertebrae (12)
Head of ribs articulate with bodies of vertebrae
Tubercles of ribs articulate with transverse processes

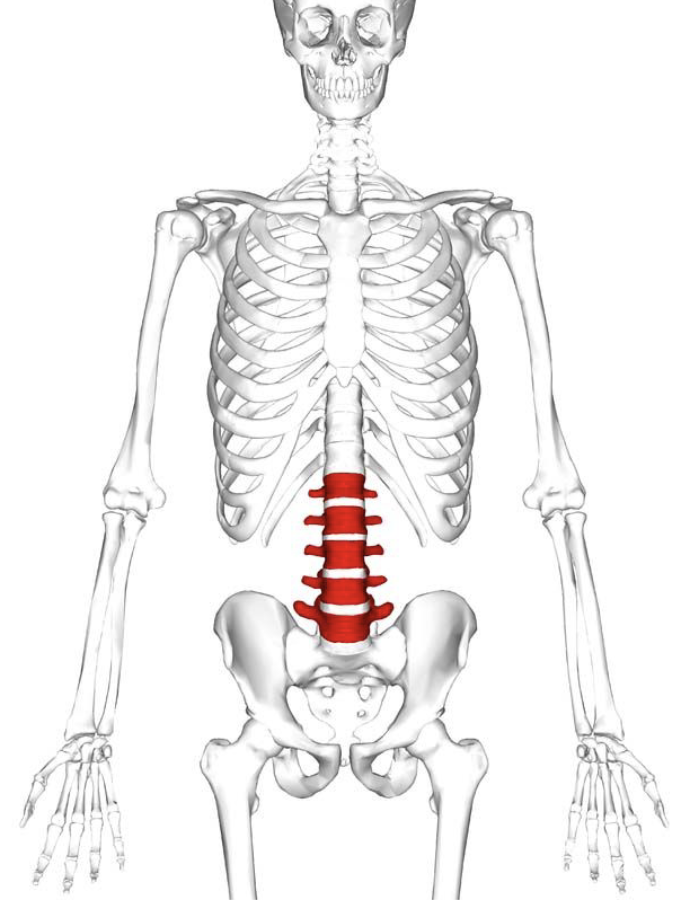
Lumbar Vertebrae (5)
Massive block-like bodies
Weight bearing and thick
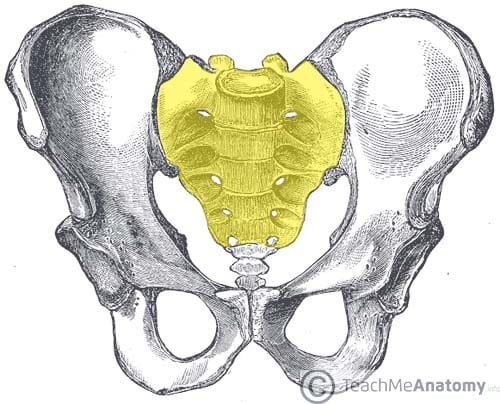
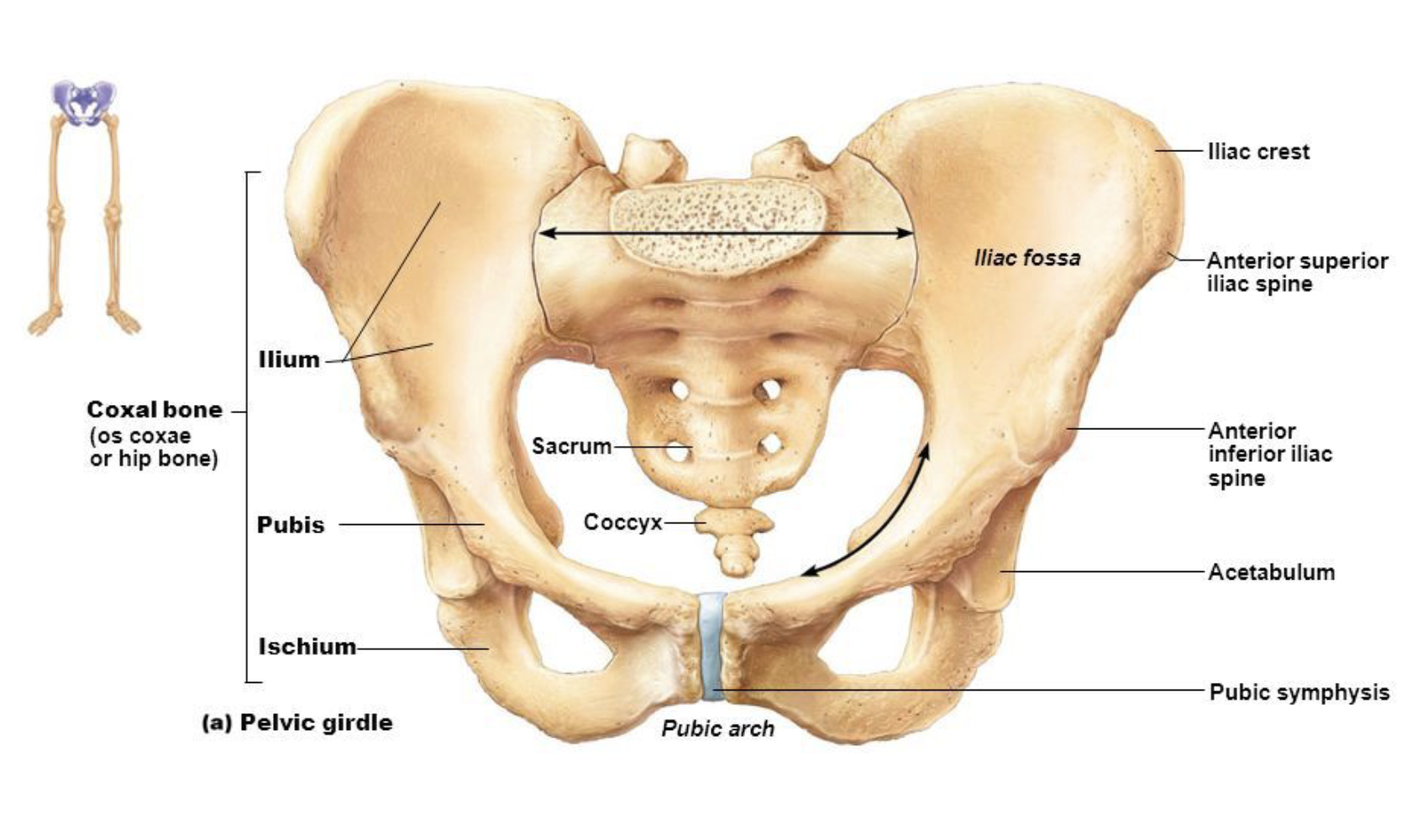
Sacrum (1) (5 fused)
Fusion begins around age 20
Forms posterior wall of pelvis
Vertebral canal continues as sacral canal
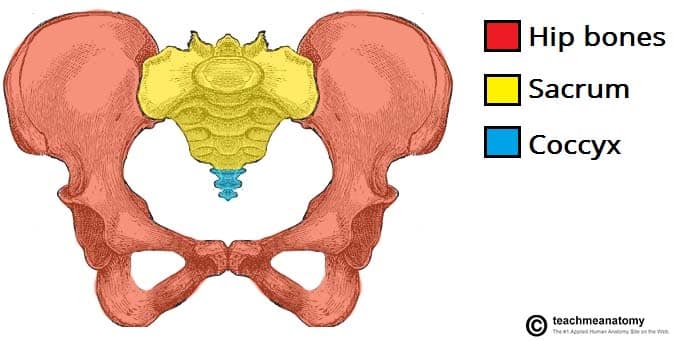
Coccyx (1) (3-5 fused)
Irregular vertebrae
Commonly known as tailbone
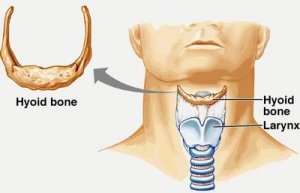
Hyoid Bone
Movable
Horseshoe shape
Located above Adams apple in men
Attachment point for movement of larynx
Gagging
Sound
Swallowing
Foundation for tongue
Breathing
Keeping mouth open
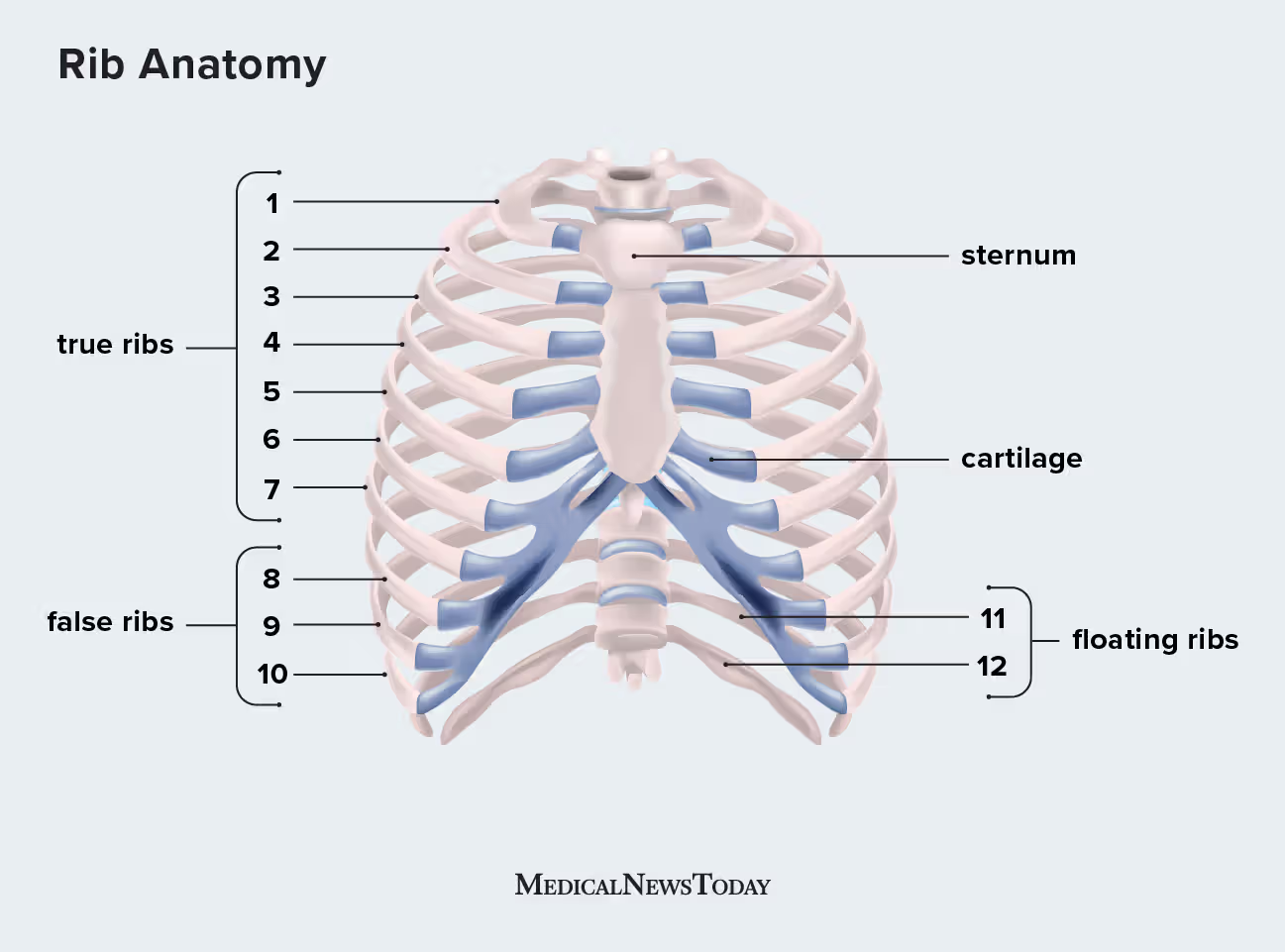
Ribs
Thorax is made up of sternum, ribs, and thoracic vertebrae.
Thoracic vertebrae attach to ribs posteriorly
Sternum attaches to ribs anteriorly
First 7 pairs are true ribs because they attach directly to sternum by costal cartilage
Next 5 pairs are false ribs because the attach indirectly to sternum
Last 2 pairs of false ribs lack attachment so are called floating ribs
Aid in breathing
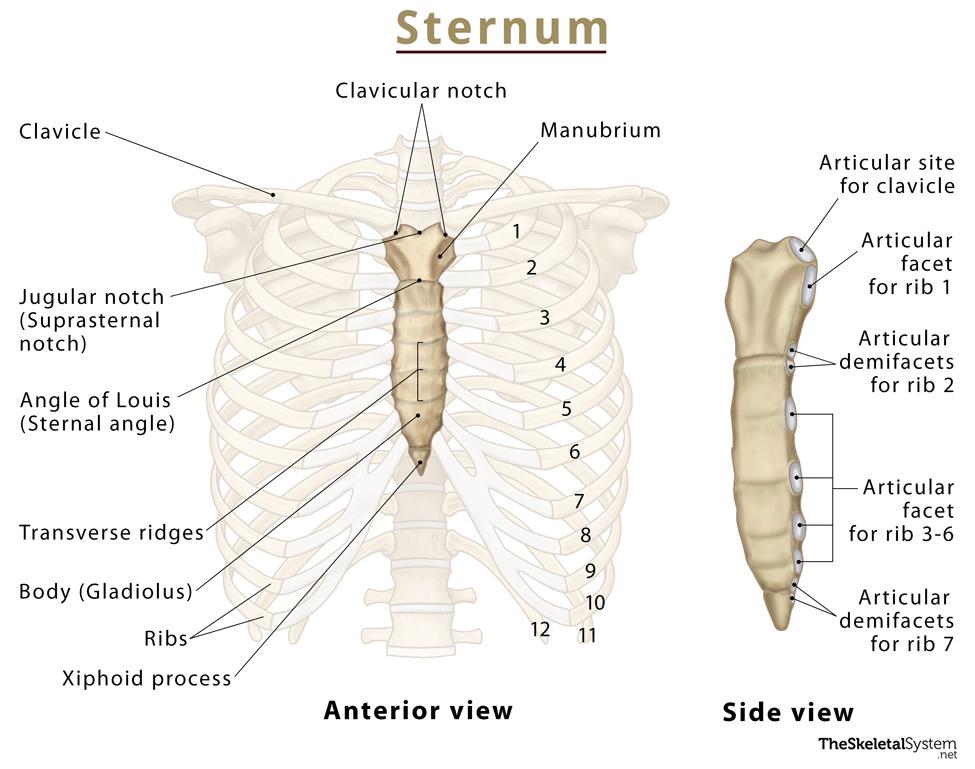
Sternum
3 fused bones (manubrium, body, and xiphoid process)
Attached to first 7 pairs of ribs
Helps protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury
Tuberosity
Obvious bump/protuberance on a bone that serves as a site for muscle or ligament attachment
Tubercle
Same as tuberosity, but smaller
Process
Projection of bone
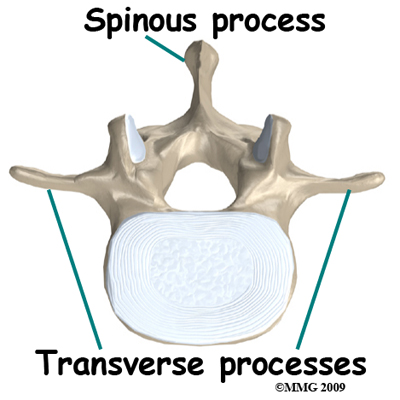
Spine
Bone projection that is longer and thinner than a tuberosity
Fossa
Hollowed area of a bone
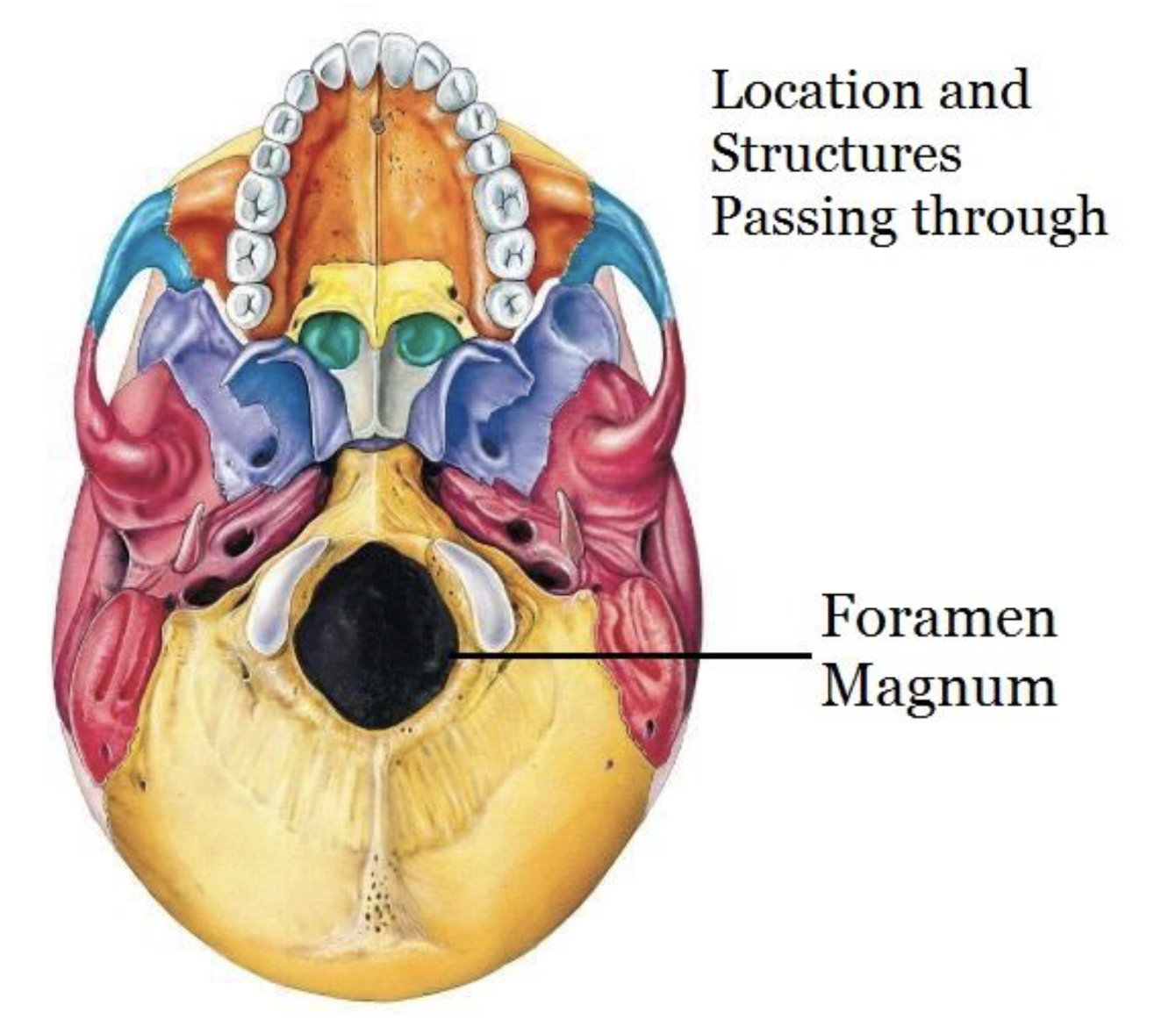
Foramen
Hole that passes through a bone
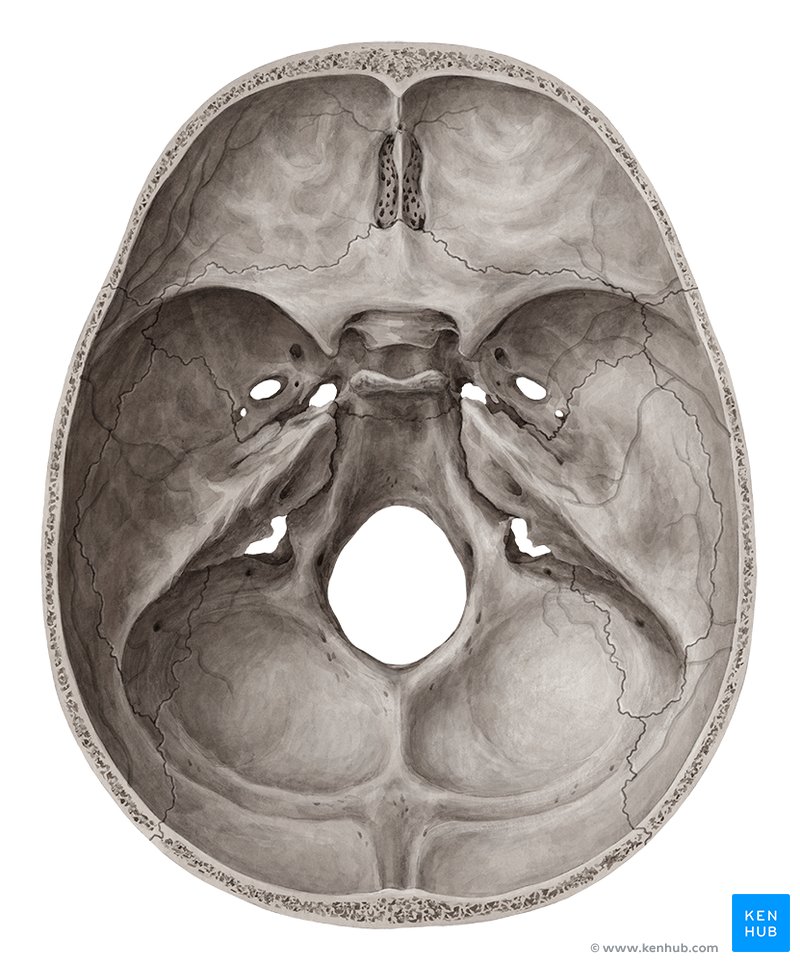
Condyles
Articular surfaces of bone
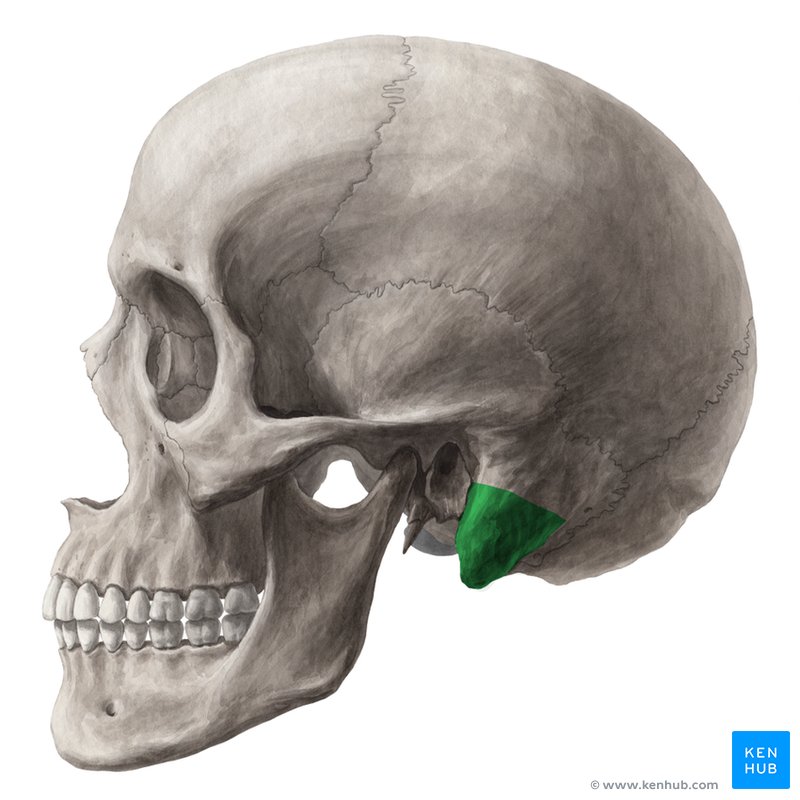
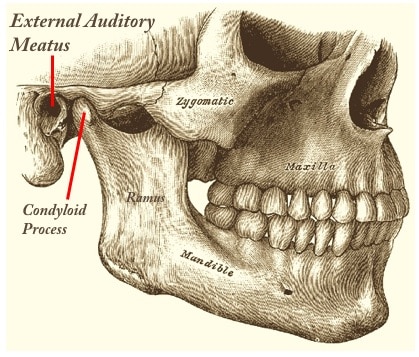
Mastoid Process
Sutures of the Skull (x4)
Coronal Suture
Lambdoid Suture
Squamous Suture
Sagital Suture
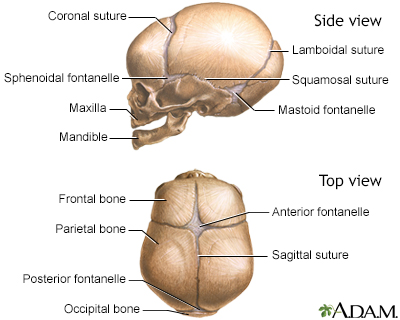
Fontanelles (x2)
Anterior Fontanelle
Posterior Fontanelle
External Auditory Meatus
Foramen Magnum
entry/exit of spinal cord
Functions of Muscular System (x3)
Locomotion - All body movements and many body functions (arms, heart, intestines…)
Posture - Even when relaxed muscles are working to keep you upright (neck, lower back…)
Heat Production - Body needs a basal temperature and muscles keep this by releasing heat as a by-product of reactions
Characteristics of Muscular System (x4)
Irritability - Sensitive to nervous stimuli
Contractility - Responds to stimuli by shortening
Extensibility - Can be stretched when relaxed
Elasticity - Return to normal length when relaxe
Muscle Tissue (3 types)
Smooth, Cardiac, and Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Usually found in hollow internal organs (stomach, intestines, bladder)
Smooth muscle cannot be consciously contracted therefore it is said to be an involuntary muscle
Smooth muscle lacks the appearance of striations
Smooth muscle cells are shorter than skeletal muscle cells
Cardiac Muscle
Occurs only in the heart
Controlled involuntarily
Can continue to function without nerve impulses
They are striated in appearance and the cells are joined end to end
Skeletal Muscle
Over 600
Contraction is voluntary
Striated in appearance (alternating dark and light bands)
When stimulated by a nerve fibre it contracts and relaxes
Includes both fast twitch and slow twitch fibers
They are attached to bones and are responsible for movement
Also used in talking, breathing, swallowing and singing
Actions of Muscular System
The movement a muscle causes depends on where it is attached to a bone and how it is crosses a joint
Origin
Immovable end (proximal end)
(When a muscle contract its insertion is pulled toward its origin)
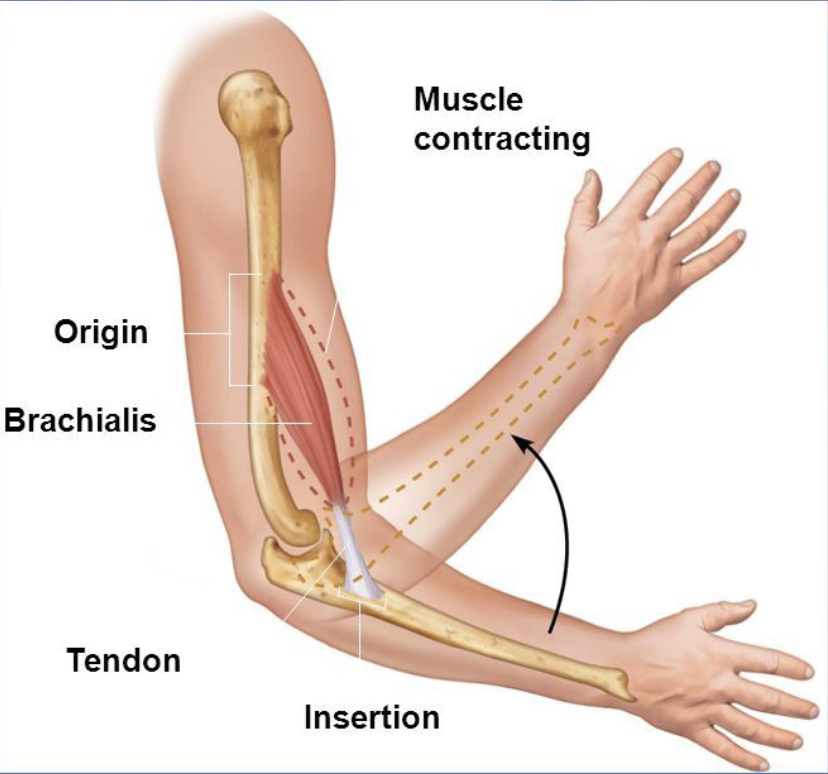
Insertion
The moveable end of the joint (distal end)
(When a muscle contract its insertion is pulled toward its origin)
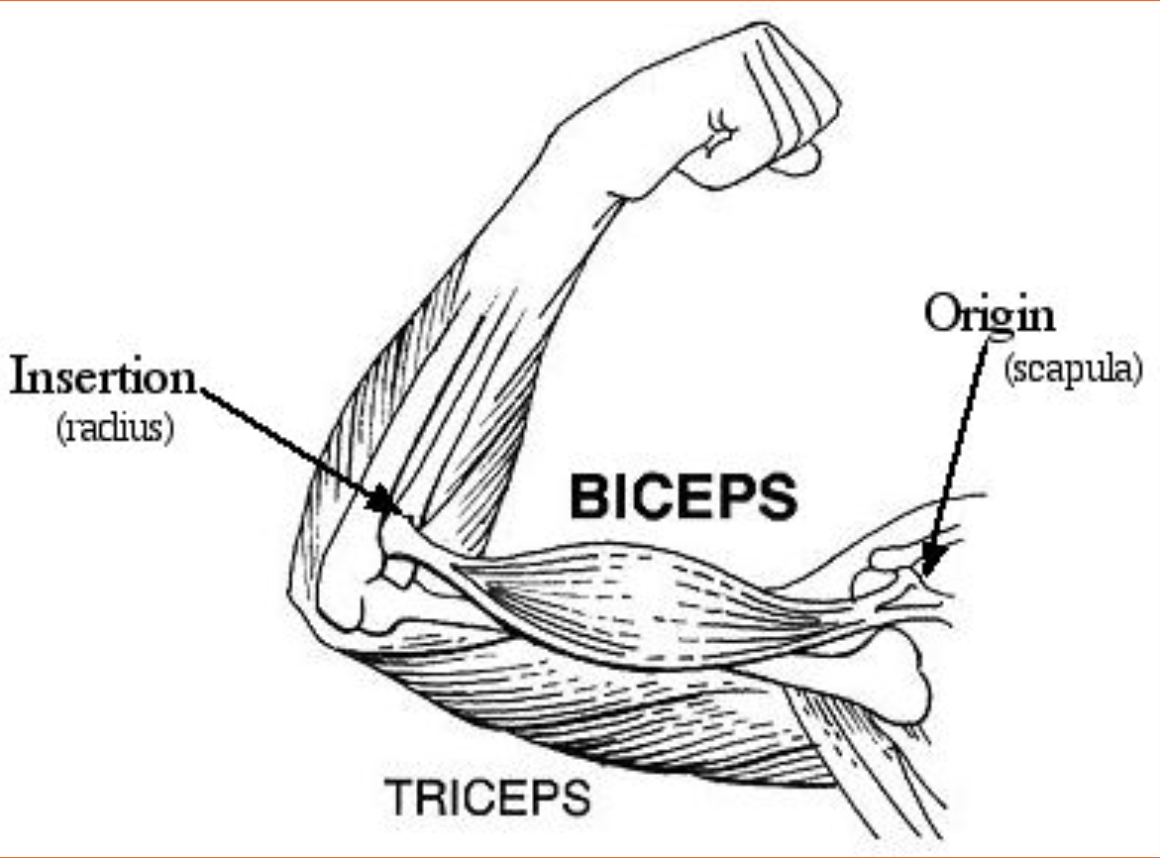
Muscles
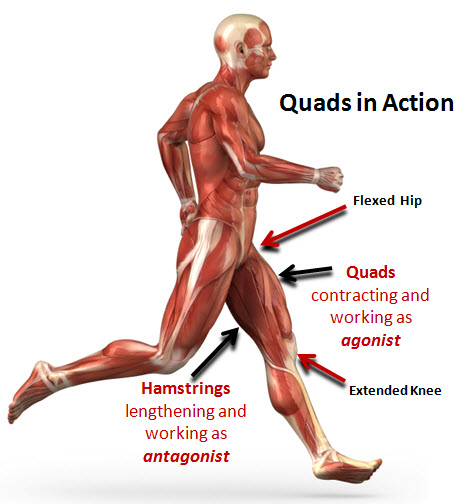
Muscles that move in a specific manner are called AGONISTS (prime movers) whereas muscles that move opposite to the agonists are called ANTAGONISTS. Many muscles are paired in agonist – antagonist relations
(eg. Bicep and Tricep)
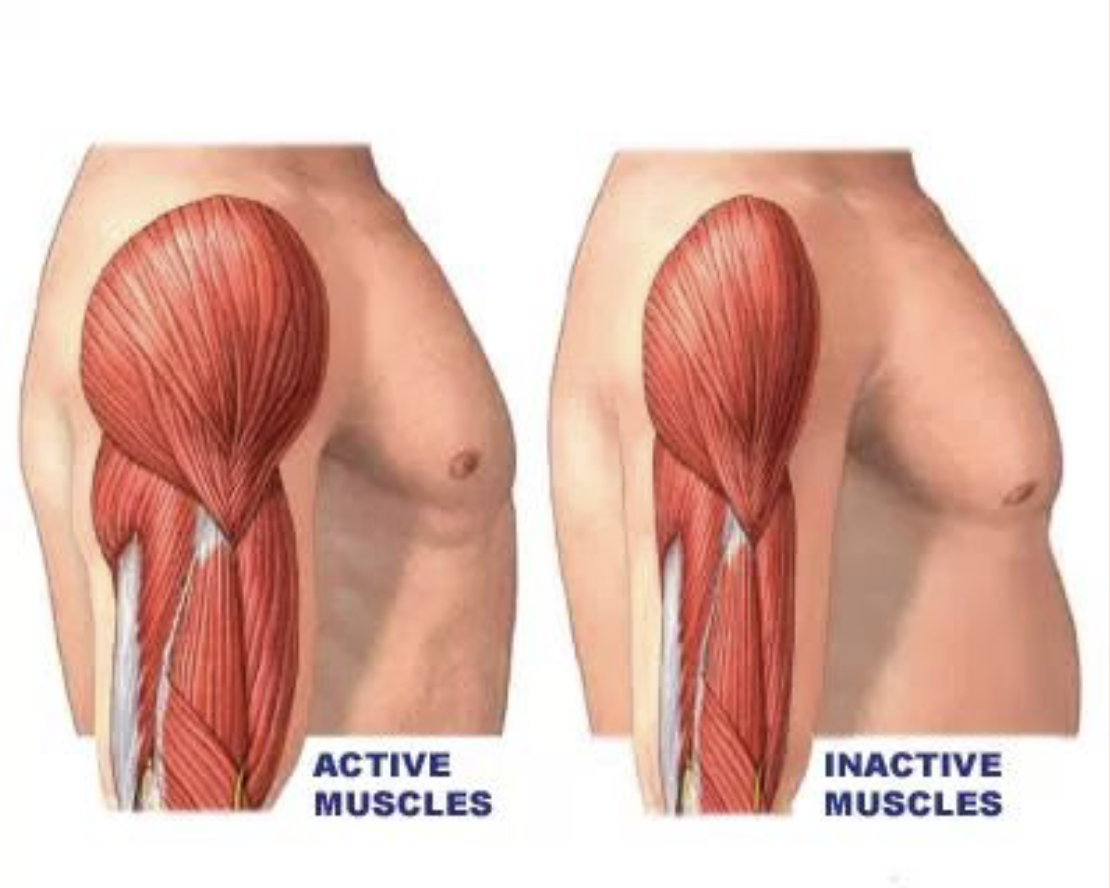
Muscle Development
Most muscles have formed by the 8th week of pregnancy. Most women can feel movement by the 17th week of pregnancy. At birth you have a fixed amount of muscle cells.
Growth of muscle cells depend on their use.
➔ Atrophy – decrease in muscle cell diameter due to neglect of stimulation
➔ Hypertrophy – increase in muscle cell diameter due to stimulation
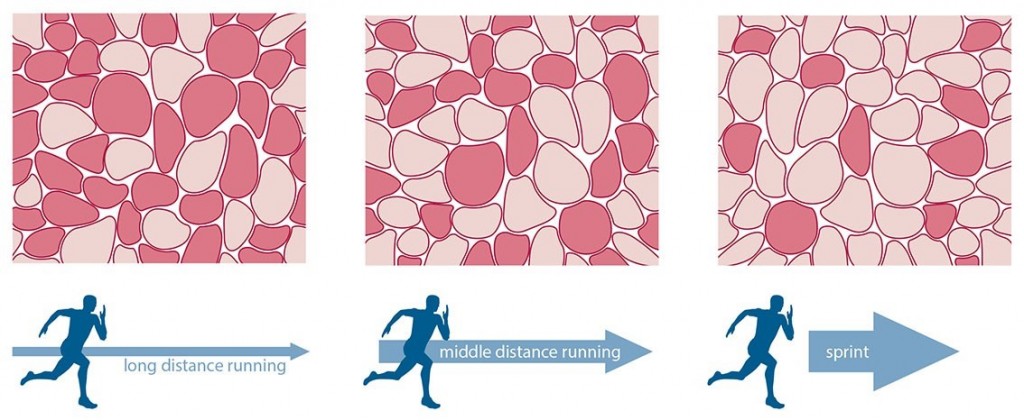
Muscle Fibre Types
Within every skeletal muscle there are two types of fibres:
Slow Twitch (Type 1) - required for endurance (eg. long-distance running, swimming, cycling…)
Fast Twitch (Type 2) - required for quick bursts of power and energy (eg. sprinting, jumping, weight-lifting…)
Fast Twitch Fibres
Fast Twitch fibres (Type 2) can be further broken down into Type 2a and Type 2b.
Type 2a = Fast Oxidative
Type 2b = Fast Glycolytic
Type 2a = Fast Oxidative
These fibres can access both anaerobic and aerobic energy systems, and so are a hybrid of slow and fast twitch fibres. They produce fast contractions but are less fatigue resistant than Type 1 fibres.
Type 2b = Fast Glycolytic
These fibres can only access the anaerobic energy system. They have the fastest contraction speed but have a very low resistance to fatigue.
Fibre Type Modification
Various types of exercises can bring about changes in the fibres in a skeletal muscle
Endurance type exercises, such as running or swimming, cause a gradual transformation of type II B fibres into type II A fibres
The transformed muscle fibres show a slight increase in diameter, mitochondria, blood capillaries, and strength
A type 2A fibre can be changed to a type 2B fibres with training
A type 1 cannot be change to type 2 fibre
Buccinator
One of the first muscles that a human cancontrol
Sucking reflex of a baby
Smiling, chewing, and whistling
Speech

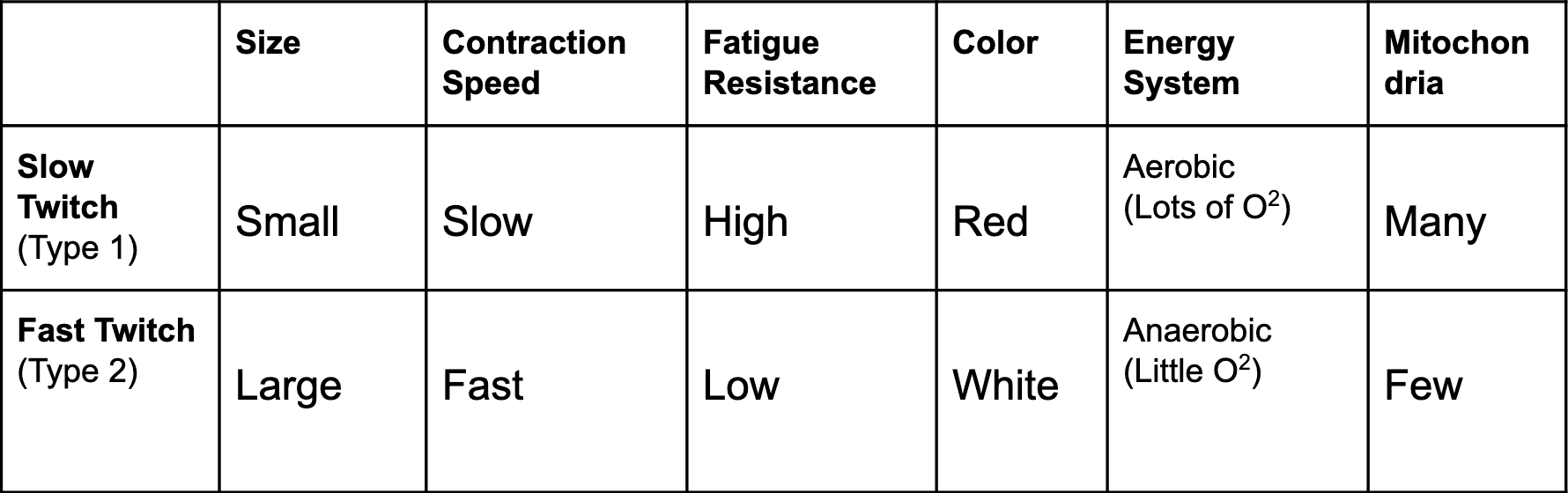
Frontalis
Change their facial expressions
Allows the eyebrows to raise and the forehead to wrinkle
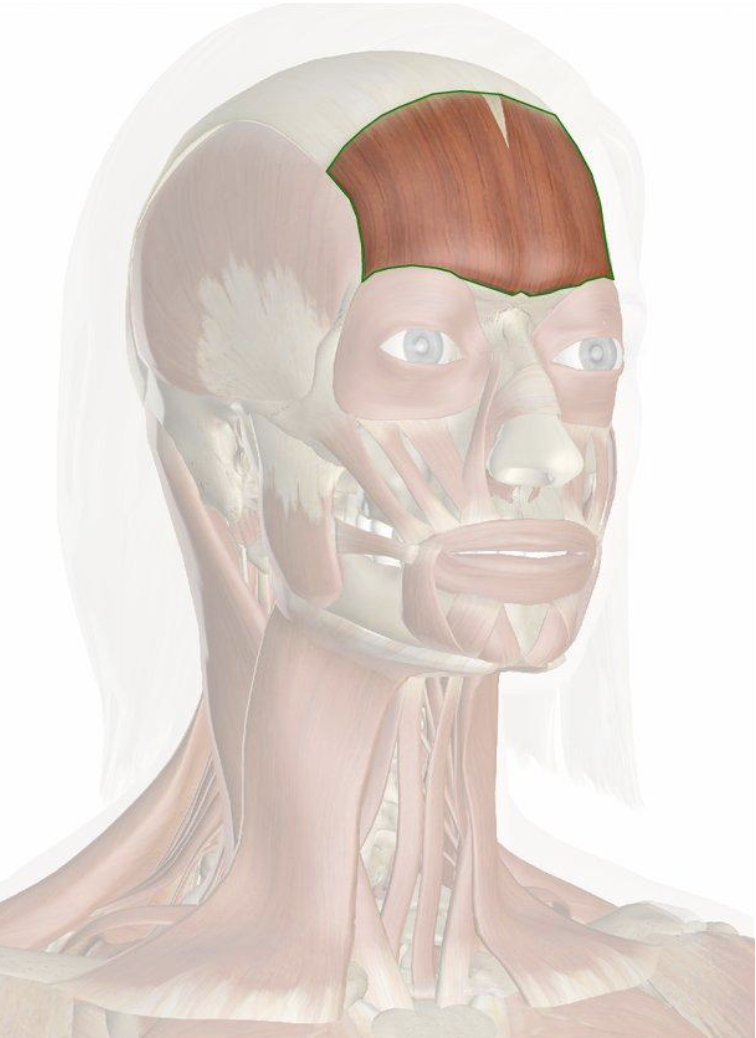
Masseter
Chewing
Strongest muscle in the human body
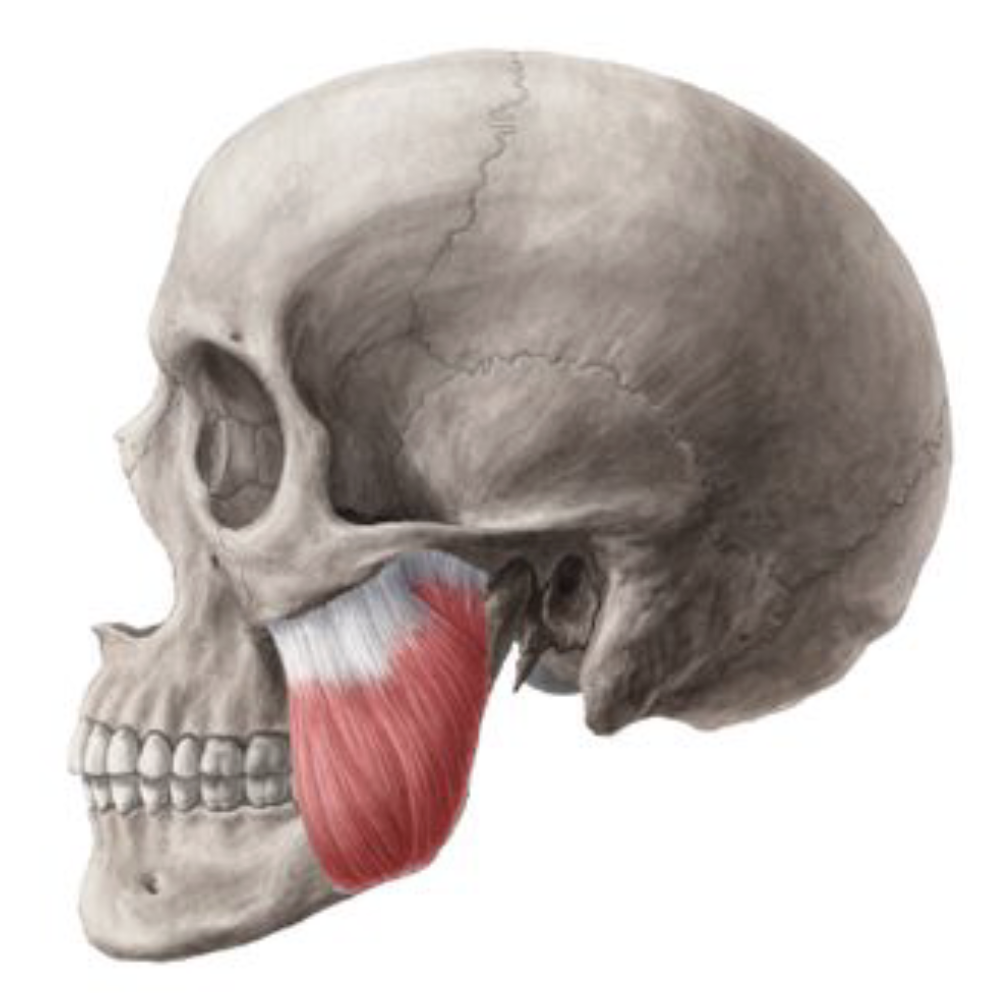
Orbicularis Oculi
Important muscle in facial expression
Close the eyelid, and to help in the passing and draining of tears
Closes the eyelids gently in involuntary or reflex blinking
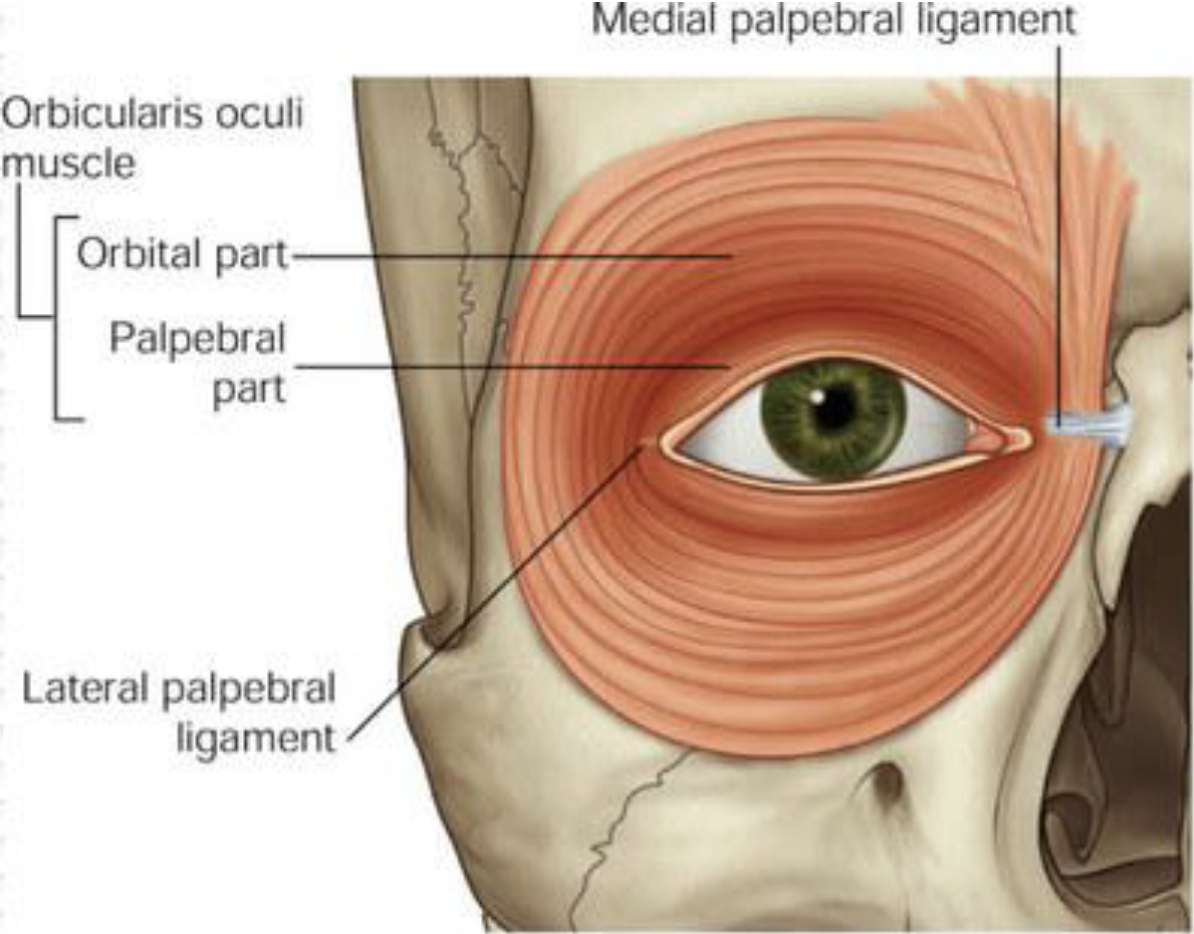
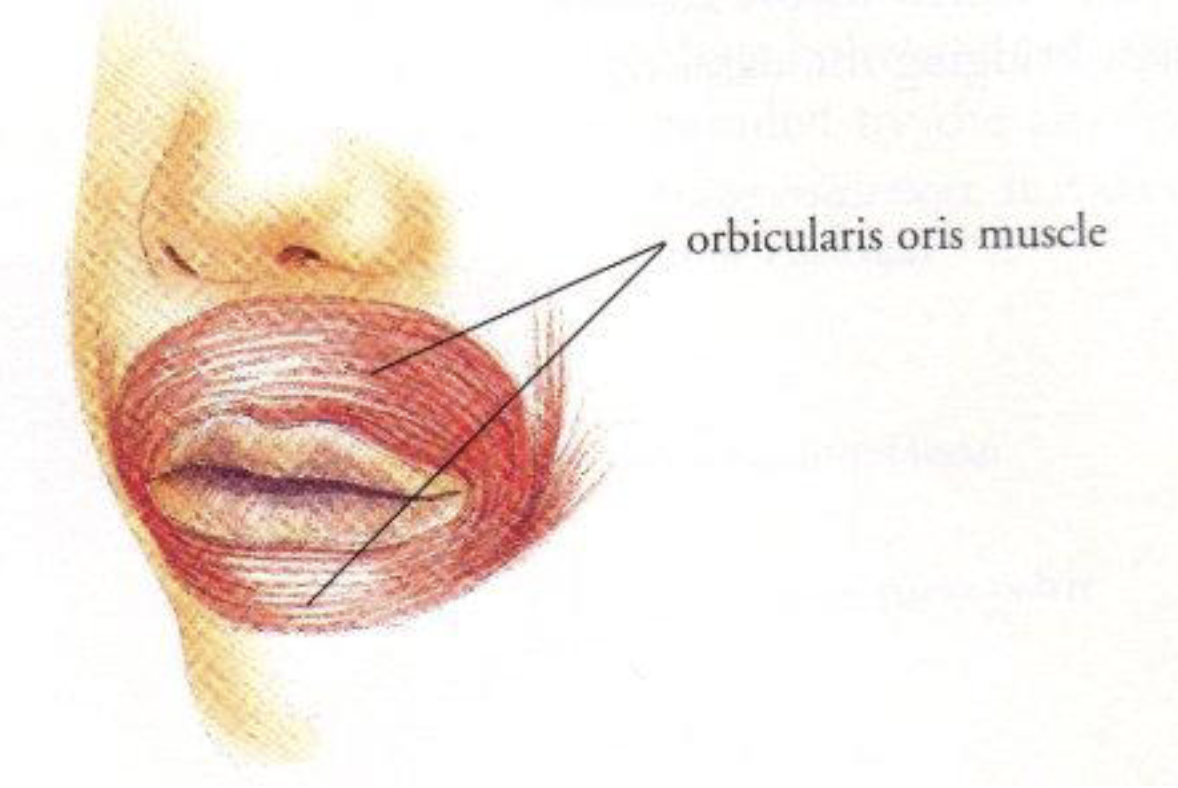
Orbicularis Oris
Controls movements of the mouth and lips
Kissing muscle
Allows for facial expression
Puckering the lips
Forcefully exhale
Closing the mouth
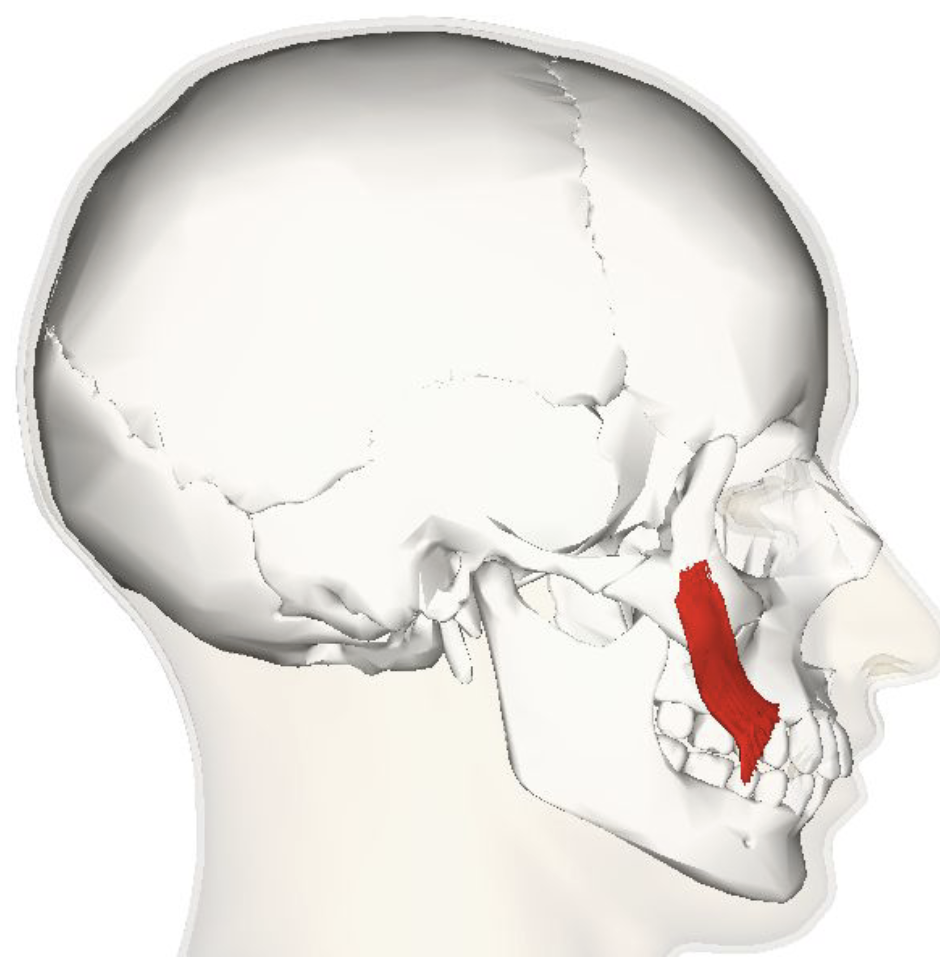
Temporalis
Chewing
Crushing and grinding objects between the molars
Focal point for a recurring condition known as “tension headaches”
Unclenching and clenching the jaw contracts this muscle
Controls both retraction and elevation of the mandible

Zygomaticus
Controls facial expression, drawing the mouth's angle upward and outward
Causes the corners of a person's mouth to rise when they smile
Cause dimples to form
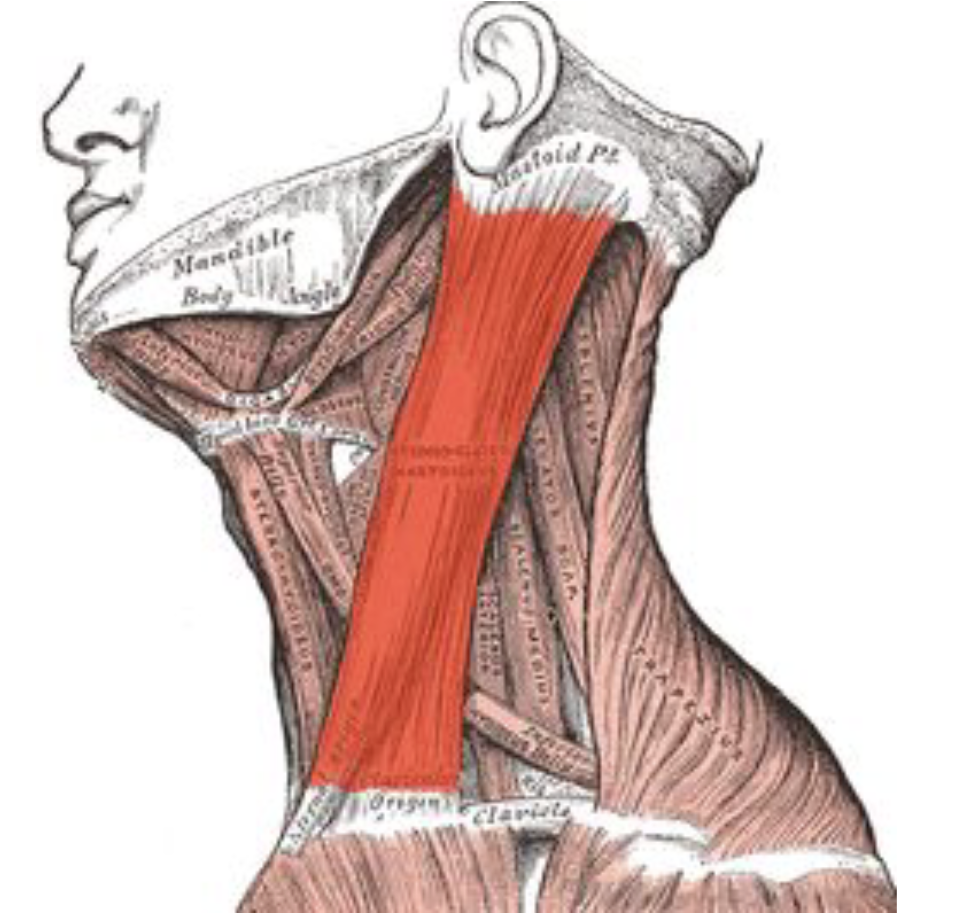
Sternocleidomastoid
Flexes the neck and helps with movement of the head
Raises the sternum
Helps the neck to turn to the side, flex to the side, and bend forward
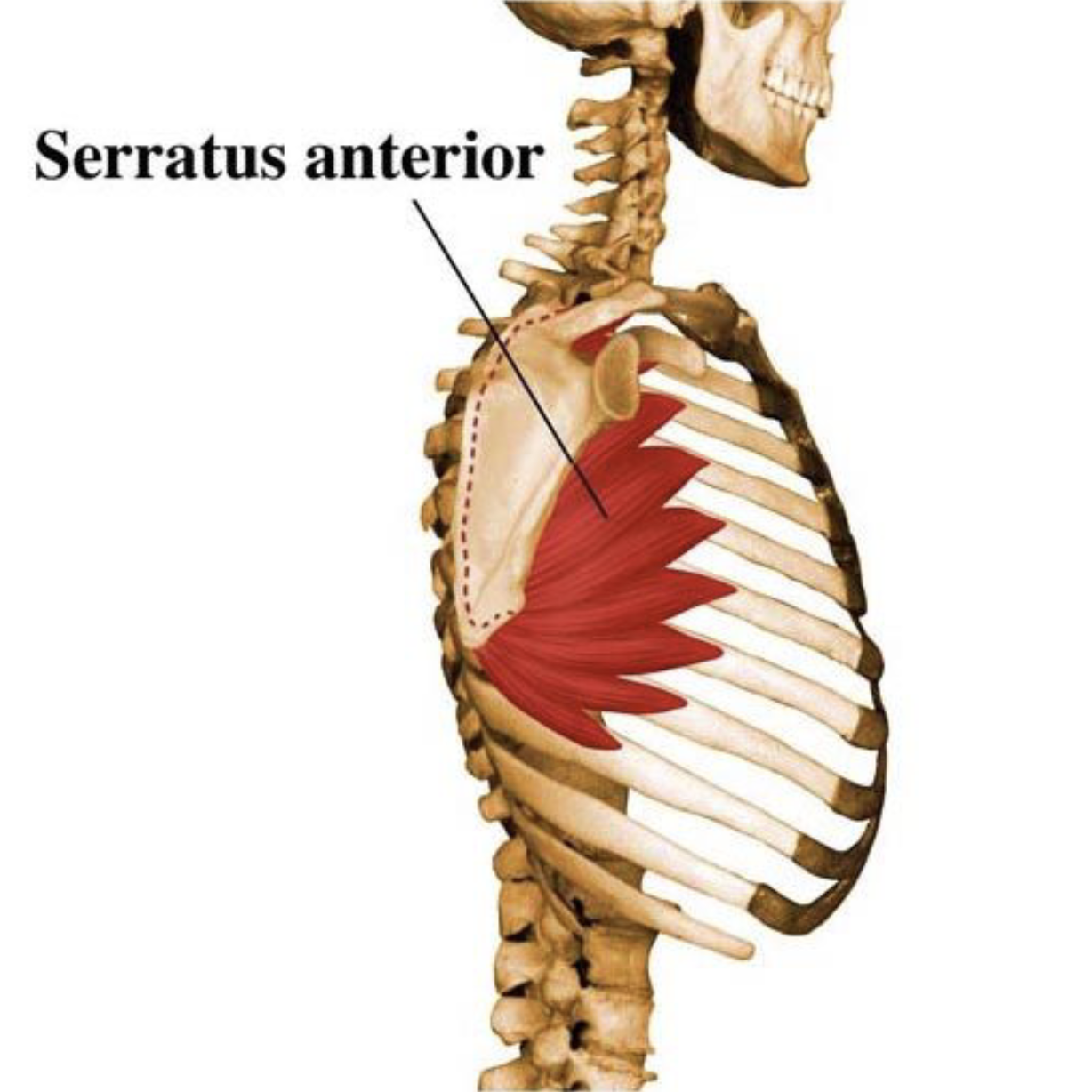
Serratus Anterior
Allows rotation of the arm and pulls the scapula forward and around the rib cage
Also supports breathing
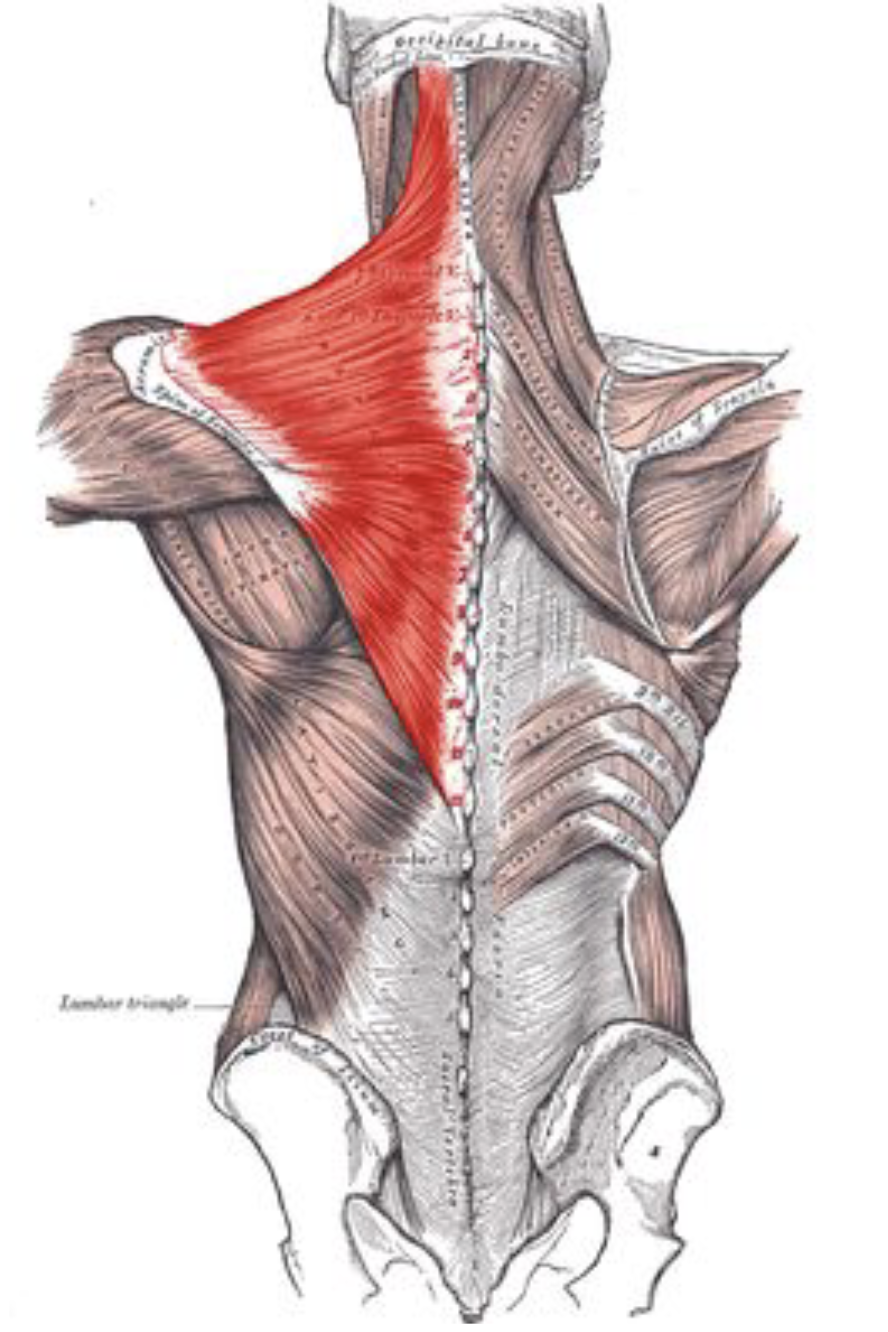
Trapezius
Provides upright posture support
Named for its trapezoid shape
Used to tilt and turn the head and neck
Shrug and steady the shoulders
Twists the arms
Elevates, depresses, rotates, and retracts the scapula
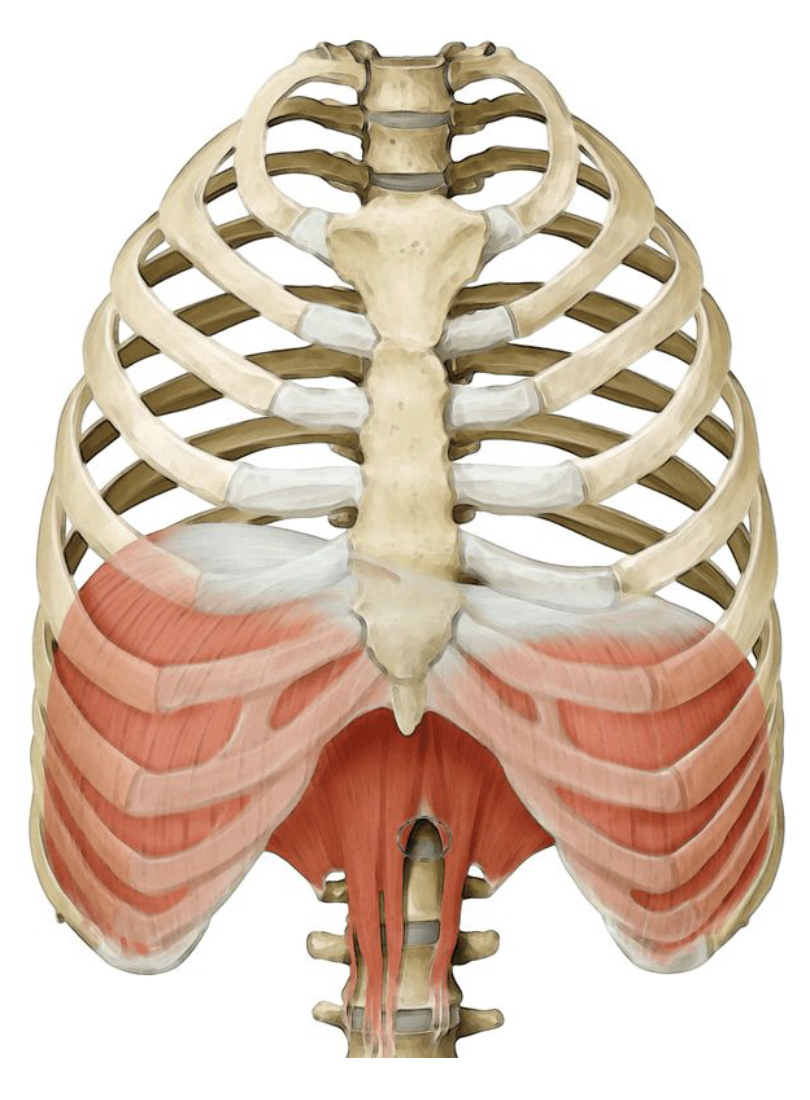
Diaphragm
Inhalation
Facilitates air to flow into the lungs
Can become irritated (hiccups)
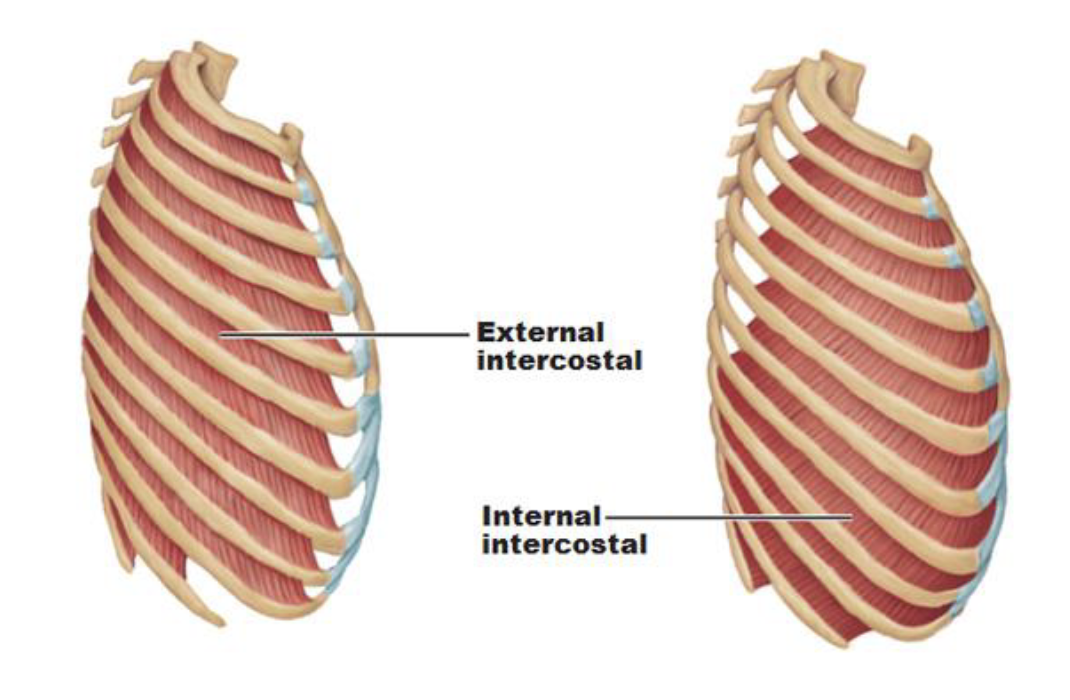
Intercostals
Create and move the chest wall
Assist with the breathing process
Forced and quiet inhalation
External and Internal Oblique and Transverse Abdominus?
Abdominal muscles
Rotates the trunk
Pulls the chest downwards to compresses the abdominal cavity
Variety of trunk movements
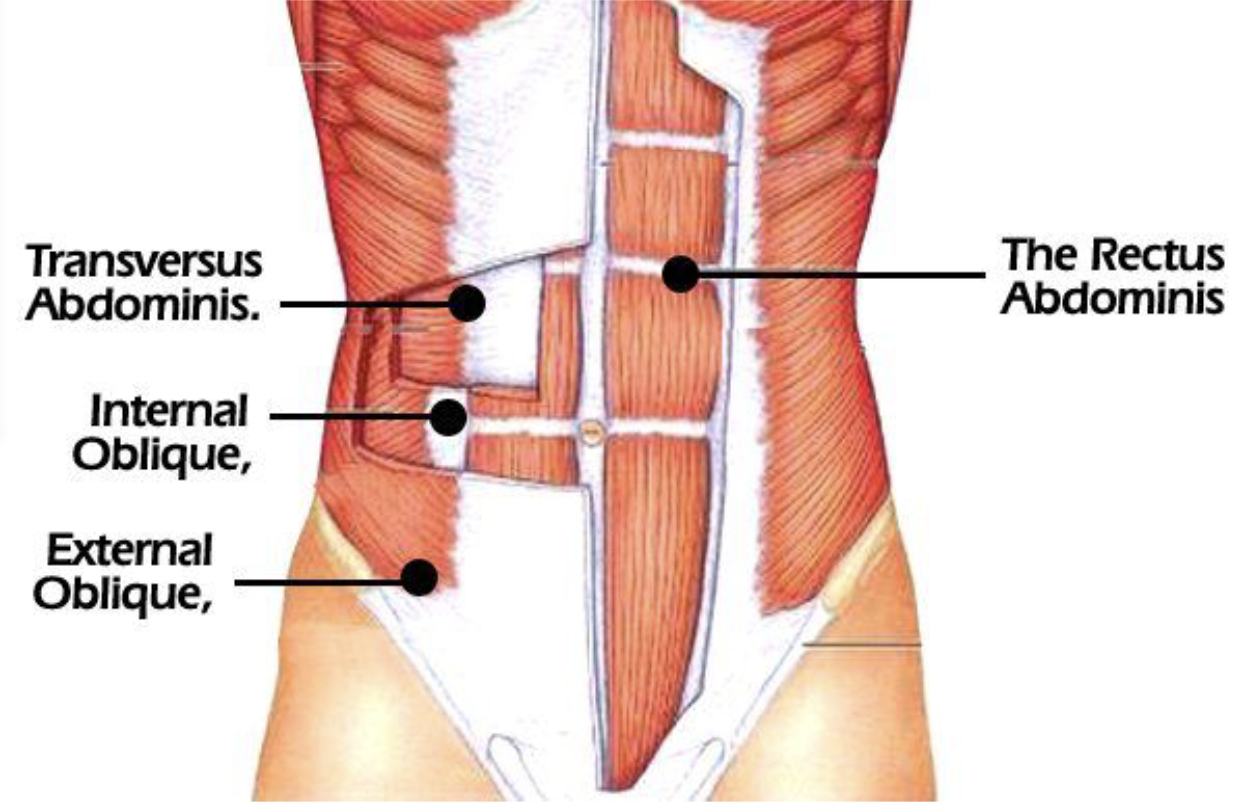
Rectus Abdominus
Flexes while doing crunches
Used when a child is delivered
Used during bowel movements
Coughing
Breathing in
“six pack”
Helps with jumping

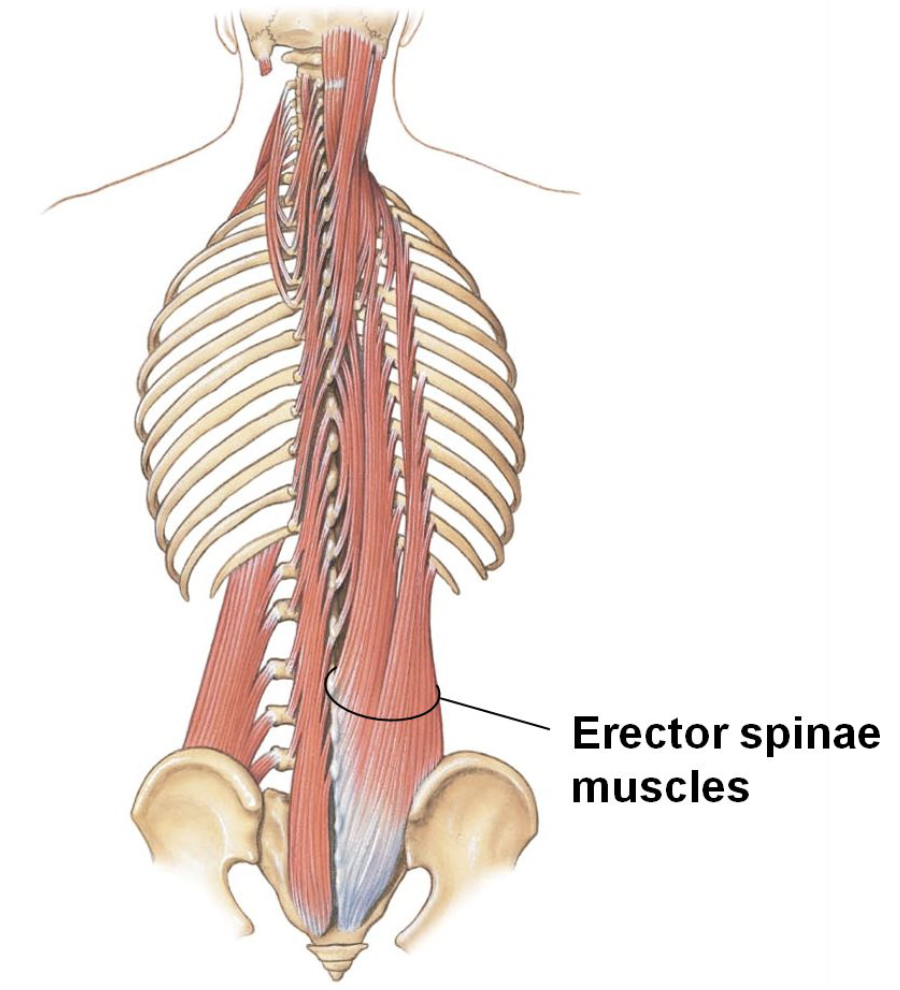
Latissimus Dorsi
Extending, adducting and rotating the arm
Pull ups and chin ups
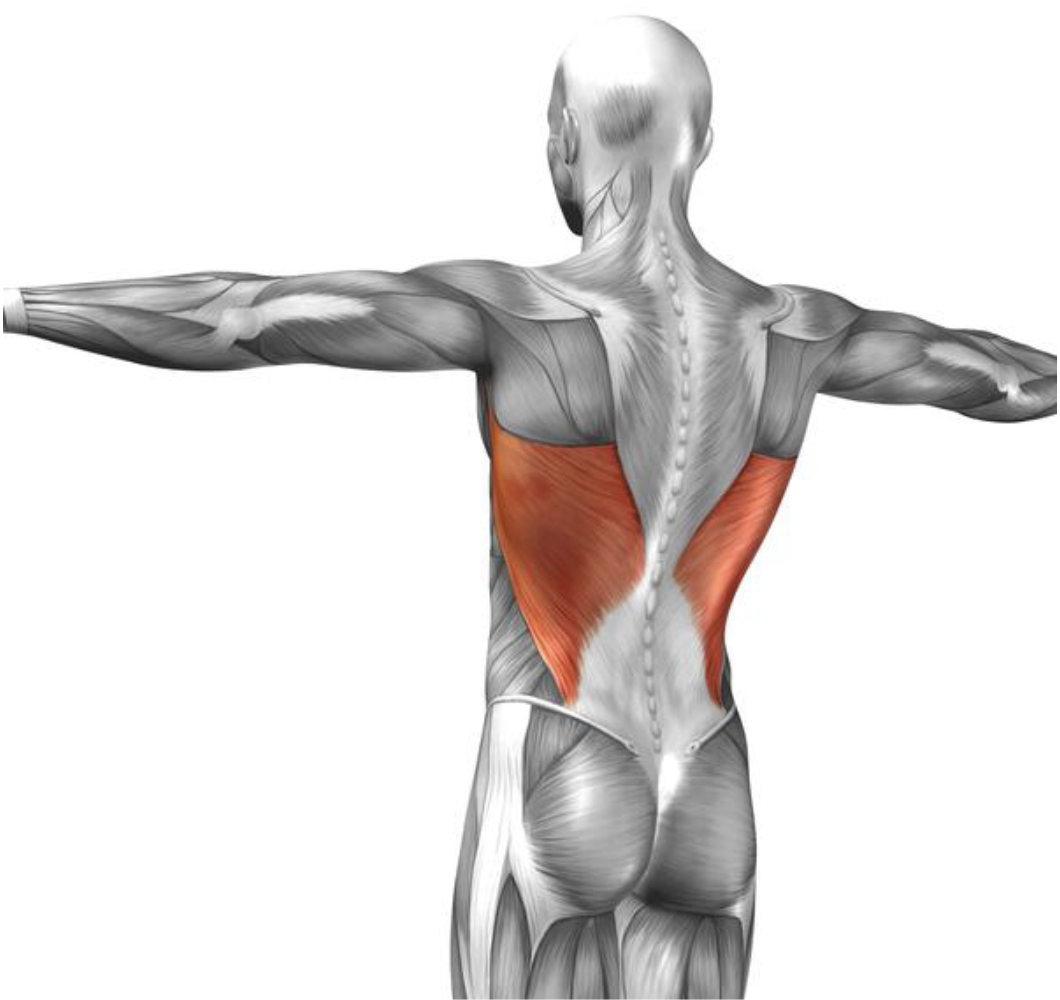
Erector Spinae
Extend and laterally (side to side) bend the neck and trunk
Grouping of 3 muscles
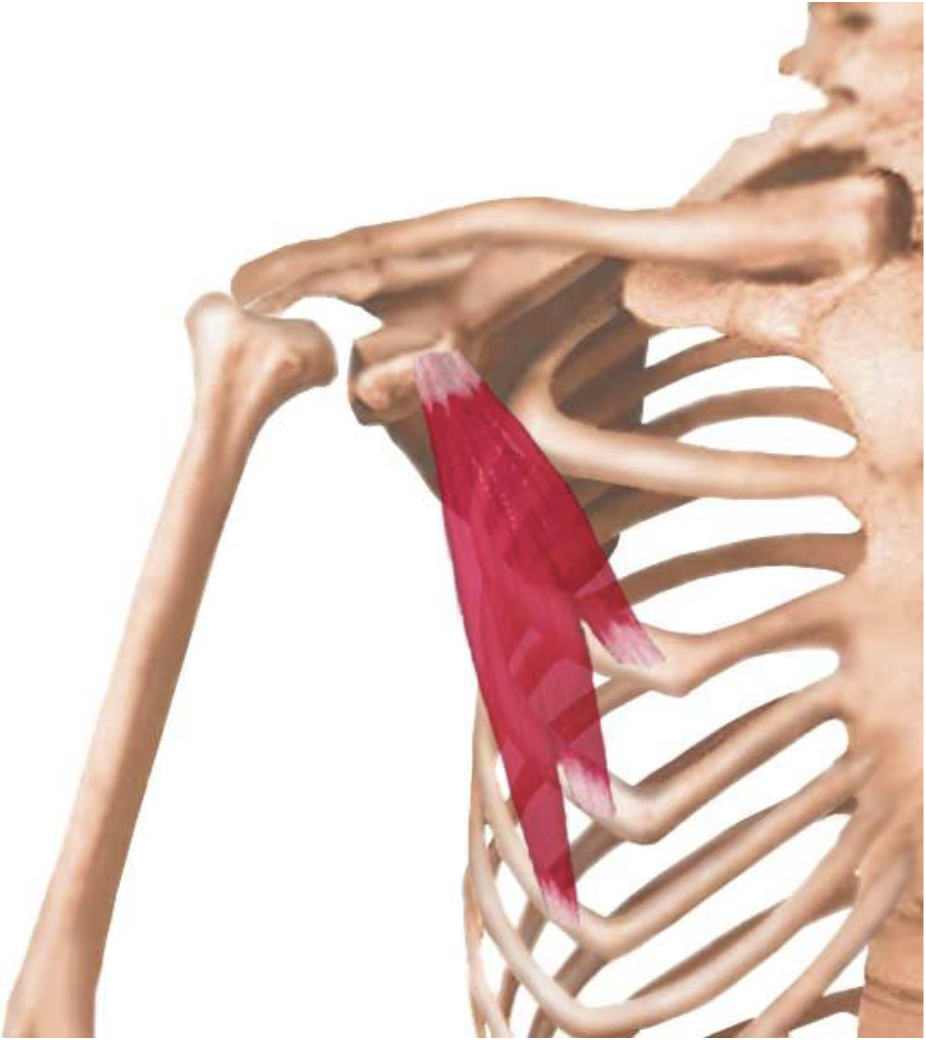
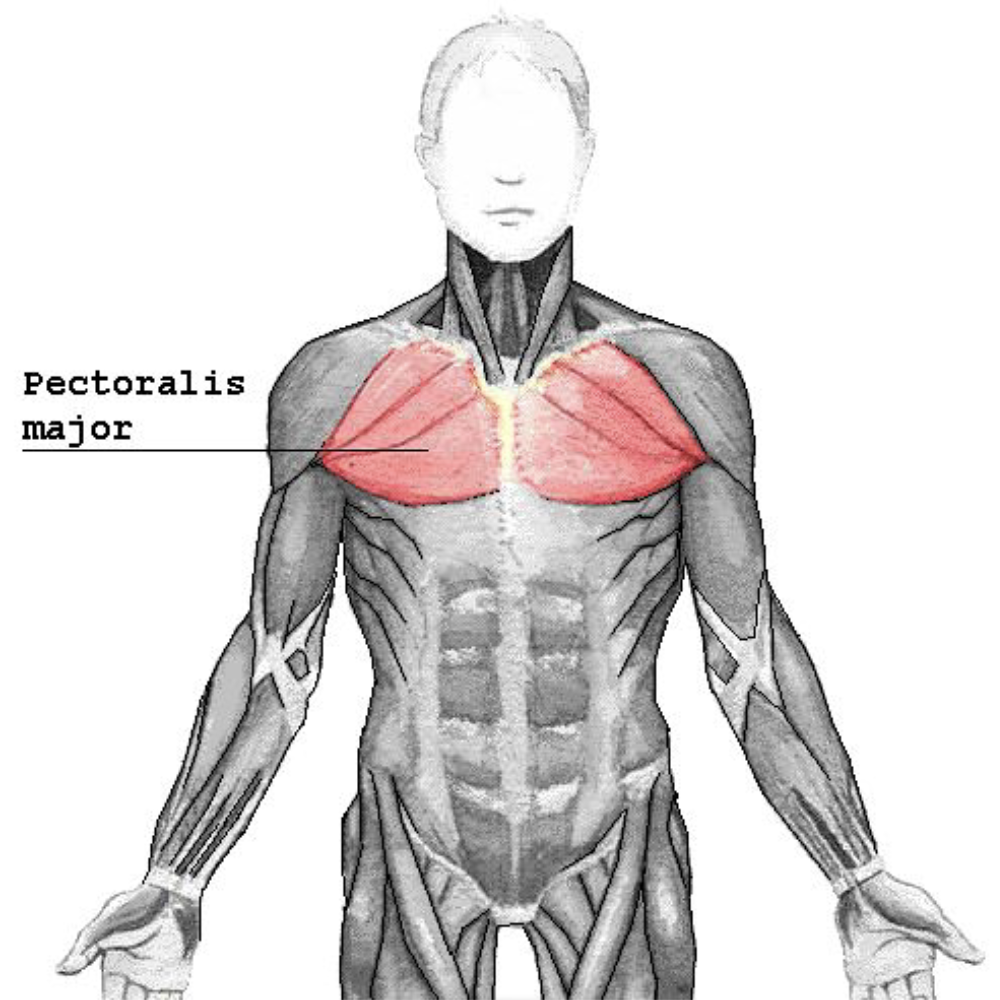
Pectoralis Major
Control the movement of the arm
Pull on the humerus to create lateral, vertical, or rotation
Pushing
Play a part in deep inhalation
Pectoralis Minor
Depresses and stabilizes the scapula