Chapter 28: The Endocrine System Overview
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
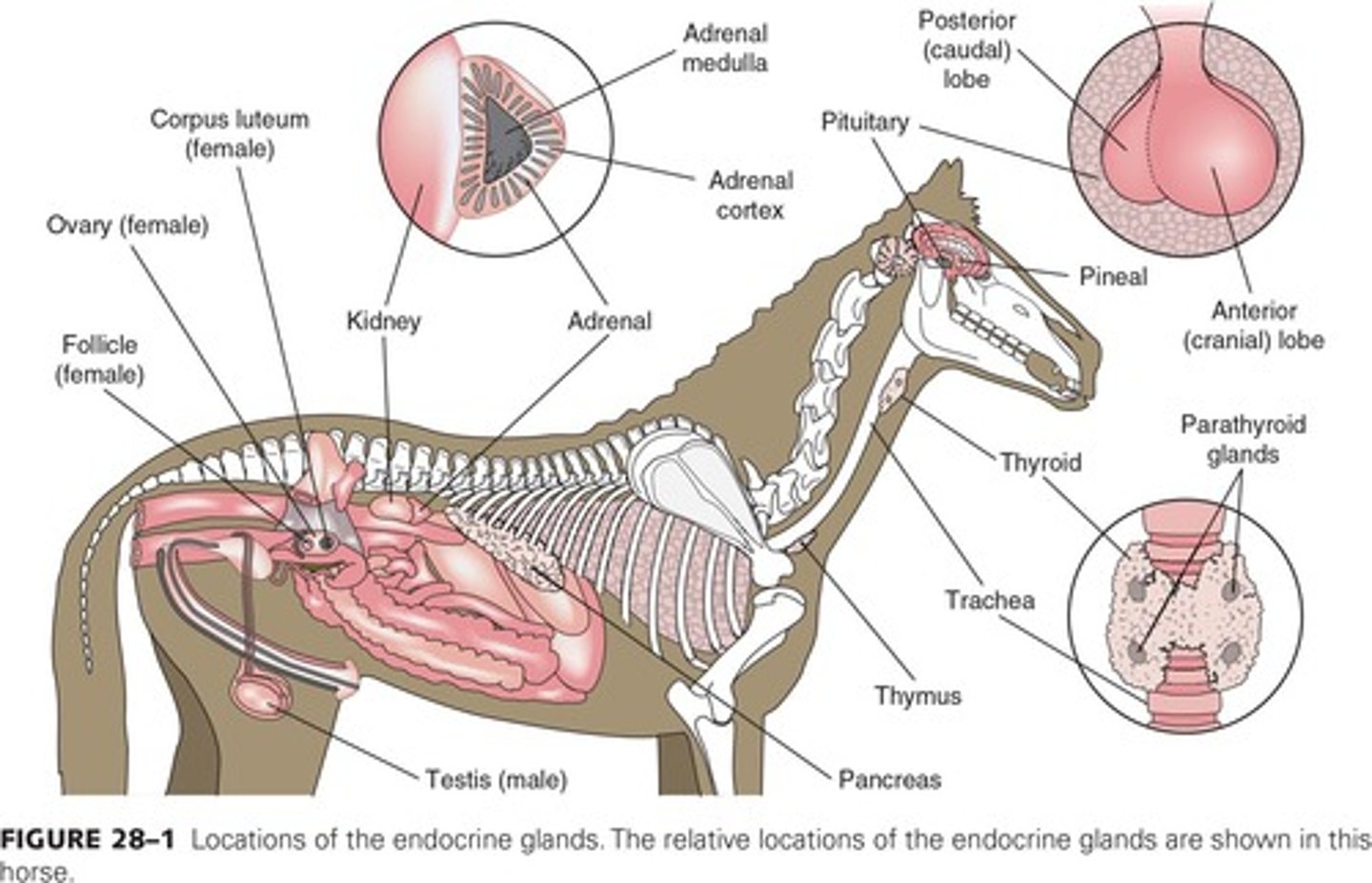
Endocrine System
Network of glands producing hormones for regulation.
Hormones
Chemical messengers regulating physiological processes.
Glands
Organs that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Homeostasis
Stable internal environment maintained by endocrine functions.
Feedback Mechanism
Process regulating hormone levels through feedback loops.
Endocrine System
Network of glands regulating body functions via hormones.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of stable internal body conditions.
Hormones
Chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands.
Glands
Organs that secrete hormones into bloodstream.
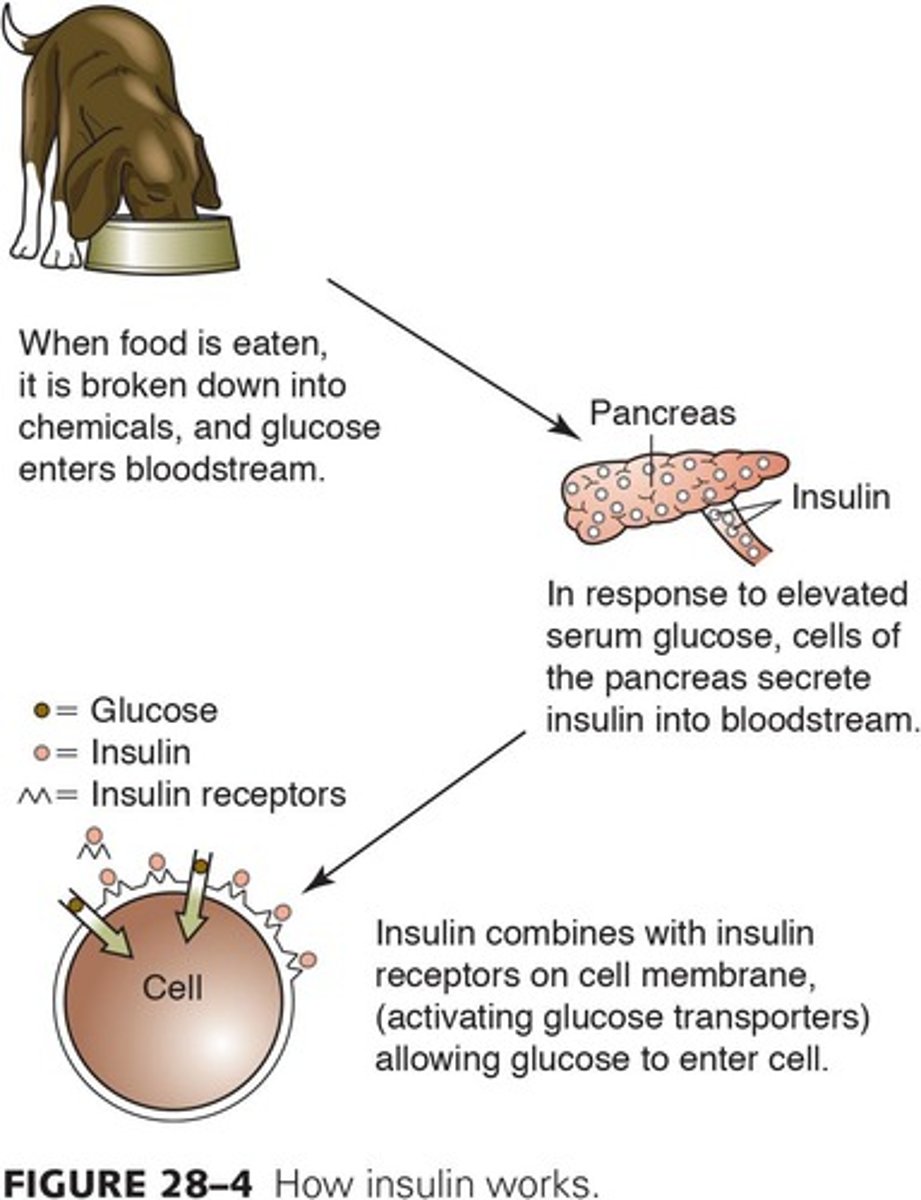
Insulin
Hormone lowering blood sugar levels after meals.
Glucagon
Hormone raising blood sugar levels when low.
Pituitary Gland
Master gland controlling other endocrine glands.
Thyroid Gland
Regulates metabolism and body temperature via hormones.
Parathyroid Glands
Regulate calcium levels in the blood.
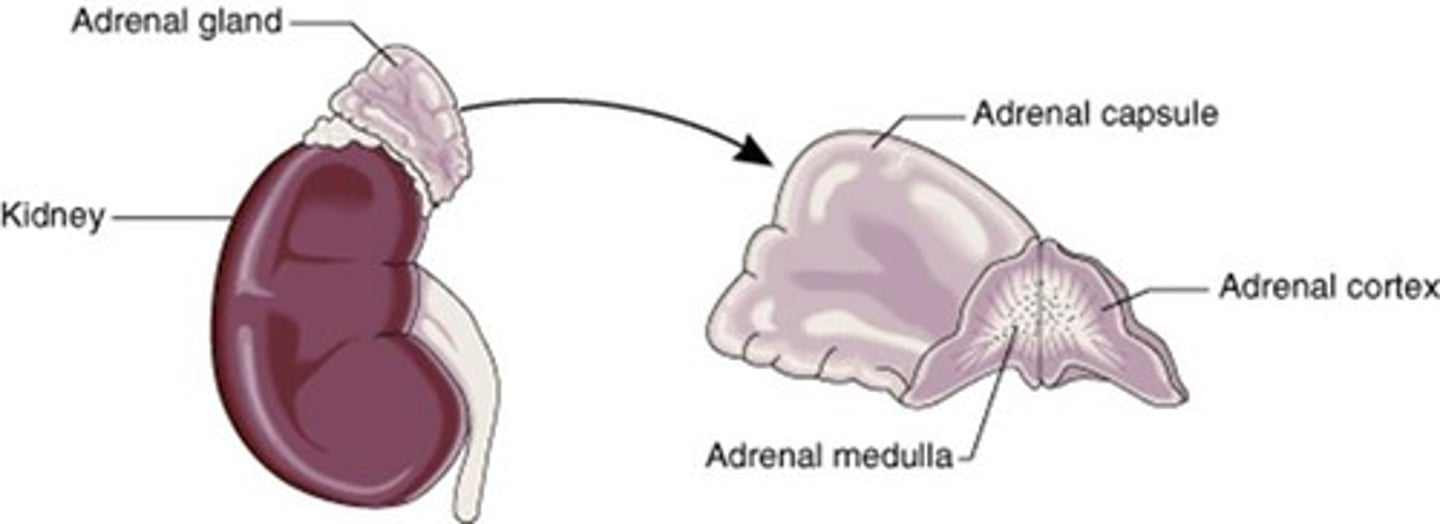
Adrenal Glands
Produce hormones for stress response and metabolism.
Thymus
Gland involved in immune system development.
Pineal Gland
Regulates sleep-wake cycles via melatonin.
Gonads
Ovaries and testes; produce sex hormones.
Oxytocin
Hormone involved in childbirth and bonding.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Regulates water balance in the body.
Thyroxine (T4)
Hormone regulating metabolism and cholesterol levels.
Triiodothyronine (T3)
More active form of thyroid hormone.
Calcitonin
Lowers blood calcium levels.
Epinephrine
Short-acting hormone for fight-or-flight response.
Norepinephrine
Long-acting hormone increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Controls adrenal gland hormone production.
Peptide Hormones
Hormones made of amino acids, like insulin.
Fatty Acid Hormones
Hormones derived from fatty acids, like prostaglandins.
Steroid Hormones
Hormones derived from cholesterol, like cortisol.
Amino Acid Hormones
Hormones derived from amino acids, like thyroid hormones.
Metabolism
Chemical processes converting food into energy.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Insulin and glucagon maintain glucose levels.
Hormone Receptors
Proteins that bind hormones to initiate effects.
Feedback Mechanism
Process regulating hormone levels in the body.
Blood sugar levels
Can be too high, too low, or normal.
Pituitary gland
Gland likely malfunctioning in abnormal growth.
Thyroid gland
Gland involved in metabolism regulation.
Pancreas
Gland that regulates blood sugar levels.
Thymus gland
Matures T lymphocytes; immunologic functions.
Pineal gland
Regulates body rhythms; functions not fully understood.
Gonads
Reproductive glands producing sex hormones.
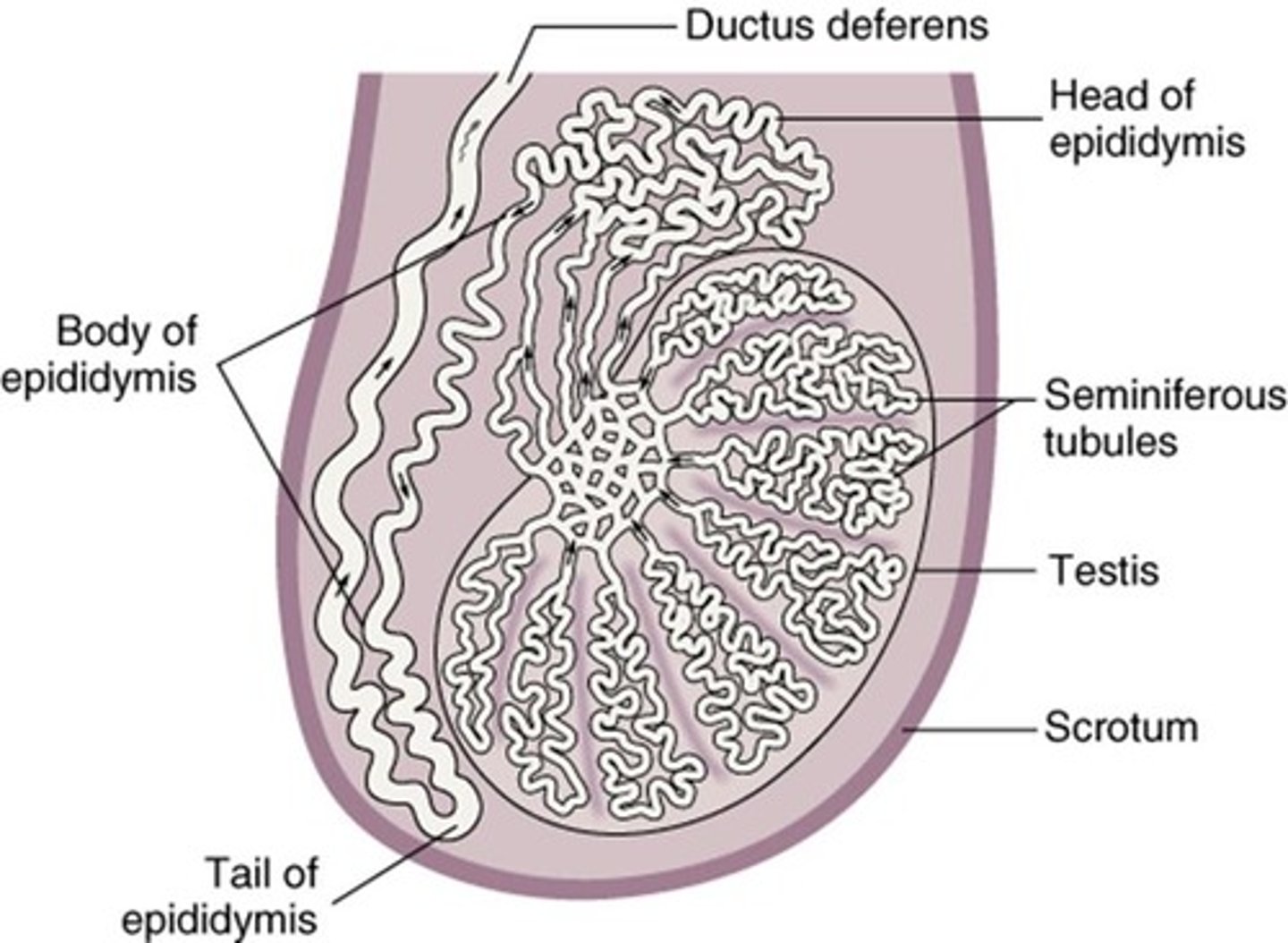
Testes
Male gonads producing testosterone and estrogen.
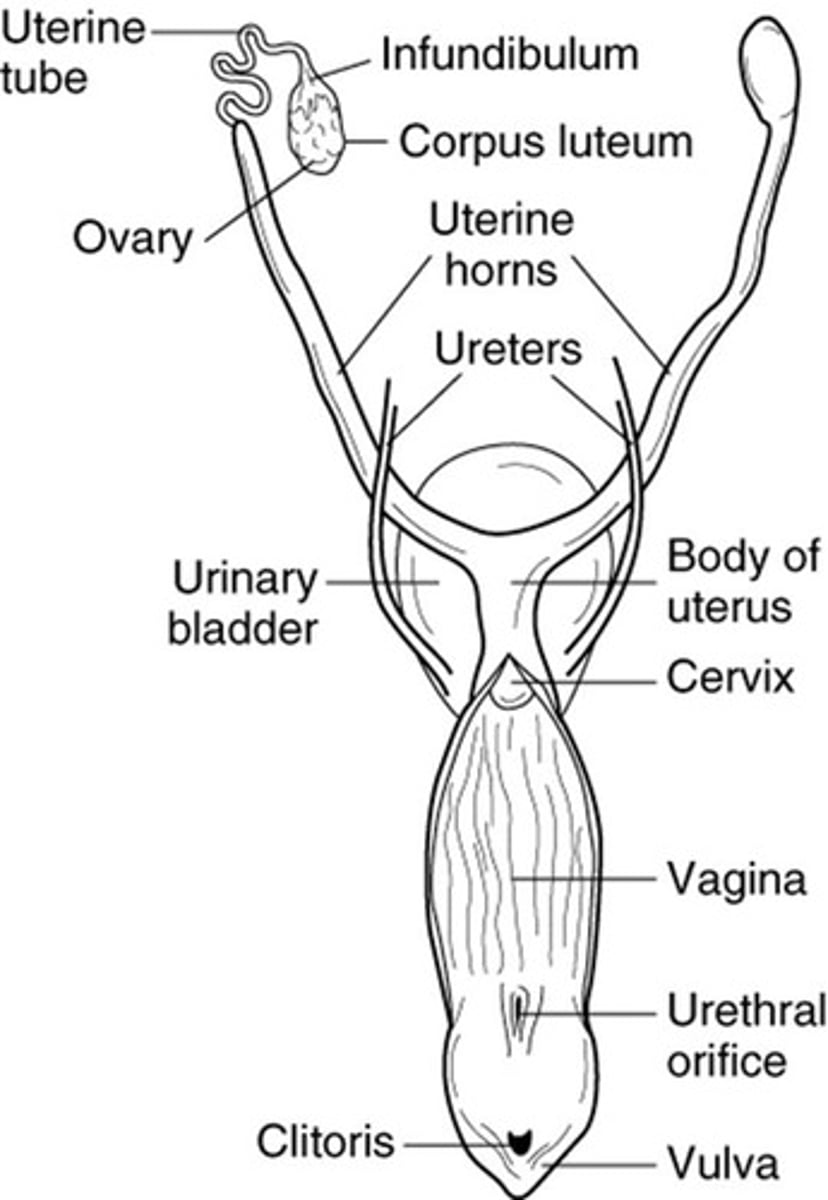
Ovaries
Female gonads producing estrogen and progesterone.
Estrogen
Produced by follicles; signals estrus onset.
Progesterone
Maintains pregnancy after ovulation.
Hormones
Chemical messengers regulating body functions.
Fatty acids
Control hormones involved in estrus.
Steroids
Regulate essential life function chemicals.
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins forming hormones.
Peptides
Control proteins in the body.
Target cells
Cells receiving hormones like a key fits a lock.
Enzymes
Create and release needed hormones.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Stimulates testosterone production and ovulation.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Regulates sperm production and female estrus cycle.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Maintains normal estrus cycle.
Corpus luteum (CL)
Formed during reproductive cycle by LH.
Estrus cycle
Female reproductive cycle regulated by hormones.
Sperm production
Stimulated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
Ovulation
Triggered by luteinizing hormone (LH).
Hypothyroidism
Decreased thyroxine production by thyroid gland.
Signs of Hypothyroidism
Weight gain, lethargy, hair/skin problems.
Alopecia
Hair loss commonly associated with hypothyroidism.
Dermatitis
Skin inflammation often seen in hypothyroidism.
Thyroxine supplementation
Lifetime therapy for hypothyroidism treatment.
Hyperthyroidism
Increased thyroxine production in cats.
Signs of Hyperthyroidism
Weight loss, increased appetite, PU/PD.
Thyroidectomy
Surgical removal of the thyroid gland.
Methimazole
Blocks thyroxine synthesis in hyperthyroidism.
Diabetes Mellitus
High blood glucose levels causing multiple symptoms.
Signs of Diabetes Mellitus
Increased appetite, weight loss, PU/PD.
Insulin therapy
Injection treatment for managing diabetes.
Insulin resistance
Condition where insulin effectiveness is reduced.
Diabetes Insipidus
Caused by ADH release issues from pituitary.
Signs of Diabetes Insipidus
Uncontrolled thirst and increased urination.
Hyperadrenocorticism
Cushing's Disease; excess cortisol production.
Signs of Hyperadrenocorticism
PU/PD, increased appetite, thin skin.
ACTH stimulation test
Diagnosis method for Addison's and Cushing's.
Hypoadrenocorticism
Addison's Disease; decreased corticosteroid production.
Signs of Hypoadrenocorticism
Lethargy, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea.
Hyponatremia
Low sodium concentration in blood.
Hyperkalemia
Increased potassium levels in blood.
Dexamethasone suppression test
Measures cortisol levels for Cushing's diagnosis.
Endocrine glands
Regulate homeostasis via hormone secretion.
Homeostasis
Stable internal environment maintained by endocrine system.
Clinical signs
Observable symptoms indicating a potential health issue.
Emergency signs in pets
Weight loss, excessive drinking, increased urination.
Veterinary assistant role
Support veterinarians in diagnosing and treating animals.
Regular diet importance
Essential for managing diabetes effectively.