Campbell: Biology Chapter 23 Flashcards
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
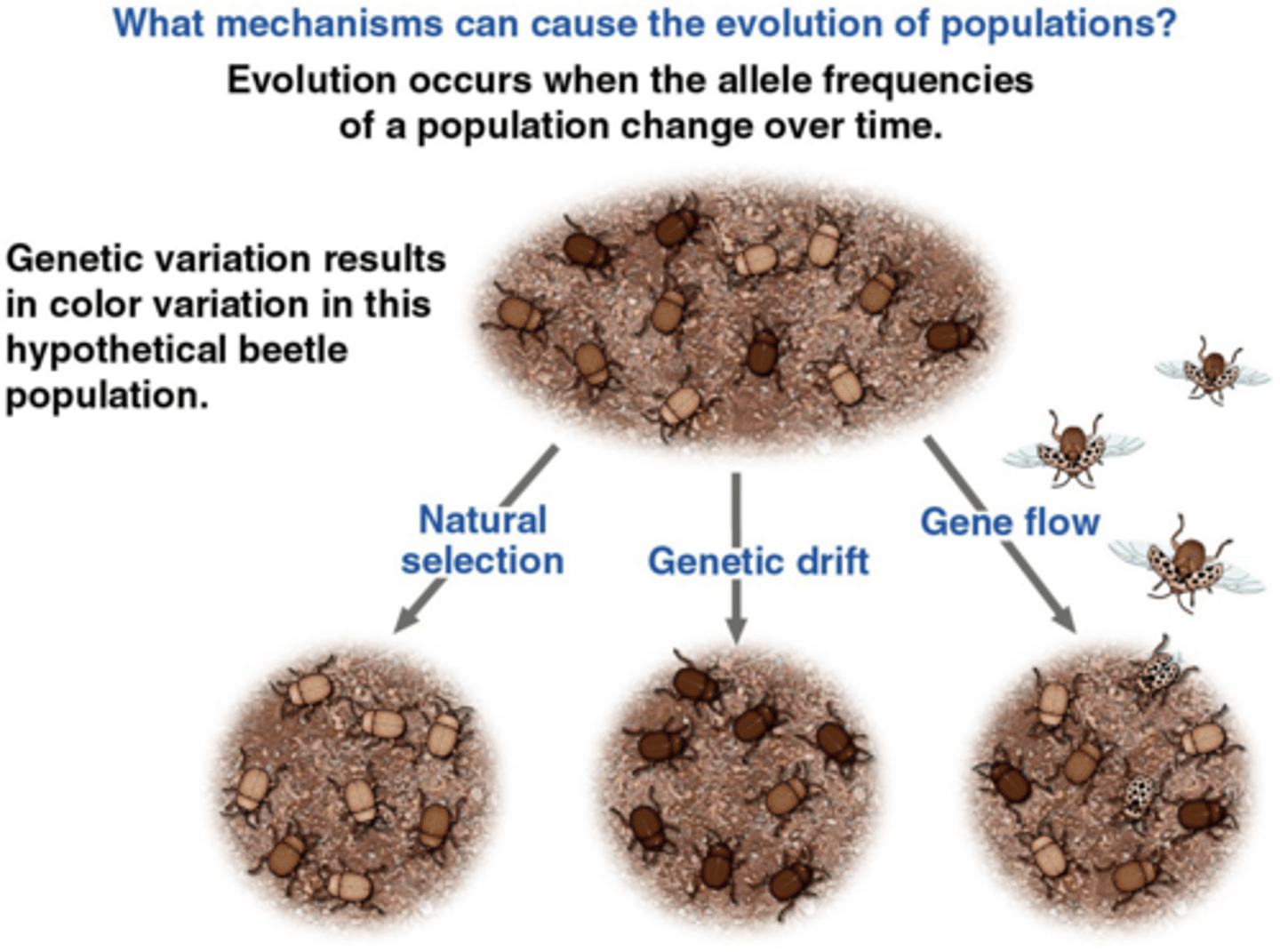
What mechanisms can cause the evolution of populations?
changes in the allele frequencies of a population over time due to either natural selection, genetic drift, or gene flow
give an example of evolution due to natural selection
there was a seed shortage in Daphne Major.
larger beaked birds that could eat the more plentiful large seeds survived at a higher rate
they had a higher fitness
the offspring of the survivors tended to have large beaks and therefore the average beak depth increased in the next generation
Define microevolution
the change in allele frequencies in a population over generations, is evolution at its smallest scale
again, what three mechanisms cause allele frequency change?
natural selection (adaptation to the environment)
genetic drift (chance events that alter allele frequencies)
gene flow (transfer of alleles between populations)
define allele
a variation of a gene
what is needed for evolution by natural selection to occur?
genetic variation
define genetic variation
refers to the differences in genes or ither DNA sequences among individuals
define phenotype
the product of an inherited genotype and environmental influences
the physical, outside effects of the genotype
define genotype
the sequence of the specific genes
i.e. Bb, BB, or bb
how does genetic variation originate?
it originates when new genes and alleles arise by: mutation gene duplication or other processes
genetic variations are produces rapidly in organisms with ______________
short generation times
sexual reproduction can produce genetic variation by______________
recombining existing alleles (crossing over)
define mutation
a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA
what are 2 ways mutations can occur?
through replication errors or exposure to certain types of radiation or chemicals
Most mutations that alter phenotype are at least _______________
slightly harmful
point mutations in noncoding regions usually cause ___________
neutral variation
in multicellular organisms, only ________________ are passed to offspring
mutations in cell lines that produce gametes
if duplicated genes persist over generations ________ and __________ may arise
mutations can accumulate, new functions
one key potential source of genetic variation
duplication of small segments of DNA
define neutral variation
usually caused by point mutations in the noncoding regions
no selective advantage or disadvantage
in multicellular organisms, only mutations in _______ are passed to offspring
give four examples of large chromosomal mutations
duplication, deletion, inversion, translocation
give an example of a genetic mutation that was highly beneficial
P53 gene. it Identifies cells that are at risk for developing cancer
elephants have extra copies and therefore have significantly lower chances of cancer
mutation rates are ____ in animals and plants
low
mutations can ______ in viruses due to _______
accumulate rapidly, to short generation times and rapid mutation rates
examples of high mutation rate in HIV and why?
drug resistance in HIV because they have a short generation time of about two days
HIV's RNA genome lacks repair mechanisms to catch mutations
what is the main cause of genetic variation in sexually reproducing organisms?
the recombination of alleles
give three mechanisms that create new combinations of existing alleles
1. crossing over (occurs in meiosis)
2. Independent assortment (also occurs in meiosis)
3. Fertilization
what does "crossing over" refer to?
the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis
what is independent assortment?
the random distribution of chromosomes into gametes during meiosis
what is fertilization
the random combination of gametes
in which stage does crossing over occur?
during prophase 1 of meiosis
what is the Hardy- Weinberg equation used for?
to test for evolution in a population
what two things are required for a population to evolve?
genetic variation and a factor that causes evolution
What is a population?
all the individuals of the same species that live in the same area at the same time and interbreed and produce fertile offspring
define gene pool
all the possible alleles that exist in a population
a locus is fixed if _____________________________
all individuals in a population are homozygous for the same allele
how do you calculate genotype frequencies?
divide the number of individuals of each genotype by the total number of individuals in the population
how do you calculate the number of copies of each allele in a population?
(# of individuals with homozygous genotype x 2) + # of individuals with heterozygous genotype
nonrandom mating can affect genotype frequencies but not _______ frequencies
allele
define natural selection
differential success in survival and reproduction based on certain heritable traits.
those with traits better suited to their environment produce more offspring than others
natural selection can cause adaptive evolution which is?
a process in which traits that enhance survival or reproduction increase in frequency over time
define genetic drift
the process in which chance events cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably from one generation to the next
the smaller the sample, the _____ the chance of random deviation from a predicted result
greater
genetic drift tends to ___________ through the random loss of allels
reduce genetic variation
what is the founder effect?
when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population
define the bottleneck effect
when there is a drastic reduction in population size due to a sudden change in the environment
the resulting gene pool may no longer be reflective of the original population's gene pool
Genetic drift summary:
genetic drift is significant in _____ populations
it can cause the ________ to change at __________
it can lead to a loss of ________ within populations
it can cause _________ to become fixed
small
allele frequencies, random
genetic variation
harmful alleles
define gene flow
the movement of alleles among populations
gene flow tends to ______ variation among populations over time and can mitigate the effects of _________
reduce, natural selection
only ________ consistently increases the frequencies of alleles that provide reproductive advantage
natural selection
define relative fitness
the contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of other individuals
what are the three ways that natural selection can alter the frequency distribution of heritable traits?
directional selection, disruptive selection, stabilizing selection
define directional selection
favors individuals at one extreme end of the phenotypic range
define disruptive selection
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
Define stabilizing selection
favors intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes
natural selection __________ the frequencies of alleles that enhance survival and reproduction
define sexual selection
the process in which individuals with certain heritable traits are more likely to obtain mates than other individuals of the same sex
define sexual dimorphism
a difference in secondary sexual characteristics between the sexes
i.e. different colors, sizes, and behaviors between males and females
define intrasexual selection
the direct competition among individuals of one sex
(often males) for mates of the opposite sex
define intersexual selection
(mate choice) occurs when individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting their mates
female choice is often dependent on the male's _______________ and although ________ can can increase the likelihood of mating, it can also ______ the chances of survival
appearance or behavior, showiness, decrease
define frequency - dependent selection
the fitness of a phenotype depends on how common it is
define heterozygote advantage and give an example
when heterozygotes have a higher fitness than both kinds of homozygotes
i.e. sickle cell disease
how does sickle cell disease happen?
a point mutation in the sickle cell allele changes one amino acid, causing improper protein folding, and binding of the proteins into chains forming a fiber
the abnormal hemoglobin fibers distort the red blood cell into a sickle shape in low oxygen conditions