Introduction to the Skeletal System
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Describe anatomical position.
Standing up: hands at sides, palms facing forward, feet together
Laying down: supine (face up), prone (face down)
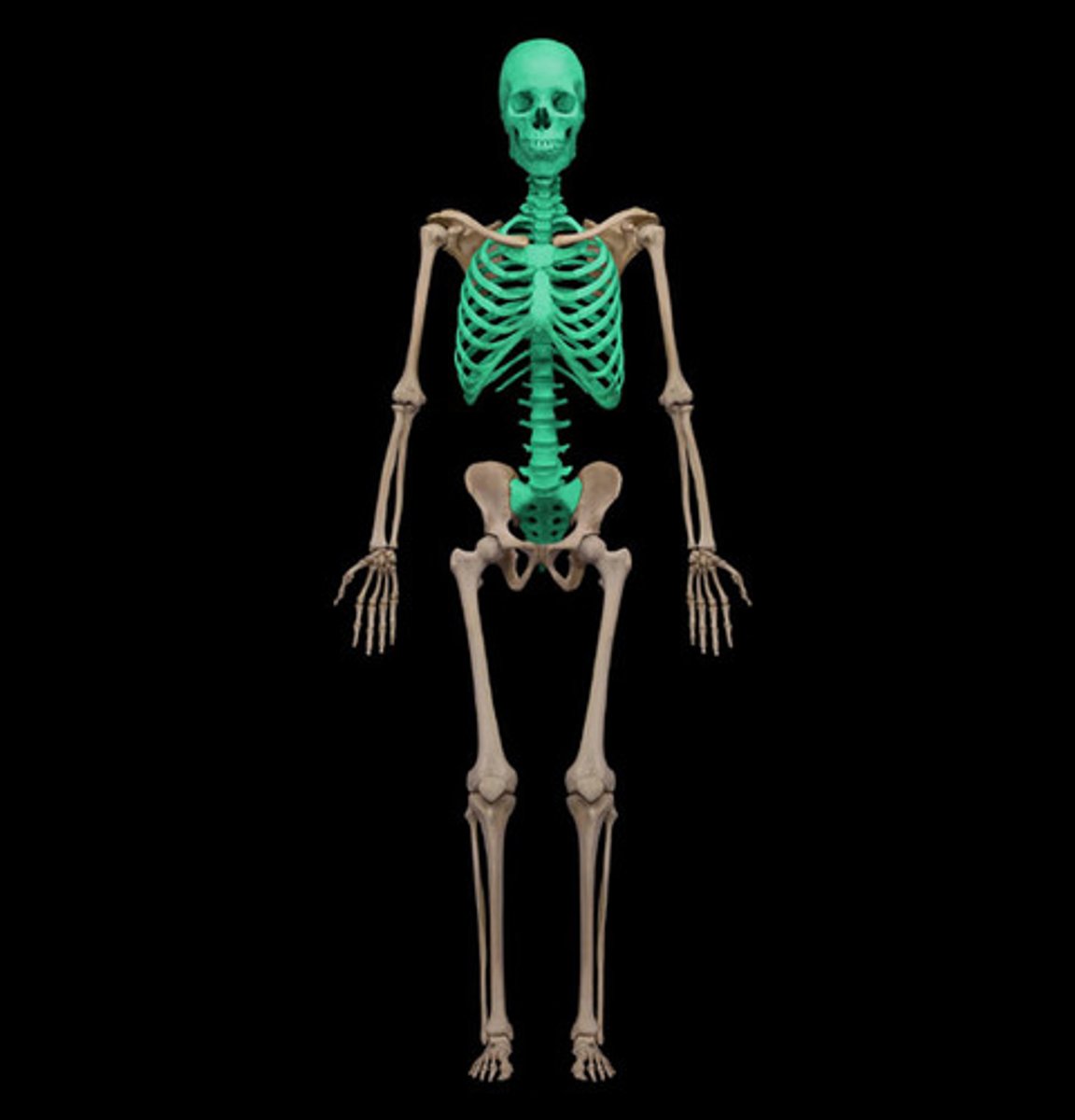
Axial skeleton
Bones along the axis of the body
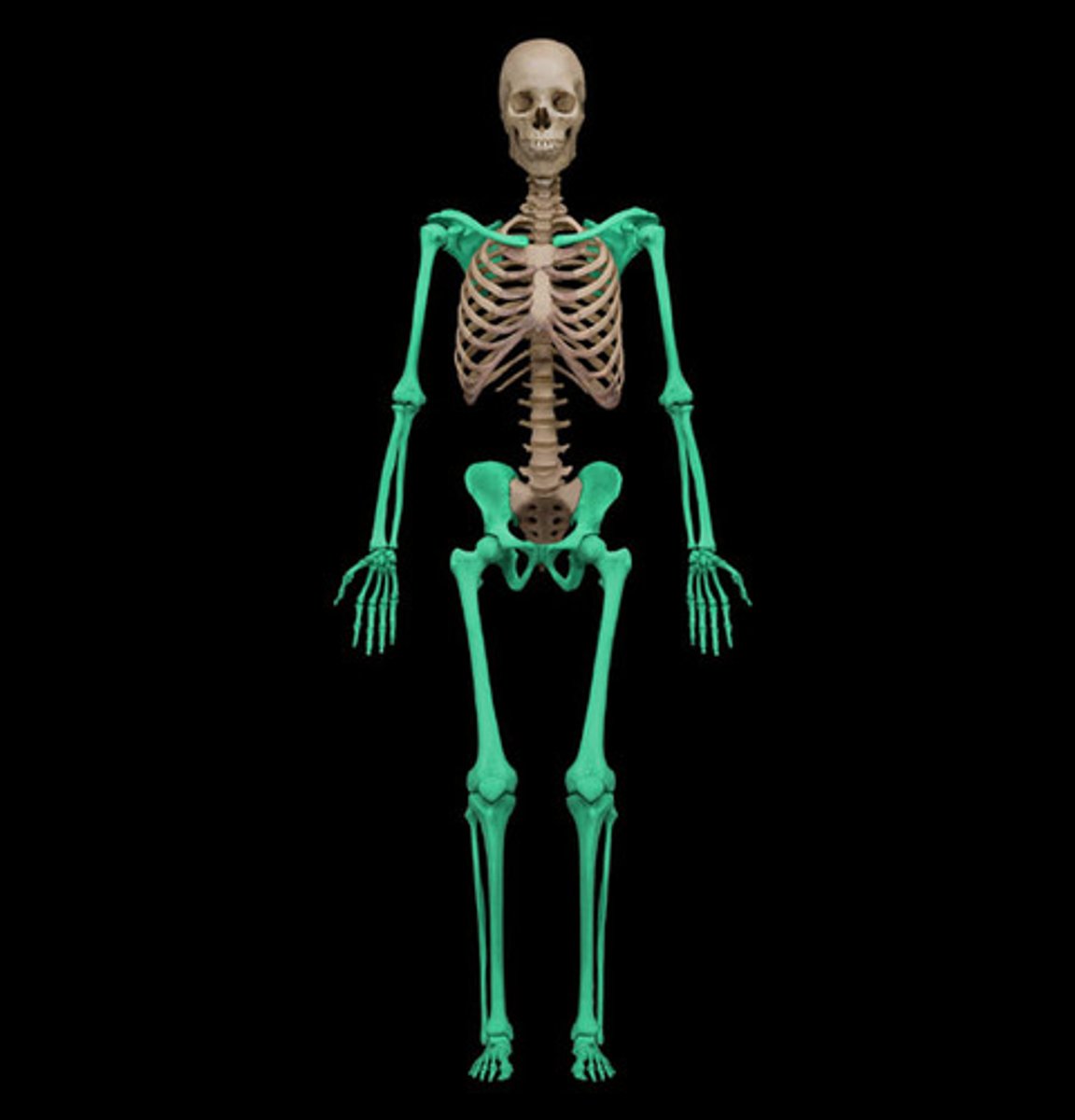
Appendicular skeleton
Bones of the appendages (arms and legs) and the girdles (shoulder and pelvic)
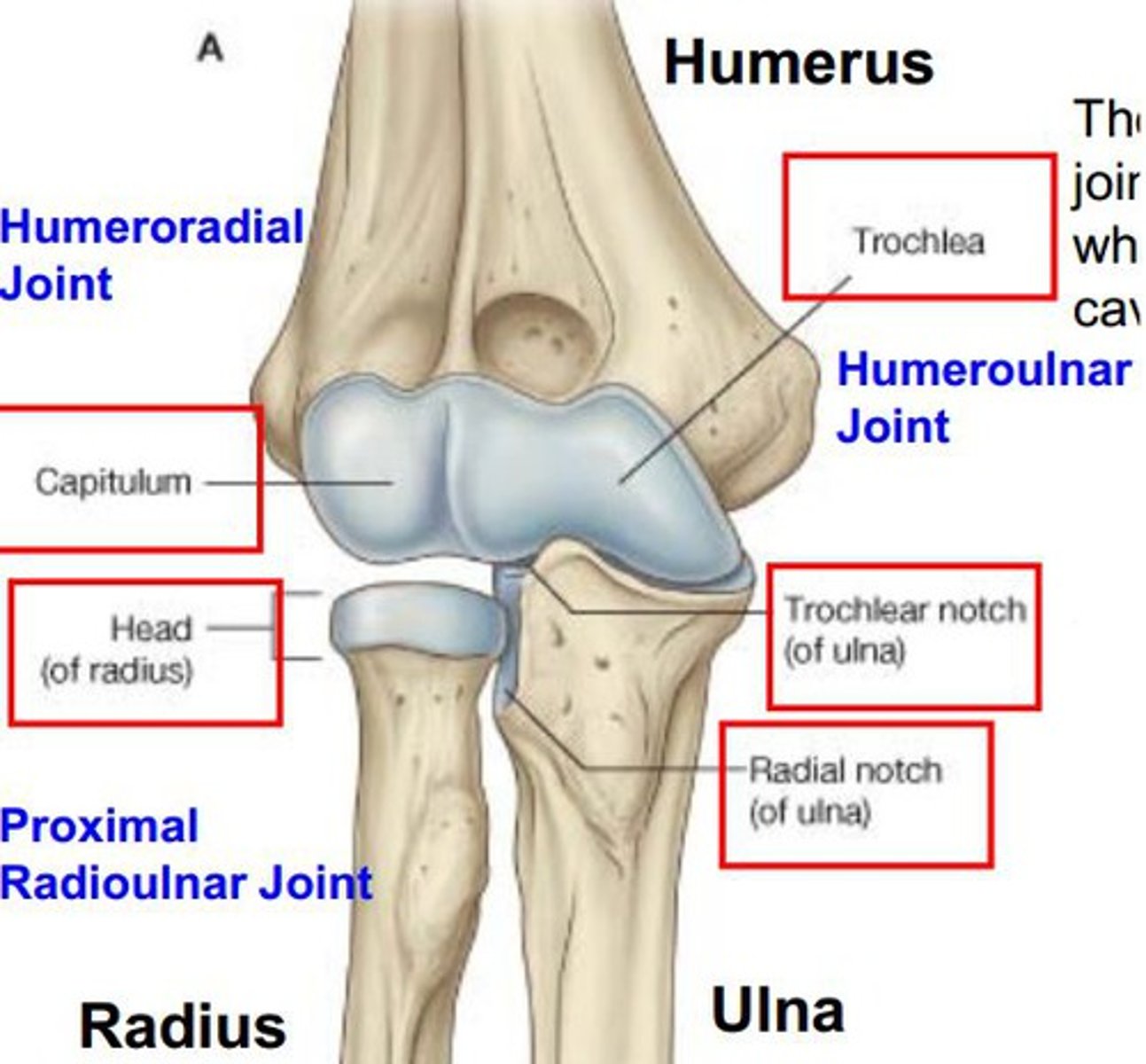
Articulations
Areas where bones contact other bones
Landmarks
Areas of muscle and ligament attachment
Foramina
Openings for nerves and blood vessels
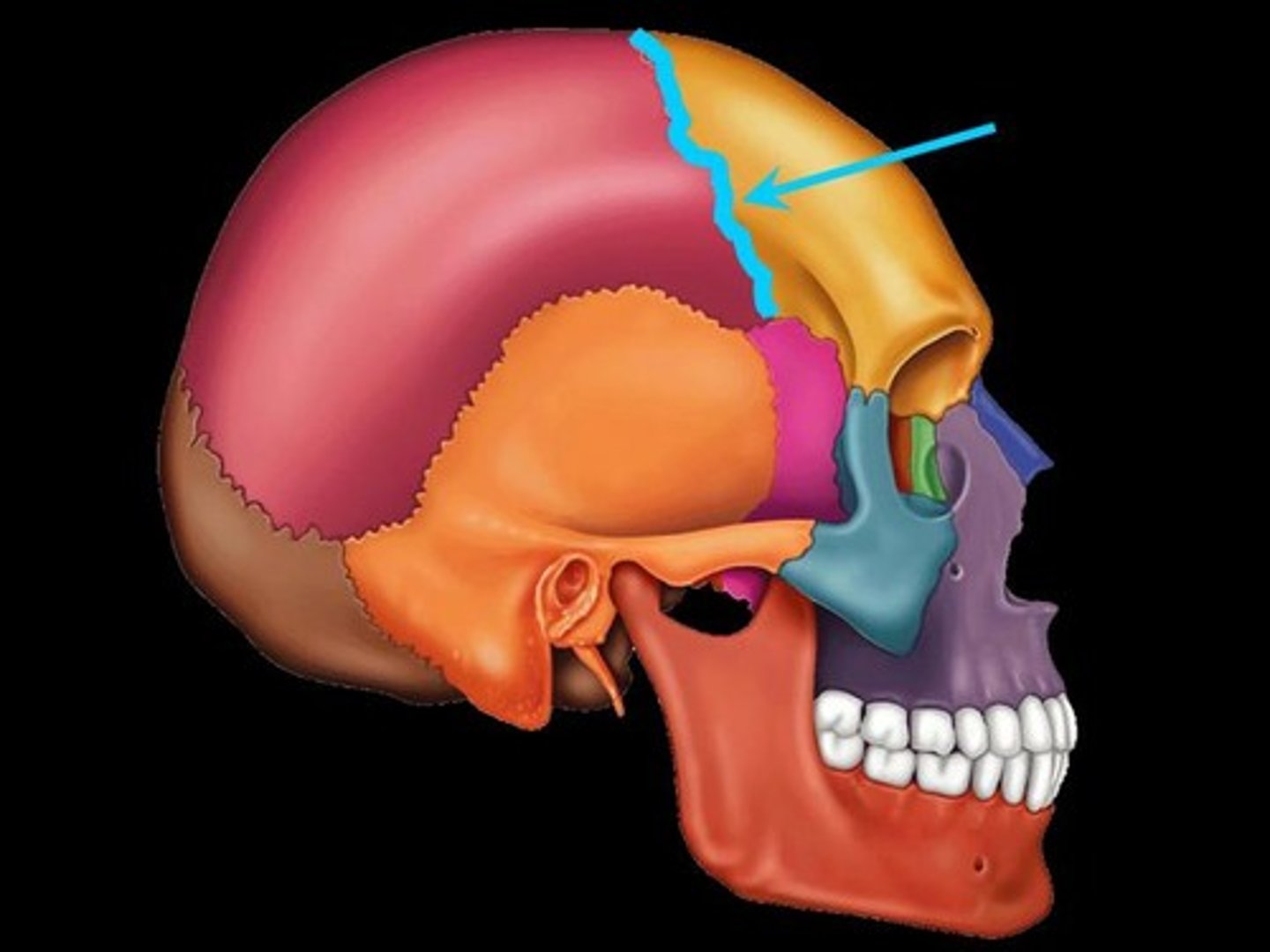
Suture
A fibrous joint that is located between the bones of the skull
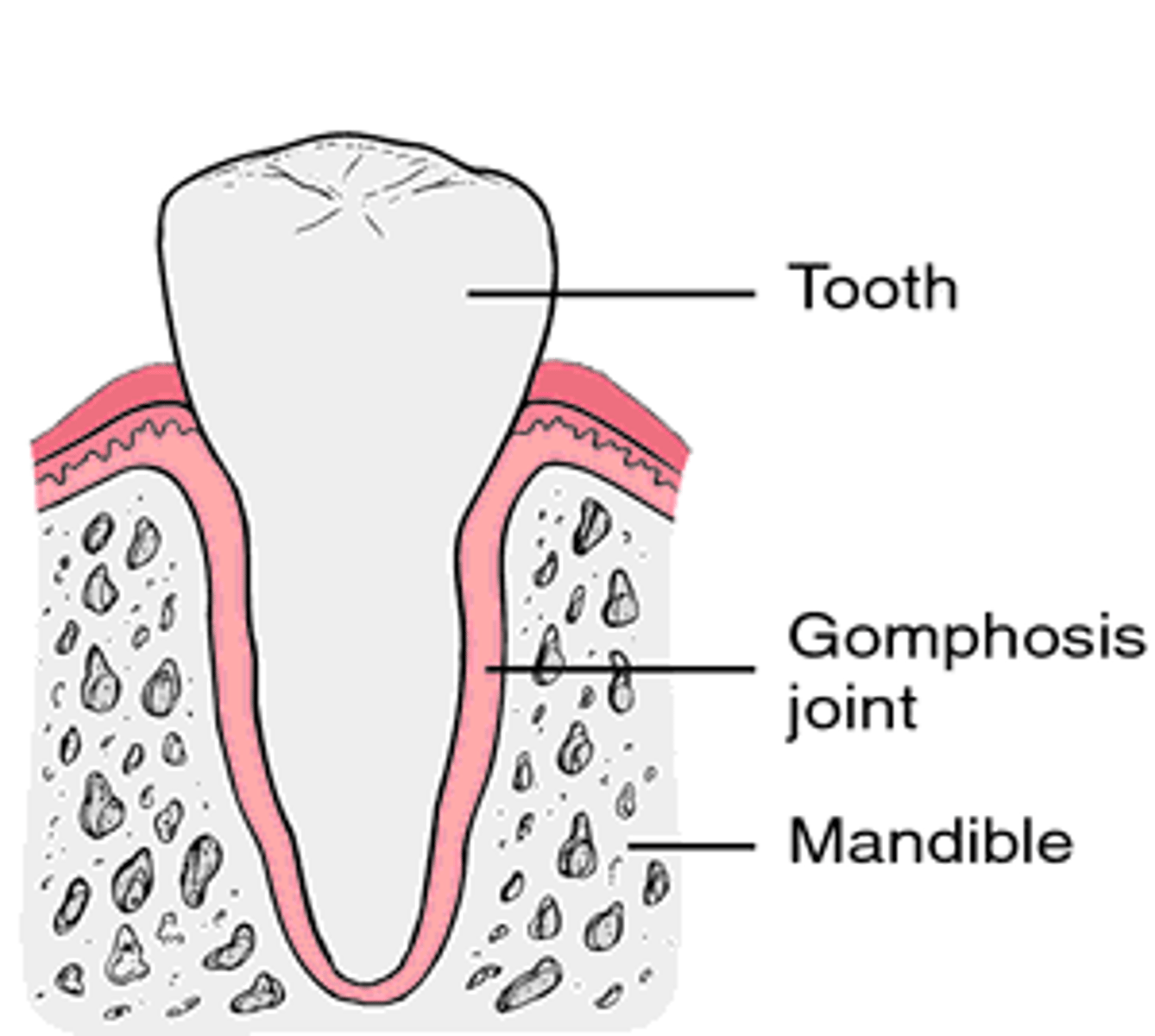
Gomphosis
A fibrous joint that is the connection between the tooth and the gum socket. This is called a periodontal ligament.
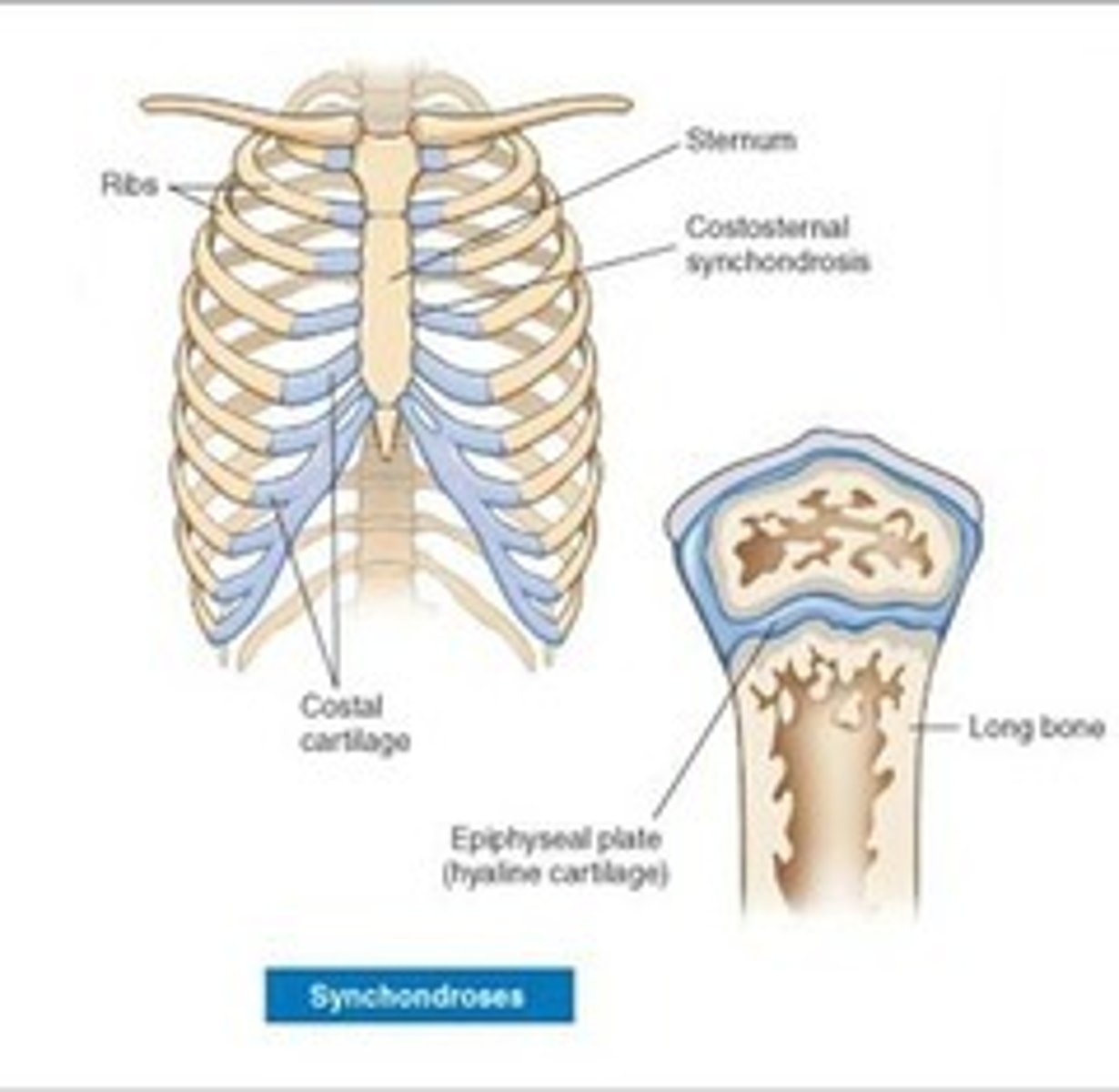
Synchondrosis
A rigid, cartilaginous bridge between two articulating bones
Ex: connection between the ends of the first pair of ribs and the sternum, epiphyseal cartilage in growing bones
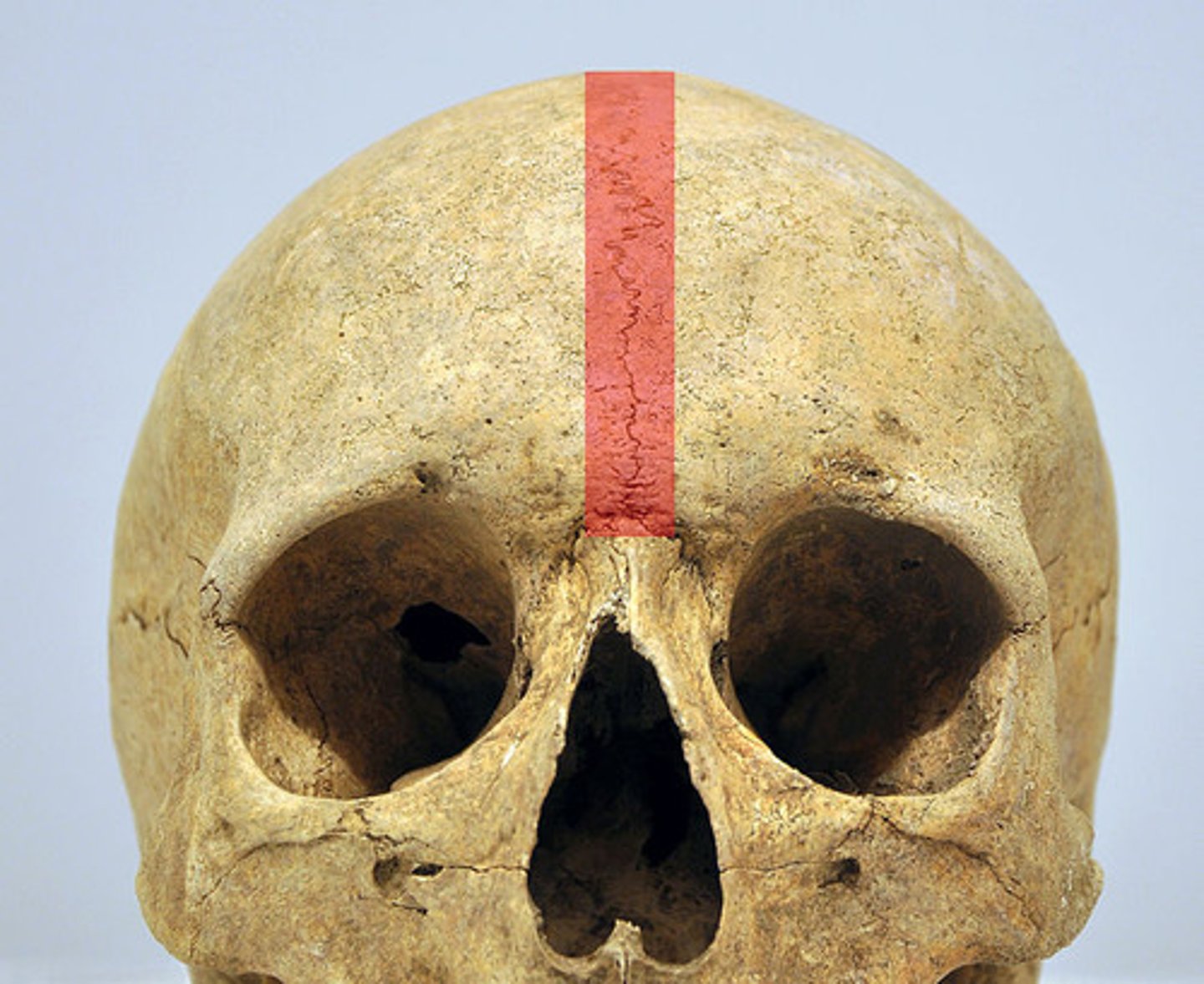
Synostosis
A totally rigid, immovable joint that occurs when two bones fuse and the boundary between them disappears
Ex: coronal suture of the frontal bone and epiphyseal lines of mature long bones
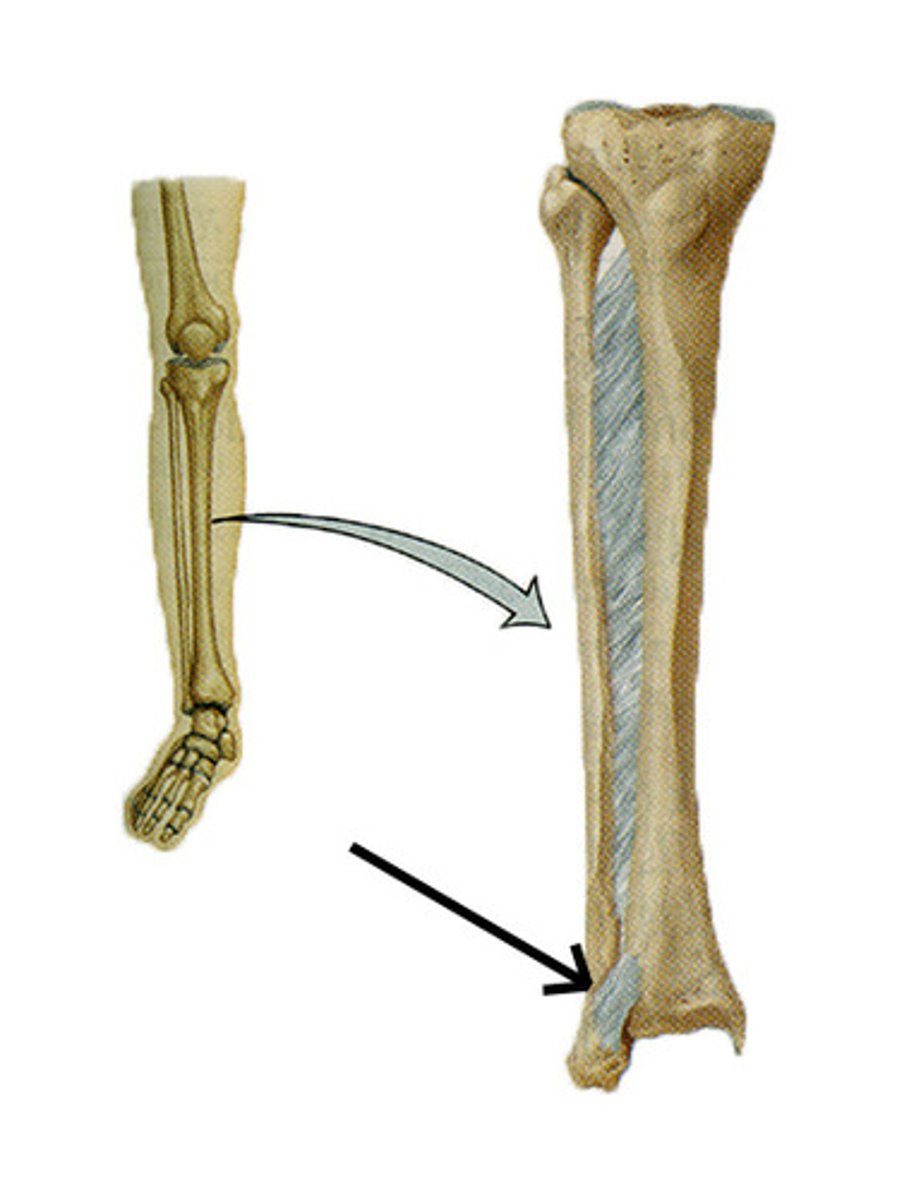
Syndesmosis
A fibrous joint in which bones are connected by a ligament.
Ex: connection between tibia and fibula
Symphysis
Cartilaginous joint in which bones are separated by a pad of fibrocartilage.
Ex: pubic symphysis
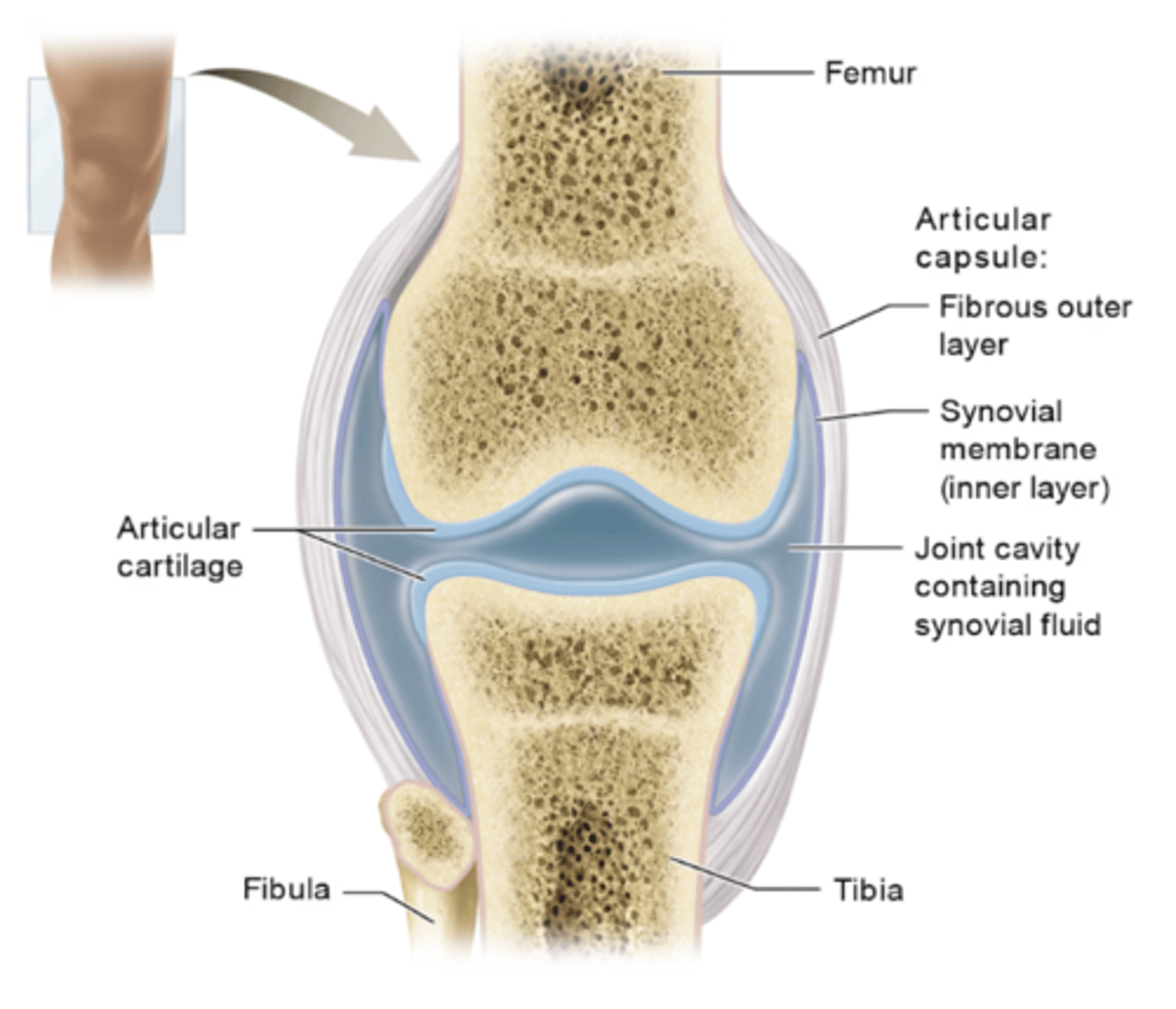
Diarthrosis/Synovial Joints
freely movable joints (gliding, hinge, pivot, ellipsoid, saddle, ball and socket)
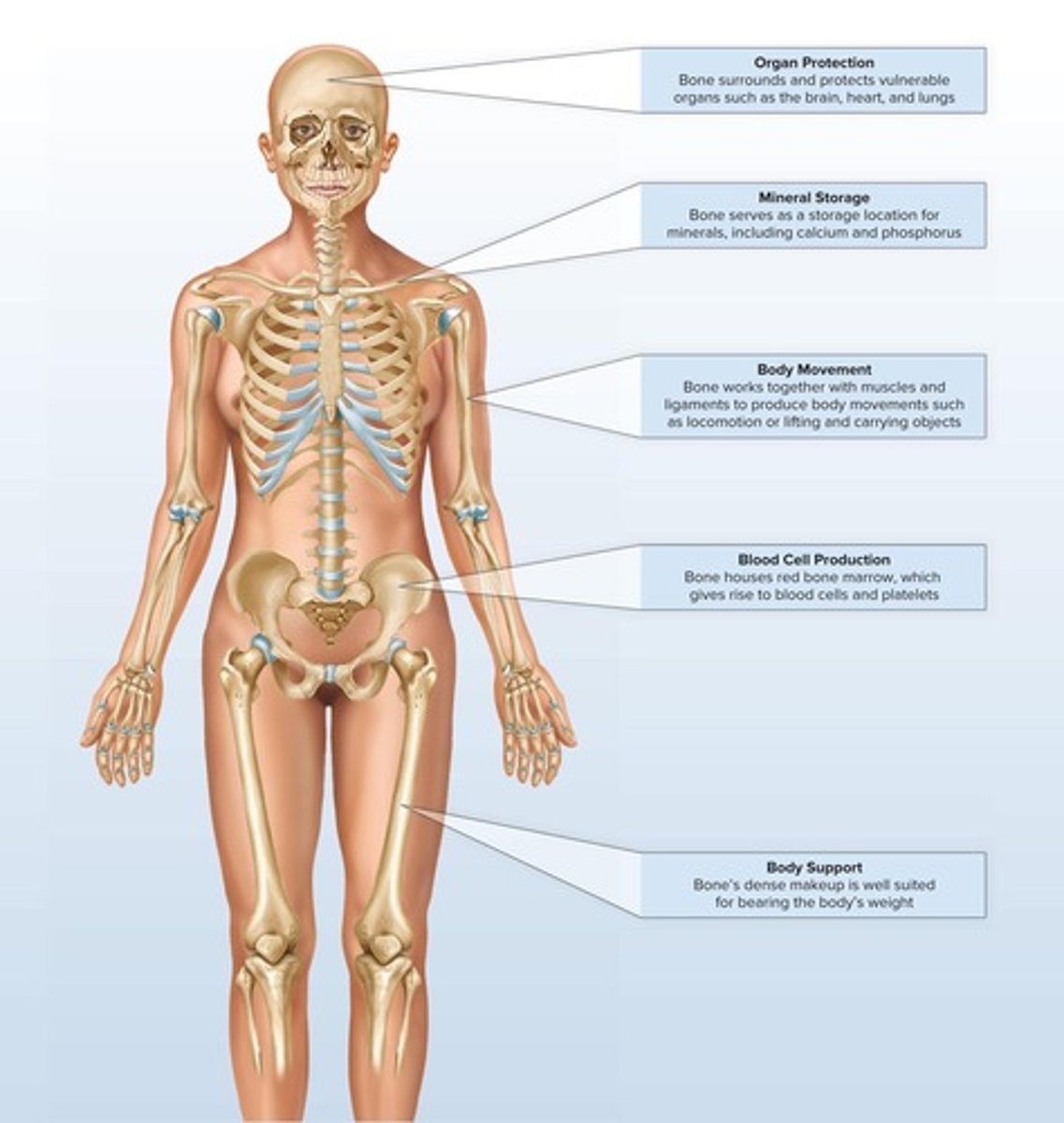
Functions of the axial skeleton
Supports and protects organs in body cavities.
1. Attaches to muscles of head, neck, and trunk
2. Performs respiratory movements
3. Stabilizes parts of appendicular skeleton
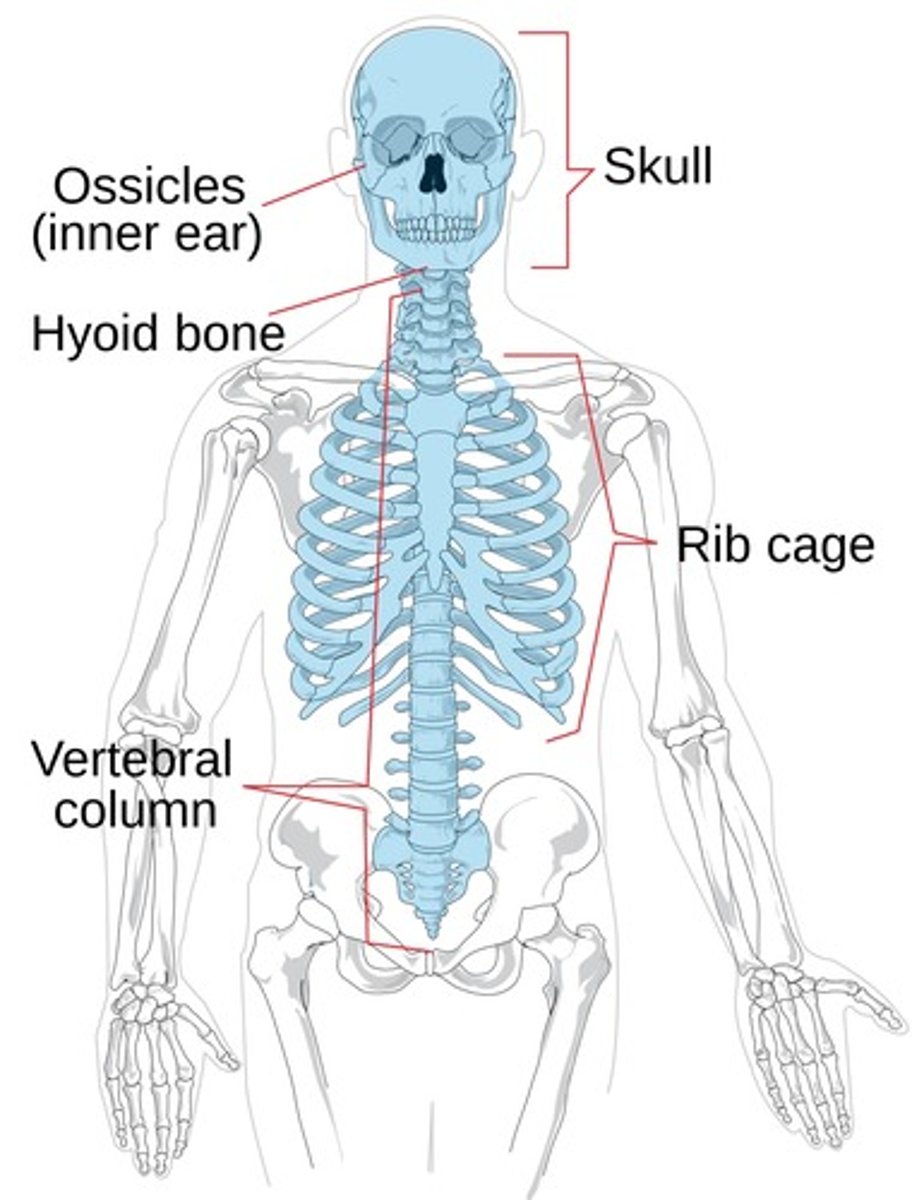
Parts of the Axial Skeleton
Skull
Vertebral Column
- protects the spinal cord
- supports the head and body
- contains 24 vertebrae, the sacrum, and the coccyx
Thoracic cage
- 24 ribs
- sternum
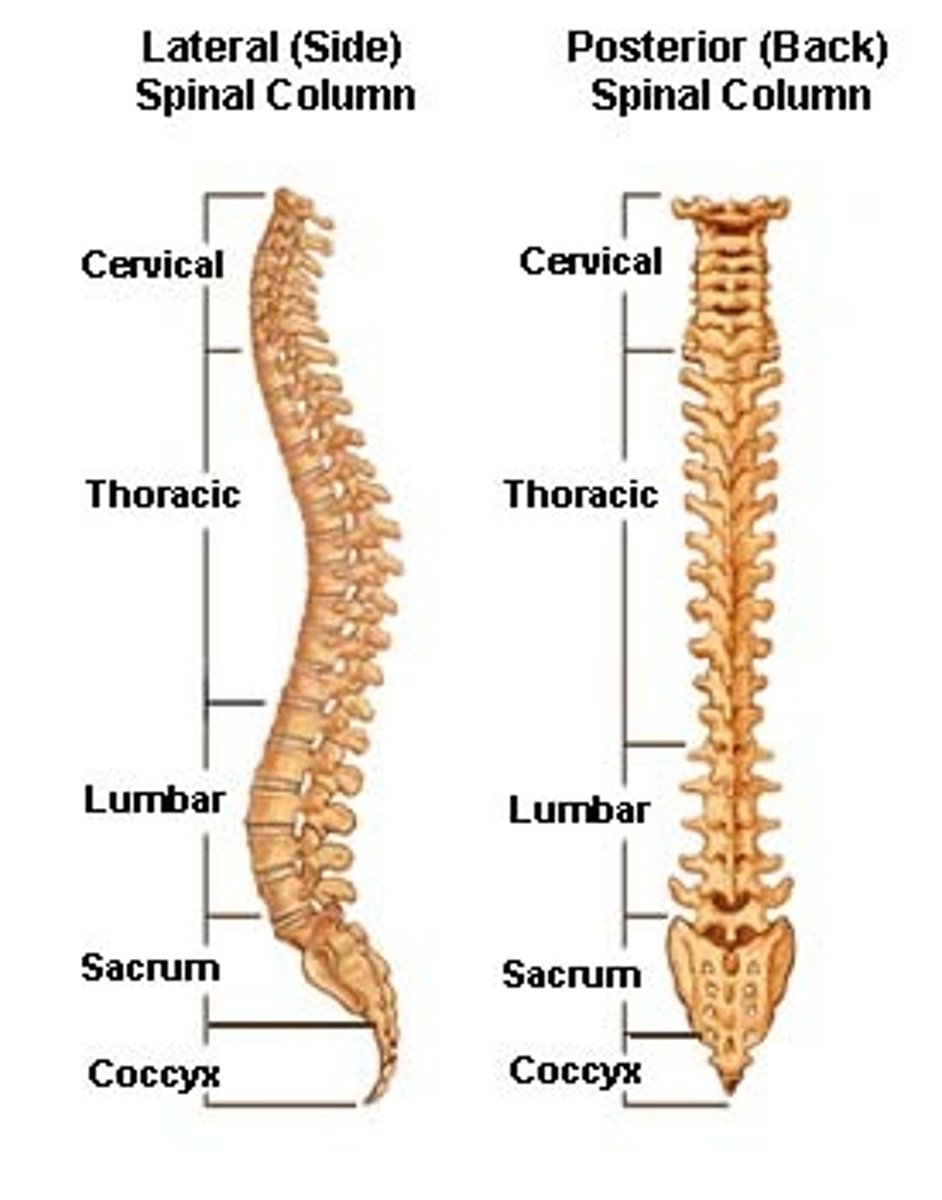
Regions of the Vertebral Column
Cervical (C) - 7
Thoracic (T) - 12
Lumbar (L) - 5
Sacral (S) - 5 fused vertebrae (not counted in the 24)
Coccygeal (Co)
Breakfast C7
Lunch T12
Dinner L5
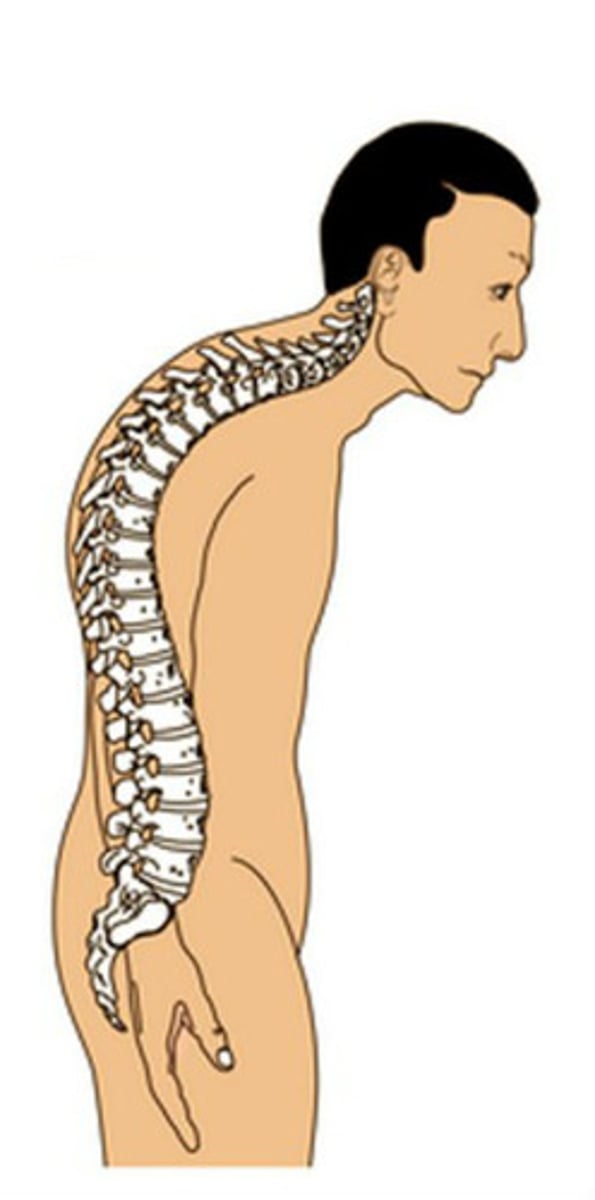
Kyphosis
excessive outward curvature of the spine, causing hunching of the back.
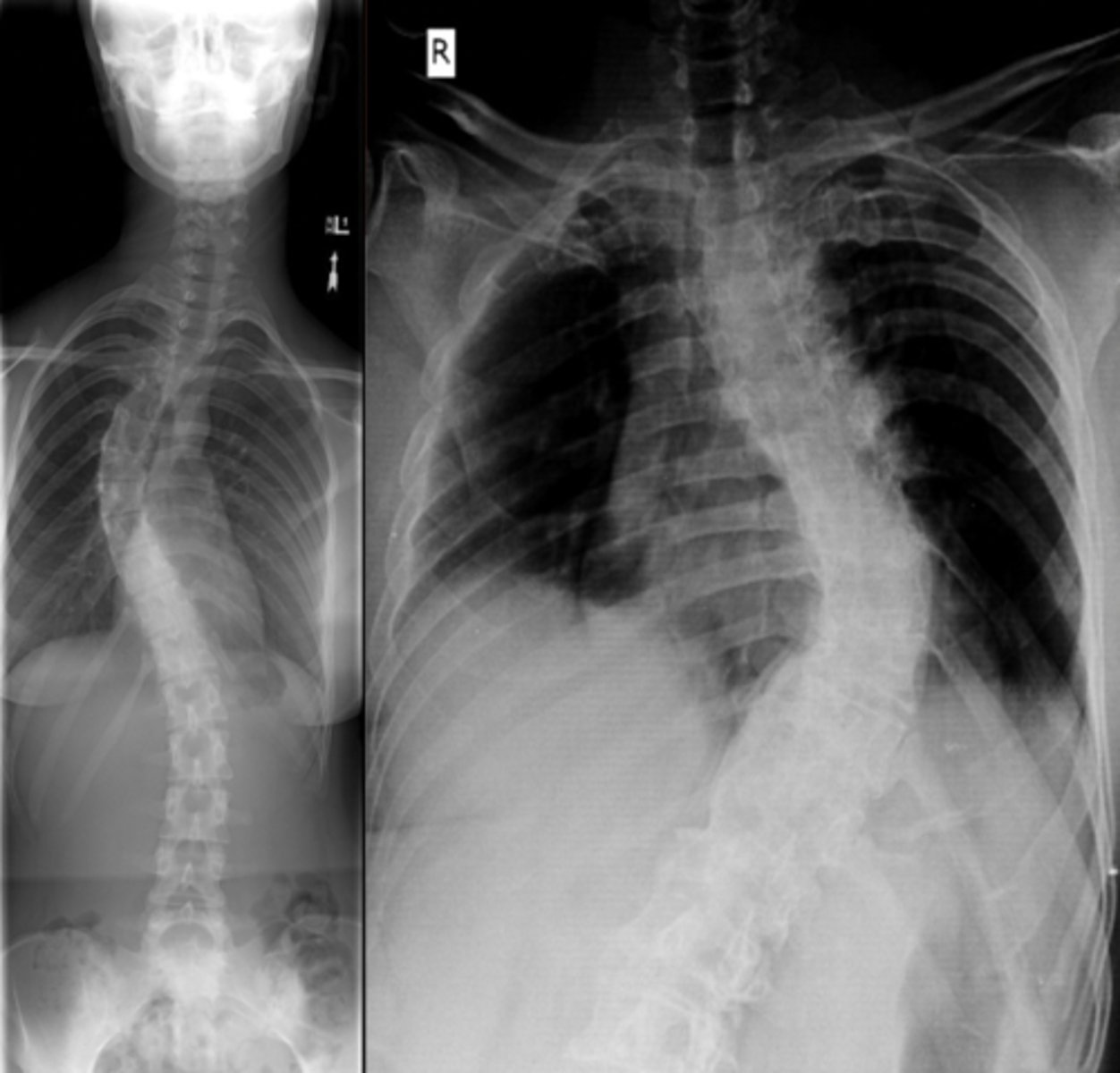
Scoliiosis
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
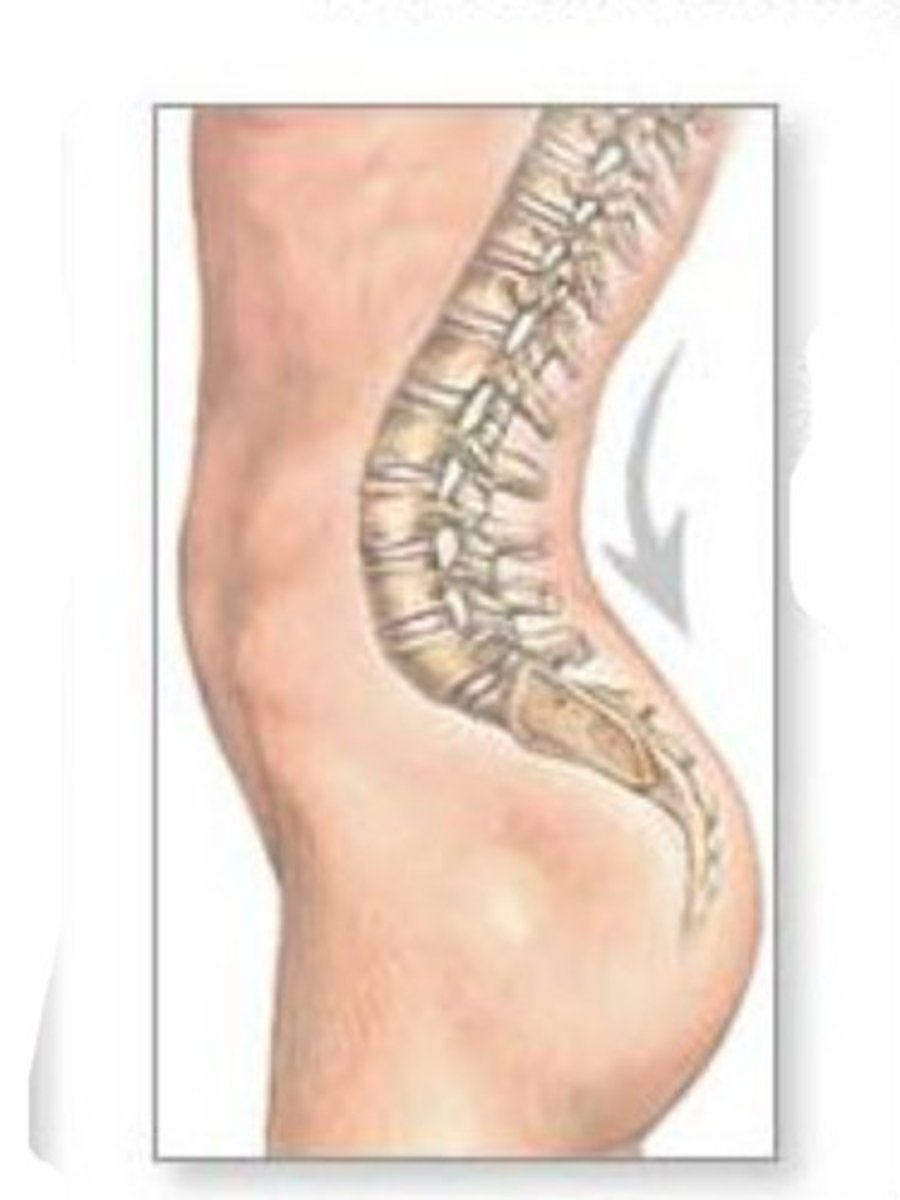
Lordosis
abnormal increase in the forward curvature of the lumbar spine
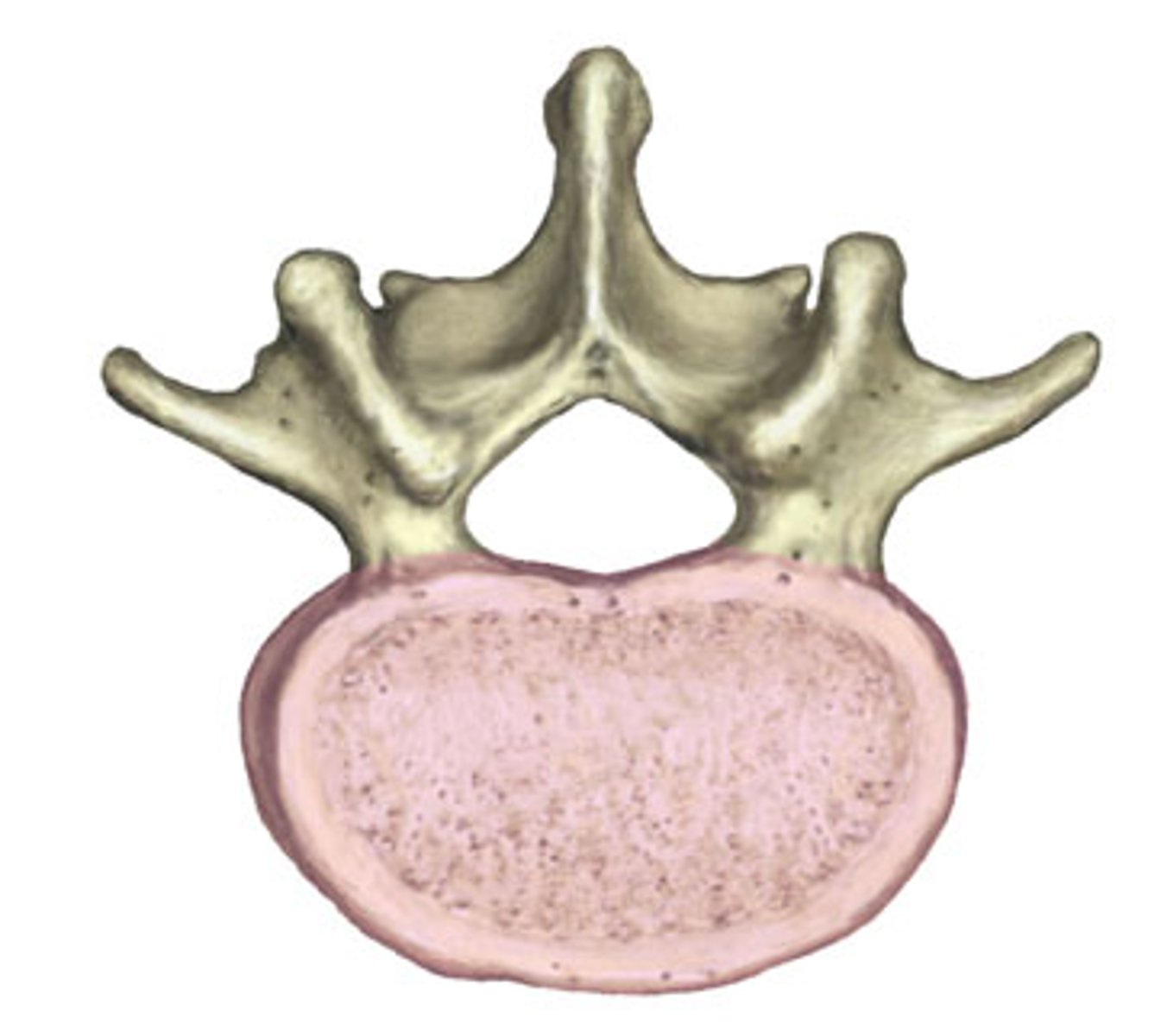
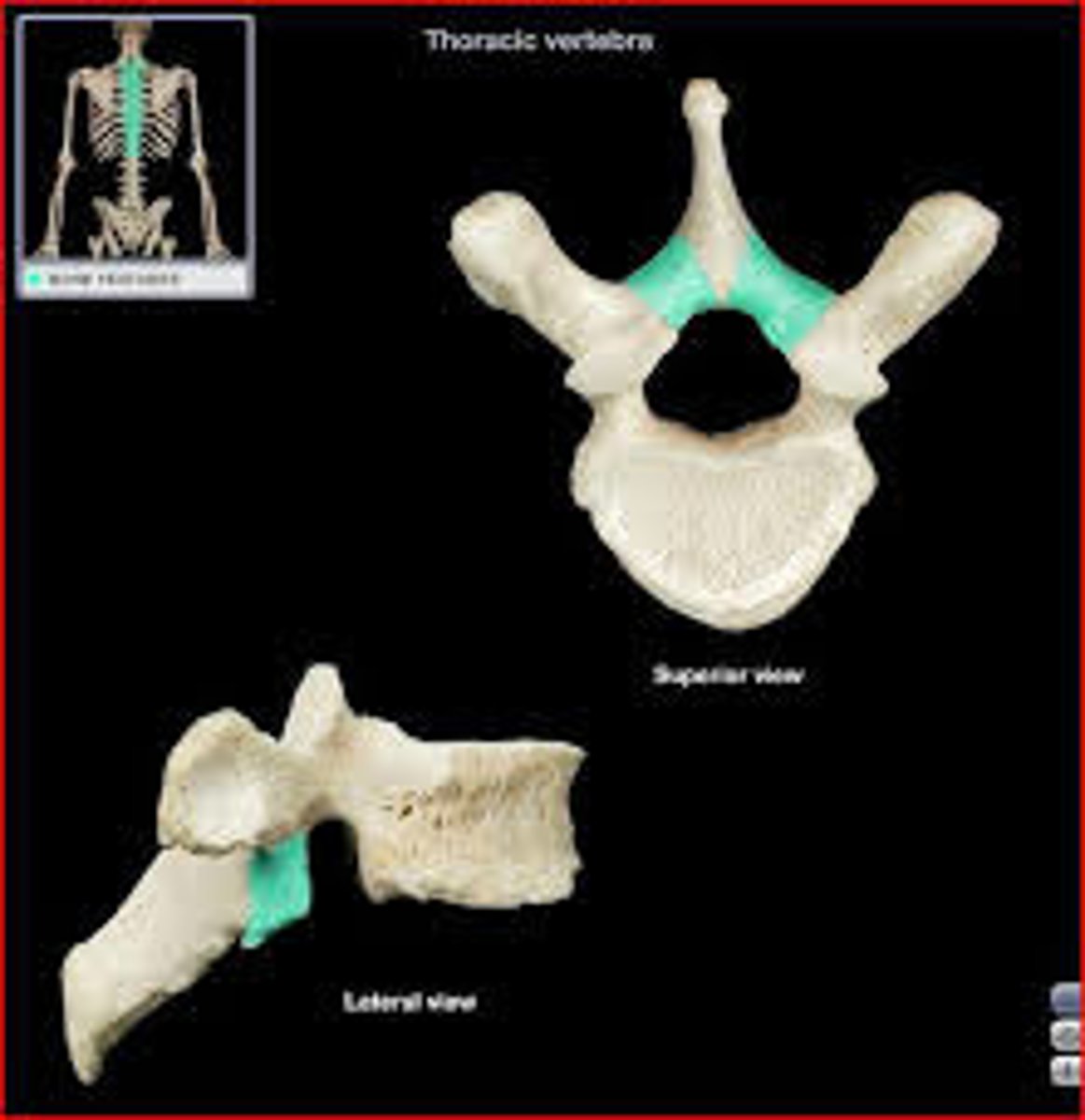
Vertebral body (centrum)
Transfers weight along the spine
Vertebral arch
Posterior margin of vertebral foramen
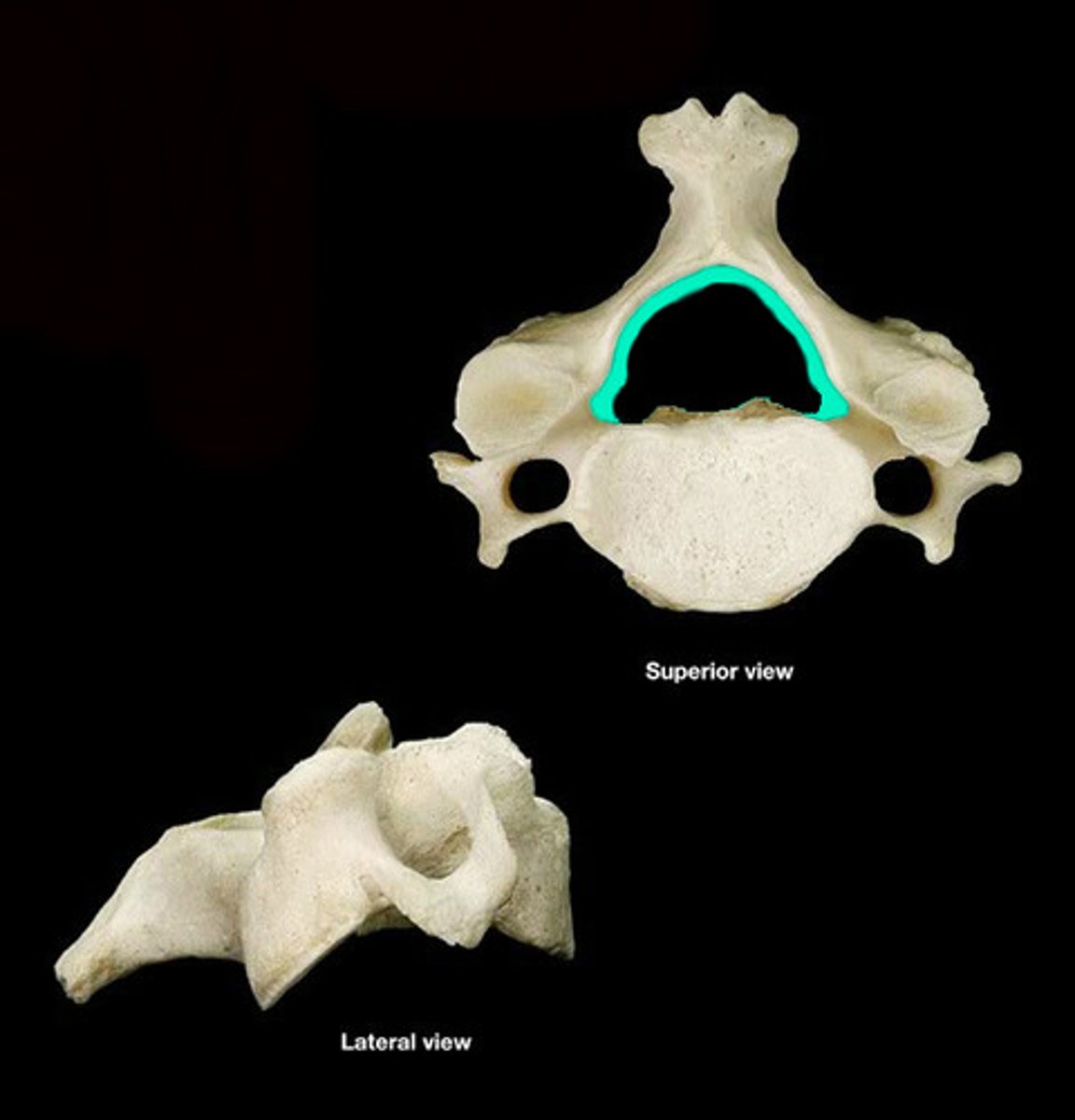
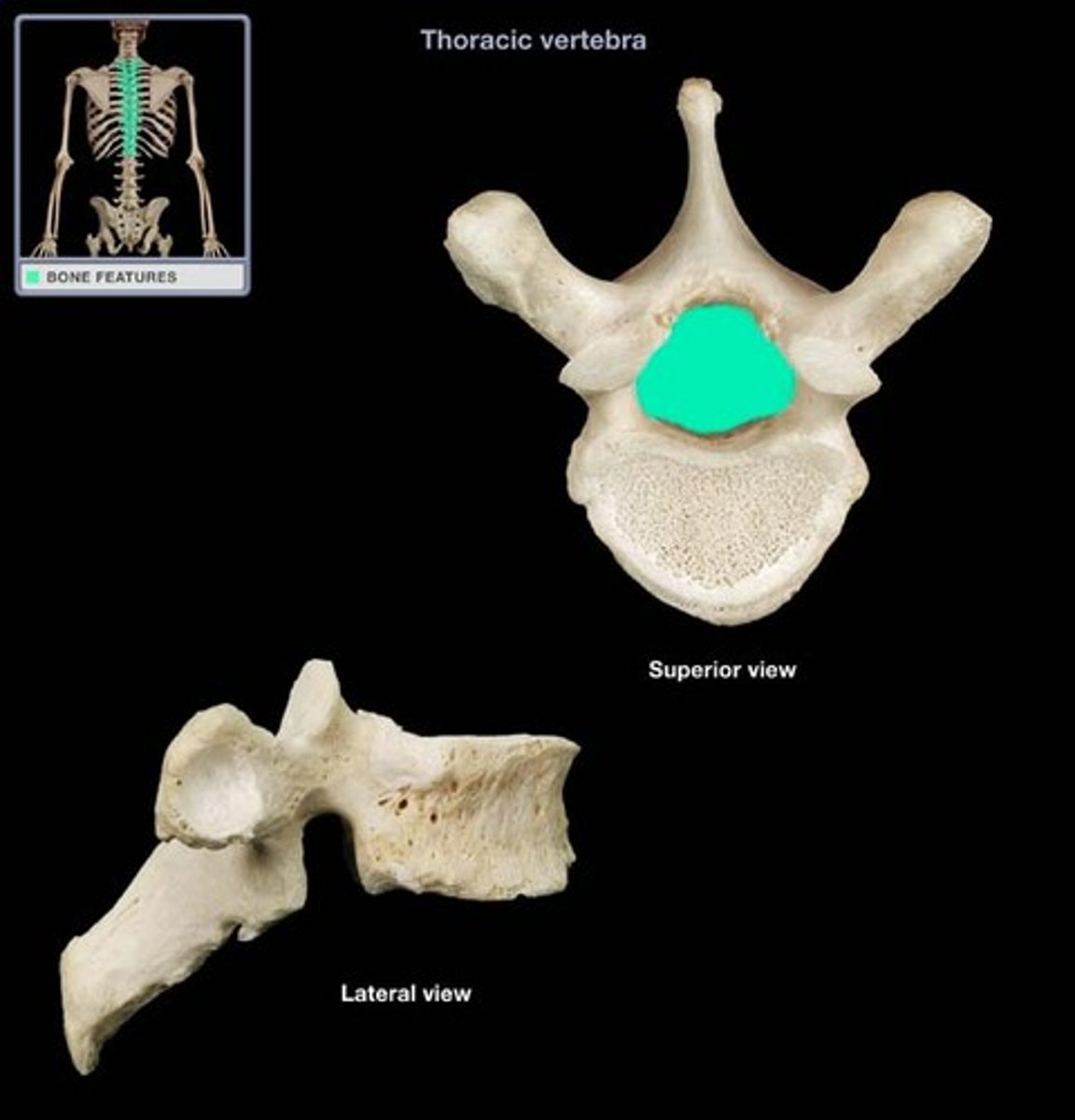
Vertebral foramen
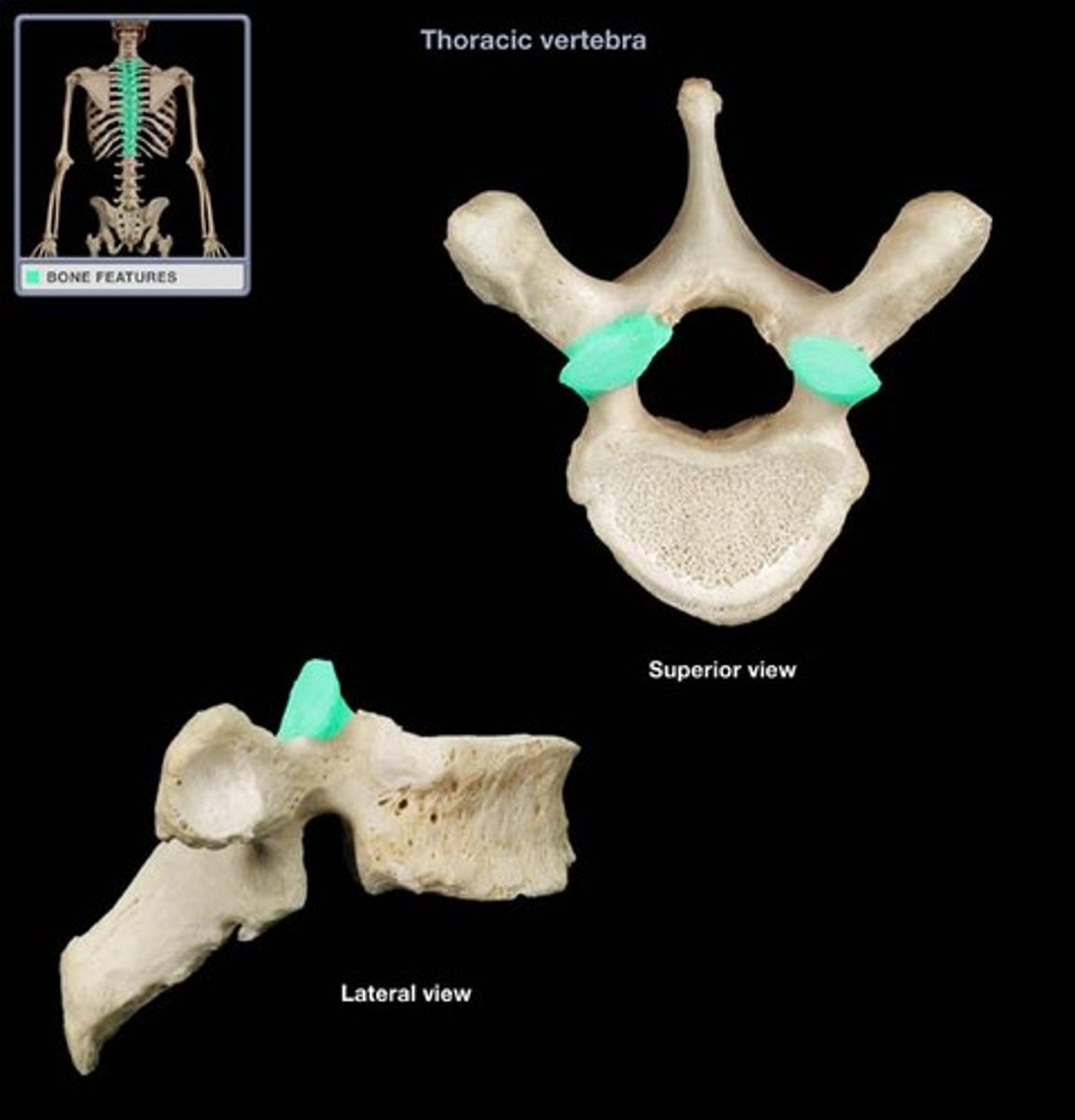
Articular processes
Lateral projections between laminae and pedicles
Lamina of vertebral arch
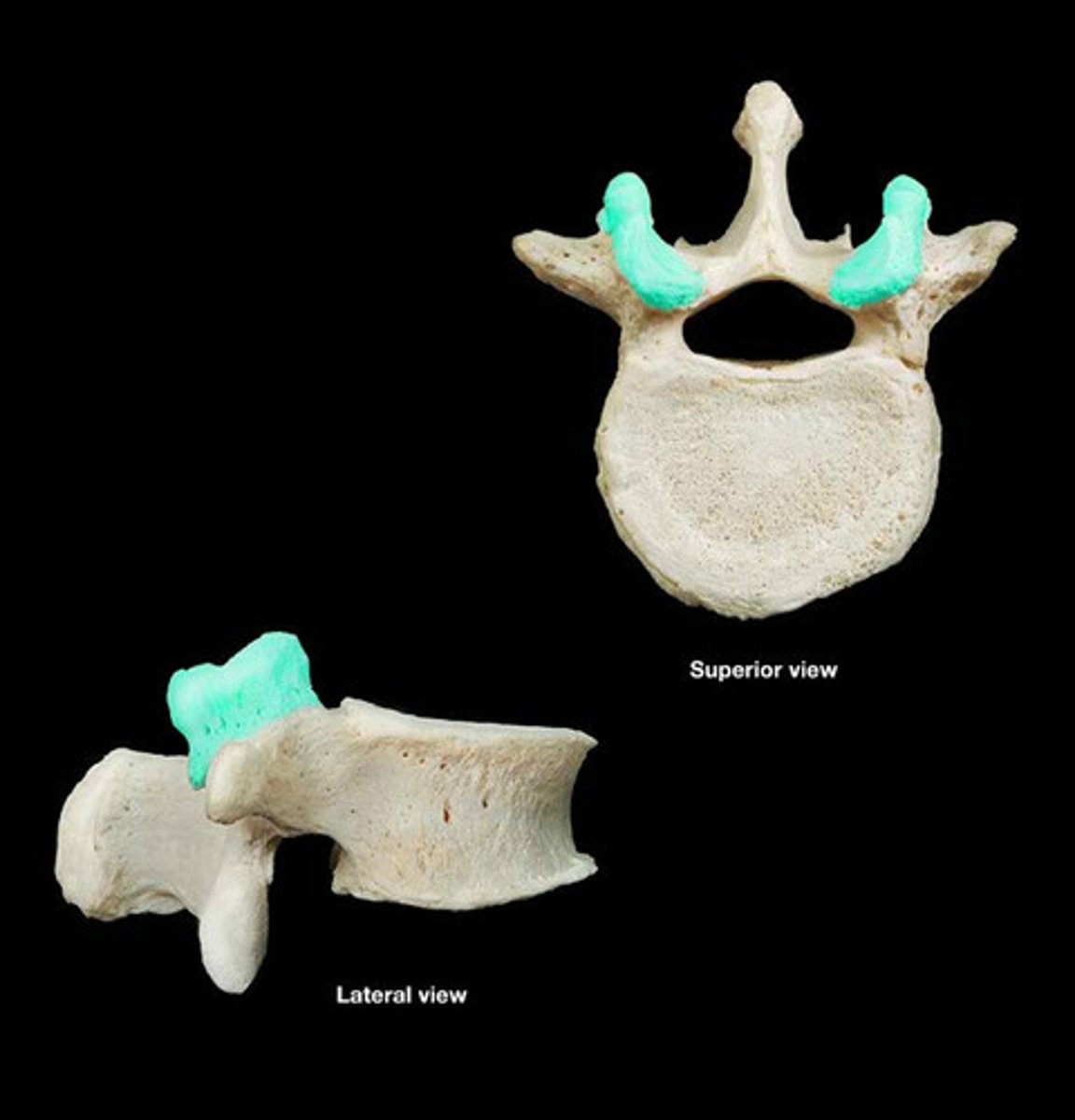
Superior articular facets
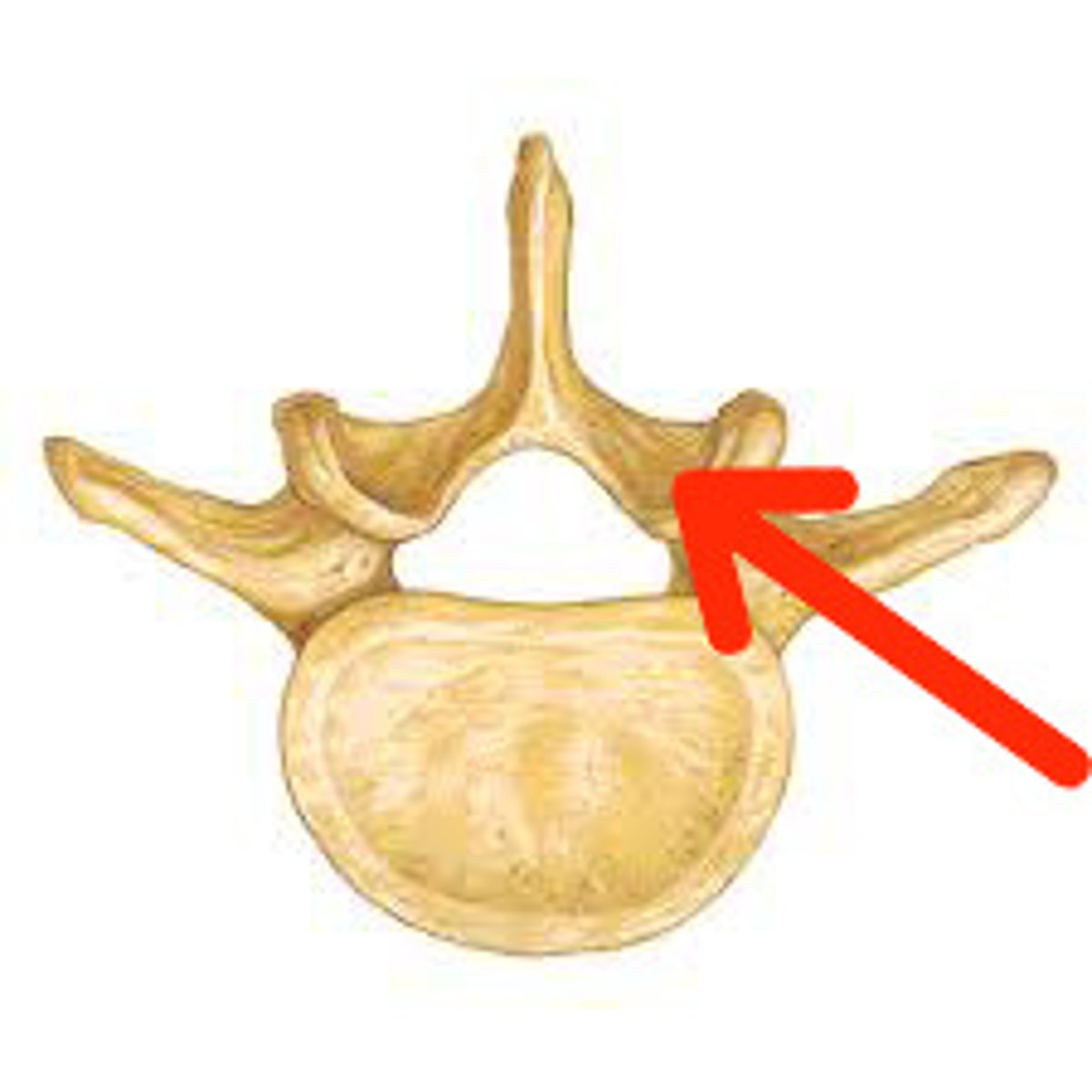
Superior articular process
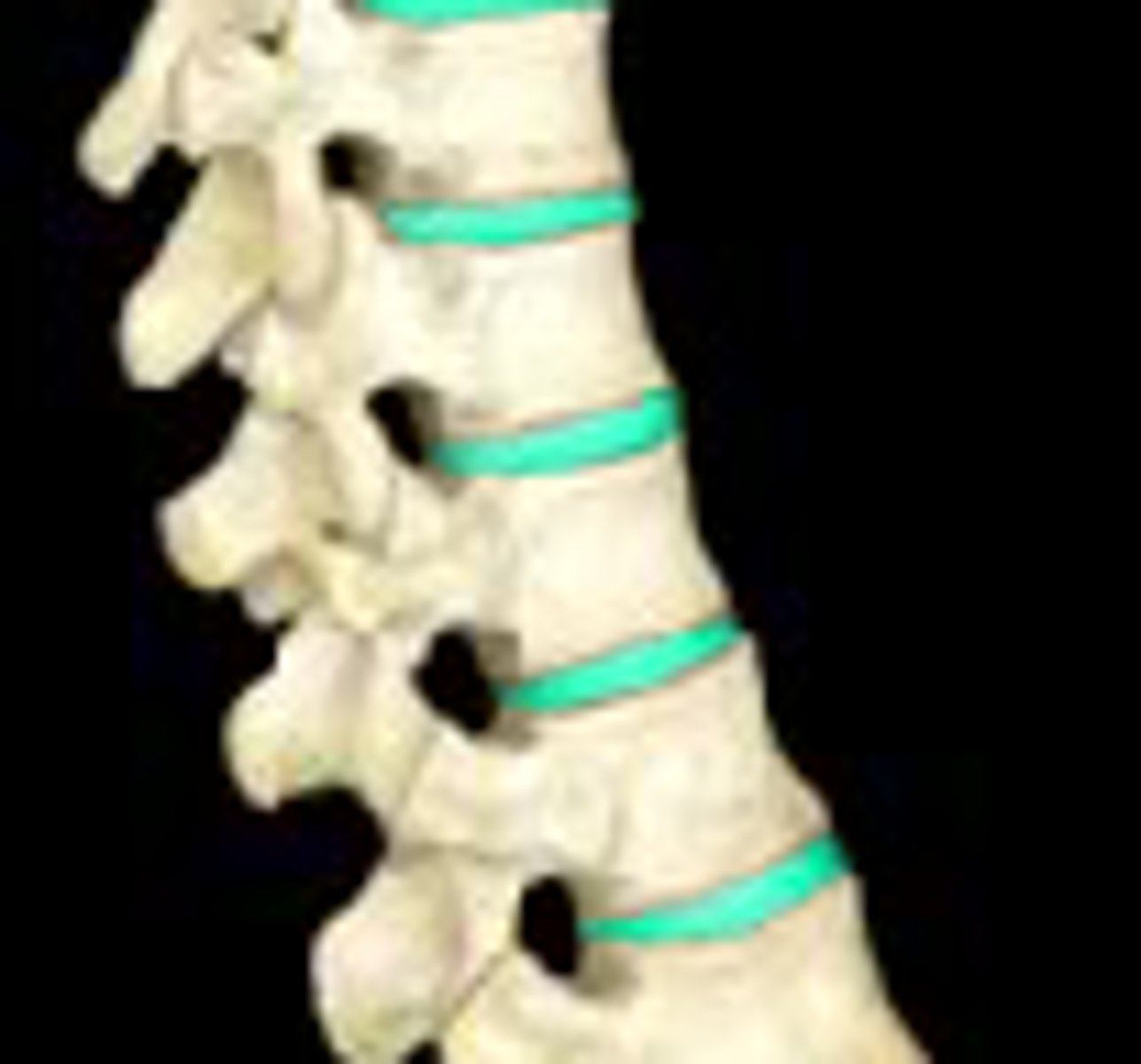
Intervertebral discs
- Pads of fibrocartilage that separate the vertebral bodies
- Absorb shock
Spinous process
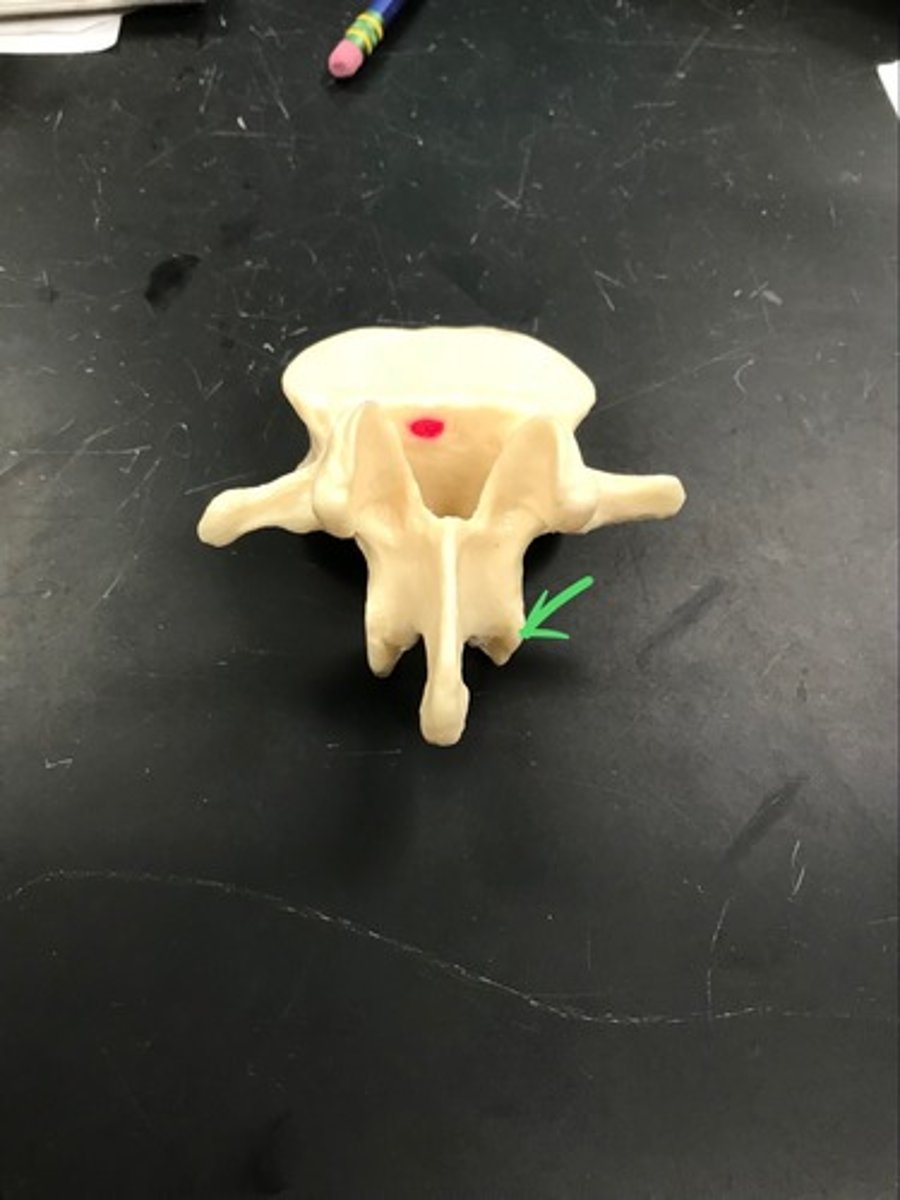
Transverse process
Inferior articulate process
- Contains the inferior articular facet
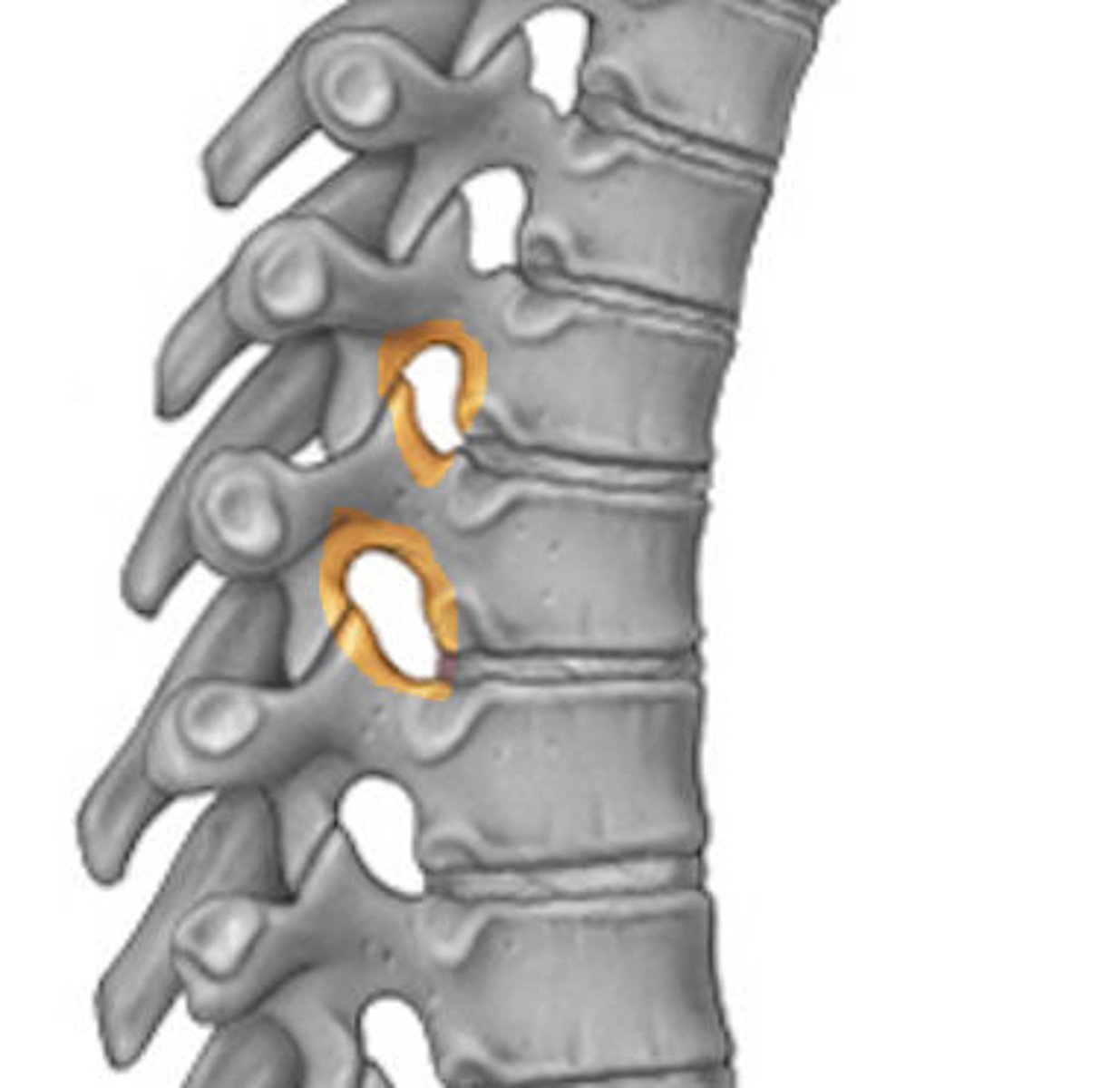
Intervertebral foramen
Vertebra prominens
C7 (has a prominent spinous process)
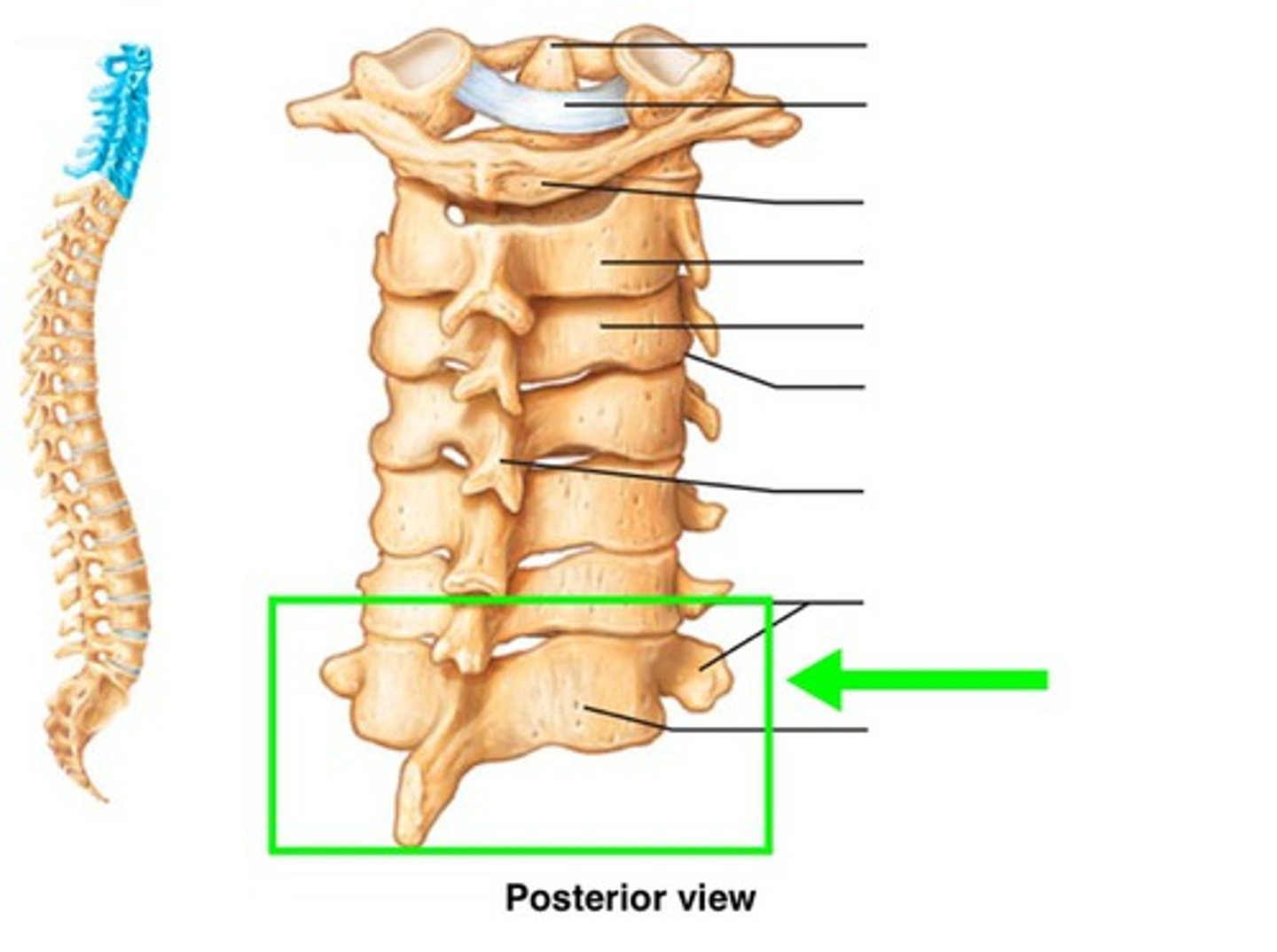
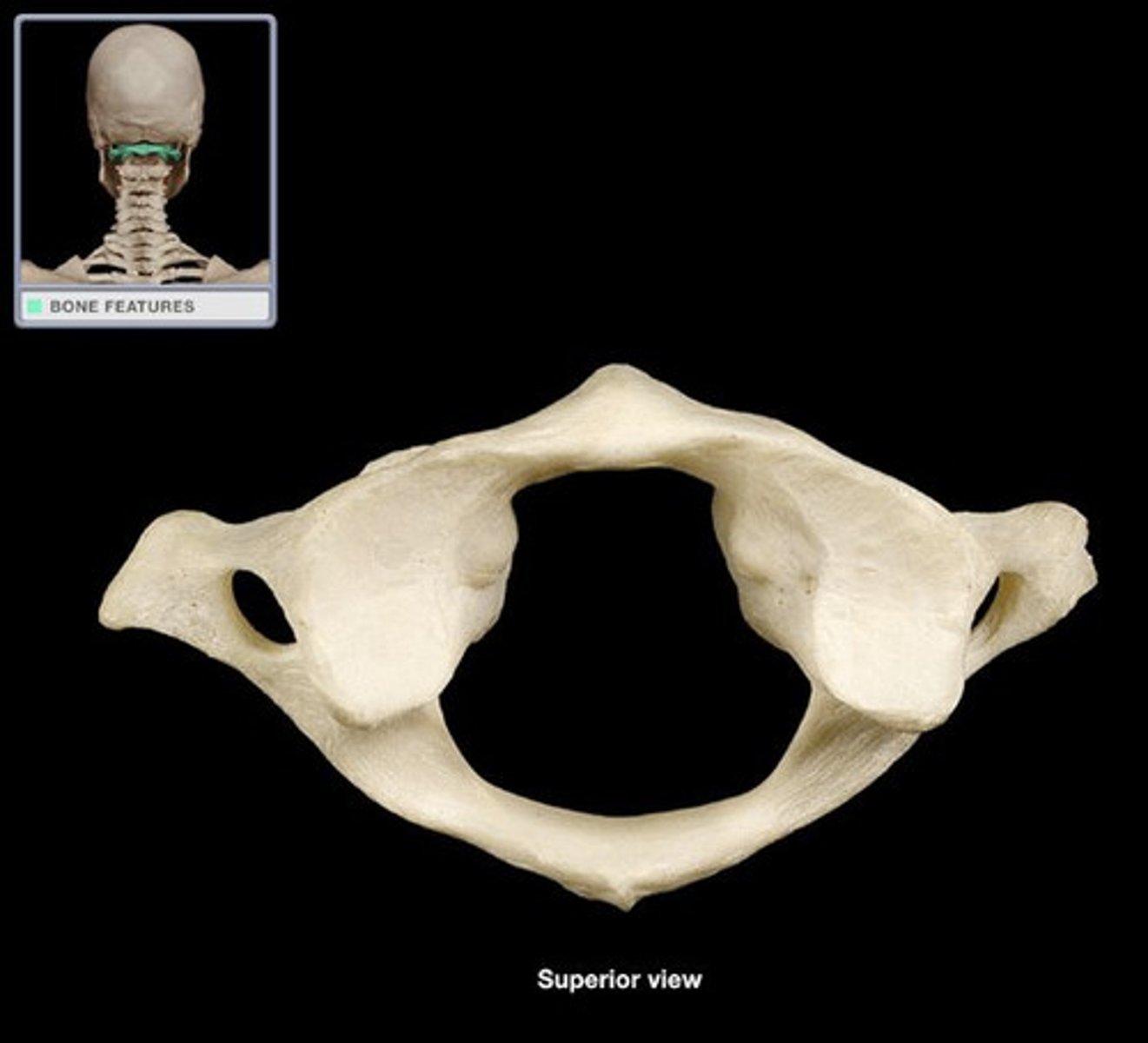
Atlas (C1)
- no spinous process
- no vertebral body
- has transverse process
- has transverse foramina (unique)
- has superior articular facets (rounded flat parts)
- has an anterior and posterior tubercle
- has an anterior arch
- articulates with axis (C2)
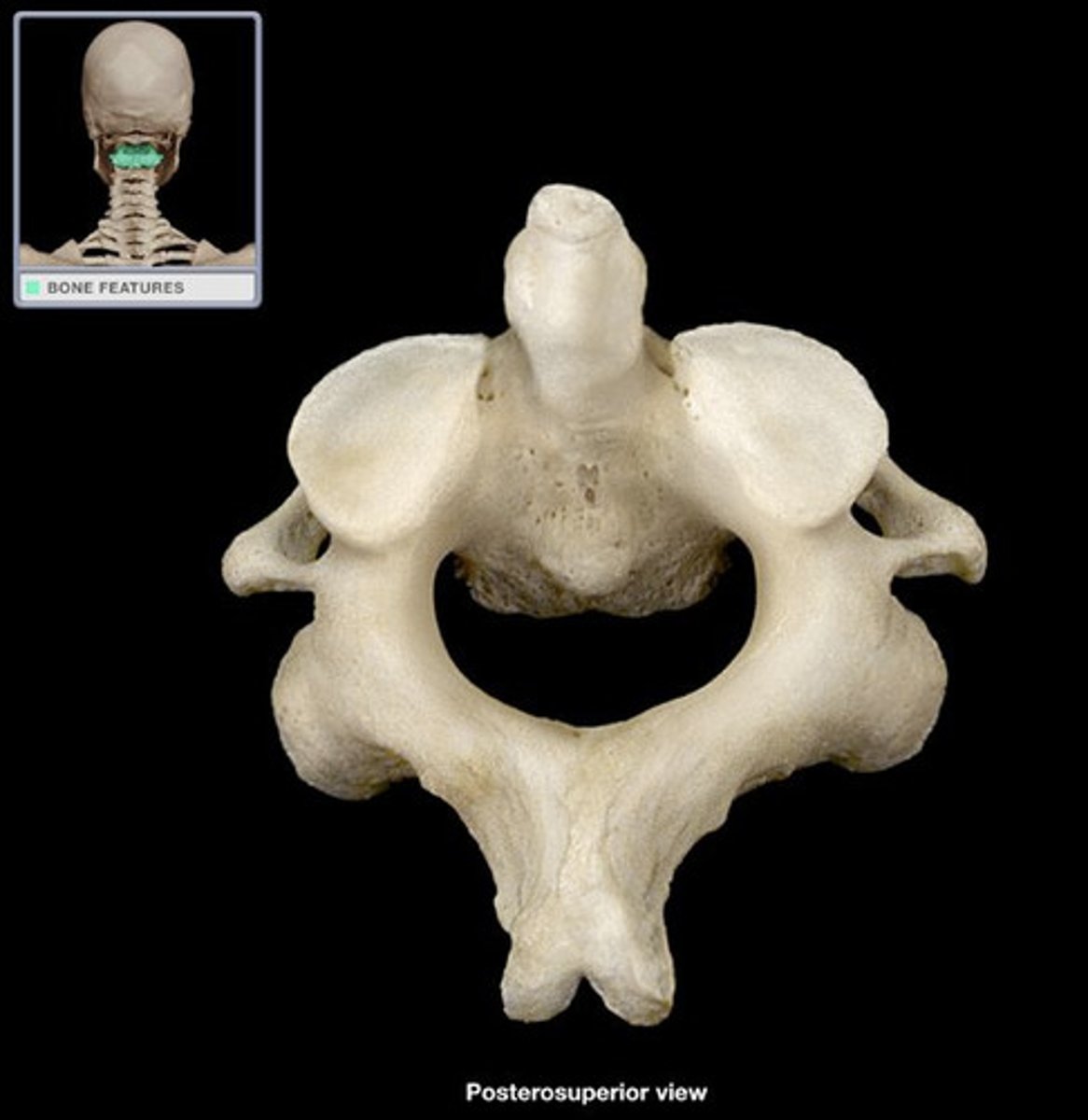
Axis (C2)
- has spinous process, vertebral arch, vertebral body, superior articular process, superior articular facet, transverse process, transverse foramen
- has a pedicle between the superior articular facet and vertebral body
- contains the dens/ordontoid process which articulates with C1
Which set of vertebrae have transverse foramina?
Cervical
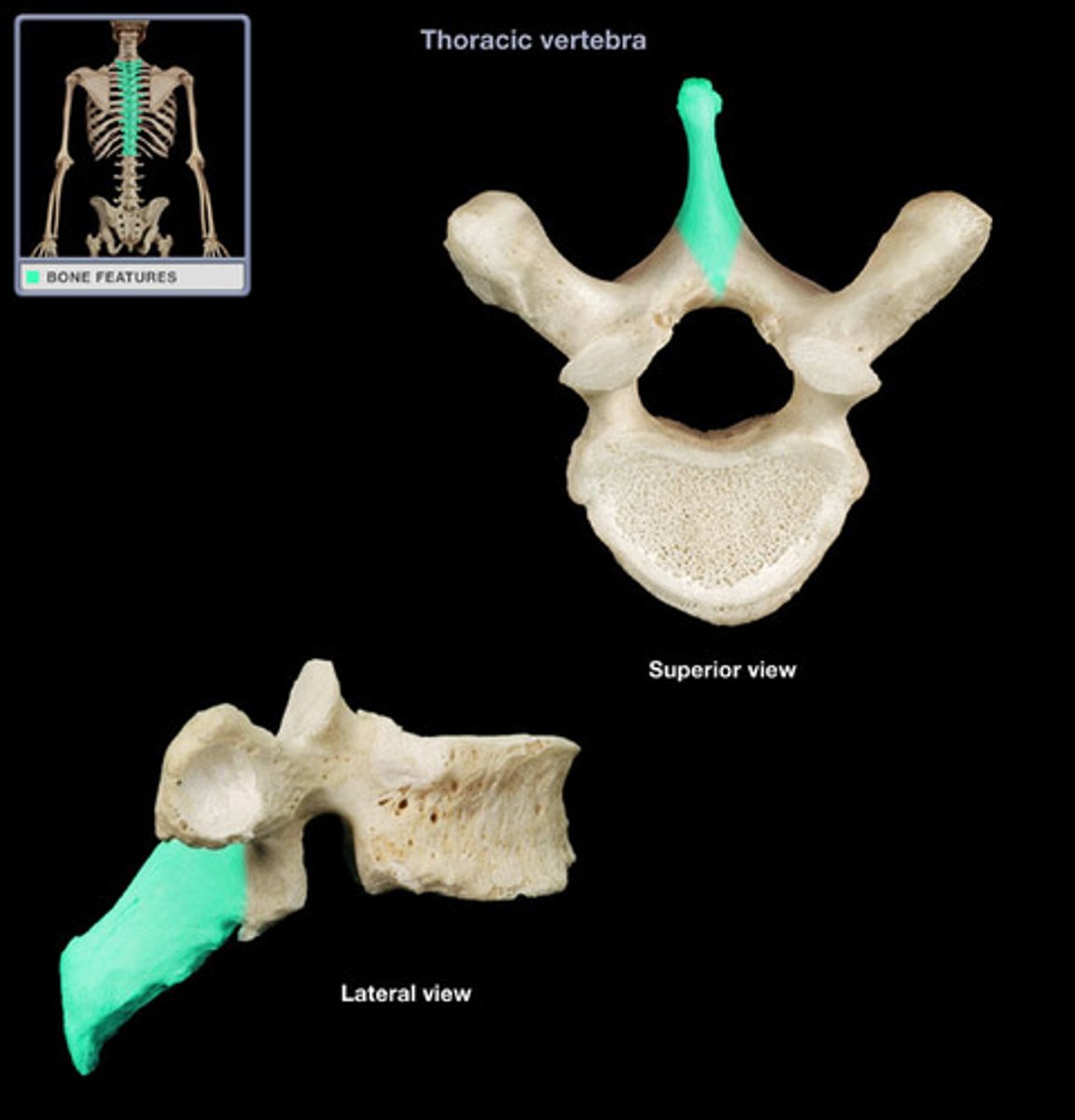
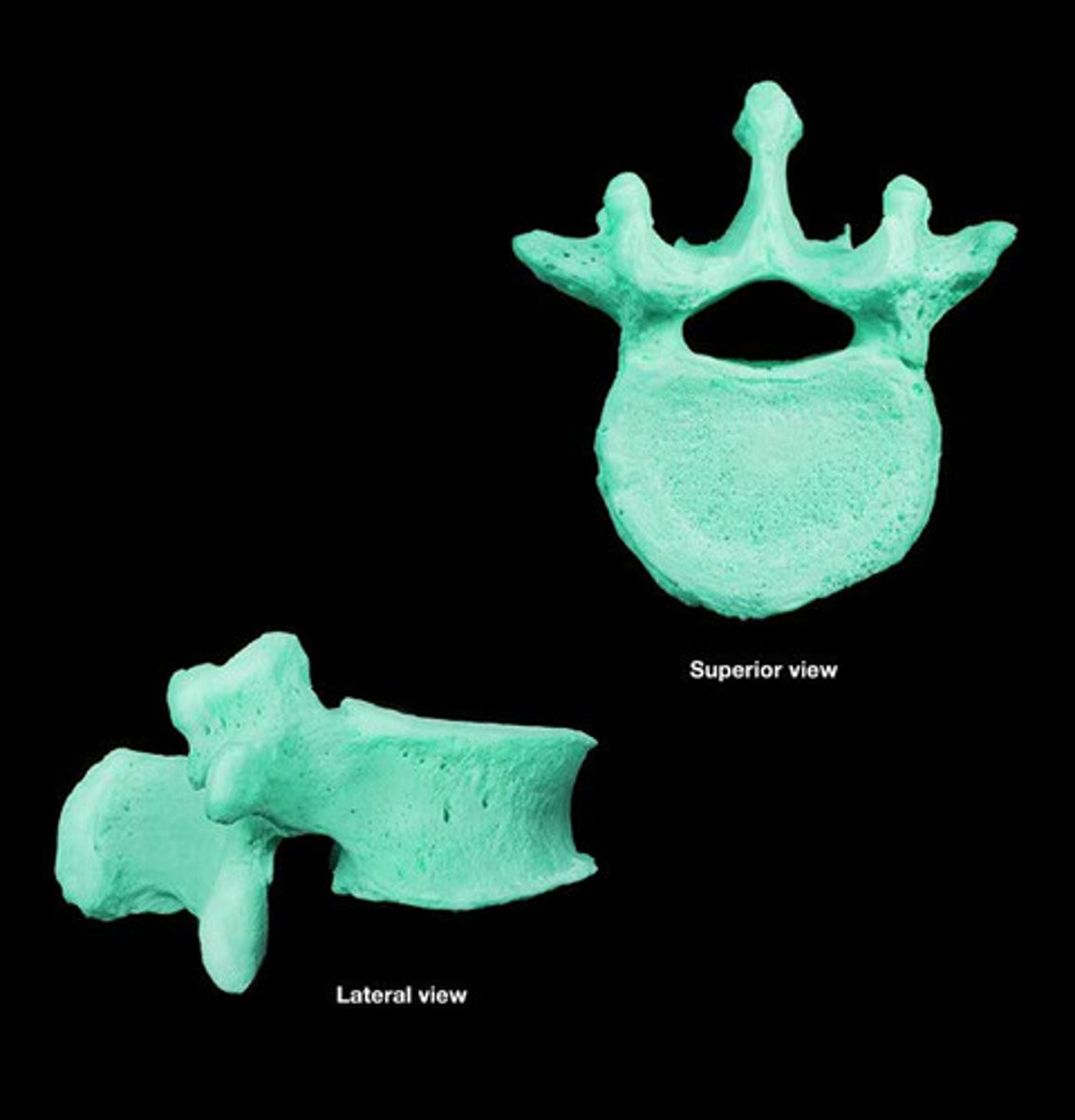
Thoracic vertebra
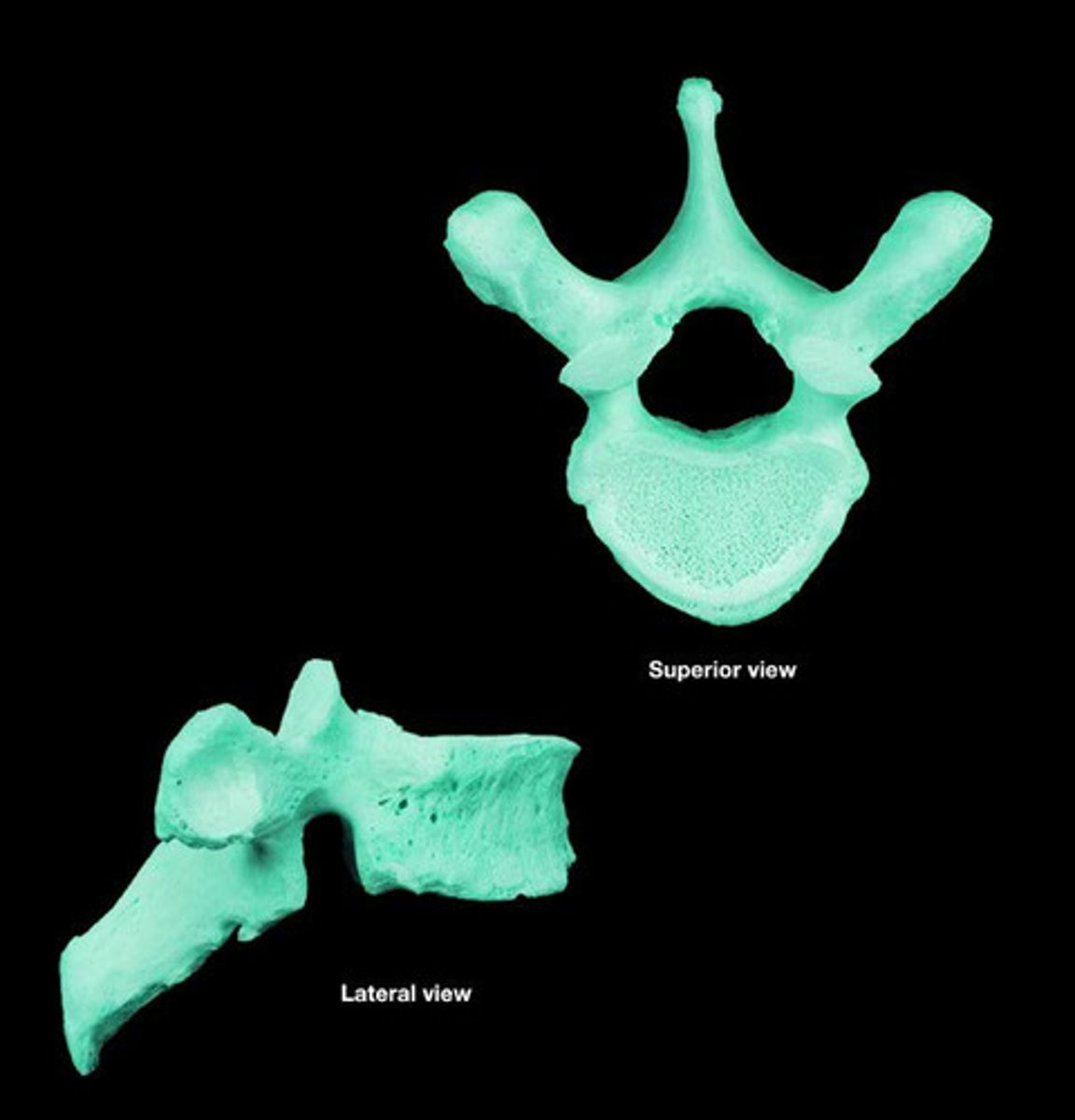
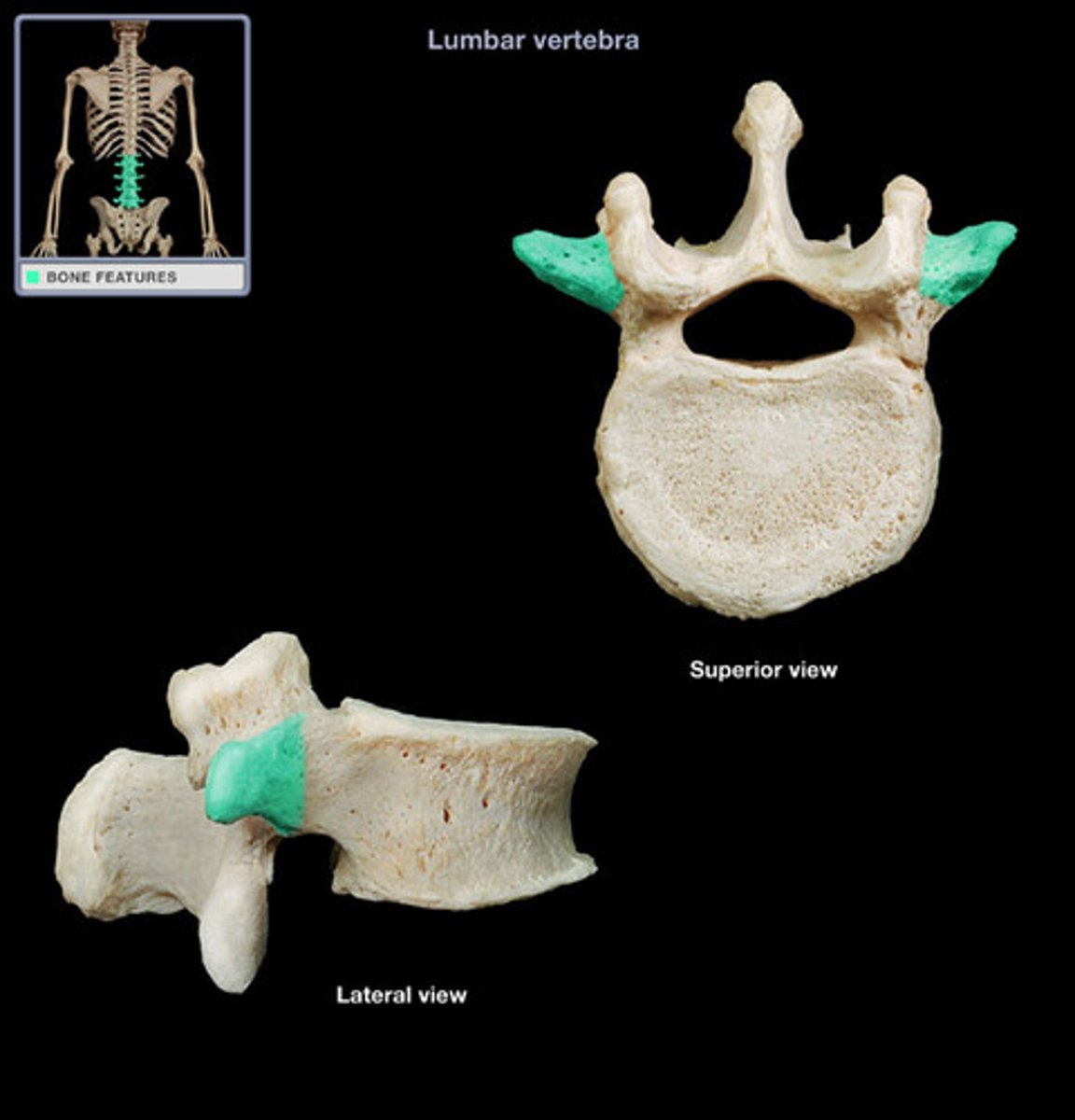
Lumbar vertebra
- contain mamillary process (unique from other vertebrae)
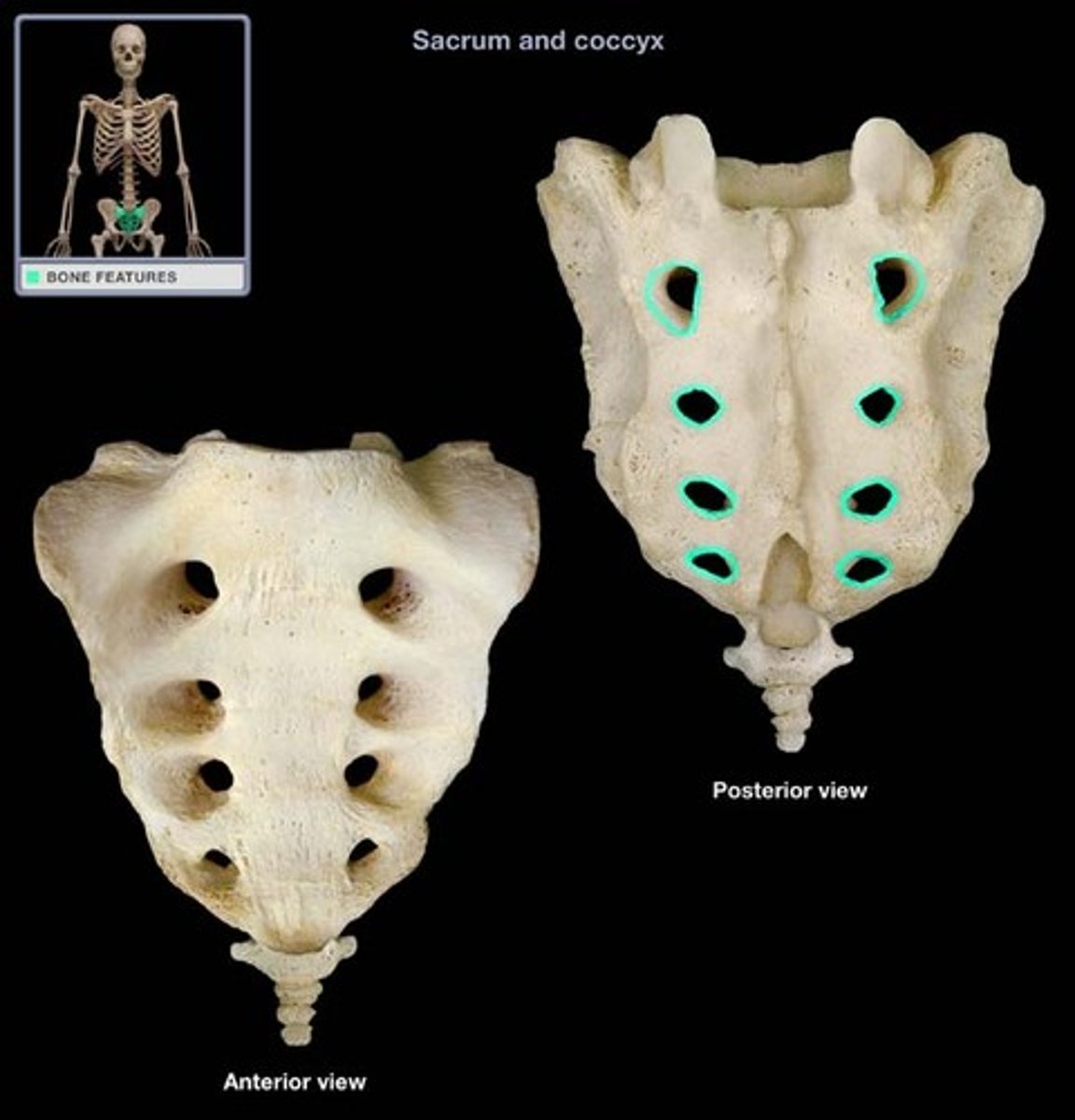
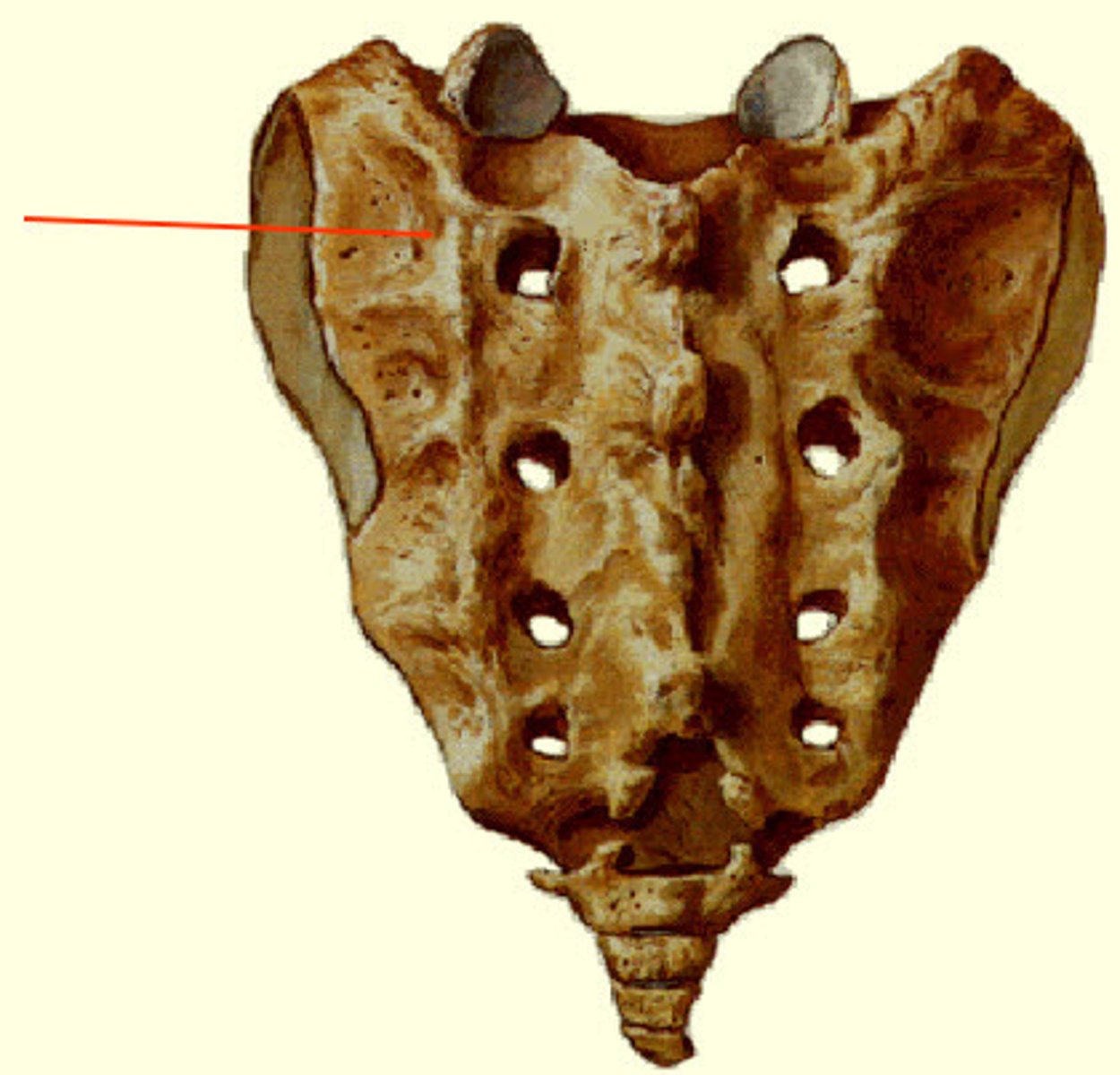
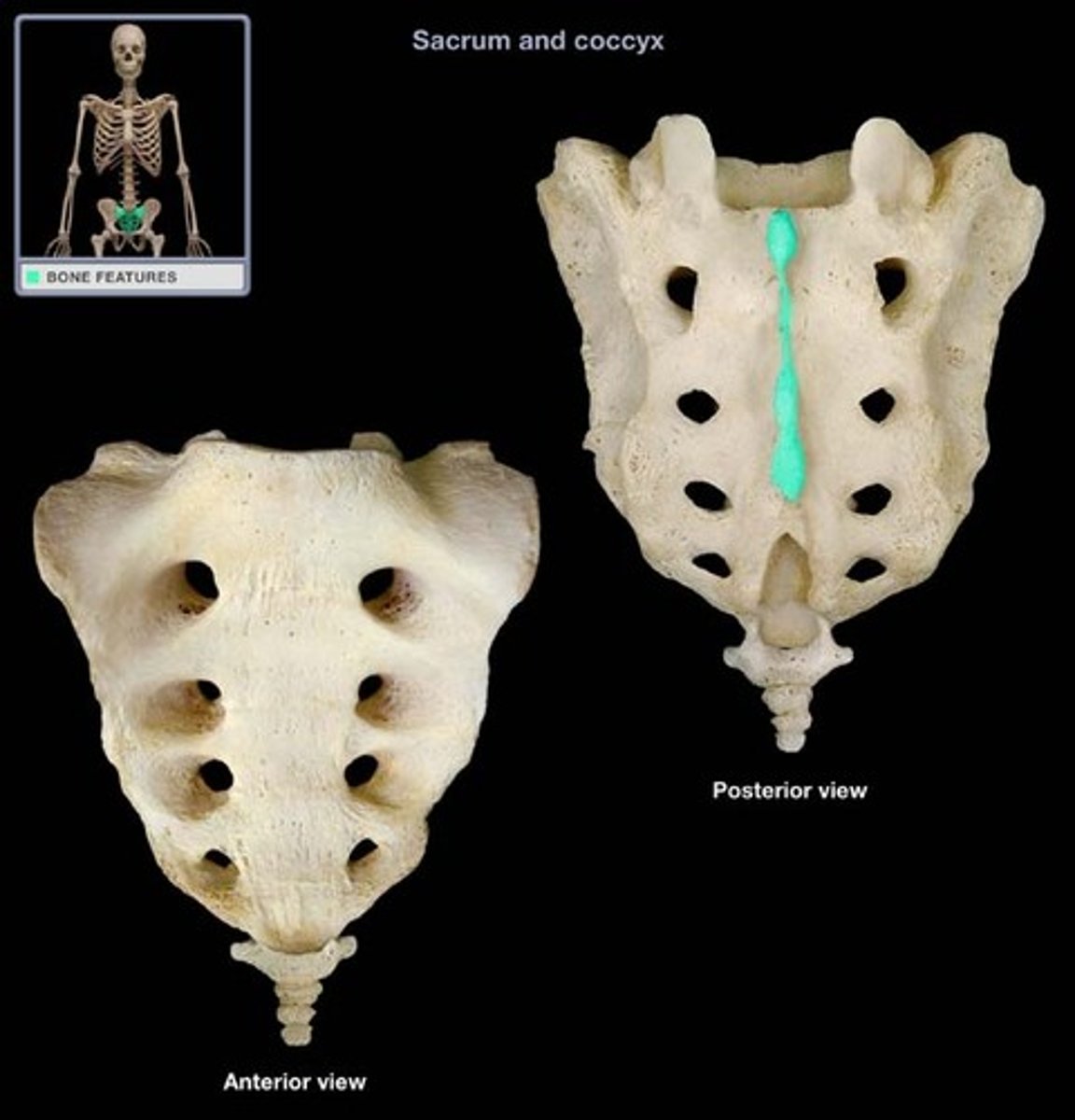
Entrance to sacral canal
Articular process of the sacrum
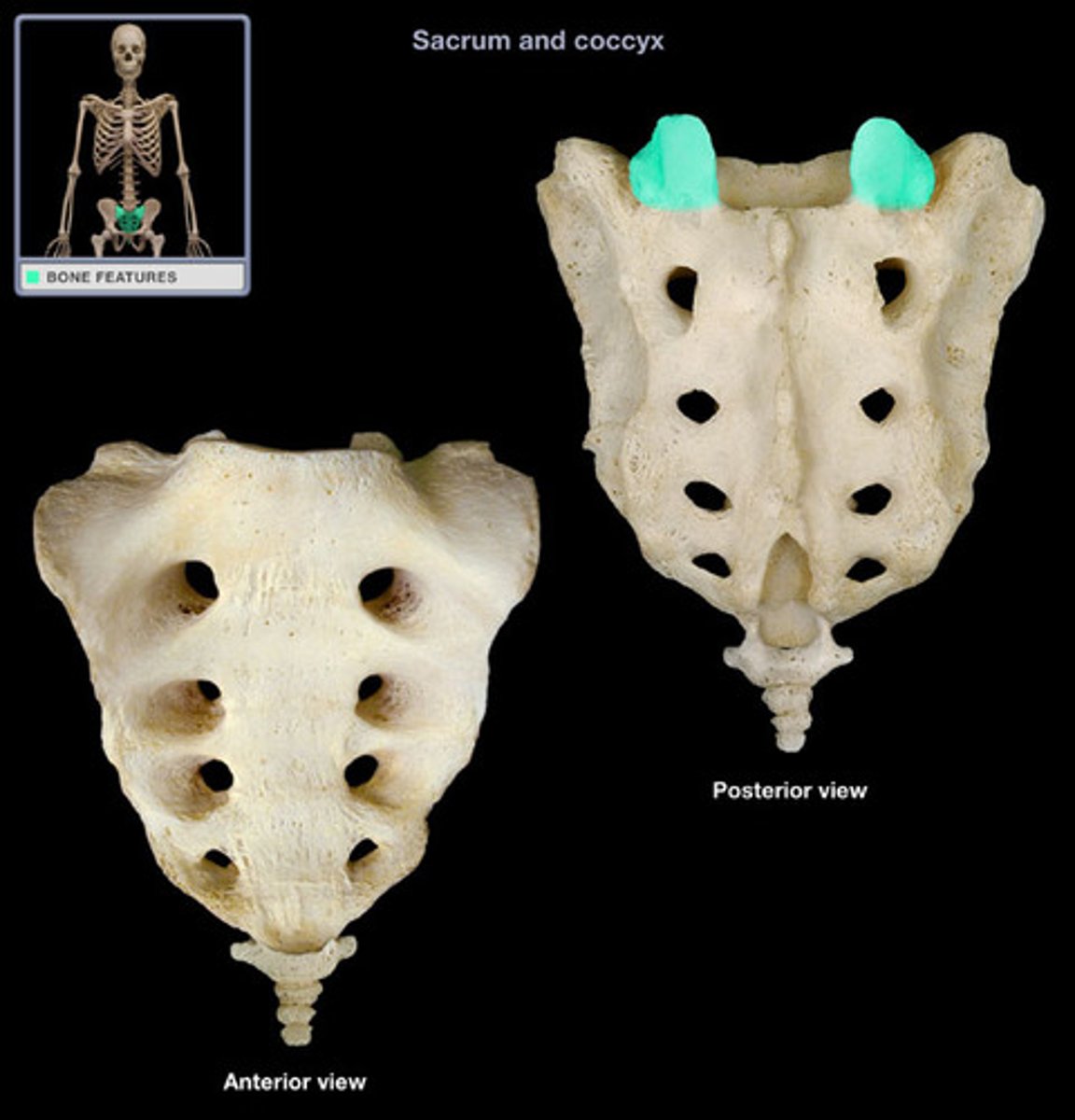
Sacral tuberosity (L & R)
(Indented portion along left and right sides)
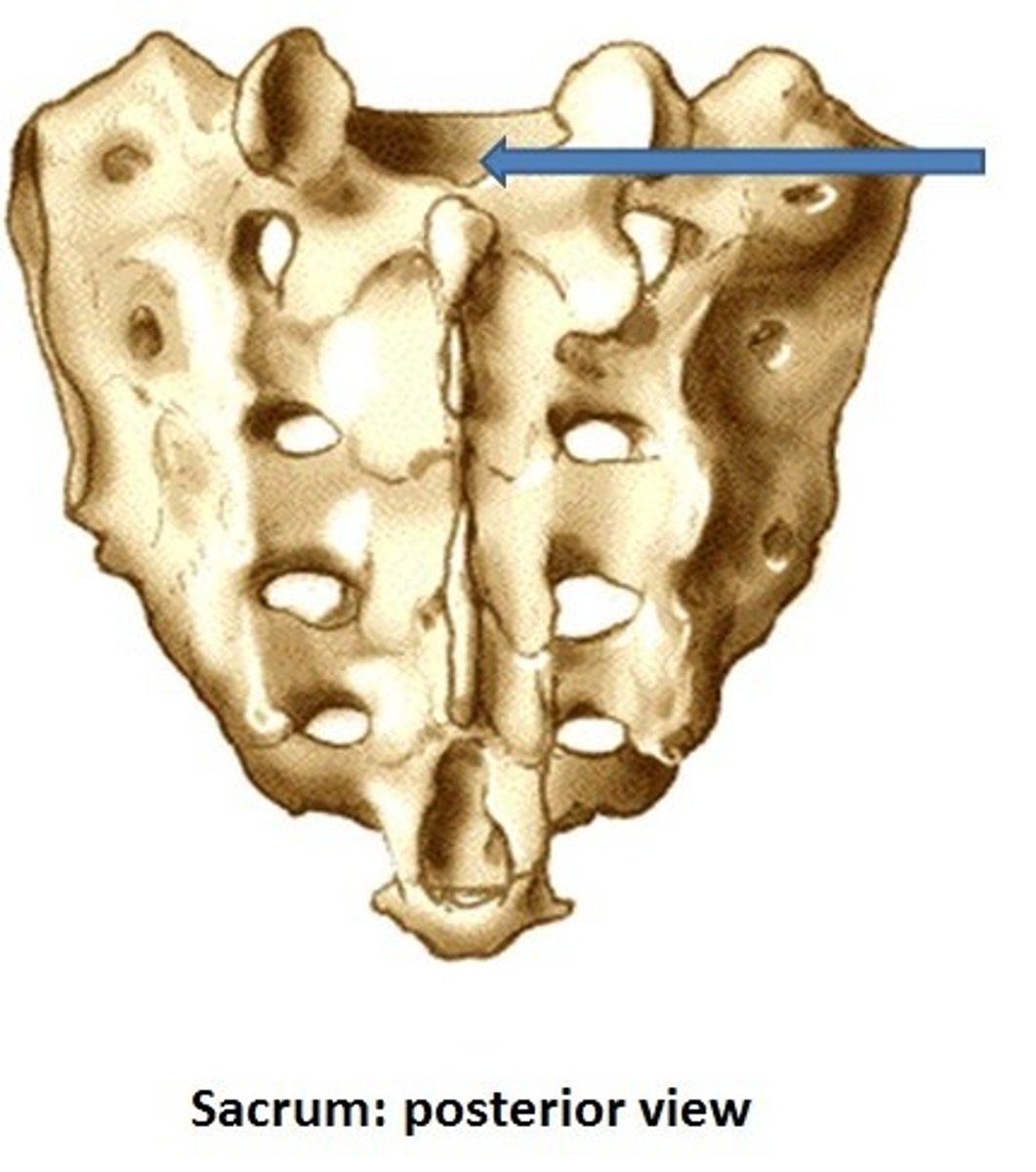
Lateral sacral crest
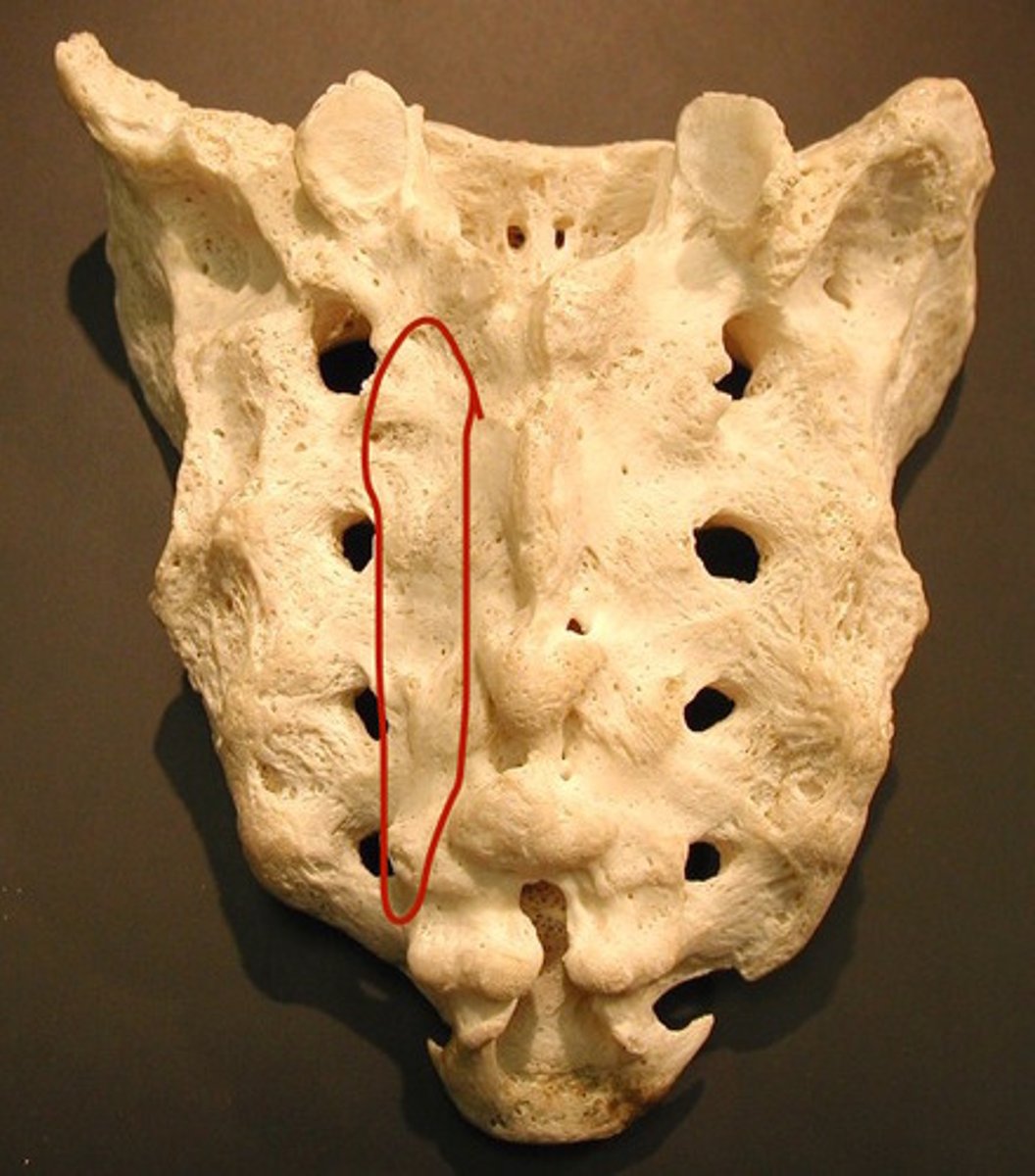
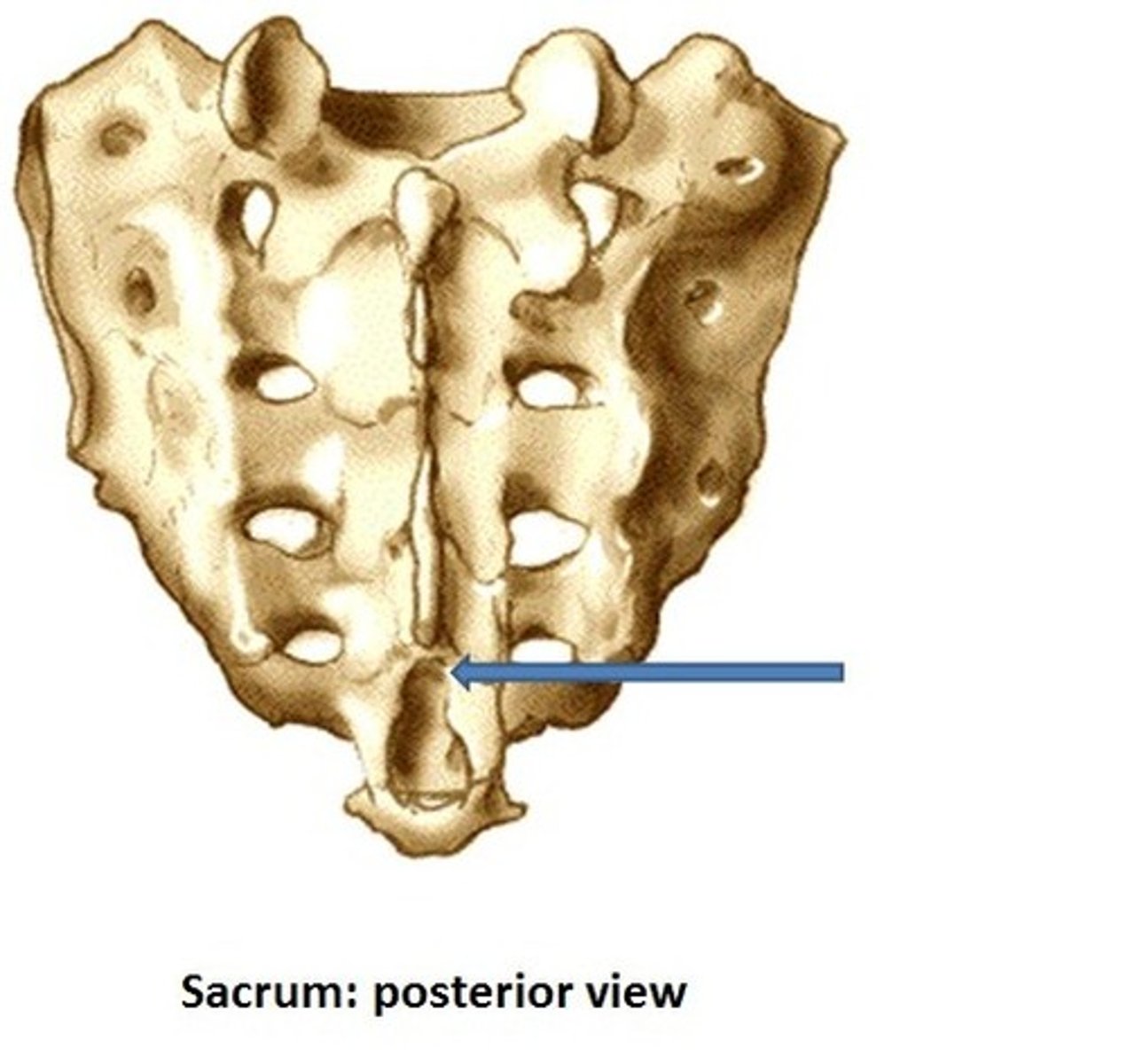
Median sacral crest
Sacral hiatus
Sacral cornu
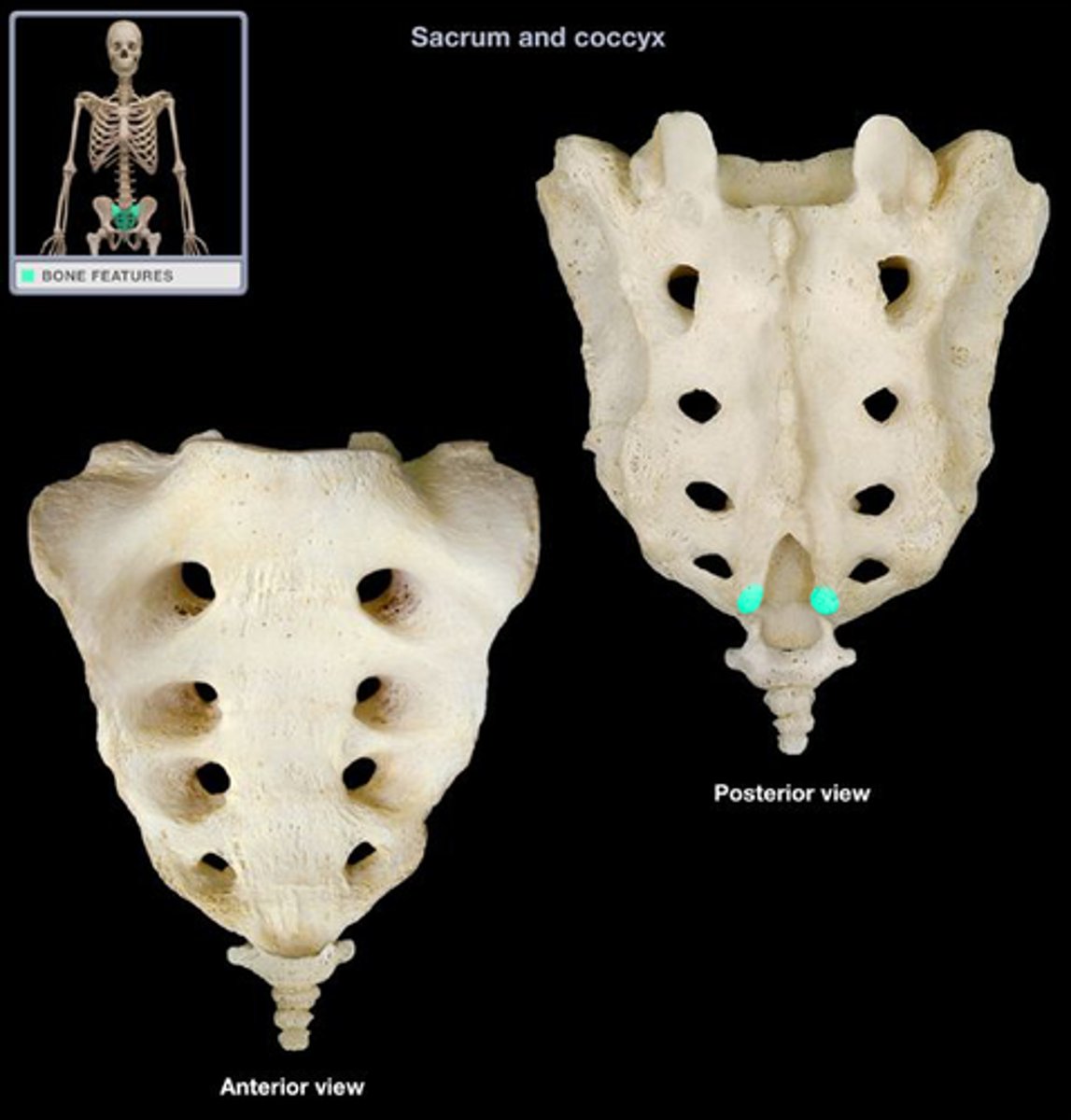
Coccygeal cornu
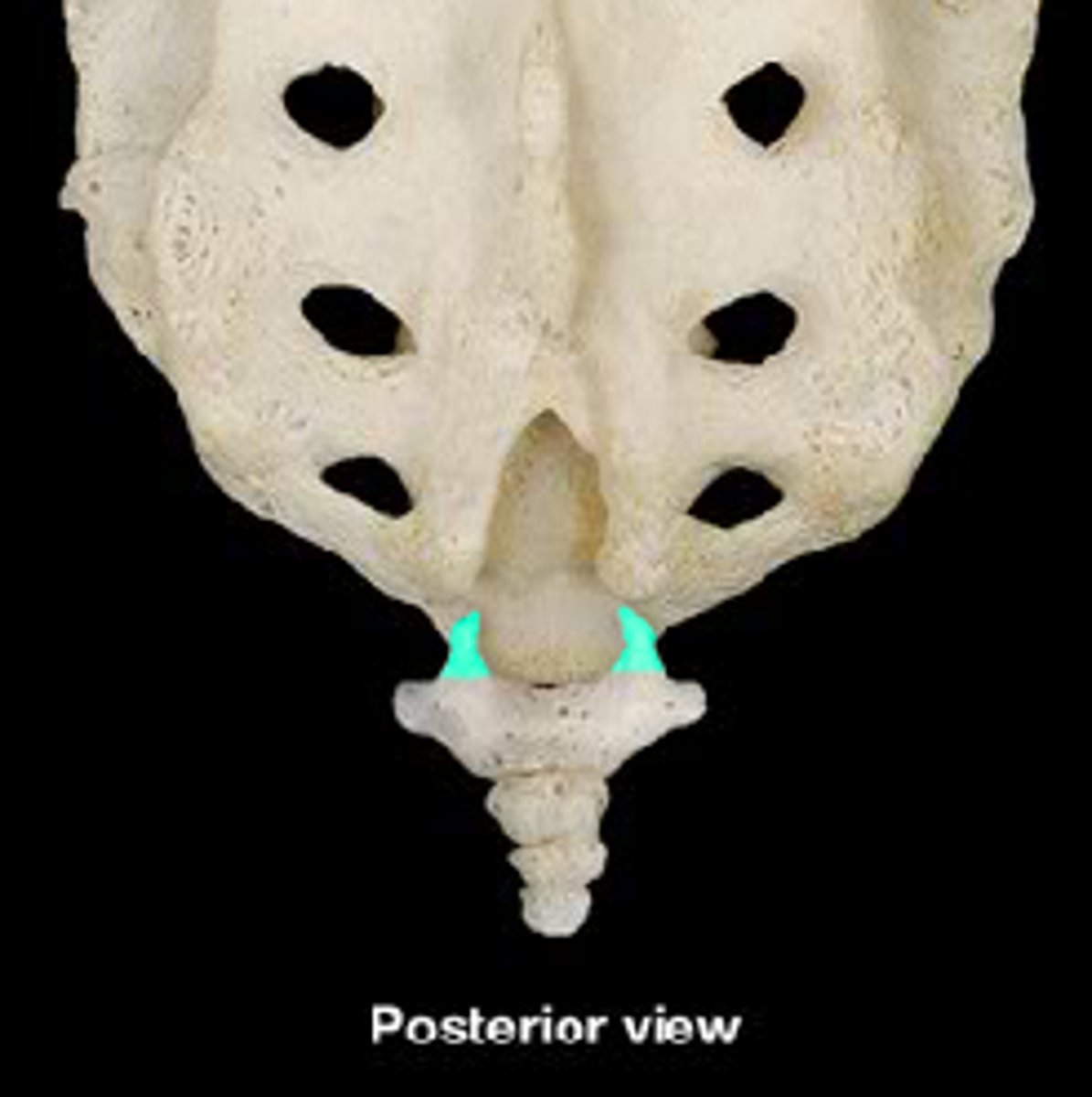
Sacral base
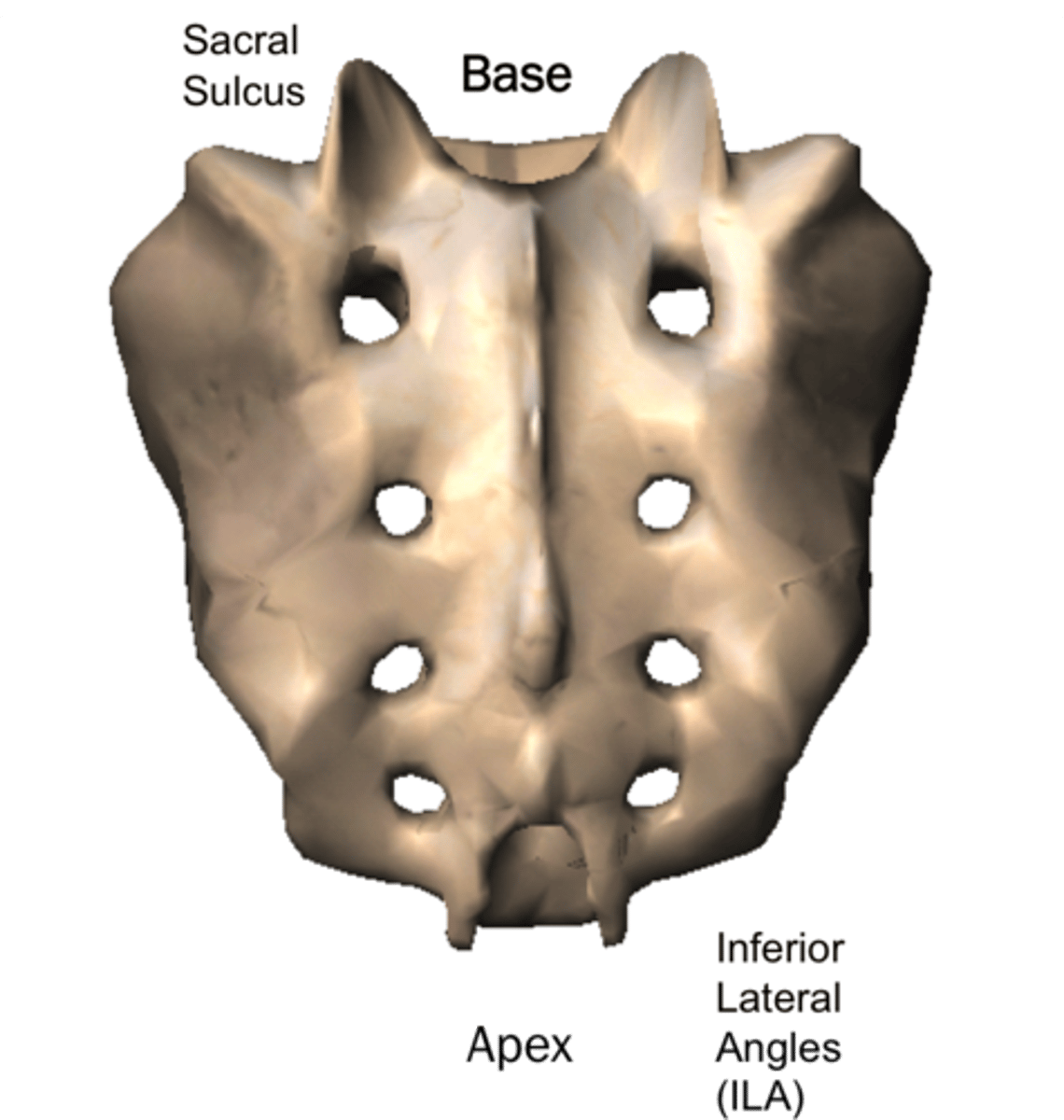
Sacral promontory
(anterior)
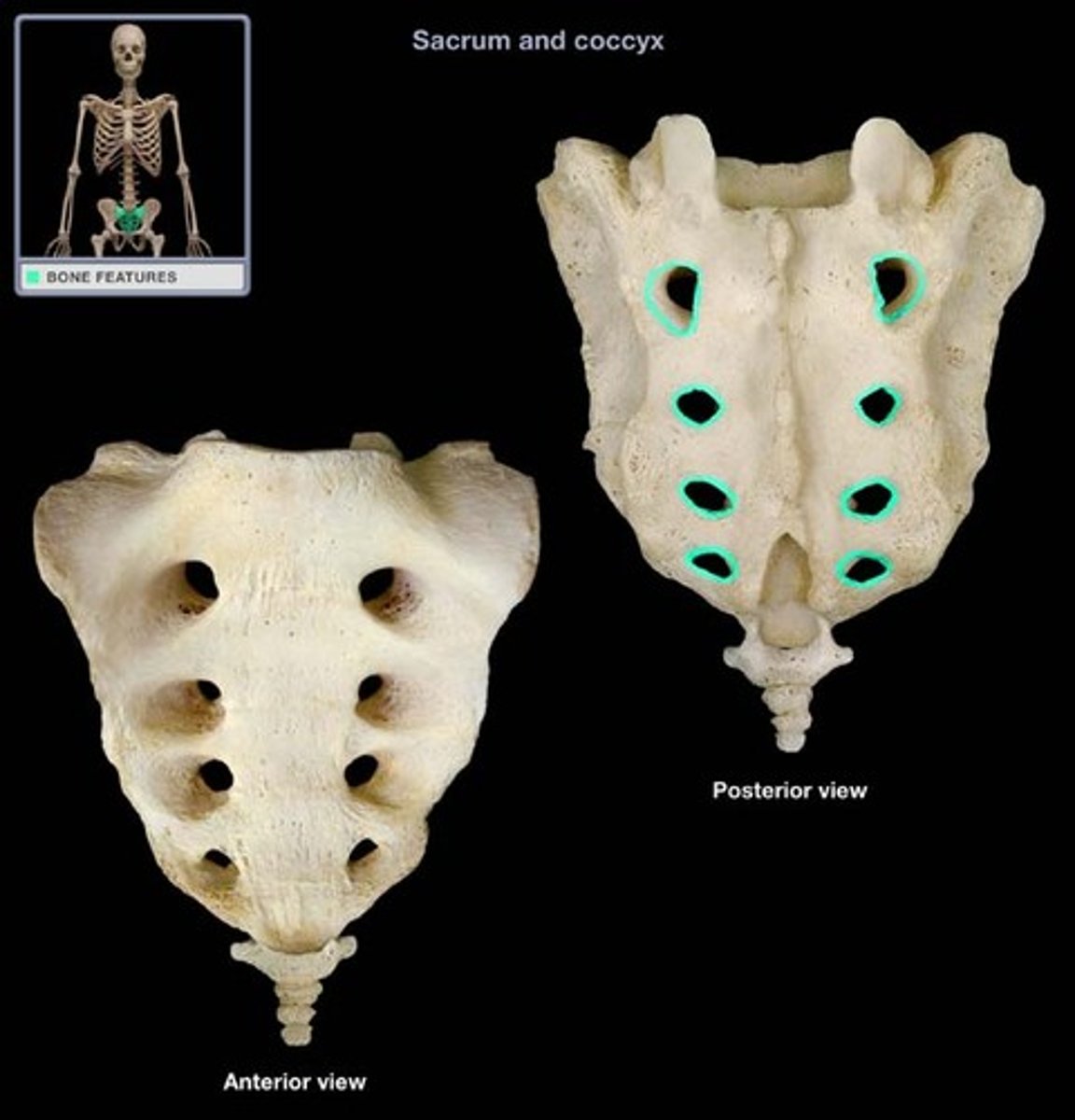
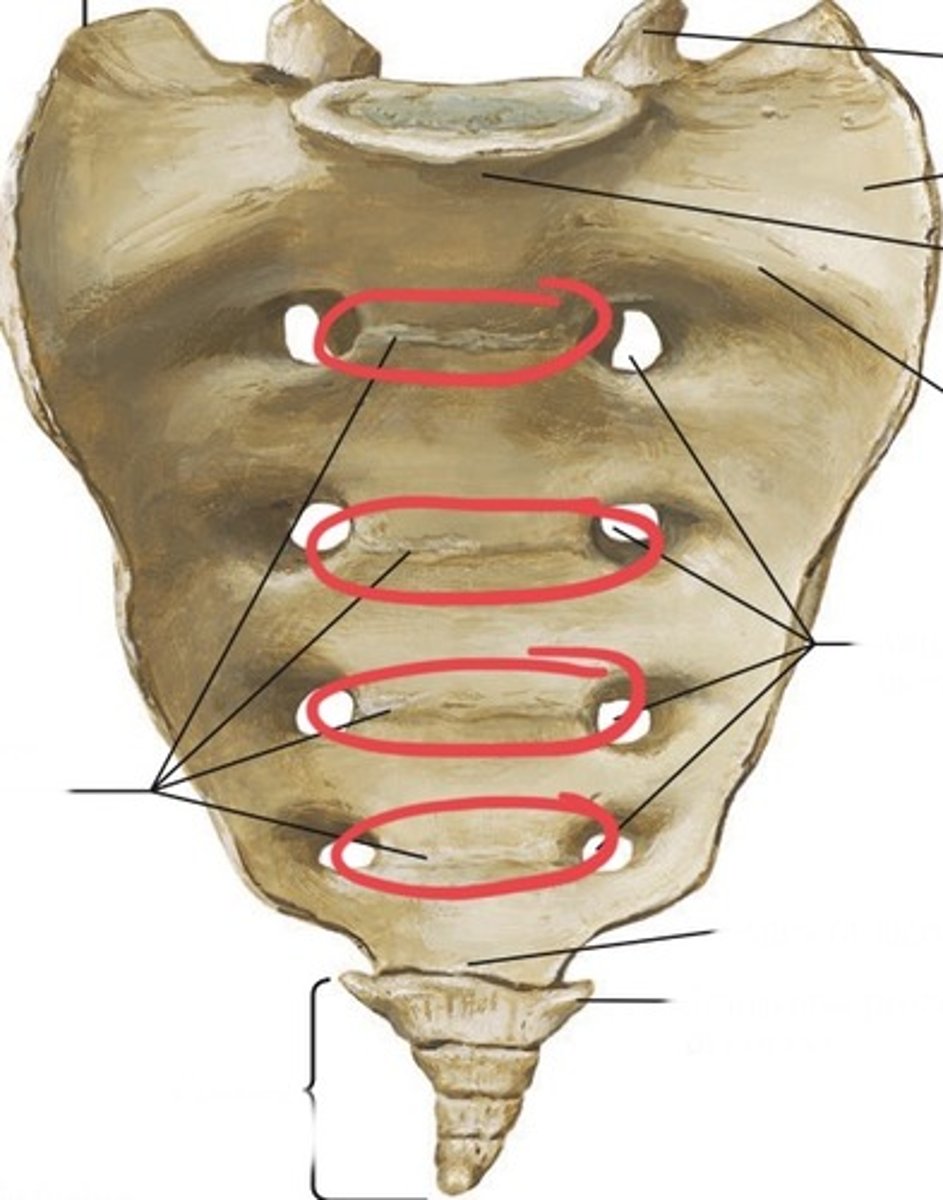
Sacral foramina
Sacral ala
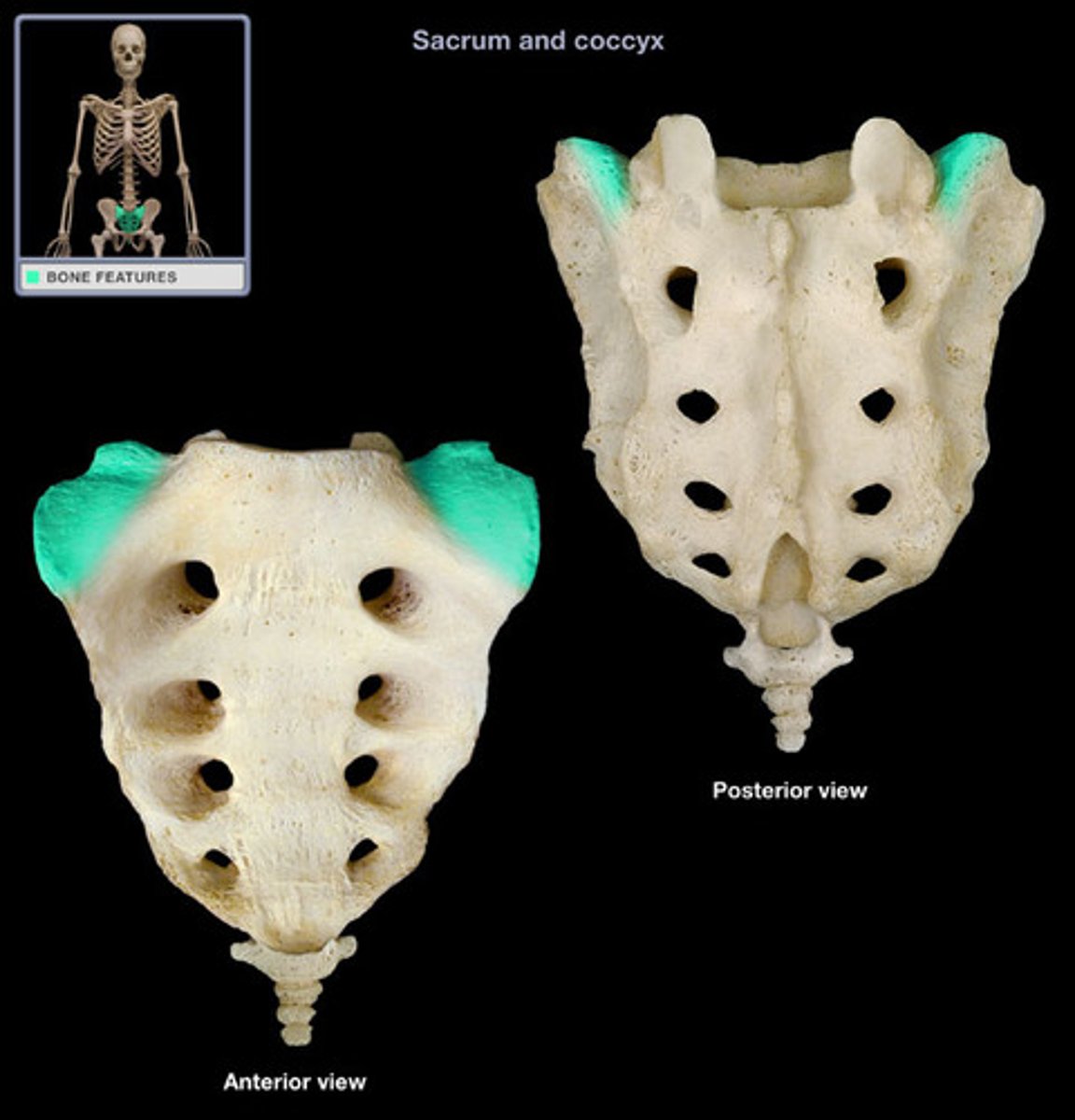
Sacral transverse lines
(anterior)
Sacral apex
(anterior)
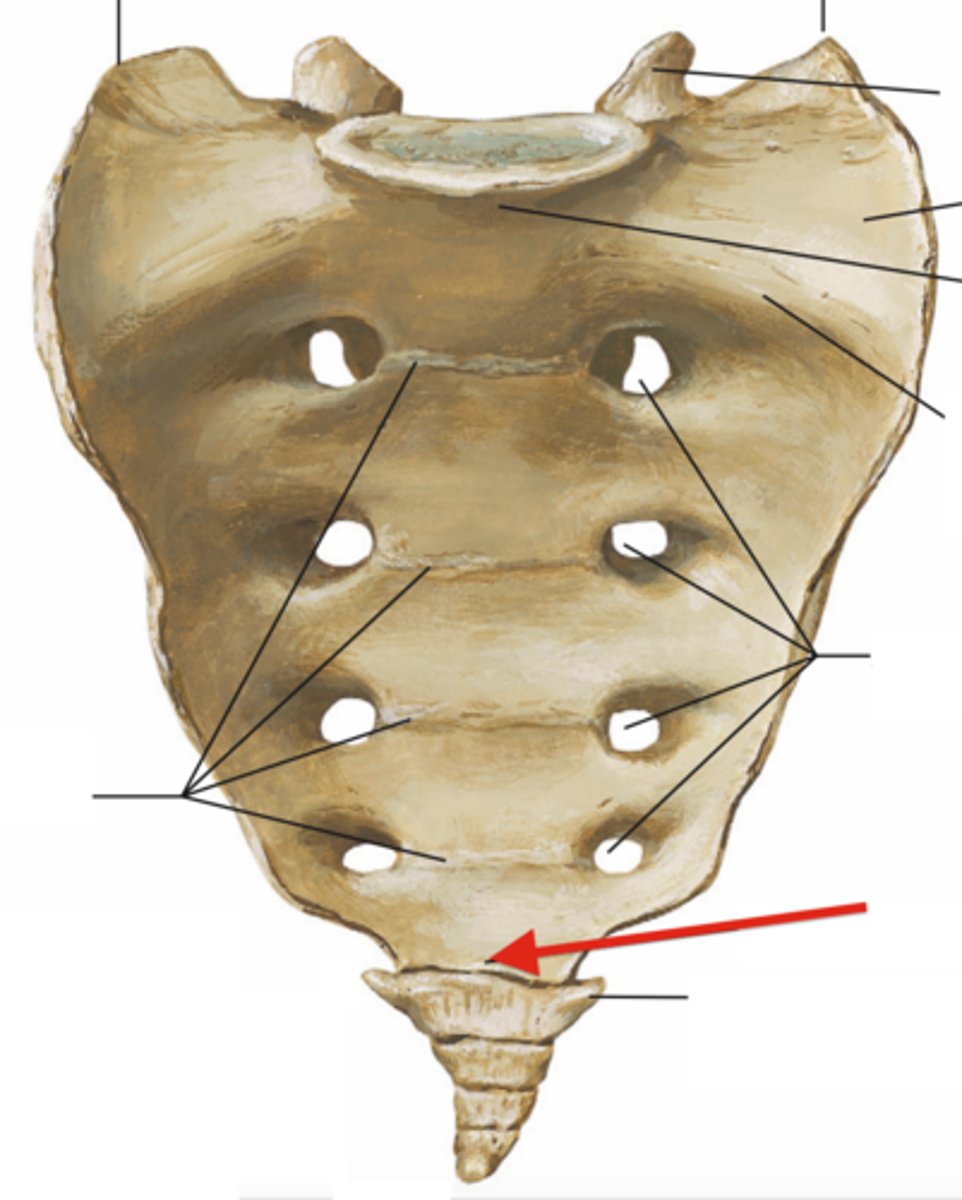
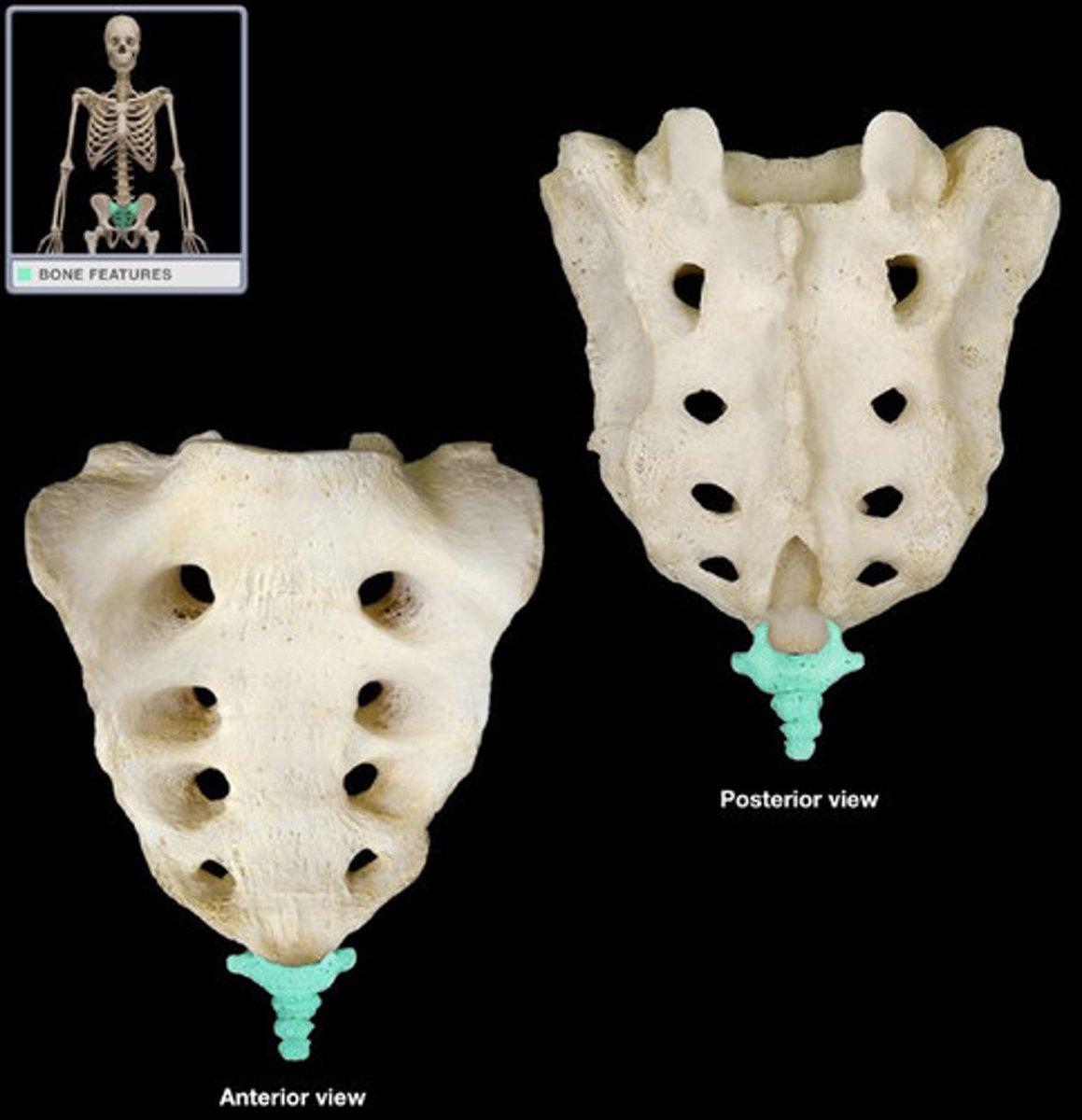
Coccyx
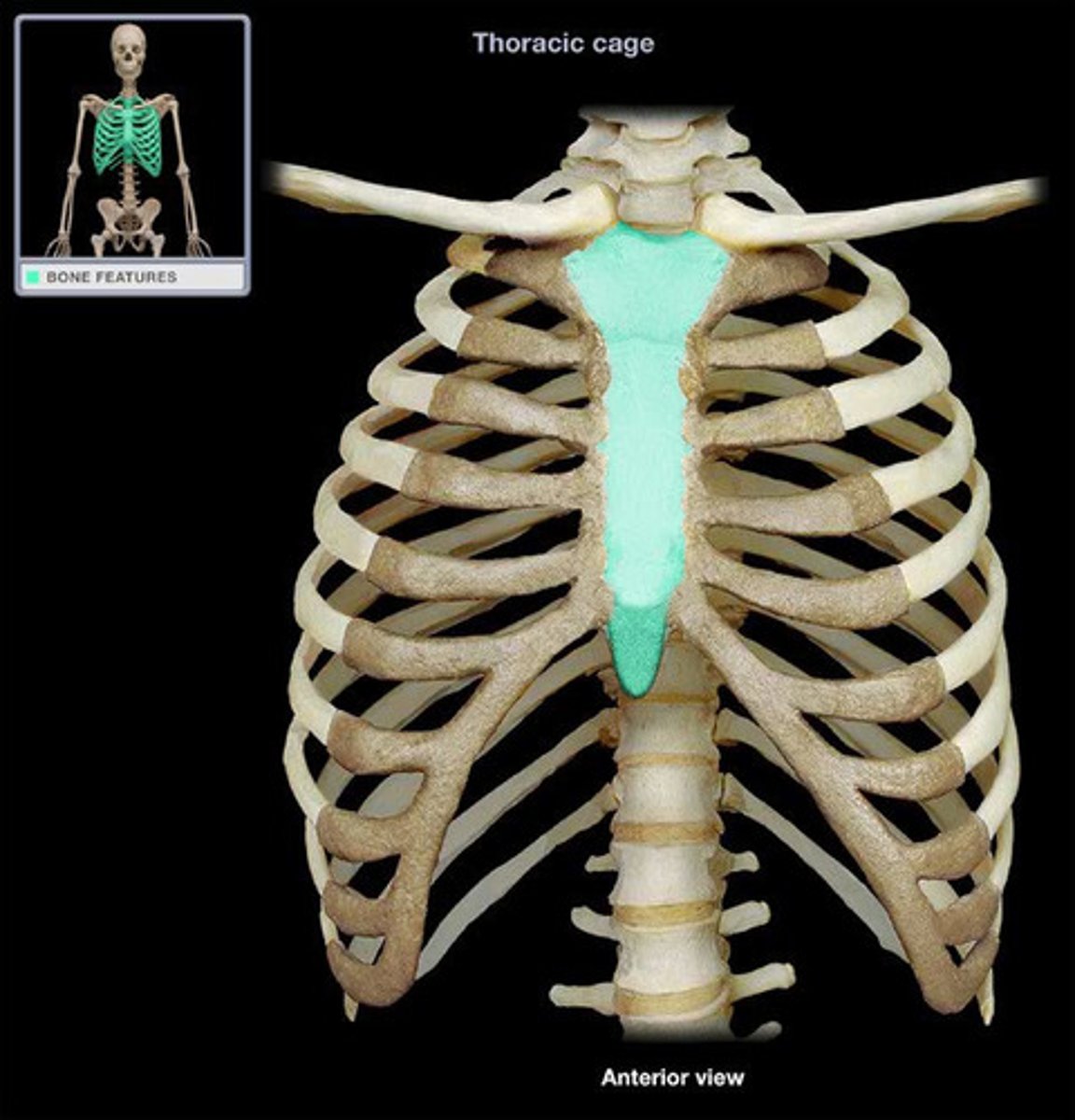
Thoracic cage/rib cage
- supports thoracic cavity
- rib cage = formed by ribs and sternum
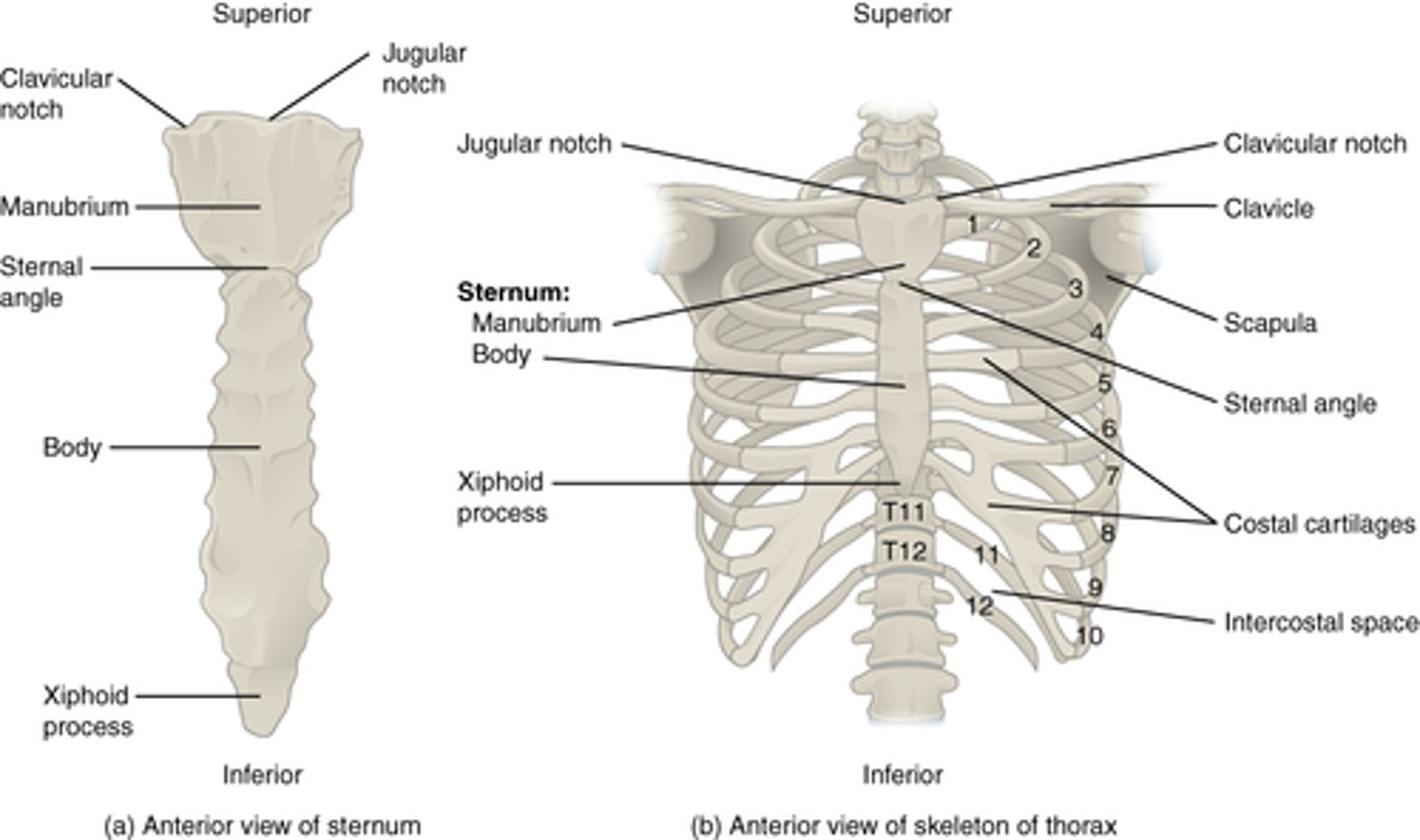
Sternum (breastbone)
Ribs (Costae)
12 pairs of long, curved, flat bones
- 7 true rib pairs (attach individually to the sternum)
- 5 false rib pairs (connect with 7 to attach or don't attach at all (11-12))
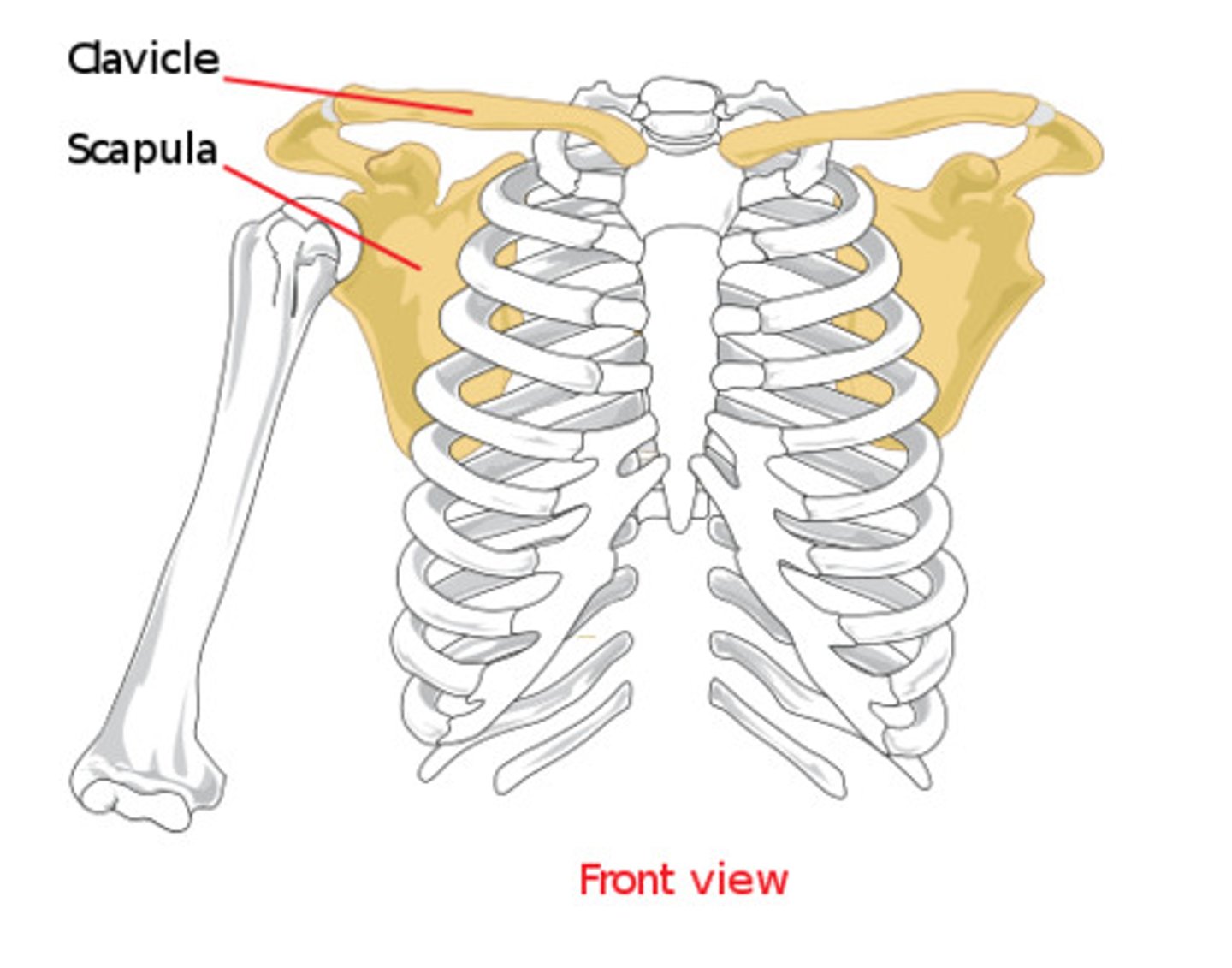
Pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle)
- connects with the axial skeleton at the manubrium
- contain two scapulae and two clavicles
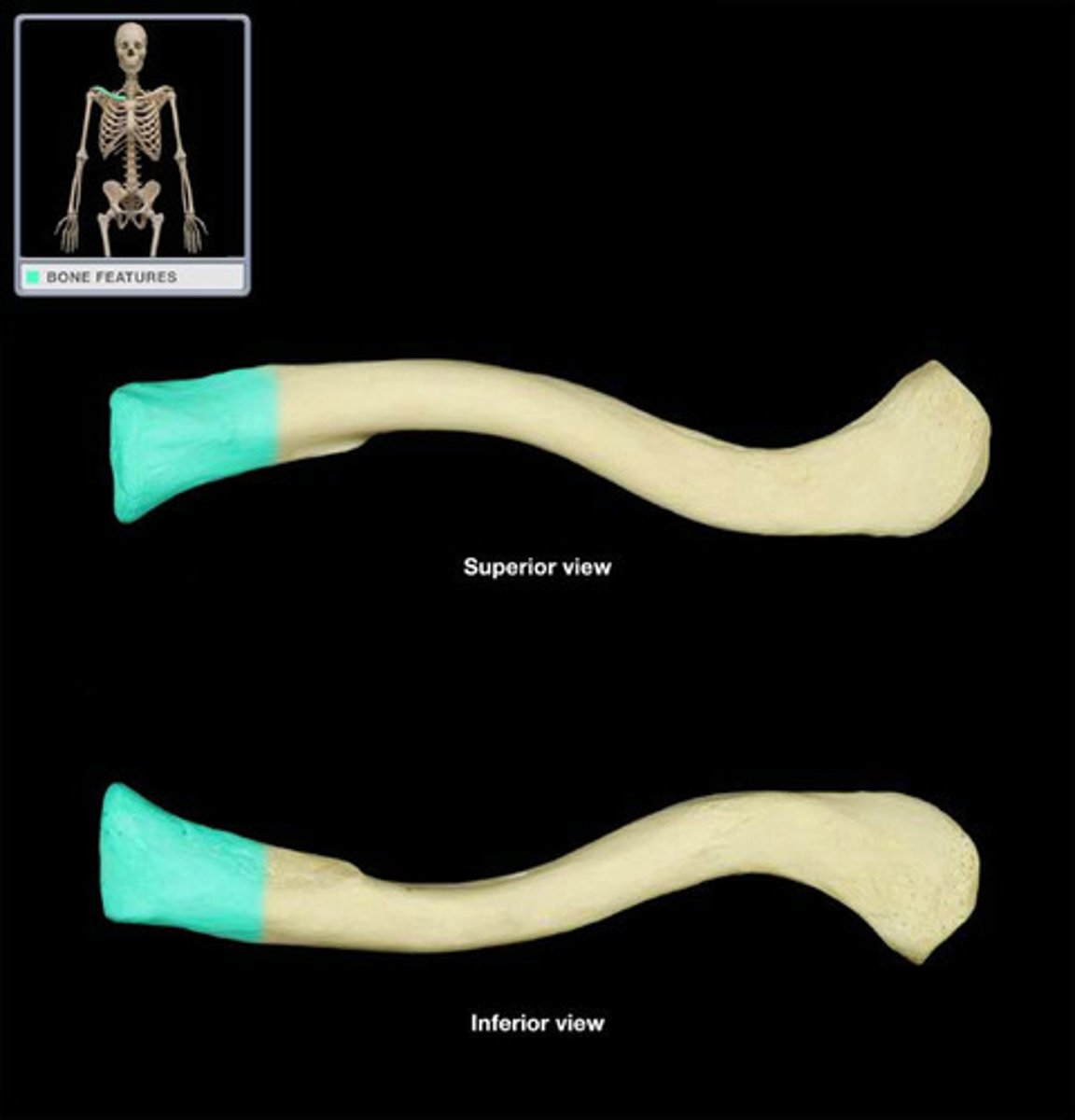
Acromial end of clavicle
- Lateral
- Facet for articulation with acromion of scapula
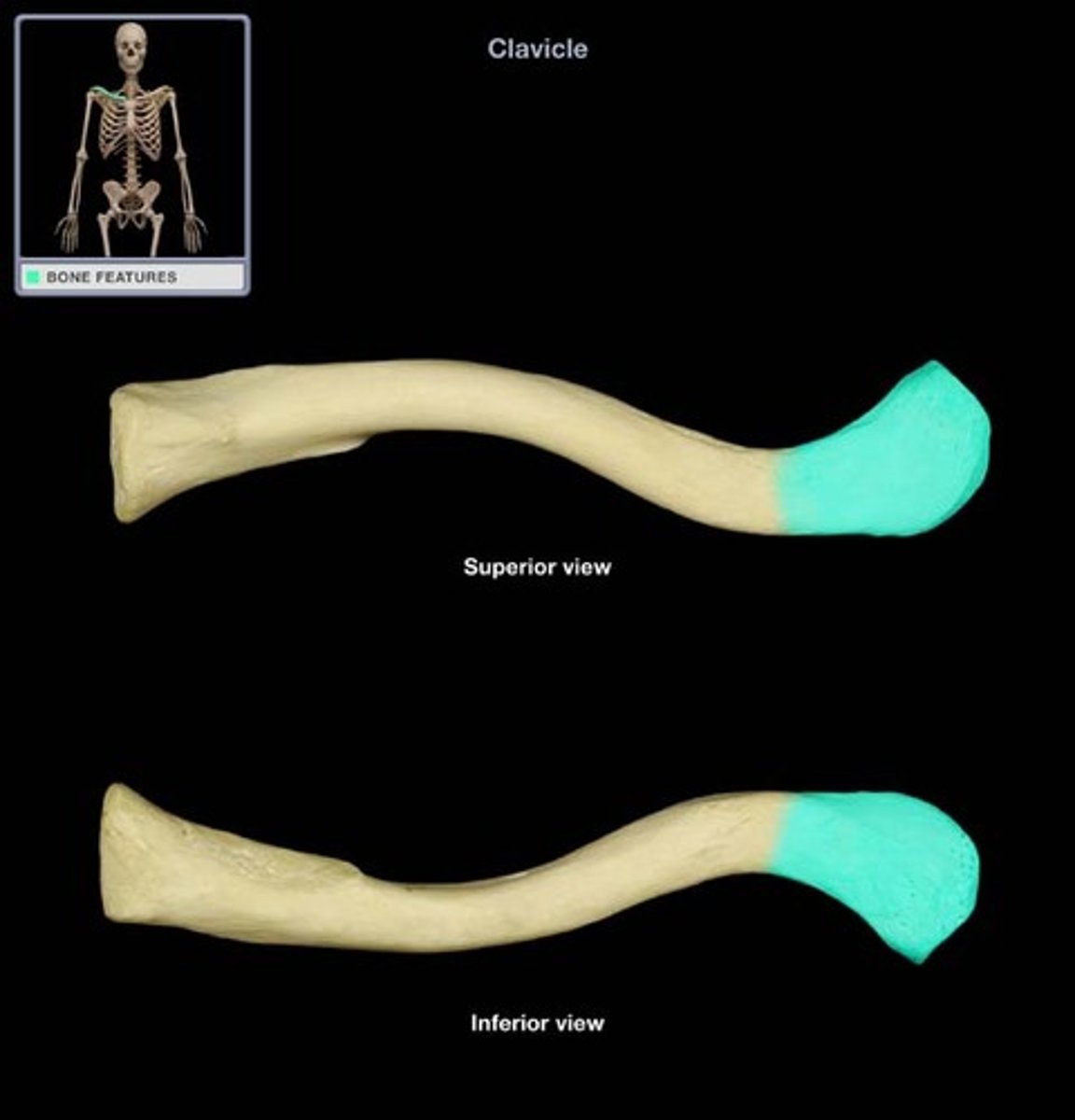
Sternal end of clavicle
- Medial
- Connects with the sternum (manubrium)
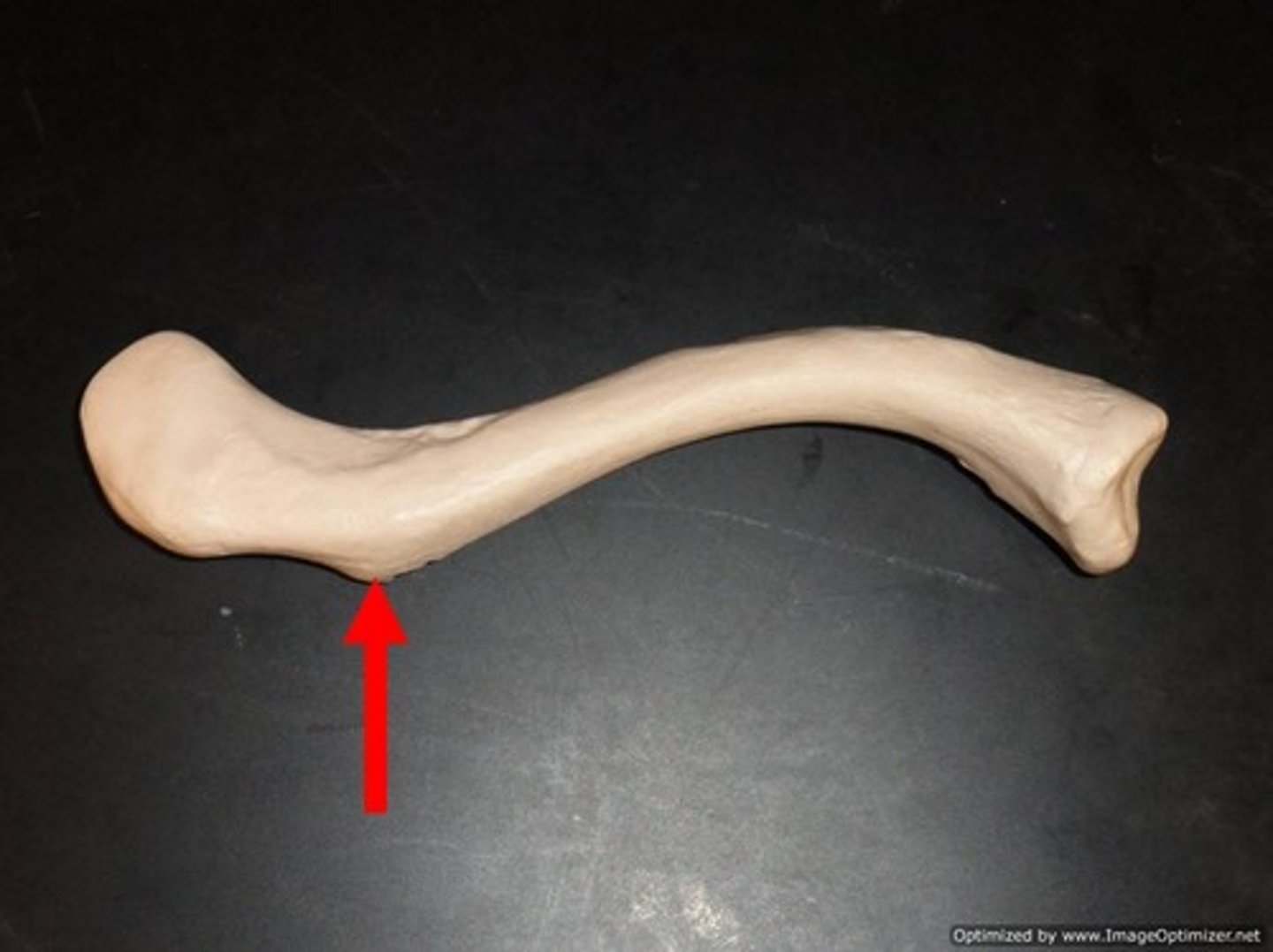
Conoid tubercle
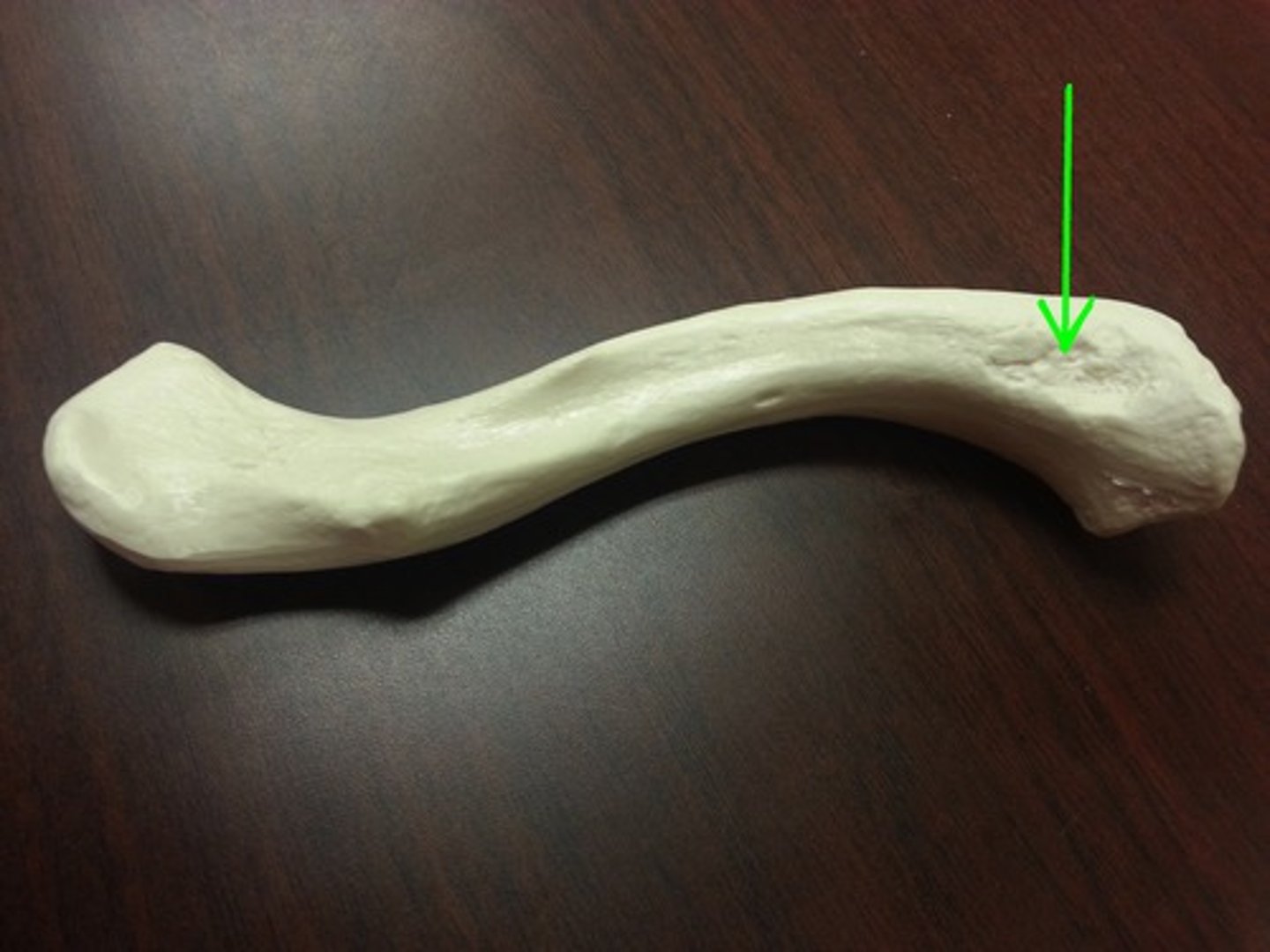
Costal tuberosity
Coracoid process
- anterior, smaller
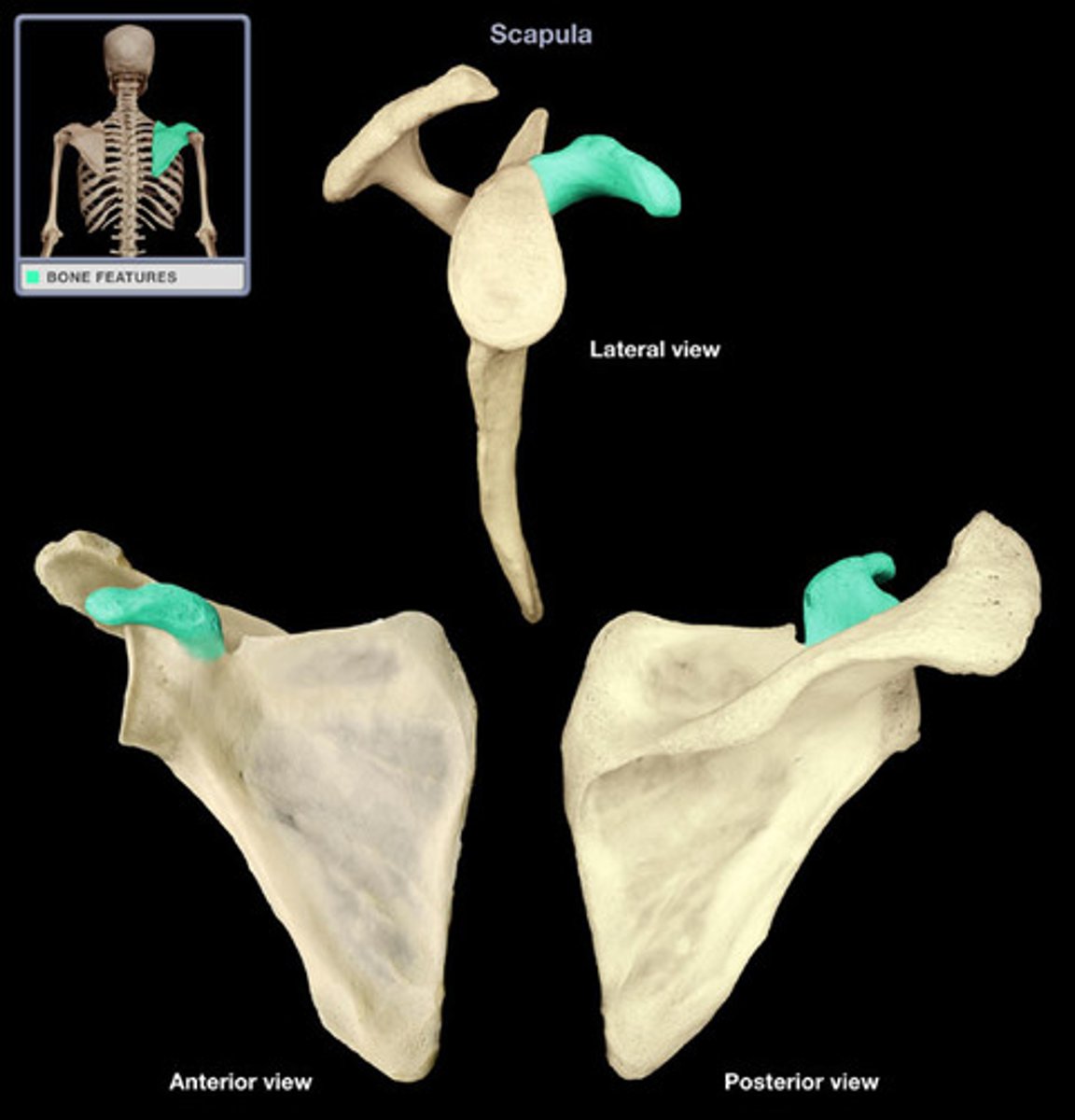
Acromion
- posterior, larger
- articulates with clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint
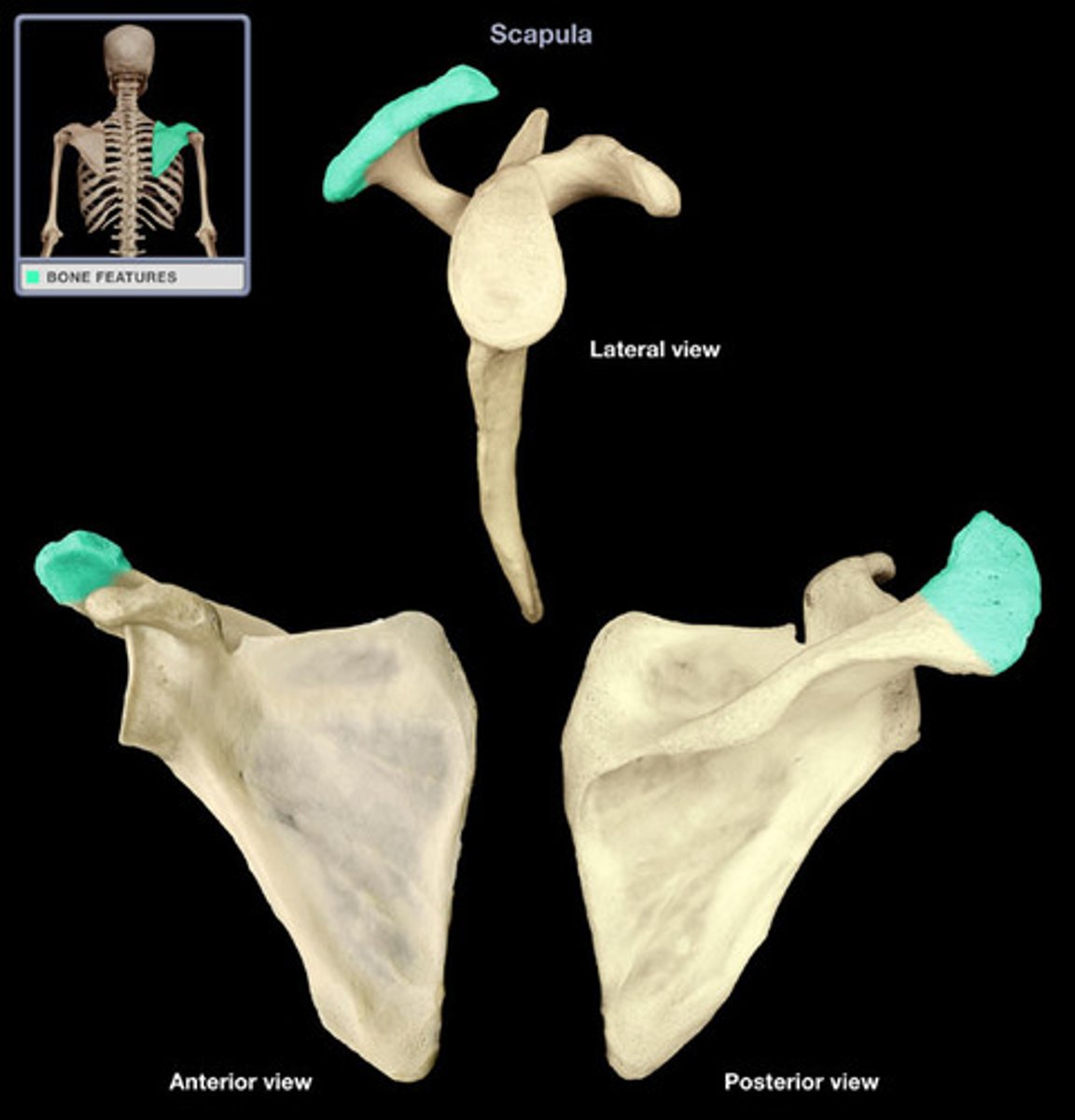
Glenoid cavity
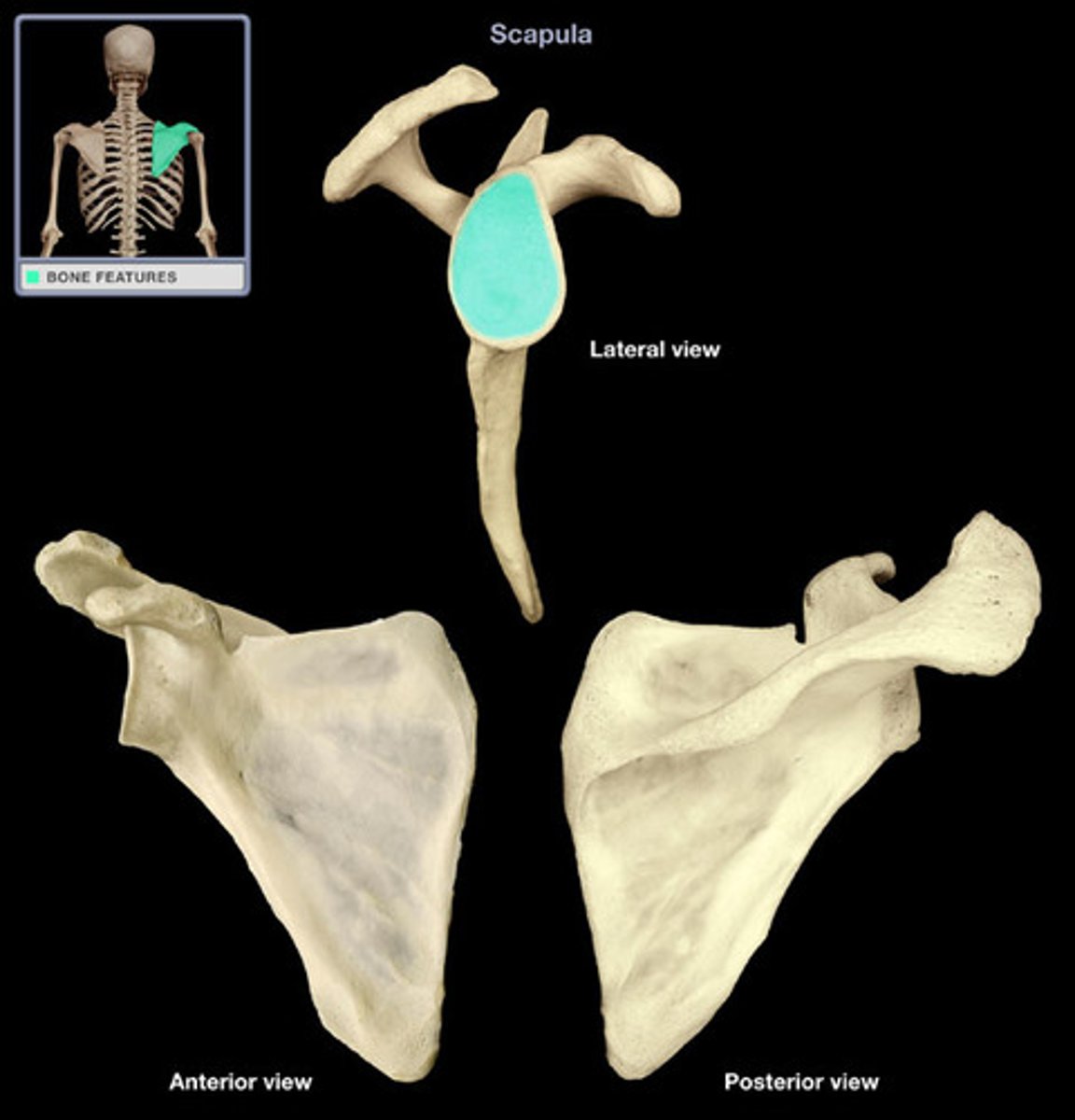
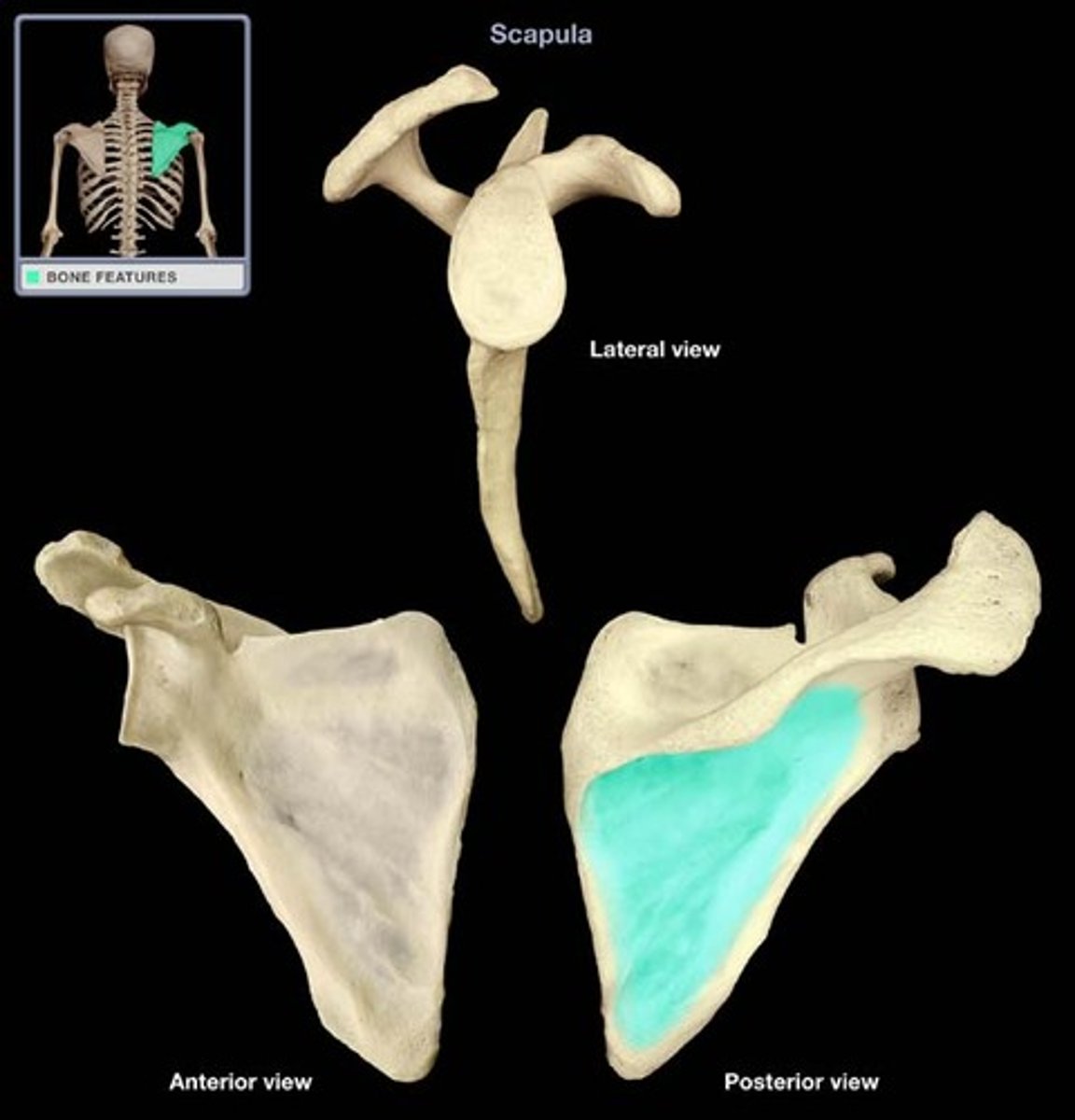
Scapula body
Has three sides:
- Superior border
- Medial border (vertebral border)
- Lateral border (axillary border)
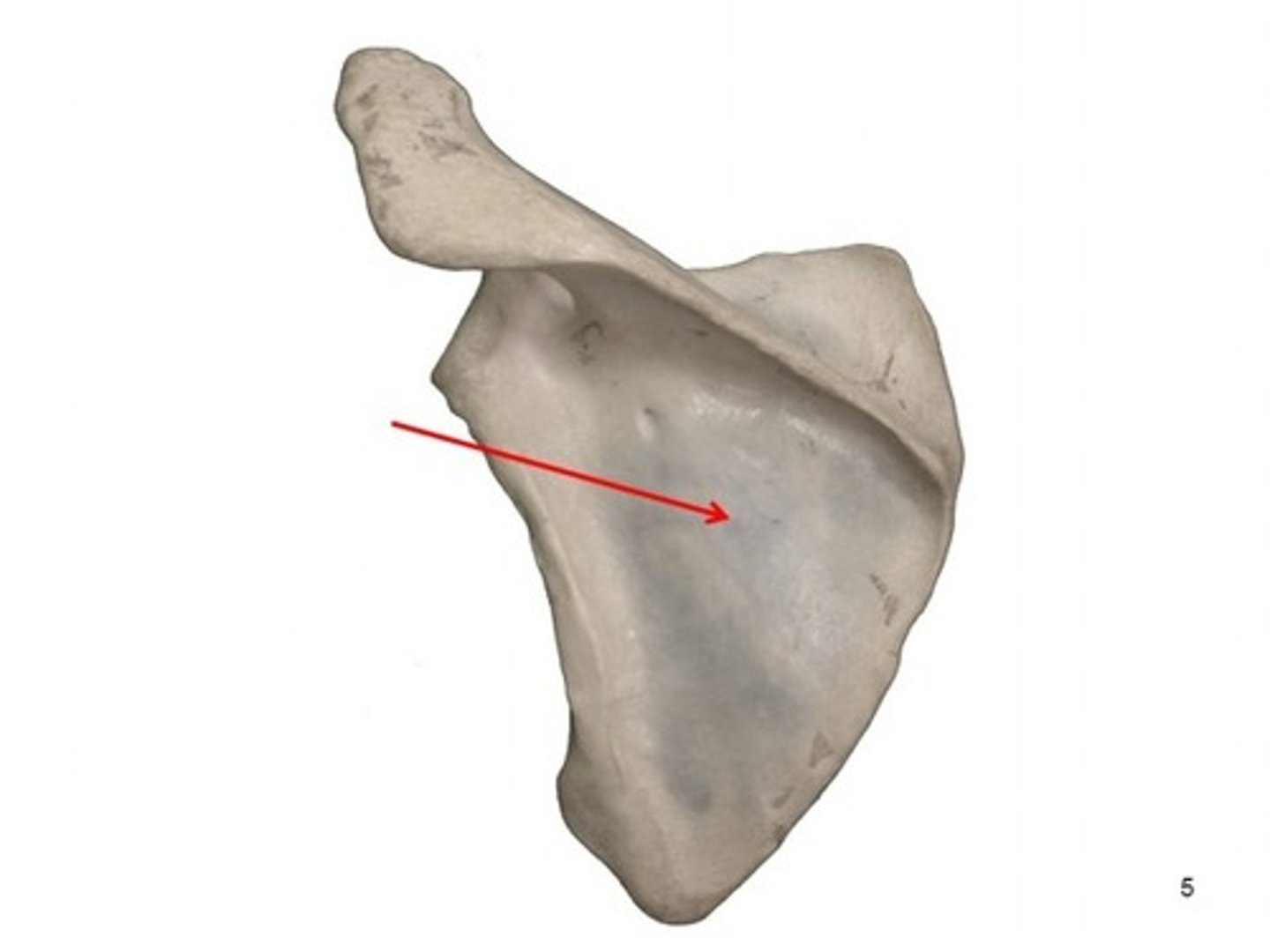
Superior border of scapula
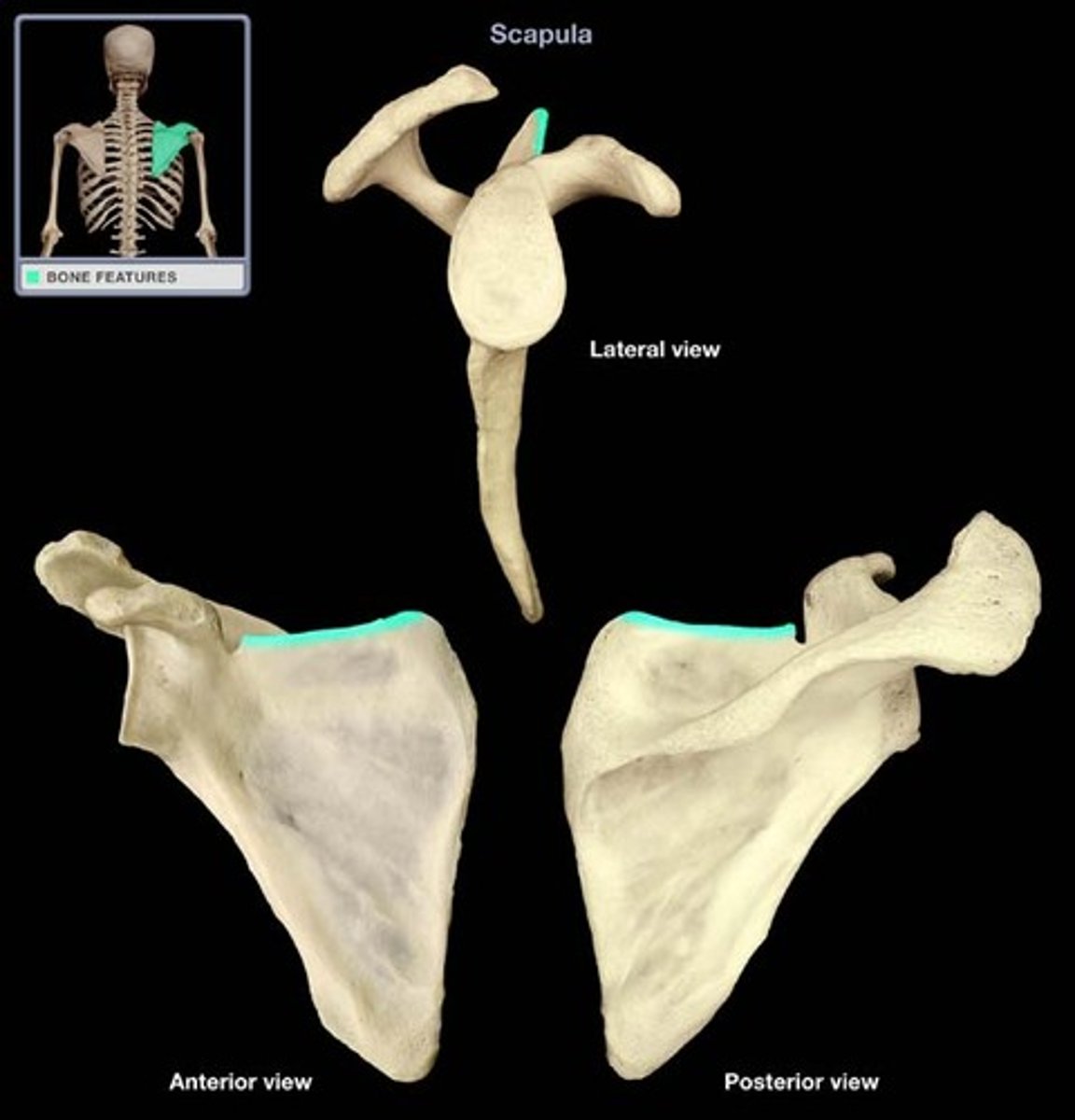
Superior angle of scapula
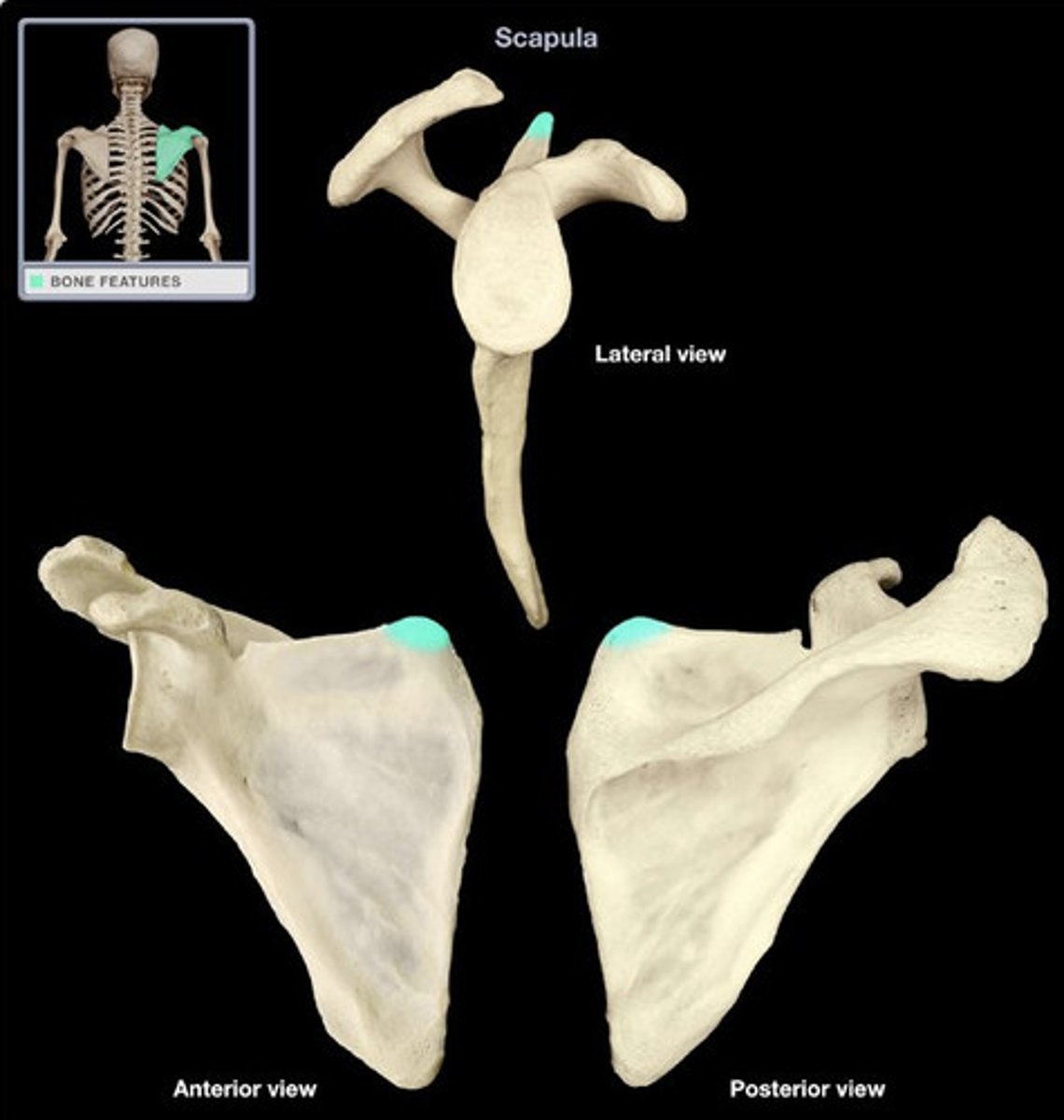
Lateral angle of scapula
- anterior view
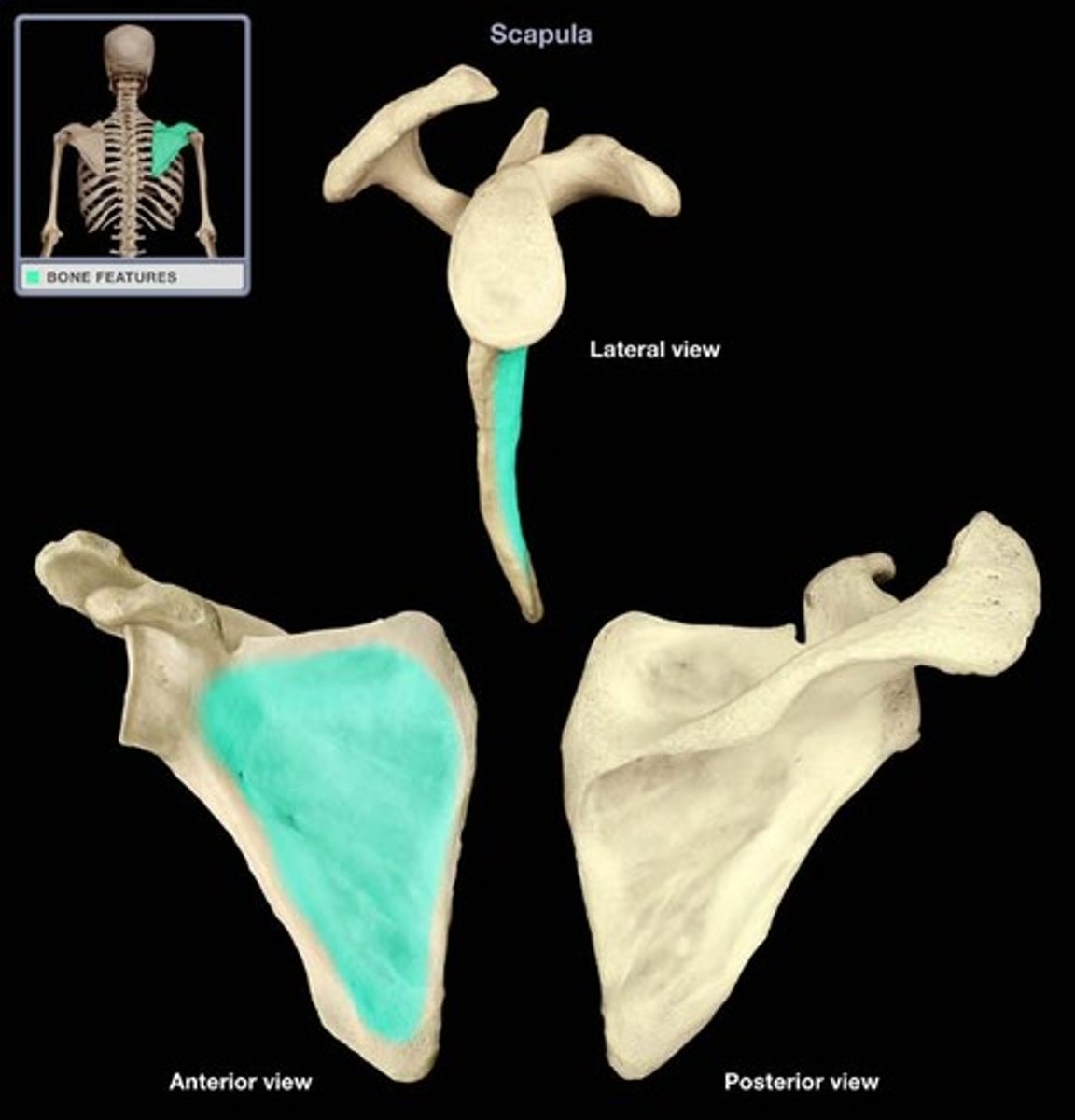
Subscapular fossa
- Anterior view
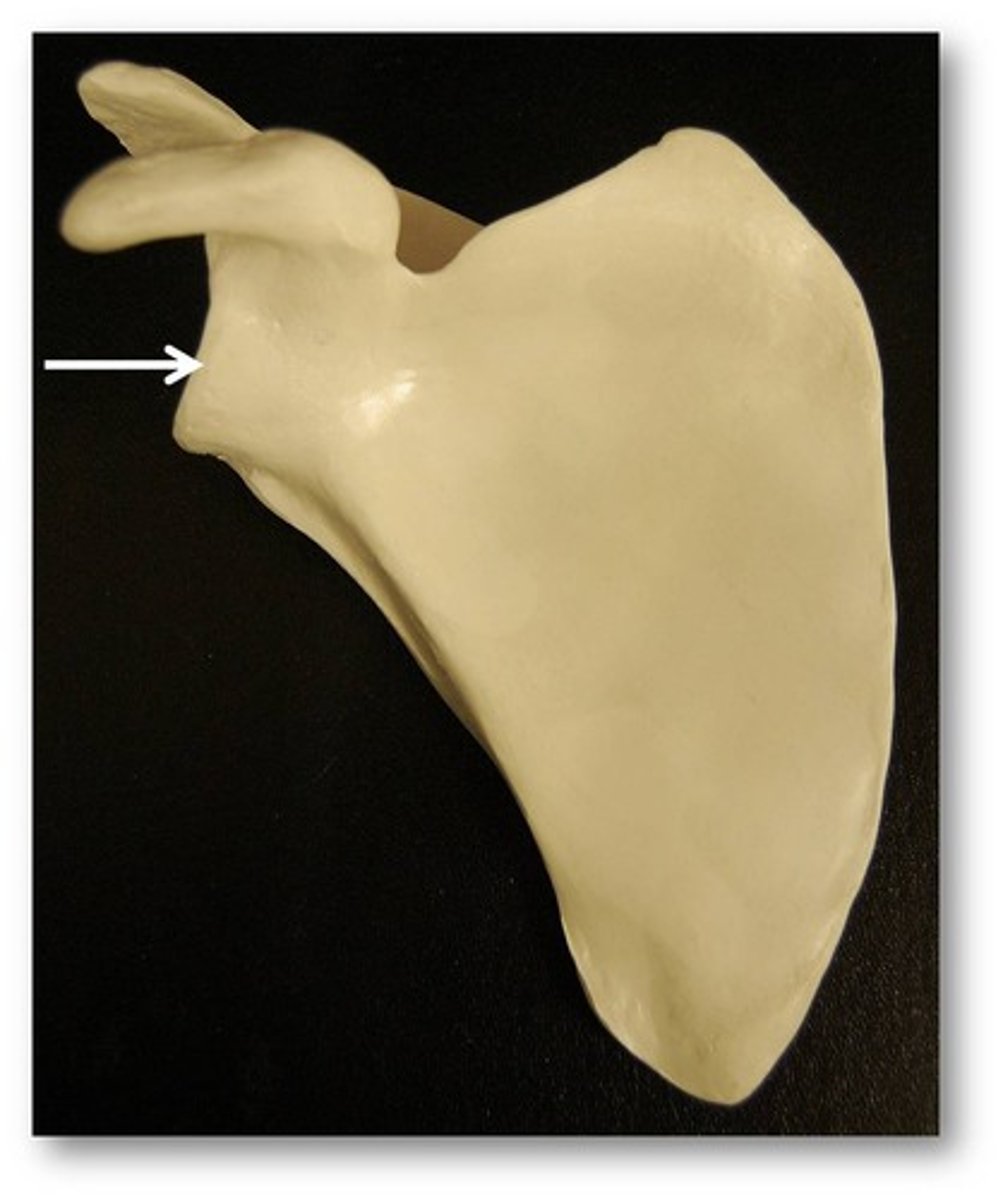
Lateral border of scapula
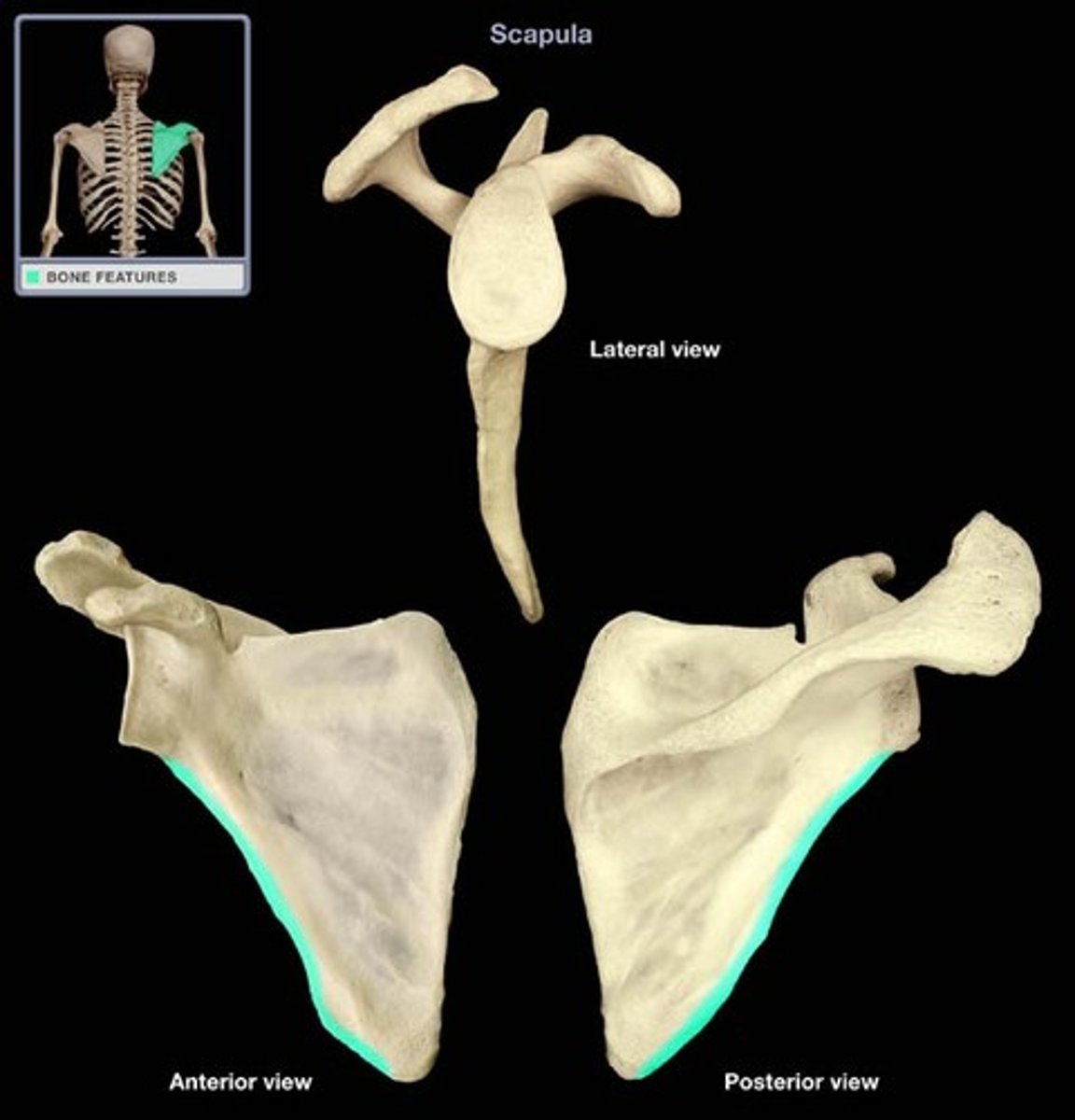
Medial border of scapula
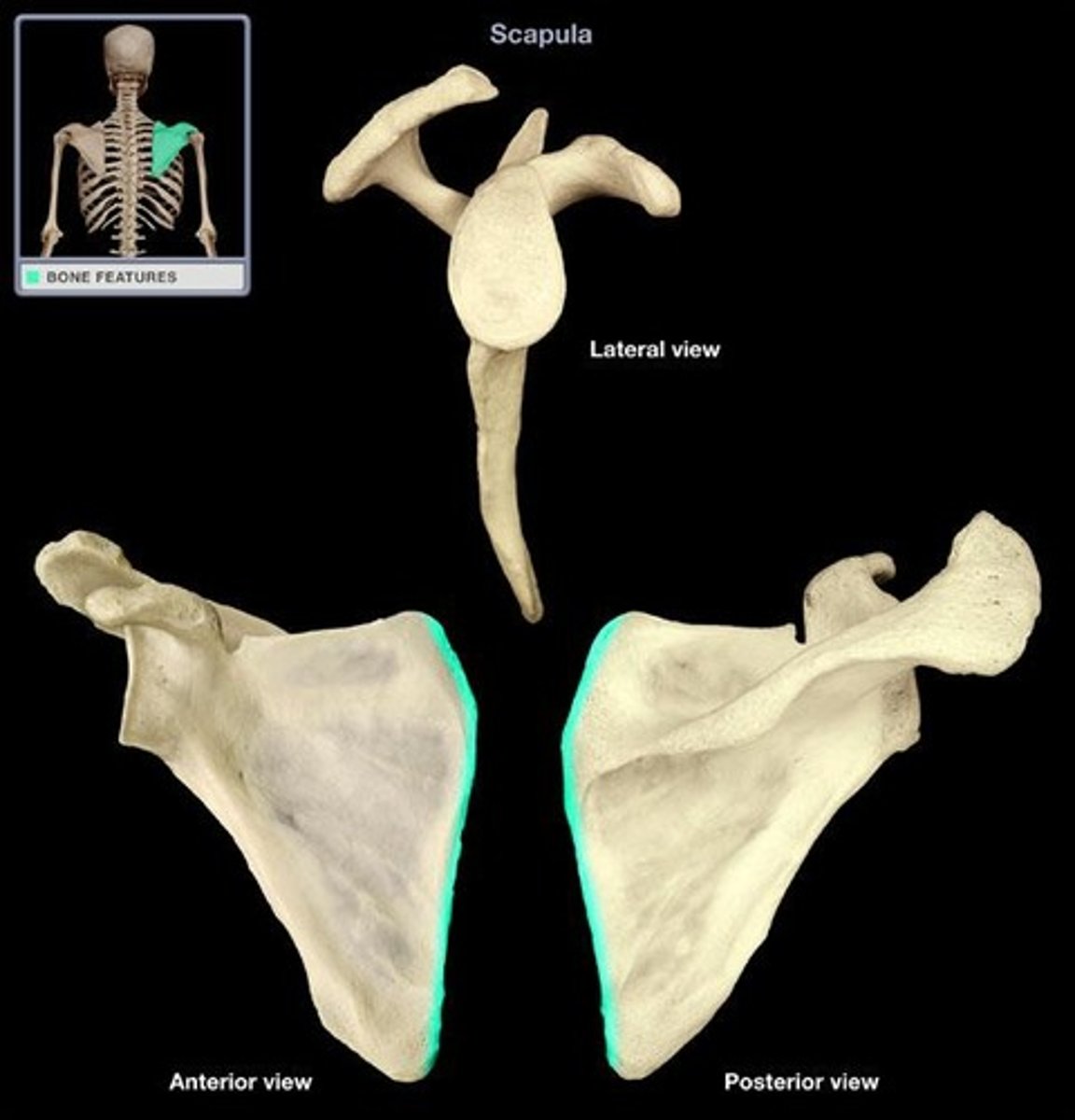
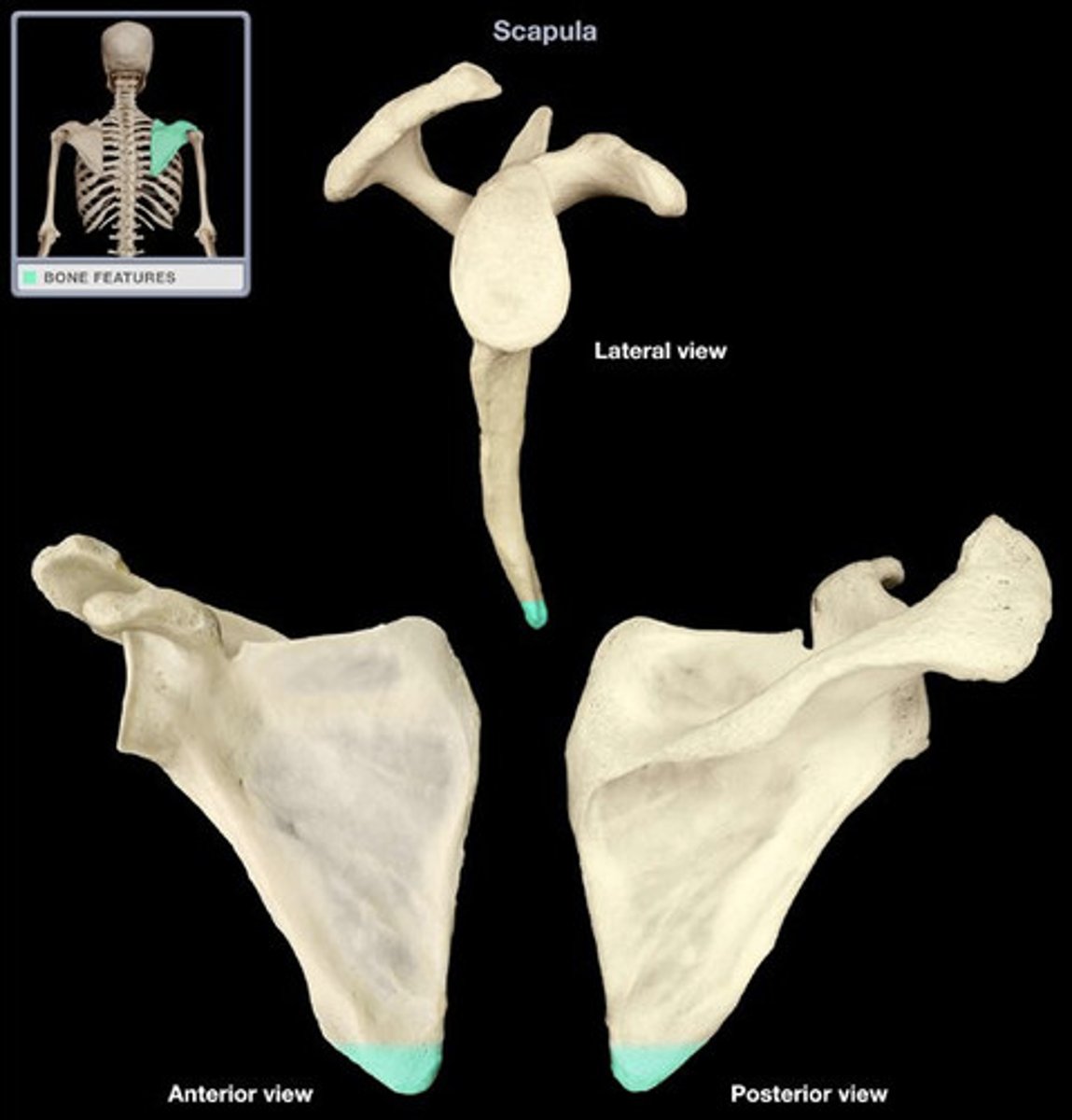
Inferior angle of scapula
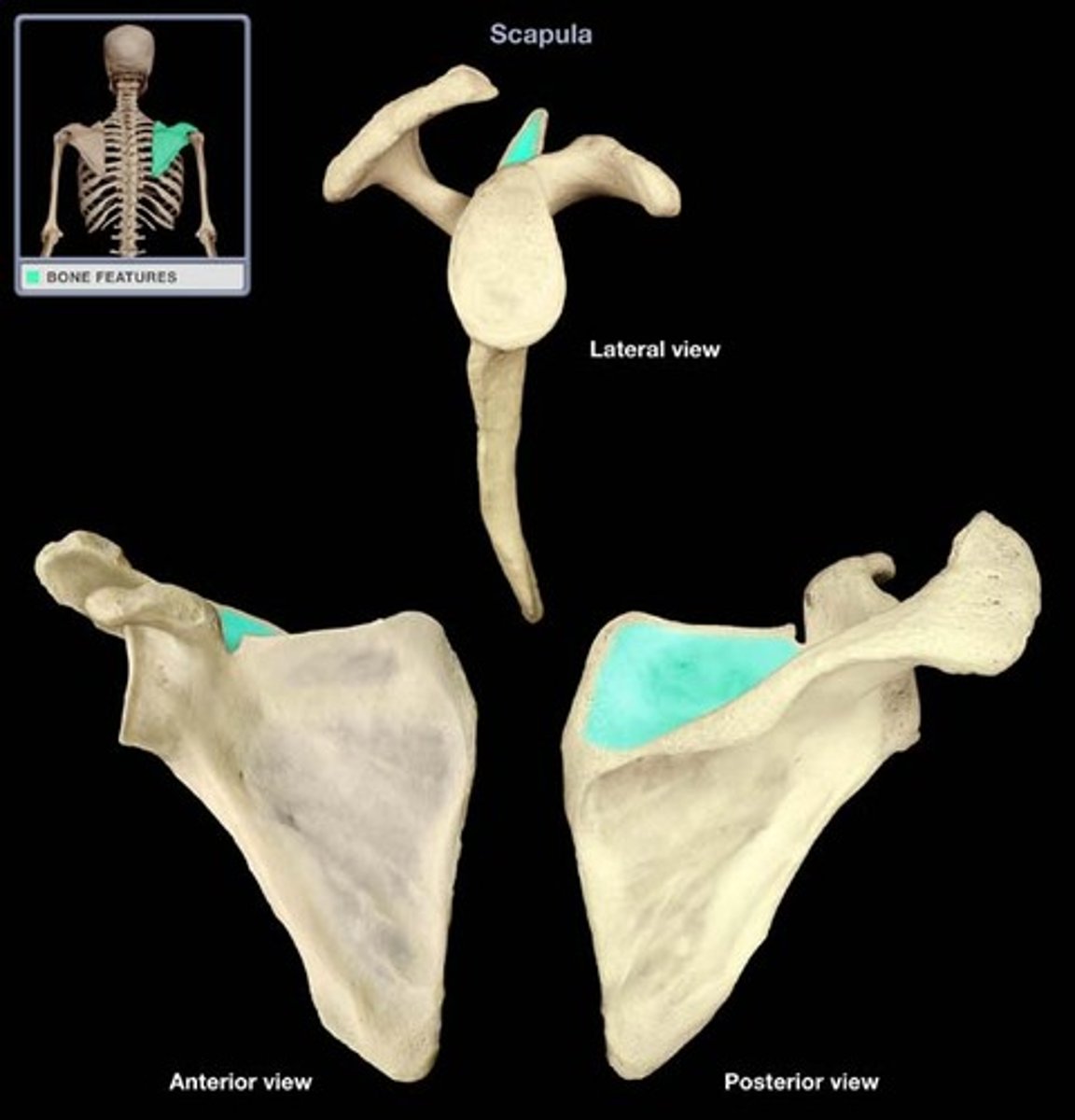
Supraspinous fossa
- posterior view
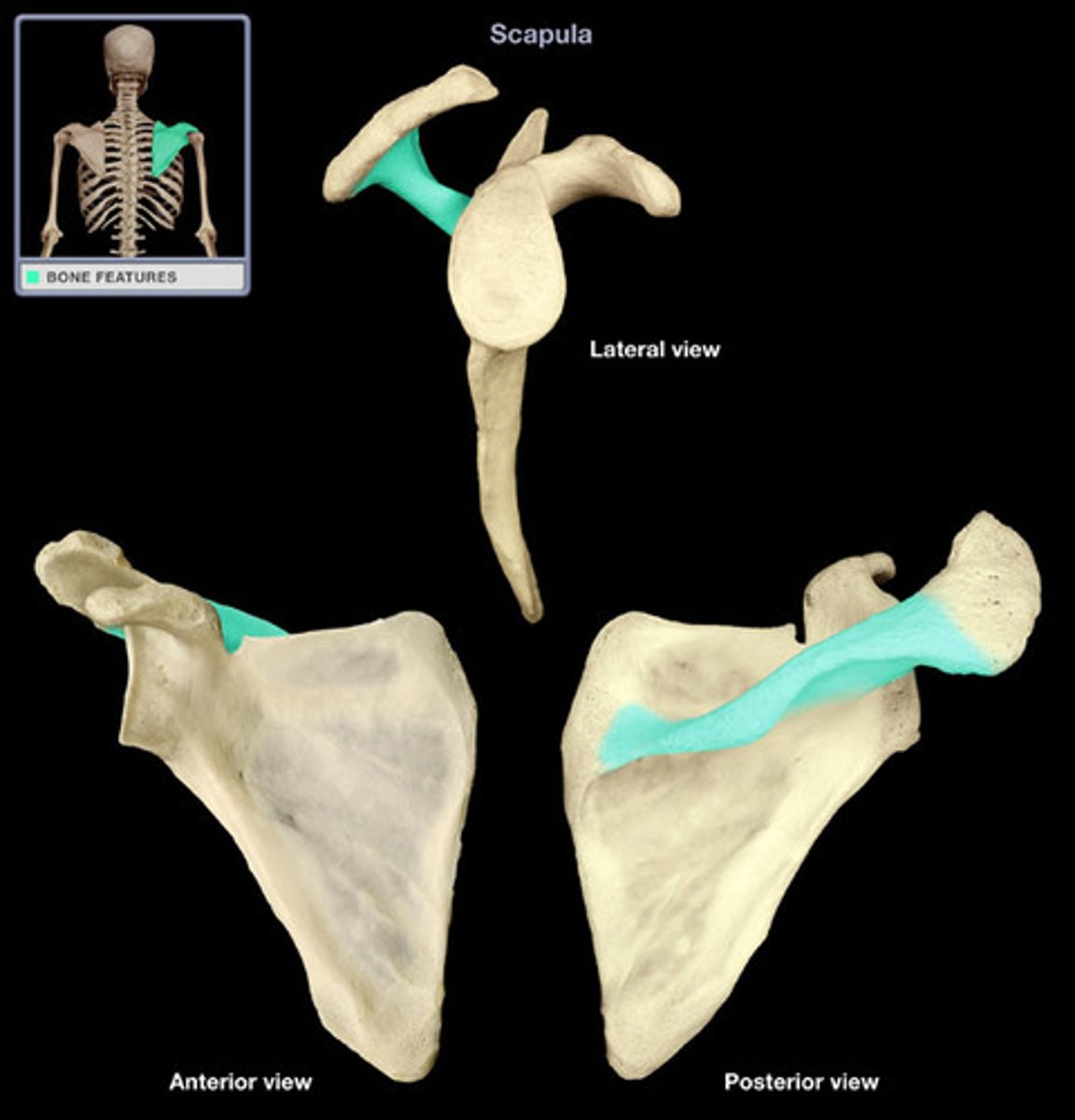
Spine of scapula
- posterior
Neck of scapula
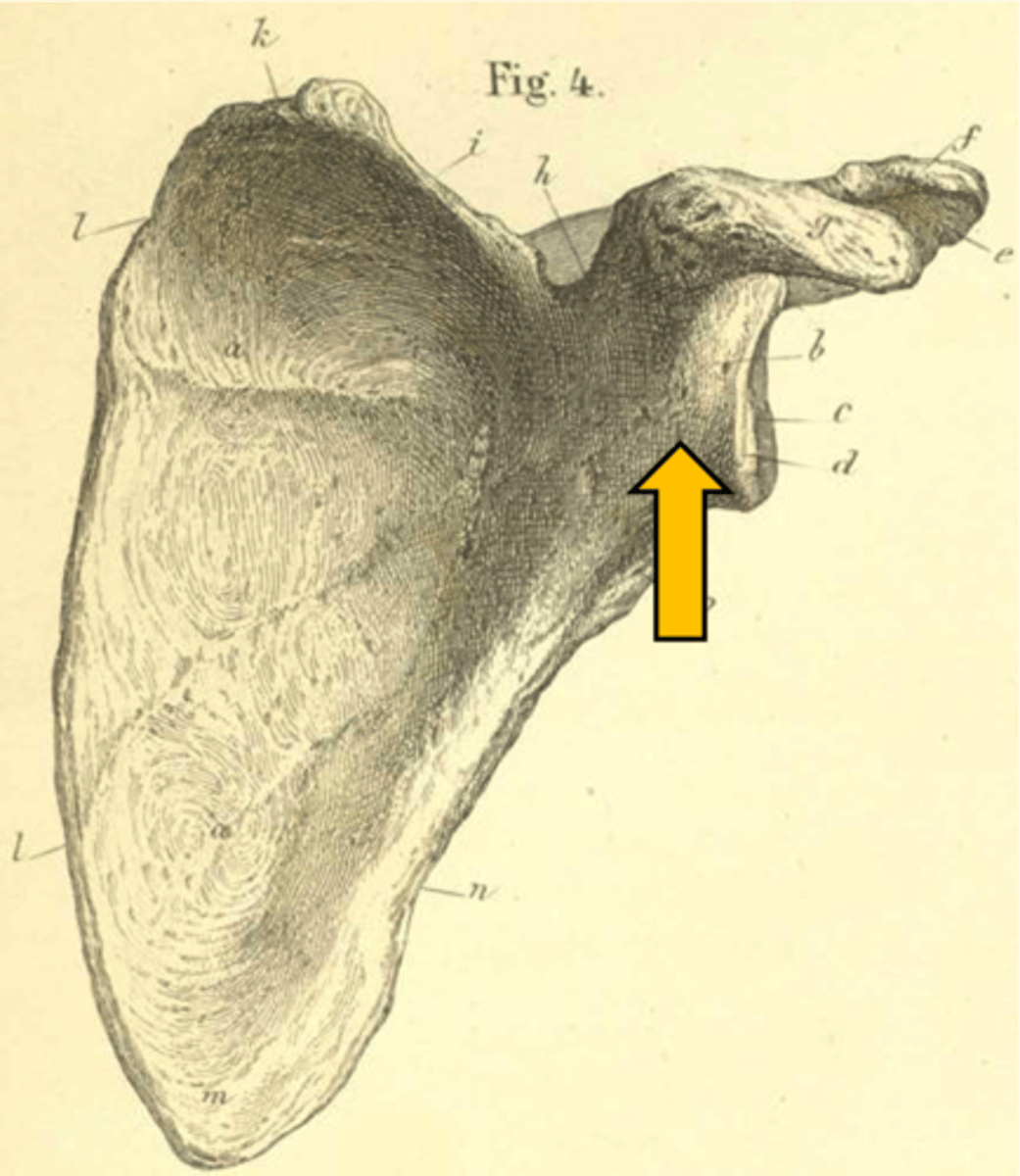
Infraspinous fossa
- posterior