Atomic structure
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of electrons. Since they have different number of neutrons, they have different masses and different physical properties
S orbital is ___ in shape and ___ (direction?)
Spherical, non-directional.
As n increases, the s orbital becomes more ___
Diffuse
P orbitals have a ___ shape and are ___ (direction?)
Dumbell, directional
The 3 p orbitals in the same subshell are degenerate.
Yes
Aufbaf Principle
Electrons fill orbitals according to this sequence
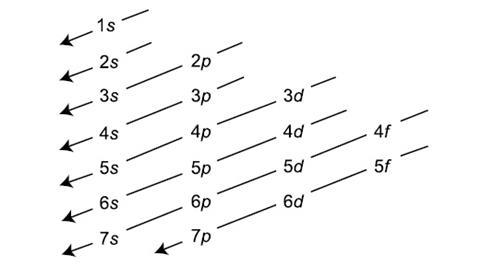
Hund’s Rule
Orbitals of a subshell must be occupied singly by electrons of parallel spins before pairing can occur
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
If there are 2 electrons in the same orbital, they must be of opposite spins
Excited state of an atom
When an electron temporarily occupies an energy state greater than its ground state
Where are electrons added to in anions?
The next available orbital
Where are electrons removed from cations?
Orbitals with the highest energy (ie. outermost)
Electrons are more easily removed from orbitals with ___ energy level
higher
Isoelectronic species
Same total number of electrons
What is the outermost electronic configuration of d-block elements?
(n-1)d^x ns^y, where n is the group number
How do the number of electron shells affect electrostatic attraction between nucleus and outermost electrons?
As the number of electron shells increase, n increases and the number of inner shell electrons increase. The EAnoe decreases
What is the electronic configuration of Cr? (24e)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4d1
What is the electronic configuration of Cu? (29e)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1
To form anions, electrons are added to the ___ ___ ___
Next available orbital
To form cations, electrons are removed from orbitals with the ___ ___
Highest energy
Isoelectronic species
Species with same total number of electrons
3 factors that affect strength of electrostatic attraction between nucleus and electrons
No. Of electron shells
Nuclear charge
Shielding effect
Shielding effect contributed by inner-shell electrons are ___ significant compared to outermost electrons.
More
Which factors are considered when discussing the trend of atomic properties
Across a period
Down a group
Nuclear charge, shielding effect
Number of electron shells, nuclear charge, shielding effect
Explain the trend in atomic radii across a period
Atomic radii decrease across a period.
Across a period,
number of electron shells remain the same
Number of proteins increases → NC increases
Number of electrons also increase but e are added to same outermost electron shells → SE remains approximately constant
EAnve increases → e cloud size decr
Explain the trend in atomic radii down a group
Atomic radii increase down a group
Down a group,
number of electron shells remain increase
shielding experienced by VE increases significantly as there are more inner shell electrons
Despite increasing nuclear charge, EAnve decreases → electron cloud size decr
Explain why the radius of a cation is always ___ than that of the parent atom.
Smaller
Both cation and parent atom have the same number of protons → same NC
However, cation has one less e shell than parent atom and outermost electrons are shielded to a smaller extent as there are less inner-shell electrons Despite increasing
EAnoe stronger in cation → smaller e cloud → smaller radius
Explain why the radius of an anion is always ___ than that of the parent atom.
Greater
Both anion and parent atom have the same number of protons → same NC
However, anion has more electrons than parent atom → shielding incr
EAnoe weaker in anion → larger e cloud → greater radius
Explain the trend of ionic radii of isoelectronic species across the period
Decrease
Na+, Mg2+, Al3+ are isoeletronic species across→ outermost electrons experience same SE
However, NC increases from Na+ to Al3+
EAnoe increases from Na+ to Al3+ → electron cloud size decr
Ionic radii decr
(Same explanation for period 3 anions)
Why is there a sharp increase in ionic radius from Al3+ to P3-?
Ionic radius of P3- is bigger than that of Al3+.
From Al3+ to P3-,
Number of electron shells increase
Shielding experienced by outermost electrons increases significantly as there are more inner shell electrons
Despite increasing NC,
EAnoe decreases → size of electron cloud incr
First ionisation energy
The energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous M atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous M+ ions.
Explain the trend in first IEs across a period
First IE generally creases across a period
Number of electron shells remain the same
Number of protons increase → NC increases
Number of electrons also increases but electrons are added to the same outermost e shell → SE remains approximately constant
EAnve incr → incr in energy required to remove VE from atom
Why is the ionisation energy of Al lower than that of Mg? [IE irregularity 1: Grp 2 and 13)
The 3p electron to be removed from Al is at a higher energy level than the 3s electron to be removed from Mg
Less energy required to remove 3p electron in Al as it is less attracted to the nucleus than 3s electron in Mg
First IE of Al lower than that of Mg
More energy is required to remove an electron at a higher energy level. T/F?
F. Less energy is required as the electron at higher energy level is less attracted to the nucleus.
Why is the IE of S lower than that of P? [IE irregularity 2: Grp 15 and 16)
The 3p electron to be removed from S is a paired electron while that to be removed from P is an unpaired electron.
Due to greater electron-electron repulsion between paired electrons in the same orbital, less energy is required to remove the paired 3p electron from S.
1st IE of S lower than that of P
Explain the trend in first IE down a group
First IE of elements generally decrease down a group.
Down a group,
Number of electron shells increases
Shielding experienced by VE increase significantly as there are more inner-shell electrons
Despite increasing NC, EAnve decreases → decr in energy required to remove a ve
First IE decr down group
Why is the first IE of grp 1 element lower than that of preceding grp 18 element?
Group 1 element has 1 more e shell than preceding grp 18 element
Shielding experienced by VE is greater in grp 1 element
Despite increasing NC, EAnve decreases → decr in energy required to remove 1 ve
First IE of grp 1 element lower than preceding grp 18 element
Explain the trend in successive IEs of an element
Increase
Number of protons same → NC remains the same
Number of electrons decr → SE experienced by remaining outermost shells decreases
EAn remaining electrons incr → incr in energy required to remove subsequent electrons
Deduce group number from large jump in IE (Eg. Between 5th and 6th IE)
Group 15
Large jump in 5th and 6th IE
Significantly more energy is required to remove the 6th electron as it is located in an inner electron shell that experiences less shielding
5 electrons in valence shell → group 15
Electronegativity
The electronegatively of an atom in a molecule is a relative measure of its ability to attract bonding electrons
Explain the Trend in electronegativity across a period
Increases across period
Number of electron shells remain the same
Number of proteins increases → NC increases
Number of electrons also increases but are added to same outermost electron shell → SE remains approximately constant
EAn bonding electrons increase
Explain the trend in electronegativity down a group
Decreases
No, of e shells increases Number
Shielding experienced by bonding electrons increases significantly as there are more inner-shell electrons
Despite increasing NC, EAnbe decreases