Fundamentals of the Brain (psyc 2200, exam 1)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Post Mortem Methods
In vitro cell recording and histology (by staining cells and examining under microscope)
Often used in animal research
Used in humans post mortem study
Invasive Methods — In Vivo
Surgically implanted electrodes record or stimulate different areas of the brain
Also includes tissue removal or tract separation
Used in animal research
Sometimes used in humans for medical reasons
Non-Invasive Methods — In Vivo
MRI, PET, fMRI, CAT, MEG, TMS, external/surface recordings
Required for most experimentation on humans
Preferred for medical purposes
Sometimes used in animal research
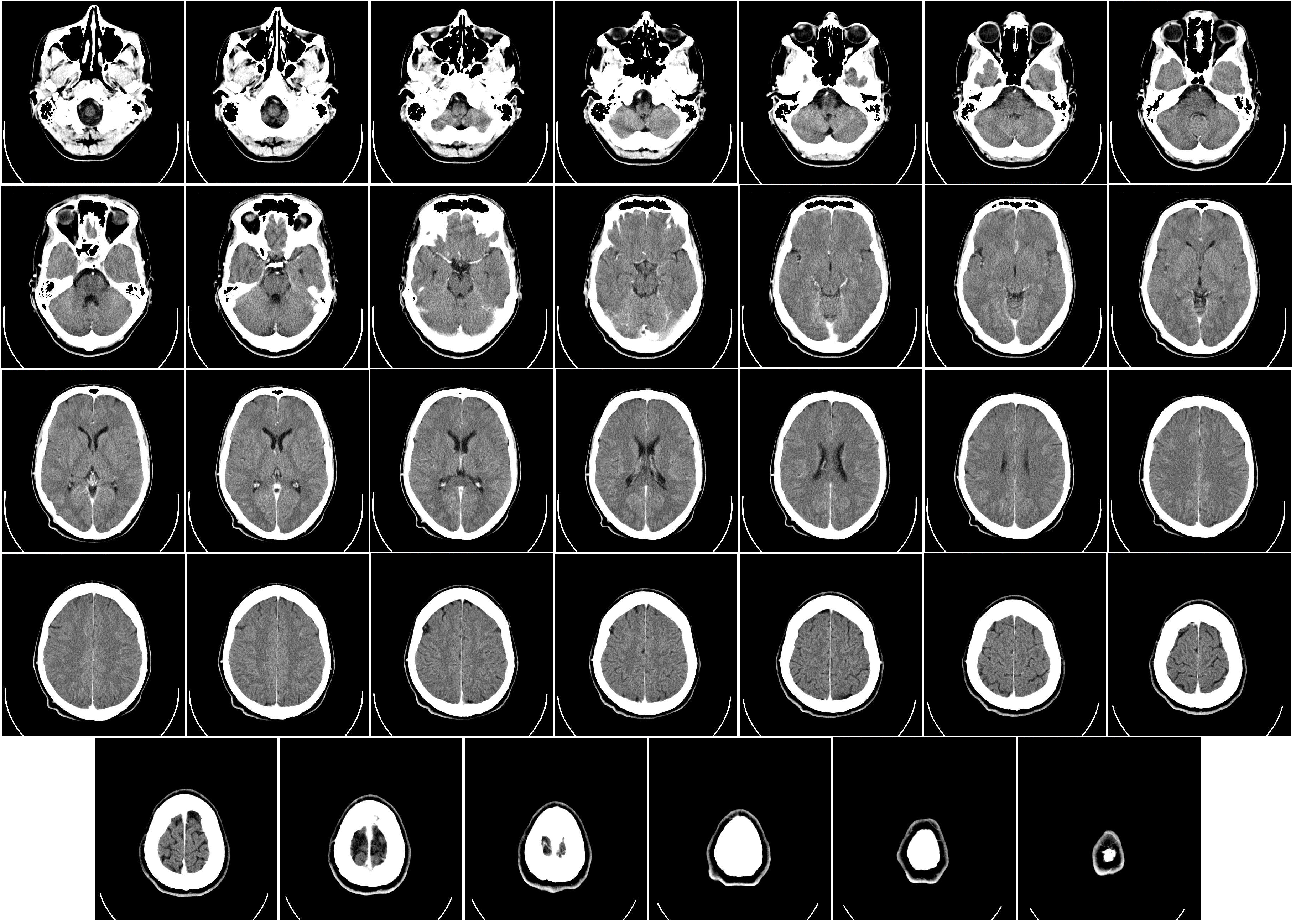
CAT
Computer Aided Tomography / CT
A process that uses a series of x-ray scans to the head in order to reconstruct 2D x-ray images into 3D images of internal organs; The subject enters a donut-shaped x-ray machine
Measures Tissue Density by X-Ray
Very dense tissue (e.g. Bone) blocks x-rays, so it appears white on the scan
Grey matter blocks some x-rays, so it appears light grey
White matter blocks less x-rays, so it appears dark grey
The images produced are not as detailed as MRI scans and there is some radiation, but these scans are cheaper than MRI
Provides an image for the STRUCTURE of the brain
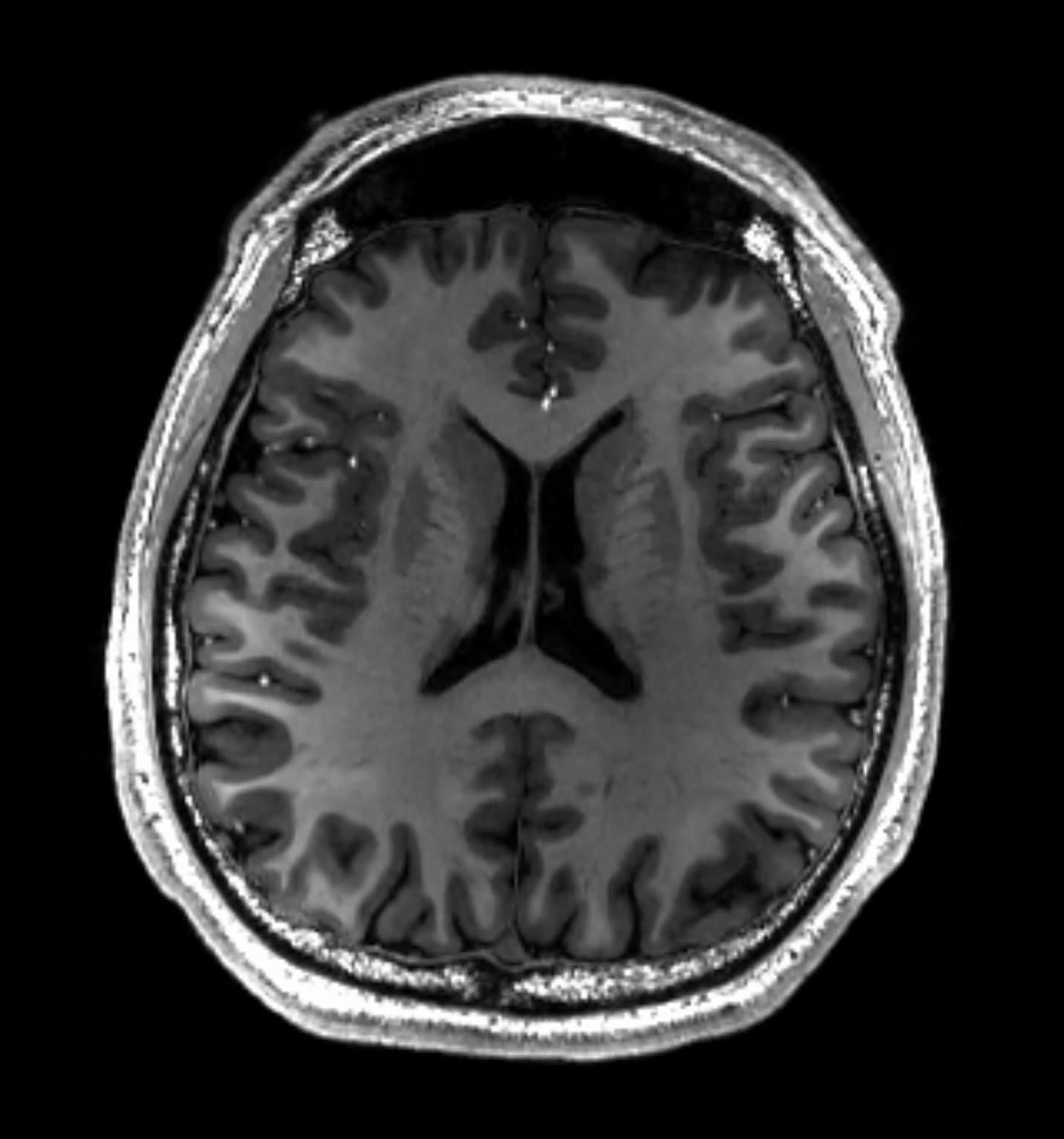
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
A scan that uses echo waves (from hydrogen atoms realigned in tissue and then being signaled) to discriminate among grey matter, white matter, and cerebrospinal fluid; Patient enters a donut-shaped giant tube that creates a magnetic field
Measures Atomic Resonance / Energy Release
White matter appears white
Grey matter appears grey
More detailed image than CAT scan
Shows the STRUCTURE of the brain
MEG
Magnetoencephalography
An imaging technique used to measure magnetic fields produced by electrical activity in the brain; Uses sensitive devices (e.g. Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices, aka SQUIDs)
Measures electromagnetic fields, resulting from neural (ionic flux) activity, at the skull’s surface
Derive electrical signals from the net effect of ionic currents flowing in the dendrites during synaptic transmission
Shows the FUNCTION of the brain

EEG
Electroencephalogram
Uses electrodes that attach to the scalp to measure electrical activity in the brain, which is shown as wavy lines on a graph recording
Finds changes in brain activity that may help diagnose brain conditions
Better for kids to use because they can move during this imaging process
Shows the FUNCTION of the brain

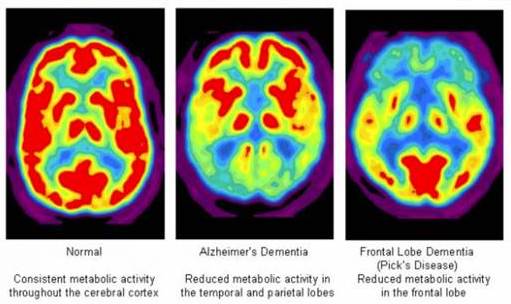
PET
Positron Emission Tomography
Measures regional glucose consumption; Subject is injected with a small amount of radioactive glucose, and this scan the absorption of radioactivity outside the head
If brain cells are more active, they will consume more radioactive glucose, and vice versa
More commonly used before the fMRI
Shows the FUNCTION of the brain
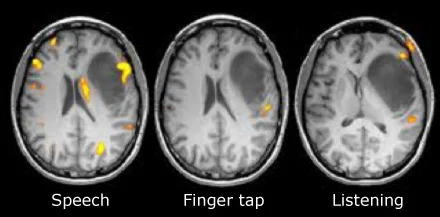
fMRI
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Uses a magnetic field (like an MRI) to create an image, but also measures blood-oxygen (haemodynamic) levels for brain activity
Brain areas with low blood oxygen (BOLD — blood-oxygen signal) are presumed to be more active
Works because the magnetic resonance signal of blood depends on the level of oxygen (More brain activity → More O2 consumption)
Doctors ask patients to do something (e.g. opening and closing their hand) while inside the MRI machine to reveal how the brain does tasks
Shows FUNCTION and STRUCTURE of the brain
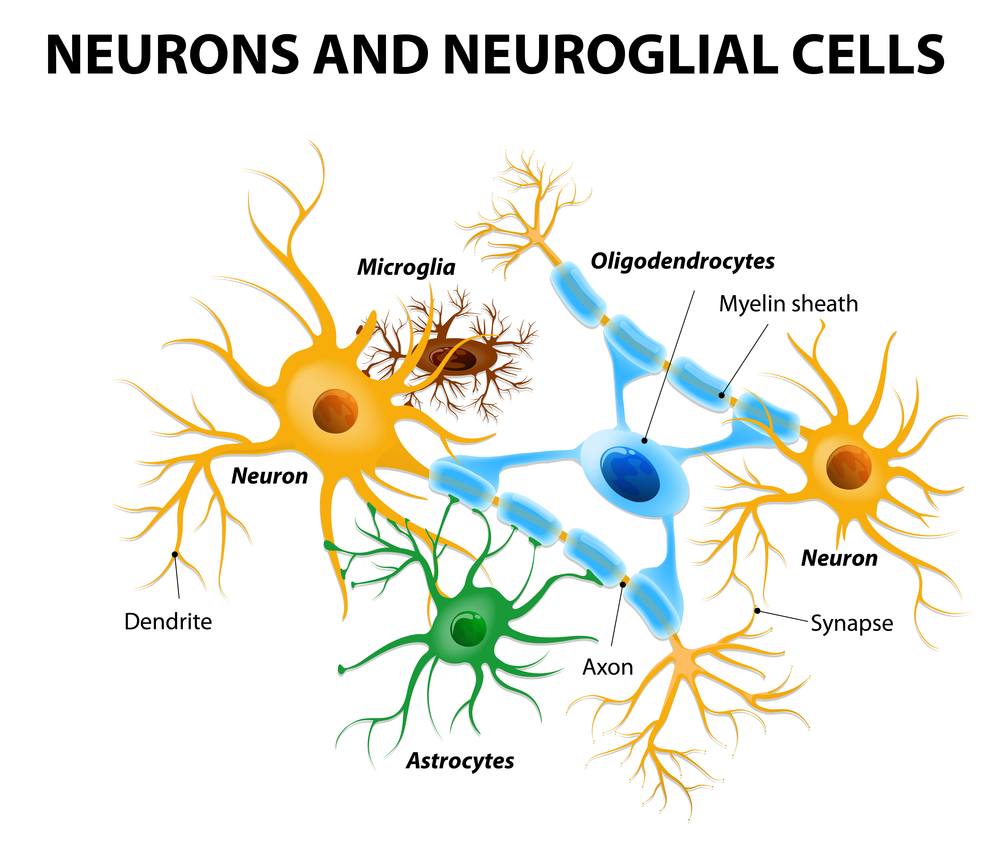
Neurons
Transmit information via action potentials and neurochemical release
A type of cell in the nervous system
Glia
Modulates, supports, and insulates neurons with myelin sheaths
CNS: Astrocytes and oligodendrocytes
PNS: Schwann Cells
Astrocytes
A star-shaped glial cell that clears excess neurotransmitters, stabilizes and regulates the blood-brain barrier, and promotes synapse formation
Found in the CNS
Oligodendrocytes
A glial cell that produces myelin in the CNS
Commonly found in areas with long axons
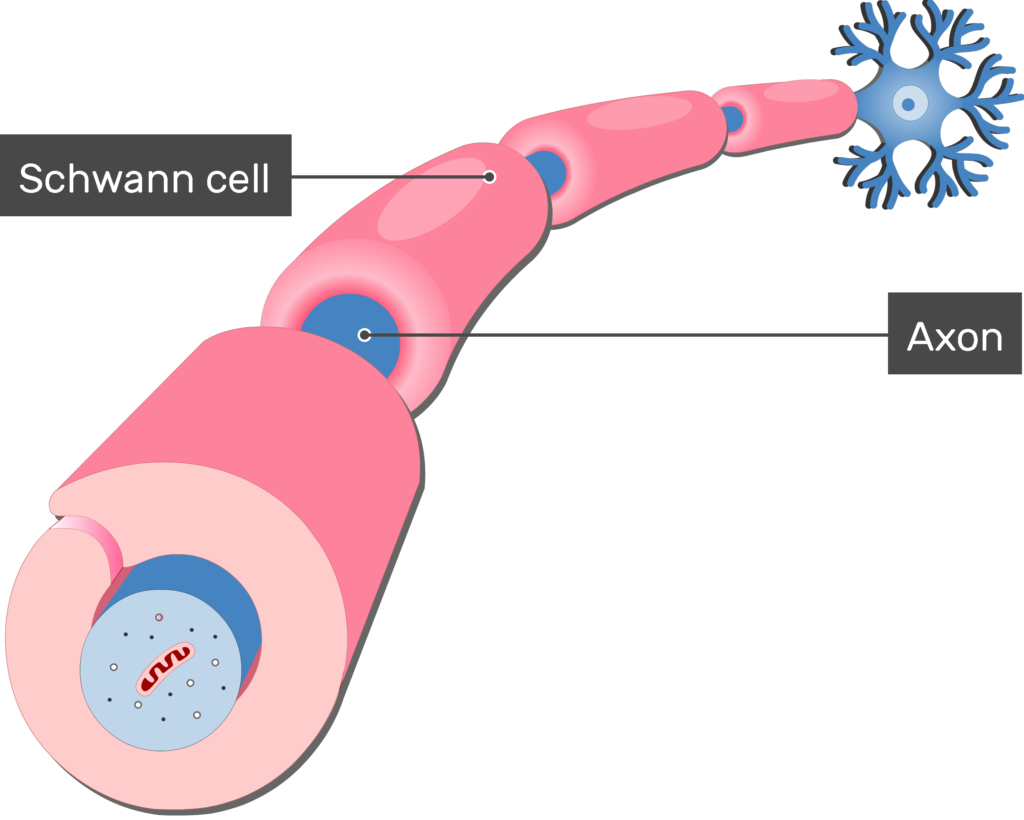
Schwann Cells
A glial cell that produces myelin in the PNS
Commonly found in areas with long axons
Grey Matter
Unmyelinated neurons and parts of neurons
Found in the outer layer of the brain
White Matter
Myelinated parts of neurons and glia
Found in subcortical (deeper tissues) areas of the brain
Cell Body
The part of a neuron that contains the nucleus
the cell’s life-support (metabolic) center
Dendrites
A neuron’s often bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages
Conducting impulses toward the cell body
Axon
The neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Conducting impulses away from the cell body
Myelin Sheath
Covers axon and insulates the cell
Speeds up signal
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps between the myelin sheath
Essential for the action potential’s speed and timing to the axon terminal
Multipolar Neurons
A neuron with a single axon and many dendrites
Complex and most common neuron
Bipolar Neurons
A neuron with one axon and one dendrite extending from the cell body
Rare in humans, but play important roles in the ears, nose, and eyes
Unipolar Neuron
A neuron with an axon that extends into dendrites
Only has one nerve process extending from the cell body
Plays a role in touch and pain
Synapse
The junction between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron
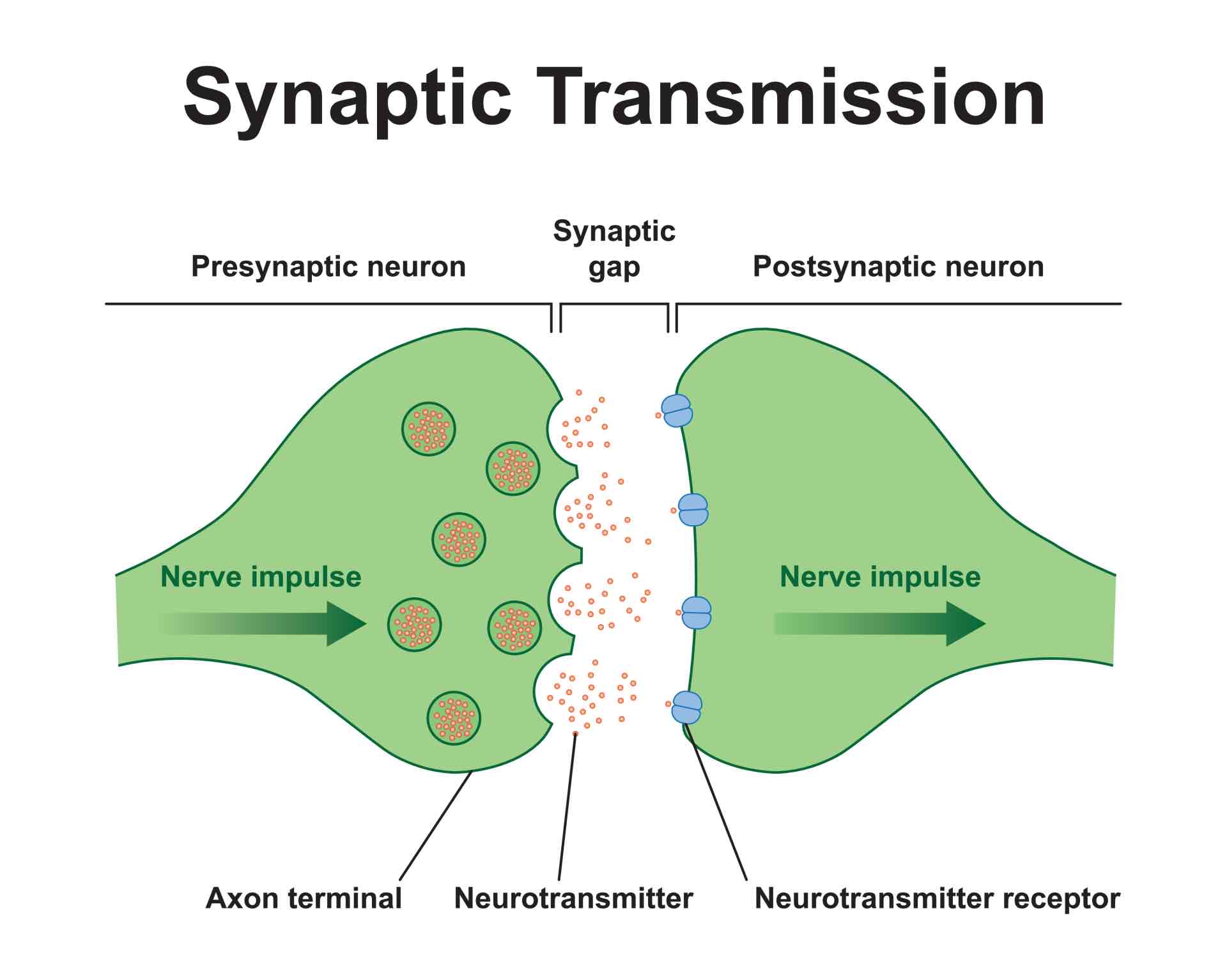
Vesicles
Stores various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse
Located in the axon terminal
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The brain and spinal cord, encased by the blood-brain barrier
Blood Brain Barrier
Surrounds membranes (dura & pia mater) in the brain; A network of “tightened” blood vessel walls for vessels supplying the brain and spinal cord
Makes it difficult for larger substances to enter the brain
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
(Cranial) Nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord
Includes
Somatic system
Autonomic system
Enteric (Gut / Digestive System)
Sympathetic System
Parasympathetic System
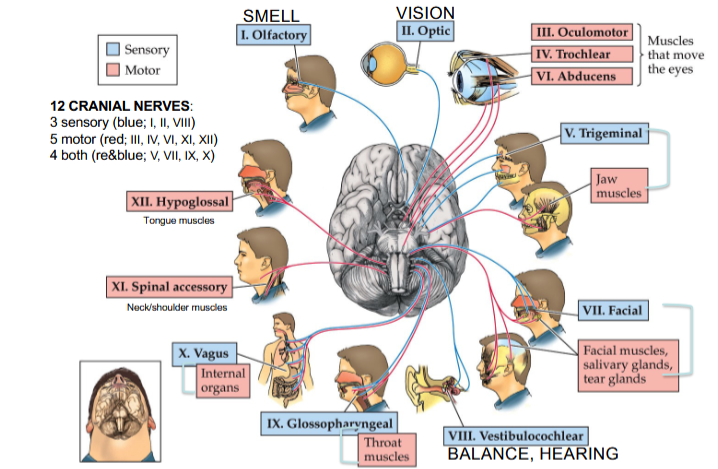
Olfactory Nerve
Cranial Nerve I
Provides the sense of smell
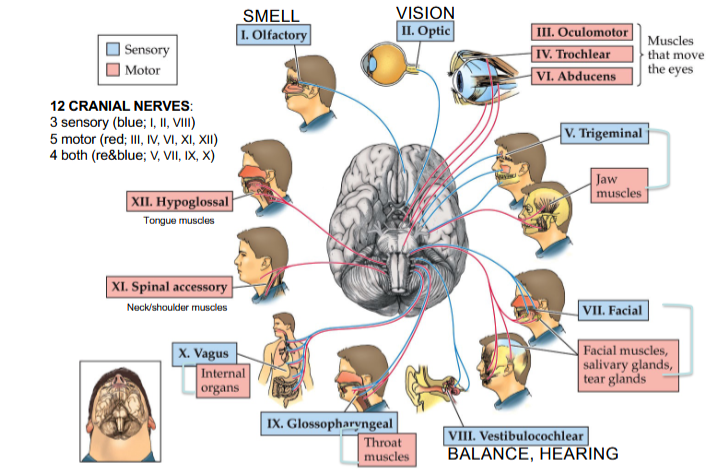
Optic Nerve
Cranial Nerve II
Provides vision
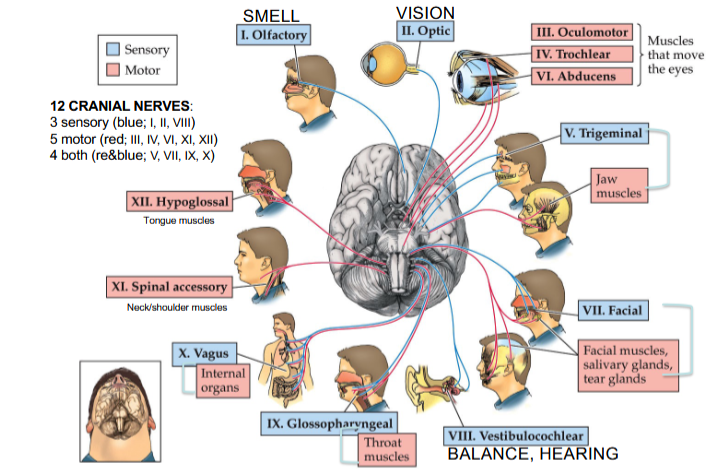
Oculomotor Nerve
Cranial Nerve III
Opening and moving your eyes and adjusting pupil width
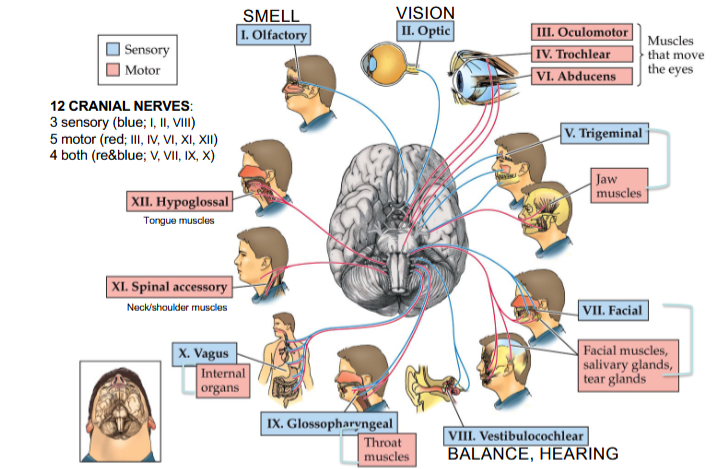
Trochlear Nerve
Cranial Nerve IV
Looking down and moving your eyes toward your nose and away from it
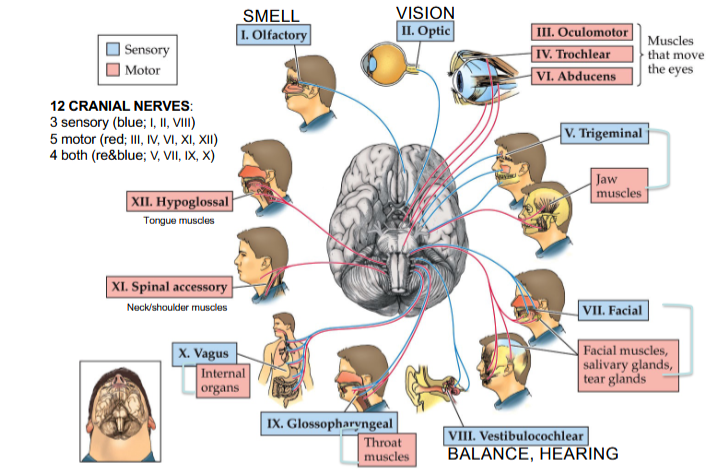
Trigeminal Nerve
Cranial Nerve V
Providing sensations in your eyes, most of your face, and inside your mouth
Allows you to chew food
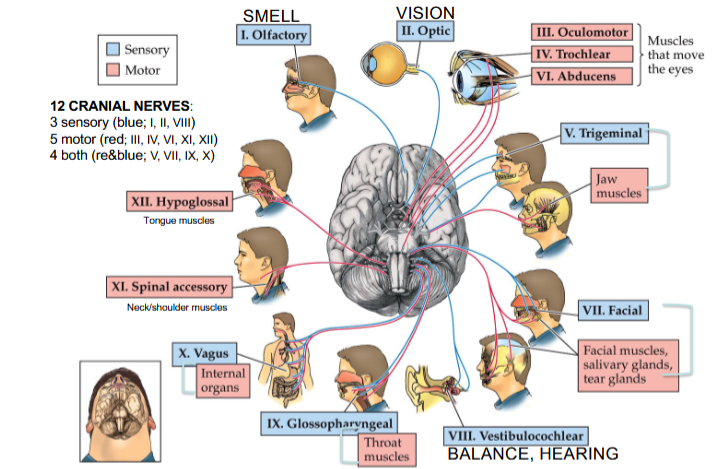
Abducens Nerve
Cranial Nerve VI
Moving your eyes from left to right
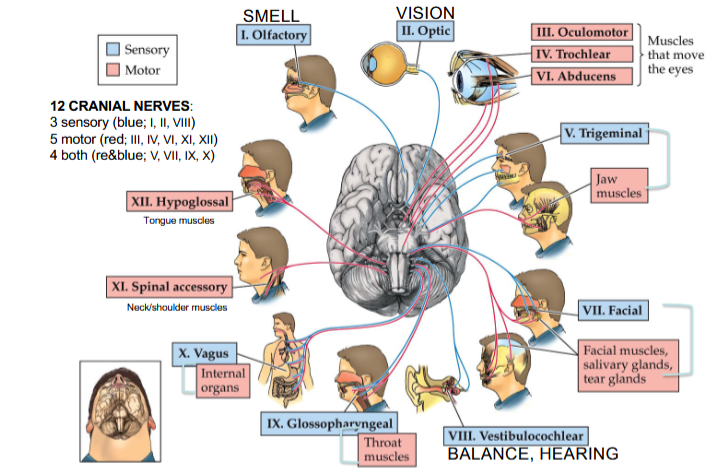
Facial Nerve
Cranial Nerve VII
Controlling several facial muscles to make facial expressions and providing taste (as a sense) in part of your tongue
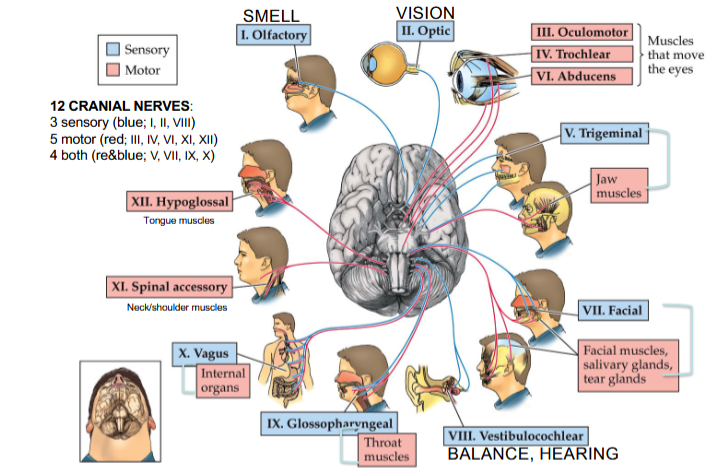
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Cranial Nerve VIII
Providing the sense of hearing and balance
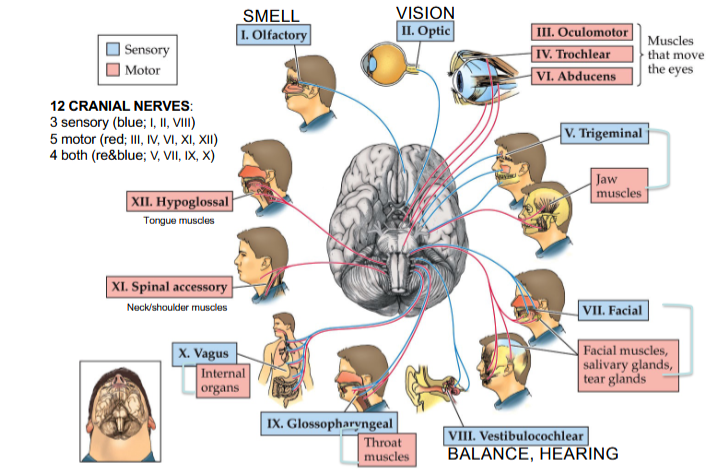
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Cranial Nerve IX
Providing taste sensations to part of your tongue and controlling muscles for swallowing
Contains parasympathetic nerve fibers that play a role in blood pressure regulation and saliva production
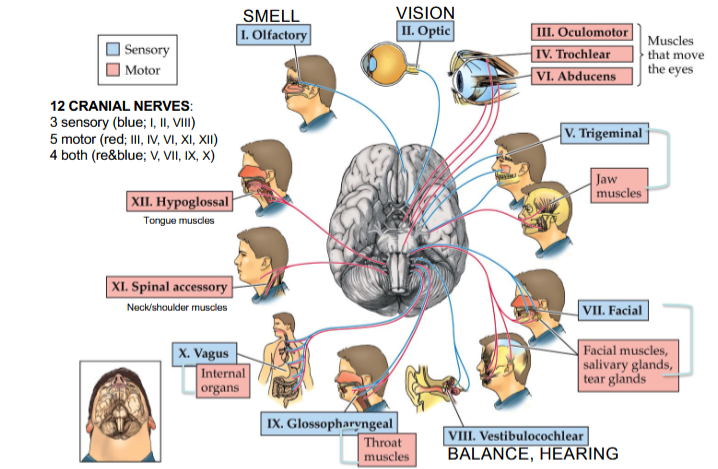
Vagus Nerve
Cranial Nerve X
The main nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system
Regulates several autonomic bodily processes:
Digestion, blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, mood, saliva production
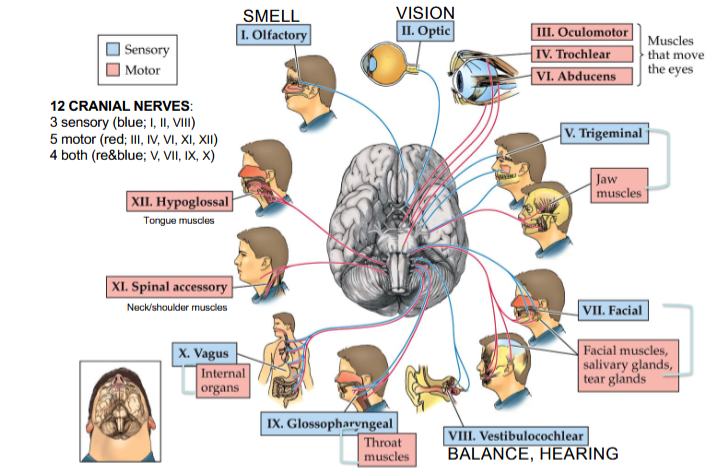
Spinal Accessory Nerve
Cranial Nerve XI
Controlling neck and shoulder movement
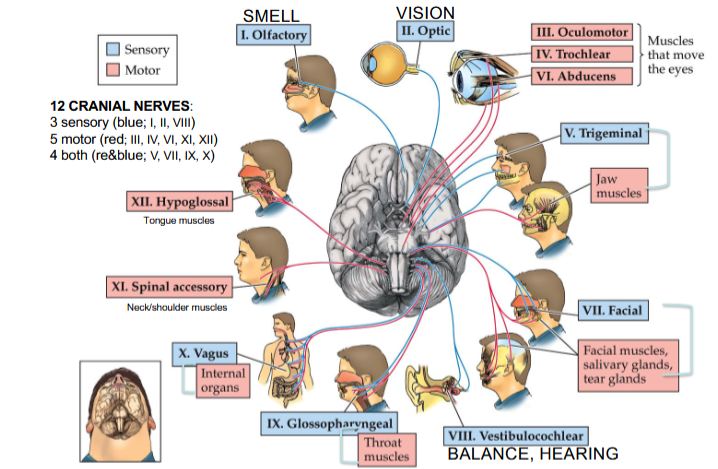
Hypoglossal Nerve
Cranial Nerve XII
Controlling tongue movement, which plays a role in speaking, eating, and swallowing
Spinal Cord
A cylinder-shaped tube of tissue that runs through the center of the spine, from the brainstem to the lower back
Composed of nerves and cells that carry messages from the brain to the rest of the body (CNS)
Four Classes of Spinal Nerves: Cervical (Neck), Thoracic (Upper Back), Lumbar (Lower Back), Sacral
Three Meninges (Protective Tissues):
Dura Mater: Outer layer; protects spinal cord from injury
Arachnoid Mater (Middle layer)
Pia Mater (Deepest inner layer)

Vertebral Cross Section
The horns (ventral and dorsal) are where the spinal nerves synapse are inside the spinal cord
Dorsal (Back): Holds the cell bodies for unipolar somatosensory neurons from the skin — touch and pain — and deep tissue — pain and proprioception
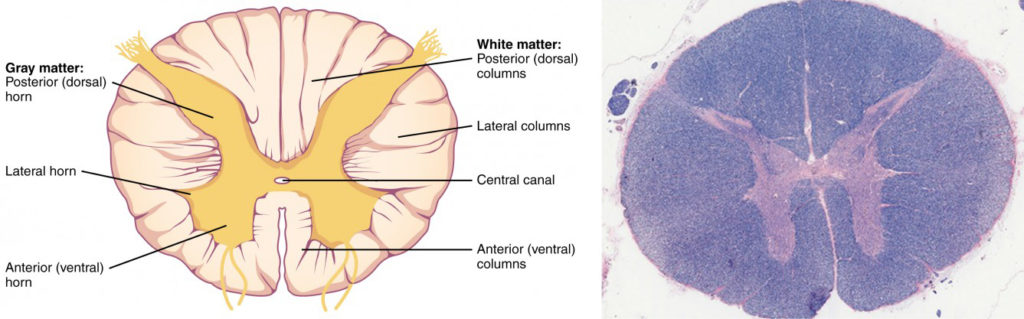
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons
Nervous system cells that receive information from the environment and transmit it to the body
Travels through the myelinated pathways of the dorsal (back) of the spinal cord
Motor (Efferent) Neurons
Neurons that carry signals from the CNS to the muscles to produce movement
Travels through the myelinated pathways of the ventral (front) root of the spinal cord
Sympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
Homeostatic functions are put on hold
Accelerates heartbeat, raises blood pressure, slows digestion, raises blood sugar, and cools the body
Prepares body to use all its oxygen and energy; Activates in “Flight or Fight” situations
Thoracic / Lumbar nerves activated, Ganglia inside spinal column connect nerves
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
Diverts oxygen and energy to promote homeostatic functions
Decelerates heartbeat, lowers blood pressure, stimulates digestion, and processes waste
Activates in “Rest and Digest” situations
Cranial / Sacral nerves activated, Ganglia are peripheral to (outside) the spinal column
Chronic Sympathetic Activation Symptoms
Skin break-outs
High blood pressure
Muscle spasms
Stomach and intestinal upset
Headaches, anxiety
Infertility & Impotence
Hair loss
Asthma
Diabetes, weight gain
Horizontal Plane
Rostral (Anterior)
Caudal (Posterior)
Sagittal Plane
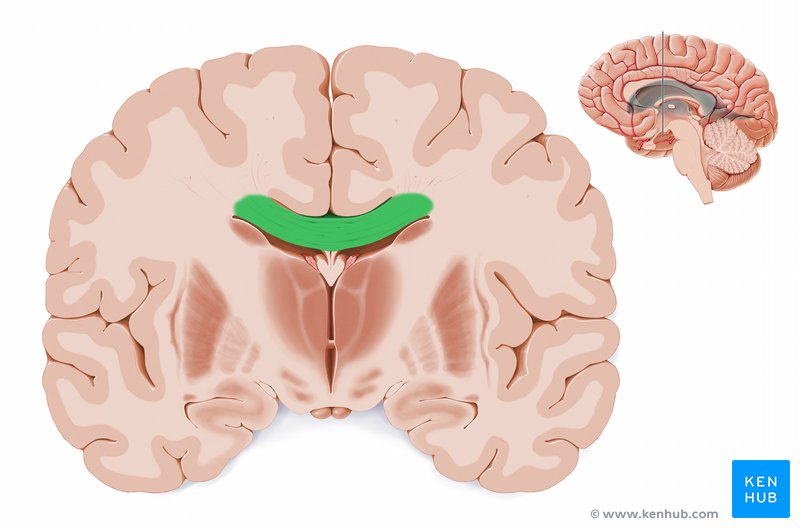
Coronal Plane
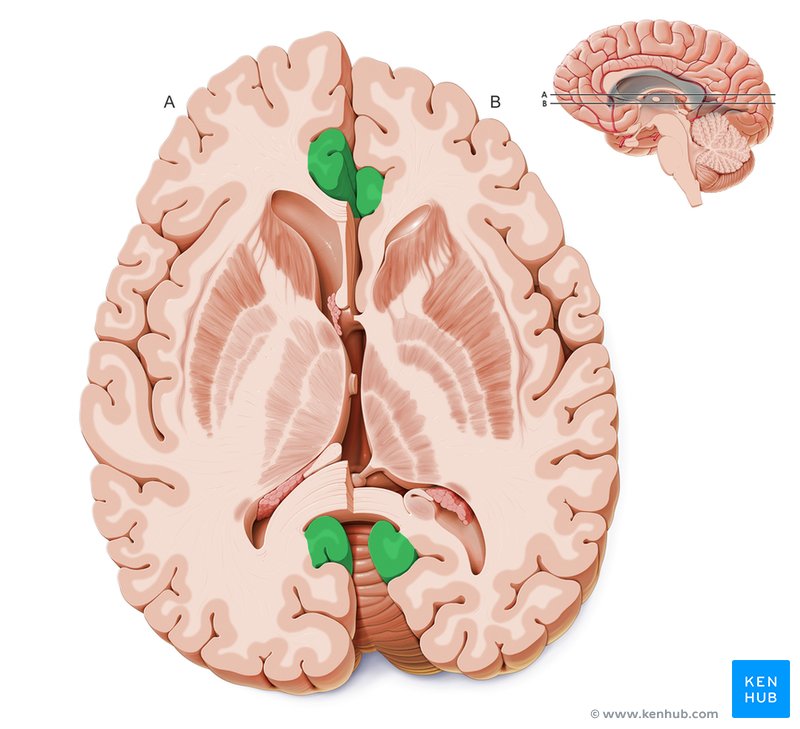
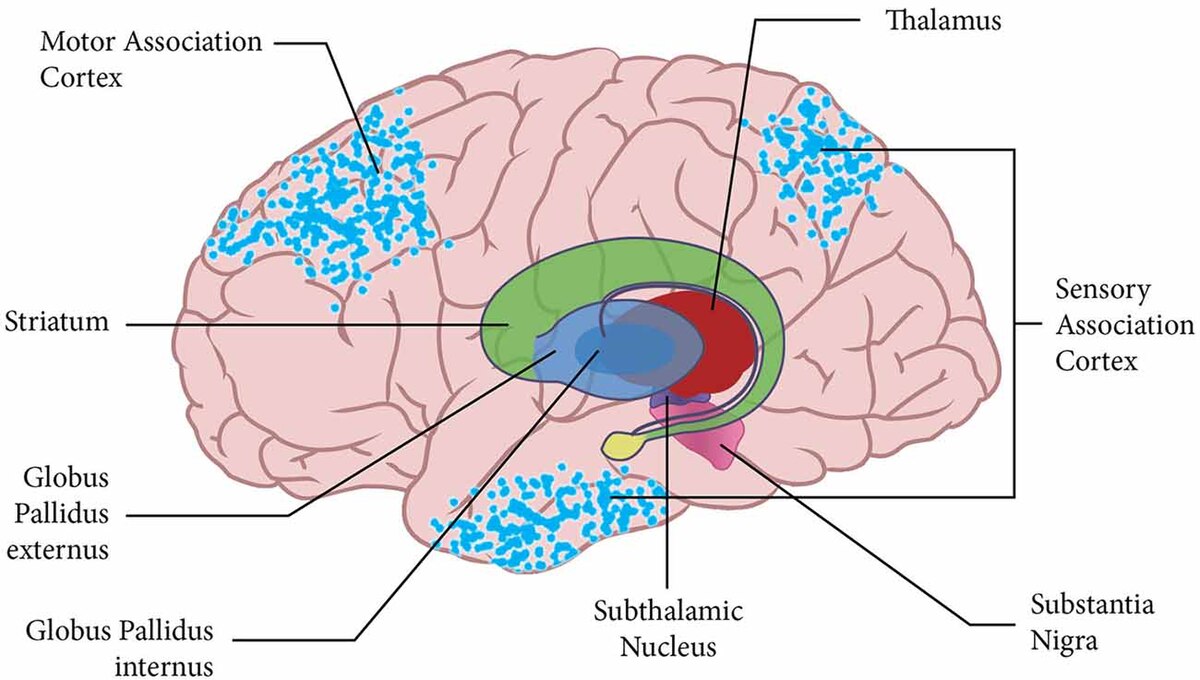
Basal Ganglia
Structures that play an important role in motivation, reward, and movement; Derived from the forebrain (except substantia nigra)
Includes:
Caudate Nucleus, Globus Pallidus, Putamen, Substantia Nigra (Midbrain), Subthalamic Nucleus, Ventral Pallidum
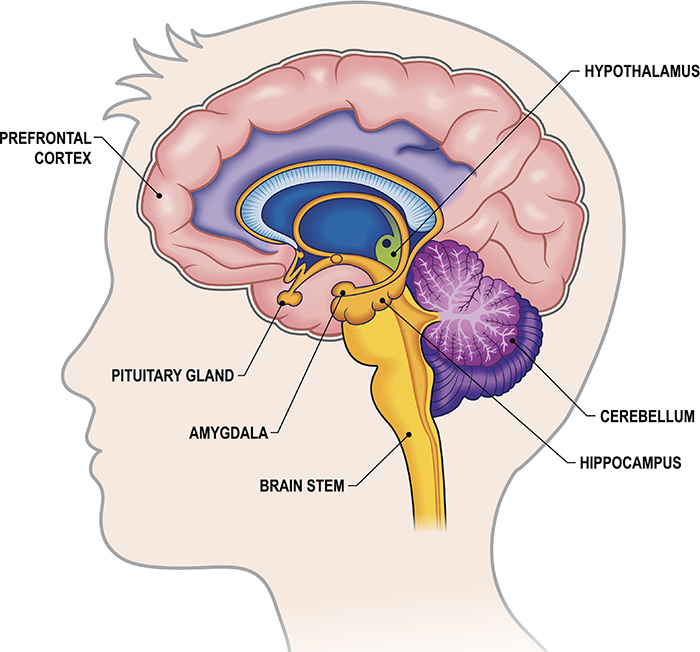
Limbic System
Plays an important role in modulating emotion and learning / memory; Derived from the forebrain
Includes:
hypothalamus, amygdala, thalamus, hippocampus
Corpus Callosum
A bundle of nerve fibers (white matter tract) that allow the left and right hemisphere’s of the brain to communicate
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Derived from the hollow center of the neural tube; Surrounds the brain and spinal cord for protection, metabolic exchange, and waste clearance
Found in the ventricles of the brain
Found in sub-arachnoid space of spinal column
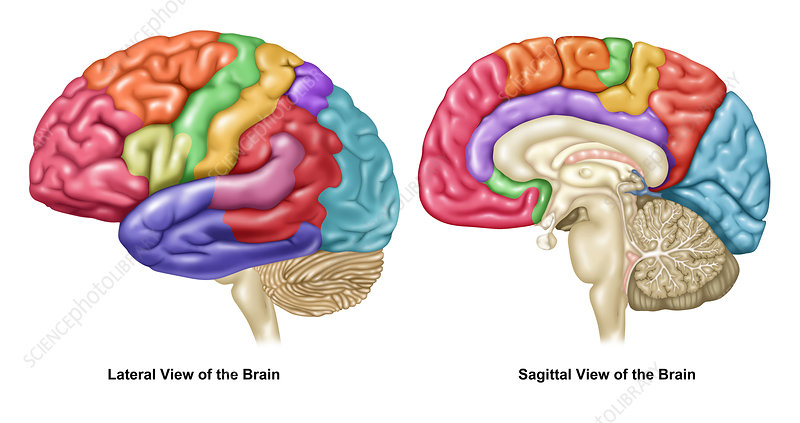
Lateral View
Displays 4 lobes — Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital — and 5 cortices (Frontal and Motor Cortex are found in Frontal Lobe)
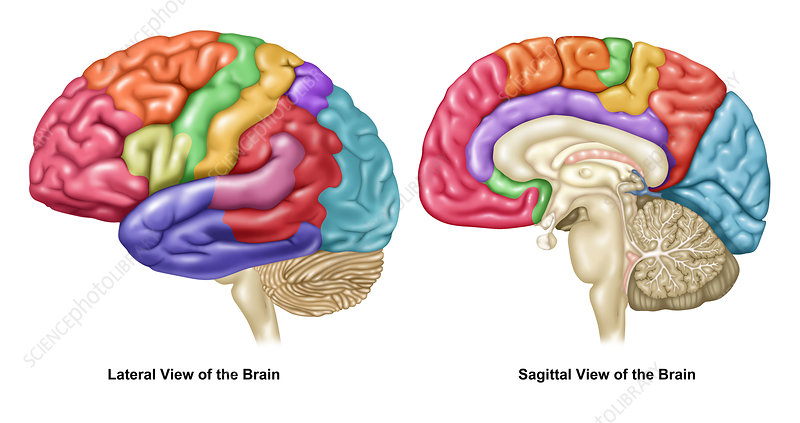
Midline View
The majority of brain structures have a left and right component, but the two sides don’t always function identically (especially in higher structures like the cortex)
Wernicke’s Area
Primarily responsible for language comprehension; Helps one understand spoken and written language
Located in the Temporal Lobe
Broca’s Area
Essential for speech production; Allows one to form words and construct grammatically correct sentences
Located in the Frontal Lobe
Laterality
Dominance of one side of the brain in controlling particular activities or functions
Crossed Auditory Pathways
Ascending auditory paths cross the midline, but not 100%
There is a stronger projection from each ear to the other side of the brain
EX: Hearing something in your left ear is processed in the right side of the brain first, but immediately sent to the left side
Split Brain
Corpus Callosum is severed, disconnecting the left and right hemispheres from each other
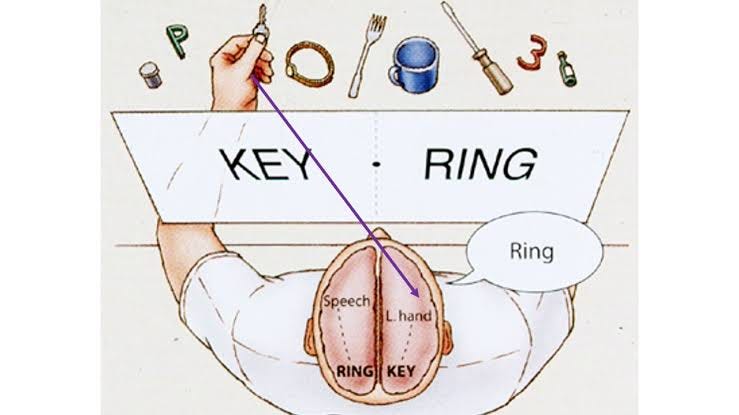
Phylogeny
The history of evolution of a species or group, especially in reference to lines of descent and relationships among broad groups of organisms
EX: Studying humans and primates
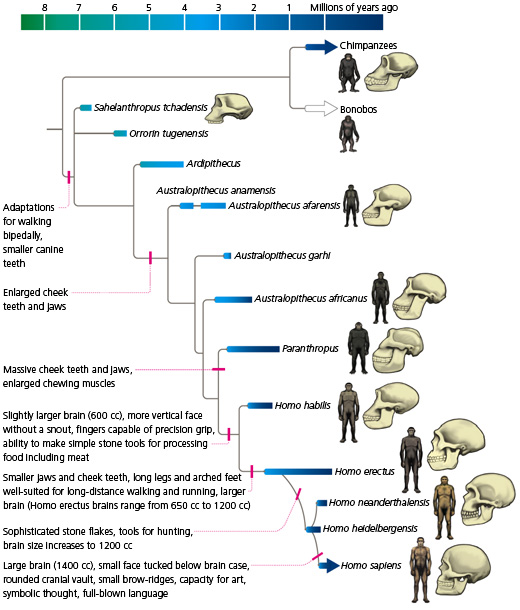
Phylogenetic Scale
Examining less evolved species with more evolved species; Comparisons suggest that higher brain structures are more recent products of evolution
“Lower” structures (that function for basic survival functions) are not that different across species
“Higher” structures (advanced functions) vary amongst species
More complex and elaborate structures in “higher” (more intelligent) species
Brain must be considered as a whole, since different species require different functions for survival
EX: Bats have an auditory cortex as complex as a dolphins, but other part of their cortex are smaller and not as complex as dolphins
Brain to Body Weight Ratio
A relative measure of brain evolution
Mammals are “higher” species than non-mammals, and humans are on top. However, larger species (e.g. blue whale) are penalized
Cortex/Sub-Cortex Ratio
A relative measure of brain evolution
Favors mammals and humans over other animals
Cortical Enfolding Index
A relative measure of brain evolution
Reflects what is known about “higher” and “lower” species, but as a measurement, it means that dolphins and whales are ‘higher up’ than humans
Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny
The development of an organism (embryo → adult) reflects its evolutionary history
EX: The developmental ‘gradient’ of the brain moves from lower structures to higher structures (bottom-up organization) — hindbrain first, midbrain second, forebrain last. This is similar to how the human brain evolved
Ontogeny (Study of Embryos) | Phylogeny (Study of Evolutionary History)
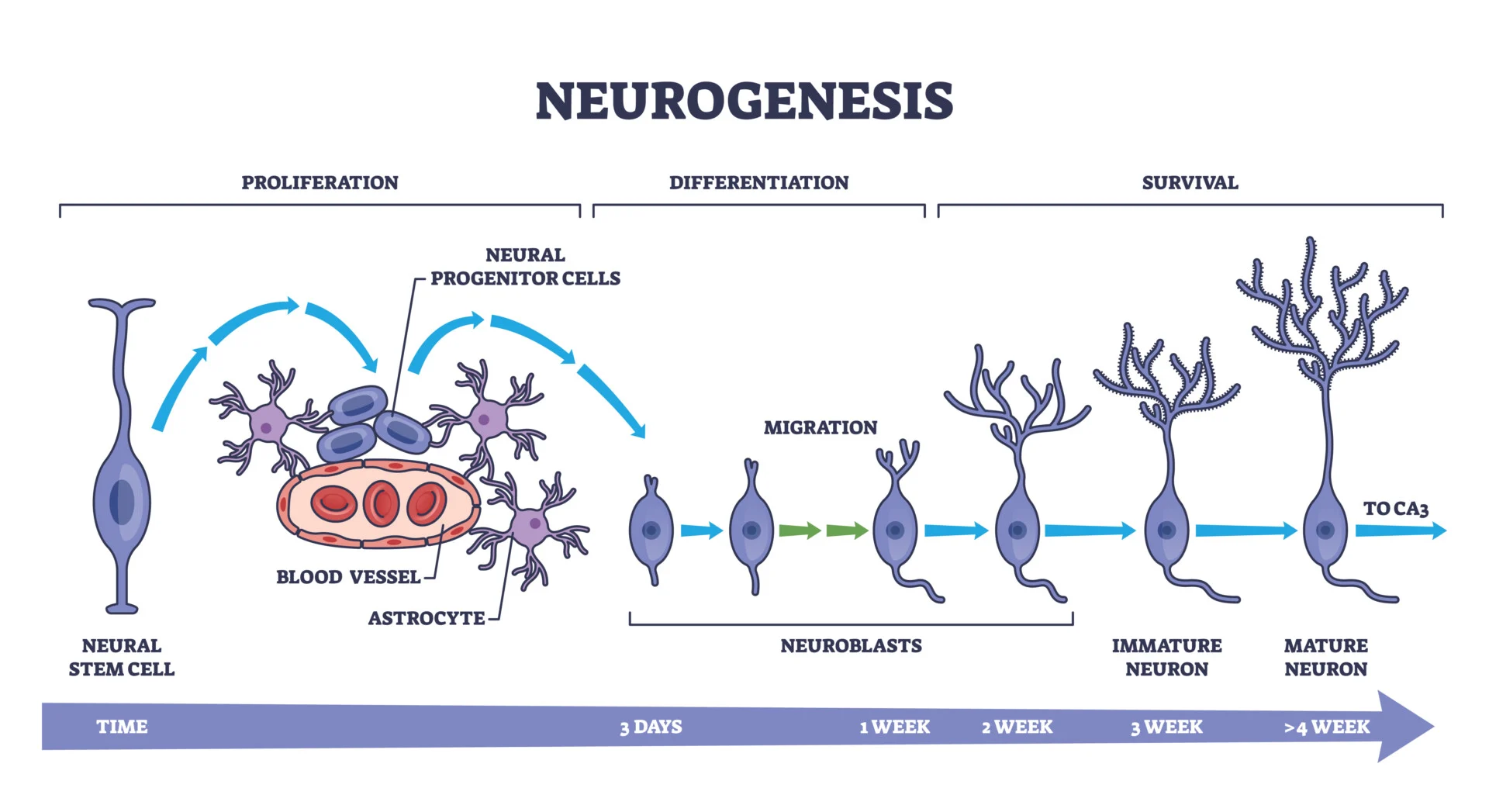
Neurogenesis
aka Neuron Proliferation
Mitotic division of progenitor (mother) cells into dedicated neural or glial precursors, occurring during prenatal infancy at the core of the neural tube, bordering CSF
Ventricular Zone is where neural progenitors are ‘born’ and start their migration
First in the neural development sequence
Neuroblastoma
A form of cancer mainly seen in infants and children, since neurons proliferate prenatally and cancer is a disorder of cell-division (run-away mitosis)
Rates go down as neurons stop dividing
Neuronal Migration
Undifferentiated precursor (daughter) cells migrate to final locations, moving from “inside” of the neural tube outward, occurring from prenatal to infancy
Second in the neural development sequence
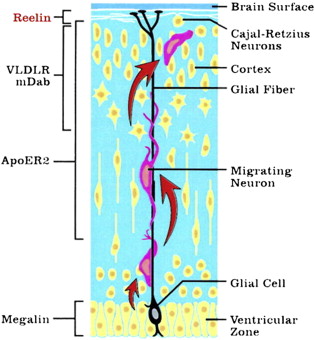
Radial Glia
Supports migrating neurons; helps form the cortical layers (lamination)
Lamination
Each neuronal precursor (daughter cell) has to migrate outward from the ventricle, pass beyond its predecessors and then stop, undergo terminal differentiation and establish its synaptic connections
aka Inside-Out layering in the cerebral cortex
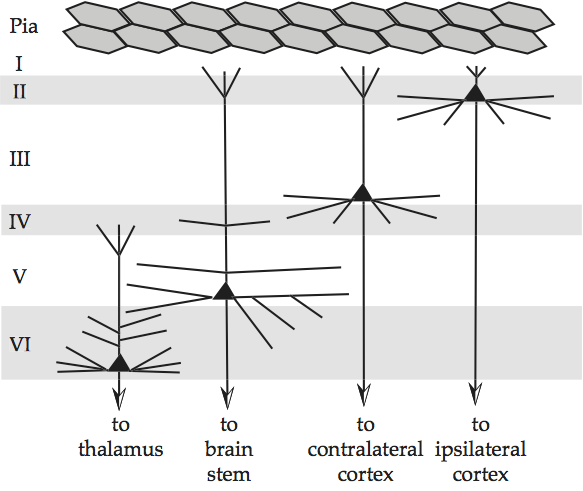
Neuronal Differentiation
Occurs from prenatal to childhood; a part of neuronal migration
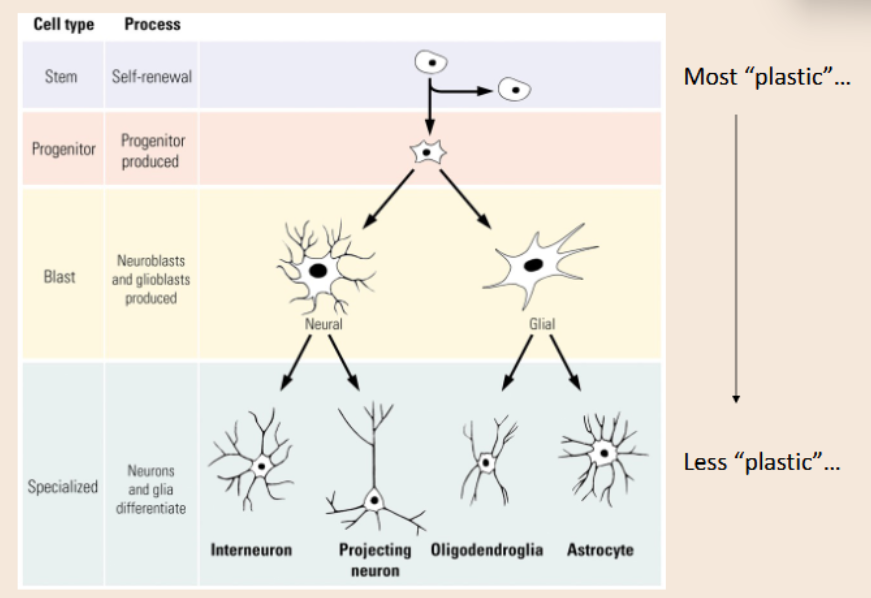
Synaptogenesis
Postnatal elaboration of synapses, occurring from infancy to adolescence
Proteins in the cytoplasm guide the movement of axonal terminals via attraction and replusion to guide this stage
Third in the neural development sequence
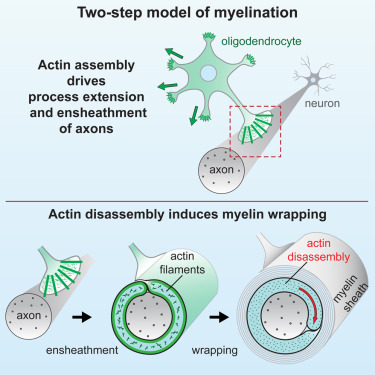
Myelination
Postnatal myelin forms, occurring from infancy to adolescence
Causes peak brain weight at ages 12-14
Fourth in the neural development sequence
Pruning
Getting rid of existing, unwanted synapses and retaining important ones, continuing late into one’s life
Either loss of neurons or the withdrawal of axons from specific synapses
EX: Continues into early 20’s for the frontal cortex
Neurotrophic Factors
A factor that promotes neuronal growth
EX: NGF = Nerve growth factor
Apoptosis
A programmed / genetic neuronal death
Necrosis
An injury-induced neuronal death
Frontal Cortex
The most recently evolved and latest developing structure
Regulates decision-making, understanding of consequences, planning, and morality