May 8th Exam 5/6
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Viruses are
Obligate intracellular parasites (Can infect anything)
General size of viruses
1-2 um (Needs electron microscope)
Viruses have
Central core or a covering
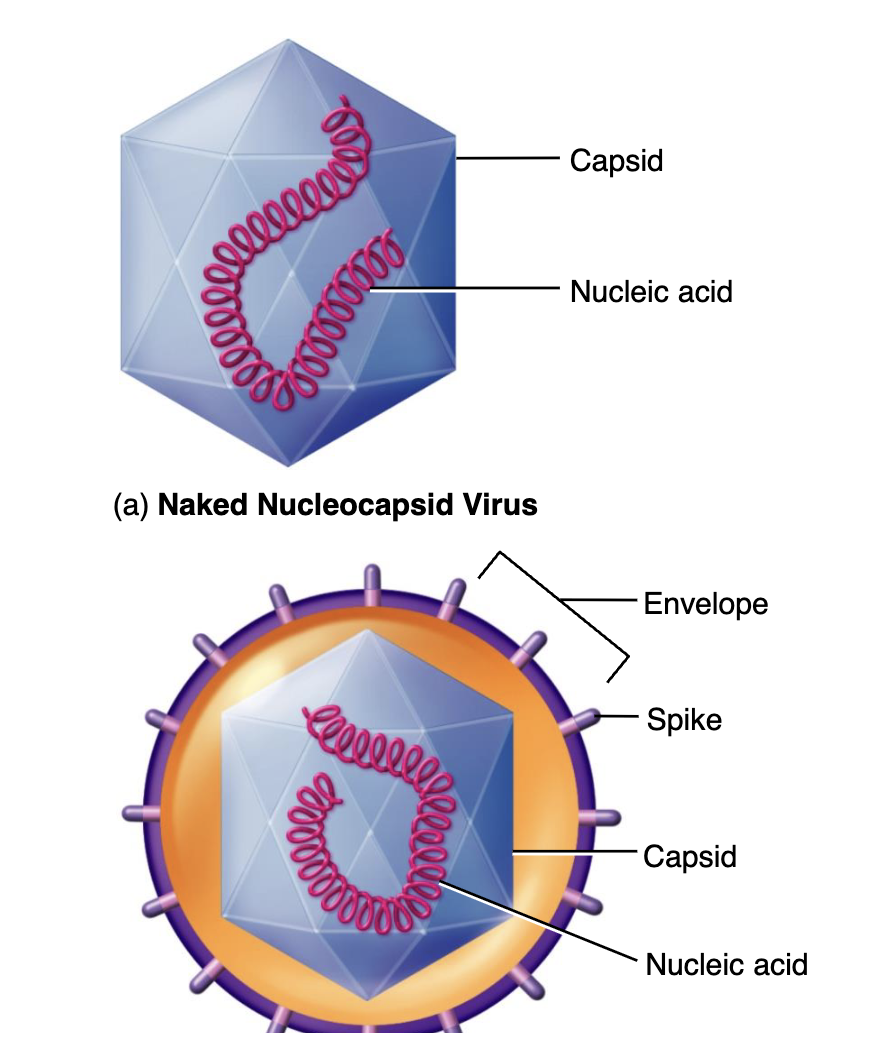
Capsids
Protein that encloses and protects their nucleic acid
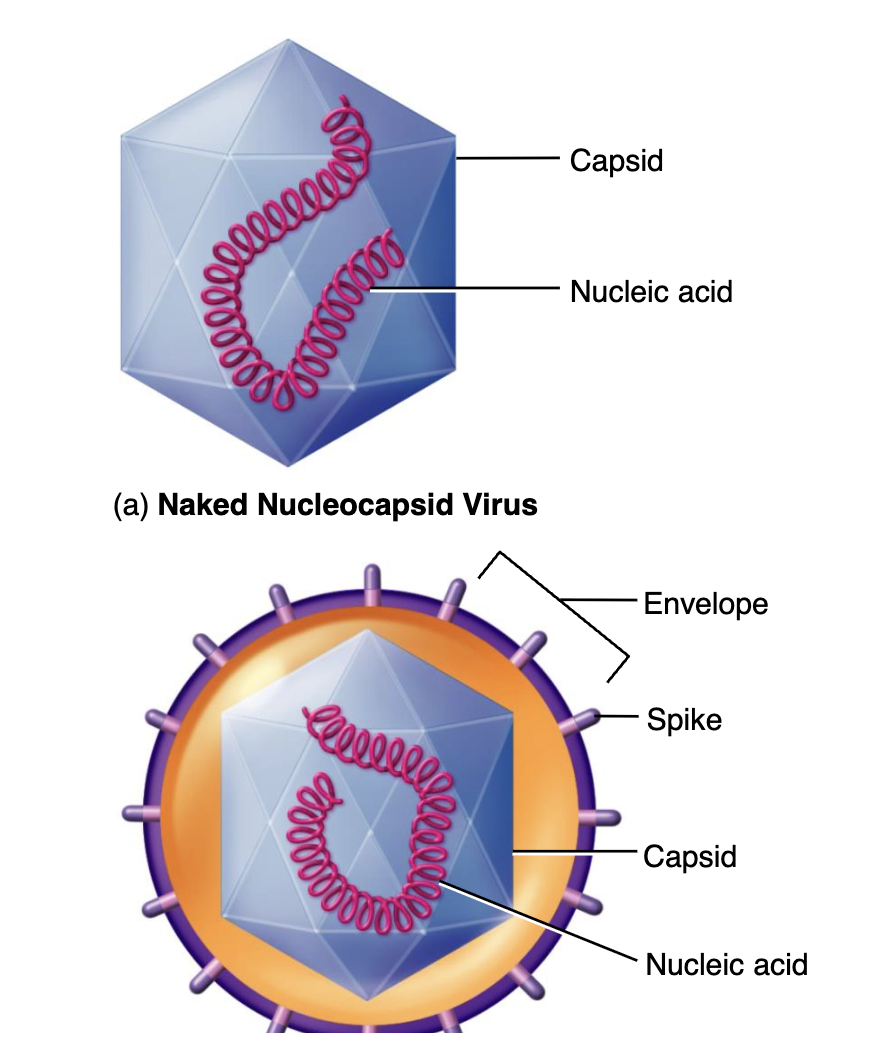
Nucleocapsid
Capsids + Nucleic acid
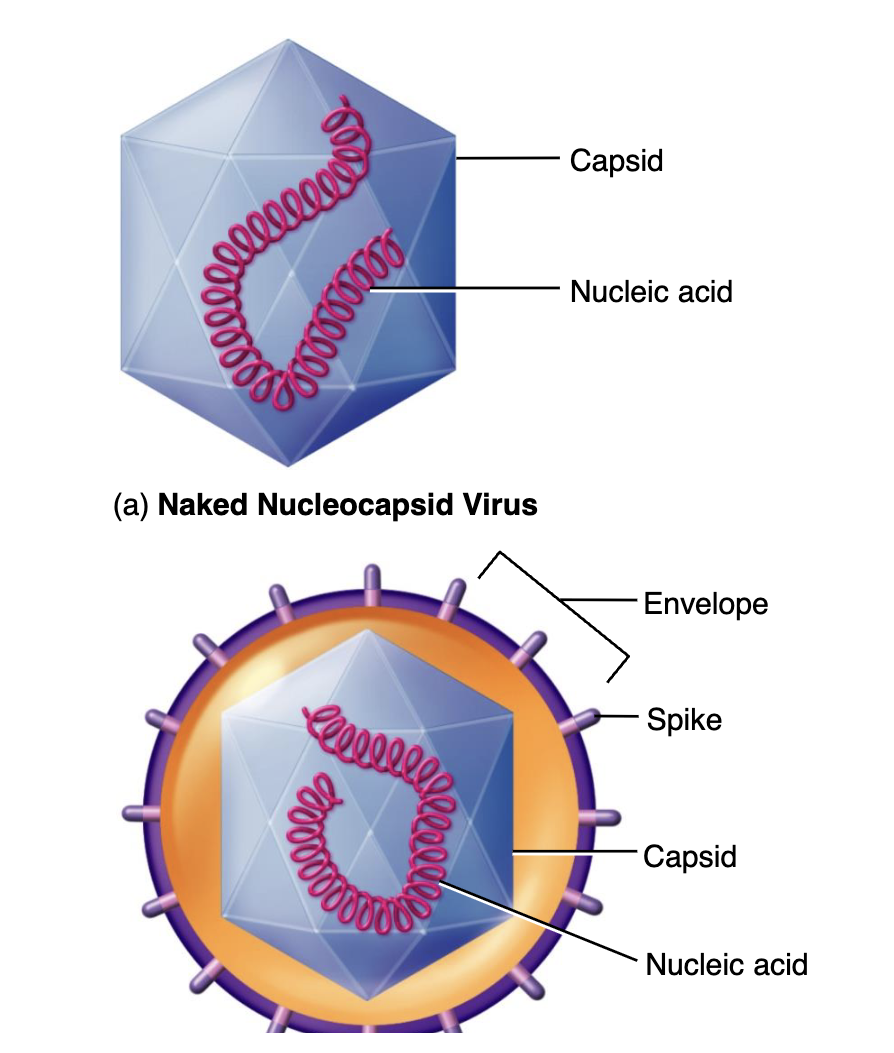
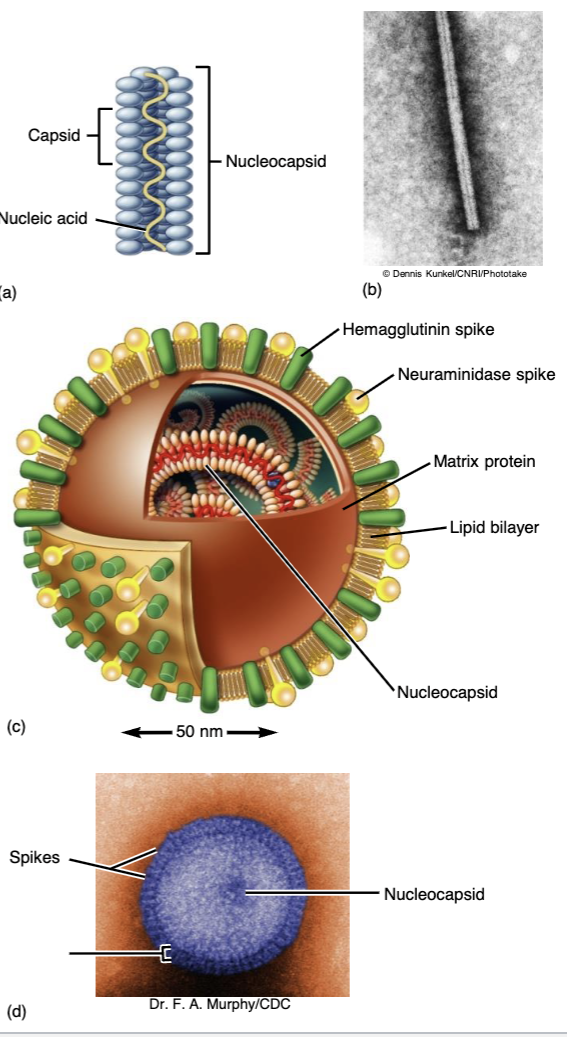
Envelope
External covering that acts as a extra layer of protection for viruses
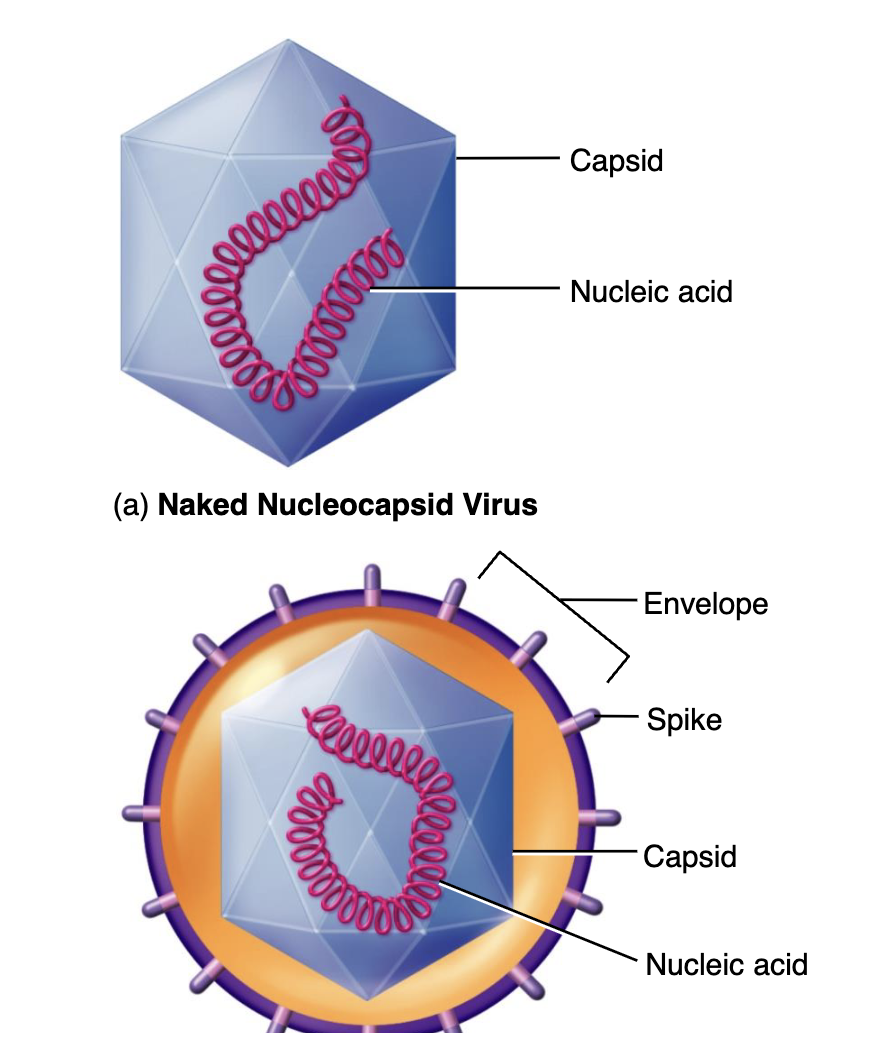
Naked
A virus that doesn’t have a envelope
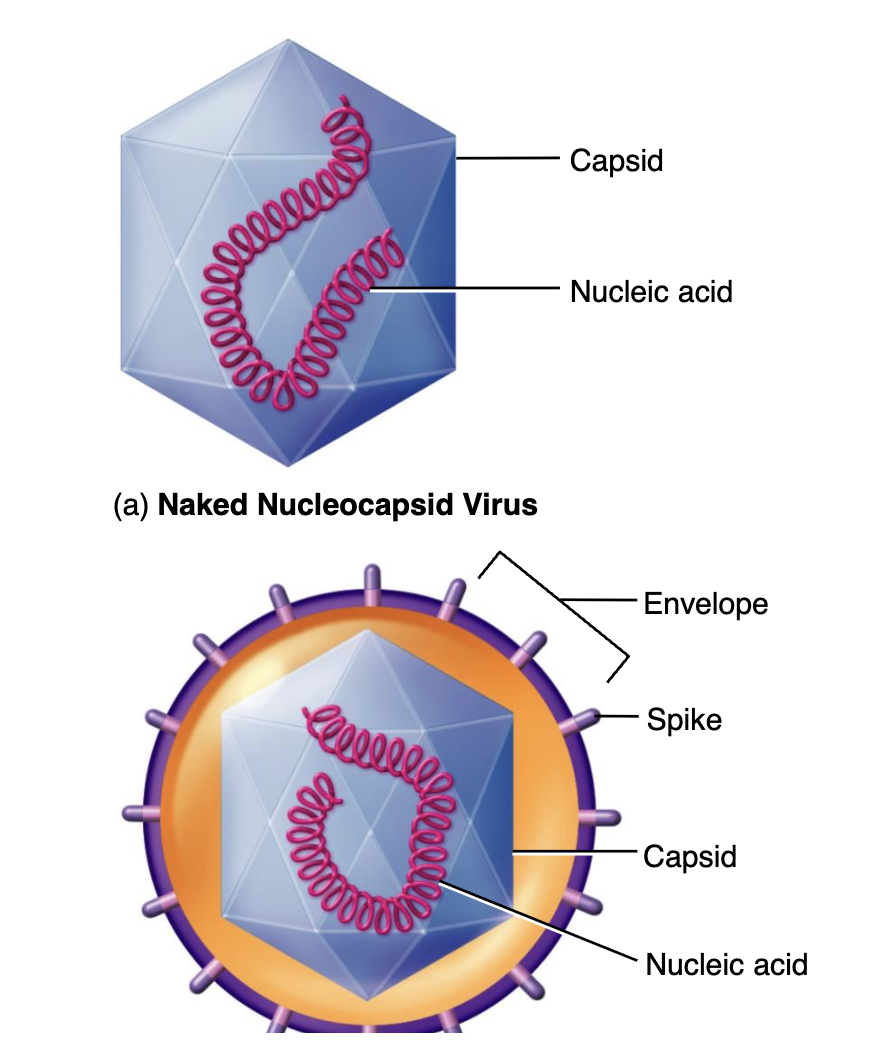
Capsomers
Identical protein subunits that makes up a capsid
Viral envelope
Mostly animal viruses, acquired when the virus leaves the host cell, has spikes on the outside used to attach to host cells
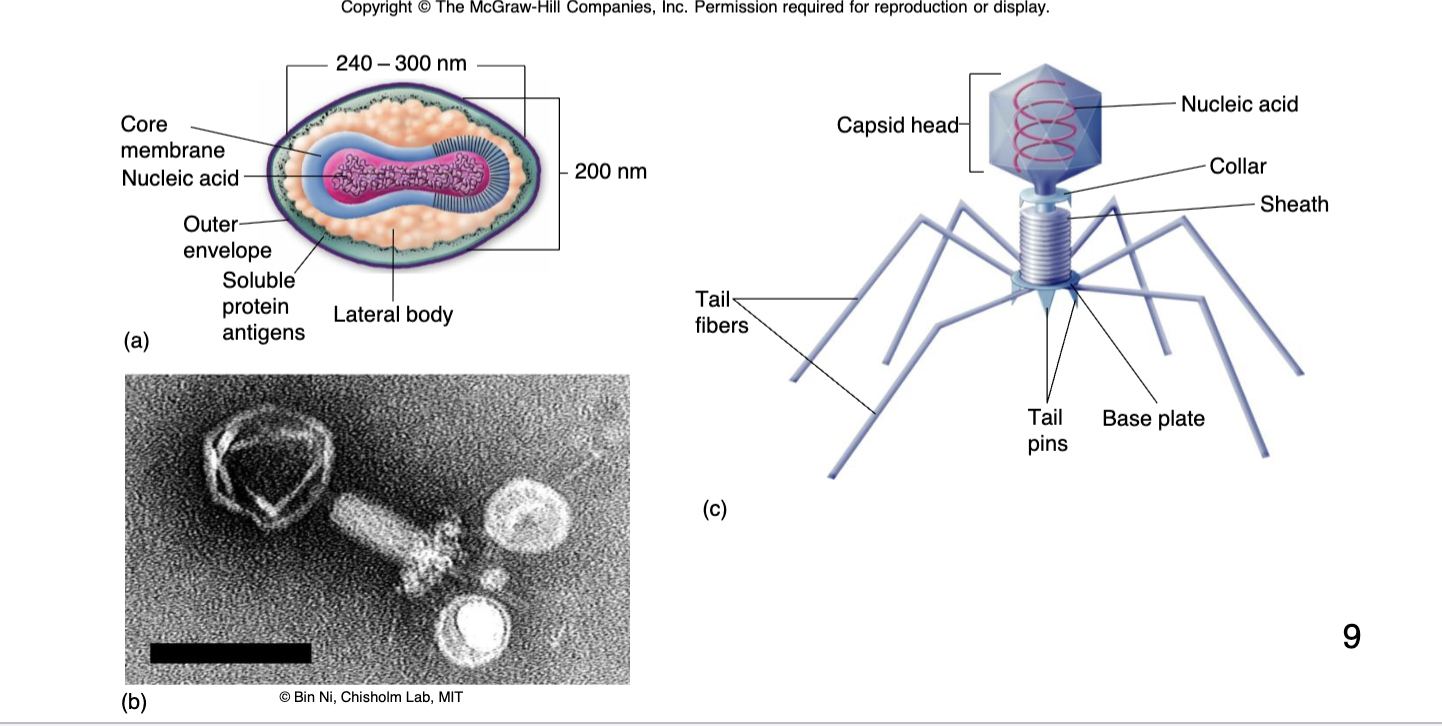
Complex/Atypical Viruses are
complex viruses
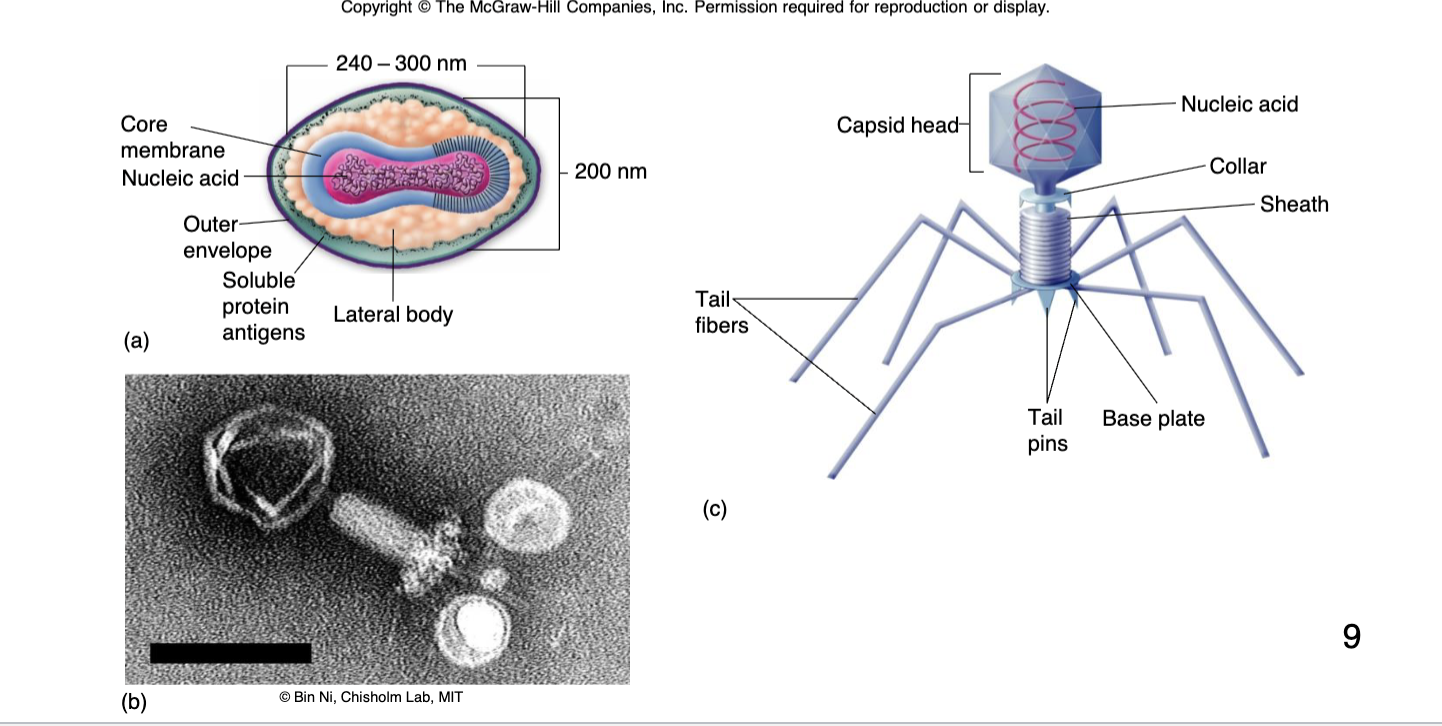
Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect bacterial cells (Complex/Atypical virus)
Viral genome
Either DNA or RNA, not both that’s used by viruses to infect host cells to create more viruses
DNA viruses
Usually double stranded (ds) but may be single
stranded (ss), Circular or linear
RNA viruses
Usually single-stranded, may be double-stranded, may
be segmented into separate RNA pieces
Enzymes in viruses
Polymerase, Replicase, and Reverse Transcription
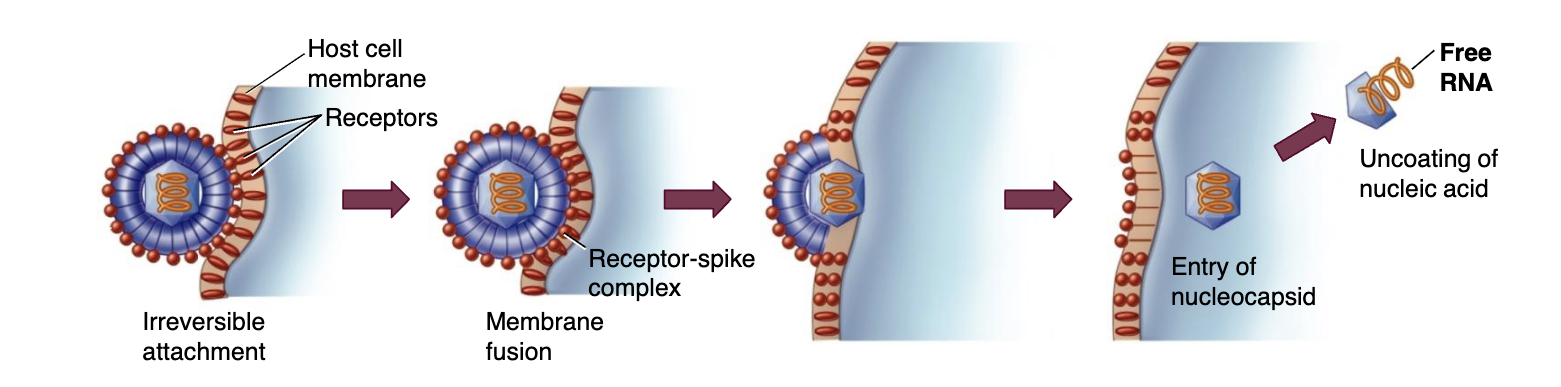
Adsorption (1/6)
binding of virus to specific molecules on
the host cell
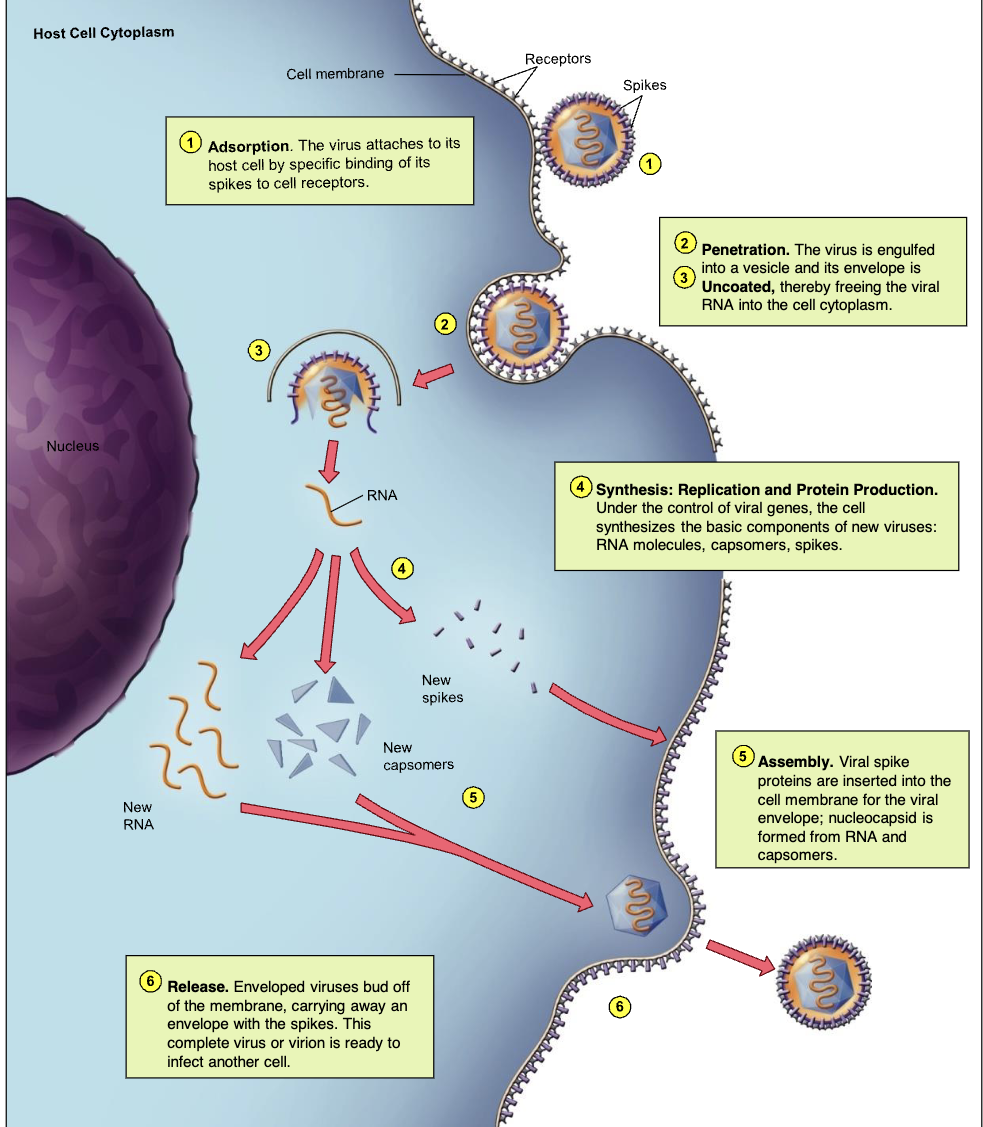
Penetration (2/6)
genome enters the host cell
Uncoating (3/6)
the viral nucleic acid is released from the
capsid
Synthesis (4/6)
viral components are produced
Assembly (5/6)
new viral particles are constructed
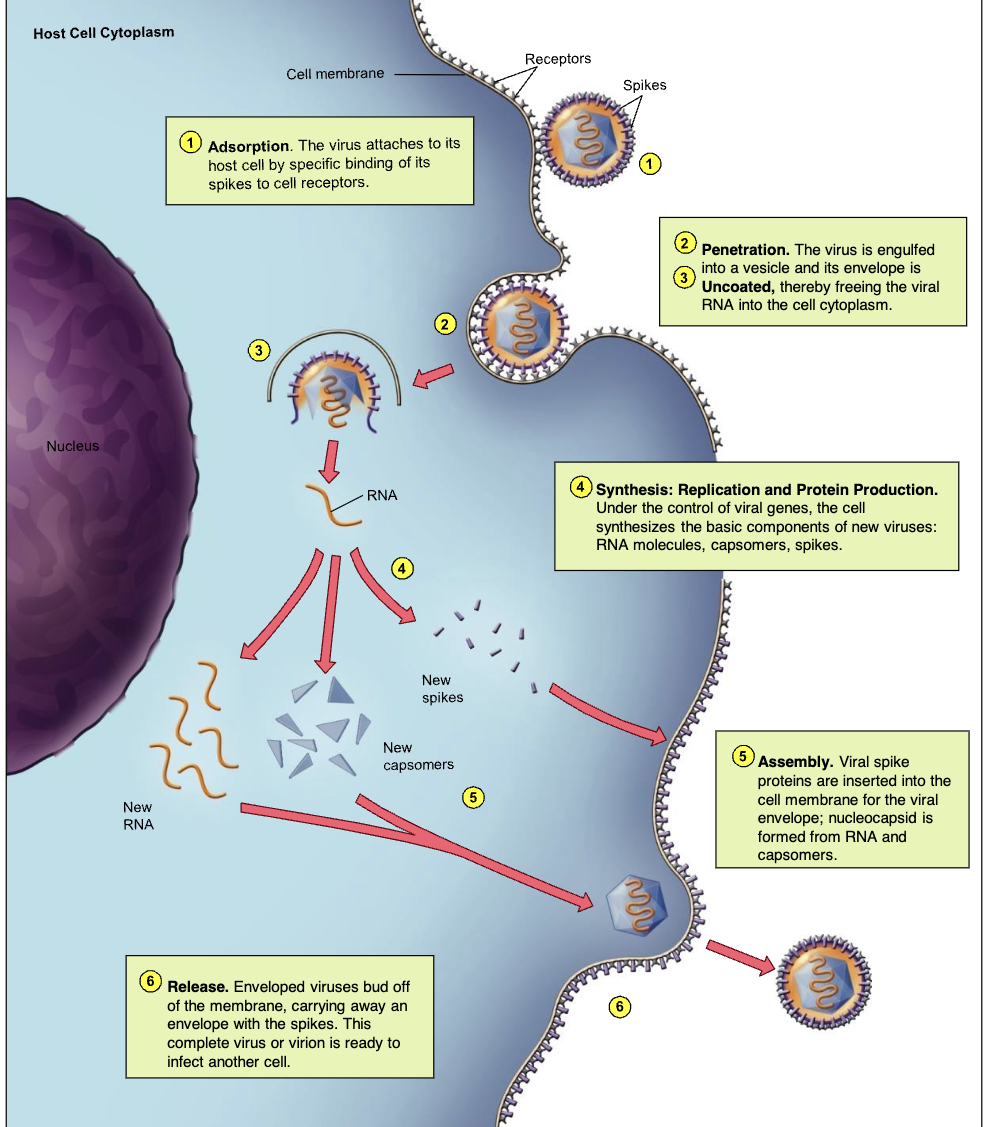
Release (6/6)
assembled viruses are released by
budding (exocytosis) or cell lysis
Host range
Variety of host cells that a virus can infect
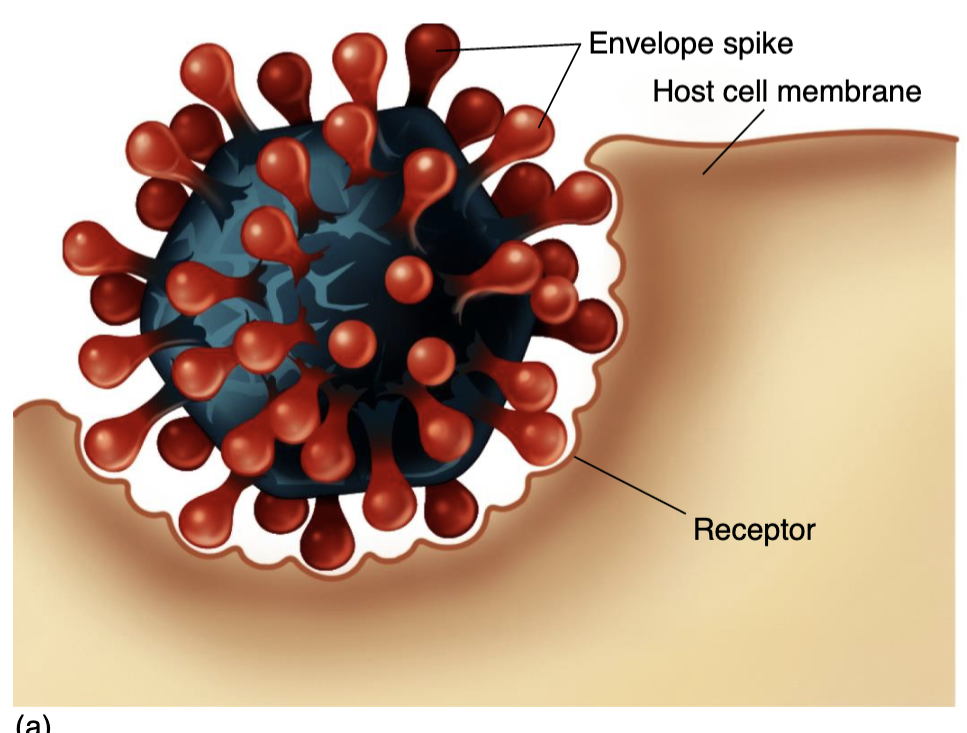
Endocytosis
entire virus is engulfed and
enclosed in a vacuole or vesicle (Penetration/Uncoating)
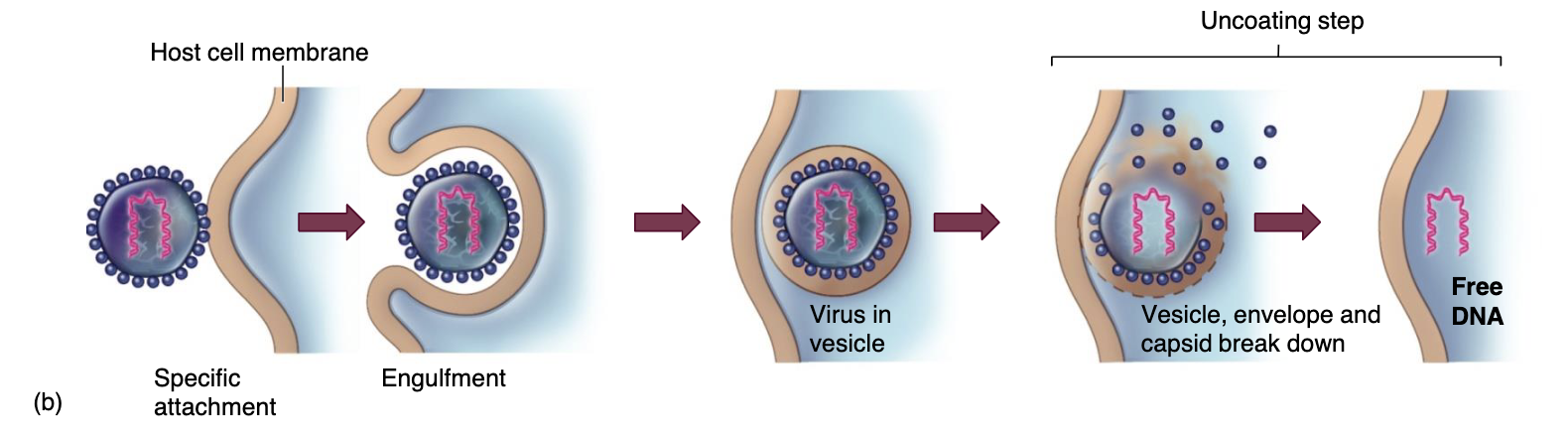
Fusion
envelope merges directly with
membrane resulting in nucleocapsid’s
entry into cytoplasm (Penetration/Uncoating)
DNA viruses generally are replicated and
assembled in the
nucleus
RNA viruses generally are replicated and
assembled in the
cytoplasm
Budding/Exocytosis (Release 6/6)
nucleocapsid binds to membrane
which pinches off and sheds the
viruses gradually; cell is not
immediately destroyed
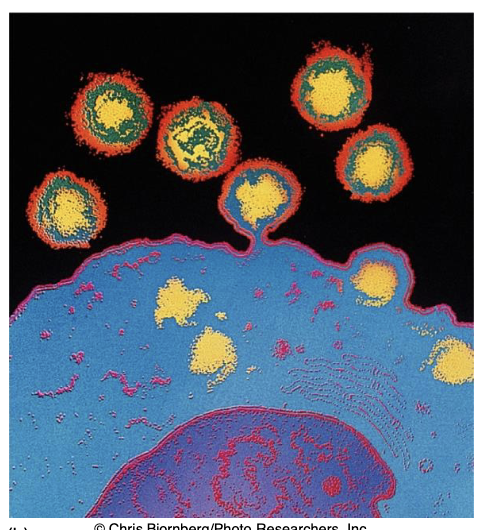
Lysis (Release 6/6)
nonenveloped and
complex viruses released when
cell dies and ruptures

Cytopathic effects
Virus-induced damage to host cells that alters the cell, i.e., becoming a cancer cell, a misshapen cell, inclusion bodies, altered DNA, cell lysis, cells clumping together, and evidence left in the cytoplasm
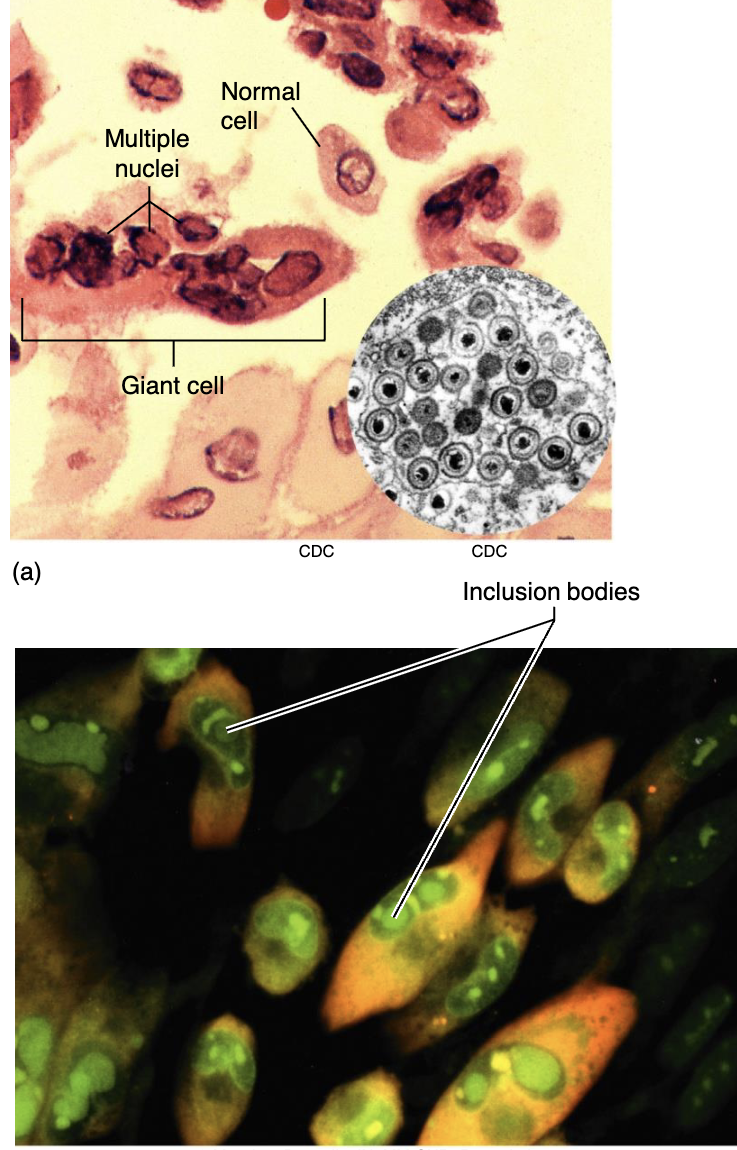
Persistent infections
When cell harbors the virus but doesn’t lysis immediately
Chronic late states
are suseptible to persistent infections
Transformed cells
Cells that have abnormal behavior via viral infections that can cause cancer, uncontrolled growth, alters in chromosomes, etc.
Oncoviruses
Mammalian viruses that are able to induce tumor growth
Method for growing viruses
Cell culture (For observation and effects of cytopathic effects) bird embryo (Ideal for virus growth), and live animal inoculation (Only when necessary)
Prions
Misfolded proteins, infectious particles that contain no nucleic acid, attacks the nervous system, hard to get rid of
Scrapie
Prions in sheep/goats
Bovine epongiform encephalopathies (Mad cow disease)
Prions in cows
Wasting disease
Prions in elk
Creutzfeldt-Jakob
Syndrome
Prions in humans
Characteristics of viruses are
Rashes, fever, muscle aches, discomfort, and involves the respiratory system and lymph nodes
Porxviruses
Enveloped DNA virus, produce eruptive skin pustules (pocks or pox) that leaves scars, loves skin and connective tissues
Smallpox
First disease eradicated via vaccinations, spreads by skin contact/inhalation, causes fever/rashes
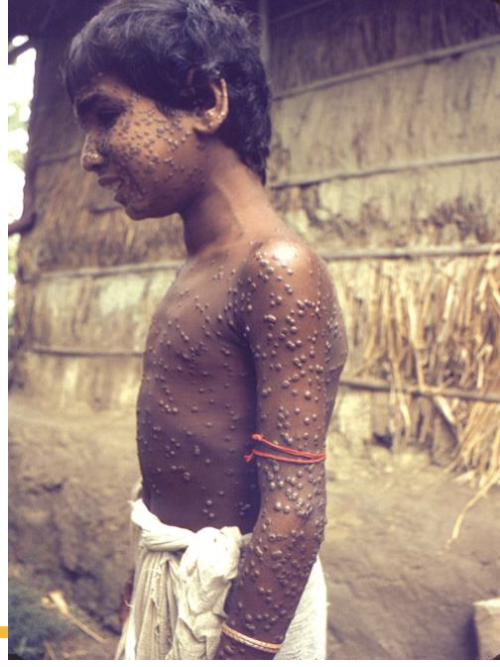
Variola major smallpox
Highly virulent, caused toxemia, shock, and causes blood to clot in the body (deadly)
Variola minor smallpox
Less virulent smallpox
Smallpox Vaccination
Single drop of vaccinia virus
punctured into the skin with a double-pronged needle
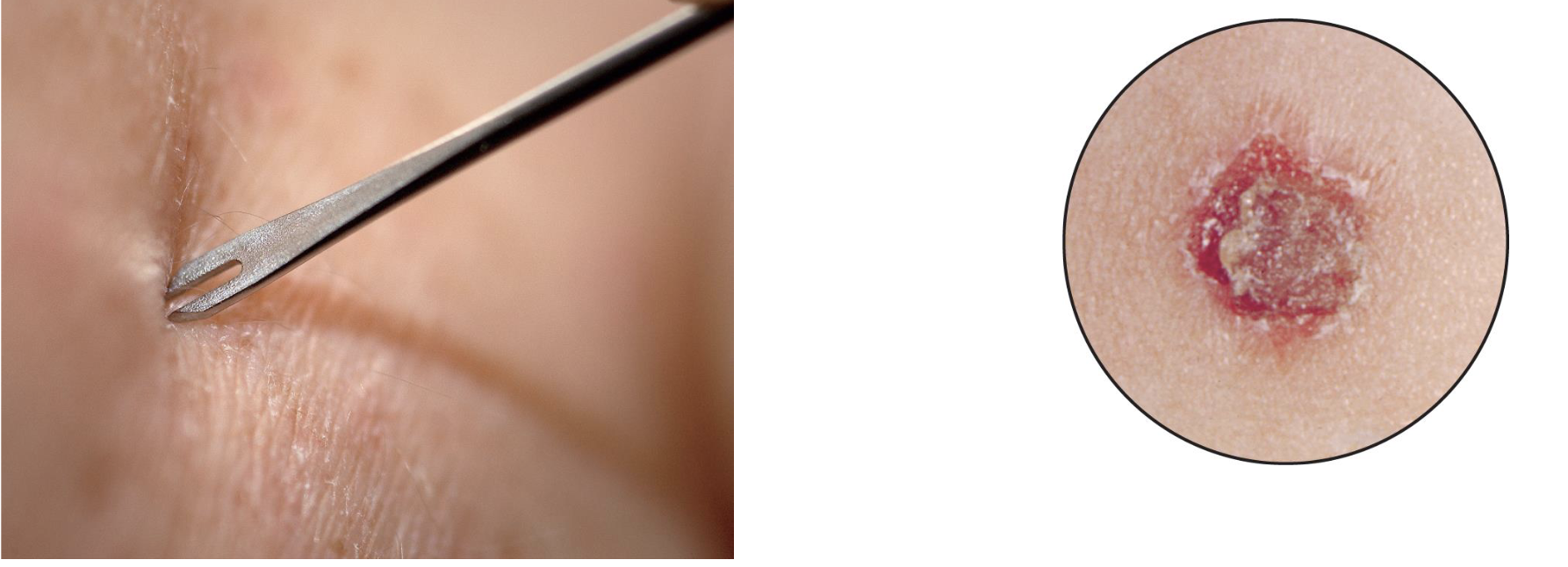
Humans can get poxviruses such as
cowpox and monkeypox
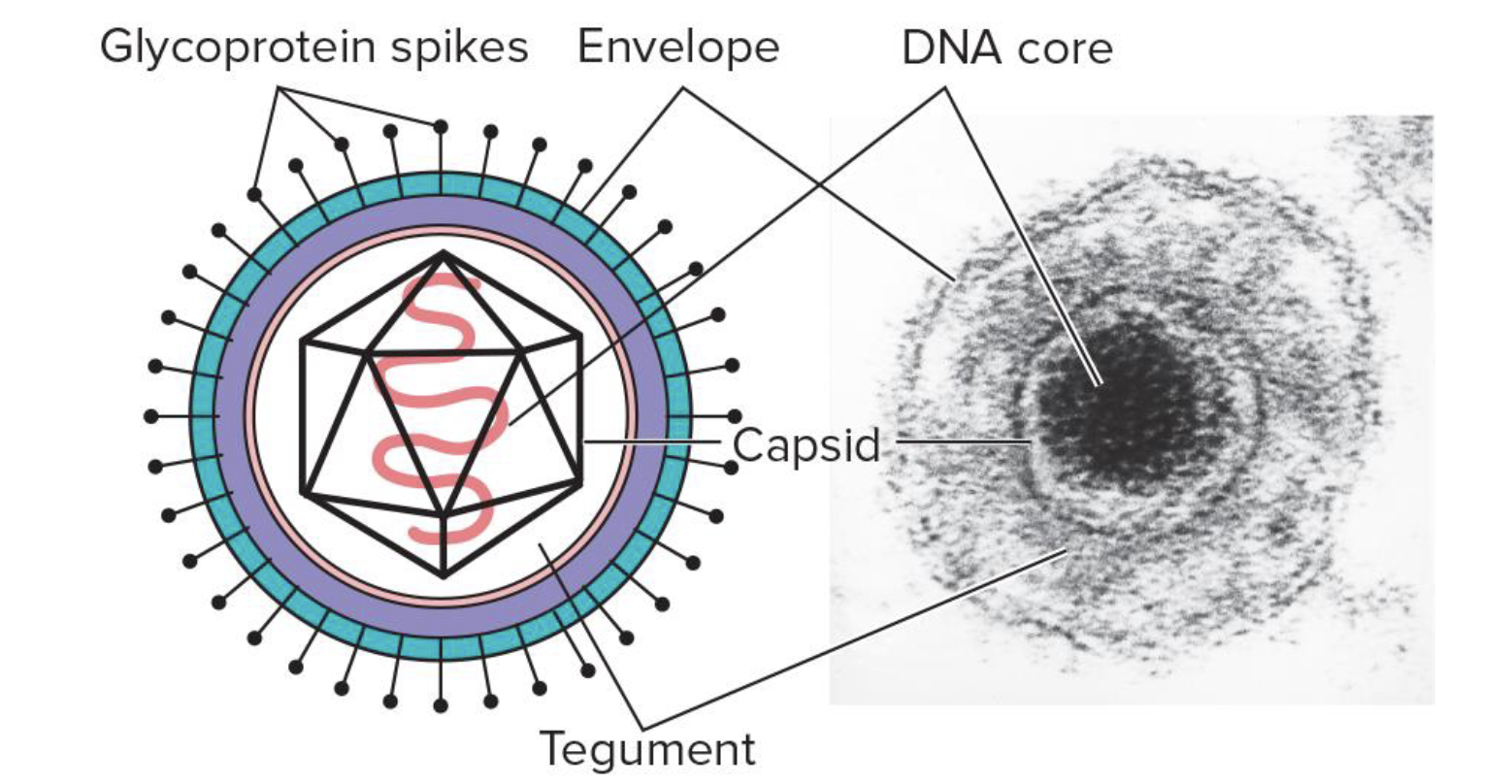
Herpesvirus
Enveloped DNA viruses that show latency and recurrent infection lives in sensory neurons of the immune system
Herpes Simplex Virus 1
Most common herpes virus, leaves cold sore and blisters around the mouth
Herpes Simplex Virus 2
Sexually transmitted herpes that leaves lesions on the genitals, can spread without visible lesions
Herpes labialis
Most common symptom, fever blister or cold sore
Herpetic gingivostomatitis
Inflammation in the oral cavity, gums, tongue, and lips
Herpetic keratitis
Inflammation of the eye, the virus travels to the optic nerve rather than the mandibular nerves
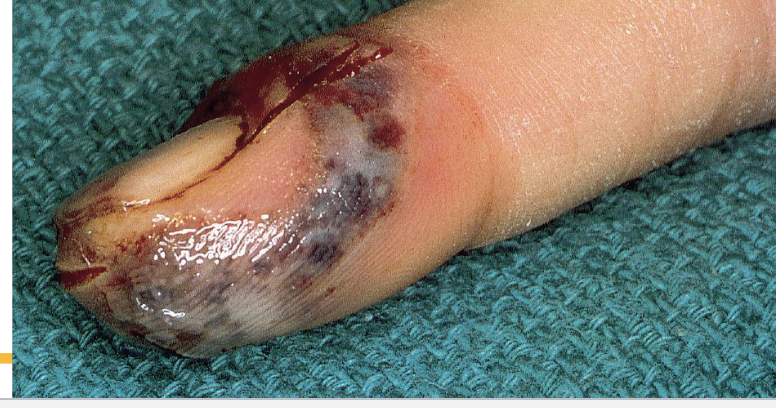
Herpetic whitlow (complication)
When Herpes penetrates the skin and causes a localized infection, usually on one finger, extremely painful and itchy
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 encephalitis
When Herpes cause inflammation of the brain (deadly)
Herpes Simplex Virus Treatment
Over the counter medication
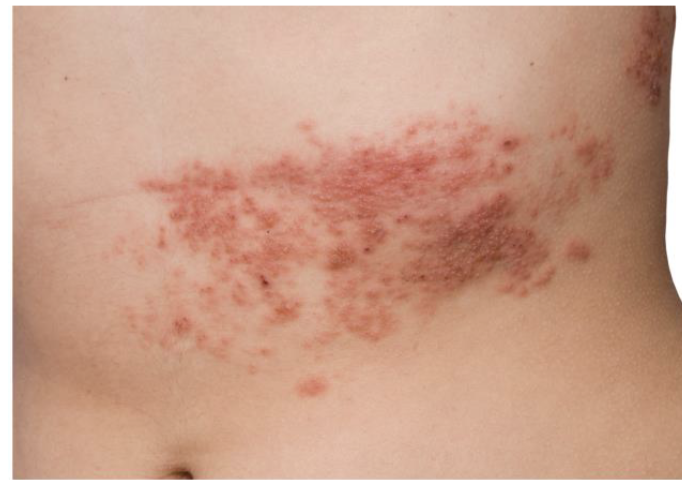
Varicella-Zoster Virus
The highly contagious virus causes a primary infection, chickenpox (Varicella), and a reactivation infection, shingles (Herpes Zoster), lives in neurons and reactivates in the neurons and goes from spine to skin
Varicella-Zoster Virus Treatment
Live attenuated vaccine (Varivax) for chickenpox and
shingles
Epstein-Barr Virus
Ubiquitous virus; infects lymphoid tissue and salivary glands, spread by infected saliva, causes sore throat and high fever
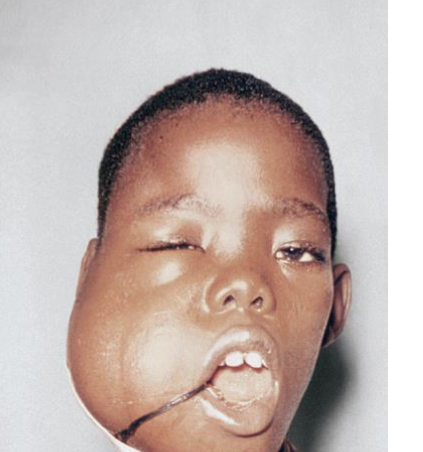
Burkitt lymphoma
Cancer in cancerous B cells that causes the cheeks and jaw to swells, commonely found in African ancestry
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Cancer of the nasopharynx, commonly associated with people of Chinese descent, involving a bleeding nose, blood saliva, etc
Hepatitis
When the liver becomes inflamed due to viral infection
Jaundice
Yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes due to the accumulation of pigments that are normally filtered out in an healthy liver
Hepatitis B virus
Multiplies exclusively in the liver, which continuously seeds
blood with viruses, increases risk of liver cancer and can lead to chronic inflammation of the liver
Papillomaviruses (Papilloma)
Causes recurring/persistent infections and tumors. Causes warts on the skin that can regress back to normal over time
Genital warts
The most common STD in the U.S. causes bumps/cauliflower like masses
Planter warts
Deep and painful warts on the foot
Common seed warts
Warts on the fingers
Influenza virus
Attaches and reproduces in cells of the respiratory tract and causes the flu, kills people through secondary infection (pneumonia) (Liquid/pus filling the lungs)
The most dangerous/infectious type of Influenza is
Influenza Type A
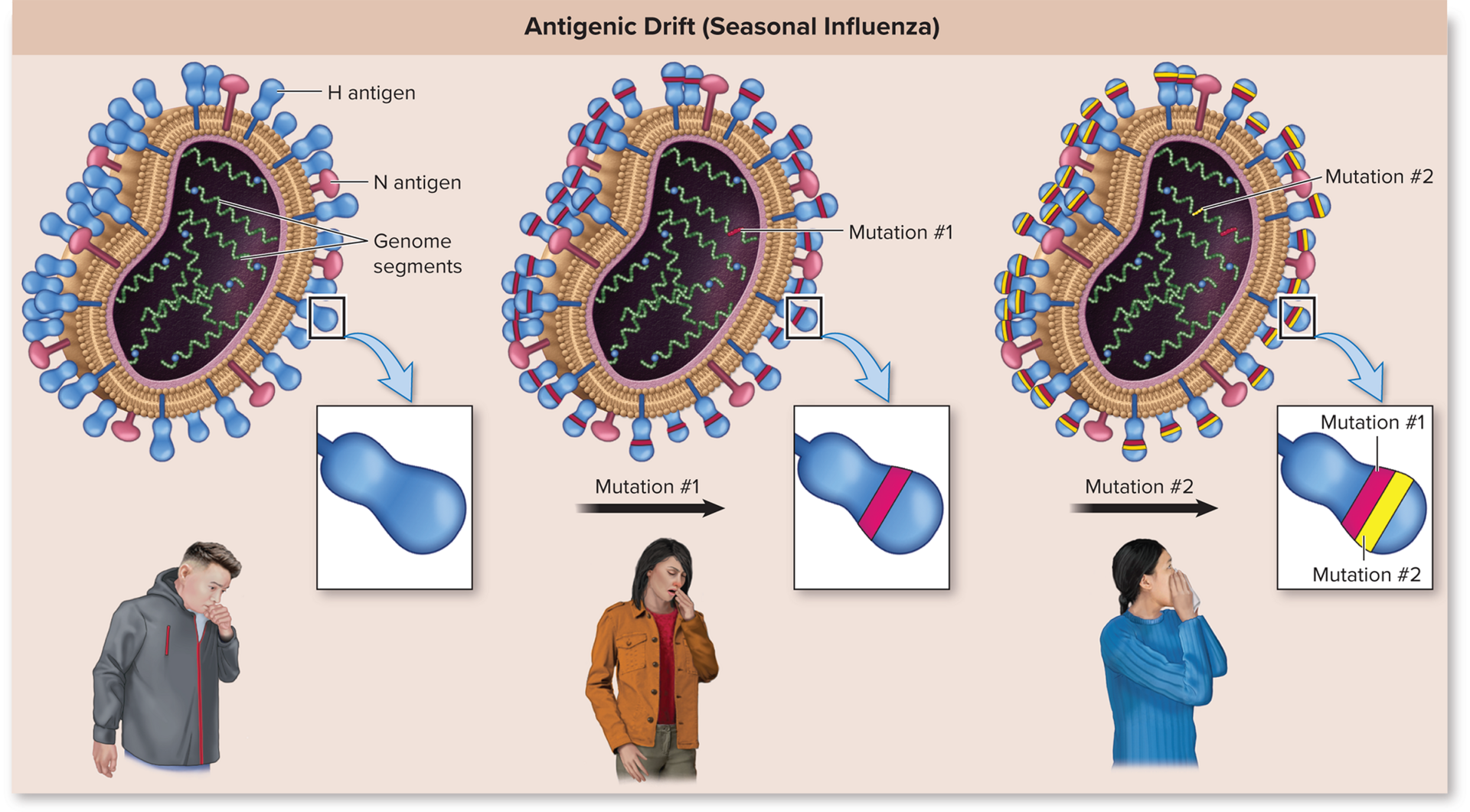
Antigenic drift
Influenza mutation where the amino acids of the virus change over time (Gradual)
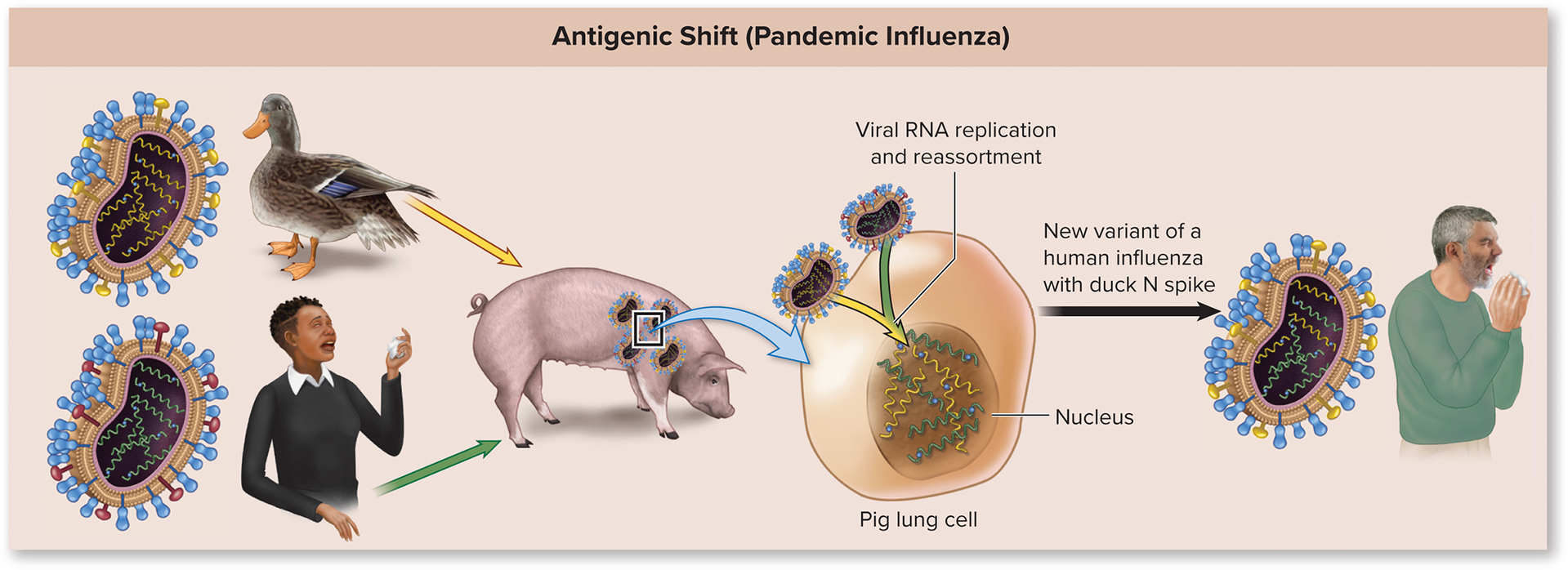
Antigenic shift
Influenza mutation where a gene/RNA strand of the virus is substituted with a gene/RNA strand from another influenza virus from a different host (Big change)
Why is the influenza vaccine so effective (Flu)
We use mathematical predictions and what’s been circulating in the other hemispheres to see which type of influenza is circulating
Why do we take the influenza vaccine seasonally? (Flu)
Because of the antigenic shift that causes influenza to mutate frequently
Hemagglutinin (H)
A molecule that causes red blood cells to clump or agglutinate. A major surface receptor on the influenza virus needed for entry.
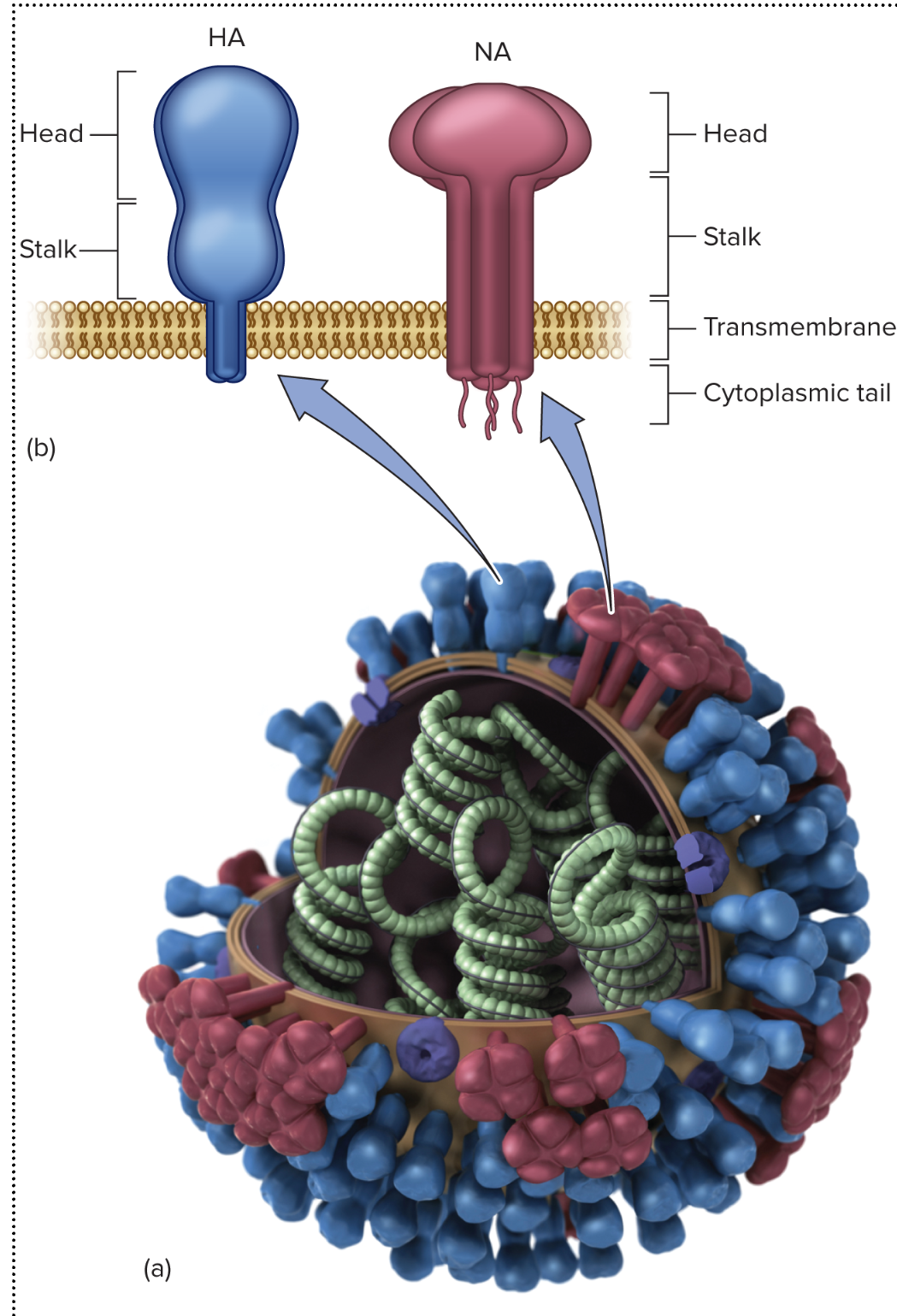
Neuraminidase (N)
A glycoprotein found in the envelope of influenza virus that facilitates release of new viruses from the host cell.
Measles
Highly infectious, spreads by respiratory aerosols, can only be found in humans, invades the respiratory tract and causes red rashes and Koplik’s spots (oral lesions)
Koplik’s spots
Oral lesions created by measles
Subacute sclerosing
panencephalitis (SSPE)
A complication of measles, leading to a progressive neurological
degeneration of the cerebral cortex, white matter, and brain
stem
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Infects the upper respiratory tract and produces giant
Multinucleate cells, commonly found in infants/babies, can be misidentified as the cold or the flu.
Rabies
Bullet-shaped zoonotic disease and commonly found in wild animals, spreads by bites, scratches and saliva droplets, multiplies at trauma sites and spreads to the spinal cord, salivary glands and brain
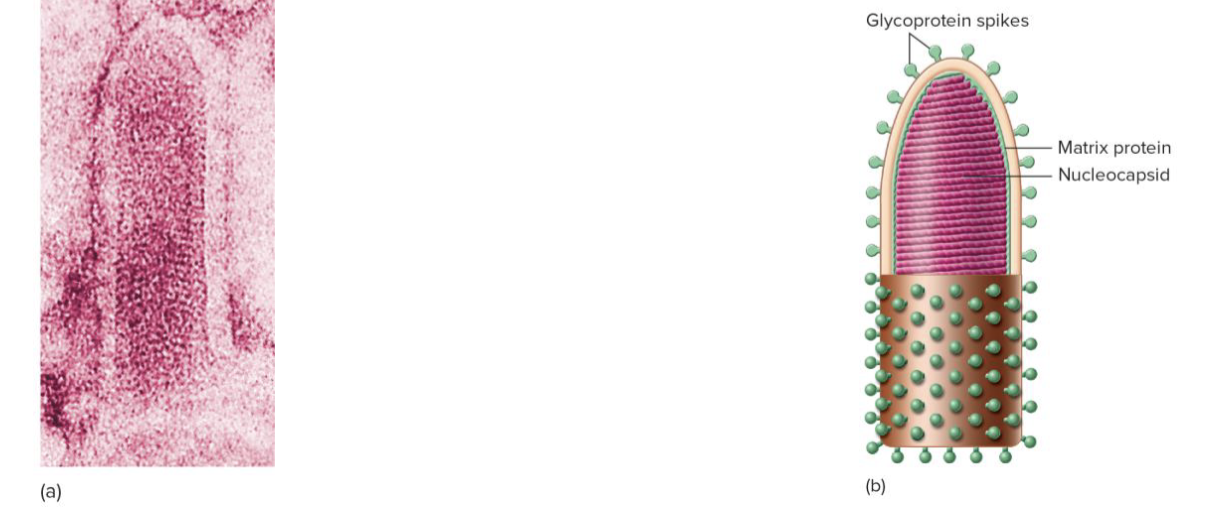
Prodromal phase (Rabies)
Fever, nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue;
some experience pain, burning, tingling sensations at site of
wound
Furious phase (Rabies)
Agitation, disorientation, seizures, twitching,
hydrophobia
Dumb phase (Rabies)
paralyzed, disoriented, stuporou
Compa phase (Rabies)
Results in death
Rabies treatment
Human diploid cell
vaccine (HDCV) and Human rabies immune globulin
(HRIG) and globulin
Negri bodies
Intracellular inclusion in nervous tissue left by the rabies virus identifiable at autopsy in the brain of animals
Rubella/German measles
Highly infectious, spreads by respiratory aerosols, can only be found in humans, invades the respiratory tract, infects children and young adults
Congenital rubella
Infection during 1st trimester most
likely to induce miscarriage or multiple defects such as
cardiac abnormalities, ocular lesions, deafness, mental
and physical retardation in the baby
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Named because it causes a deficiency of the human immune system, can convert RNA to DNA, spreads by intercourse, infected mother to child or by infected blood
(AIDS)
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
When CD4 cell levels fall below 200/mL, or their CD4 cells account for fewer than 14% of all lymphocytes
Reverse transcriptase (RT) in HIV
Enzyme which makes a
double stranded DNA from the single-stranded RNA genome,
viral genes permanently integrated into host DNA
HIV diagnosis
ELISA, Western blot analysis, latex agglutination, rapid antibody tests
Asymptomatic phase (HIV)
2 to 15 years (10 average)
Poliomyelitis/Poliovirus
Infectious by consumption (fecal oral), has acid acid-resistant capsid that can survive stomach acid, causing infection of the
spinal cord that can cause neuromuscular paralysis, usually only causes mild symptoms
Post-polio syndrome (PPS)
Progressive muscle deterioration occurs in 25-50% of patients infected with polioviruses in childhood
Paralytic Disease
Paralysis of the muscles of the legs, abdomen, back,
intercostals, diaphragm, pectoral girdle, and bladder can
result, caused by infection of the brainstem, medulla and or cranial nerve, leads to muscle atrophy and limb deformaties
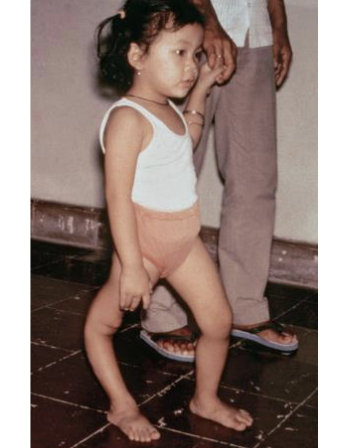
Bulbar poliomyelitis
Rare complication of Paralytic Disease, requires mechanical
respirators
Treatment of Paralytic Disease (Polio)
Inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) Salk vaccine
Reovirus
Cold-like upper respiratory infection, inflammation off the airways and the intestines
Rotavirus
Oral-fecal transmission; primary viral cause of
mortality and morbidity resulting from diarrhea in infants
and children