CH 30: duplex scanning and color flow imaging in venous evaluation
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
List the 5 reasons why a upper/lower venous exam is performed.
R/O or identify thrombus
Better accuracy than other noninvasive techniques in diagnosing calf lesions
Documents the presence of nonvascular soft tissue masses (Baker’s Cyst)
Aids in the diagnoses of venous incompetence
Evaluate for evidence of collaterals
What does ‘R/O’ stand for?
Rule out
Performing a upper/lower venous exam can be done to rule out or identify a thrombus. It can be categorized as…
________ vs. ________
_________ vs. ___________
Acute vs. Chronic
Occlusive vs. Non-occlusive
Describe venous incompetence. (2)
Valves do not maintain unidirectional flow
Retrograde flow is occurring
Define collateralization.
Other vessels have formed to bypass occluded vessel
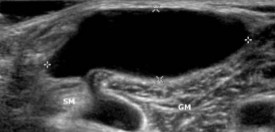
If the sonographer is scanning behind the knee/popliteal area, what pathology is seen here?
Baker’s Cyst
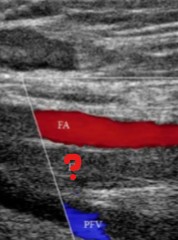
What is seen at the question mark?
Explain your answer.
Occlusive thrombus
No blood flow going through
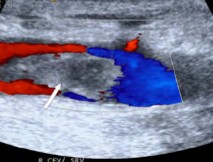
What is seen at the question mark?
Explain your answer.
Non-occlusive thrombus
Blood flow is going through
List the 5 reasons why an US exam is useful when assessing the abdominal and pelvis veins.
Documents the presence of elevated venous pressure
Identify venous thrombus
Distinguishes extrinsic from intrinsic compression
Assessing shunts
Evaluates liver disease by assessing the portal venous system
What is another term for elevated venous pressure in the MPV?
Portal hypertension
What is a disease process that can cause portal hypertension?
Cirrhosis
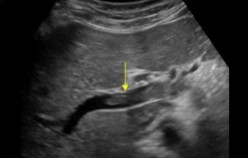
What structure is seen here?
What pathology is seen within it?
MPV
Thrombus
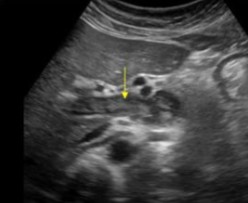
What structure is seen here?
What pathology is seen within it?
MPV
Thrombus
List the 3 limitations for a venous exam.
Edema
Recent surgery
Obesity
What is the gold standard for venous imaging?
Venogram
List the 4 sources of false positive studies for a venous exam.
Extrinsic compression
Peripheral arterial disease
COPD
Improper doppler angle or probe pressure
List the 2 sources of false negative studies for a venous exam.
Technically limited
Proximal obstruction
List a structure for a lower venous exam that can have proximal obstruction.
Iliacs
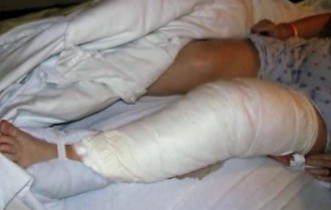
Based on this image, what did the patient just have?
Surgery
When performing a venous exam, the sonographer should ensure that the vein is identified by the appropriate landmarks such as the…
Accompanying artery
When performing a venous exam, the sonographer will find that the vein lies _______ to the artery.
Medial
In what plane should the vein be visualized to ensure complete compressibility?
Transverse
What is the number 1 way to determine if there’s a thrombus on US?
Compression
Velocity signals should be obtained in the (1)_________ view to maximize the (2)_________________.
Sagittal
Doppler shift
If the sonographer wants to maximize color fill and flow patterns, what 5 settings should be adjusted?
Decreasing scale
Decrease wall filter
Increase color gain
Steer color box in the appropriate direction
Heel toe transducer to optimize angle of insonation
Decreasing scale will help to detect what?
Slow flow
What is another term for ‘heel toeing’ the probe?
Rocking
When the sonographer wants color fill in the vessel, how should the vessel not be on the screen to obtain this?
Straight across
Color box steering is done to change what?
The angle of insonation
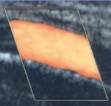
Is this color box steered in the right or wrong direction?
Explain your answer. (2)
Right
Small angle
Good image

Is this color box steered in the right or wrong direction?
Explain your answer. (2)
Wrong
Moderate angle
Flow is not optimal

Is this color box steered in the right or wrong direction?
Explain your answer. (2)
Wrong
Large angle
Unusable image
If the sonographer is seeing crazy aliasing and bleed out, what can be done to fix this?
Increase scale
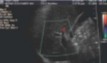
Color flow is not seen here.
The screen reads that velocity scale is at 69 cm/s.
What should be done to correct this issue?
Decrease scale
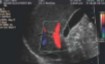
Color flow is seen well here.
The screen reads that velocity scale is at 30 cm/s.
What should be done to correct this issue?
Nothing, color fills fine
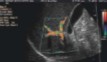
Color aliasing is seen in the portal vein and its branches.
The screen reads that velocity scale is at 2 cm/s.
What should be done to correct this issue?
Increase scale
Adjusting color wall filter will adjust the filter setting displayed on (1)_______ scale ((2)____________ arrow))
Color
Horizontal
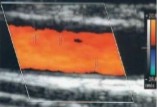
If we are talking about color wall filter, explain why the vessel appears this way. (2)
Wall filter is too high
Removing low flow

If we are talking about color wall filter, explain why the vessel appears this way. (2)
Wall filter is reduced
Displaying low flow
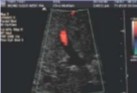
Color gain is set at 44% and this was seen on US.
Is this an adequate image to have or what should be done to correct it?
No, increase color gain
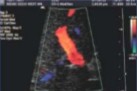
Color gain is set at 65% and this was seen on US.
Is this an adequate image to have or what should be done to correct it?
Yes, adequate image
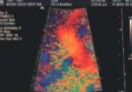
Color gain is set at 100% and this was seen on US.
Is this an adequate image to have or what should be done to correct it?
No, decrease color gain
Color gain should eb set as high as possible with the exception of not displaying…
Random color speckles
To facilitate venous filling in the evaluation of a DVT, how should the patient be positioned?
Reverse Trendelenburg
Describe the reverse Trendelenburg position.
When the feet are lower than the head and heart
Why does the sonographer set the patient in a reverse Trendelenburg position for a venous exam?
Allows the legs to fill with more blood
To evaluate for venous reflux, describe how the patient will be positioned? (3)
Standing
Extremity evaluated should be in non-weight bearing state
All weight should be on the contralateral extremity
When performing a venous exam, what plane is scanned in first?
Explain your answer.
Transverse
To assess complete compressibility of the vein walls
In the sagittal view of a venous exam, Doppler signals are evaluated for what 3 factors?
Spontaneity
Phasicity
Augmentation with distal compression and proximal release
Proximal release can also be done in the form of what ‘maneuver’?
Valsalva
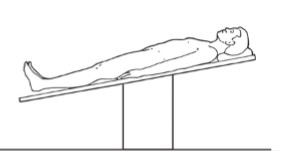
What patient positioning is seen here?
The patient in this position is used to evaluate for what pathology?
Reverse Trendelenburg
DVT
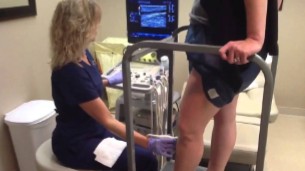
Why is this patient standing during the exam?
Will the extremity scanned be in a weight bearing or non-weight bearing state?
To evaluate for venous reflux
Non-weight bearing state
What is the name of the area where the GSV and CFV join together?
Saphenofemoral junction (SFJ)
List the 2 vessels involved in the SFJ.
GSV
CFV
Why is the SFJ evaluated carefully?
Because thrombus in a superficial system near the deep system requires more aggressive treatment
Which requires more aggressive treatment?
Thrombus in the superficial system near the deep system
Thrombus in the superficial system
Thrombus in the superficial system near the deep system
At some point, it is difficult to image the femoral vein.
Explain why.
Explain how this can be maneuvered to improve visualization.
Dives deep distally
Scanning at the posterior thigh, near the popliteal fossa
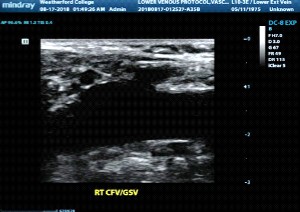
Where is the sonographer scanning in this image?
Will a thrombus here be a cause for concern?
If yes, why is that?
SFJ
Yes
Because it’s near the deep system, which can require more aggressive treatment
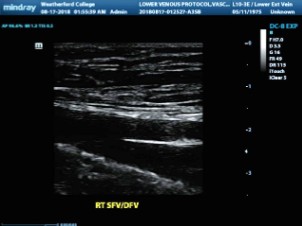
Where is the sonographer scanning in this image?
Will a thrombus here be a cause for concern?
If yes, why is that?
SFV and DFV (Profunda Femoris)
Yes
Thrombus would be in the deep system
Is the superficial femoral vein apart of the superficial or deep venous system?
Deep venous system
Where does the popliteal vein become the femoral vein?
Adductor Canal/Hunter’s Canal
The femoral vein will become the popliteal vein at what area?
Adductor Canal/Hunter’s Canal
What does the popliteal vein become at the Adductor Canal/Hunter’s Canal?
Femoral vein
List the 2 veins that form the popliteal vein in the calf area?
ATV
Tibio-Peroneal Trunk
The ATVs an Tibio-Peroneal trunk come together to form what vessel?
Popliteal vein
What pathology should the sonographer be on the look out for when scanning the popliteal vein? (2)
Cystic structures
Masses (Baker’s Cyst)
When we move the probe distally from the popliteal vein, what 2 other veins can we see around the popliteal area?
Gastrocnemius veins
Small saphenous vein (SSV)
When scanning in the popliteal area, what should the sonographer carefully evaluate for? (Aside from cystic structures and masses, BE SPECIFIC)
Thrombus where the SSV joins the popliteal vein
The sonographer scans behind the knee and carefully evaluates when the SSV joins the popliteal vein for a thrombus.
Why is that connection important to monitor for thrombus?
Because that’s where the superficial system joins with the deep system
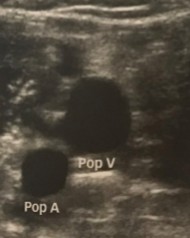
In what area are we scanning to see these vessels?
Behind the knee/Popliteal fossa
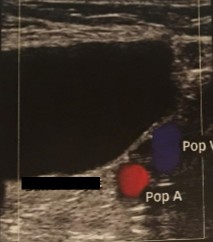
The sonographer is scanning behind the knee during a venous exam and stumbles upon this anechoic finding.
What can be assumed here?
Baker’s Cyst
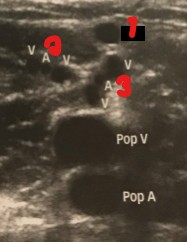
Label the other vessels seen in this image.
SSV (small saphenous vein)
Lateral Gastrocnemius Vein
Medial Gastrocnemius Vein
What is the medial malleolus?
Bone on the medial side of the ankle and achilles tendon
Where should the probe be placed to locate the PTVs?
Between the medial malleolus and achilles tendon
Where can the peroneal veins be located?
A few centimeters up the calf
Which appears ‘deeper’ on US?
Peroneal Veins
PTVs
Peroneal Veins
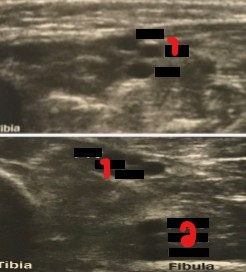
Label the vessels crossed out on the image.
PTVs
Peroneal veins
Where can we locate the peroneal veins?
Which appears more ‘posterior’ on US? PTVs or Peros?
Few centimeters up the calf
Peroneal Vein
What position is used for examining chronic venous insufficiency?
Standing
List the 2 types of techniques used for a chronic venous insufficiency exam.
Manual
Automatic cuff inflator
When performing a chronic venous insufficiency exam, it is important that the leg examined has no…
Weight bearing
During a chronic venous insufficiency exam, while the vein of interest is being imaged and evaluated with spectral analysis, what movement is the patient asked to perform to determine the presence/absence of venous reflux?
Valsalva
On a pulse wave doppler, when a patient performs the Valsalva maneuver, how should the waveform appear?
Halted
During a chronic venous insufficiency exam, after the sonographer has had the patient Valsalva, when is then done?
What does this observe for?
Distal compressions
Presence/Absence of reflux with augmentation
List the 2 manual techniques that occurs during a chronic venous insufficiency exam.
With the techniques, explain what is looked for when this technique is performed?
Valsalva - Presence/Absence of venous reflux
Distal compression - Presence/absence of reflux with augmentation
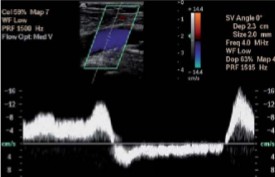
The sonographer is performing a chronic venous insufficiency exam. When the sonographer applies distal compressions, this waveform was seen.
Describe the appearance of this waveform.
This waveform can indicate the presence/absence of…
Augmented
Reflux
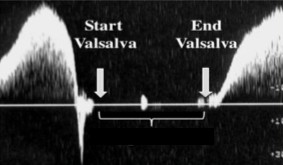
The sonographer is performing a chronic venous insufficiency exam. When the sonographer tells the patient to valsalva, this waveform was seen.
Describe the appearance of this waveform.
This waveform can indicate the presence/absence of…
Halted
Venous reflux
For the chronic venous insufficiency exam, the sonographer is using an automatic cuff inflator.
What kind of cuff is used?
Where is it placed when evaluating the CFV?
12×40 cm
High-thigh level
For a chronic venous insufficiency exam, where is the automatic cuff inflator placed to evaluate the popliteal vein and GSV?
Calf level
For a chronic venous insufficiency exam, where is the automatic cuff inflator placed to evaluate the PTVs?
Trans-Metatarsal level
For the chronic venous insufficiency exam using an automatic cuff inflator, the duplex system is used to obtain what 2 things?
Image
Waveform
Where should the transducer be placed when using an automatic cuff inflator?
Proximal to the cuff
Because our transducer is placed proximal to the automatic cuff inflator, what other maneuver is it essentially mimicking?
Distal compressions OR Augmentation
For the chronic venous insufficiency exam using automatic cuff inflators, when optimal doppler signals are obtained, what is then done? (2)
The cuff is inflated to 80 mmHg
Maintained for 1-2 seconds
For the chronic venous insufficiency exam using automatic cuff inflators, after the cuff has been inflated, it will then deflate by the (1)_________/_______ or manually.
What should the sonographer note for after cuff deflation?
Auto-inflator/deflator
Reversal of venous flow
For the chronic venous insufficiency exam using automatic cuff inflators, after inflation and deflation, if the sonographer notes reversal of venous reflux (flow reversal), what 2 things are measured?
PSV
Duration of flow reversal
For the chronic venous insufficiency exam using automatic cuff inflators, when noting the duration of flow reversal, what units will it be recorded in?
Seconds
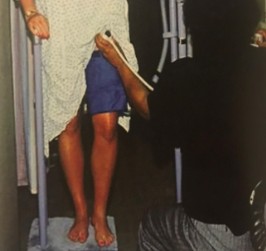
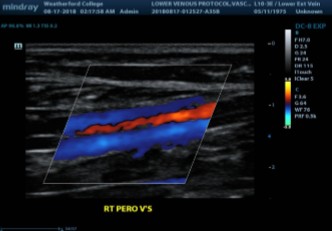
What exam is being performed here?
Chronic venous insufficiency
How much is the automatic cuff inflator inflated to when evaluating the CFV?
80 mmHg
How much is the automatic cuff inflator inflated to when evaluating the popliteal vein and GSV?
100 mmHg