Physio Lect 15 - Cardiac Cycle
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
How does blood enter the heart?
Flows in through the inferior vena cava
After entering the atrium, what valve opens to allow blood to flow into the right ventricle?
Tricuspid valve
After flowing into the right ventricle, where does the blood flow during contraction?
Out through the pulmonary artery to the lungs
T/F: Arteries always flow away from the heart.
T
T/F: Veins always flow away from the heart.
F, Veins always flow TO the heart.
From the lungs, where does the blood flow?
Back to the heart via the pulmonary vein
Where does the blood flow from the pulmonary vein?
Into the left atria
What valve does the blood pass through to enter the left ventricle?
Mitral valve
What valve does the blood pass through to leave the heart after the left ventricle contracts?
Aortic Valve
Where does the blood go after leaving the heart via the aortic valve?
Passes through aorta.
Does the circulation of blood happen synchronously on both sides of the heart?
Yes!
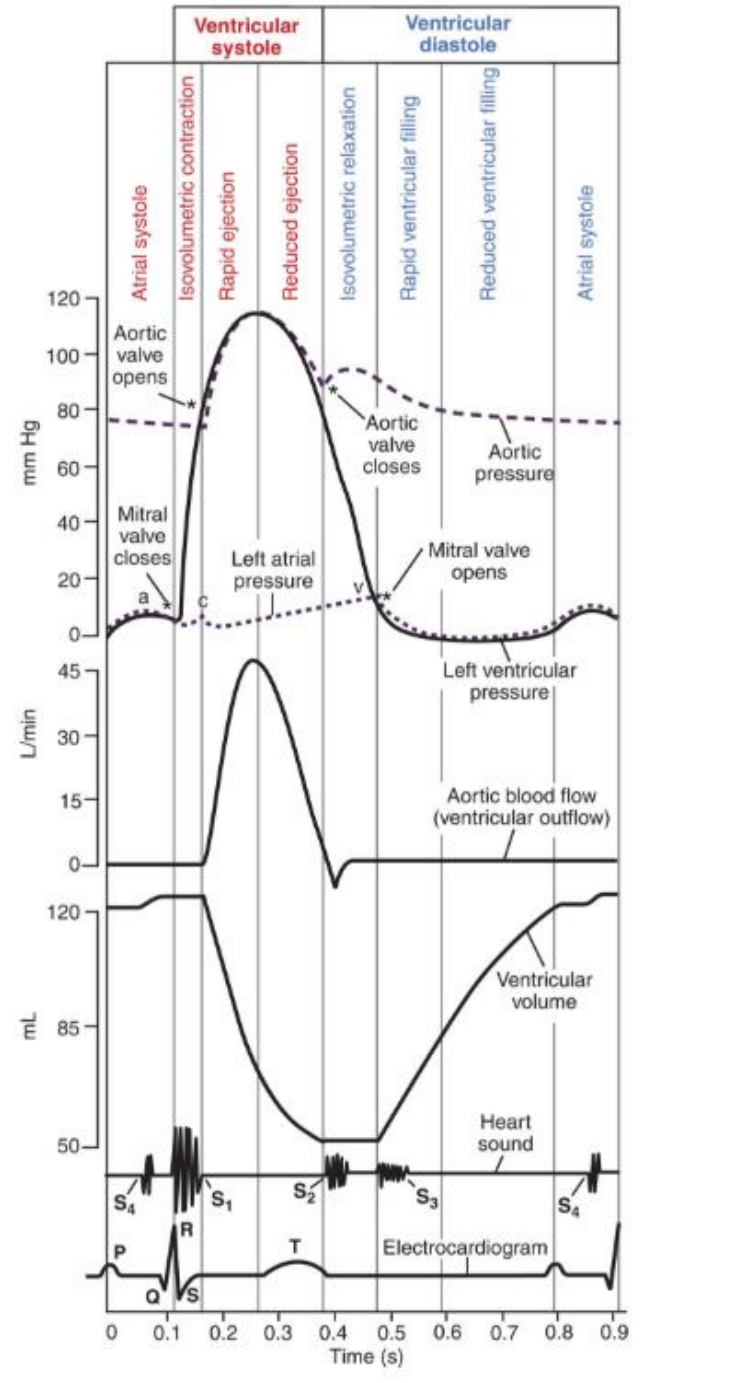
When does the P-wave in the heart start related to Wigger’s diagram?
Right before atrial systole (atrial contraction)
T/F: There is always some volume of blood in the heart after each heartbeat.
T
T/F: Blood flow in the aorta is opposite volume in the left ventricle.
T
Which takes longer in the heart, the systole or diastole process?
diastole
How many phases are there in ventricular systole?
4
How many phases are there in ventricular diastole?
4
What occurs during Atrial Systole? What wave on an ECG coincides with this phase? What valves open? What valves close?
Coincides with P-Wave. A-V valve opens, semilunar valves close.
What happens during isovolumetric contraction?
All the valves close
What happens during Rapid Ejection? What valves are open? Which valves are closed?
Sarcomere shortens. Aortic and pulmonic valves open, AV valves remain closed.
What happens during reduced ejection? What valves are open, which are closed?
Aortic and pulmonic valves are open, AV valves remain closed.
What happens during isovolumetric relaxation?
All blood is out of left ventricle. All valves are closed. Lowest volume in the heart.
What happens during rapid ventricular filling? Which valves are open, which are closed?
Ventricular pressure decreases lower than atrial pressure. AV Valves are open and semilunar valves are closed.
When we say semilunar valves, which valves are we referring to?
Aortic and Pulmonary
What happens during reduced ventricular filling?
The AV valves are open, semilunar are closed.
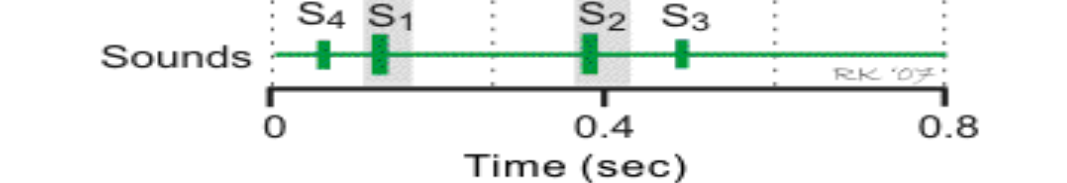
When we talk about the sounds of the heart, what causes S1?
the closing of the mitral valve
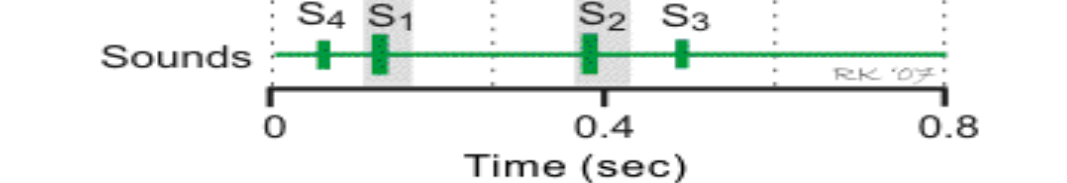
When we talk about the sounds of the heart, what causes S2?
The closing of the aortic valve
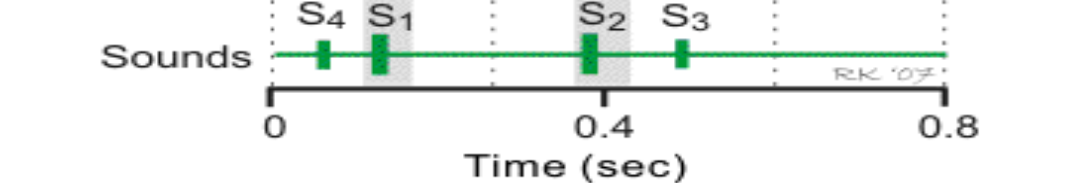
When we talk about the sounds of the heart, what causes S3?
Pathology, occurs during diastole
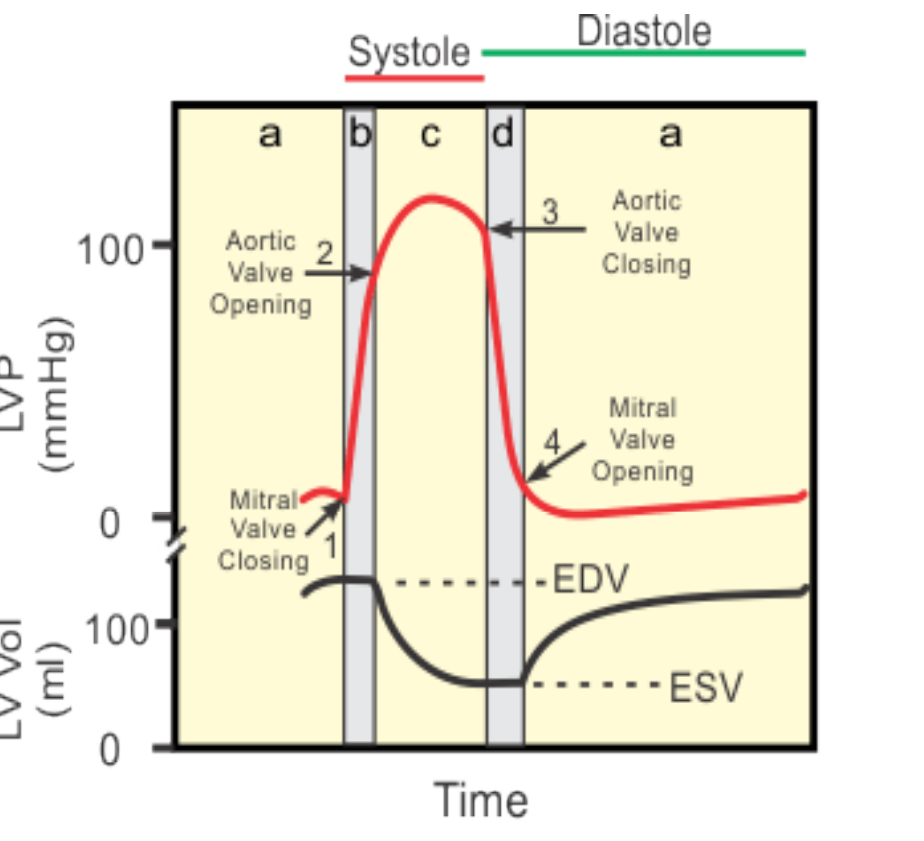
Take a moment to look at the Wigger’s diagram and understand how we can translate it to the Pressure Volume Loop: (flip back and forth on this slide)
Make sure you’re comfortable reading either one of these diagrams, the information could be presented either way and there was emphasis on knowing this.
EDV - End Diastolic Volume
ESV - End Systolic Volume
Know when valves open and close
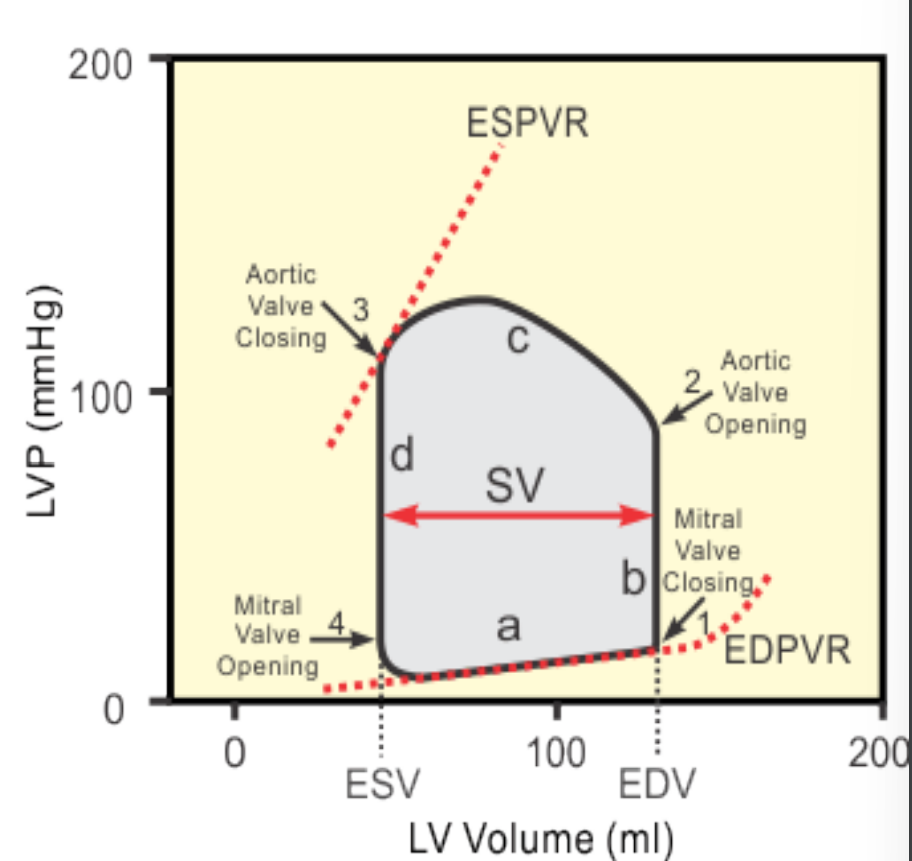
What happens when the pressure in the left ventricle is higher than in the left atria?
Mitral valve closes, we get isovolumic contraction
T/F: The heart works at maximal load most of the time.
F, the heart usually operates at submaximal load, allows the heart to increase function as needed.
What is the primary function of the heart?
to impart energy to the blood
What is the formula for cardiac output?
CO = SV*HR
Cardiac output = Stroke Volume * Heartrate
How many determinants effect stroke volume?
3
What is a normal value for cardiac output?
6 liters/minute resting, 17.5 liters/minute exercising.
What are the 3 determinants of stroke volume?
Preload, afterload, inotropic state.
When we say Atrioventricular valves, which valves are we referring to?
Tricuspid, Mitral