1A +1B Conditioning and social Cognitive Theory, Behaviorism
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
1\. Imagine you would like to train a dog to get the newspaper out of the mailbox. Which form of conditioning would you use and how would you do this?
positive reinforcement operant conditioning → most successful conditing
* pairing a positive behavior with positive reinforcement
* pairing a positive behavior with positive reinforcement
2
New cards
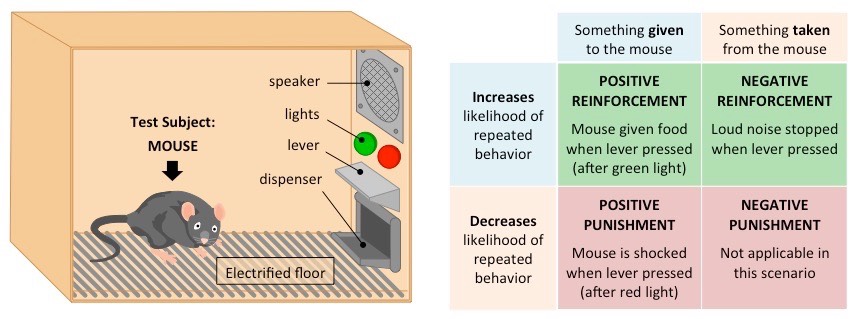
what are the different ways to do operate conditions?
* positive reinforcement
* negative reinforcement
* positive punishment
* negative punishment
* negative reinforcement
* positive punishment
* negative punishment
3
New cards
2\. What is the main difference between operant and Classical conditioning?
4
New cards
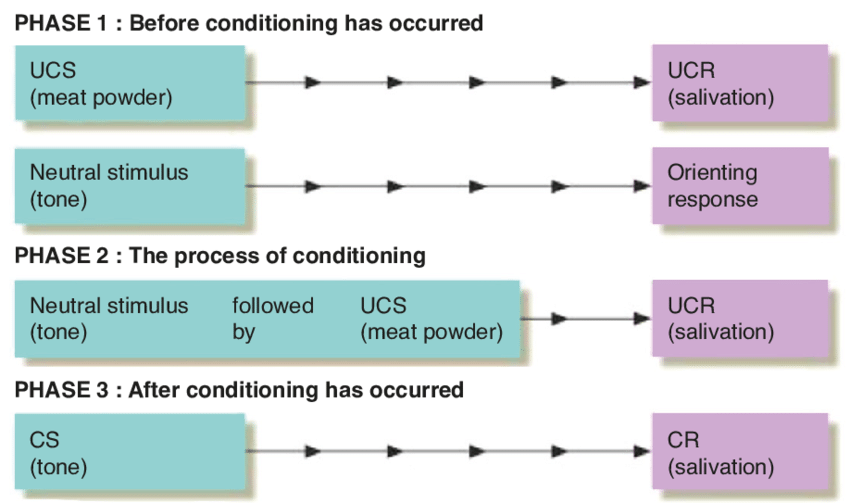
how does classical conditioning work?
organism associates a neutral stimulues(NS) with a conditioned response(CR)
5
New cards
3\. Why is the learning-performance distinction such an important concept in Social Cognitive Theory?
6
New cards
what is learning? And what are the criteria of learning?
“Learning is an **enduring change in behavior**, or in the capacity to behave in a given fashion, which results from practice or other forms of experience.”
^^criteria of learning:^^
* earning involves change
* learning endures over time
* learning occurs through experience
^^criteria of learning:^^
* earning involves change
* learning endures over time
* learning occurs through experience
7
New cards
1\. How does human learning differ from animal learning?
human learning is more **complex, elaborate, raid** and involves more **languag**e
\
\
8
New cards
2\. What is the difference between rationalism and empiricism?
**Rationalism**: information is acquired with our 5 senses → true knowledge, or the knowledge of ideas, is innate and is brought into awareness through reflection
**Empiricism**: experience is the only source of knowledge and at birth, we are *tabula rasa* ( blank tablet)
**Empiricism**: experience is the only source of knowledge and at birth, we are *tabula rasa* ( blank tablet)
9
New cards
Who are representative of rationalism and empiricism?
**Rationalism:**
* Plato
* Immanuel Kant
**Empiricism:**
* Aristotle
* Plato
* Immanuel Kant
**Empiricism:**
* Aristotle
10
New cards
3\. How do we know that learning has taken place?
long term change in behavior
11
New cards
4\. How long should a memory or skill last to be considered as “learned”?
\
12
New cards
5\. “The whole is greater than the sum of its parts”. What is the point Gestalt psychologists were trying to make here?
even though we can study small things like behavior and this can be very insightful, gestalt psychology emphasizes that the complexes of everything explains human cognition and behavior( therefore also taking into account, group dynamics, developmental, social factor)
13
New cards
6\. Why was the opening of the first psychological laboratory by Wundt so important for the field of psychology?
* was the cause for first **psychological journal**
* was the important step between the philosophical start of psychology and to real **scientific experimentation and instrumentation**
* was the important step between the philosophical start of psychology and to real **scientific experimentation and instrumentation**
14
New cards
7\. Although his experiments were a bit questionable, Ebbinghaus was an important figure in the history of psychology. Why?
* he was **pioneer** of bringing **higher mental processes into experimental laboratory**
* helped validate and introduce systematic **experimental method** into psychology
* he did a lot of experiments about memory and learning
* possible **biased bad validity** because he only did experiments on himself
\
* helped validate and introduce systematic **experimental method** into psychology
* he did a lot of experiments about memory and learning
* possible **biased bad validity** because he only did experiments on himself
\
15
New cards
9\. Structuralists relied on the method of introspection. What is it and why is its use problematic?
it is when you verbally announce how you experience/perceive the external world without addressing cognitions.
* Problematic because :
* unreliable because you had to learn it and difficult to asses if that if you are doing it correctly
* Problematic because :
* unreliable because you had to learn it and difficult to asses if that if you are doing it correctly
16
New cards
what is the main point functionalist propose?
* consciousness is a **continuous process** rather than a collection of discrete bits of information
* the purpose of **consciousness** as helping individuals **adapt to** their **environments**
* the purpose of **consciousness** as helping individuals **adapt to** their **environments**
17
New cards
10\. When and why should you conduct experimental studies?
Experimental: One or more variables are altered and effects on other variables are assessed
→ to find causale relationships: cause and effect
→ to find causale relationships: cause and effect
18
New cards
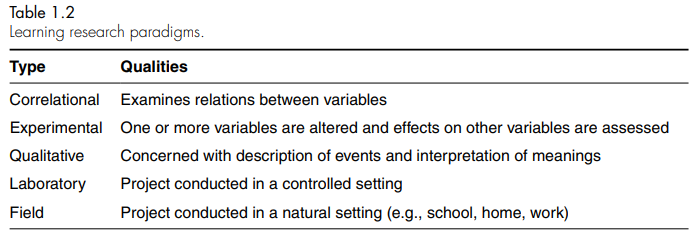
what are the different types of research paradigms?
19
New cards
11\. Why is the assessment of learning to some extent problematic?
* most of the time, we only look at the results of learning, like grades
* we neglect overall understanding problem just if we see a the right behavior it does not mean they did it for the right reasons
* we neglect overall understanding problem just if we see a the right behavior it does not mean they did it for the right reasons
20
New cards
12\. In assessment, what is the problem with direct observations?
* subjective
* does not address cognition of the other person
* does not address cognition of the other person
21
New cards
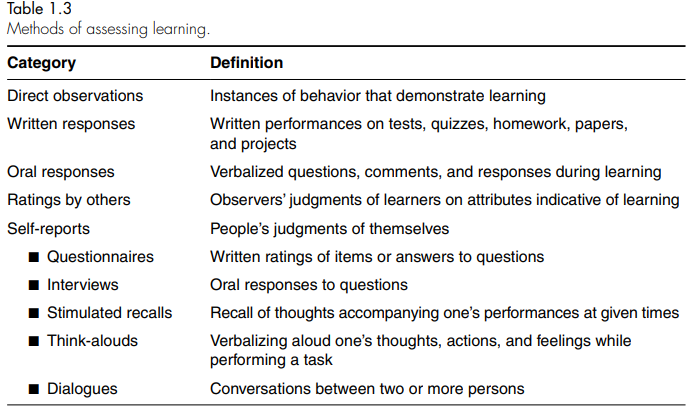
what are the different methods of assssing learning?
22
New cards
1. What is the main difference between modern education and that of 100 years ago?
* nowadays learning teachers use more student-focused approaches
* the skills needed for learning are more → level of literacy; ability to think critically; ability to problem solve
* emphasis is now less about remembering and repeating and more about being able to applying knowledge
* the skills needed for learning are more → level of literacy; ability to think critically; ability to problem solve
* emphasis is now less about remembering and repeating and more about being able to applying knowledge
23
New cards
2\. How does trial-and-error learning work?
Learning by doing spontaneous behavior which results is a positive or negative event → this experience not remembered and does not give future insight to a similar problem
24
New cards
3\. We make a distinction between Behaviorism and behaviorism. Why?
* big B → traditional “old school” approach of behaviorism
* small b → modern approach of behaviorism takes into account internal processes are an important factor
* small b → modern approach of behaviorism takes into account internal processes are an important factor
25
New cards
4\. Why is the use of pre-existing knowledge so important in an educational setting and what is the link with constructivism?
* teachers know where they can teaching about new conepts → which topics need more time
* easier to rember when if you can sort new knowlege into pre-existing knowlh
* easier to rember when if you can sort new knowlege into pre-existing knowlh
26
New cards
5\. How good are you predicting your grades and what has this to do with “metacognition”?
**Metacognition:** refers to people’s abilities to predict their performances on various tasks
27
New cards
7\. Is lecture-based learning less good than inquiry-based learning? The authors argue that in general this is not a good question. Why?
* lecture-based and inquiry based learning address two different goals
* lecture based lecture→ understand information
* inquiry based lectures-> deepen understanding through experience and make facts and ideas manageable
* lecture based lecture→ understand information
* inquiry based lectures-> deepen understanding through experience and make facts and ideas manageable
28
New cards
8\. The role of formative assessment has become very important in modern education. Why?
formative assesment: assesment that is only made to help the teacher and studnent acknowlege on what knowlge level they are
* provied feedback for studnet + teachers
* guide modicfiation and refeinments to class/ study structure
* provied feedback for studnet + teachers
* guide modicfiation and refeinments to class/ study structure