In-Depth Notes on Human Reproduction
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Indiana University bloomington Biology 112
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Sexual reproduction
the fusion of male and female gametes to develop a zygote
Asexual reproduction
producing a offspring without the fusion of gametes, resulting in genetically identical clones of the parent.
Budding
Mechanism of Asexual reproduction: new individuals develop from a bud on the parent organism.
Example: In Hydra, a portion buds out and grows into an adult.
binary fission
Mechanism of Asexual reproduction: a single organism is divided into two equal parts, producing two new organisms. (bacteria/amoeba)
Example: In bacteria, the cell replicates its chromosomes and divides into two diploid cells.
Fragmentation
Mechanism of Asexual reproduction: a parent organism breaks into pieces, and each piece develops into a new organism.
Example: Segmenting an earthworm can produce multiple adults from cut pieces.
Twofold cost
The evolutionary cost of sexual reproduction as females have half the amount of daughters compared to asexual females, limiting population growth.
illustration: Starting with one female in asexual reproduction results in all female progeny, while sexual reproduction results in half female and half male.
Hermaphroditism
An individual has both male and female reproductive systems and can reproduce with themselves or other hermaphrodites (snails, worms)
sex reversal
Some species can change sex ratios; for instance, certain oysters exhibit male-to-female or female-to-male changes.
External fertilization mechanisms
Methods of fertilization that occur outside the female's body→ the eggs are shed and then fertalized
commonly seen in aquatic organisms like fish and amphibians.
Internal fertilization mechanisms
Sperm is deposited in or near the female reproduced tract leading to fertilization occurring inside the female's body. This process is typical in terrestrial animals, ensuring higher survival rates for embryos.
Temperature regulation in the male reproductive system
Sperm production requires low temperatures then the bodies coreto ensure optimal sperm viability and function. This is typically managed by the scrotum, which keeps the testes cooler than the internal body temperature.
Seminiferous tubules
coiled tubes in the testes where sperm is produced
Leydig cells
Secrete testosterone and are found in between the seminiferous tubules
Sertoli cells
provide nutritional support for germ cell development (nurse cells)
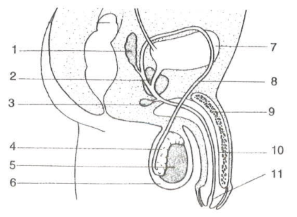
Lable the penis
Scrotum
The pouch of skin that holds the testes and helps regulate their temperature external to the body.
Testes
The male reproductive glands that produce sperm and hormones, primarily testosterone, and are located in the scrotum.
Epididymis
A coiled tube that stores and matures sperm, located behind each testis.
Vas deferens
The duct that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct as part of the male reproductive system.
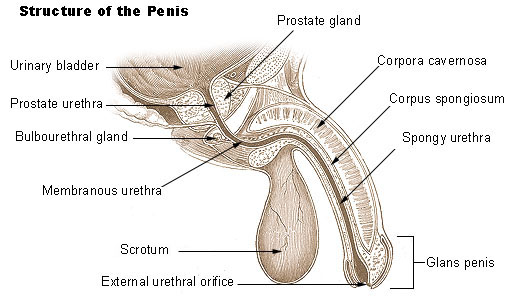
prostate
A gland located below the bladder produces a fluid that nourishes and transports sperm during ejaculation.
prostate gland
secretes its products directly into the urethra through several small ducts – buffer pH
Penis structure
Composed of three cylinders of erectile tissue, which fill with blood during arousal, causing an erection.
The head of the penis (glands) is sensitive, covered by foreskin.
Urethra
The duct that carries urine from the bladder and sperm from the reproductive system to the outside of the body.
Ejaculation process
From the testis > seminiferous tubules > sperm pass into the coiled duct of the epididymis > vas deferens > ampulla > seminal vesicle > ejaculatory duct, > urethra
Semen
Consists of sperm, fructose (energy for sperm), prostaglandins (triggers contractions), buffer (neutralized urine acidity), and mucus (liberation)
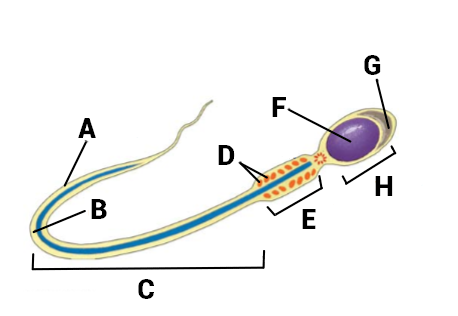
Lable the sperm
A- Tail sheath
B- Flagellum
C- Tail
D- Mitocondria
E- Midpiece
F- Nucleus
G- Acrosome
H- Head
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm cell development within the male reproductive system, occurring in the testicles.
Takes about 7-10 weeks for sperm to mature, with an approximate cycle of 74 days.
Meiosis leads from primordial germ cells to mature sperm
Male hormonal regulation of reproduction
Hypothalamus releases Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH), stimulating anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
Inhibin is secreted by Sertoli cells to provide negative feedback to the anterior pituitary.
FSH and LH hormones
FSH promotes Sertoli cells, aiding in spermatogenesis. LH stimulates Leydig cells for testosterone production (in the gonads
Testosterone
The primary male sex hormone, produced mainly by Leydig cells in the testes, is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and the regulation of spermatogenesis.
regulates the production of GnRH, FSH, & LH through negative feedback mechanisms
Inhibin
secretes Sertoli cells that reduces FSH secretion
Estrogen
A primary female sex hormone, produced mainly by the ovaries, crucial for the regulation of the menstrual cycle and the development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
Ovaries
Female reproductive organs that produce eggs and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
Oviducts
Also known as fallopian tubes, structures connecting the ovaries to the uterus, facilitating the transport of eggs and the site of fertilization
Endometrium
Lining of the uterus that thickens during the menstrual cycle in preparation for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
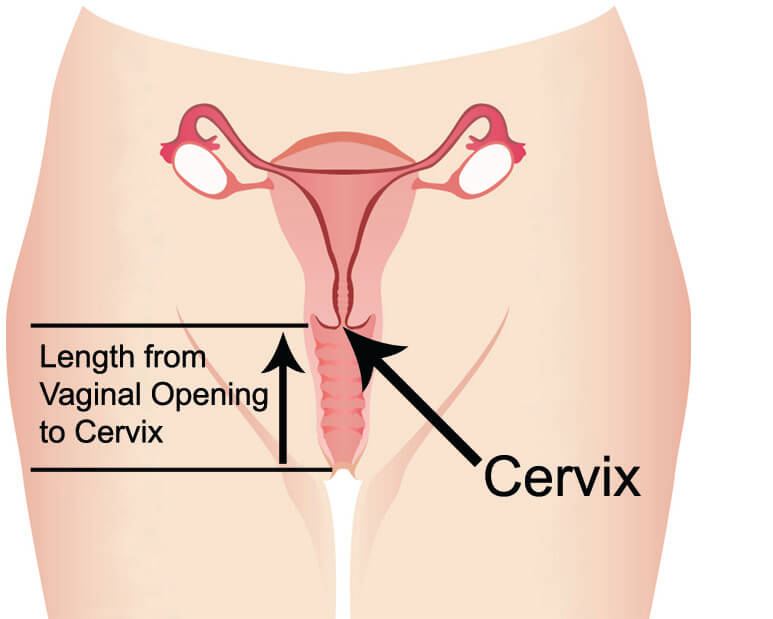
Cervix
The lower, narrow end of the uterus (womb) that connects the uterus to the vagina (birth canal), plays a crucial role during labor and menstruation.
Clitoris
A small, sensitive organ located at the top of the vulva, it plays a key role in female sexual arousal and pleasure.
Mammary glands
Glands in the breasts that produce milk during lactation and play a vital role in nourishing infants.
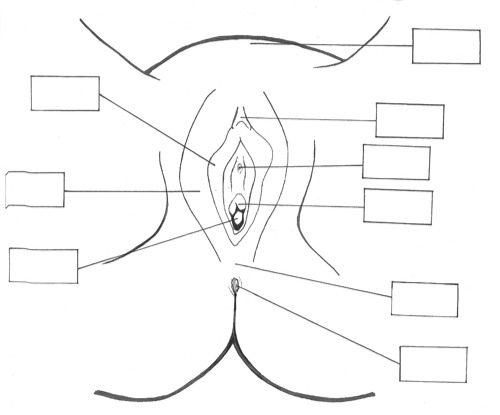
Lable the vulva
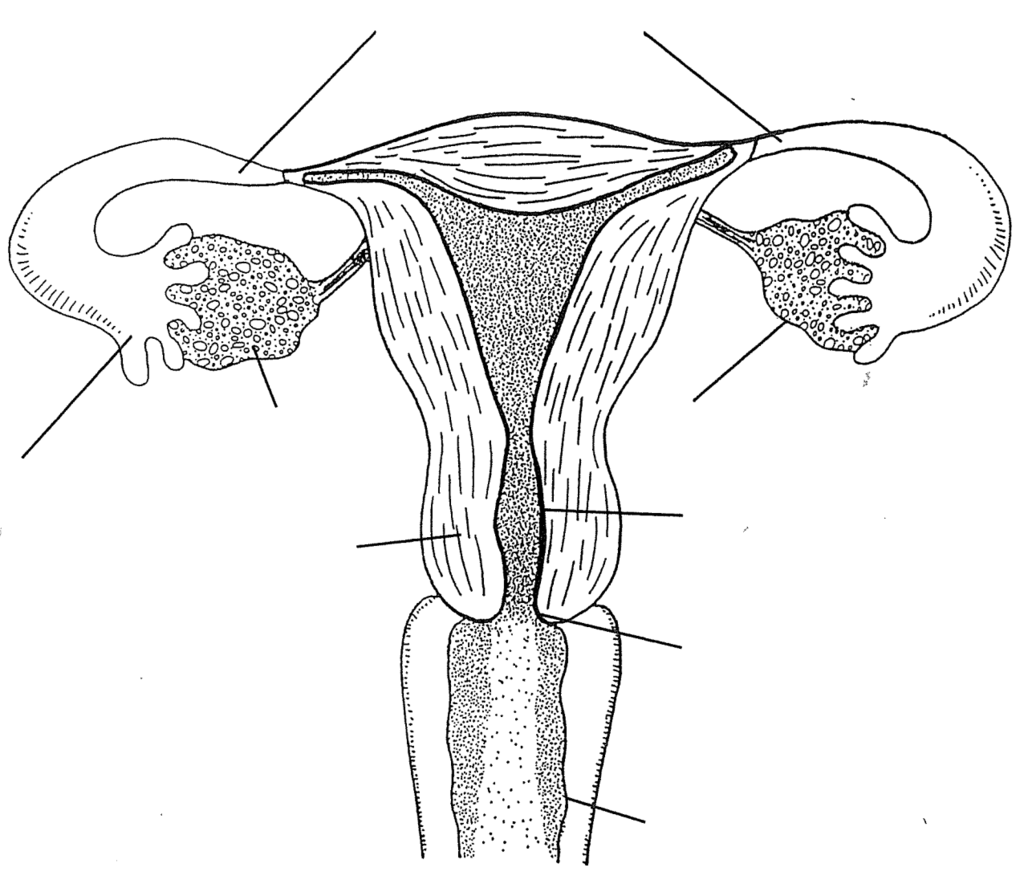
Lable the vagina
Oogenesis
The process of egg cell formation in females, occurring in the ovaries. It involves meiosis and results in the development of mature ovum(s) for fertilization.
At puberty, one primary oocyte matures and is ovulated approximately every 28 days.
Ovarian cycle
The sequential release of GnRH then FSH & LH stimulates follicle growth
Follicle growth & an increase in the hormone estradiol characterize the follicular phase
The follicular phase ends at ovulation & the secondary oocyte is released
Luteal phase
The phase of the ovarian cycle that follows ovulation, characterized by the formation of the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to prepare the uterine lining for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
progesterone
A hormone produced by the corpus luteum that maintains the uterine lining during the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle, facilitating implantation. From a negative Feeback on the hypothalamus and pituitary
estradiol
A form of estrogen produced primarily by the ovaries, playing a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and promoting the growth of the uterine lining. From a negative Feeback on the hypothalamus and pituitary
Menstruation cycle
divided into three phases: menstrual flow phase, proliferative phase, and secretory phase. If no implantation occurs, menstruation begins again.
Menopause
The natural cessation of menstruation and ovarian function, marking the end of a woman's reproductive years, usually occurring between ages 45 and 55.