Unit 5 AP Psychology (Cognition)
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
memory
the persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of information.

encoding
the processing of information into the memory system—for example, by extracting meaning.

storage
the retention of encoded information over time.
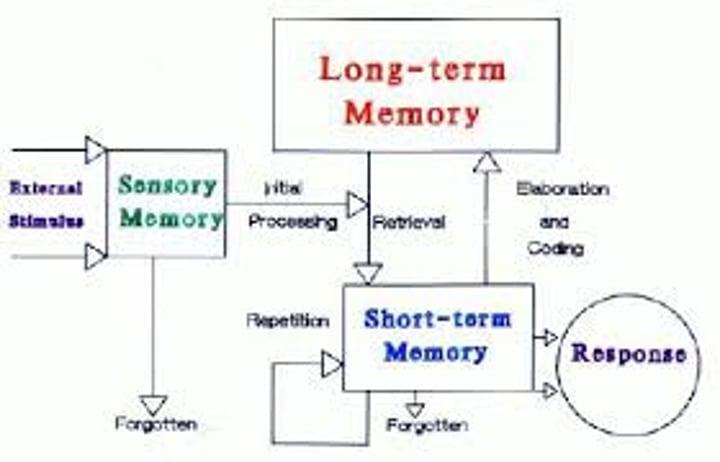
retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage.
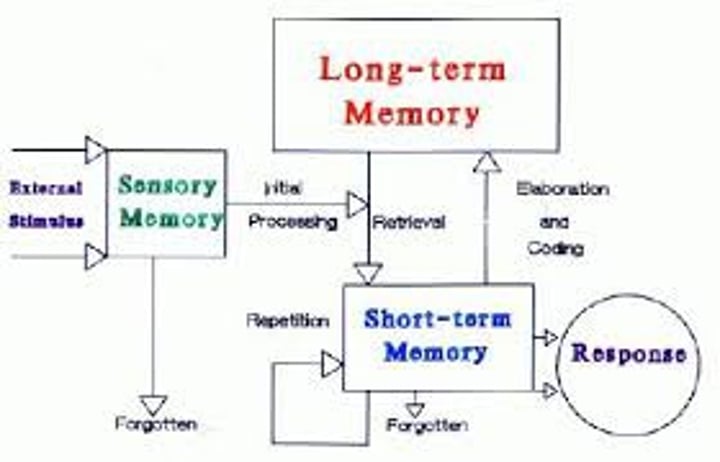
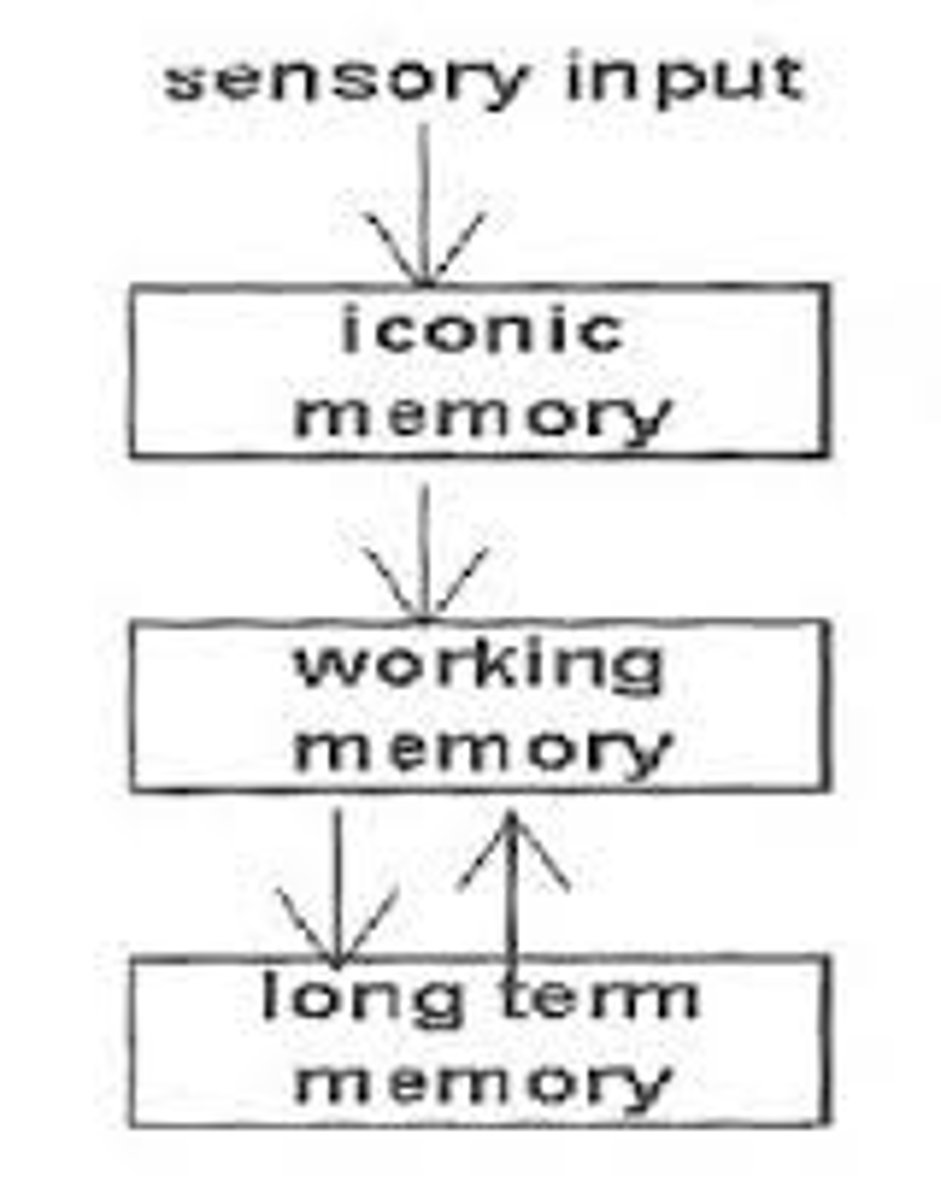
sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system.
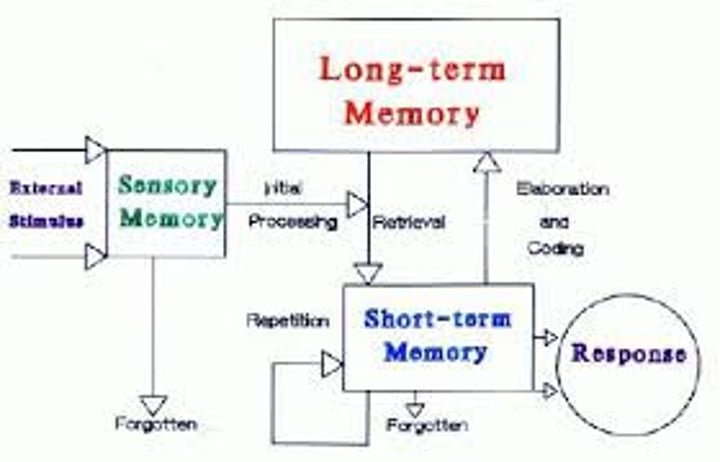
short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly, such as the seven digits of a phone number while dialing, before the information is stored or forgotten.
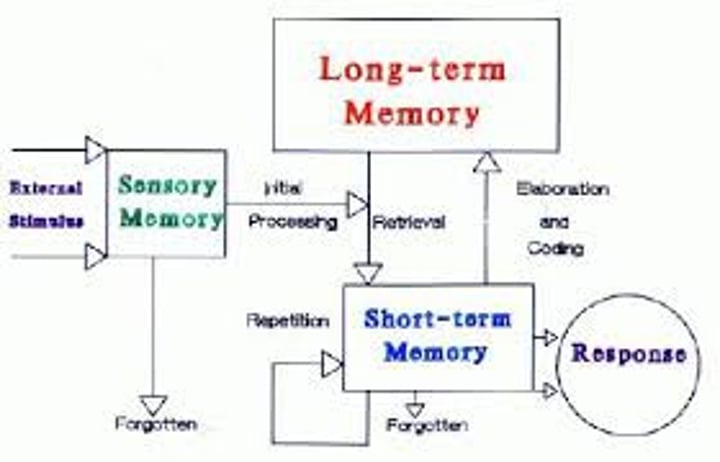
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences.
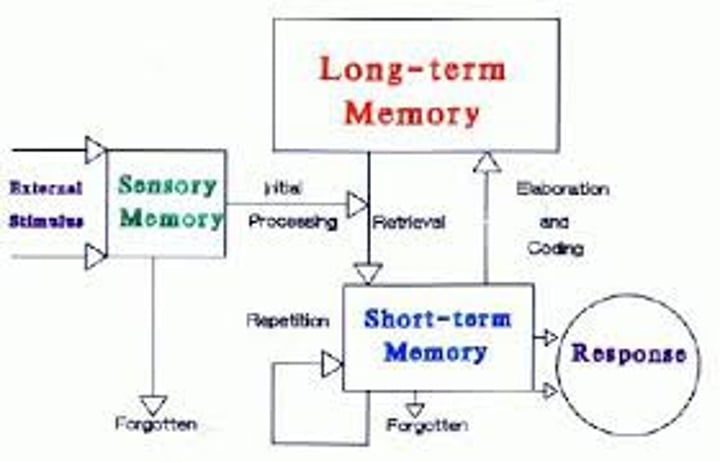
working memory
a newer understanding of short-term memory that focuses on conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual-spatial information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory.
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information, such as word meanings.
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort.

rehearsal
the conscious repetition of information, either to maintain it in consciousness or to encode it for storage.

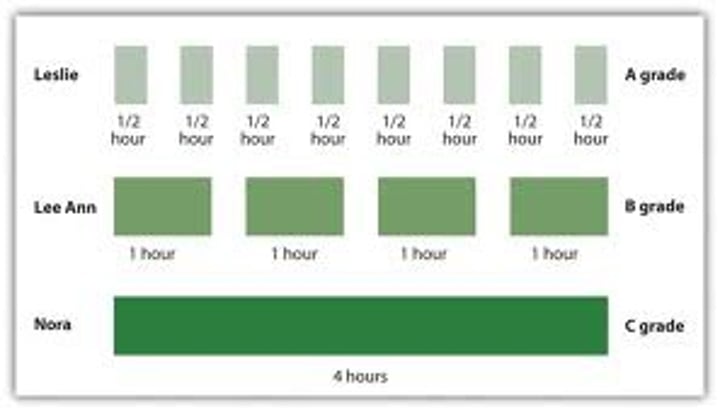
spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice.
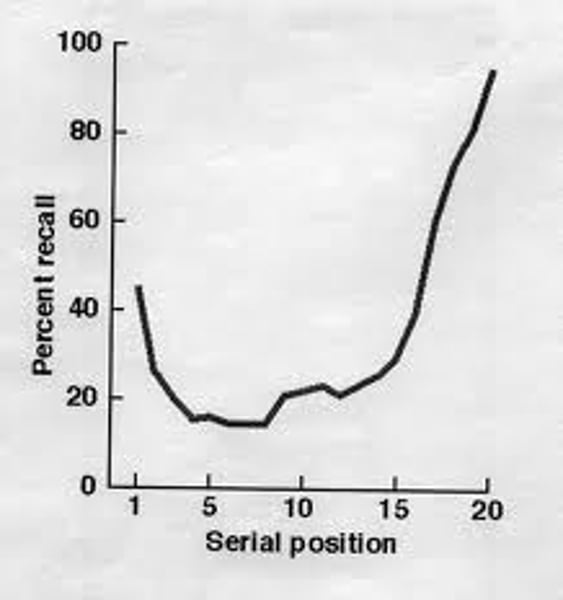
serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last and first items in a list.
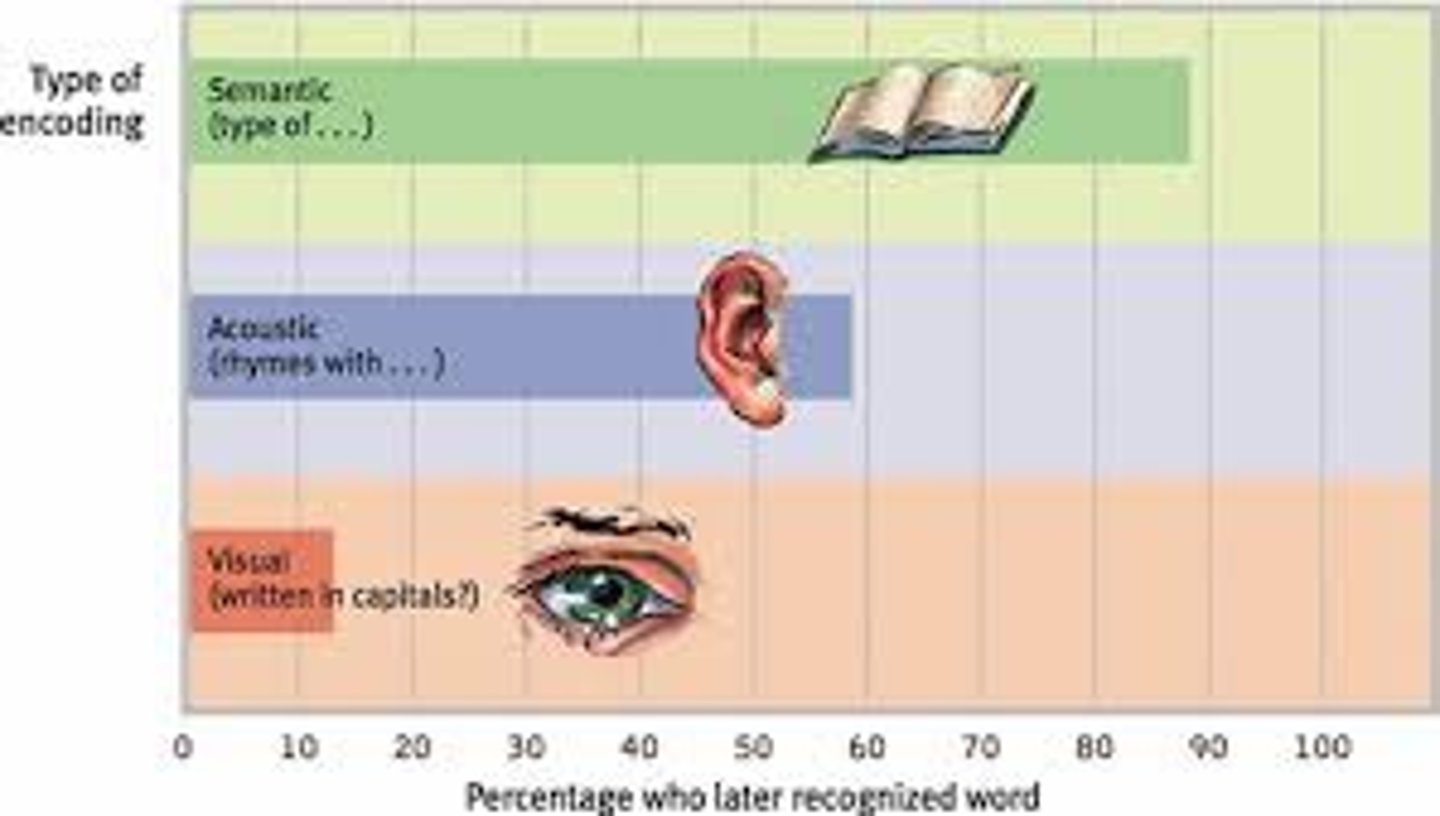
visual encoding
the encoding of picture images.

acoustic encoding
the encoding of sound, especially the sound of words.
semantic encoding
the encoding of meaning, including the meaning of words.
imagery
mental pictures; a powerful aid to effortful processing, especially when combined with semantic encoding.
mnemonics
memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices.

chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically.

iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second.
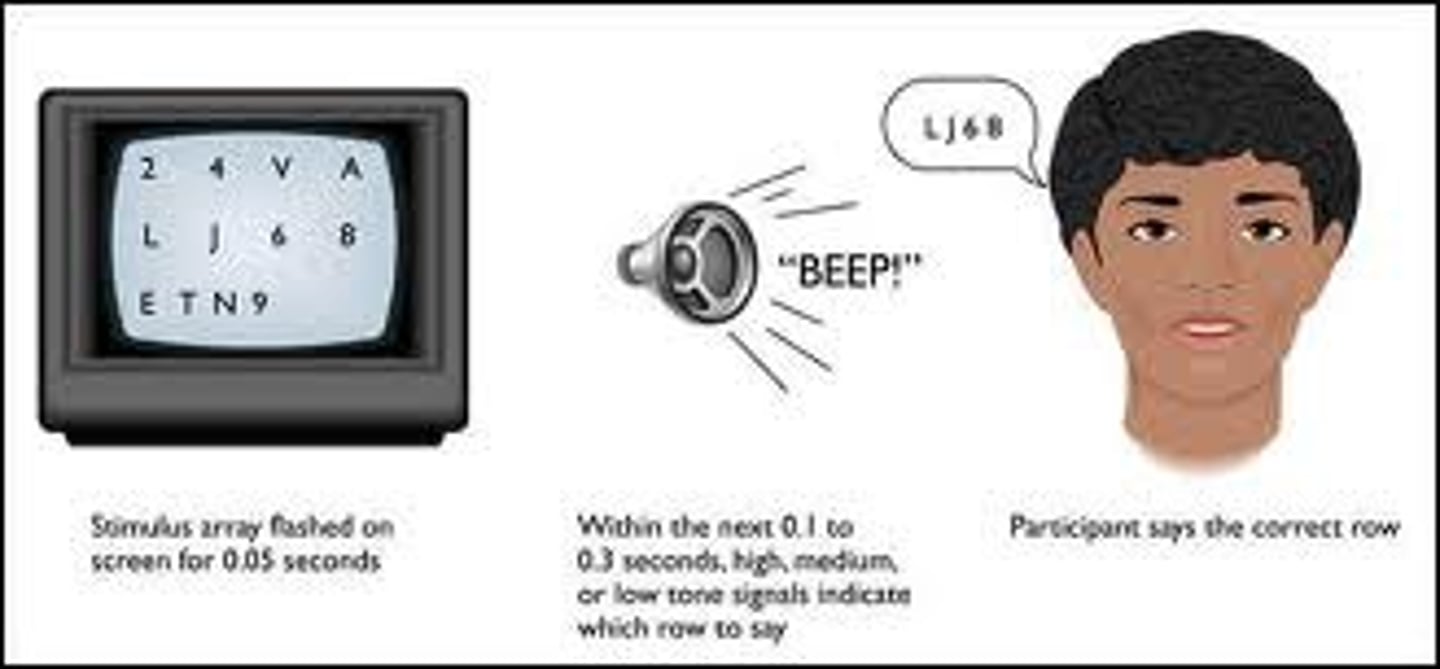
echoic memory
A momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds.
long-term potentiation (LTP)
an increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation. Believed to be a neural basis for learning and memory.

flashbulb memory
a clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event.

amnesia
the loss of memory.

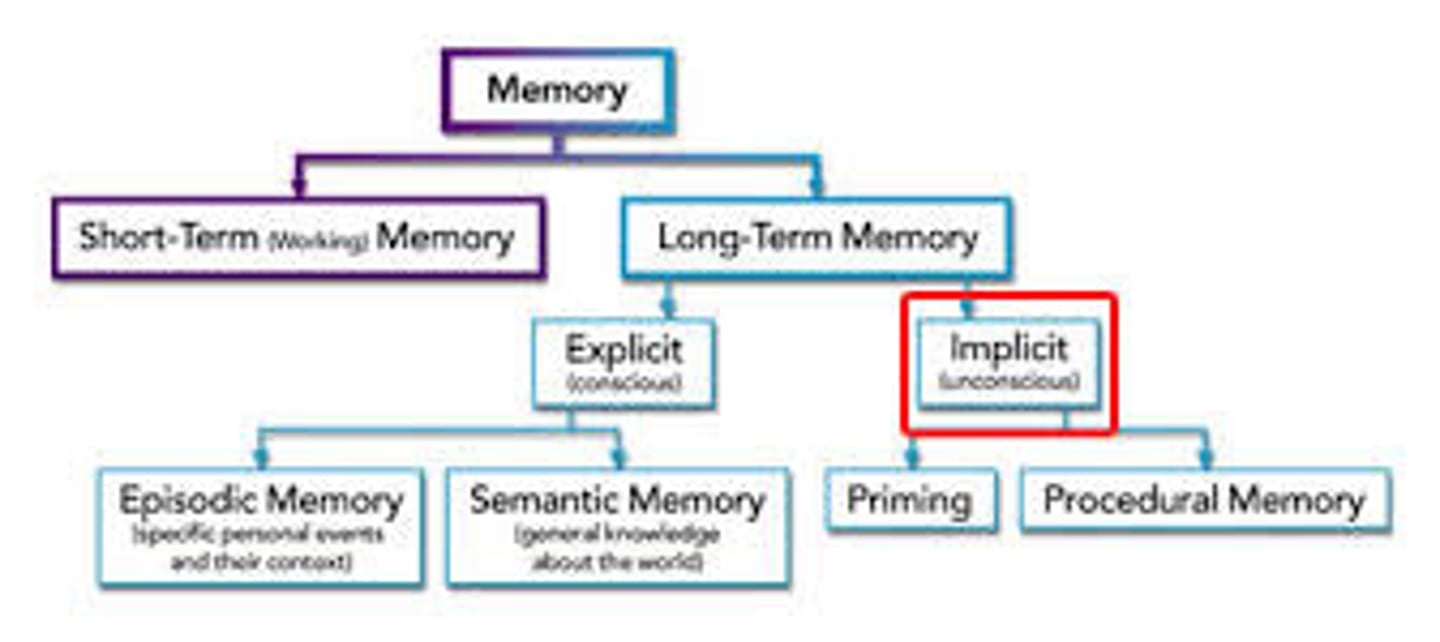
implicit memory
retention independent of conscious recollection. (Also called non-declarative or procedural memory.)
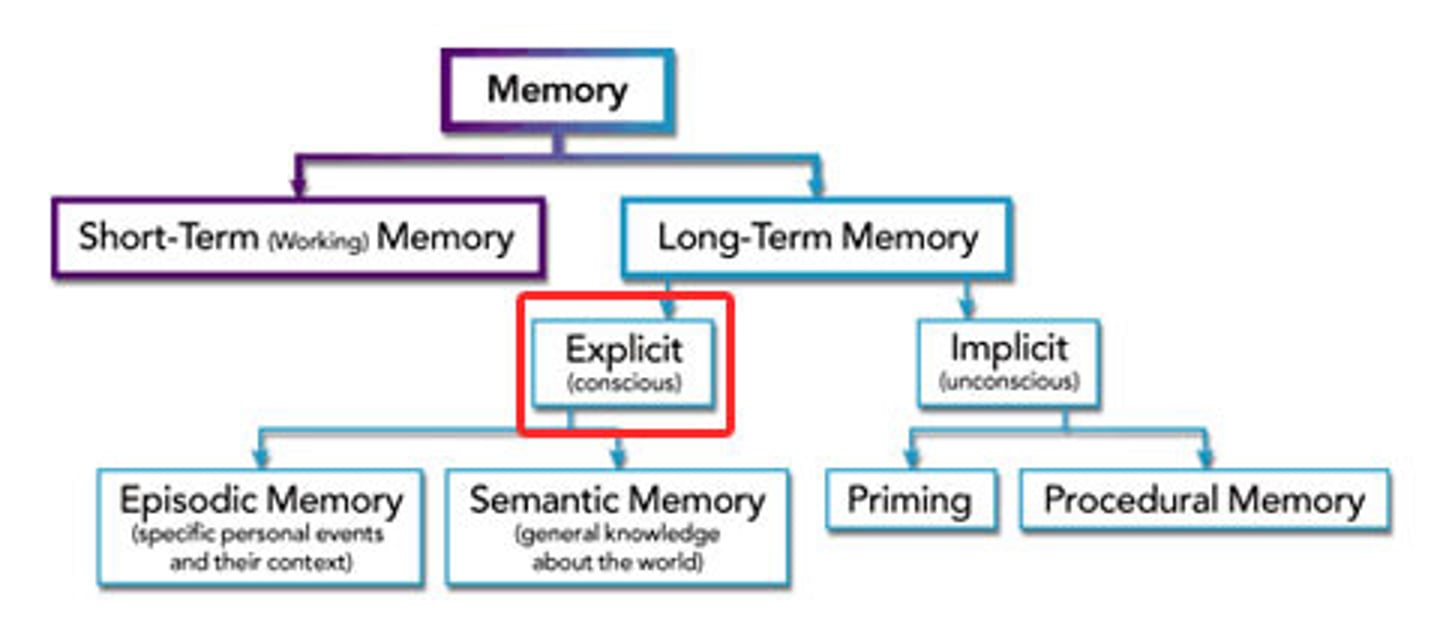
explicit memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare." (Also called declarative memory.)
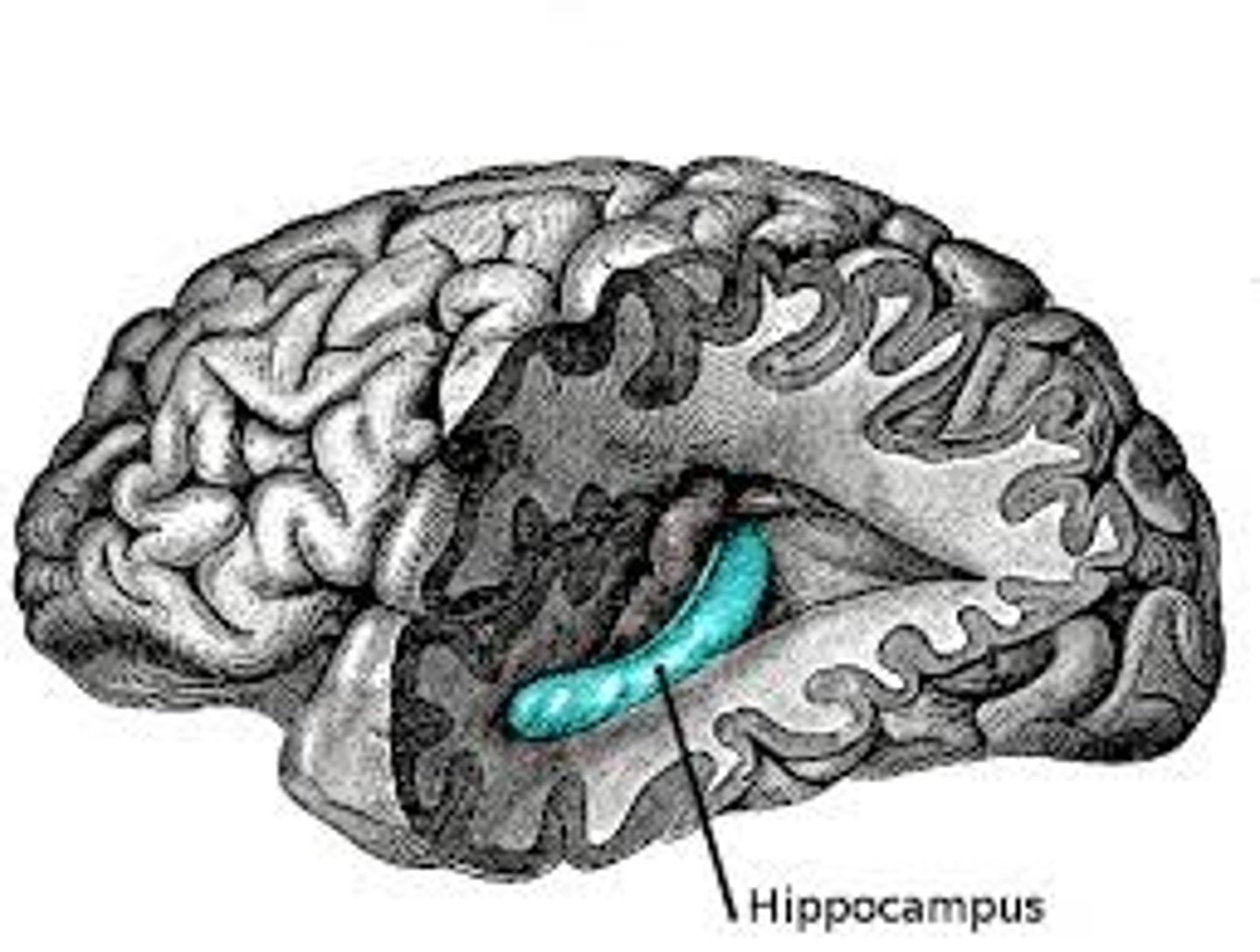
hippocampus
a neural center that is located in the limbic system; helps process explicit memories for storage.
recall
a measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test.

recognition
a measure of memory in which the person need only identify items previously learned, as on a multiple-choice test.

relearning
a measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material for a second time.

priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one's perception, memory, or response.

déjà vu
that eerie sense that "I've experienced this before." Cues from the current situation may subconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience.

mood-congruent memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current good or bad mood.

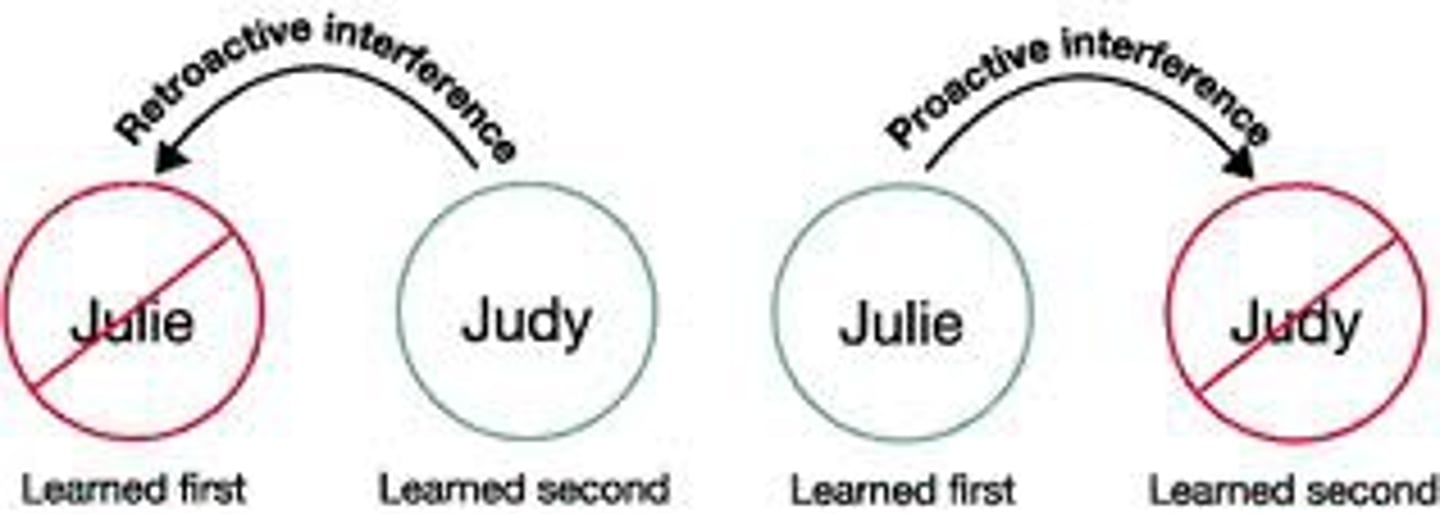
proactive interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information.
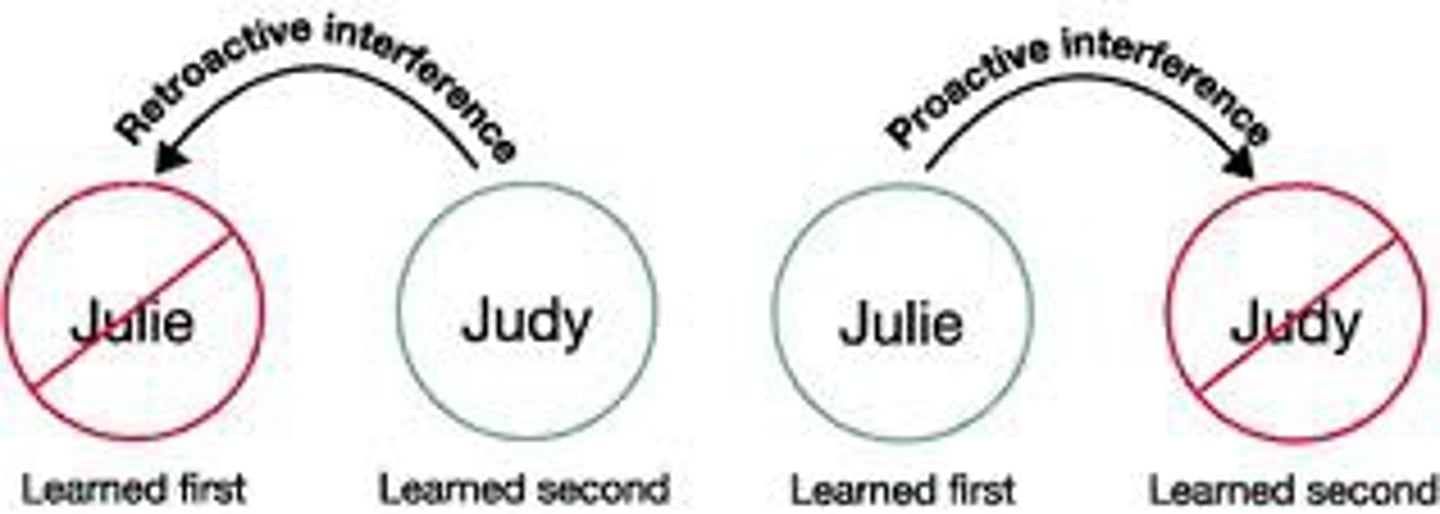
retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information.
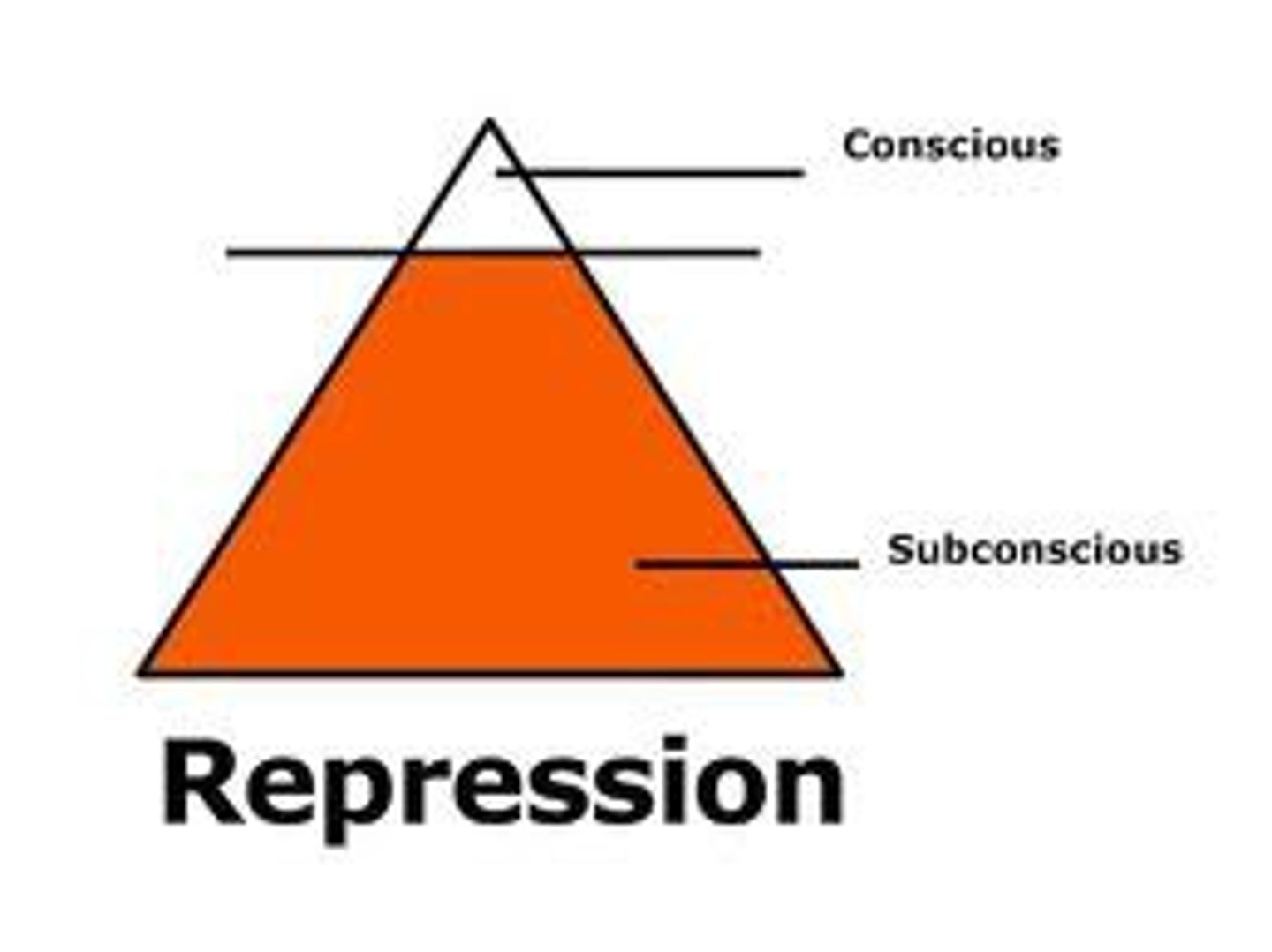
repression
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories from consciousness.
misinformation effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event.

source amnesia
attributing to the wrong source an event we have experienced, heard about, read about, or imagined. (Also called source misattribution.) Source amnesia, along with the misinformation effect, is at the heart of many false memories.

Hermann Ebbinghaus
the first person to study memory scientifically and systematically; used nonsense syllables and recorded how many times he had to study a list to remember it well, identified the forgetting curve
Elizabeth Loftus
Her research on memory construction and the misinformation effect created doubts about the accuracy of eye-witness testimony
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations

Charles Spearman
used and developed factor analysis (identifies clusters of related items), focused on the importance of general intelligence (g)
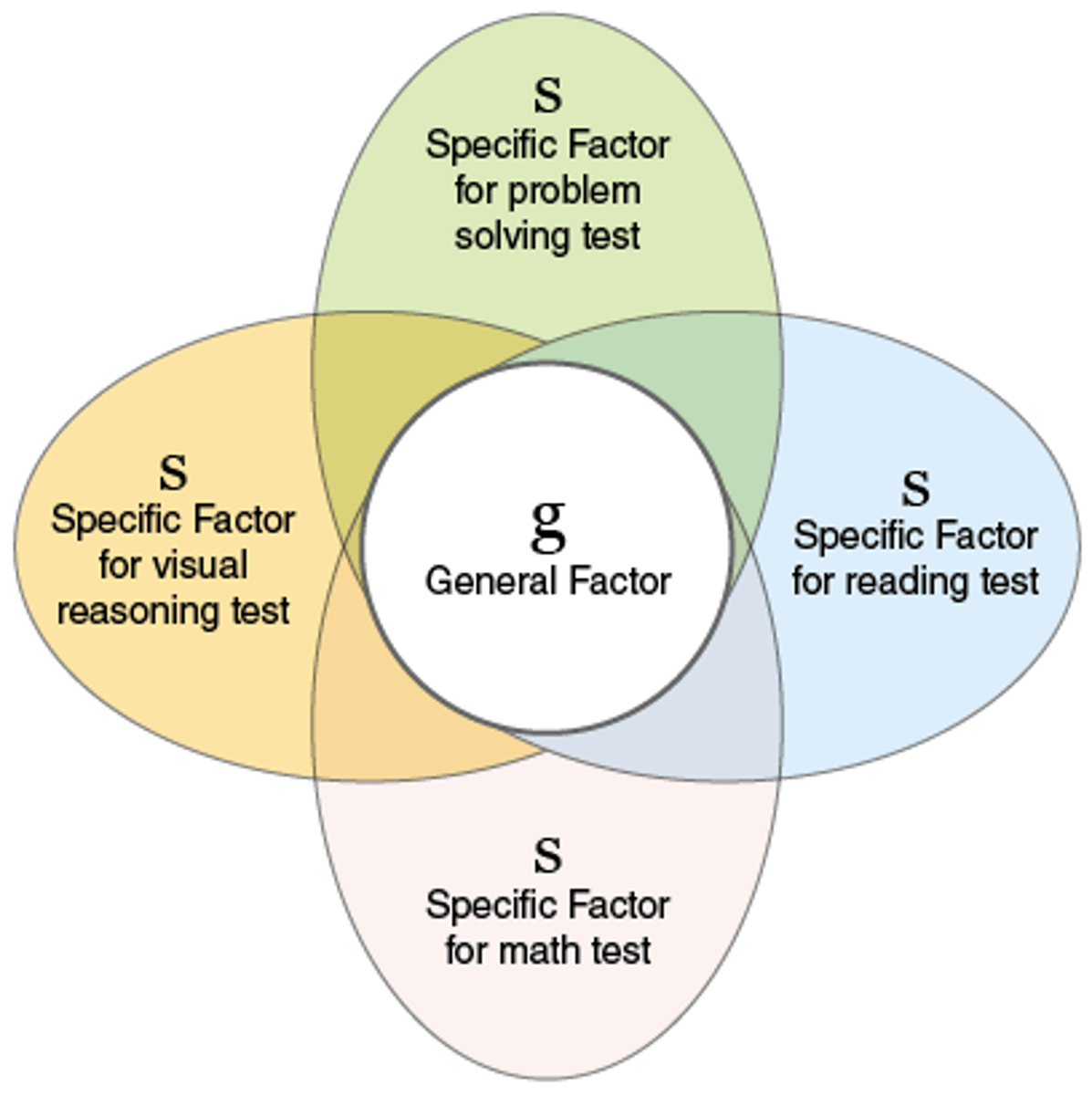
general intelligence (g)
a general intelligence factor that according to Spearman and others underlies specific mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
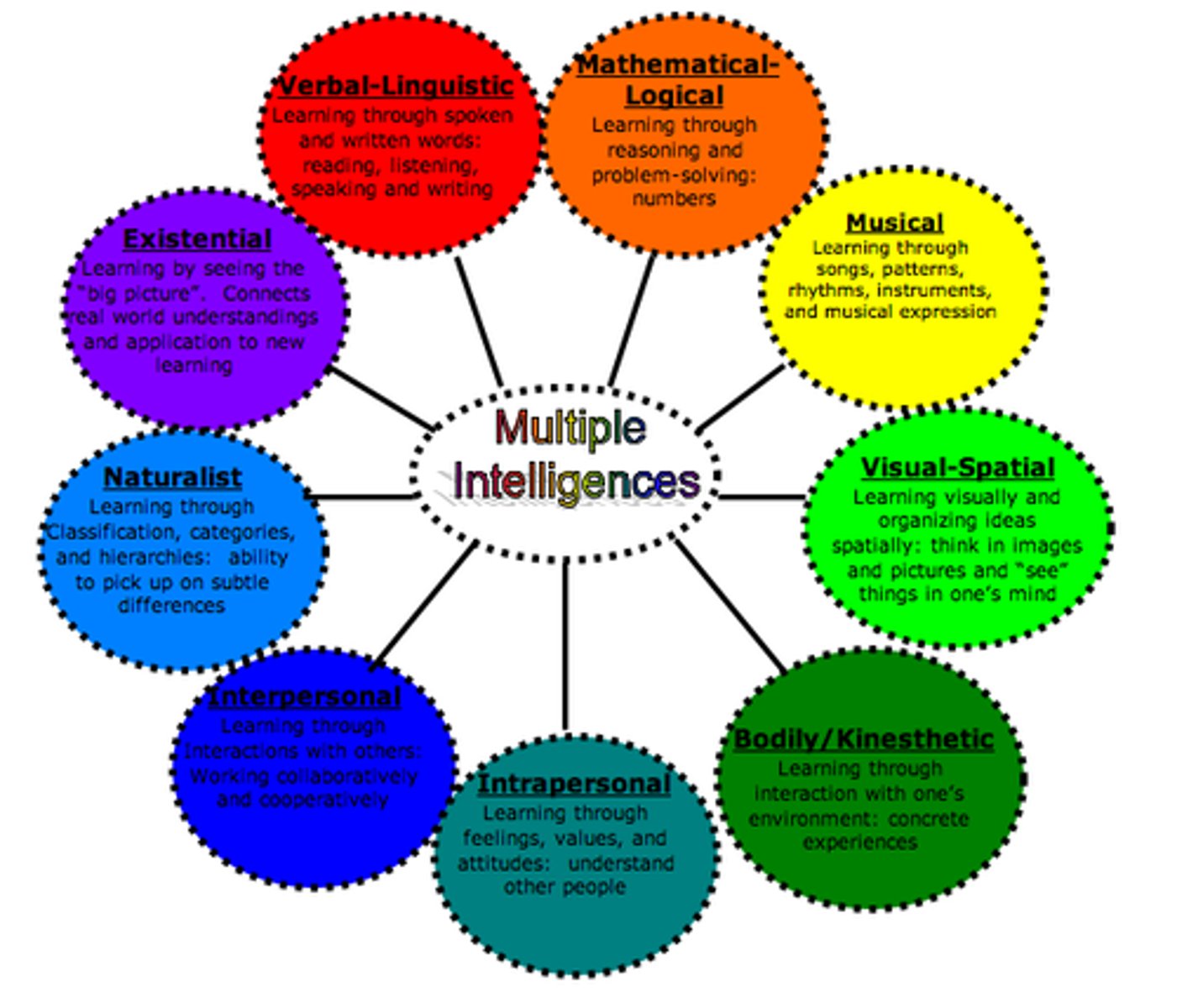
Howard Gardner
He said abilities are best classified into 8 intelligence including spatial, musical, logical-mathematical, linguistic, naturalist, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and bodily-kinesthetic.
savant syndrome
condition where a person has limited mental ability but is exceptional in one area

Gardners Multiple Intelligences
visual/spatial
verbal/linguistic
musical/rhythmic
logical/mathematical
bodily kinesthetic
interpersonal
intrapersonal
naturalistic
grit
passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals

analytic intelligence
(academic-problem-solving) traditional intelligence traits

creative intelligence
reacting adaptively to novel situations and generating novel ideas

practical intelligence
required for everyday tasks where multiple solutions exist

emotional (social) intelligence
perceiving emotions understanding emotions managing emotions using emotions

delayed gratification (self-discipline)
one aspect of emotional intelligent tied to success in life (measured in the Stanford Marshmallow Experiment)

Alfred Binet
helped label kid's mental ages to help predict future performance in school

mental age
the chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance

Lewis Terman
He was a Stanford professor and created the Stanford-Binet IQ test.
IQ score
(Mental Age/Chronological Age) x 100
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
most widely used adult intelligence test; contains verbal and performance (nonverbal) subtests
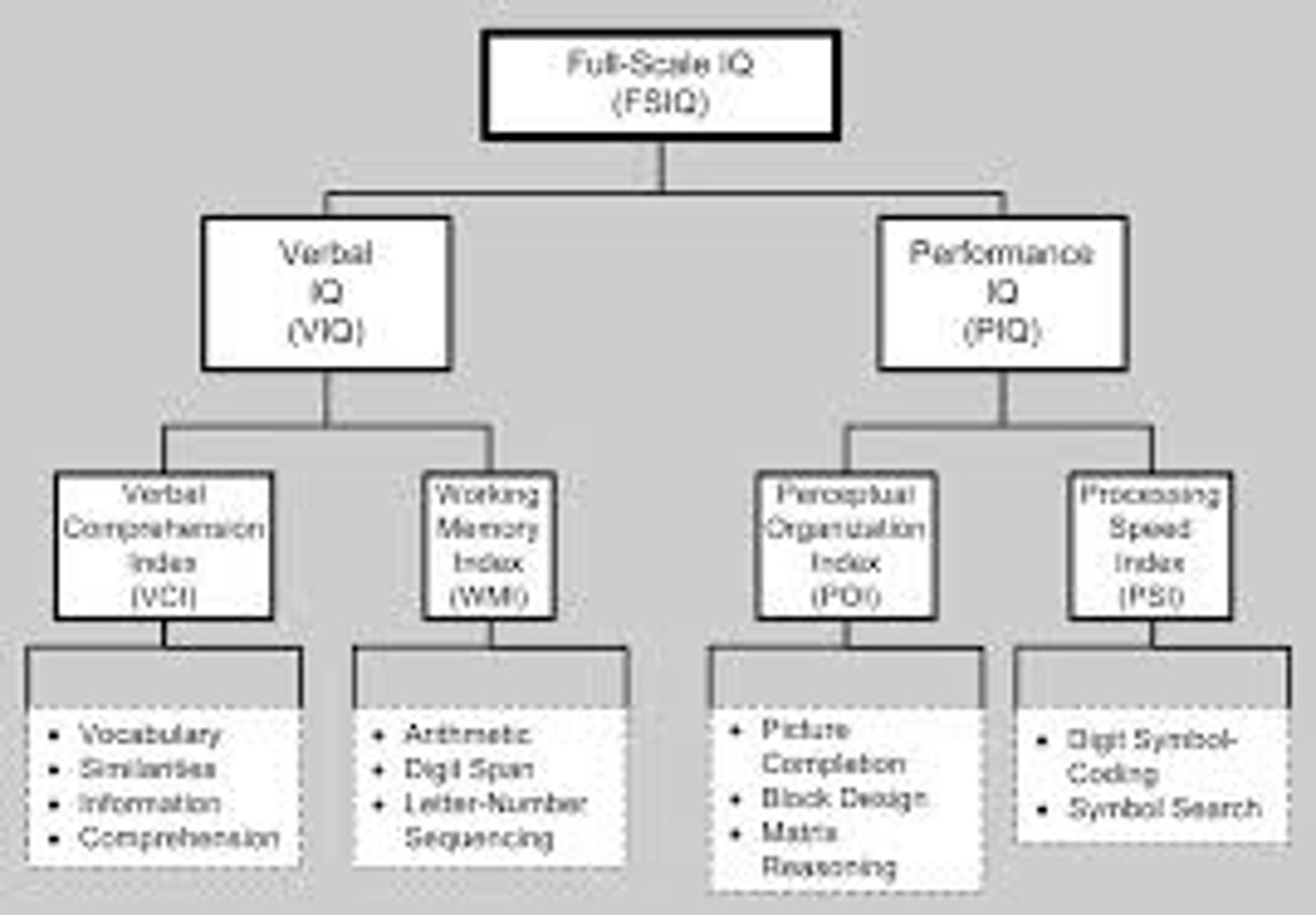
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC)
intelligent test for children, for 6-16 year olds
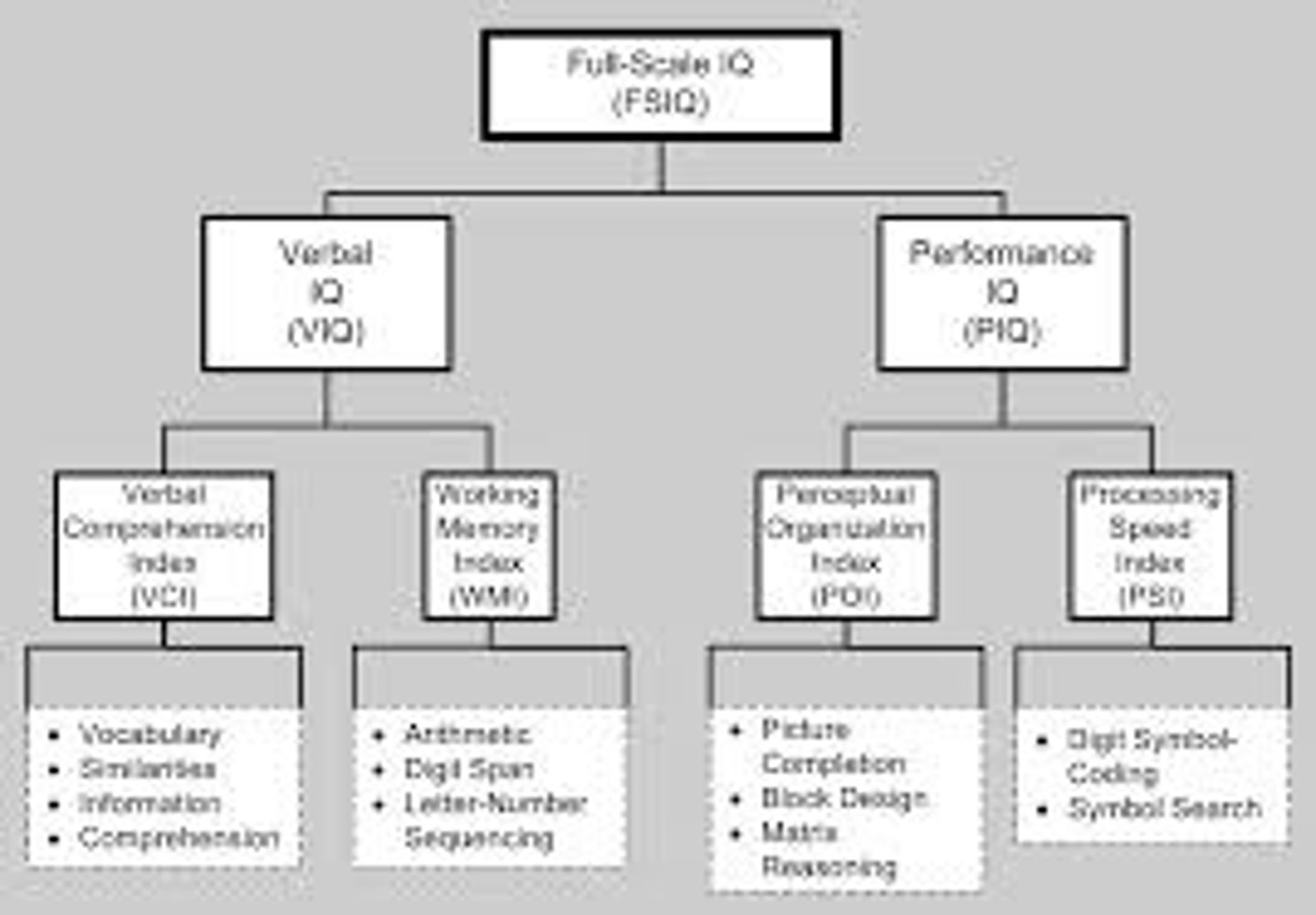
achievement test
a test designed to asses what a person has learned

aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person's future performance, aptitude is the capacity to learn

standardization
defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group (Representative sample) form a normal distribution or bell curve
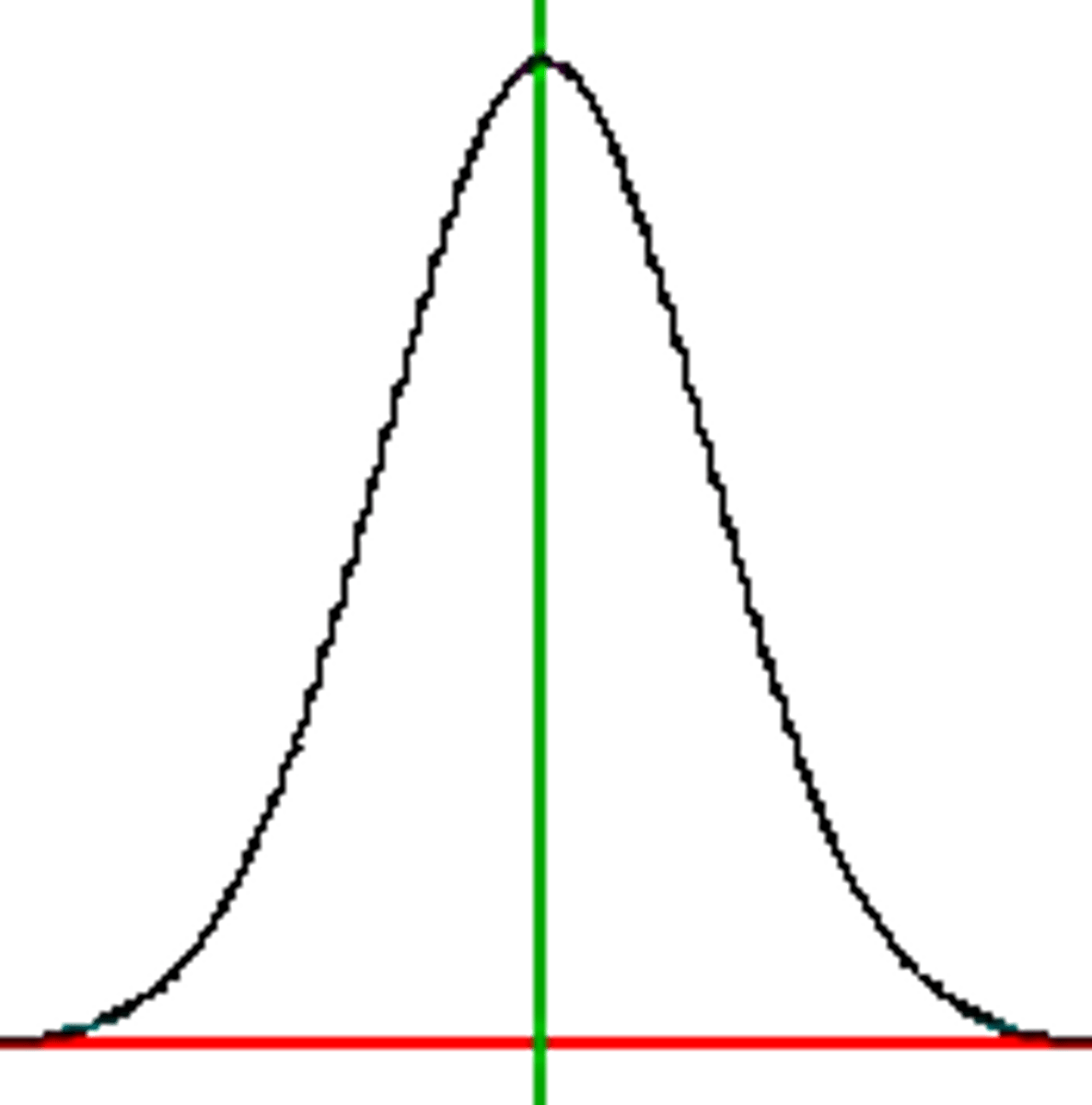
normal curve (normal distribution)
symmetrical, bell shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data most scores fall near the mean
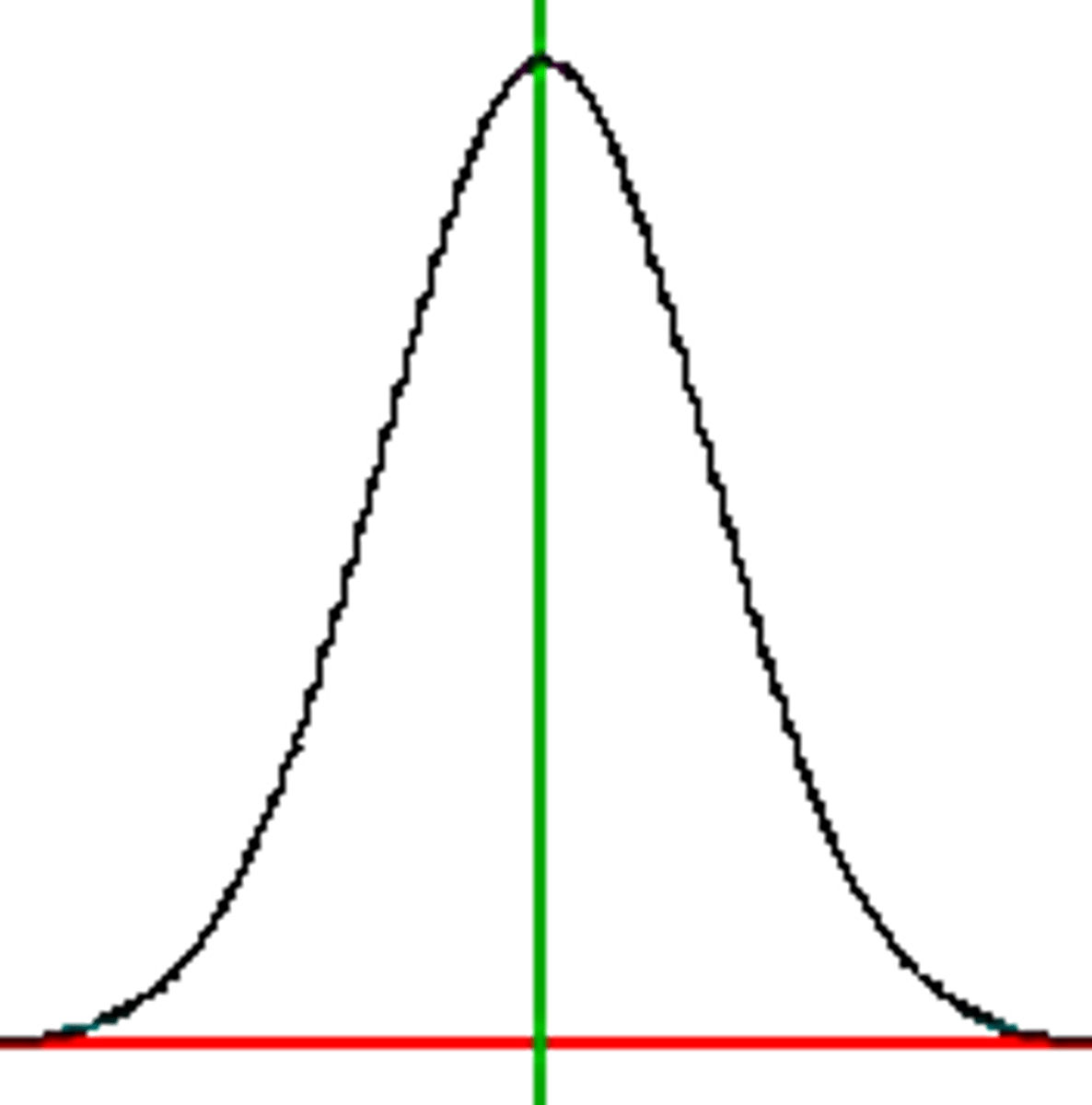
68%
Amount of people with IQs between 85 and 115 (one SD of the mean)
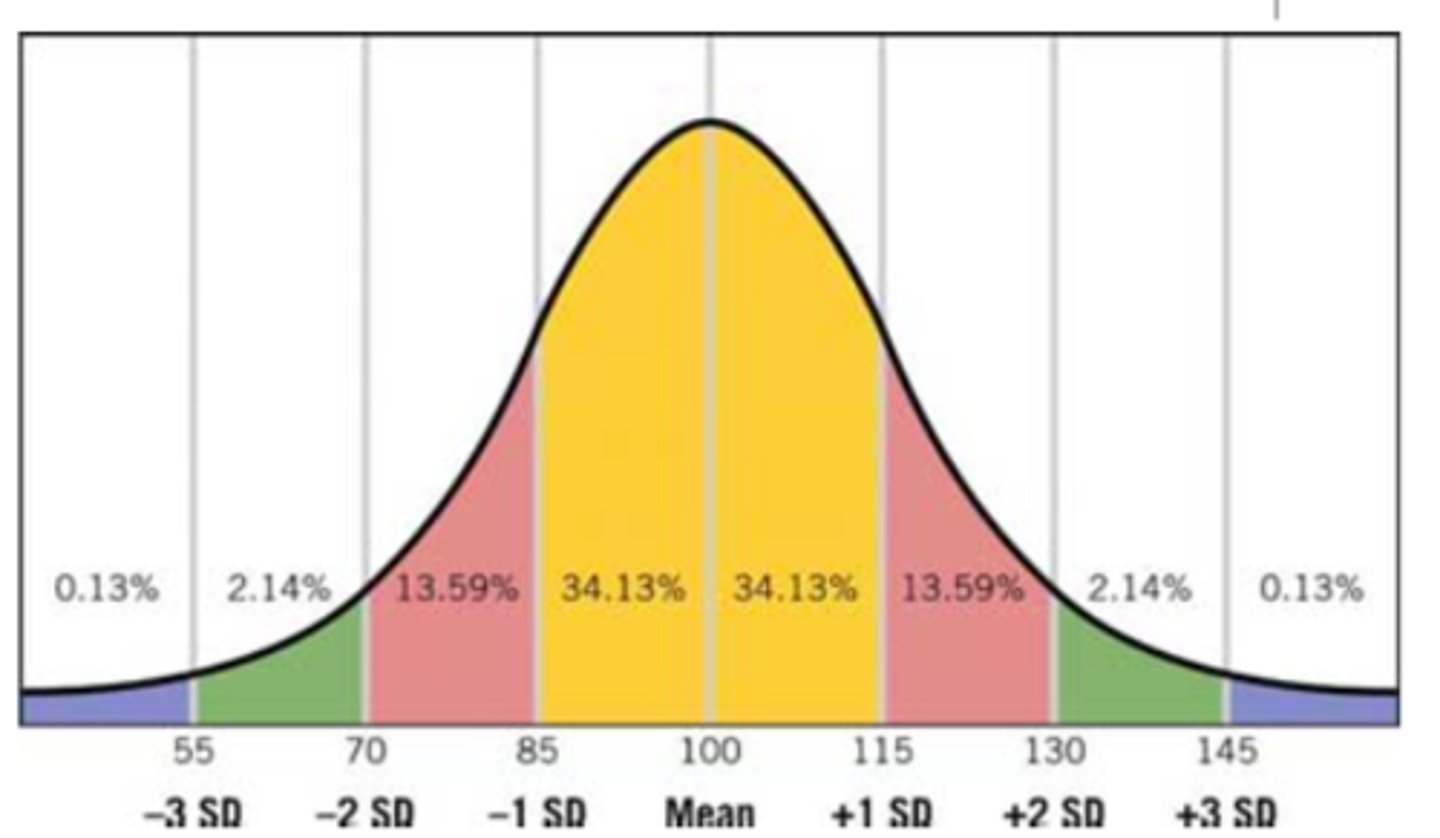
95%
Amount of people with IQs between 70 and 130 (two SD of the mean)
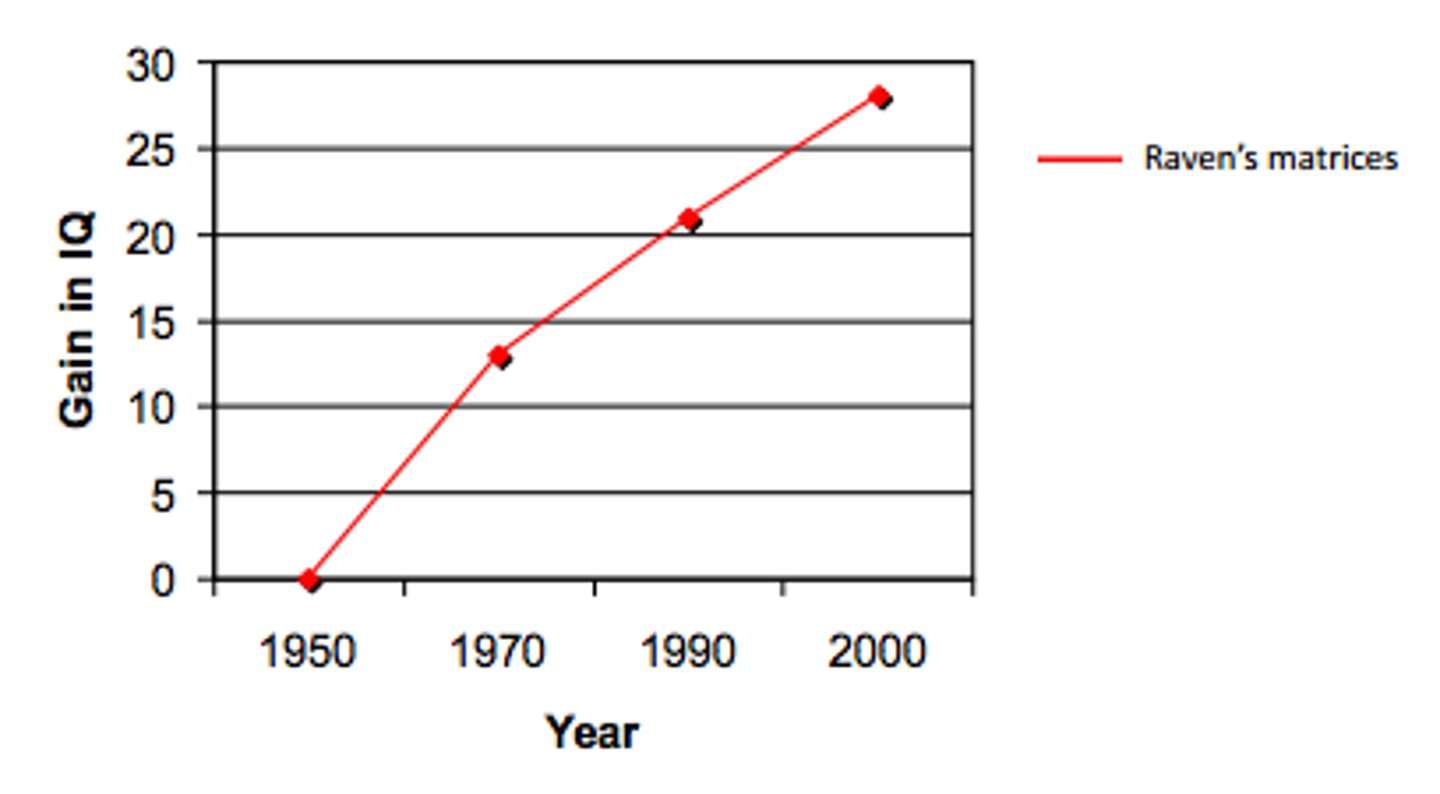
The Flynn Effect
intelligence scores have risen throughout the last 100 years or so (due to environment)
reliability
when a test yields consistant results
split- half reliability
dividing the test into two equal halves and assessing how consistent the scores are
alternate-forms reliability
using different varieties of the test to measure consistency between them
test-retest reliability
using the same test on two occasions to measure consitency
validity
the extent to which a test measures what it is supposed to meaure
content validity
extent to which a test accurately measure the subject intended to measure (entirety, breadth, etc.)
predictive validity
the extent to which test score forecasts future behaviors or results
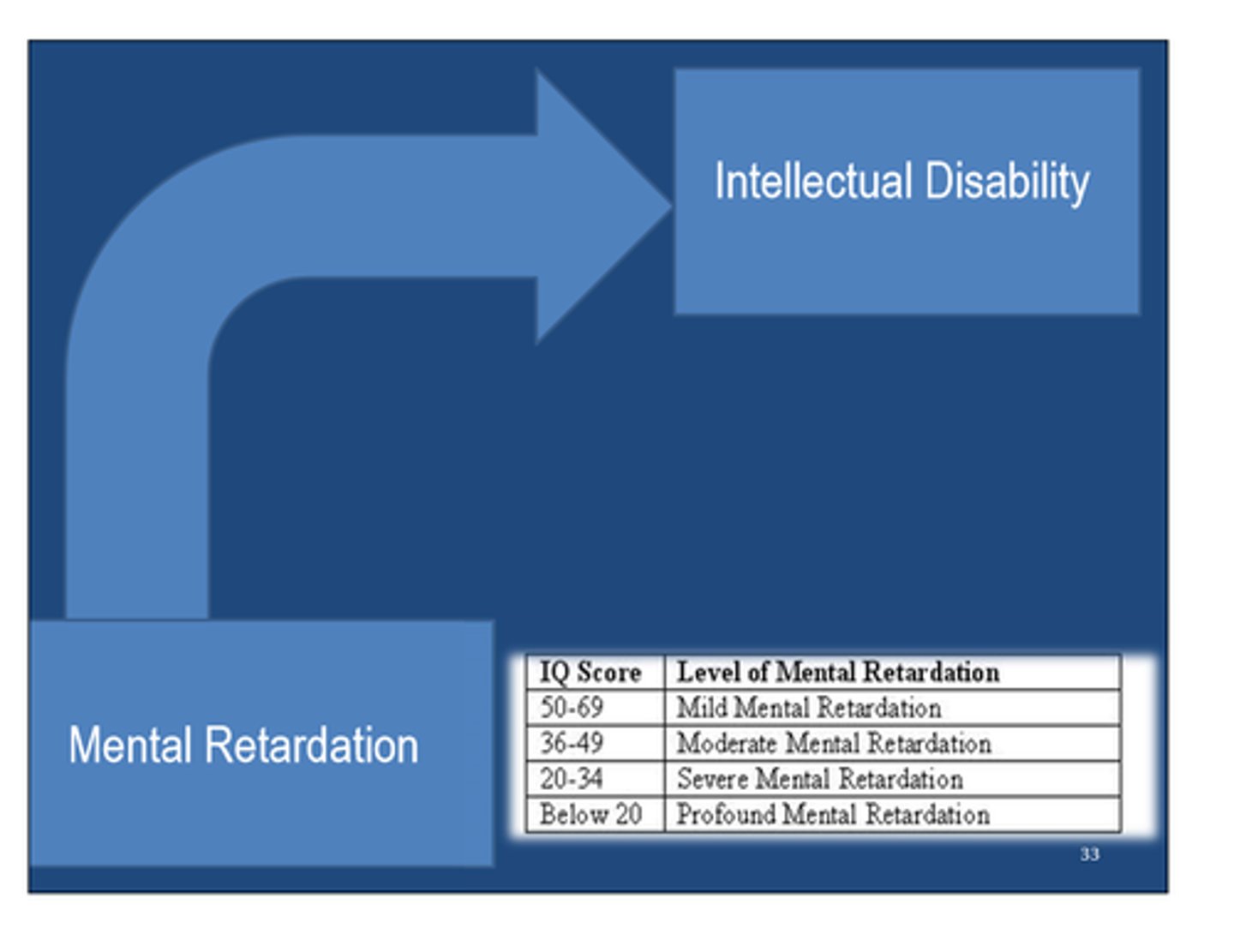
intellectual disability
limited mental ability intelligence score of 70 or below formerly referred to as mental retardation
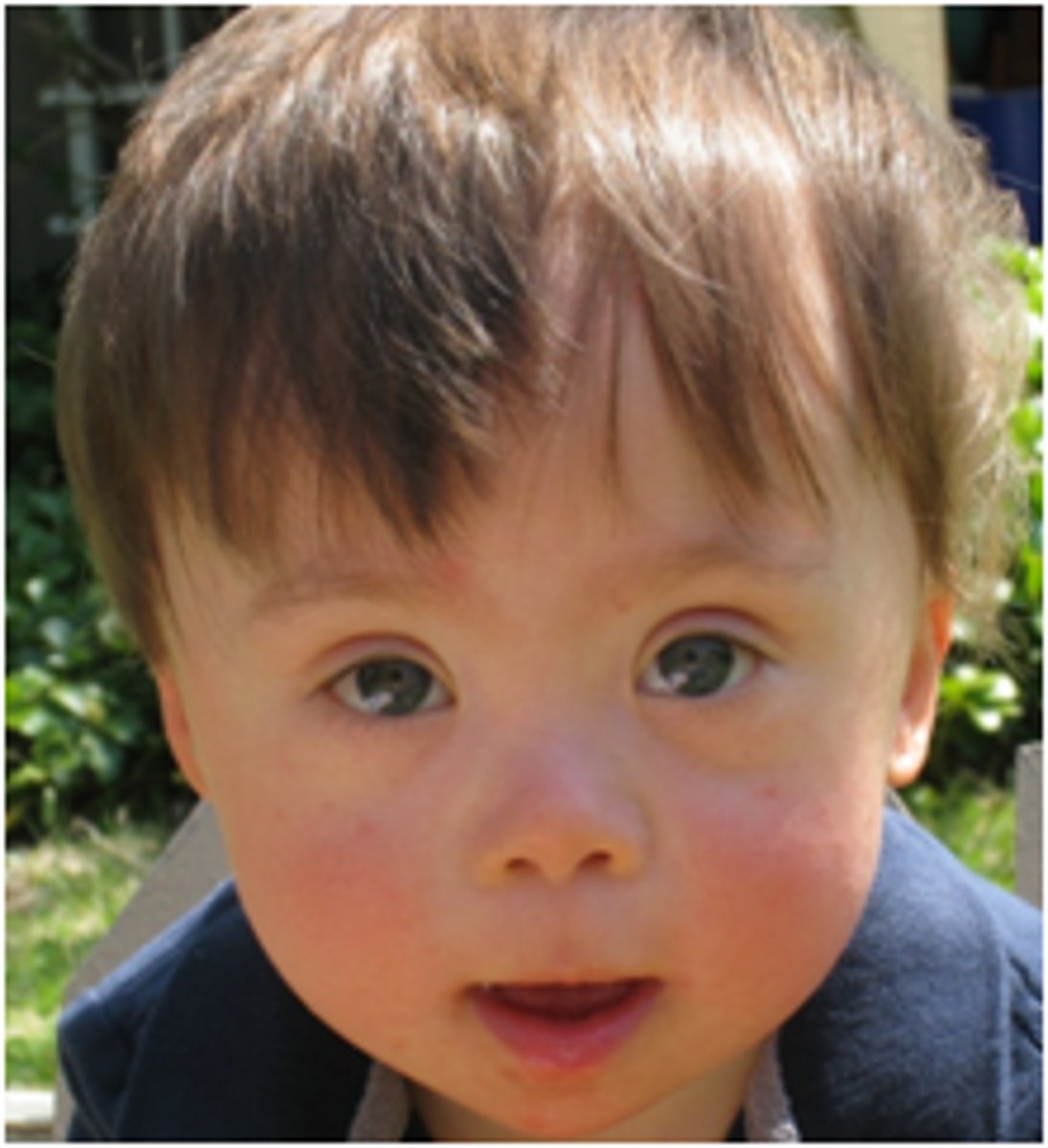
down syndrome
mild to severe intellectual disability and associated physical disorders extra copy of chromosome 21
High Intelligence
typically 130 IQ and above gifted education programs

z-score
tells us whether a particular score is equal to the mean. below the mean or above the mean, by how many standard deviations
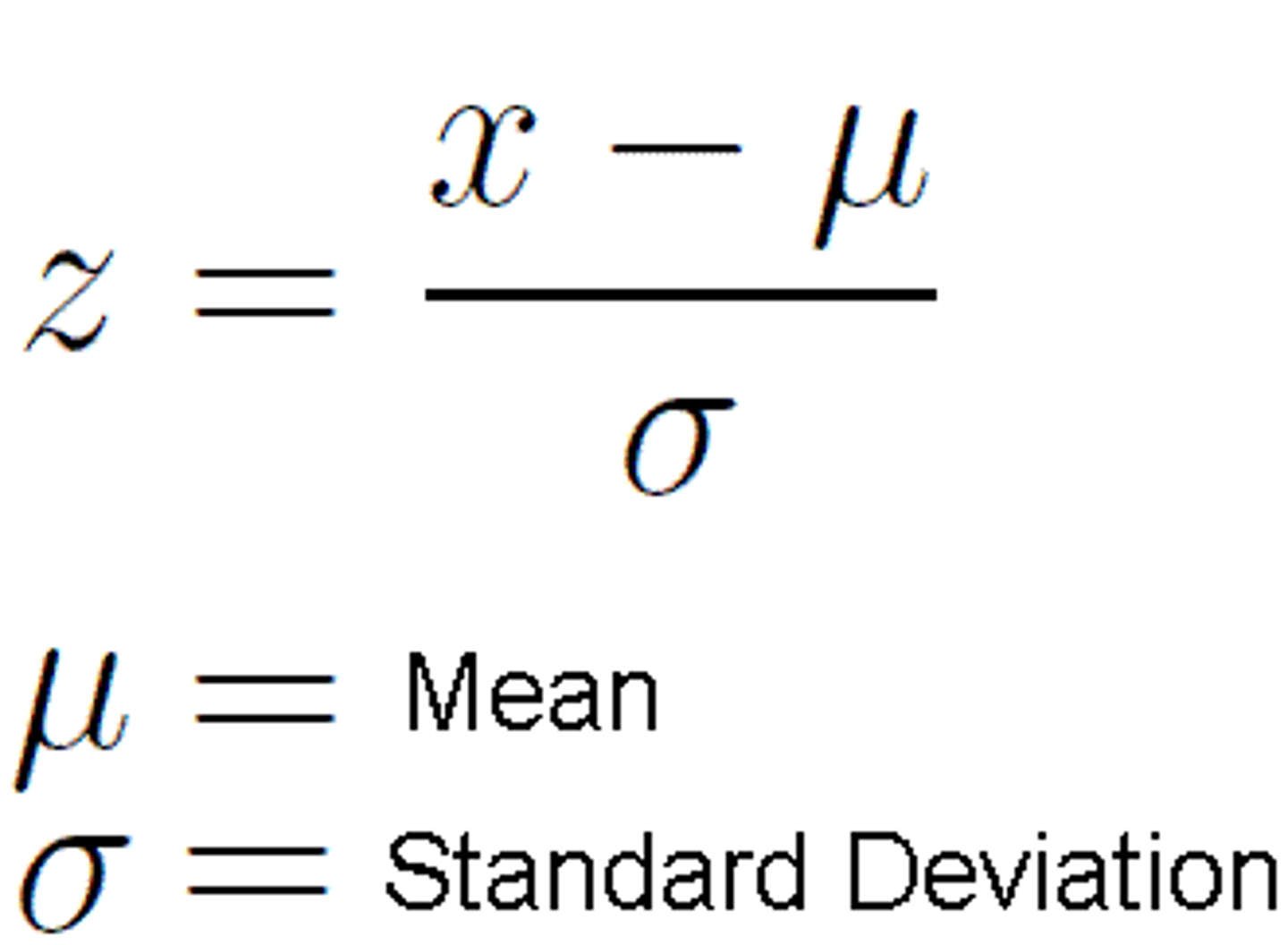
percentile rank
percentage of scores that fall below a given score
heritability
proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes

stereotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype

Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
This theory holds that there are three types of intelligence- analytic intelligence, practical intelligence, and creativity
Robert Sternberg
devised the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence (academic problem-solving, practical, and creative)
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating.

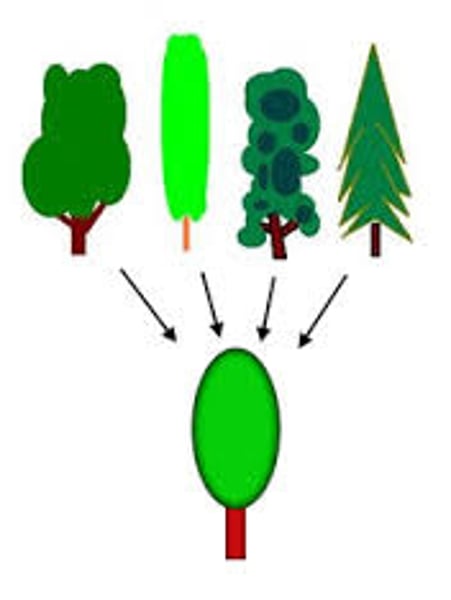
concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people.
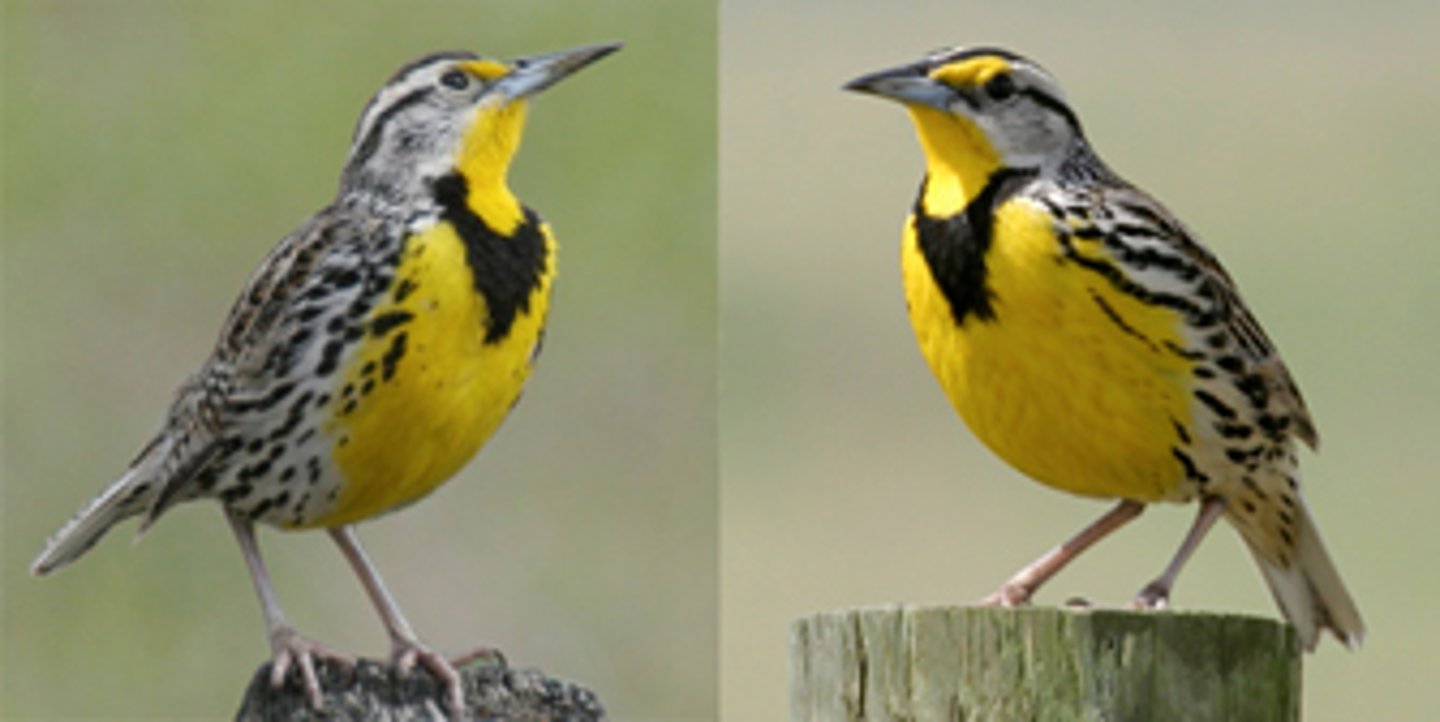

prototype
a mental image or best example of a category
algorithm
a methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem.

heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently;

insight
a sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem

confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that confirms one's preconceptions.

fixation
the inability to see a problem from a new perspective; an impediment to problem solving.
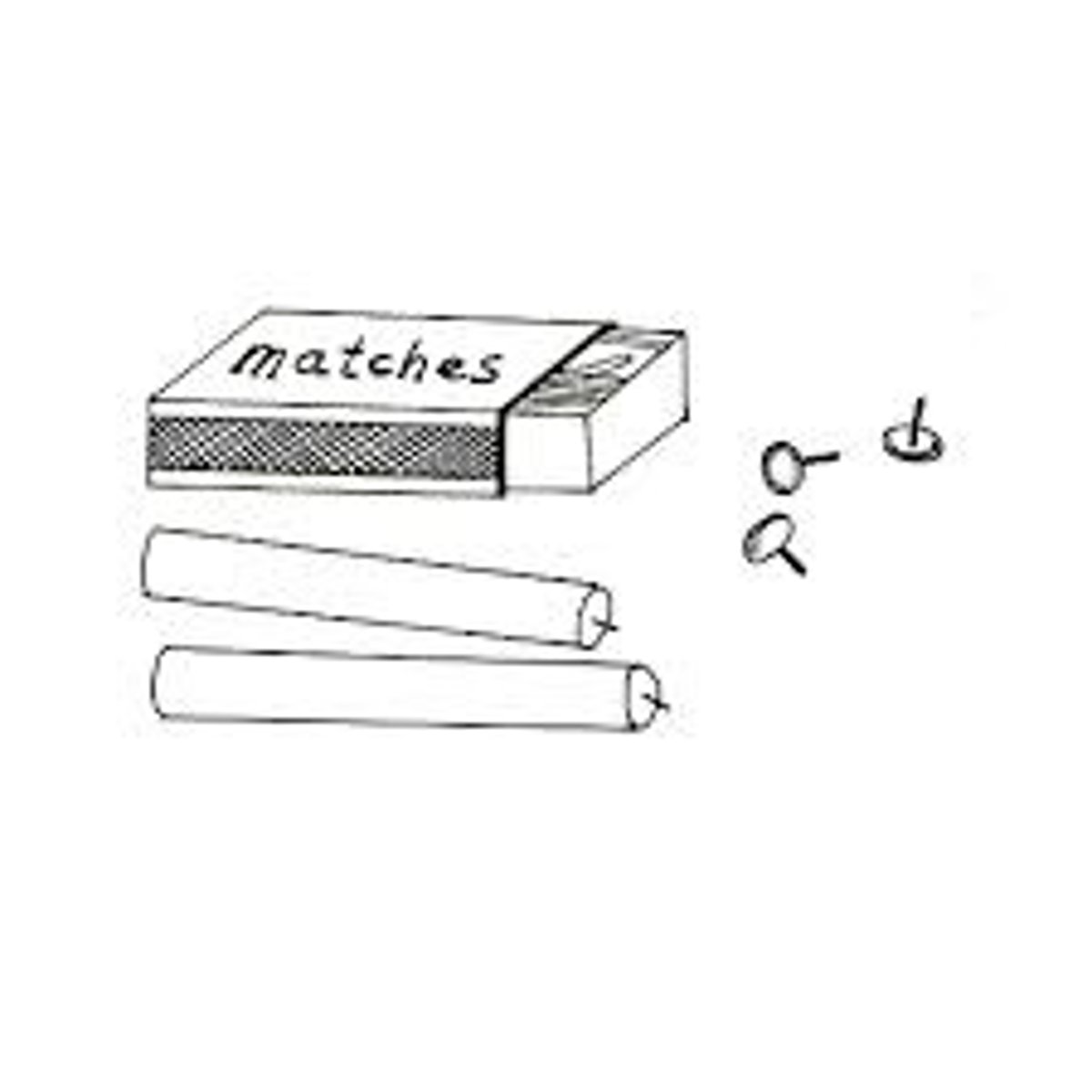
functional fixedness
the tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions

mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in a particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past.

representativeness heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to match particular prototypes; may lead one to ignore other relevant information.

availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on how readily instances come to mind (perhaps because of their vividness); we presume such events are common.

overconfidence
the tendency to overestimate the accuracy of one's beliefs and judgments.

framing
the way an issue is posed;

belief bias
the tendency for one's preexisting beliefs to distort logical reasoning, sometimes by making invalid conclusions seem valid, or valid conclusions seem invalid
belief perseverance
clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited.
phoneme
in a language, the smallest distinctive sound unit.
morpheme
in a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning; may be a word or a part of a word (such as a prefix).

babbling stage
beginning at about 4 months, the stage of speech development in which the infant spontaneously utters various sounds at first unrelated to the household language