JHS HGAP Course Vocab Test Review (CHECK DESC)
1/364
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IMPORTANT: the definitions for commodity theory and edge cities may be partially or completely wrong, research them using your own sources also if you're using this after the 24-25 school year the HGAP teachers might have modified the course/vocab so just be wary that these definitions could be wrong
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
365 Terms
Absolute location
The precise point on the Earth's surface, usually measured by longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates.
Census data
The collection of information about a population, including demographics, housing, and economic characteristics, by the government, typically conducted every ten years in the United States via the U.S. Census Bureau.
Clustering
The condensing of some phenomena in a relatively small area. (e.g. people)
Distortion
An unpreventable phenomena in ALL maps that alters the globe in some way that will misrepresent some aspect of its data.
Environmental determinism
The theory that human behaviors and cultures are directly influenced by the physical environment.
Field observation
The process of collecting qualitative data and information by observing events, behaviors, and interactions in their natural settings.
Flows (migration)
The movement patterns of people as they move from one place to another.
Formal region
An area defined by at least one measurable data statistic/characteristic. All undisputed political boundaries define a formal region.
Functional region
An area organized around a central point or node, defined by some function, where the surrounding areas are connected through economic or social activities.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system dedicated to capturing, storing, analyzing, and managing spatial and geographic data.
Geographical data
Information that is related to the locations, characteristics, and relationships of physical features on the Earth's surface.
Land Use
The way land is utilized by humans for certain activities. (e.g. agriculture)
Landscape analysis
The examination of spatial patterns and relationships in land to understand humans’ interactions with the natural environment.
Map projection & distortion
The way a 2D surface represents the Earth. All maps have some degree of distortion, resulting in inaccuracies in shape, area, distance, or direction.
Toponym
A place name.
Friction of distance
The distance between two locations makes it more difficult or costly to interact.
Natural resources
Materials that occur in nature which are used by humans.
Perceptual/Vernacular region
An area defined by people’s feelings towards a place, like “The South”.
Place
An area that has some connection or attachment to a person. (e.g. “home”)
Possibilism
A theory that humans can adapt to environmental limitations and even modify them. (the environment is still able to limit humans, but just not as much)
Reference maps
Maps that display general information about geographical locations and space, split up into political and physical maps.
Regional analysis
The study of characteristics and spatial relationships in a specific area.
Regional scale
The analysis level of a specific area with definable characteristics.
Relative location
The position of a location relative to other locations.
Remote sensing
The gathering of data about an area from satellites or other aerial mechanisms.
Satellite imagery
Pictures of the Earth from a satellite in orbit.
Satellite navigation system (GPS)
A system that uses satellites in order to find absolute location of someone or something on Earth.
Map scale
The relationship/ratio of a map to its actual size on Earth.
Scale of analysis
The spatial level of data that is being analyzed within a map. For example, a map of Europe that shows individual countries would have a state scale of analysis.
Space
The physical distance between two locations.
Spatial patterns
The arrangement of phenomena/objects across space.
Sustainability
The ability to be maintained over a long period of time without threatening ecological balance.
Thematic maps
Maps that overlay some economic, physical, or cultural data onto standard geographic/political maps. (e.g. choropleth, cartogram, isoline/isopleth, dot map, etc.)
Time-distance decay
The decrease in interaction between two locations as the distance between them increases.
Site
The physical characteristics of a location.
Situation
The relationship between a location and other locations, usually with comparison. (basically relative location)
Aging population
A population that has an increasing proportion of elderly individuals.
Agricultural population density (agricultural density)
The number of farmers per unit of arable land.
Anti-natalist population policies
Governmental policies that attempt to reduce the birth rates of a country usually due to overpopulation. (e.g. China’s one child policy) Also called restrictive population policies.
Arable
The state of land where it is able to support agricultural production and growth.
Arithmetic population density
The amount of people per unit of land.
Asylum Seekers
People who emigrated from their home country as a refugee in order to gain asylum, or protection, from a foreign country.
Boserup Theory
A theory that states the growth of population will support and drive the increase in agricultural production so that the former never outpaces the latter. (exact opposite of Malthusian Theory)
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number of people that can be supported by a location without environmental degradation or strain on resources.
Census
An official (by government) survey of the population that gathers demographic data.
Chain migration
The migration of people to a location because of previous migrants of the same nationality or bloodline.
Contraception
Any artificial device that prevents or attempts to prevent pregnancies. Governments may supply contraceptives to lower birth rates.
Counterurbanization
The exact opposite of urbanization; the movement of people from urban to rural areas.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The number of live births per 1000 people.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths per 1000 people.
Cyclic movement
Repetitive patterns in movement that typically take place seasonally.
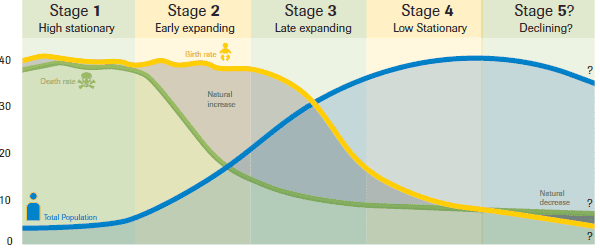
Demographic transition model (DTM)
A model that describes relationships between birth rates, death rates, and population growth.
Stage 1 (High Stationary) shows high birth & death rates, resulting in a small population that is either stable or grows slowly.
Stage 2 (Early expanding) shows high birth rates and decreasing death rates, resulting in increasing population.
Stage 3 (Late Expanding) shows decreasing birth rates and low death rates, resulting in a population increasing at a decreasing rate. (concave down)
Stage 4 (Low Stationary) shows low birth and death rates, resulting in a relatively large population that either remains stable or grows slowly.
Stage 5 (Declining) shows extremely low birth rates and low death rates, resulting in a decreasing population.
Demography
The study of human characteristics, such as births or deaths.
Dependency ratio
The percentage of the population that is under 15, or the percentage of the population that is at least 65.
Doubling Time
The amount of time it takes for a population to double, calculated based on the NIR. (The actual formula is much more complicated, but as a general rule, divide 70 by the NIR.)
Ecumene
The portion of the Earth’s surface that is permanently inhabited by humans.
Ehrlich Theory
A theory very similar to Malthusian theory that states that humans are unable to prevent famine, disease, and other consequences as a result of overpopulation.
Emigration
The movement of people out of a country/location.
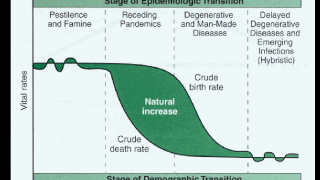
Epidemiological transition model (ETM)
A model that explains the changes in death rates from the DTM and directly correlates its stages with the DTM’s stages. (up to 4)
Stage 1 (Pestilence and Famine) show high death rates from pandemics, endemics, and standard diseases that are easily preventable and treated with modern medical technology.
Stage 2 (Receding Pandemics) show decreasing death rates from these infectious diseases due to increases in medical knowledge, sanitation, and nutrition.
Stage 3 (Degenerative and Man-Made Diseases) show lower death rates as medical technology advances, but chronic diseases start appearing such as cancer or heart disease.
Stage 4 (Delayed Degenerative Diseases and Emerging Infections) show increasing death rates, but chronic diseases progress and the evolution of diseases has resulted in them being able to infect and kill humans again, even with advanced medical technology.
Some suggest that Stage 4 may just be the decrease in chronic diseases, while there is a Stage 5 that shows a massive increase in death rates due to the evolution of infectious diseases combined with an aging population that is susceptible to these types of diseases.
Eugenic population policies
Extremely controversial policies that basically attempt selective breeding with humans. Governments may try to “improve the genetic quality” of the population by promoting reproduction of people with desirable traits, while discouraging reproduction of others.
Family planning
The controlling of children numbers within a family (such as through contraceptives or sterilization); encouraged by anti-natalist policies.
Forced migration
The movement of people (or a group of people) that is done against their will.
Guest worker
A person that temporarily works in a foreign country.
Immigration
The movement of people into a country.
Immigration policies
Policies that aim to control the flow of people into a country, determining who is able to stay and who cannot.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The amount of infant deaths per 1000 infant births.
Internal migration
Migration within a country or regions borders.
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
Someone obliged to migrate out of their house, but stays within a country’s borders.
International migration
Migration that occurs between foreign countries.
Interregional migration
A branch of internal migration that describes migration between regions within a country.
Intervening Obstacle/Opportunity
Something that prevents or obstructs the migration of an individual, such as political issues or physical barriers.
Something that presents itself as a better option than the original intended destination of the migrant.
Intraregional migration
Migration that happens within a region within a country.
Less Developed Country (LDC)
A country that has relatively low levels of economic, social, and/or political development.
Life Expectancy
The average amount of years someone is expected to live to.
Literacy Rate
The percentage of the population that is able to read.
Malthusian Theory
A theory that states that human population will outpace agricultural output, resulting in famine and wars. Any factor that decreases fertility rates are called negative checks, and any factor that increases mortality rates are called positive checks.
Medical revolution
Significant improvements in medical knowledge and advancements in medical technology that result in lower death rates and higher life expectancy. Takes place in Stage 2 of the DTM.
Migration
The movement of an individual or group of individuals.
More Developed Country (MDC)
A country that has relatively high levels of economic, social, and/or political development.
Neo-Malthusian
A name for modern believers in Malthusian Theory, that expands his thoughts to resources in general rather than just agricultural output.
Newly Industrializing Country (NDC)
A country with levels of development between an LDC and MDC, that is undergoing rapid industrialization.
Nomadism
The frequent movement from place to place, rather than settling in one location for a long period of time.
Overpopulation
Human population exceeding the carrying capacity of a region.
Periodic movement
Migration away from a person’s home temporarily, then coming back.
Physiological population density
The number of people per unit of arable land.
Population density
The amount of people living within a certain area.
Population Distribution
The way people are spread across a region/area.
Population Pyramids
A device that divides human population of an area (usually a city, country, or the world) into age cohorts, separated by gender.
Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary economic sectors
Primary - The production and harvesting of raw materials.
Secondary - The manufacturing of raw materials into goods.
Tertiary - Also known as the “service” sector, the distribution of these goods and services.
Quaternary - Research/Development and information technology
Quinary (only for economics) - Highest levels of decision making (president)
Pro-natalist population policies
Policies that promote reproduction and high birth rates due to a decrease in population growth and worries about an aging population (South Korea & Japan). Also called expansive population policies.
Pull factors
Factors that entice migrants into a country due to desirable conditions like job/economic opportunities or political stability.
Push factors
Factors that actively drive people to leave their homes because of undesirable conditions, especially natural disasters, wars, or political issues.
Natural Increase Rate
CBR - CDR, does not factor in migration.
Ravenstein’s laws of migration
A set of general rules about migration, created by Ernst Georg Ravenstein in the 1880s.
1. Most migration is over a short distance.
2. Migration occurs in steps.
3. Long-range migrants usually move to urban areas.
4. Each migration produces a movement in the opposite direction (although not necessarily of the same volume).
5. Rural dwellers are more migratory than urban dwellers.
6. Within their own country females are more migratory than males, but males are more migratory over long distances.
7. Most migrants are young adult males.
8. Large towns grow more by migration than by natural increase.
9. Migration increases with economic development.
10. Most migration moves from rural to urban.
11. Migration is mostly due to economic causes.
Refugees
People who leave their country due to war, natural disasters, or discrimination.
Remittances
Money sent to the home country, usually to the family, typically by guest workers and immigrants.
Rural-to-urban migration
The most common type of migration, where rural individuals move to urbanized areas with higher population density and economic development, usually to find work.
Sex ratio
The number of males per 100 females.
Step migration
Migration that occurs step by step in small sections, usually done to reduce risks or costs of a full one-step journey.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average amount of children a woman is expected to have within her lifetime. Replacement TFR is 2.1, as 2 replace the parents and 0.1 gives room for any deaths that may occur.