Ketone Bodies and Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Low levels of glucose in the blood trigger the release of ____, which binds its receptor in the _____ membrane and stimulates the release of ____ ____ via a ____ ____ to produce _____, which activates ______
glucagon; adipose; adanyl cyclase; G protein; cAMP; PKA
Active PKA _______ the hormone-sensitive ____ and ____ molecules on the surface of the ____ ____.
phosphorylates; lipase; perilipin; lipid droplet
_______ of perilipin permits hormone sensitive _____ access to the surface of the lipid droplet, where it ______ _________ to _____ _____ _____
phosphorylation; lipase; hydrolyzes triacylglycerols; free fatty acids
____ ____ leave the adipocyte, bind serum ____, and are carried in the blood. They are released and enter a _____ via a specific ____ ____ ____
fatty acids; albumin; myocyte; fatty acid transporter
in the monocyte fatty acids are _____ to ____ and the energy of ____ is conserved in ______
oxidized; CO2; oxidation ATP
When the diet provides a ready source of carbohydrate as fuel, ____ _____ of ____ ____ in unnecessary and is therefore ____-regulated
beta oxidation; fatty acids; down
the first enzyme in the synthesis of fatty acids
acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC)
enzyme in fatty acid synthesis that limits the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria
carnitine acyltransferase I
1 - phosphatase
2 - PKA
3 - Acetyl - CoA
4 - malonyl - CoA
5 - Fatty acyl-CoA
6 - Fatty acyl - carnatine
7 - Fatty acyl - carnatine
8 - CoASH
9 - Fatty acyl-CoA
10 - beta oxidation
11 - Acetyl -CoA
Fill in the diagram
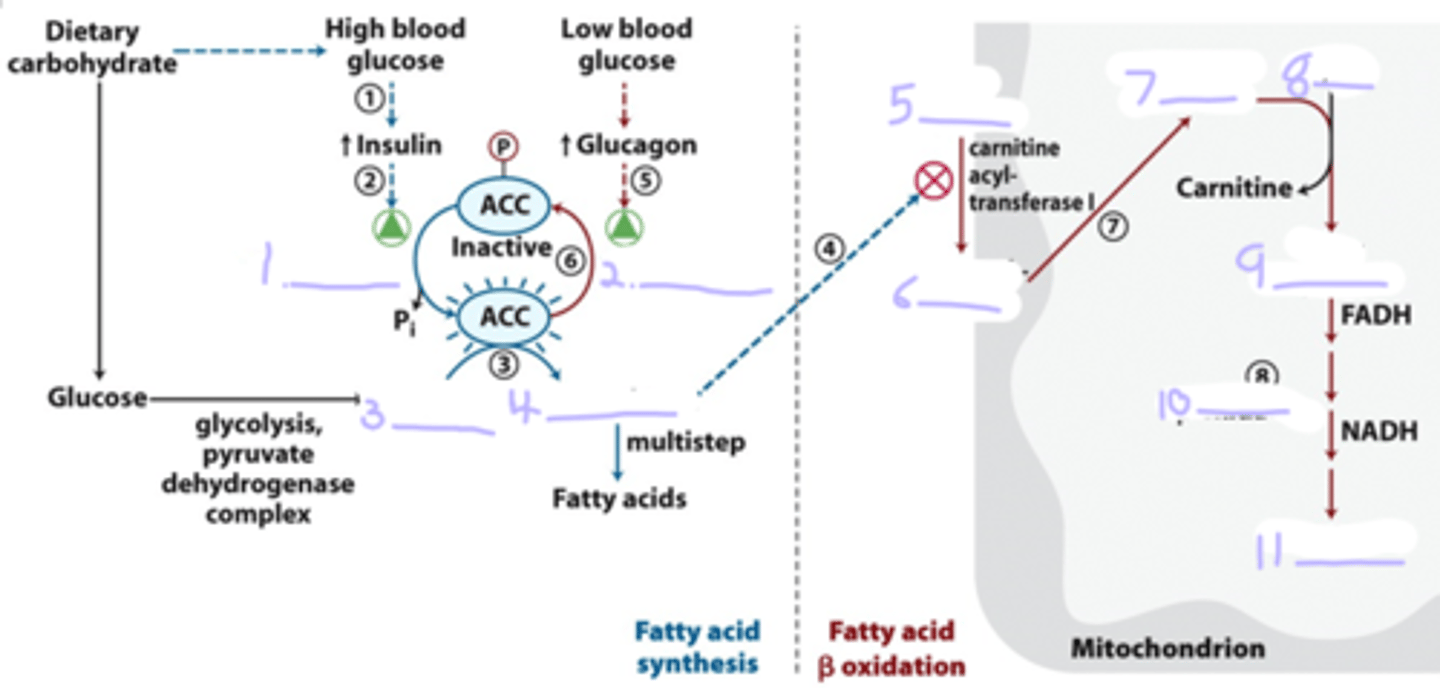
insulin-dependent protein phosphatase _______ ACC, _____ it
dephosphorylates; activating
when blood glucose levels drop between meals, ____ release activates _______
glucagon; PKA
Because glucagon also triggers the _____ of fatty acids in adipose tissue, a supply of fatty acids begins arriving in the ____
mobilization; blood
In the liver during starvation, ______ is being consumed for ________. Therefore, there may not be enough for the _____ to function effectively. As a result, _____ produced by ______ builds up and cannot produce the normal amount of _____. So it is only produced from ____ and ______
oxaloacetate; gluconeogenesis; TCA; acetyl-CoA; beta oxidation; ATP: NADH; FADH2
because the last step of beta oxidation is ______, acetyl-CoA can be used to make ____ _____, a ___ soluble form of ____ energy. The liver lacks the enzyme to convert _____ into _____ ____ so the liver cant use ketone bodies, but _____ tissue can.
reversible; ketone bodies; water; lipid; acetoacetate; acetoacetyl CoA; extrahepatic
3 main ketone bodies
acetone, acetoacetate, D-B-hydroxybutyrate
high levels of ______ will lead to acidosis, which can be fatal
D-B-Hydroxybutyrate
ketone bodies are formed in the ____.
liver
since albumin cannot cross the blood brain barrier, the brain cannot use ____ ___ from the blood as an energy source. Under starvation conditions, the brain can adapt to use ____ or ______ when glucose is unavailable
fatty acids; acetoacetate; D-B-hydroxybutyrate
1 - thiolase
2 - CoA-SH
3 - HMG - CoA synthase
4 - Acetyl-CoA
5 - CoA-SH
6 - HMG - CoA lyase
7 - Acetyl -CoA
8 - acetoacetate decarboxylase
9 - CO2
10 - HADH + H+
11 - HAD+
12 - D-B-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
fill in the chart

1) B-ketoacyl-CoA transferase
2) Succinyl-CoA
3) Succinate
extrahepatic tissues
Fill in the graph. In what kind of tissues does this take place?
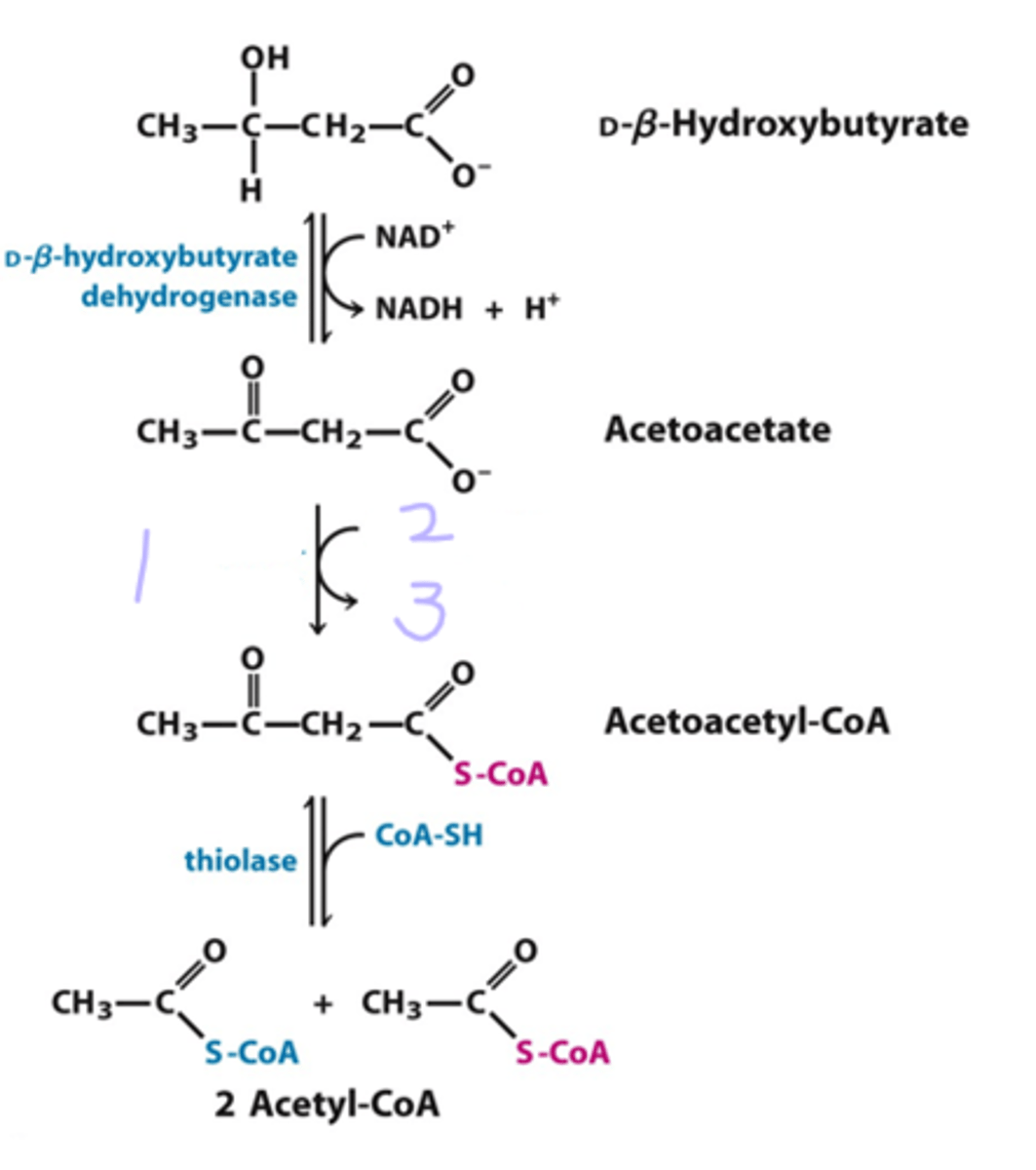
ketone bodies are overproduced in _____ and during _____
diabetes; starvation
conditions that promote gluconeogenesis slow the _____ by drawing off _____ and enhance the conversion of ____ to _____. The released _____ allows continued ____ of fatty acids
TCA; oxaloacetate; acetyl-CoA; acetoacetate; coenzyme A; beta oxidation
the purpose of fatty acid biosynthesis is primarily the storage of excess fuel as _____. Synthesis occurs in the ____ utilizing _____ as compared to Beta oxidation, which occurs in the _____ using ______
TAG; cytoplasm; NADPH; mitochondria; NAD+
3 functional regions of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
biotin carrier protein, biotin carboxylase, and transcarboxylase
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase rxn will produce a ____ carbon intermediate (_______) from a ___ carbon intermediate (_______). The added carbon will come off as _____ during chain elongation, causing the rxn to be pulled in the direction of ______
3; malonyl-CoA; 2; acetyl-CoA; CO2; biosynthesis
During fatty acid synthesis, the production of the first intermediate, malonyl-CoA, shuts down ______ by inhibiting _________ in the mitochondrial outer membrane. This control mechanism illustrates another advantage of segregating synthetic and degradative pathways in different cellular compartments.
beta-oxidation; carnitine acyltransferase I
the long carbon chains of fatty acids are assembled in a _____ ____ _____ _____
repeating four step sequence
label the type of reaction taking place
1 - condensation
2 - reduction
3 - dehydration
4 - reduction
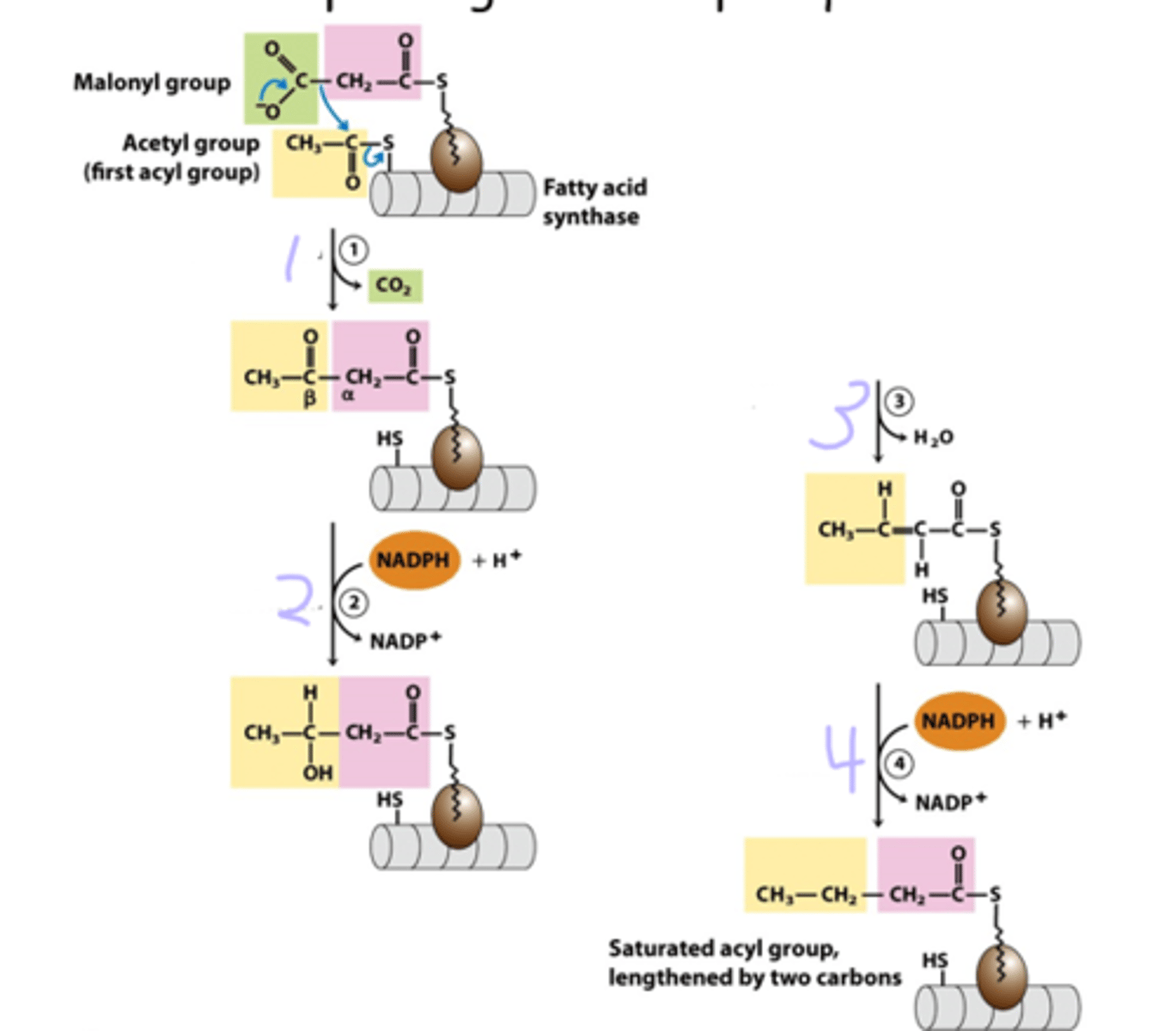
The mammalian fatty acid synthase is a single large polypeptide that contains _________. It synthesizes ____ fatty acids simultaneously
all 7 enzymatic functions; 2
during palmitate, each new _____ ____becomes the _____ group while the ___ group is at the far end of the chain
malonyl CoA; carboxyl; acetyl
____ _____ _____ (___) is the attachment site for each malonyl-CoA and the growing fatty acid chain. It has the prosthetic group _________ with a terminal _____ group for acyl attachment
Acyl carrier protein (ACP); 4'-phosphopanthetheine; -SH
________-____-____ transferase transfers ____ group from ____ to ____ of a cysteine on beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase (the first acyl group)
malonyl/acetyl-CoA-ACP; acetyl; CoA; -SH
______-____-____ transferase transfers the malonyl group from CoA to ACP
malonyl/acetyl-CoA-ACP
1 - condensation, B-ketoacyl-ACP synthase
2 - reduction of B-keto group, B-ketoacyl-ACP reductase
3 - dehydration, B-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase
4 - reduction of double bond, enoyl-ACP reductase
5 - translocation of butyryl group to Cys on B-ketoacyl-ACP synthase, B-ketoacyl-ACP synthase
6 - recharging of ACP with another malonyl group , malonyl/acetyl-CoA-ACP transferase
determine the type of reaction happening and the domain of fatty acid synthase that does it.
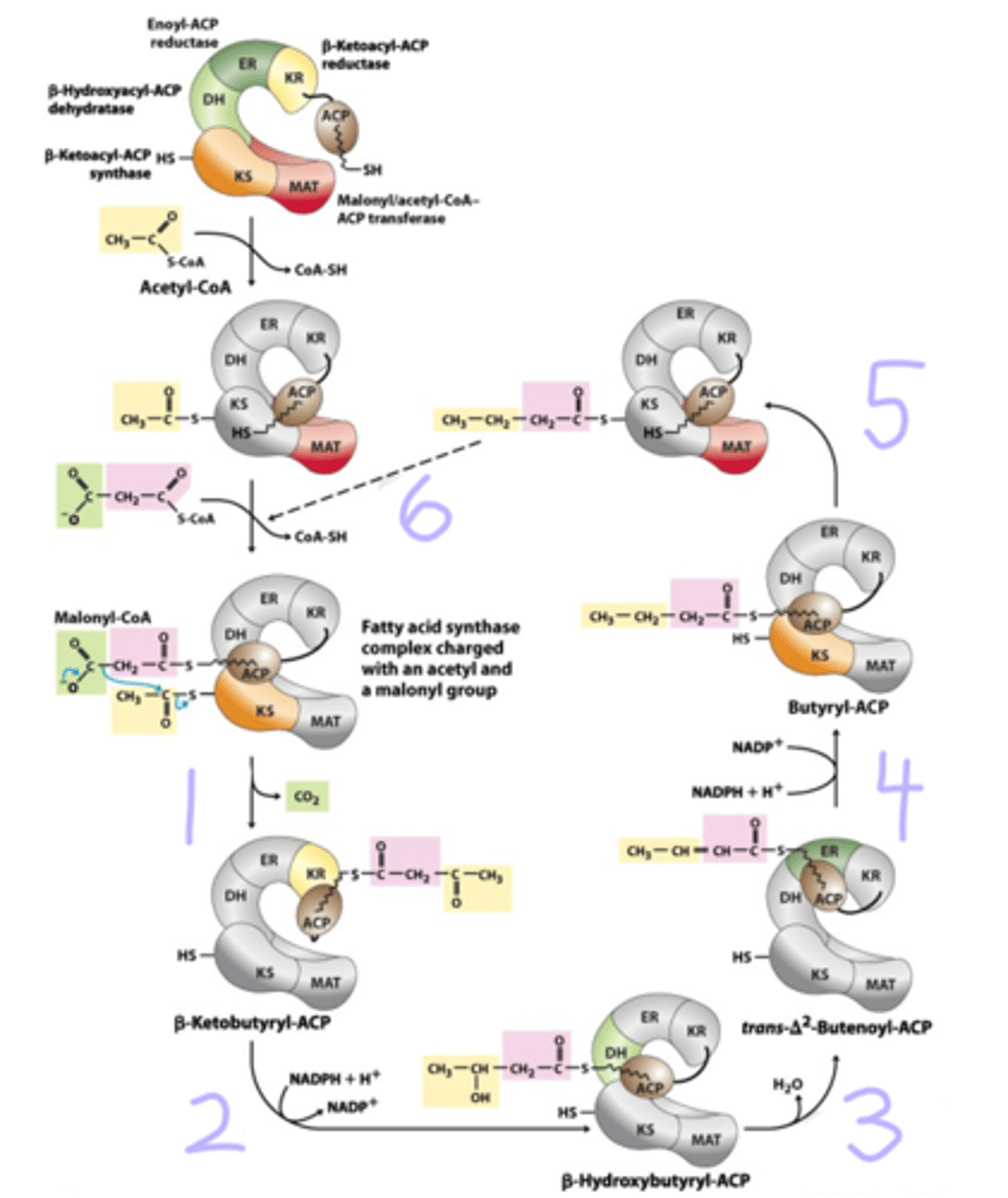
condenses acyl and malonyl groups to form the b-ketoacyl intermediate bound to ACP. CO2 is a product and loss of CO2 pulls the reaction toward b-ketoacyl formation.
b-ketoacyl-ACP synthase
reduces b-keto group to the D-b-hydroxyacyl-ACP.
b-ketoacyl-ACP reductase
removes water and converts D-b-hydroxyacyl-ACP to trans-D2-acyl-ACP.
b-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase
reduces the double bond to form a saturated acyl-ACP 2 carbons longer than the starting material.
Enoyl-ACP reductase
the two sites where a fatty acyl derivative can be found during fatty acid synthesis
4'-phosphopantetheine group on acyl carrier protein (ACP) and Cys on b-ketoacyl ACP synthase
in fatty acid synthesis, the reductive steps are the reverse of _______
beta oxidation
the overall process for the synthesis of palmitate from acetyl-CoA:
___ Acetyl-CoA + ___ATP + ___NADPH + ___ H+ ---->
Palmitate + ___ CoA + ___ ADP + ___Pi + ___NADP+ + ___ H2O
8; 7; 14; 14; 8; 7; 7; 14; 6
In making palmitate, we need ____ malonyl CoA and ____ acetyl CoA
7; 1
palmitate synthesis occurs in the ____. It takes more energy to make fatty acid than you get back out of it because some of the energy is lost as _____
cytoplasm; heat
In general, NADPH-->NADP+ is used for _____ _____, whereas NAD+-->NADH is used for ____ ______
NADPH is produced mainly by ____ _____ in adipocytes and by____ _____ _____ in hepatocytes.
synthetic reactions; energy generation; malic enzyme; pentose phosphate pathway
malate dehydrogenase reduces ______ to ____.
oxaloacetate; malate
malate is converted to _____ by ___ ____, producing _____
pyruvate; malic enzyme; NADPH
For each citrate coming out of the citrate shuttle, one ____ ___ and one ____ are produced
acetyl CoA; NADPH
the citrate shuttle moves citrate out of the ____ and into the ____. The net effect is to provide _____ in the _____ where fatty acid synthesis occurs
mitochondria; cytoplasm; acetyl CoA; cytoplasm
1 - malate dehydrogenase
2 - acetyl - CoA
3 - malate dehydrogenase
4 - NADP+
5 - NADPH + H+
6 - pyruvate malic enzyme
fill in the missing substrates and enzymes. What enzyme is responsible for 4--> 5?
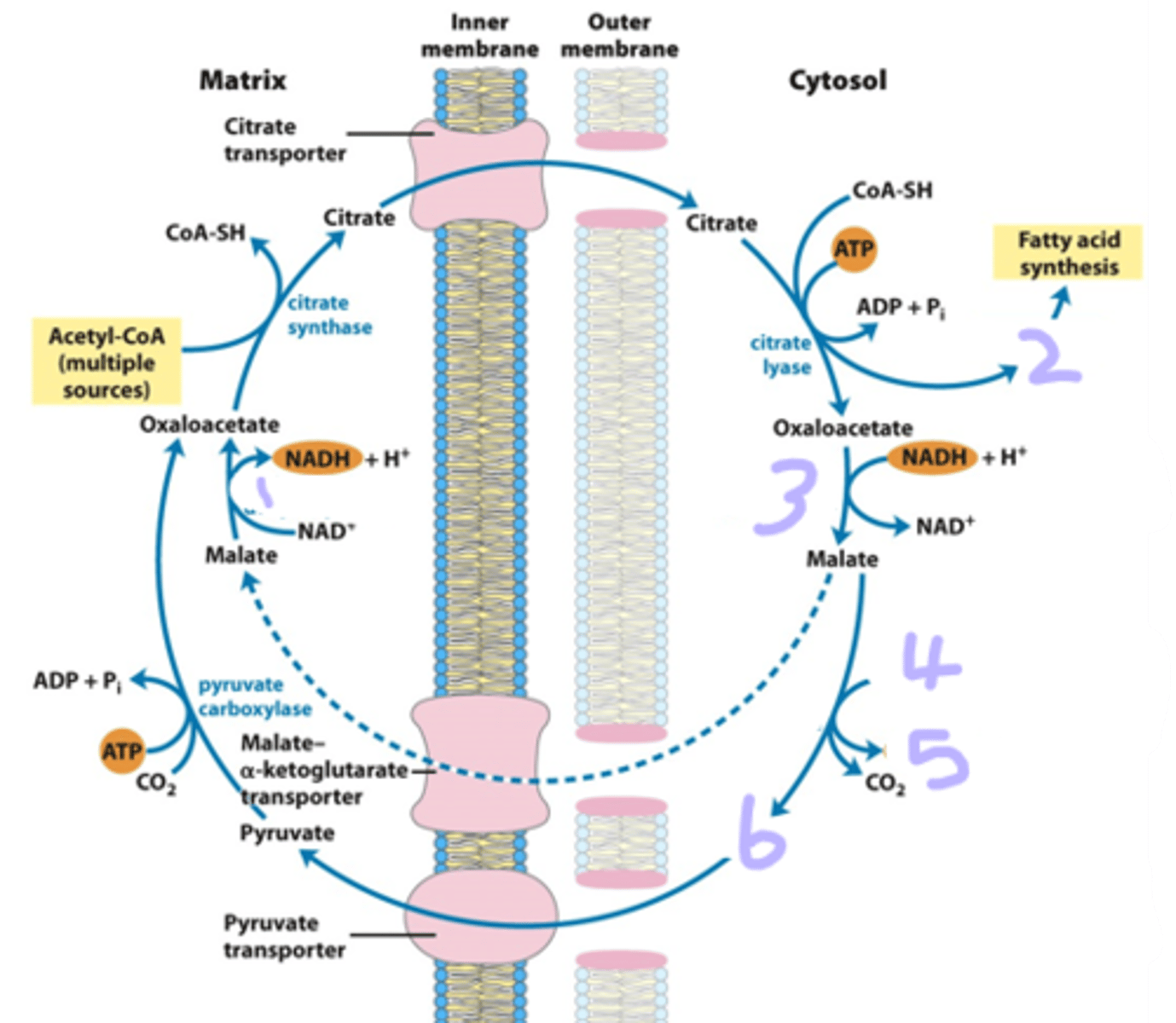
The reaction catalyzed by _______ _______ is the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of fatty acids
acetyl-CoA carboxylase
When mitochondrial acetyl-CoA and ATP increase, citrate is transported ______ ____ ____. it then becomes both the precursor of _____ and an activation signal for _____ ______
out of mitochondria; acetyl-CoA; acetyl-CoA carboxylase
1 - citrate
2 - acetyl-CoA carboxylase
3 - Palmitoyl-CoA
fill in the diagram
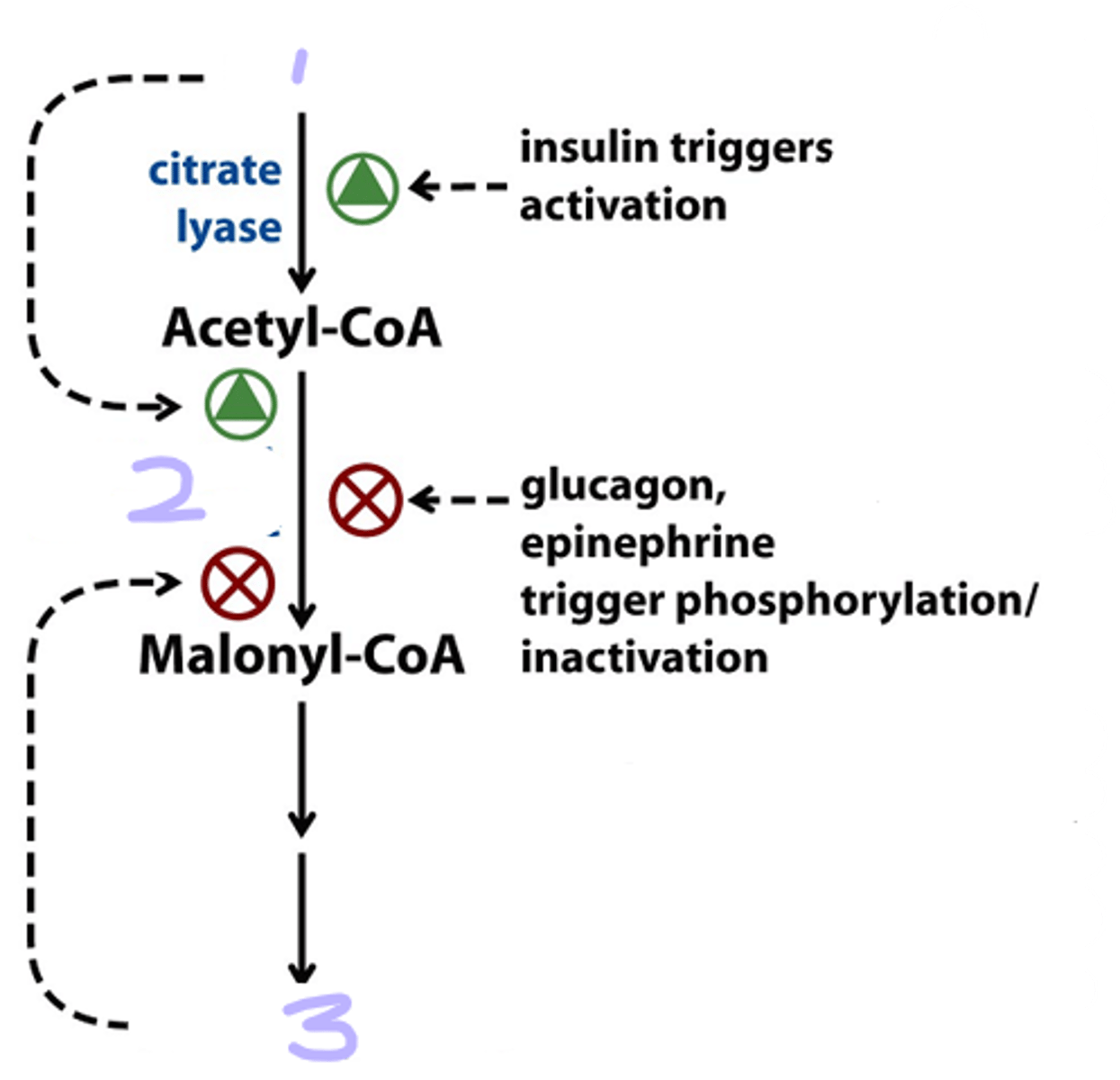
in its _____ (dephosphorylated) form, acetyl-CoA carboxylase polymerizes into long filaments
active
In the well fed state the body wants to store energy so fatty acid synthesis should be turned _____ while lipase should be _____. So in the well fed state insulin is ____, glucagon is ____, cAMP is ____, so protein kinase A activity is _____, the hormone-sensitive lipase is in the _____ dephosphorylated state while the carboxylase is active because it is dephosphorylated.
on; off; up; down; down; down; inactive
Long-chain saturated fatty acids are synthesized from _______
palmitate
______ is the principal product of fatty acid synthesis
palmitate
palmitate can be lengthened to form ____ ____ (__:__) or longer saturated fatty acids. Palmitate moves to the _____ where elongation occurs by addition of ____ ____ units
stearic acid; 18:0; sER; 2 carbon
Desaturation of fatty acids requires what enzyme?
fatty acyl-CoA desaturase
two essential fatty acids
linoleic acid; linolenic acid
arachidonic acid can be synthesized from ___ ___
linoleic acid