AP Psych Unit 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/153
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
1
New cards
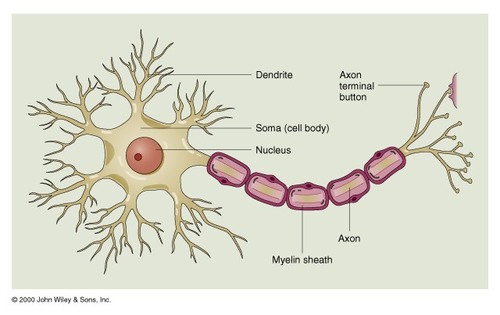
Neurons
Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information.
2
New cards
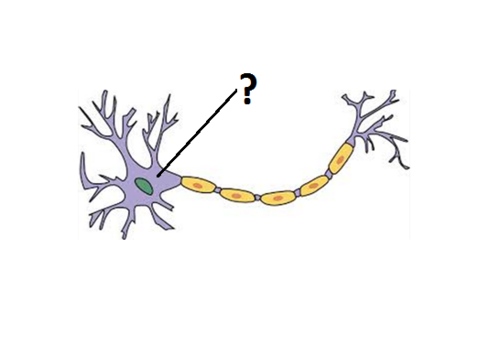
Soma/Cell Body
contains the cell nucleus and much of the chemical machinery common to most cells
3
New cards
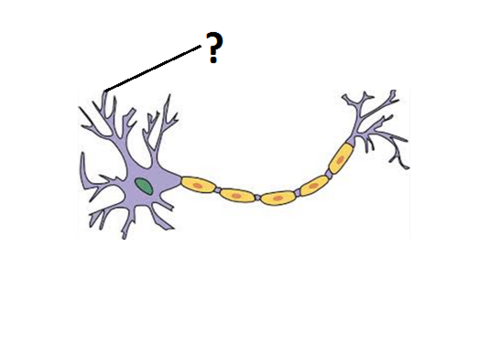
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
4
New cards
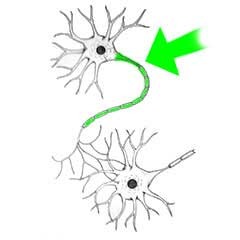
Axon
Long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body of a neuron and transmits signals to other neurons
5
New cards
Myelin Sheath
insulating material that encases some axons
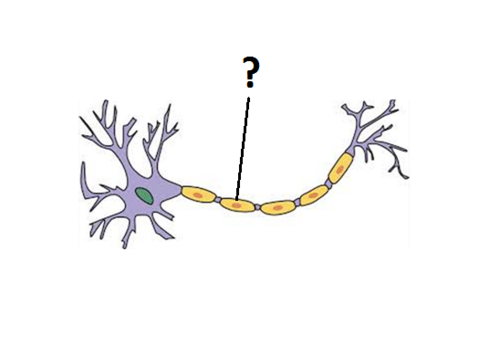
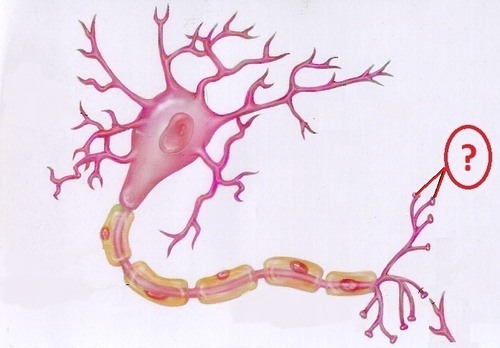
6
New cards
Terminal Button
small knobs that secrete neurotransmitters
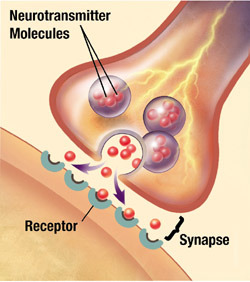
7
New cards
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons and activate other neurons
8
New cards
Resting Potential
the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse/inactive, a stable negative charge (-70mV)
9
New cards
Action Potential
A brief shift in a neuron's electrical charge positively that travels along an axon.
10
New cards
Absolute Refectory Period
minimum length of time before another action potential can begin (1-2 milliseconds)
11
New cards
All or None Law
neurons must fire or not fire, all action potentials are equal in strength (but not rate)
12
New cards
Presynaptic Neuron
neuron that sends the signal (neural impulse) to another neurons
13
New cards
Postsynaptic Neuron
neuron that receives the signal (neural impulse)
14
New cards
Postsynaptic Potential (PSP)
a voltage change at a receptor site on a postsynaptic cell membrane, does not follow All or None Law (varies in charge/strength)
15
New cards
Inhibitory PSP
a negative voltage shift that decreases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials
16
New cards
Excitatory PSP
a positive voltage shift that increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials
17
New cards
Reuptake
the reabsorption of inactive neurotransmitters by a presynaptic neuron's terminal button
18
New cards
Synaptic Pruning
the elimination of old or less-active synapses
19
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter
-involved in motor neurons
-contributes to attention, arousal, memory, learning, movement and sleep
-excess: depression
-deficit: dementia
-agonist: nicotine
-involved in motor neurons
-contributes to attention, arousal, memory, learning, movement and sleep
-excess: depression
-deficit: dementia
-agonist: nicotine

20
New cards
Dopamine (DA)
neurotransmitter
- involved in voluntary movement, attention, alertness
- known as the reward pathway
-excess: schizophrenia
-deficit: parkinson's disease
-cocaine increase dopamine synapse activity
- involved in voluntary movement, attention, alertness
- known as the reward pathway
-excess: schizophrenia
-deficit: parkinson's disease
-cocaine increase dopamine synapse activity

21
New cards
Norepinephrine(NE) / Epinephrine
neurotransmitter
- contributes to change in mood, arousal, fight or flight response
- cocaine elevates synapse activity
- excess: high blood pressure, schizophrenia
- deficit: depression
- contributes to change in mood, arousal, fight or flight response
- cocaine elevates synapse activity
- excess: high blood pressure, schizophrenia
- deficit: depression

22
New cards
Serotonin
neurotransmitter
- regulates sleep, wakefulness, eating, aggression, mood regulation
-deficit: depression, anxiety disorders, OCD
- antagonist: LSD
- Prozac & SSRIS stop serotonin reuptake
- regulates sleep, wakefulness, eating, aggression, mood regulation
-deficit: depression, anxiety disorders, OCD
- antagonist: LSD
- Prozac & SSRIS stop serotonin reuptake

23
New cards
GABA
neurotransmitter
- tends to work as an inhibitor
- regulates anxiety, sleep and arousal
- agonist: valium, anti-anxiety drugs, alcohol
- excess: seizures, insomnia
- deficit: anxiety disorders
- tends to work as an inhibitor
- regulates anxiety, sleep and arousal
- agonist: valium, anti-anxiety drugs, alcohol
- excess: seizures, insomnia
- deficit: anxiety disorders

24
New cards
Endorphins
neurotransmitter
- contributes to pain relief, stress response and eating
- agonist: opiates (heroin & morphine)
- deficit: addiction
- contributes to pain relief, stress response and eating
- agonist: opiates (heroin & morphine)
- deficit: addiction
25
New cards
Agonist
A chemical that mimics the action of a neurotransmitter.
26
New cards
Antagonist
chemical that blocks receptor sites
27
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
28
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
all nerves outside of brain and spinal cord
29
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
nerves that connect to the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscles and glands (automatic, involuntary functions)
30
New cards
Somatic Nervous System
nerves that connect to voluntary skeletal muscles and to sensory receptors (movement and senses)
31
New cards
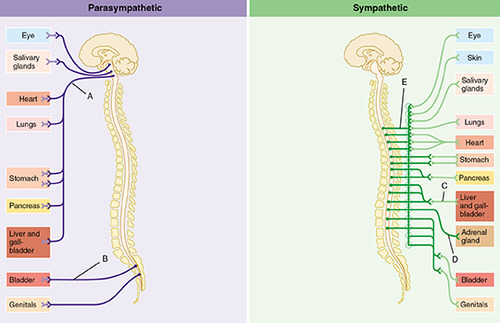
Sympathetic Division
branch of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) that uses the body's resources for emergencies, division in flight or flight
32
New cards
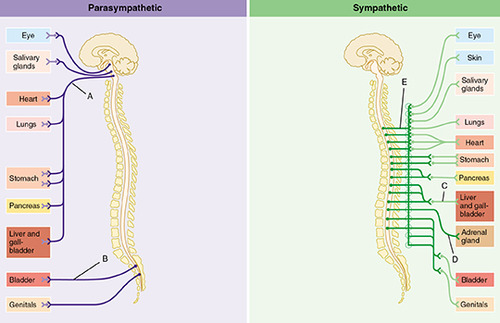
Parasympathetic Division
branch of Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) that conserves the body's resources
33
New cards
Fight or Flight Response
autonomic, bodily and emotional response to either fight or flee a threat
34
New cards
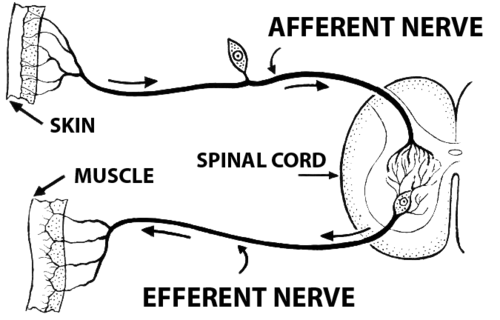
Afferent Nerve Fibers
axons carry info from the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) to Central Nervous System (CNS)
35
New cards
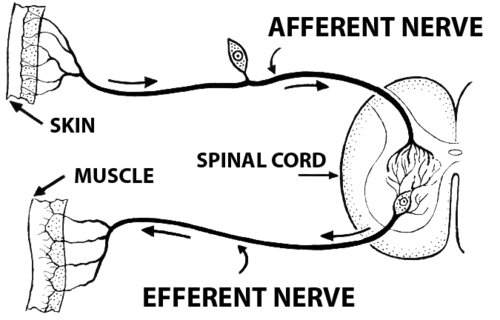
Efferent Nerve Fibers
axons carry info from the Central Nervous System (CNS) to Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
36
New cards
Spinal Cord
connects brain to the rest of the body through the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
37
New cards
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
fluid that cushions and protects the brain
38
New cards
Lesioning
destroying a piece of the brain
39
New cards
Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB)
Sending a weak electric current into a brain structure to stimulate (activate) it.
40
New cards
James Olds' research on pleasure centers
rats would press a lever (hundreds of thousands of times) to stimulate the pleasure center of the brain (aka dopamine)
41
New cards
Computerized Tomography scan (CT)
computer enhanced x-ray of brain structure
42
New cards
magnetic resonance imaging scan (MRI)
use of magnetic fields, radio waves and computerized enhancements to map the brain, better at mapping the brain than CTs
43
New cards
Position Emission Tomography scans (PET)
use of radioactive markers to map the chemical activity in the brain
44
New cards
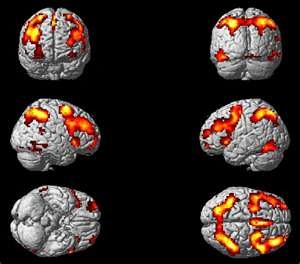
functional magnetic resonance imaging scans (fMRI)
new variations of MRI scans that monitor oxygen & blood consumption in the brain, and activity over time
45
New cards
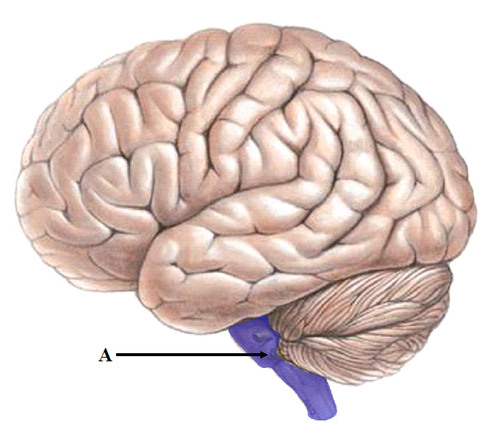
brainstem
responsible for automatic survival functions, connects the spinal cord to the brain
46
New cards
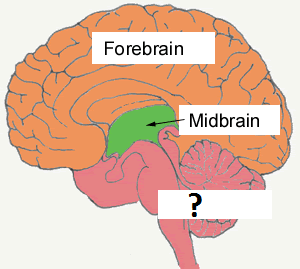
Hindbrain
-lowest part of the brainstem
-medulla, pons, cerebellum
-medulla, pons, cerebellum
47
New cards
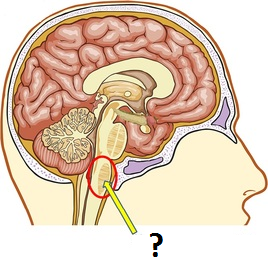
Medulla
-part of hindbrain
-attached to spinal cord
-controls unconscious essential functions, breathing, heartbeat, etc.
-attached to spinal cord
-controls unconscious essential functions, breathing, heartbeat, etc.
48
New cards
Pons
-part of hindbrain
-fibers that connect brainstem to the cerebellum
-fibers that connect brainstem to the cerebellum
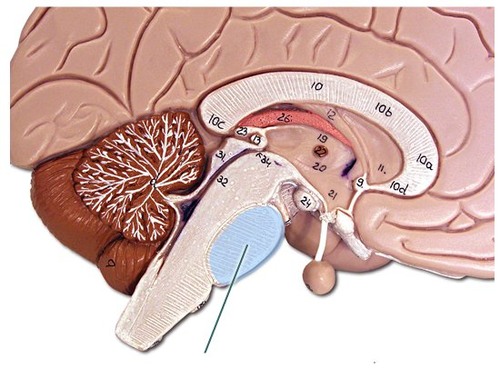
49
New cards
Cerebellum
-part of hindbrain
-largest structure next to the back of the brain stem
-controls movement coordination, physical balance and fine motor skills
-largest structure next to the back of the brain stem
-controls movement coordination, physical balance and fine motor skills
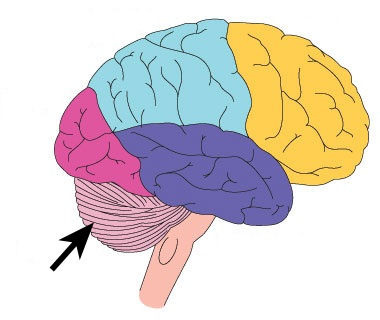
50
New cards
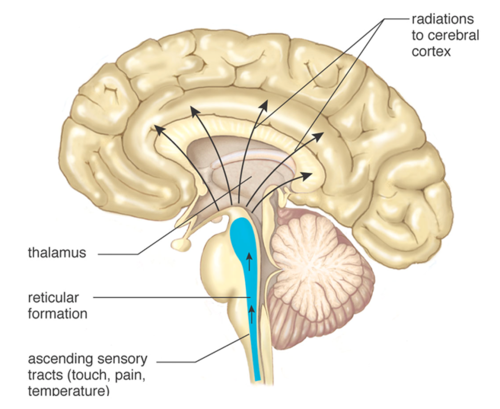
Reticular Formation
-between hindbrain and midbrain
-contributes to controlling muscle reflexes, breathing and pain perception
-contributes to controlling muscle reflexes, breathing and pain perception
51
New cards
Forebrain
-largest, most complex region of the brain
-cerebrum, cerebral cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system
-cerebrum, cerebral cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system
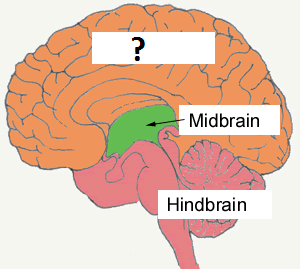
52
New cards
Midbrain
-between hindbrain and forebrain
-helps with sensory processes, voluntary movement and releasing dopamine
-helps with sensory processes, voluntary movement and releasing dopamine
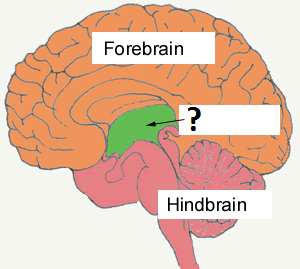
53
New cards
Cerebrum
-helps with complex thought
-part of forebrain
-part of forebrain
54
New cards
Cerebral Cortex
-wrinkled surface of the cerebrum
-part of forebrain
-part of forebrain
55
New cards
Thalamus
-part of forebrain
-cluster of cells/axons
-help pass sensory info (besides smell) to the cerebral cortex, integrates info from senses
-cluster of cells/axons
-help pass sensory info (besides smell) to the cerebral cortex, integrates info from senses
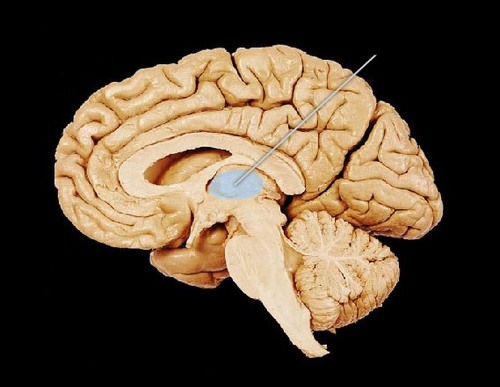
56
New cards
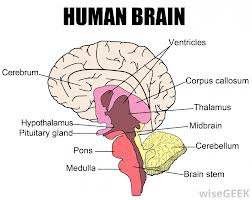
Hypothalamus
-part of forebrain
-cluster of cells
-regulate basic biological needs and controls the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
-supports endocrine system
- four Fs: fight, flee, feed, fornicate
-cluster of cells
-regulate basic biological needs and controls the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
-supports endocrine system
- four Fs: fight, flee, feed, fornicate
57
New cards
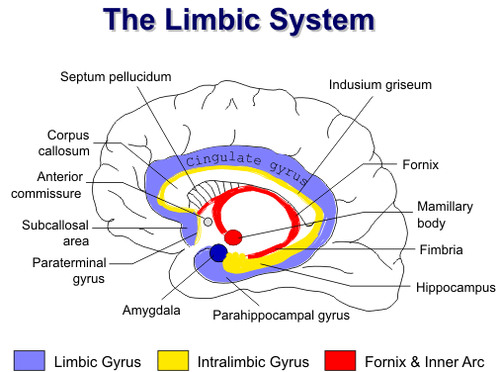
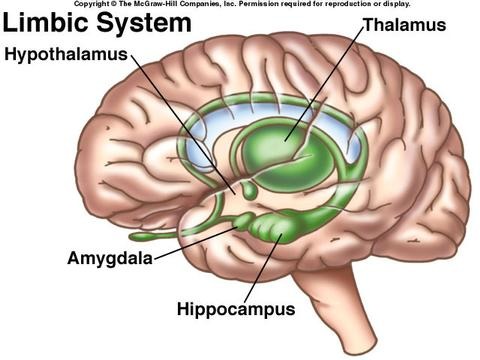
Limbic System
-part of forebrain
-loosely connected network of structures, including parts of the thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygalda, etc.
-helps memory processes, experience emotion, contains pleasure centers
-loosely connected network of structures, including parts of the thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygalda, etc.
-helps memory processes, experience emotion, contains pleasure centers
58
New cards
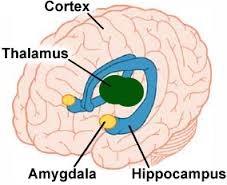
Hippocampus
-helps in transferring short term to long term memory
-forebrain
-forebrain
59
New cards
Amygalda
-helps in basic emotional responses
-forebrain
-forebrain
60
New cards
cerbral hemispheres
right and left halves/hemispheres of the cerebrum
61
New cards
corpus callosum
connects the two cerebral hemispheres
62
New cards
Lobes
the different regions into which the cerebrum is divided
63
New cards
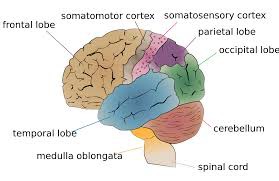
Occipital Lobe
- includes visual cortex, which helps with visual signals and visual processing
- includes visual processing
- includes visual processing

64
New cards
Parietal Lobe
- includes somatosensory cortex, which helps with sense of touch
- registers touch, integrating input and monitoring the body's position
- includes sense of touch, feeling of temperature and pain, causing phantom limb syndrome, processing info from body
- registers touch, integrating input and monitoring the body's position
- includes sense of touch, feeling of temperature and pain, causing phantom limb syndrome, processing info from body
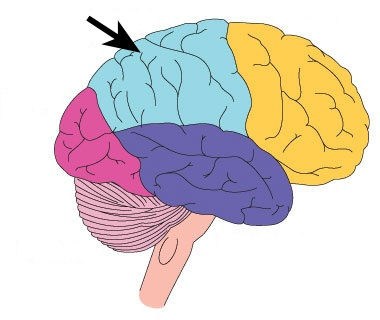
65
New cards
Temporal Lobe
- includes auditory cortex, which helps with auditory processing
- helps with speech and language, hearing, speaking, verbal language
- includes wernicke's area, which helps with understanding language
- helps with speech and language, hearing, speaking, verbal language
- includes wernicke's area, which helps with understanding language
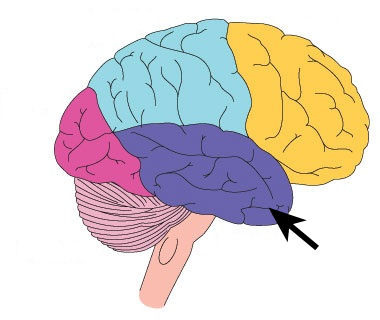
66
New cards
Frontal Lobe
-largest lobe
- includes motor cortex, which helps with controlling muscle movement
- includes prefontal cortex, which helps with reasoning, planning, paying attention, decision making, etc.
- includes broca's area
- includes motor cortex, which helps with controlling muscle movement
- includes prefontal cortex, which helps with reasoning, planning, paying attention, decision making, etc.
- includes broca's area
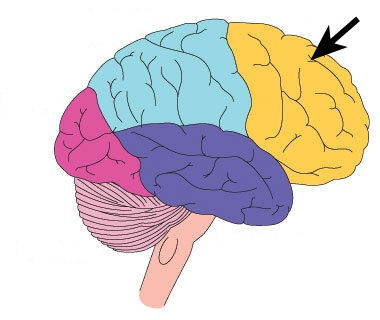
67
New cards
Mirror Neurons
neurons that are activated by performing an action or by seeing another monkey or person perform the same action
68
New cards
Prefrontal Cortex
very large, contributes to decision making and self control, reasoning, planning, decision making, impulse control
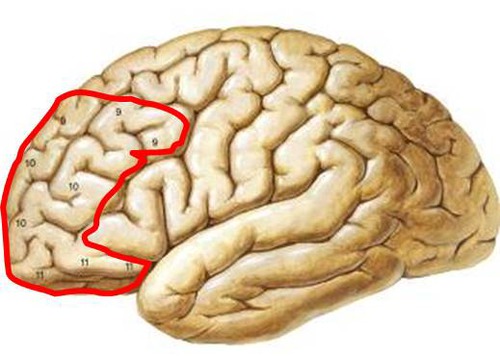
69
New cards
Brain Plasticity
-parts of the brain are anatomically flexible
-aspects of experience changes brain structure
-damage of sensory pathways/brain tissue leads to neural reorganization
- adult brains can generate new neurons
-aspects of experience changes brain structure
-damage of sensory pathways/brain tissue leads to neural reorganization
- adult brains can generate new neurons
70
New cards
Neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
71
New cards
Right Brain
controls left side of body, non verbal expressions, spatial skills, creativity
72
New cards
Left Brain
controls right side of body, language, math, logic, analytics
73
New cards
Robert Sperry's and Michael Gazzaniga's Research
cut and removed the corpus callosum to try and find treatment for epilepsy, found that it reduced seizures, but transfer of information between the two brains is lost
74
New cards
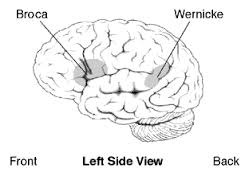
Wernicke's Area
- temporal lobe
- comprehension of language
- comprehension of language
75
New cards
Broca's Area
- frontal lobe
- production of speech
- production of speech
76
New cards
Homunculus Brain Map
a map of brain areas showing what parts of the brain control parts of the body
77
New cards
Electroencephalogram (EEG) scan
monitors electrical activity of the brain (brain waves)
78
New cards
ventricles
cavities within the brain that store cerebrospinal fluid (csf)
79
New cards
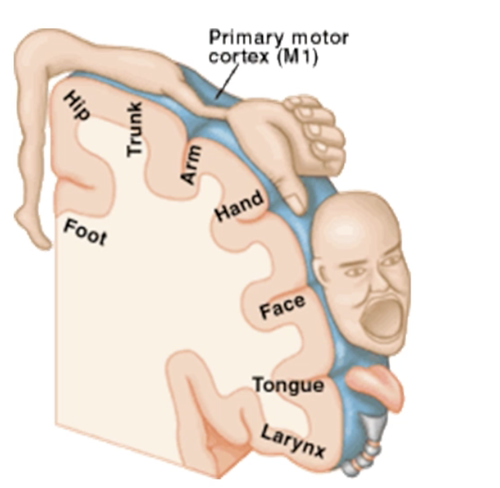
Motor Cortex
helps with precise, fine muscle movement
80
New cards
Somatosensory Cortex
helps control sensory info
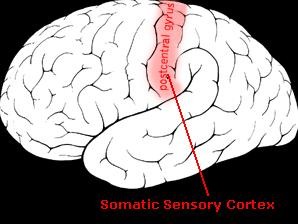
81
New cards
Auditory Cortex
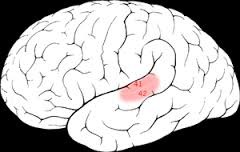
82
New cards
Visual Cortex
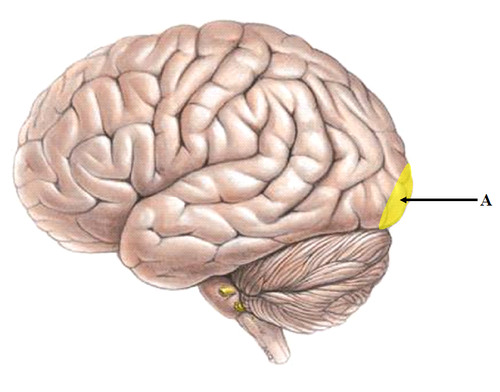
83
New cards
Endocrine System
the glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream that help control bodily functions, heavily supported by the hypothalamus
84
New cards
Hormones
chemical substances released by the endocrine systems (last long term and through the bloodstream, unlike neurotransmitters)
85
New cards
pituitary gland
pea sized, releases variety of hormones, stimulates actions of other endocrine glands (called the master gland), part of endocrine system and CNS
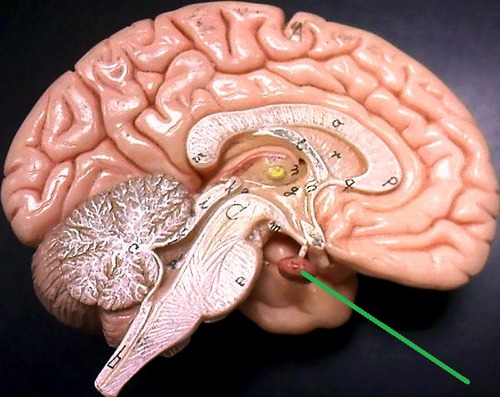
86
New cards
Oxytocin
released by pituitary gland, controls reproductive behavior
87
New cards
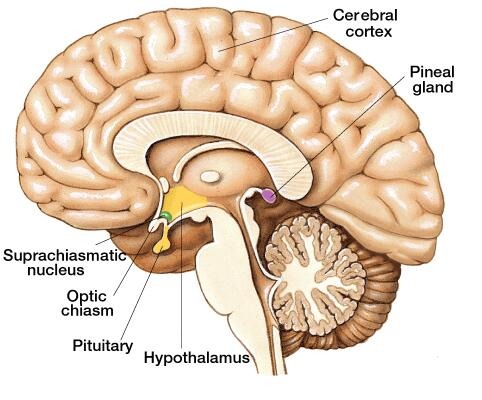
Pineal Gland
part of endocrine system, secretes melatonin, helps circadian rhythm
88
New cards
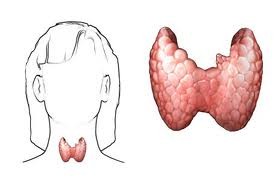
Thyroid Gland
part of endocrine system, produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
89
New cards
Liver
supports endocrine system, helps with bloodwork
90
New cards
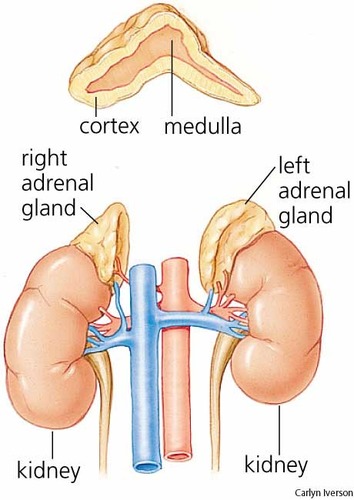
adrenal glands
glands that help the body recover from stress and respond to emergencies, secretes adrenaline
91
New cards
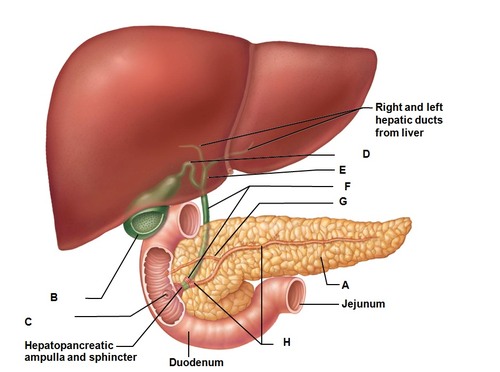
Pancreas
part of endocrine system, Regulates the level of sugar in the blood, secretes insulin, near the liver
92
New cards
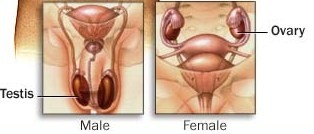
Ovary (Gonads)
part of endocrine system, helps with reproductive health and fertility, secretes estrogen
93
New cards
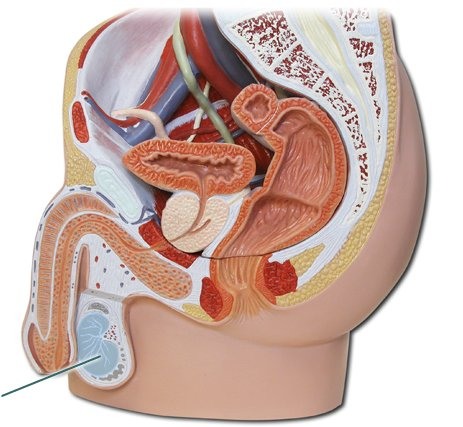
Testis/Testicles (Gonads)
helps with reproductive health and fertility, secretes testosterone
94
New cards
Chromosones
threadlike strands of DNA molecules that carry genetic info 46 choromsones in cells, 23 from each parent
95
New cards
Genes
DNA segments that pass on hereditary info
96
New cards
Polygenic Traits
characteristics influenced by more than one part of genes
97
New cards
Family studies
researchers assess hereditary influence by examining blood relatives to see how closely they all have one specific trait, correlative not causative, easily confounded
98
New cards
Twin Studies
hereditary influence is assessed by comparing identical/fraternal twins on a specific trait, more accurate than family studies
99
New cards
Monozygotic Twins
one egg splits, identical twins, 100% identical genes
100
New cards
Dizygotic Twins
two eggs are fertilized at the same time, fraternal twins, 50% identical genes