Fuels
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Exothermic Reaction
An Exothermic reaction transfers thermal energy to the surroundings therefore losing heat this leads to an increase in the temperature of the surroundings.
Exothermic reaction involves bond making
Example: Burning
Endothermic Reaction
Takes in thermal energy from the surroundings therefore gaining heat this leads to a decrease in temperature of the surroundings
Endothermic reaction involves bond breaking
Examples: Ice cube melting, respiration
Reaction Pathway Diagrams
Activation Energy
Activation Energy is the minimum energy that colliding particles must have to react
Which is an endothermic process
Bond Breaking
What is an exothermic reaction
Bond Making
3 Main fossil fuels
Coal, Natural gases, Petroleum
Main constituent of Natural gases
Methane
What are hydrocarbons
Compounds that contain : Hydrogen and Carbon
Petroleum is a mixture of _____________
Petroleum is a mixture of Hydrocarbons
Fractional Distillation: Petroleum/ Crude Oil
Fractional Distillation is the separation of petroleum(crude oil) utilizing the different boiling points in the mixture
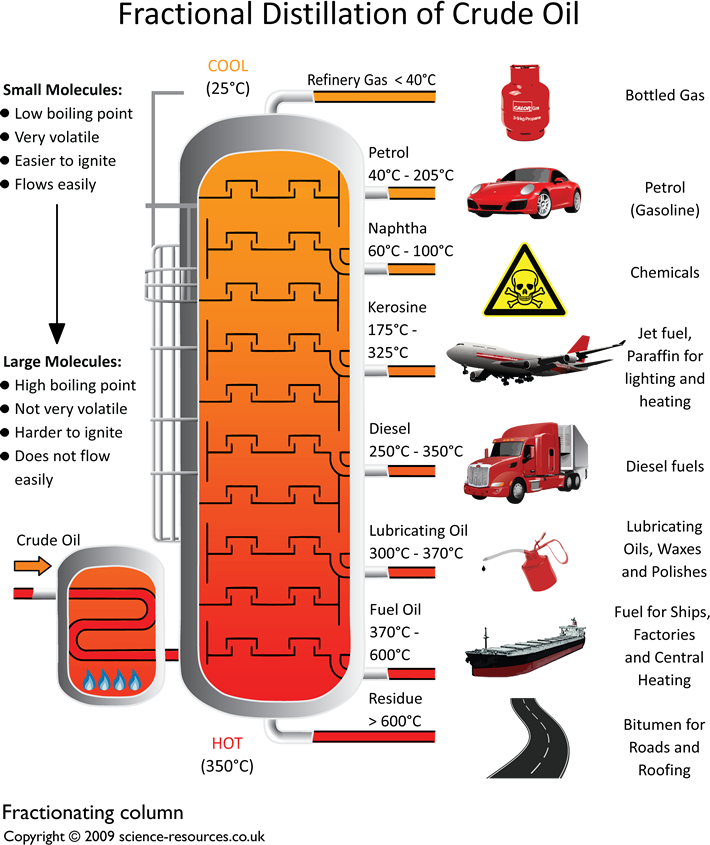
Describe how the fractionating column separates the crude oil
The Crude oil gets heated to a vapour and enters the fractionation coloumn, which then rise through the column. As the vapours rise, they cool and condense at different levels according to their boiling points, with higher-boiling (larger, more viscous, less volatile) fractions collecting at the bottom and lower-boiling (smaller, less viscous, more volatile) fractions collecting at the top. These distinct collections of hydrocarbons, called fractions, are then collected for various uses
uses of fractions in fraction distillaion
Properties of hydrocarbons
Saturated Compounds
A Saturated compound is a compound which all carbon bonds are single bonds
Unsaturated Compounds
A Unsaturated compounds is a compound is which one or more carbon bonds are not single bonds
Homologous Series
Homologous Series is a family of similar compounds with similar chemical properties
General Characteristics of Homologous Series
Having the same general formula
Displaying a trend in physical properties
Manufacture of Alkenes and Hydrogen- Cracking
Alkenes and hydrogens are produced by the cracking of larger alkane molecules
Cracking:
Thermal Cracking- by using high temperature and pressure to break the bonds
Catalytic Cracking- by using a low temperature and pressure with a catalyst
They are separated by fractional Distillation
Bonds in Alkenes
Includes a double carbon covalent bon and alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons
Test: Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons
Bromine Water is used to tell the difference between an alkane and alkene
An alkene will turn brown bromine water colourless
An alkane will stay brown
Polymers
Polymers are large molecules built up from many smaller molecules called monomers
Formation of Polyethene
Formation of Polyethene is an example of additional polymerisation using ethene (an alkene) monomer
poly- multi