Sports Psychology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
sports and exercise psychology definition
the scientific study of people and their behaviors in sport and exercise activities and the practical application of that knowledge
objective of S&E psych
understanding how psychological factors influence performance and how sports impact mental health and general well being
Three main roles of S&E psychologists
research, teaching, consulting
Sport psychology specialties
clinical sport psychologists and educational sport
clinical sport psych specialty
licensed psychologists that are trained to work with people with severe emotional disorders ie helping athletes with eating disorders and substance abuse
educational sports psych speciality
mental coach approach - understand psych of human movement and training in physical education, kinesiology, or exercise and sports science. Educate and increase athletes and coaches awareness of issues such as anxiety management and confidence development
sports science knowledge domain
Biomechanics
Exercise physiology
Motor development
Motor learning and control
Sports medicine
Sports pedagogy
Sport sociology
Psychology knowledge domain
Abnormal psych
Clinical psych
Counseling psych
Developmental psych
Experimental psych
Personality psych
Physiological psych
How hormones and internal states impact mental state
Scientific approach
a process, or method, of learning of about the world through the systematic controlled, empirical, and critical filtering of knowledge acquired through experience
Systematic - standardized the conditions
Controlled - no confounding variables
Empirical - based on observation
Critical - analysis of observation
methods of knowing
Scientific method
Systematic observation
Single case study
Shared (public) experience
Introspection
Intuition
Three approaches to s&e psych
Psycho-physiological orientation
Social-psychological orientation
Cognitive-behavioral orientation
approach to s&e psych: Psycho-physiological orientation
Examines underlying psychophysiological processes of the brain in terns of primary causes of behavior (heart rate, brain wave activity)
ie trained marksmen - they have to shoot in between their heart beats
how the brain reacts to the body and vice versa
“I’m so tired. I want to quit”
approach to s&e psych: social psychological orientation
behavior is determined by a complex interaction of the social environment and the personal makeup of the athlete or exerciser
how the general population or team affects your psyche and how people as a whole impact you. Again, also, vice versa
approach to s&e psych: cognitive-behavioral orientation
behavior is determined by both the environment and thoughts (cognitions)
link of sports psych and business
Lessons learned in high performance sport can be applied to business
Corporate athlete notion focuses on helping people in business reach their goals through principles of sports psych and training
Sustain high business performance through leadership development seminar, team building exercises, and one-on-one coaching
personality
the characteristics or blend of them that make a person unique
structure of personality
Psychological core
Who you are at your base - the deepest part
Typical responses
Related to social environment
Role related behavior
Who you are in different places/ with different people - dynamic
How one acts in a particular social situation
approaches to understanding personality
Psychodynamic approach
Trait approach
Situational approach
Interactional approach
Phenomenological approach
psychodynamic approach to understanding personality
Behavior determined by unconscious and changing factors that often conflict with one another
Emphasize understanding the person as a whole and not their isolated traits
Freud
trait approach to understanding personality
Personality is hereditary - born with certain traits that are fundamental units of personality and predispose you to act a certain way
situational approach to understanding personality
Personality is dependent of context or environment and states that the situation is more determinant of behavior than particular personality traits
not widely embraced
interactional approach to understanding personality
Personality is determined by the interaction of your environment and your traits you already had
You are an anxious person and are in an unsettling environment making you closed off and very anxious
Majority of sports and exercises psychologists accept this
phenomenological approach to understanding personality
Type of international approach but says you are influenced by traits, environment, but also how you perceive it
Also well liked
perfectionism
multidimensional construct that consists of various components, including setting high standards, feeling concern over mistakes, and being highly organized
self oriented Degree to which one sets high personal standards and stringently self evaluate relative to those standards
Socially prescribed: Perceives significant others hold high standards for the person and based approval on meeting those standards
can either be good or bad
Others oriented: One holds others to extremely high standards
depending on specific components can either be functional/dysfunctional
measuring personality: traits and states
Trait is a typical style of behavior
State is the situation’s effects on behavior - a “right now” feeling that can change from moment to moment
Situation-specific trait tests predict behavior more accurately than general trait measures
Often more effective to compare personality test scores to a person’s own previous test results than to a group norm
Projective tests are interesting but difficult to score
Do’s and donts in personality testing
Do inform participants of the purpose of the personality test and how it will be used
Do allow only qualified individuals who understand testing principles and measurement error to give personality tests
Don't use tests to predict behavior in sports and exercise settings without considering other sources of information
Don't use personality tests to decide who makes a team or program and who does not
cognitive strategies and athletic stress
Cognitive strategies and mental strategies are skills and behaviors athletes have
Not personality traits but they reflect behavior aspects of personality and interact with personality characteristics
Cognitive strategies are related to superior performance in elite athletes and help them to cope with adversity and mentally prepare non elite athletes
Arousal
the blend of physiological and psychological activation,varying in intensity on a continuum
Anxiety
is a negative emotional state with feeling of worry, nervousness and apprehension associated with activation or arousal of the body
Stress
a substantial imbalance between physical and psychological demands placed on an individual and his or her response capability under conditions in which failure to meet demands has important consequences * you have to do something difficult and the outcome it’s important
Measuring arousal and anxiety
physiological signs (heart rate, respiration, skin conductance, biochemistry)
Global and multidimensional self reported scales: competitive state anxiety inventory, sport anxiety scale
Relationship between trait and anxiety state
State refers to right now feelings that change from moment to moment
Trait anxiety is a personality disposition test is somewhat stable over time
High versus low trait anxious people usually have more state anxiety in highly evaluative situations
emotions
“short lived feeling states that occur in response to events”
Both physiological and psychological components
Distinctions are made between mood and emotion but boundaries are often blurred
Emotions influence performance while sport and physical activity participation influence emotions
This is in essence the objective of sports and exercise psychology
stress process
Environmental demand (physical and psychological)
Individual’s perception of the environmental demand (amount of psychological or physical “threat” perceived)
Stress response (physical and psychological)
Behavioral consequences (performance or outcome)
sources of stress and anxiety
Situational sources
Event importance
Can create positive stress
Or can create negative stress/ anxiety that hinders performance
Uncertainty
Personal sources
Trait anxiety
Self esteem
Social physique anxiety
izof
people have different levels of ideal arousal that are in varying zones
stressor to control schematic
Different events create different feelings and emotions for different people and those people are going to react differently according to their characteristics and then they will feel they can or cannot control the situation
arousal
it is multifaceted and consists of the following:
Physical activation
Interpretation - can be facilitative or debilitative
to perceive as facilitative self confidence and perception of control is important
Doubtful that the optimal level of arousal is always at the midpoint of the arousal scale
Interaction of physiological activation and arousal interpretation is more important than actual levels of each
psyching up
strategies that should be employed with caution because it is difficult to recover from a catastrophe
Athletes should have well- practiced self talk, imagery, relaxation, and goal setting skills for coping with anxiety
why anxiety influences performance
Increased muscle tension, fatigue, and coordination difficulties
Changes in attention, concentration, and visual search
Narrowing of attention
Attending to inappropriate cues
Visual cues are differently identified and processed when performers are anxious
Performance worries and situational- irrelevant
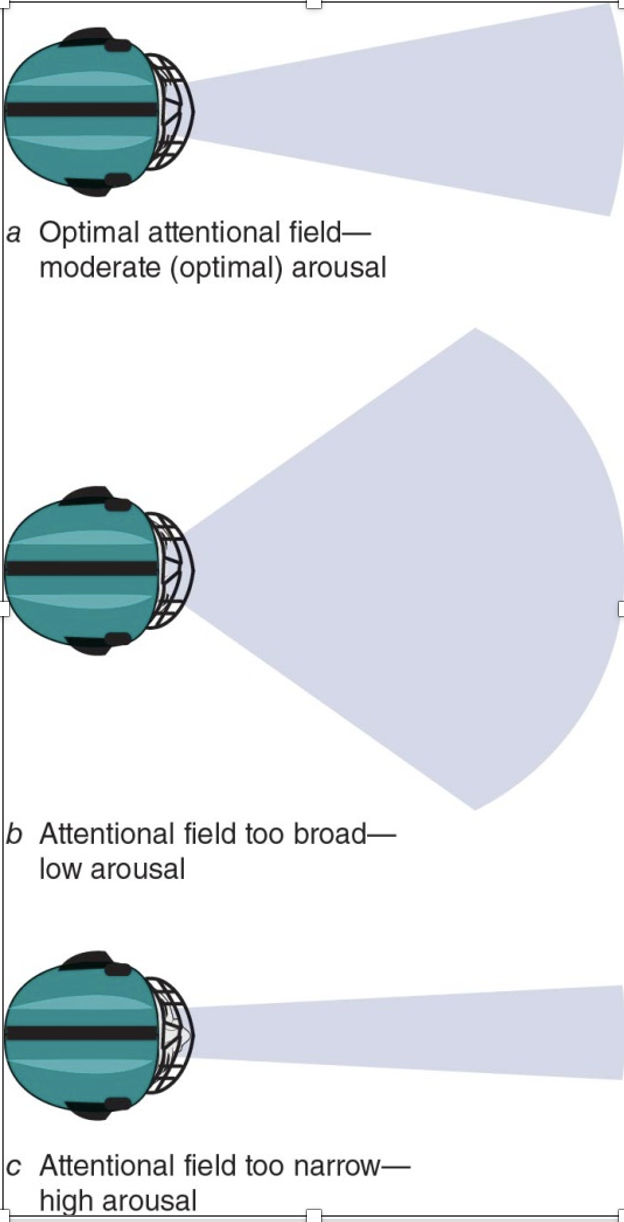
motivation
is the direction and intensity of effort
Direction of effort whether an individual seeks out, approaches, or is attracted to situations.
Intensity of effort refers to how much effort an individual puts forth in a situation
Both are related
views of motivation
Participant- or trait-centered view
Situation-centered view
Interactional view
Participant- or trait-centered view - Views of motivation
Motivated behavior is primarily a function of individual characteristics
situation-centered view - views of motivation
Motivation level is determined primarily by situation
interactional view - view of motivation
Motivated behavior results from the interaction of participant factors and situational factors
guidelines for building motivation
Both situations and traits motivate people
People have multiple motives for involvement. Understand why people participate in physical activity
Change the environment to enhance motivation
Provide both competitive and recreational opportunities
Provide for multiple motives and opportunities
Adjust to individuals within groups
Leaders influence motivation directly and indirectly
Use behavior modification to change undesirable participant motives
Reward good behavior and reinforce good behavior
Last resort of having consequences for negative behavior if other resorts fail
key things to remember with motives of involvement
May be multiple motives
May have competing motives for involvement
People can have shared and unique motives
Motives can change over time
Motives differ across cultures
In America competition and improvement are motives while in China social affiliation and wellness are
how to identify a participants motives
Observe
Talk
Ask
major motives for sports participants
Improving skills
Having fun
Being with friends
Experiencing thrills and excitement
Achieving success
Developing fitness
major motives for exercisers
Health factors
Weight loss
Fitness
Self challenge
Feeling better
reasons people continue with sports
Enjoyment
Liking instructor
Liking type of activity
Social factors
developing a realistic view of motivation
Recognizing that Physical and psychological factors also influence behavior
Some motivational factors are more easily influenced than others. (change motivational style rather than the building)
implications of motivation for professional practice
Recognize the interaction of personal and situational factors influencing achievement behavior.
Goal orientation: ego (outcome) or task (mastery)
Attributions
Situations approached or avoided
Emphasize mastery (task) goals and downplay outcome goals. Create a mastery motivational climate
Focus on approach goals
Monitor and correct attributional feedback
Determine when competitive goals are appropriate
Enhance feelings of competence and control
mood
any short lived emotional state, usually of low intensity
Disposition to respond emotionally in a particular way that lasts for hours, day, or even weeks perhaps at a low level and without the person knowing what prompted the state
Disturbances in mood are characteristic of mood disorders
Emotions are intense feelings at are directed at someone or something
moods v emotions
Moods lack an object; anger can be aroused by an insult but an angry mood may arise when one does not know what one is angry about or what elicited the anger
Moods are feelings that tend to be less intense than emotions and that often lack a contextual stimulus
attribution theory
where do you attribute failure and success
Internal unstable - something you can change about yourself
Skill
Internal stable - something you cannot change about yourself
Height
External unstable - something you cannot change about the conditions
Im unlucky, the weather was bad, my opponents are lucky
competition
a social process that occurs when rewards are given to people for how their performance compares with the performance of others during the same task or when participating in the same event
cooperation
a social process through which performance is evaluated and rewarded in terms of collective achievement of a group of people working together to reach a particular goal
four step model of competition
Objective competitive situation
See something like a scoreboard with your name on it -> makes you think you are about to compete
Subjective competitive situation
Not everyone would view something as competitive -> someone that has never seen a scoreboard before wouldn't see it and get aroused
Response
Arousal or not getting aroused
Consequences
Performance