Year 10 Civics & Citizenship + Wellbeing
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Constitutional Monarchy
A form of monarchy where the monarch is not alone in making decisions.
Democracy
To rule by the people
Constitution
A set of rules that Australia is governed by, and outlines the structure, roles and powers of Parliament.
3 Levels of Government
Local, State, Federal
3 Branches of Government
Legislative, Executive and Judicial
Separation of Powers
The division of government with the aim of providing a system of checks and balances that prevents the concentration of powers to one group.
Legislative Arm
Parliament makes/changes laws
A law that has been passed by parliament is called legislation, a statute or an Act.
Executive Arm
The government
Administers the legislation passed by parliament. Executive power officially lies with the governor-general but government ministers exercise this power.
Eg. The Department of Health administers the running of Australia’s health system.
Judicial Arm
Consisting of the judiciary and the courts, makes judgements about the law.
Settles disputes and enforcing the law.
The High Court of Australia is responsible for interpreting and applying the Constitution.
How do the 3 branches of government run?
The legislature makes the laws; the executive puts the laws into operation; and the judiciary interprets the laws.
Federal Elections
When Australians vote for people to represent them in the Senate and House of Representatives.
House of Reps
Lower House
Green
151 Seats
Introduces Laws
The Senate
Upper House
Red
76 Seats
12 Reps/State and 2 Reps/Territories
Reviews Laws
Preferential Voting
When voters indicate an order of preference for candidates in a federal election.
House of Reps Elections
Every 3 years
Voters vote for the representative in their electorate.
76 or more of the 151 electorates have to be voted in from the same party to form government.
Senate Elections
Every 3 years, only half the senators: Each senator are elected for 6 year terms.
Voted through proportional voting
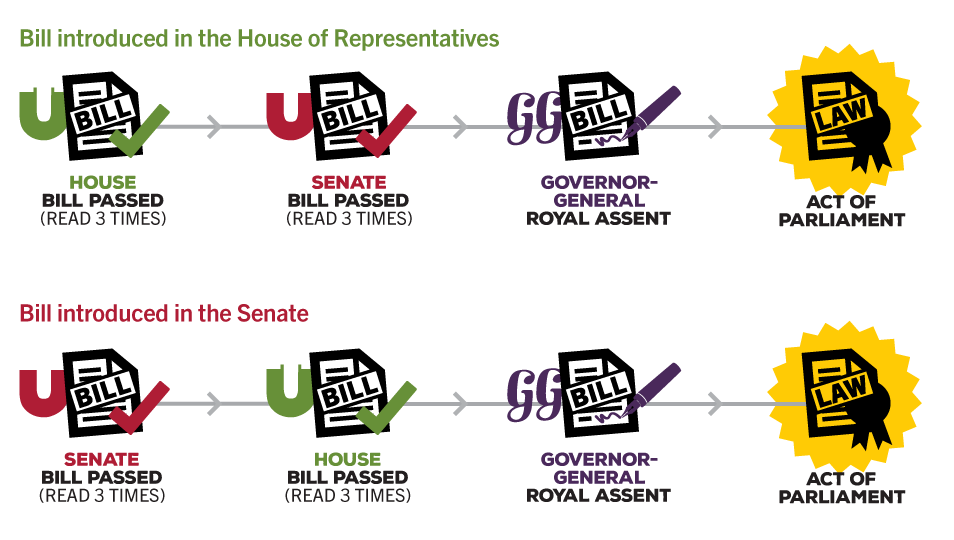
How are decisions made in parliament?
Foreign Aid
Assistance that one country voluntarily transfers to another, which can take the form of a grant, gift or loan.
Purpose of Foreign Aid
Development assistance
Humanitarian relief
Security
Diplomatic goals
Addressing global challenges
Examples of Foreign Aid
Economic development
Humanitarian assistance
Food Aid
Education
Agriculture
Military Support
Healthcare
Infrastructure
Water
2 Categories of Foreign Aid
Developmental Aid
Emergency Aid
Developmental Aid (Economic)
Addresses issues that contribute to poverty and human suffering.
Emergency Aid (Humanitarian/Disaster Relief)
Relieves suffering during emergency situations.
Humanitarian Aid VS Economic Aid
Humanitarian aid is immediate, while economic aid is long term.
How does emergency aid work?
Crisis is assessed
Resources are mobilised
Emergency aid is delivered
Where is most foreign aid distributed?
Africa, South Asia, Middle East, South America, Caribbean
Regions of Australia’s Foreign Aid Program
Indonesia
Papua New Guinea
Pacific Island nations
Who administers foreign aid in Australia?
Department of Foreign Affairs & Trade- AusAid
2 Types of Foreign Aid Programs
Bilateral Aid- 1 to 1 country
Multilateral aid –Multiple countries work together through organizations like the United Nations or the World Bank.
Non Government Organisation
A group that functions independently of any government. It is usually non-profit and provides services.
Non Government Organisation Example
Oxfam- A global movement of people who are fighting inequality to end poverty and injustice. They deliver development programs, public education, and humanitarian assistance.
The United Nations
International peacekeeping organisation
Discuss and debate international crises
Deploys peacekeepers
Creates and enforces international law
Aims of the UN
Promote human rights, world peace, international relationships and cooperation
Structure of the UN
General Assembly
Security Council
Economic and Social Council
The Trusteeship Council
International Court of Justice
UN Secretariat
When was the UN formed and why?
October 24 1945, with fifty countries
Response to the atrocities committed by the Axis powers of WW2
Sustainable Development Goals
A set of 17 goals established by the United Nations Development Program, which aim to end poverty, protect the Earth and promote peace, equality and prosperity.
General Assembly
All 193 Member States
On important issues a two/third majority is required; other questions require a simple majority vote.
All member states can bring issues of concern
Provides a forum for discussion
United Nations Security Council
Primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security.
Investigate any dispute which might lead to international friction
Take military action against an aggressor
Recommend admission of new members of the UN
Appoints Secretary-General
15 members, 5 permanent
Non permanent members are elected for 2 year terms
Powers held by the Security Council
Ceasefire Directives
Economic and international sanctions
Peacekeeping missions
Collective military action
Permanent Members of the Security Council
China, France, Russia, America, UK
Purpose of the UN’s Security Council veto power?
Allows each of the five permanent members to block any resolution that they believe go against their essential national interests or principles
Prevents any single country from domination of the UN
How many votes are required for a resolution to pass in the United Nations Security Council?
9/15 and all permanent members
Australia’s Increasing Contribution and Role in the UN
Aided peacekeeping missions, policy development, and financial support.
Australian representatives have championed gender equality, rights of women and whaling: banning Japan from conducting annual whale hunt.
Doc Evatt and his issue with the UN
Leading Australia's delegation, advocated for increased influence of smaller nations within the UN General Assembly to balance the dominance of larger countries in the Security Council.
Lobbied for the power of the General Assembly to be increased
Played a crucial role in developing the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, was President of the General Assembly in 1948.
The Declaration of Human Rights
Declares that human rights are universal – to be enjoyed by all people, no matter who they are or where they live.
UN Peacekeepers
Military that protect civilians, prevent conflict, strengthen security and maintain peace.
11 peacekeeping operations across Africa, the Middle East, Europe, and Asia.
Principles of Peacekeeping
Consent of the parties; Impartiality; Non-use of force except in self-defence and defence of the mandate.
Which country was one of the primary contributors to the establishment of UN peacekeeping forces?
France
Where has Australia sent Peacekeepers?
Solomon Islands
Cambodia
Afghanistan
Papua New Guinea
Wellbeing
A good or satisfactory condition of existence, experienced when people have what they need for life to be good.
Aspects of Wellbeing
Sense of Worth
Making an impact
Purpose
Happiness
Human Needs
Food/Water
Home/Shelter
Work/Income stability
Friends/community/belonging
Safety
Indicators
A value that help us to monitor and evaluate progress, or lack of it. There are quantitative (numerical) indicators and qualitative (descriptive) indicators.
Economic indicators:
Measure aspects of the economy and analyses performance.
Social indicators:
Demographic, social and health measures.
Environmental indicators:
Assess resources that provide economic development, and the health of the environment.
Political indicators:
Government effectiveness helping to improve people’s standard of living by ensuring access to essential services.
Technological indicators:
Fields such as transport, industry, agriculture, mining and communications.
Development
Development encompasses fulfilling basic needs, ensuring equity, sustainability, freedom, and safety, as well as economic growth.
Successful programs prioritize overall wellbeing, not just economic metrics like GDP.
Developed
A country that has attained a level of economic, social, and political success. MEDC: More economically developed country,
Developing
Countries that are still working towards a higher level of living standard or economic growth. LEDC: Less economically developed country.
PQE
Poverty
A denial of choices and opportunities, and a violation of human dignity.
First World
The bloc of democratic-industrialised countries within the American sphere of influence, the "First World," also known as The West.
Second World
The Eastern bloc of the communist-socialist states, where the political and economic power should come from the up to now oppressed peasants and workers.
Third World
The remaining three-quarters of the world population, countries that did not belong to either bloc, were considered "Third World."
Population Density
The number of people with a given area, usually per square kilometre.
Population Distribution
The spread of people across the globe.
Ageing Population
Percentage of people in older age groups in a population.
Factors that Vary Population Density
Availability of:
Freshwater resources, fertile soil
Inhospitable Features:
Mountains
Jungles
Deserts
Human Factors:
Urban places attract due to the availability of employment
Government policies
Migration where the demand for unskilled labour is high close to the border.
Chinese government policy led to the movement of Han Chinese into Tibet.
Establishment of service centres in Australia based around resource development, and the use of migration to combat population shrinkage and labour shortages in other regional communities.
However, not all regions of high density are urban places; rural environments, such as in parts of central Europe and South-East Asia, may contain large numbers of people per square kilometre.
Life Expectancy
The number of years a person can expect to live, based on the average living conditions within a country.
Child Mortality Rate
Rate of deaths in children in the under 5 age group, expressed per 1000 live births.
Infant Mortality Rate
The number of deaths of infants under 1 year of age, expressed per 100,000 births.
Factors to consider when analysing infant mortality rates
The sanitation levels
Nutrition
Education levels
Housing quality
Access to hospitals
The healthcare system
The income/wealth
How safe people feel
A woman’s right to choice / freedoms and rights
What is the link between high child mortality rates and life expectancy?
Life expectancy is closely interconnected with child mortality: countries with high death rates for children under five years of age have low life expectancy.
Child mortality is a huge factor in overall life expectancy — a large number of children dying can cancel out many people living to old age, and bring down the average lifespan.
Fertility Rate
The average number of children born per woman.
What happens when you don’t have clean water?
Non decent toilets
Children and babies die from diarrheal diseases and unclean environments.
Children do not have soap and water for washing.
Groundwater levels decline
Lakes disappear
Ecosystems and biodiversity are harmed
Sanitation
Provision of facilities that safely dispose of human waste.
Water Security
The reliable availability of acceptable quality water to sustain a population.
Maternal Mortality
The death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy.
S.H.E.E.P.T Factors
Social: Factors relating to values of a particular society: attitudes, religion, language, working skills, ethnicity.
Historical: Factors relating to events from the past that somehow affect the current situation in a country.
Economic: Factors relating to creating and spending money: Income, industry monies.
Environmental: Factors relating to features of the natural environment: Landforms, climate and vegetation.
Political: Factors relating to governments and non governments, including laws, regulation and policies (Cause and effect).
Technological: Factors relating to science, engineering, and communication.
Afghanistan S.H.E.E.P.T Factors
Social: Islamic religion, Gender inequality
Historical: Transitioned for most of history, and was under the rule of many different people. Eg. Different Empires, 4 Decade of War: US, Russia
Economic: Struggling economy, high taxes, high unemployment.
Environmental: Iran to the West, Pakistan to the East. Tall forbidding mountains, dug desserts, mountains covered in snow most of the year.
Political: Weak controlled government, many different political issues. Eg. Taliban.
Technological: Not technologically advanced.
GDP
The value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period by a country or countries. Often used to measure the economic health of a country or region.
What does the Human Development Index (HDI) measure and what three key factors are measured by the HDI?
Happy Planet Index
The Happy Planet Index shows how efficiently residents of different countries are using environmental resources to lead long, happy lives. It is calculated by multiplying experienced well being and life expectancy and dividing ecological footprint.
Gross National Happiness
In 2011 the Prime Minister of Bhutan developed the world’s first measure of happiness.
The Gross National Happiness Index is a single number index developed from 33 indicators categorised under nine domains.
Standard of Living
Level of material comfort in terms of goods and services available.
Absolute Poverty
Experienced when income levels are inadequate to enjoy a minimum standard of living (also known as extreme poverty).
Relative Poverty
Where income levels are relatively too low to enjoy a reasonable standard of living in that society.
Poverty Line
An official measure used by governments to define those living below this income level as living in poverty.
What is malnutrition and explain two types of malnutrition.
Lack of some or all nutritional elements necessary for human health. There are two basic types of malnutrition.
Lack of food that provides energy (measured in calories) obtained from all the basic food groups, and a lack of protein. Micronutrient (vitamin and mineral) deficiency, which may or may not occur with hunger.
Conflict Minerals
Natural resources that are mined in a conflict area and sold to extend/perpetuate a war. Examples: Blood diamonds, gold, copper, cobalt.
Favela
The name given to slums or shanty towns around the larger cities of Brazil.
List some effects of living in favelas.
Lack of infrastructure such as sanitation and piped water
Vulnerability to weather extremes
Lack of access
Lower household income
A sense of insecurity felt by residents