Neuroanatomy NSCI320 w/pics
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
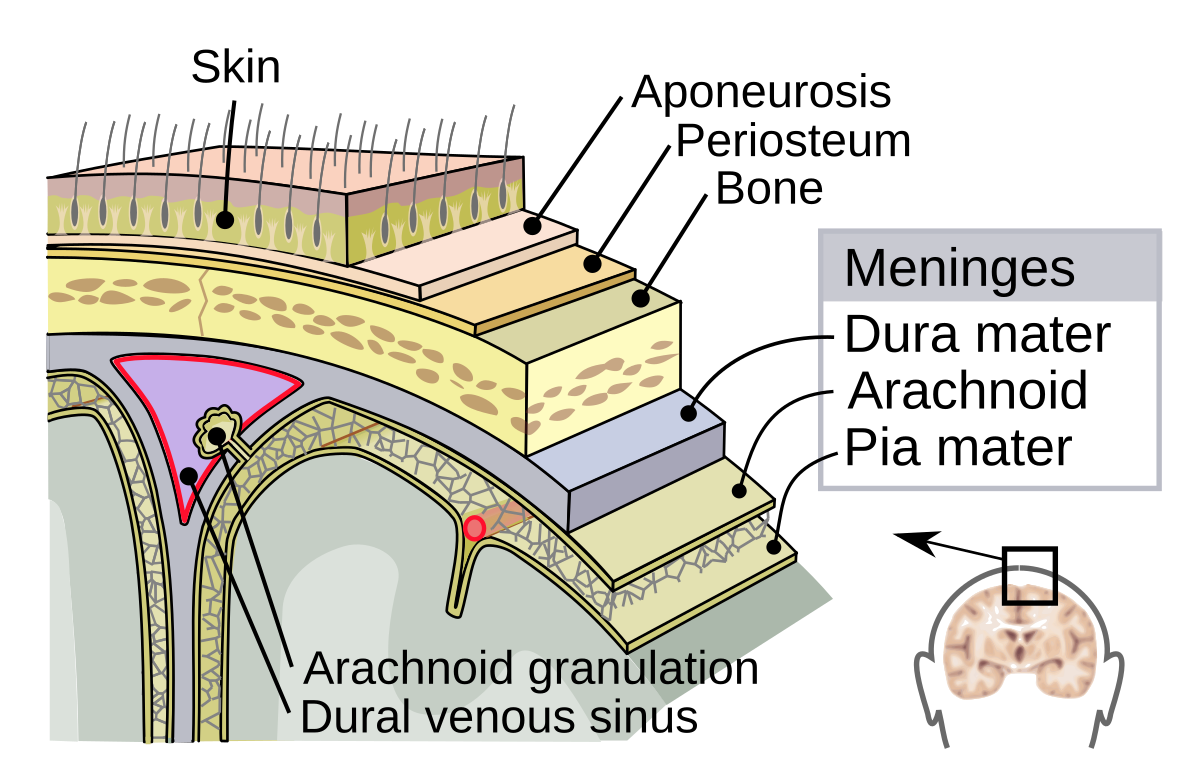
Dura Mater
Meninge closest to the skull. Thickest of the three and is an added layer of protection for the brain and spinal cord
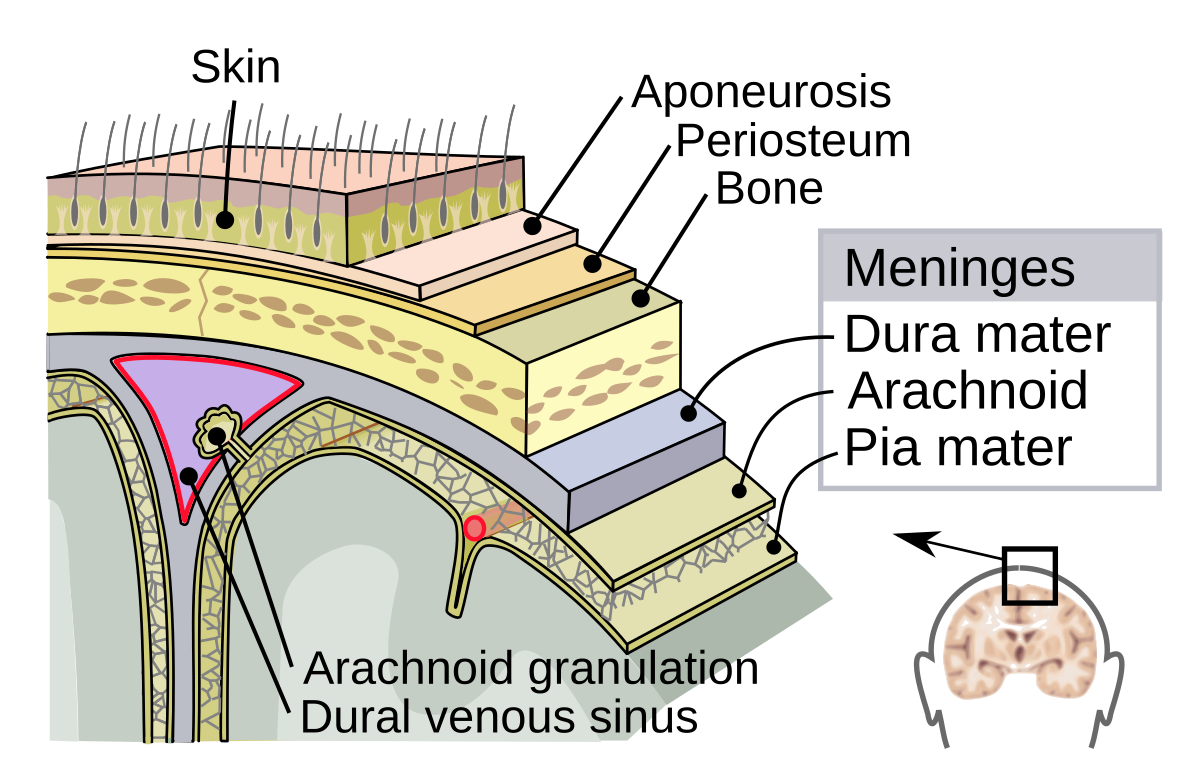
Arachnoid Membrane
Middle meninge. Important for protection, blood-brain barrier, and CSF
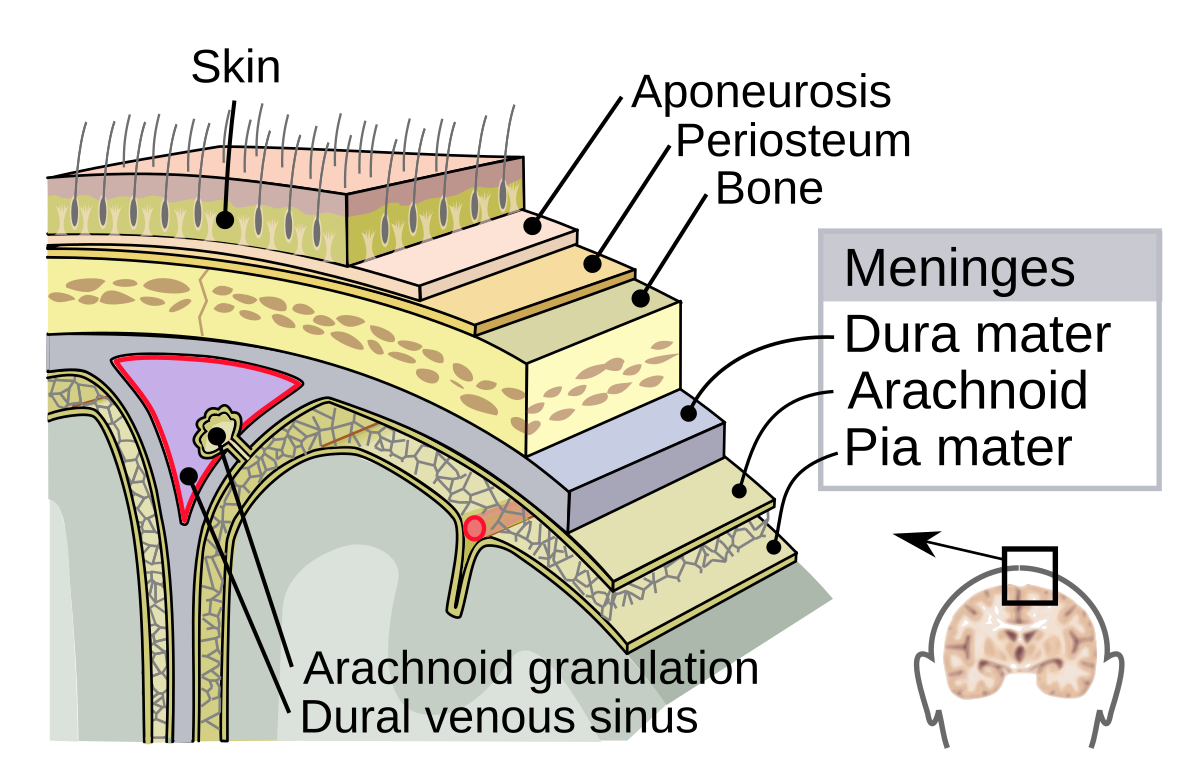
Pia Mater
Meninge closest to the brain. Important for protection, supporting nervous blood vessels, and seperating the brain from CSF
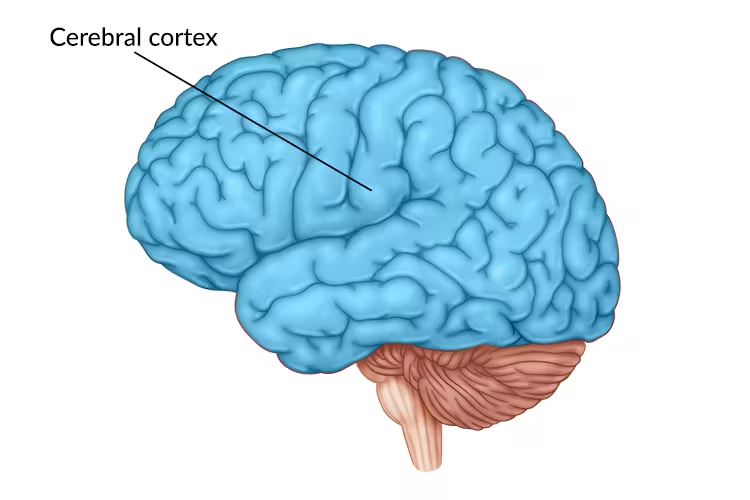
Cerebral Cortex / Cerebrum / Telencephalon
Outermost area of the brain. The pink stuff we see. Contains four lobes
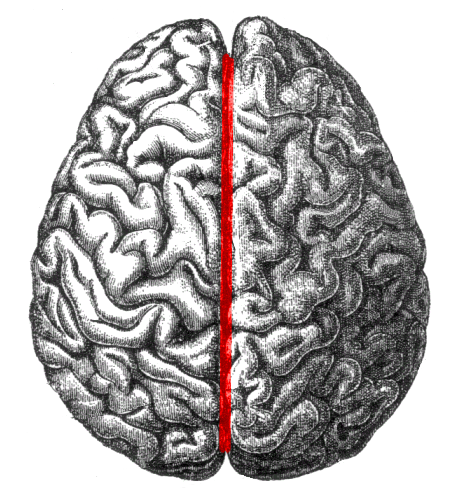
Longitudinal Fissure
Deep grove that runs from the back of the brain to the front. Creates the two hemispheres of the brain
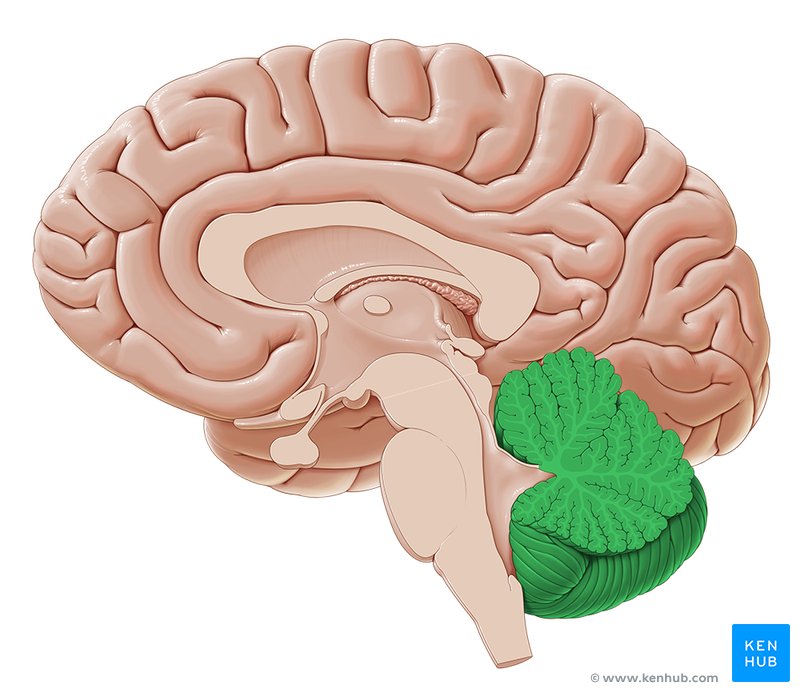
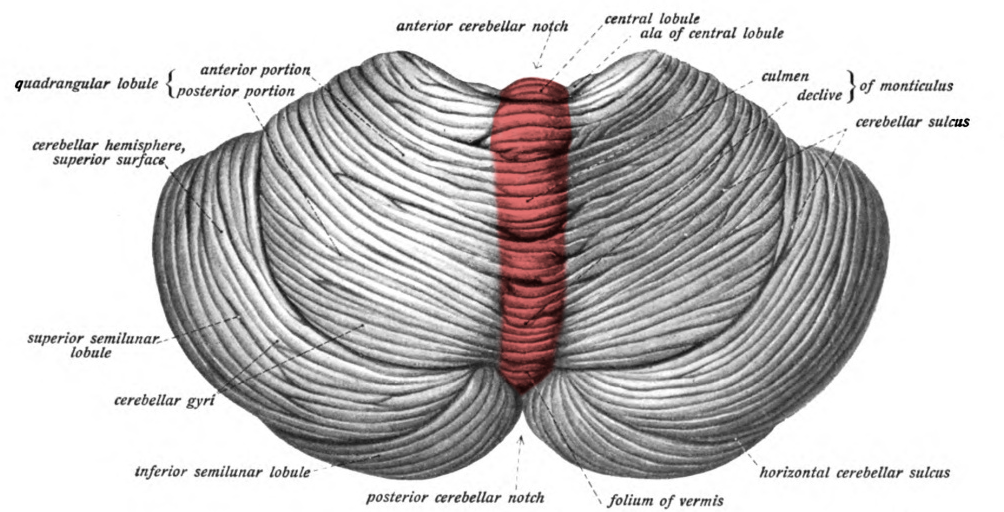
Cerebellum
portion of the brain located in the back of the head. Important for polishing motor controls and maintaining balance and posture
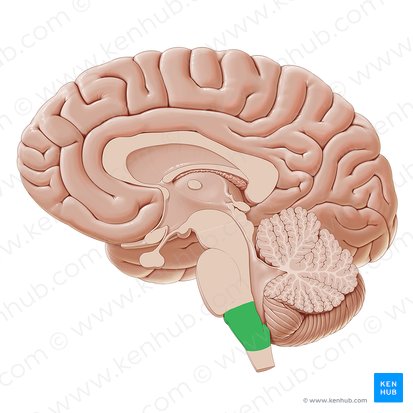
Medulla
bottommost region of the brain stem that controls vital functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure
Pons
middle region of the brainstem important for motor control and sensory processing
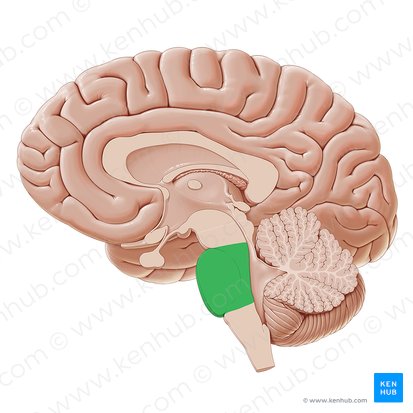
Midbrain
topmost area of brainstem important for motor control and sensory processing
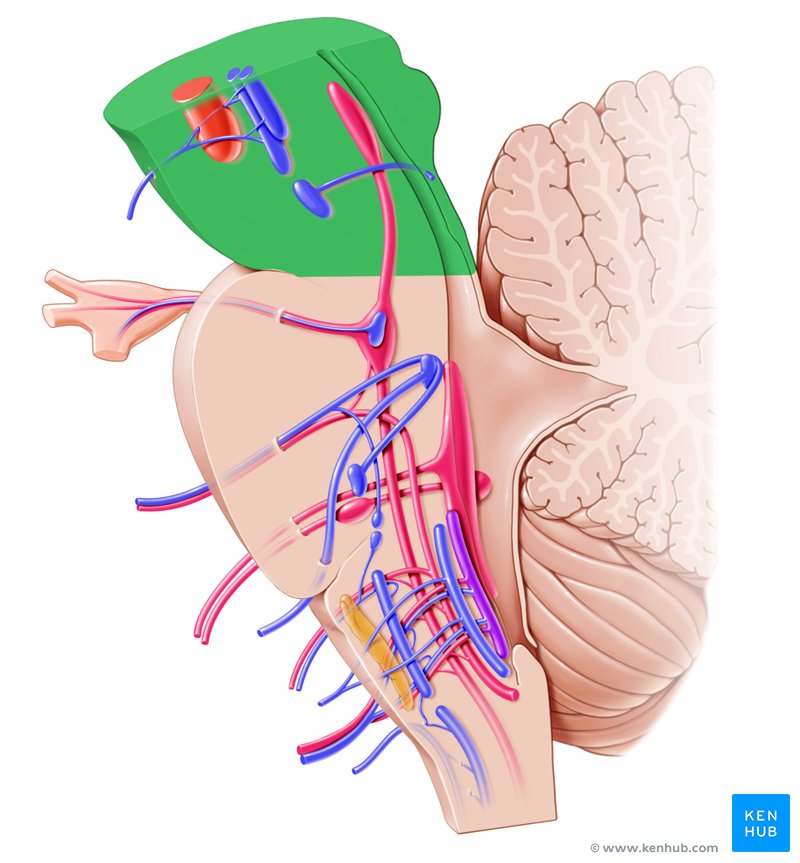
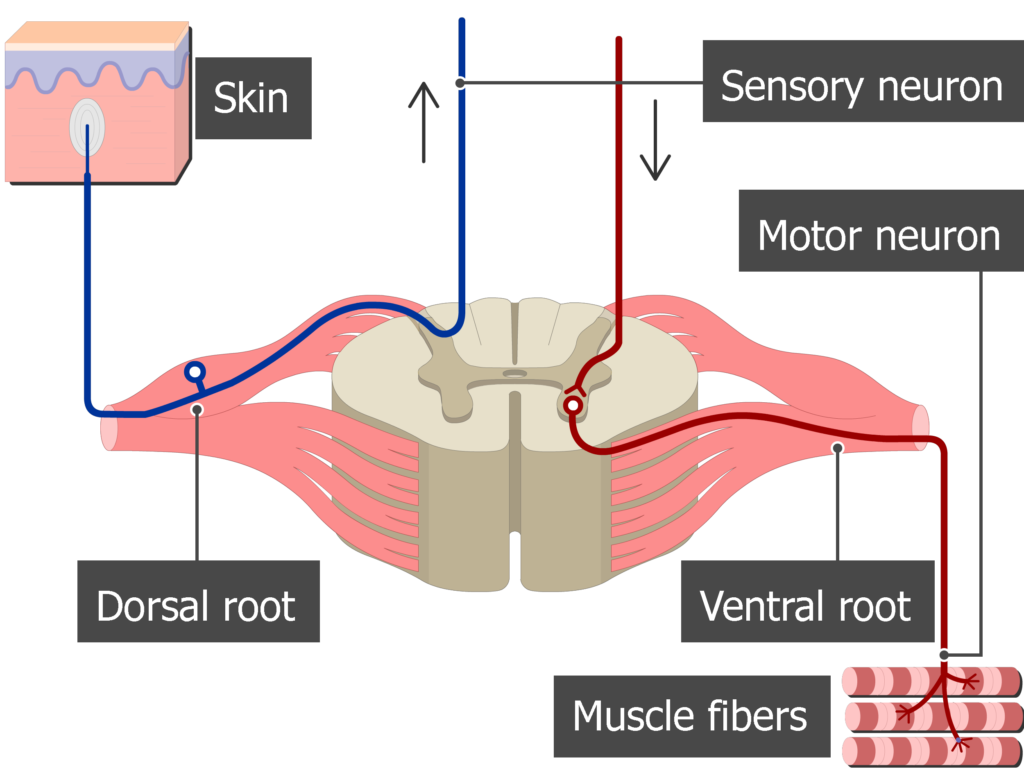
Spinal Cord
cylindrical bundle of nerves that travel down the spine, carrying information between the muscles and the brain
Dorsal Root
Area that branches of the spinal cord that sends signals from the PNS to the CNS (brain)
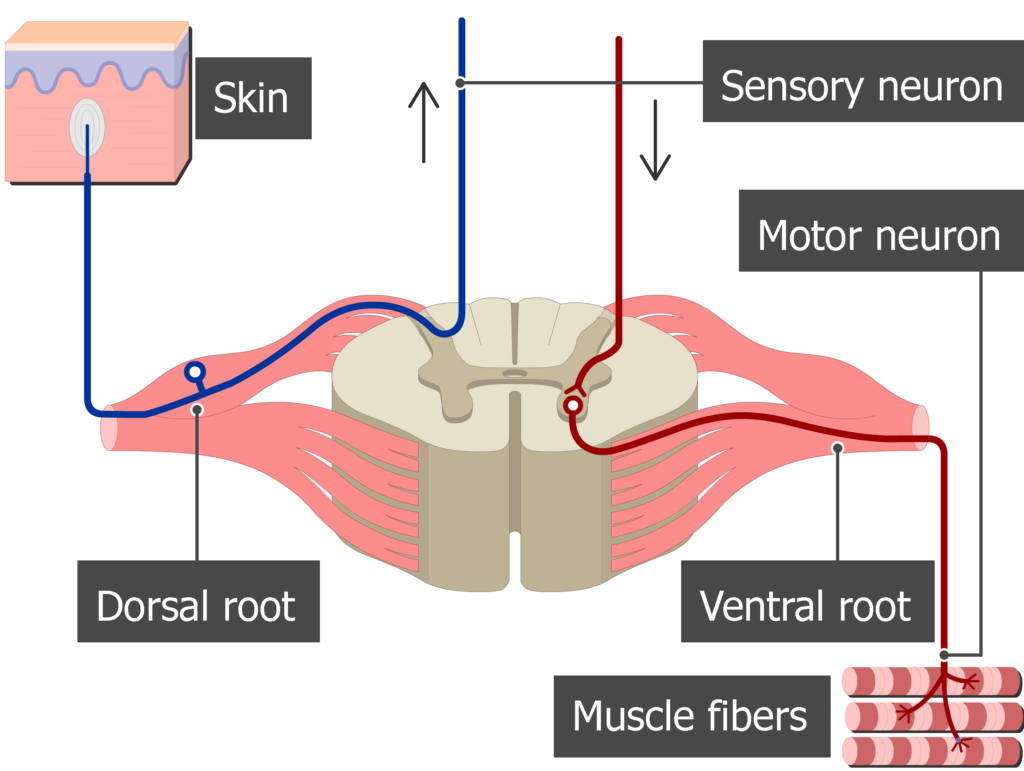
Ventral Root
Area that branches off the spinal cord that sends signals from the CNS to the PNS
Gyri (gyrus)
hilly areas of the cortex

Sulci (sulcus)
valley-like areas of the cortex

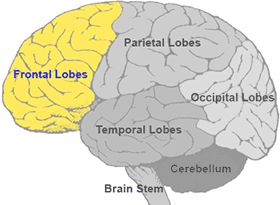
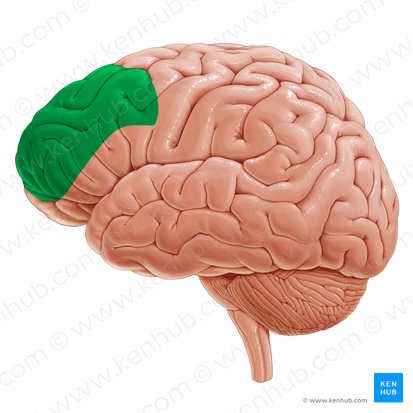
Frontal Lobe
Rostral most lobe of the brain. Important for higher order thinking, motor control, and language. Contains pre motor and primary motor cortices, and brocas area. Seperated from parietal by central sulcus and from temporal by lateral fissure
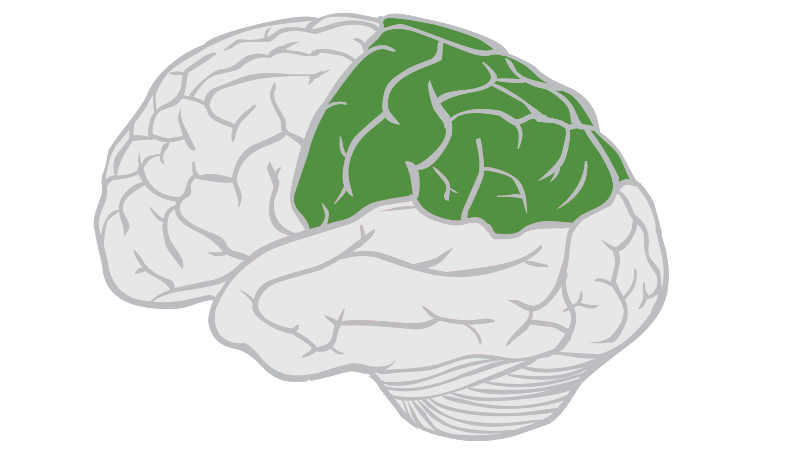
Parietal Lobe
Central-most lobe of the brain. Important for sensory processing and integrating them into other cognitive functions. Contains primary somatosensory cortex. Seperated from the frontal lobe by the central sulcus
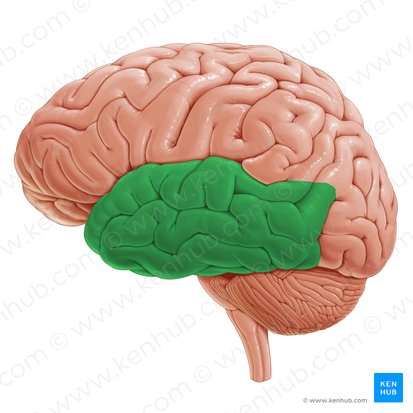
Temporal Lobe
Ventral-most lobe of the brain. Important for auditory processing and encoding of memory. Includes superior temporal gyrus and fissure.
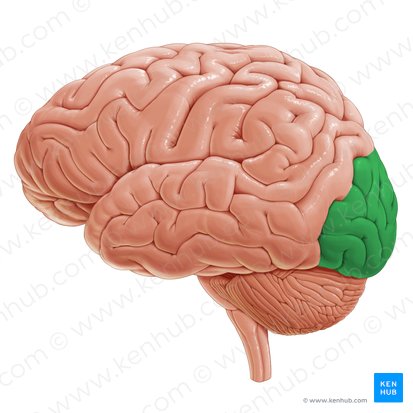
Occipital Lobe
Caudal most lobe of the cortex. Important for processing visual information. Includes primary visual cortex
Lateral Fissure/Sulcus
Large fissure that separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal
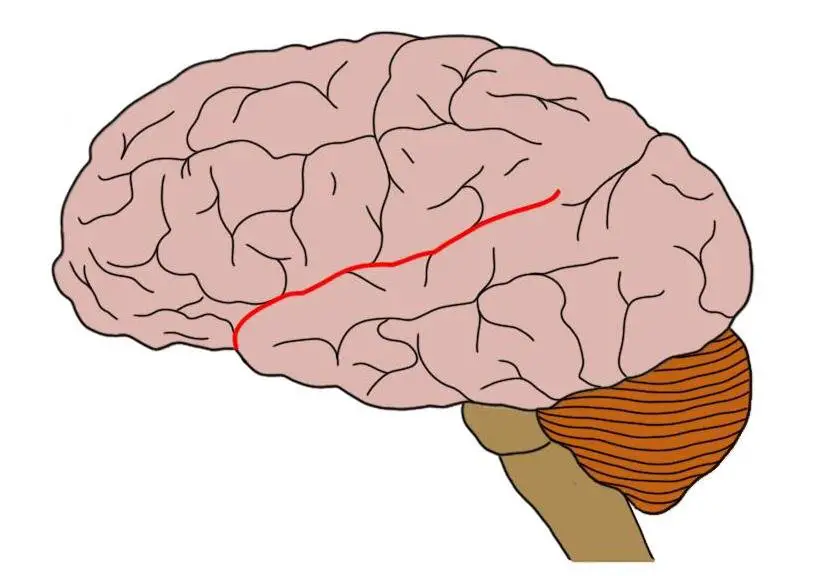
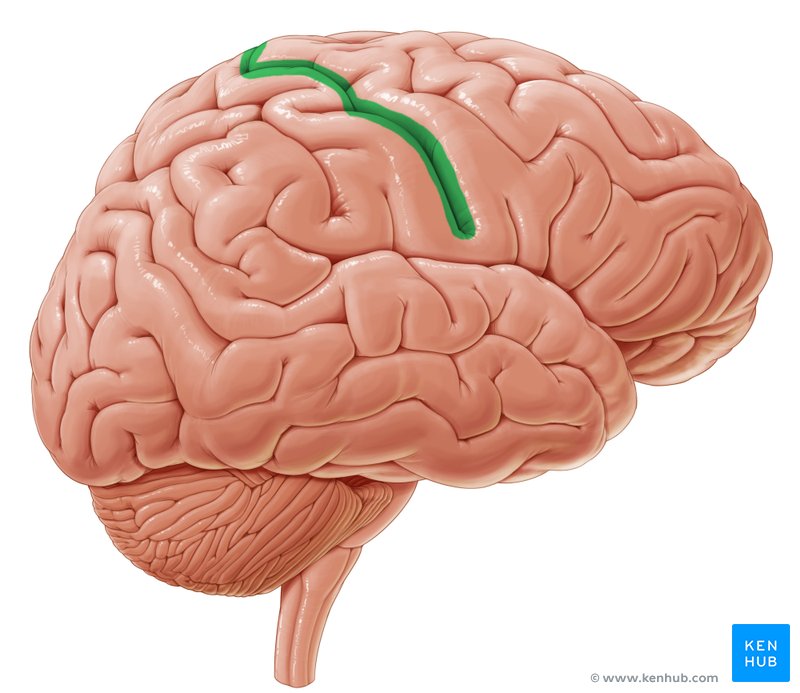
Central Sulcus / Fissure of Ronaldo
Large fissure that separates the frontal lobe from the occipital lobe. Precentral gyrus contains primary motor cortex and postcentral gyrus contains primary somatosensory cortex
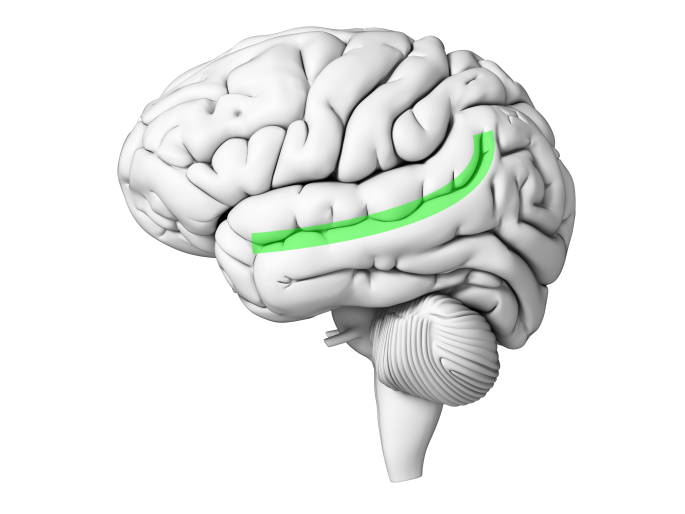
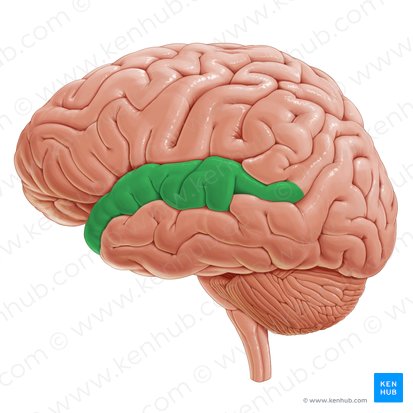
Superior Temporal Sulcus
Sulcus located superiorly on the temporal lobe
Olfactory Sulcus
Sulcus located on the bottom of the frontal lobe near the olfactory bulb
Superior Temporal Gyrus
Gyrus located in the temporal lobe directly above the superior temoral sulcus
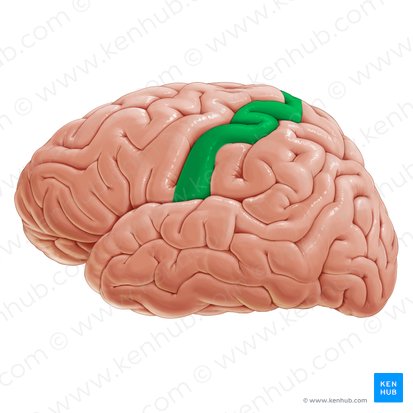
Precentral Gyrus
anterior side of the central gyrus, located in the frontal lobe. Contains the primary motor cortex
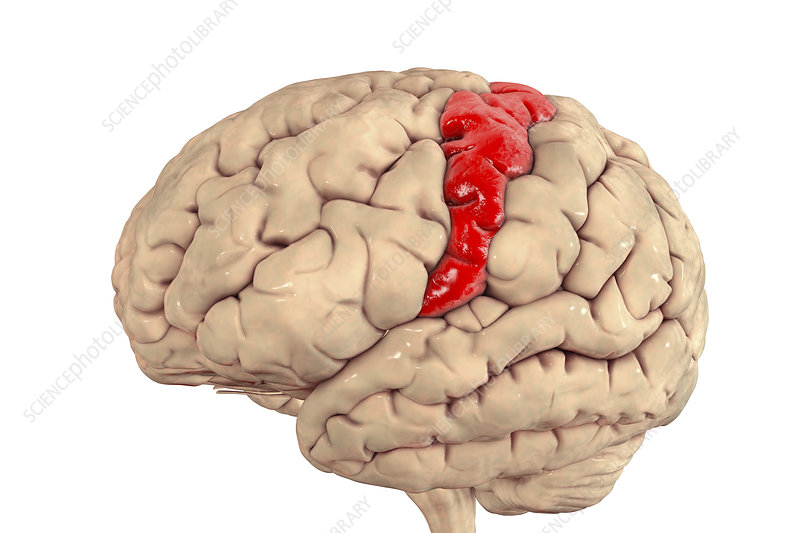
Postcentral Gyrus
Posterior side of the central gyrus. Located in the Parietal lobe. Contains the primary somatosensory cortex

Prefrontal Cortex
Anterior portion of the frontal lobe. Important for personality
Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex
Ventral area of the frontal lobe important for cognitive, social, and emotional behaviors
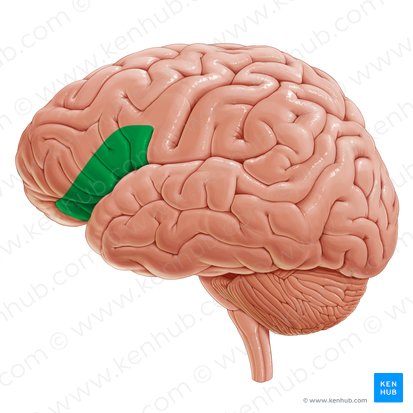
Striate Cortex / Primary Visual Cortex
First area of the brain to recieve visual information. Processes visual information and spreads it throughout the cortex
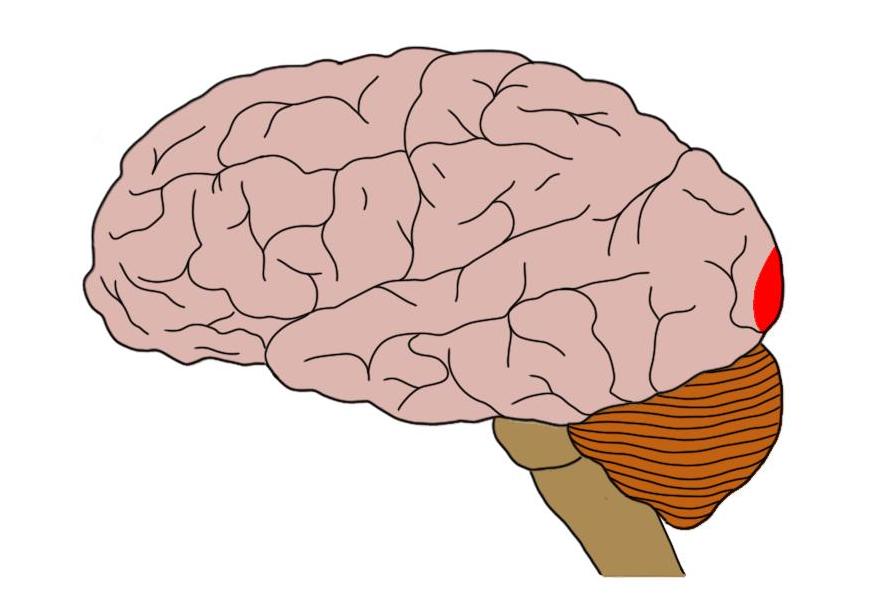
Extrastriate Cortex
Area of occipital lobe surrounding the primary visual cortex.
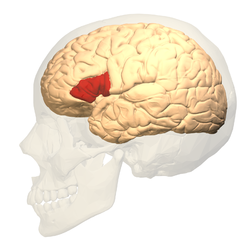
Broca’s Area
Region of the frontal lobe crucial for producing speech. Found in the left hemisphere
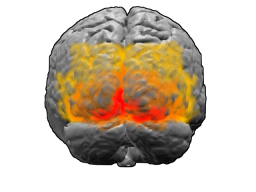
Wernicke’s Area
Area of the posterior superior temporal gyrus crucial for comprehending language. Found in the left hemisphere
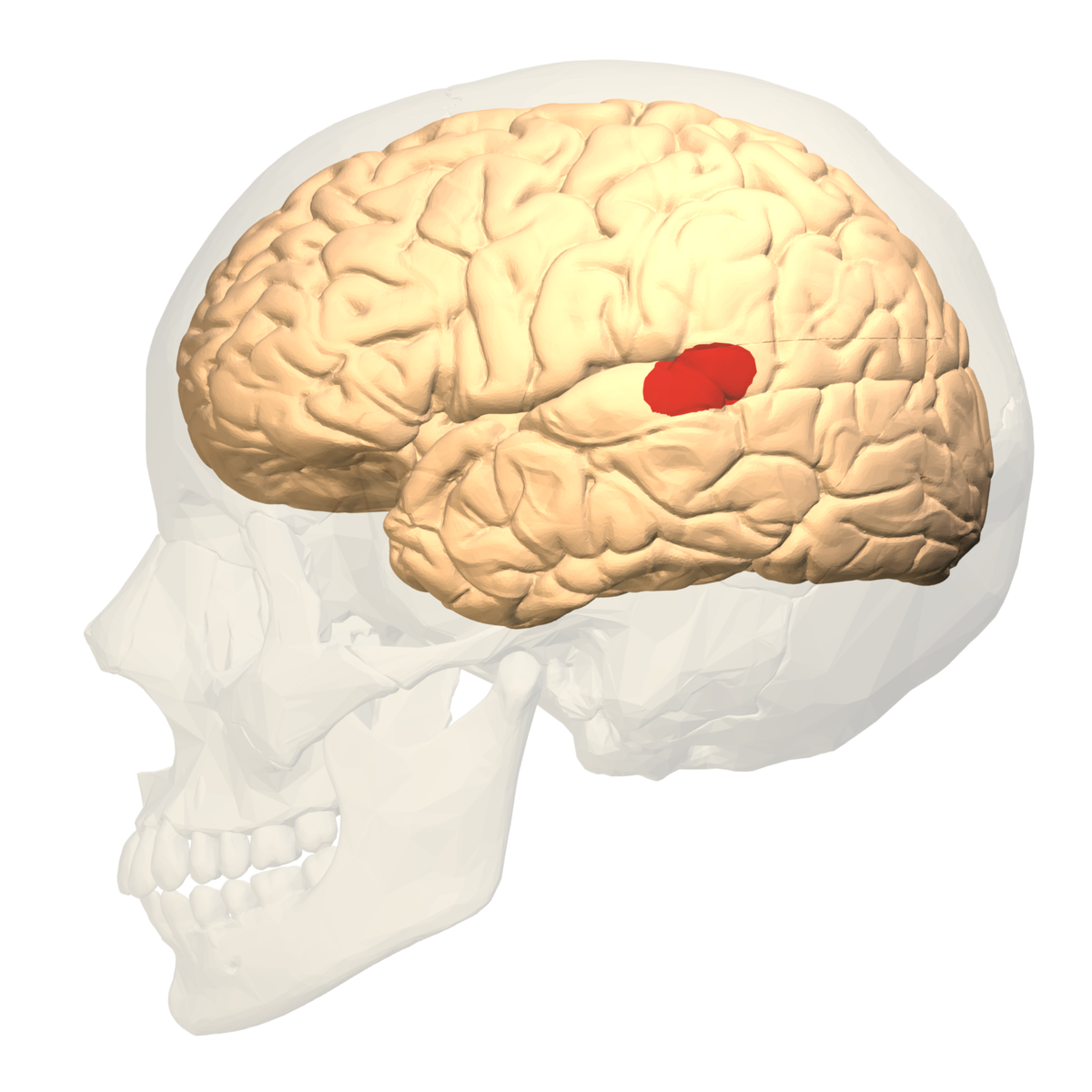
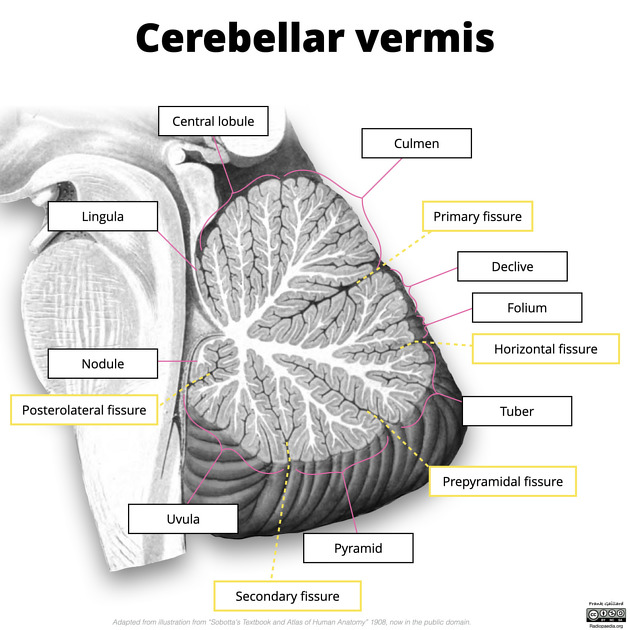
Cerebellar Vermis
Connects the two cerebellums hemispheres together. Spans vertically down the midsagittal plane
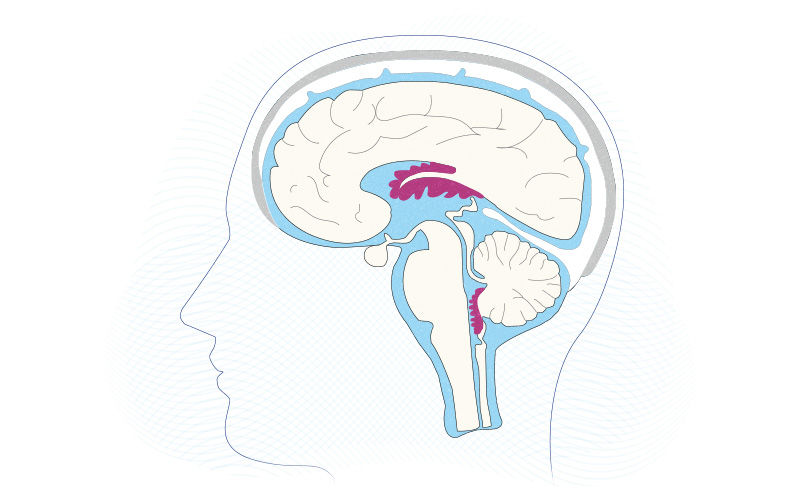
Ventricles
cavernous spaces in the brain that contain Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) - help cushion the brain, reduce pressure, and regulates chemical properties.
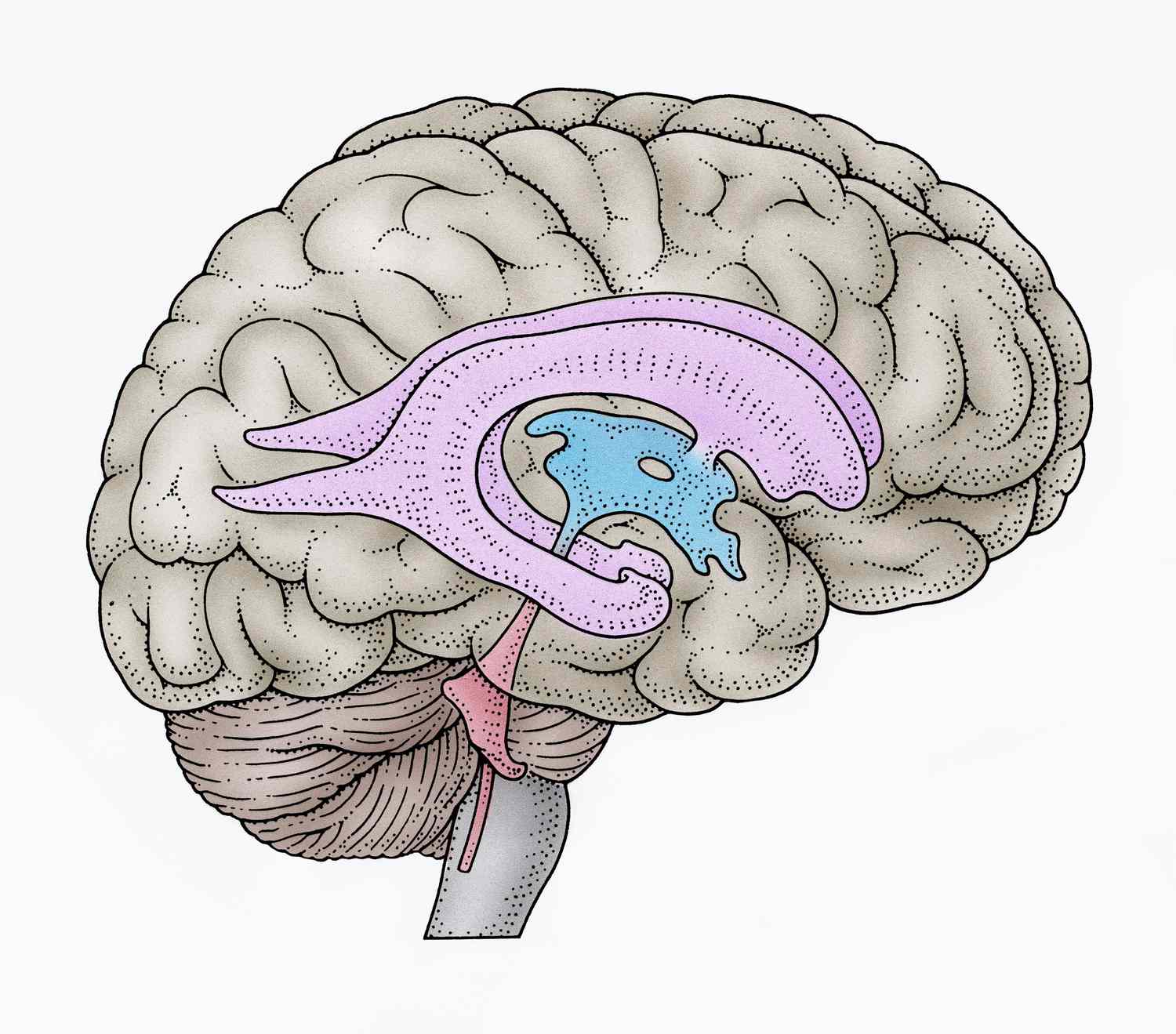
Choroid Plexus
Structure that secretes CSF into the ventricles. Spongy blood vessel like structure.
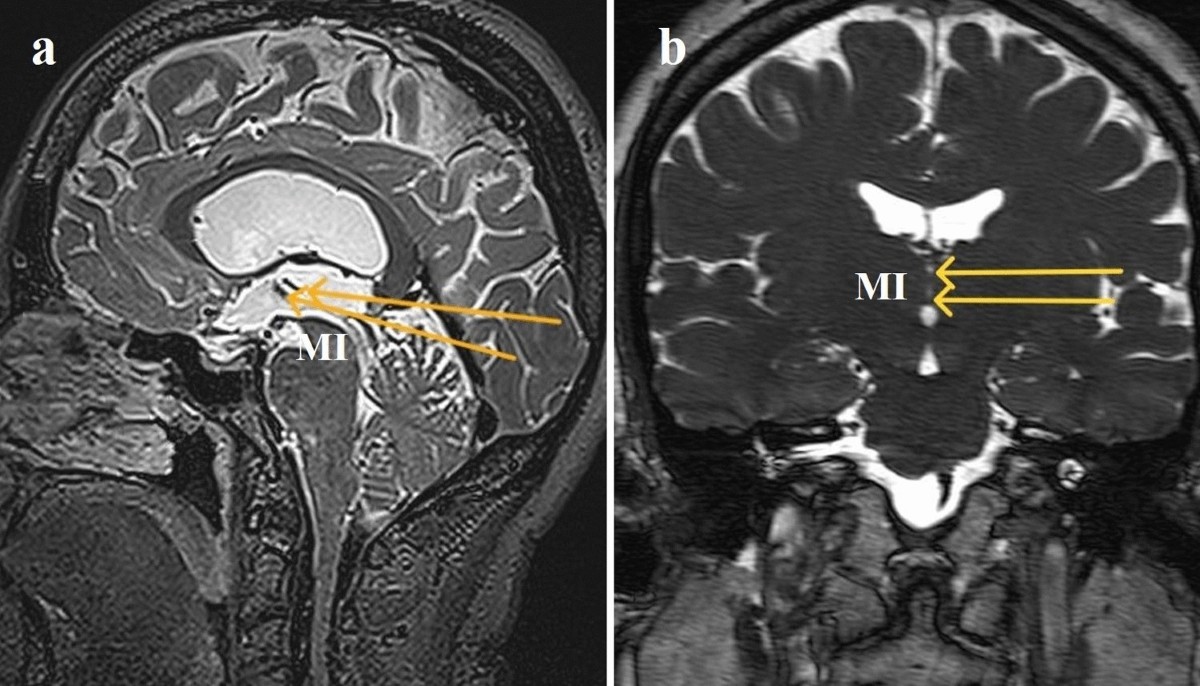
Massa Intermedia
structure that attaches the left thalamus to the right thalamus by passing through the third ventricle.
Foramen
term used to represent a hold or opening in the ventricles that allow CSF to pass from one area to another
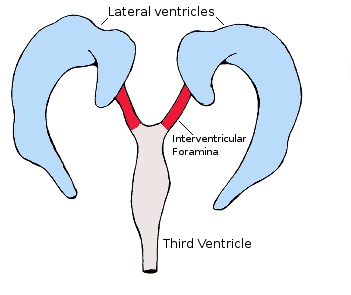
Intraventricular Foramen / Foramen of Monroe
a small opening that connects the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle, allowing CSF into it and beyond
Frontal/Coronal
Vertical plane that runs side to side, splitting the body/brain into a front and back
Sagittal/Lateral
Vertical plane that runs front to back, splitting the body/brain into a left and right
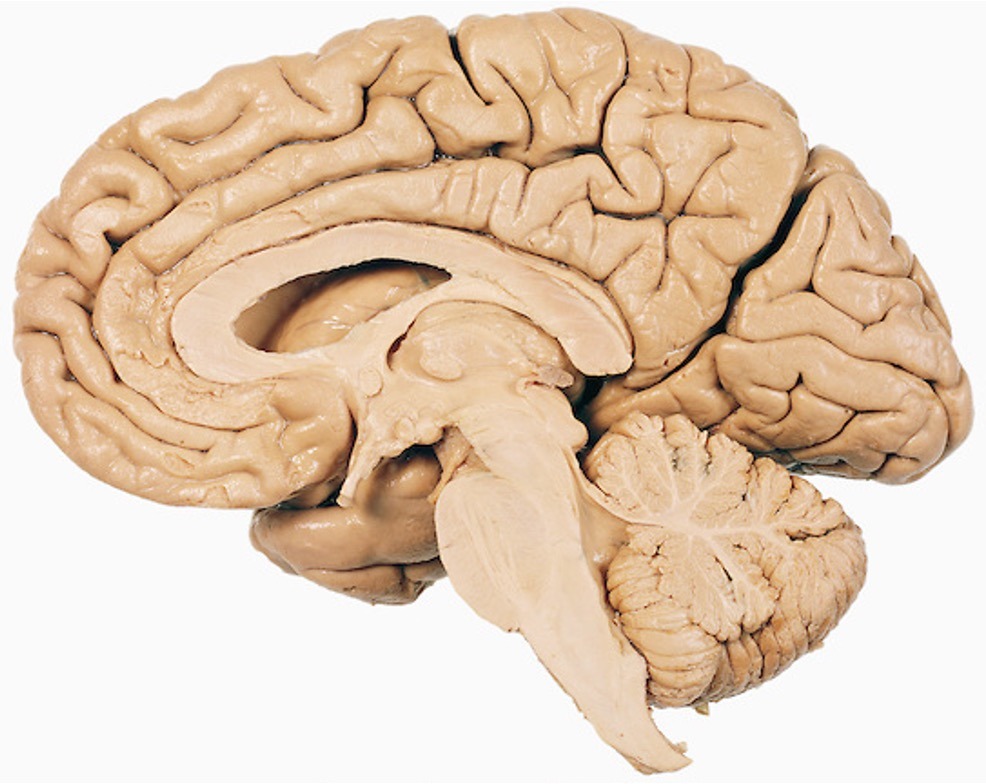
Horizontal/Axial/Transverse
Horizontal plane that runs front to back, splitting the body/brain into a top and bottom
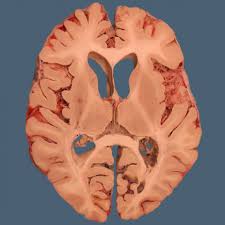
Superior
above
Inferior
Below
Anterior
infront of
Posterior
Behind
Medial
Toward the middle
Lateral
Toward the side
Dorsal
Top
Ventral
Bottom
Basilar Artery
Large blood vessel located on the bottom of the brain
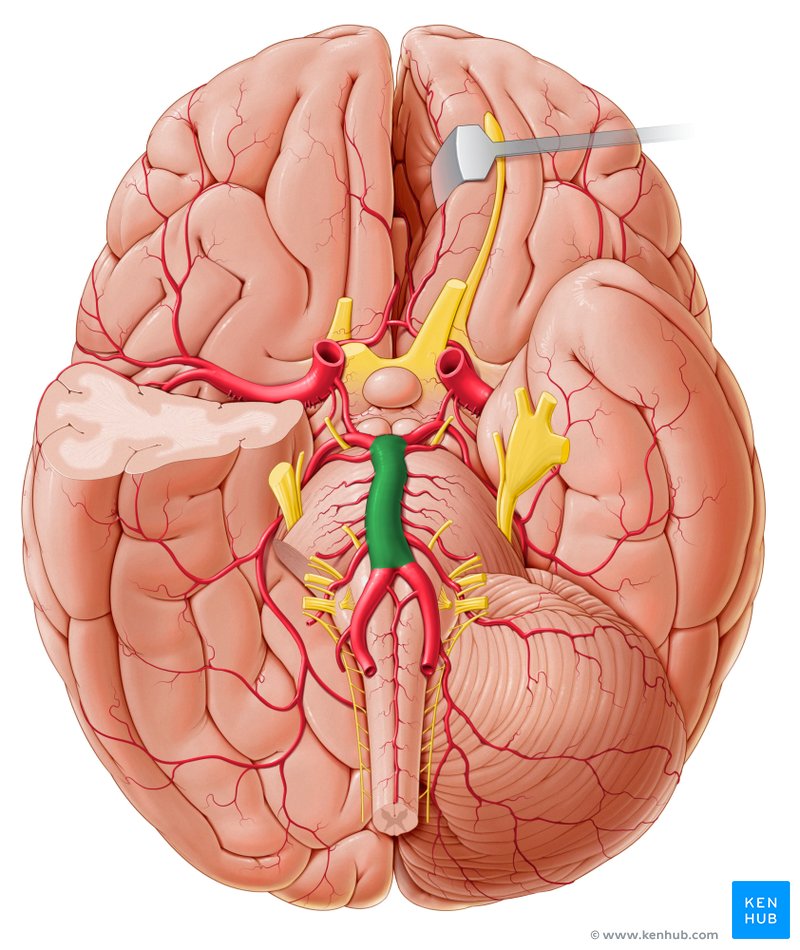
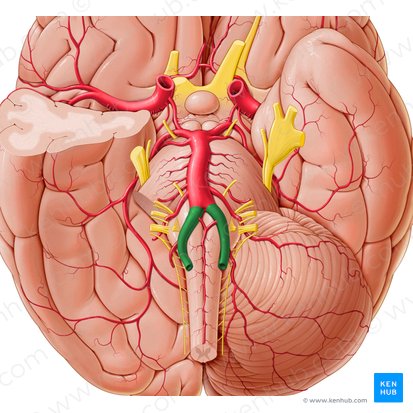
Vertebral Artery
Large blood vessels on the bottom of the brain that come together to form the basilar artery
Pineal Gland
Gland located in the diencephalon, just behind the thalamus. Important for secreting melatonin and regulating sleep cycle. Directly above (superior to) superior colliculi.
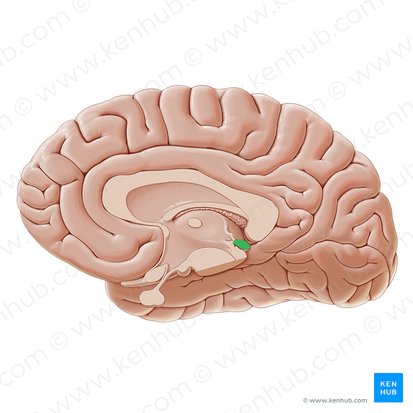
Pituitary Gland/Infundibulum
Gland that regulates bodily functions by secreting hormones. Located directly below hypothalamus
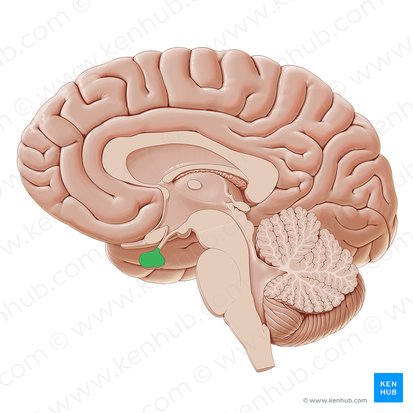
Superior Colliculus
Located in the midbrain and is part of the dorsal brain stem. Important for visual attention and eye movements
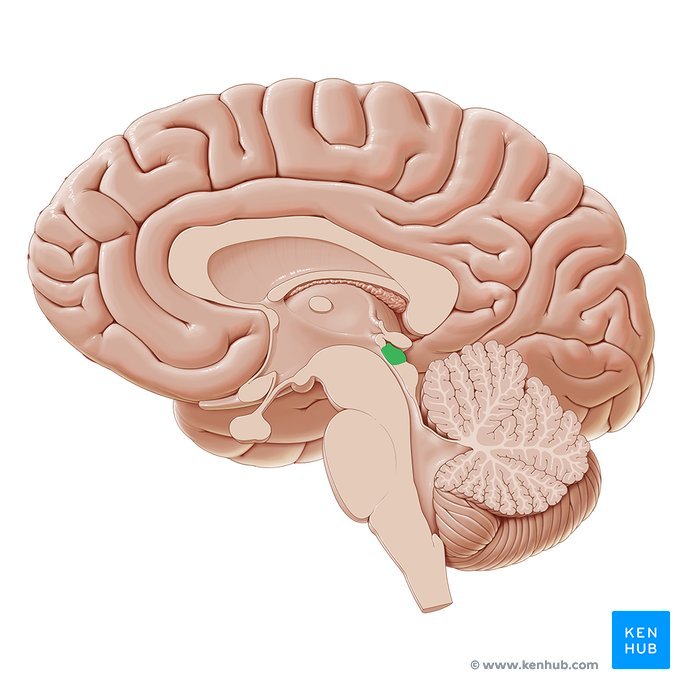
Inferior Colliculus
Located in the midbrain directly below the superior colliculus. Important for auditory cues
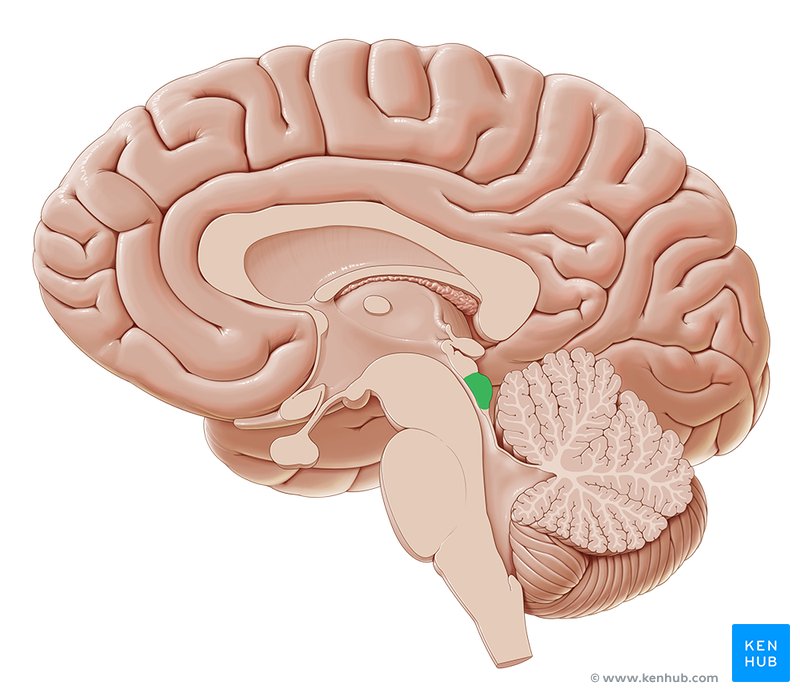
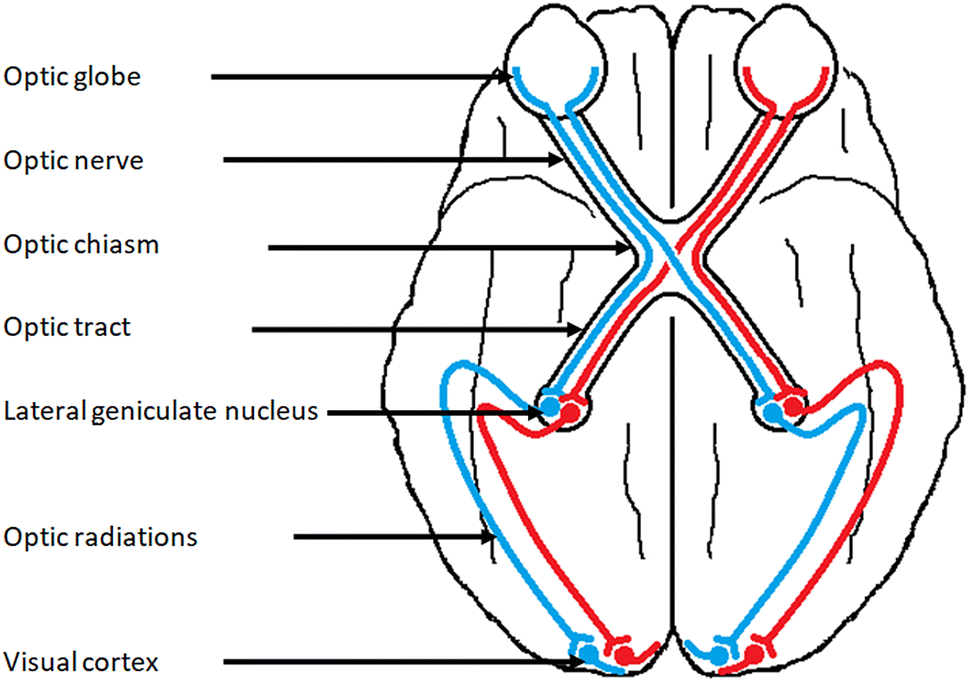
Optic Nerve
Nerve that sends visual info from the retina to the optic chiasm
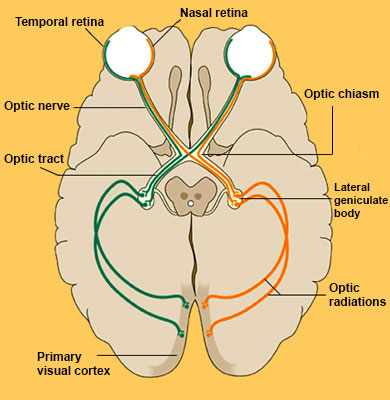
Optic Chiasm
Area where optic nerve diverges and visual info heads to the two different hemispheres
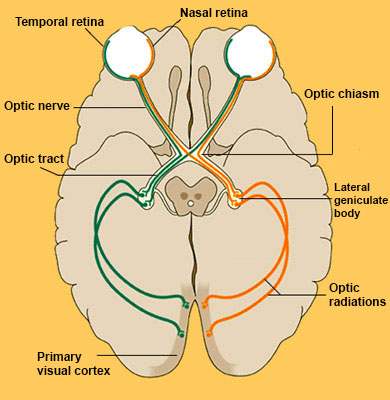
Optic Tract
Post-Optic Chiasm nerve that sends visual info to the thalamus (LGN)
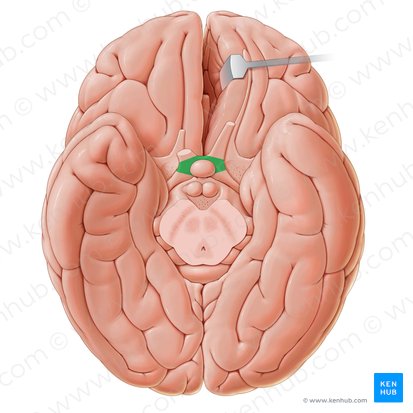
Mammilary Body
Small structures located under the brain in the posterior hypothalamus. Important for memory consolidation and spatial navigation
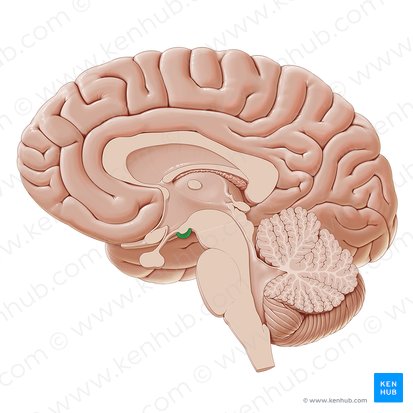
Olfactory Nerve (Bulb and Tract)
Nerve that carries olfactory information to the brain. Begins in the bulb where odorants turn into electrical signals, travelling down the olfactory tract
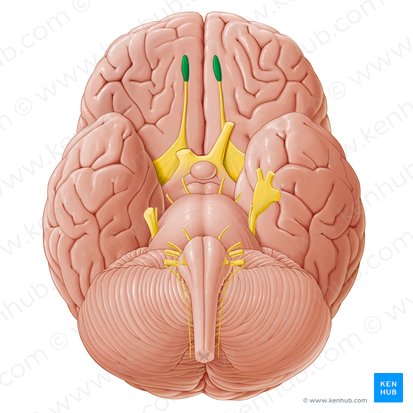
Crus Cerebri/Cerebral Peduncle
bundle of nerve in the midbrain that connect the cerebral hemispheres to the cerebellum and other parts of the brainstem. Mickey Ears

Vagus Nerve
Nerve that begins in the medulla oblongata, sending motor commands to the body
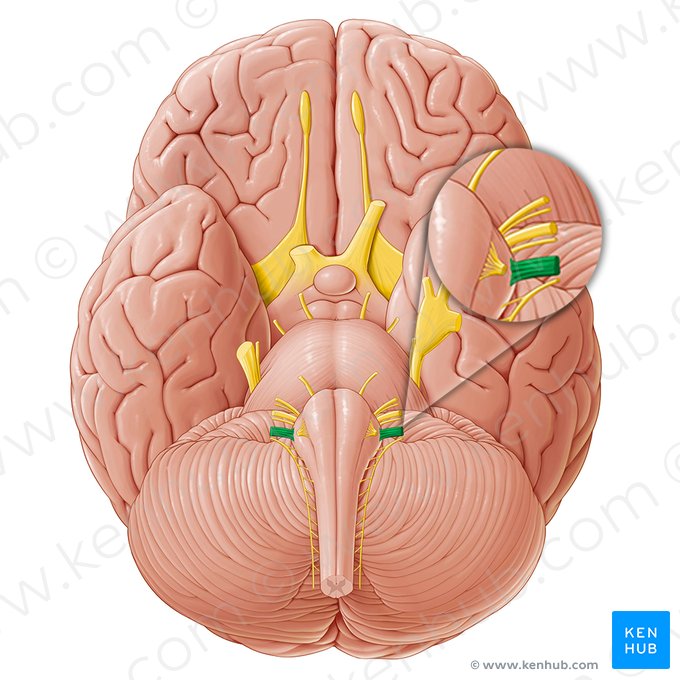
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Nerve that carries auditory info from the ears to the opposite hemisphere of the brain. Located on the bottom of the brain
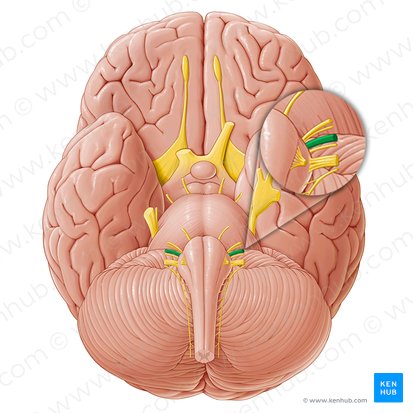
Amygdala
Almond shaped structure located in the temporal lobe in the limbic system. Involved in emotion, memory, and motivation
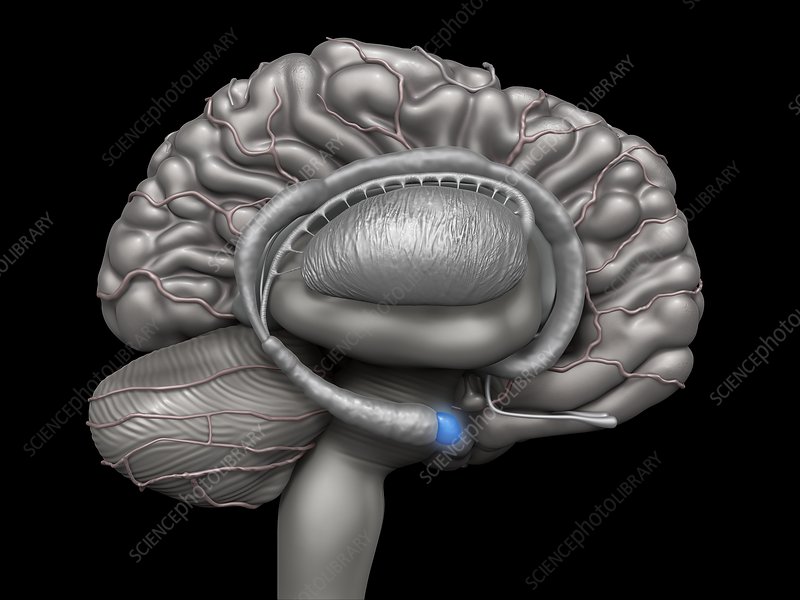
Fornix
Area in the limbic system responsible for being the primary output pathway for the hippocampus. Connects hippocampus to mammillary bodies and hypothalamus
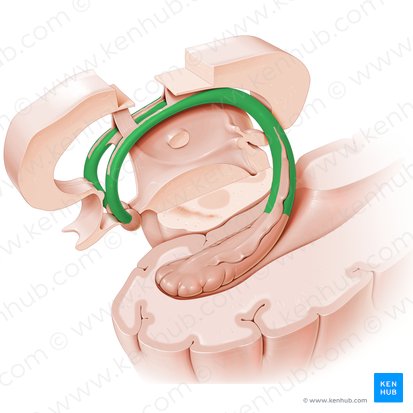
Hippocampus
Seahorse shaped structure in the limbic system in the temporal lobe important for consolidation of memory and memory.
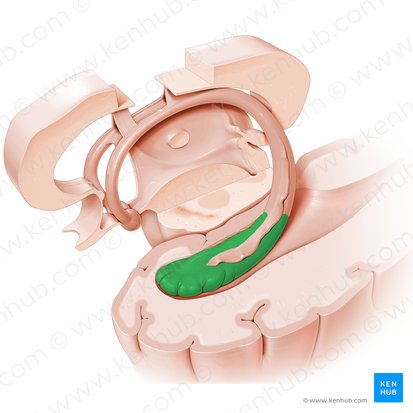
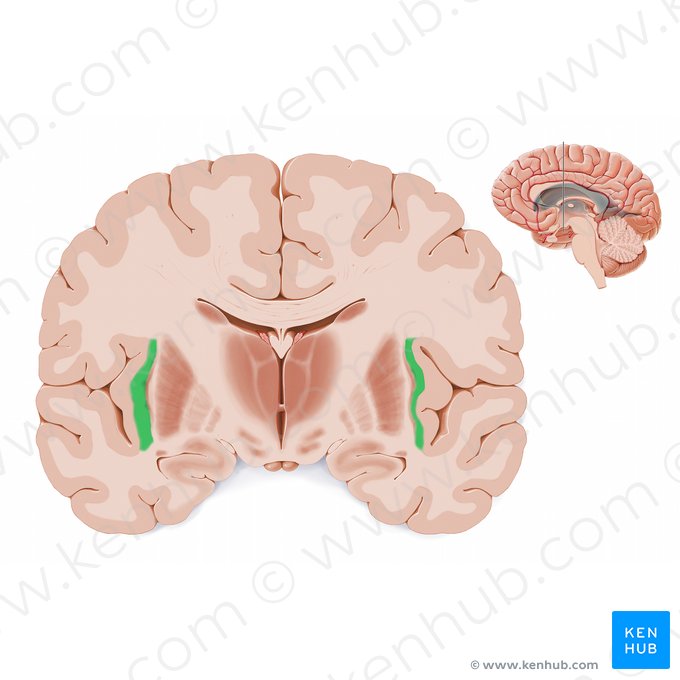
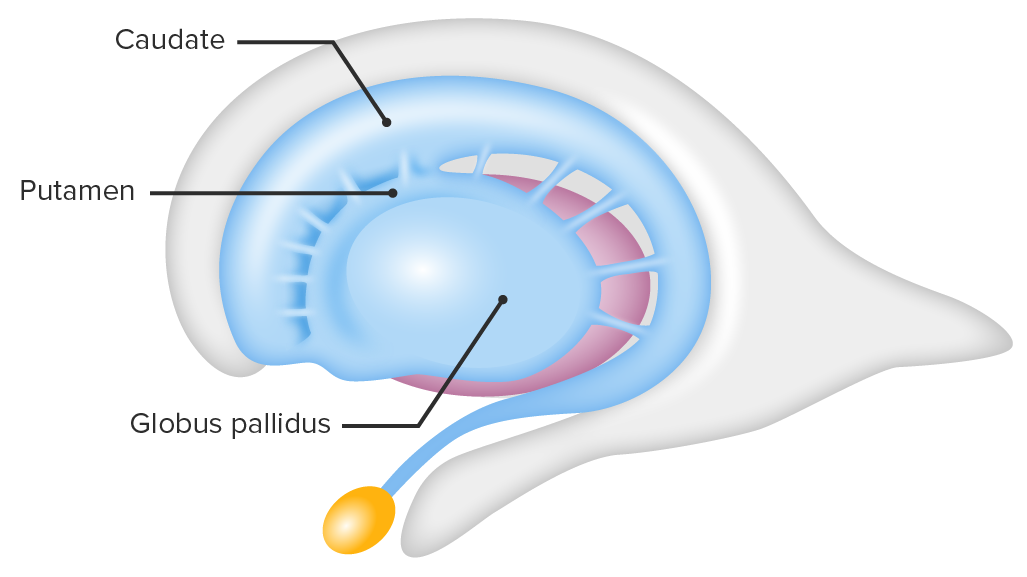
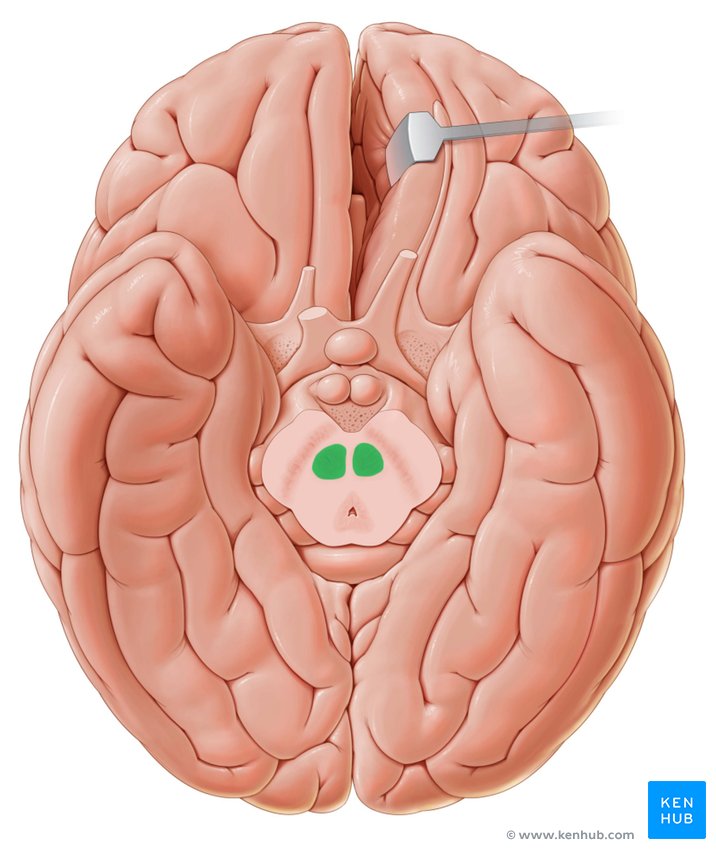
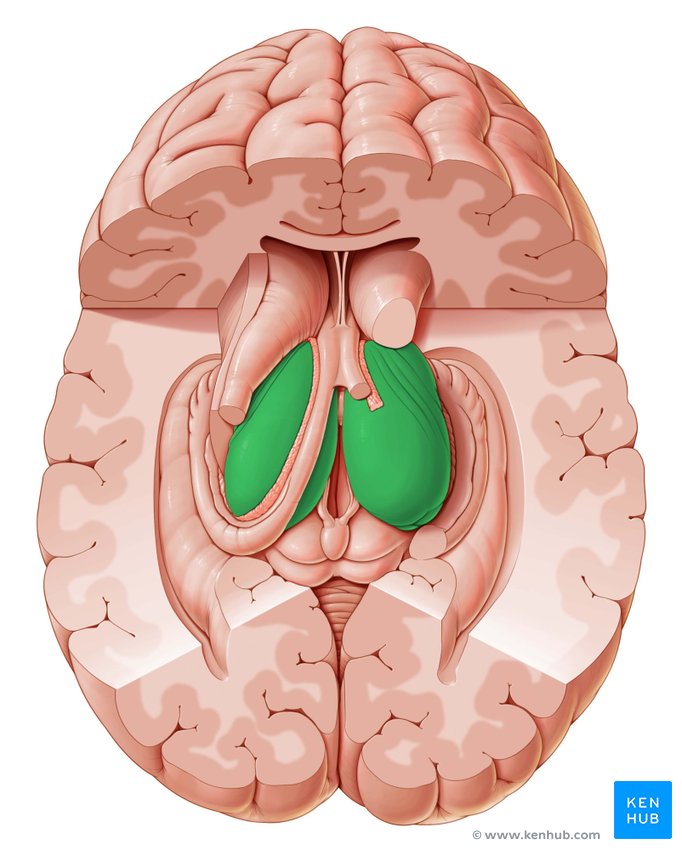
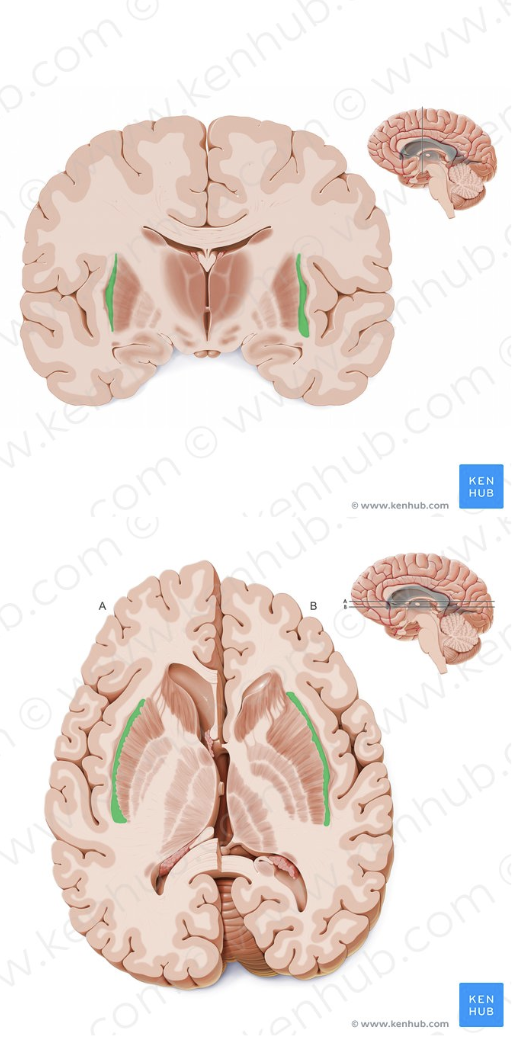
Caudate Nucleus
C-shaped structure in the basal ganglia important for movement, learning, and decision-making (green in photo)
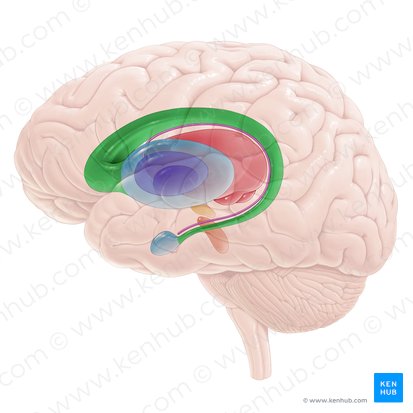
Corpus Callosum
Thick band of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres with each other. Largest white matter area in the brain
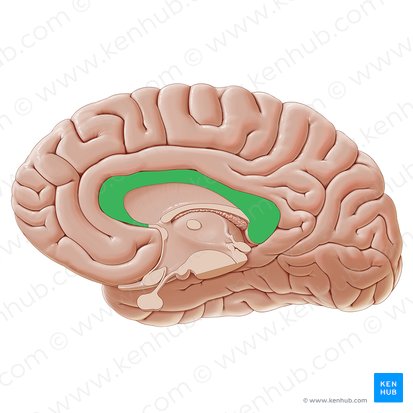
Anterior Commissure
Bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain at the midline. Primarily connects the olfactory bulbs and temporal lobes. Located below the corpus callosum
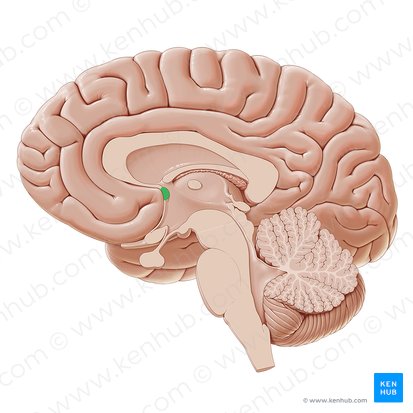
Posterior Commissure
Bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. Located dorsally to the midbrain.
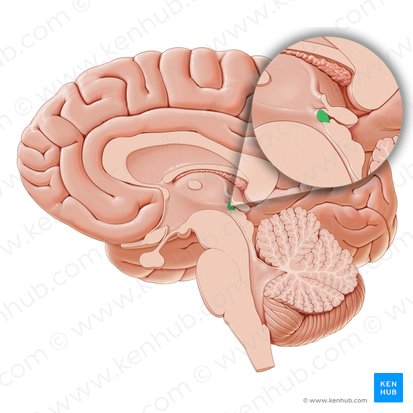
Globus Pallidus
Structures in the basal ganglia important for regulating movement, reward, and motivation. Laterally surrounded by the putamen
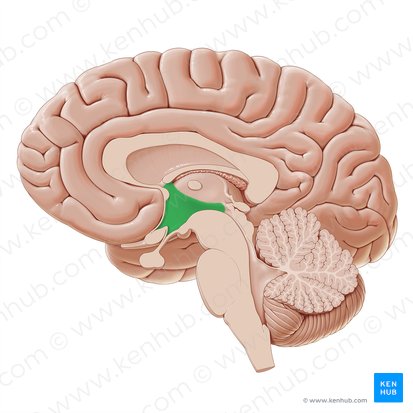
Hypothalamus
Structure located under the thalamus that is important for vital bodily functions like sleeping and waking. Part of the diencephalon
Insular Cortex (Insula)
Cortical area located in the lateral sulcus. Important for pain, attention, and language. Often called the “fifth lobe”
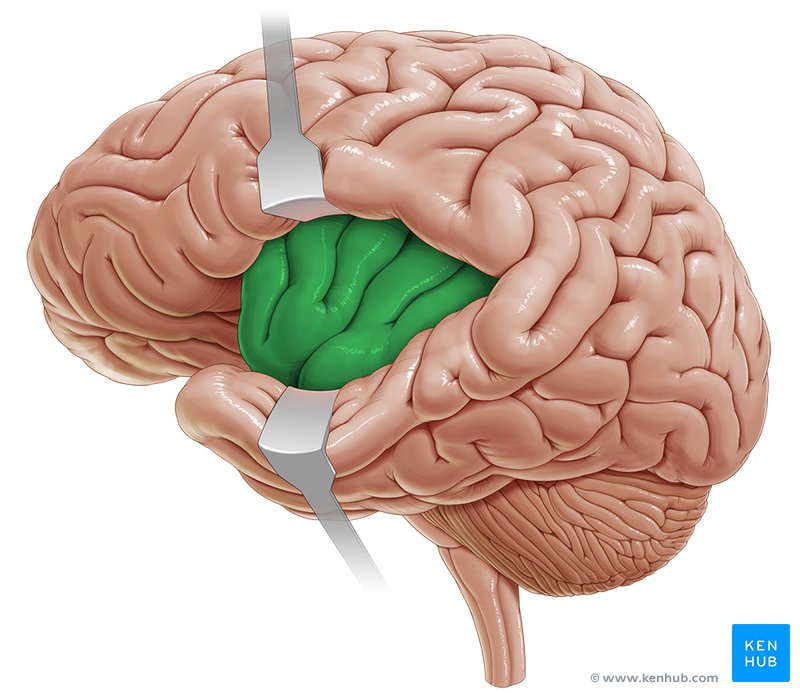
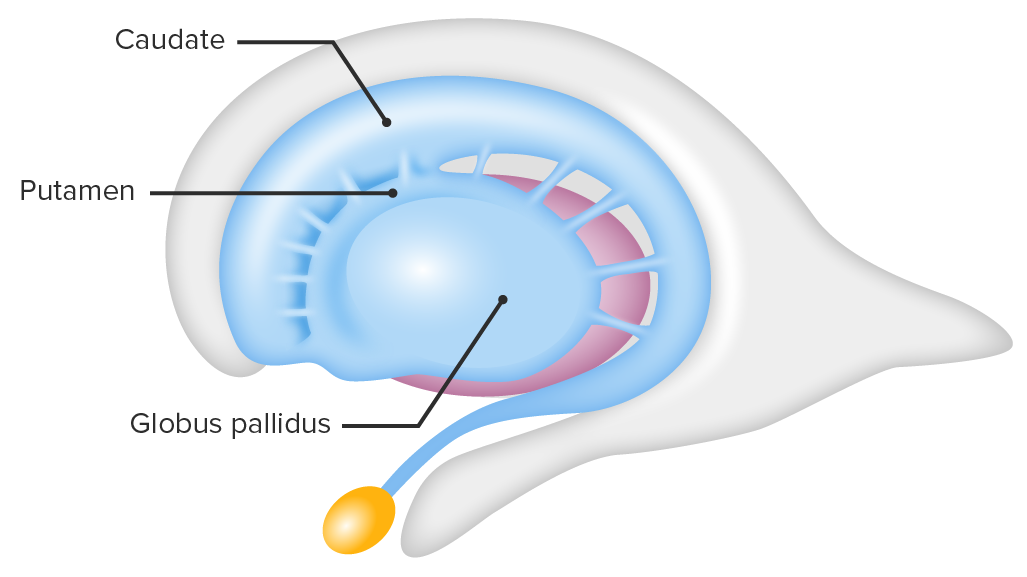
Putamen
Basal ganglia structure involved in motor control, cognition, and reward processing. Laterally surrounds the globus pallidus
Red Nucleus
Large gray matter area in the upper midbrain important for controlling muscle tone and limb movement. Located in the ventral midbrain tectum
Substantia Nigra
Area of midbrain important for controlling movement and reward pathways. Disfunctional ones can lead to Parkinsons
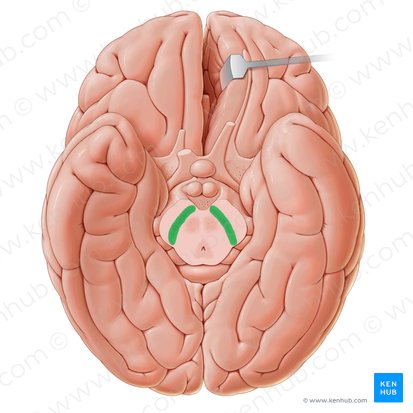
Thalamus
Structure that is the first to recieve sensory info and relays it to the rest of the brain. Located in the middle of the brain. Superior to the midbrain
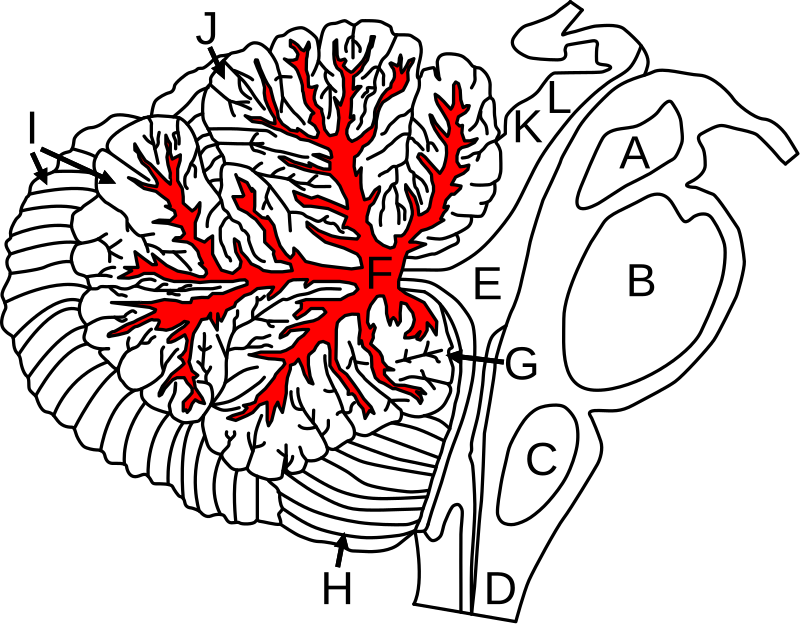
Arbor Vitae
a network of white matter tracts within the cerebellum. Responsible for coordinating movement and balance. Looks like the roots/branches of a tree
Folia
The leaf-like folds that coveres the surface of the cerebellum. Increases surface area of the cerebellum, allowing for a greater number of neurons to be present
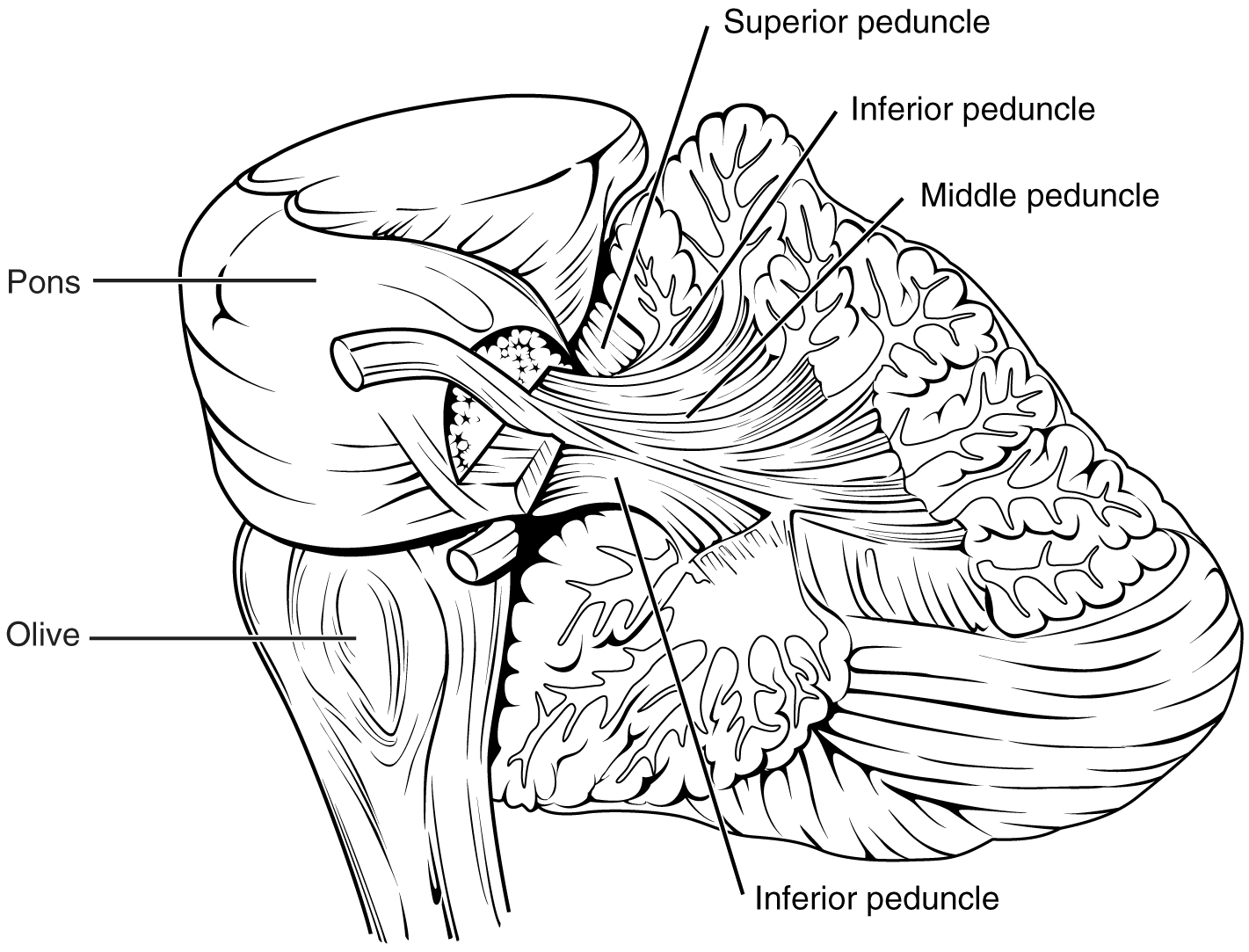
Cerebellum Peduncles
three pairs of nerve tracts that connect the cerebellum to the brainstem. They play a crucial role in transmitting information between the cerebellum and other parts of the central nervous system
Nucleus Accumbens
Small brain structure in the basal ganglia located in the ventral striatum. Lies below the anterior commisure. Key part in the brains reward system
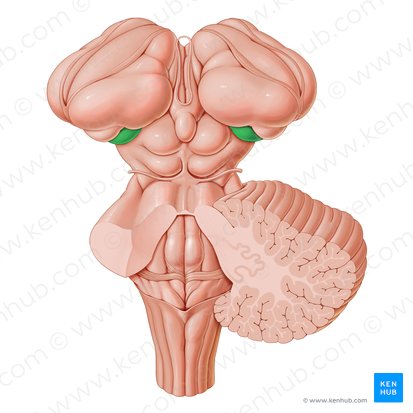
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
a part of the thalamus that relays auditory information from the midbrain and hindbrain to the auditory cortex
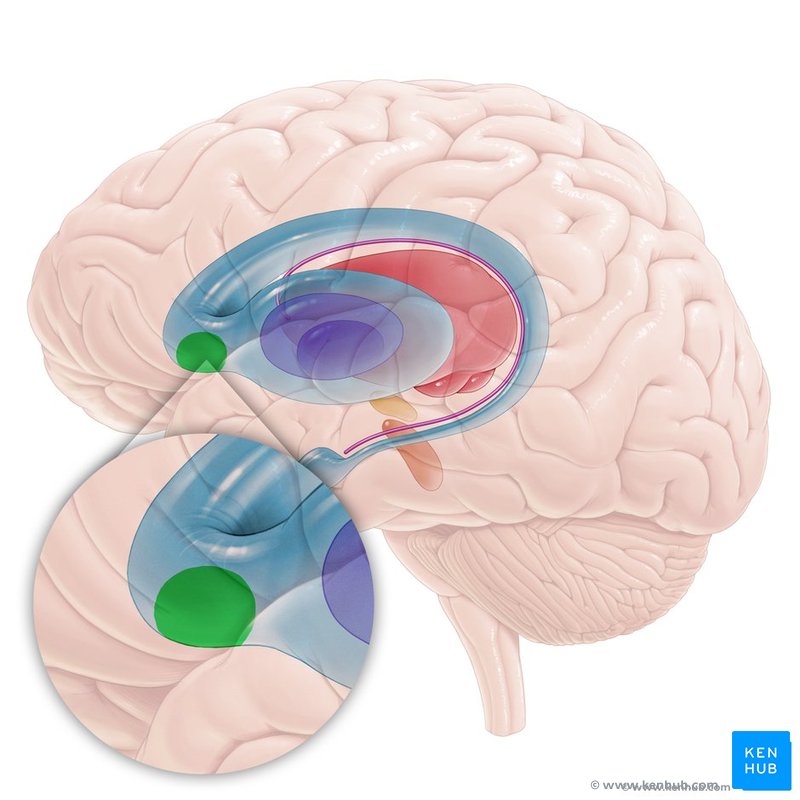
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
Area of the thalamus that relays visual info to the cortex and superior colliculus. Located in posterior portion of thalamus
Optic Radiations
White matter tracts that carry visual info from lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) in the thalamus to the primary visual cortex.
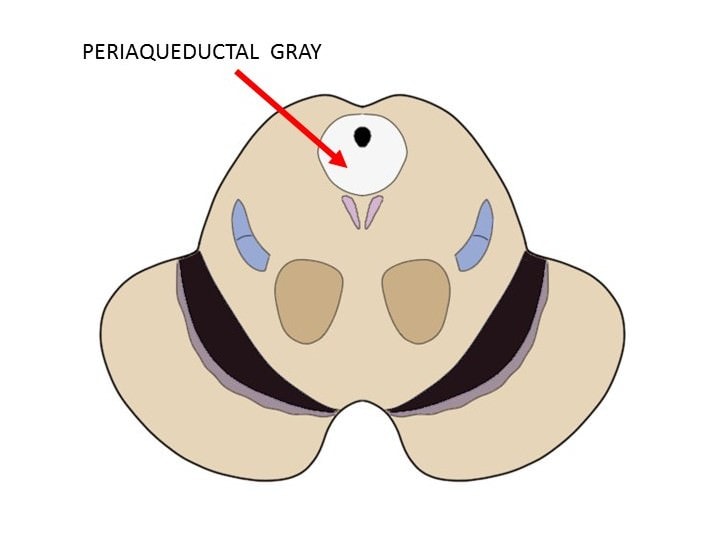
Periaqueductal Gray (PAG)
gray matter surrounding the cerebral aqueduct important in autonomic function and pain modulation
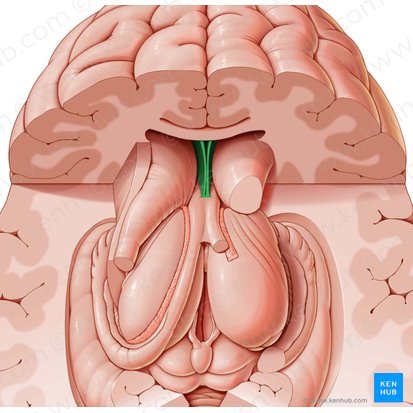
Septum Pellucidum
Thin membrane that separates the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles medially
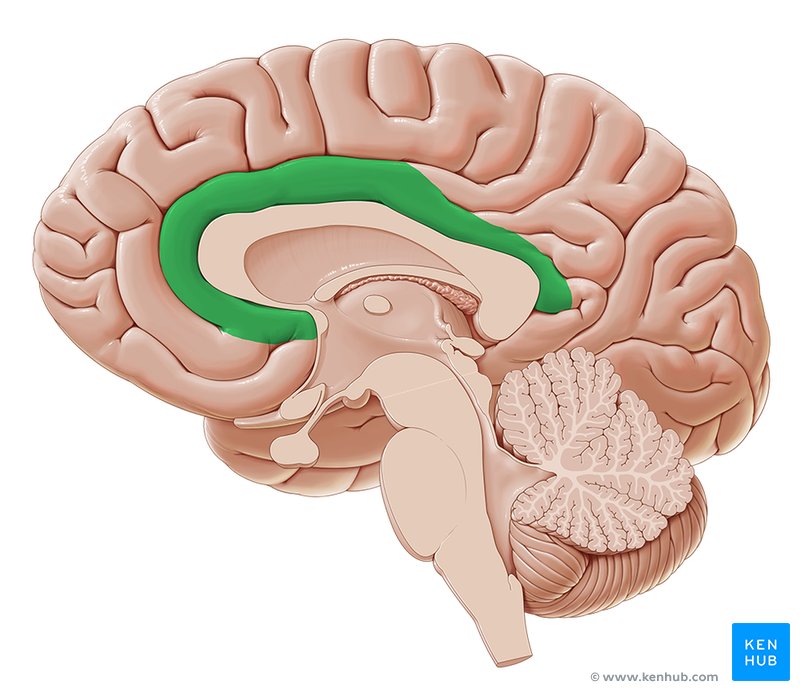
Cingulate Gyrus
Gyrus located on top of the corpus callosum. Plays an important role in the limbic system
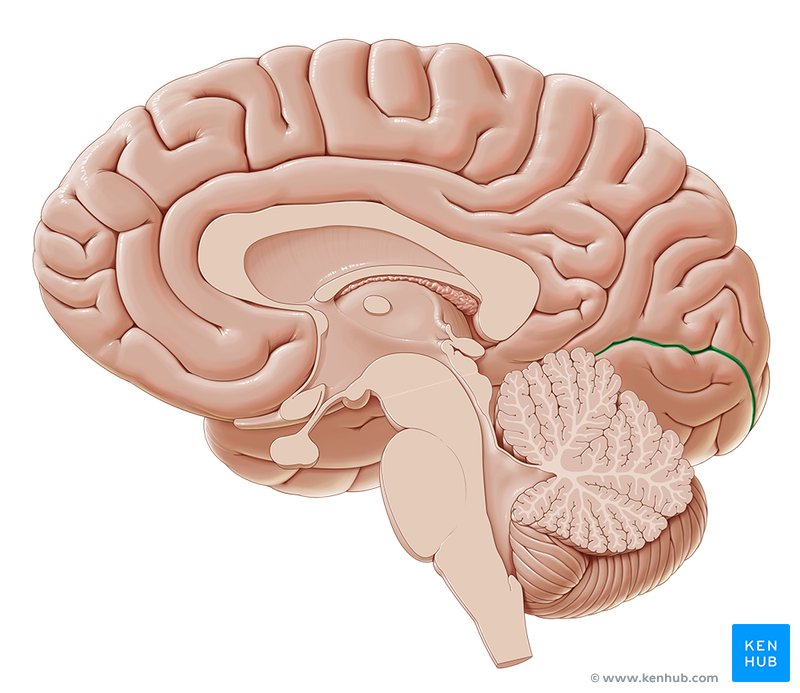
Calcerine Fissure
Large sulcus in the occipital lobe where the primary visual cortex is located. Divides the occipital lobe in half, separating upper and lower half of vision
Locus Coeruleus
small cluster of neurons in the brainstem, located in the dorsal pons, near the floor of the fourth ventricle. Important for physiological responses to stress and panic
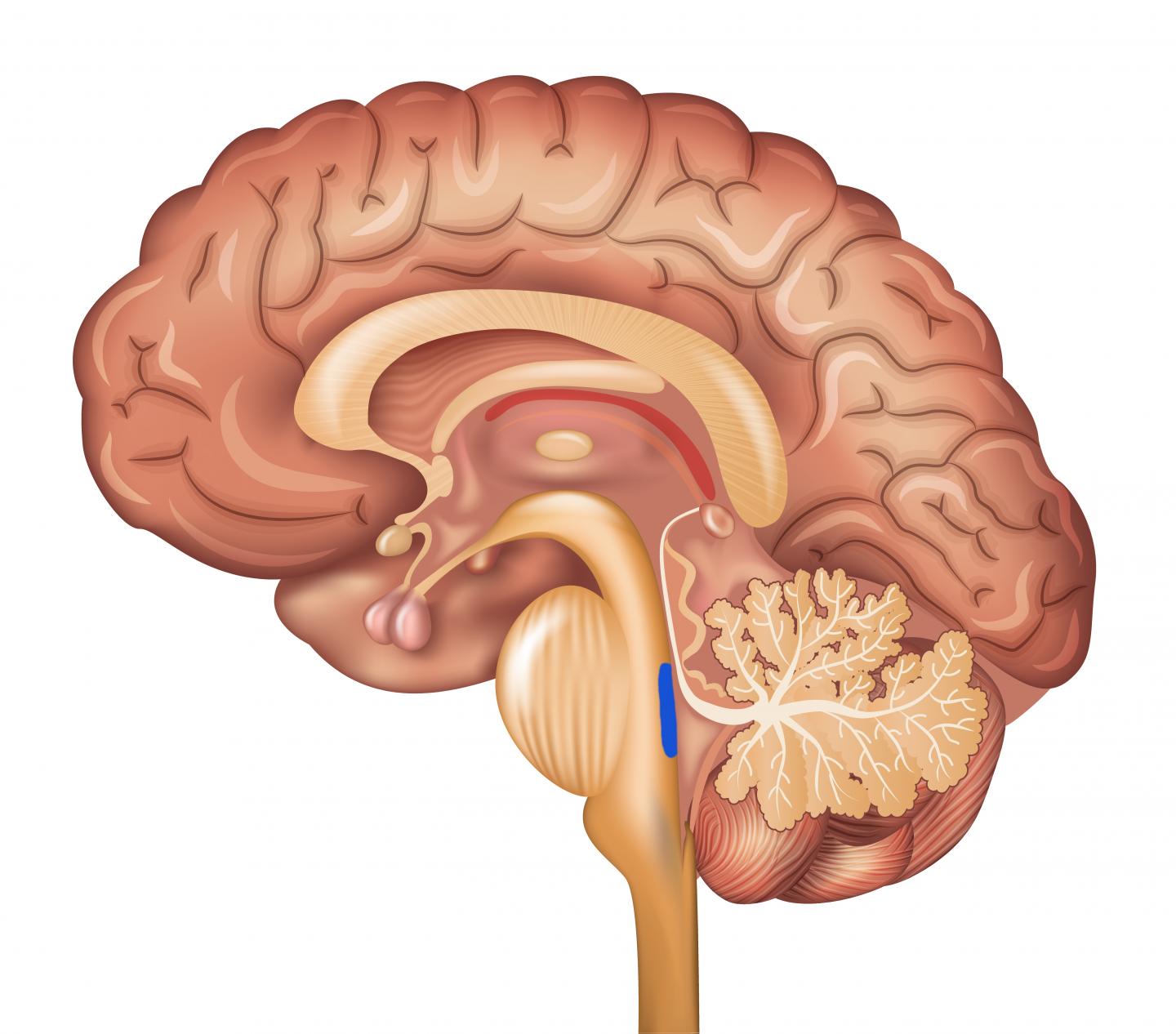
Uncus
area in temporal lobe that plays a role in emotion, memory, and smells. Anterior part that covers amygdala and posterior is apart of hippocampal formation
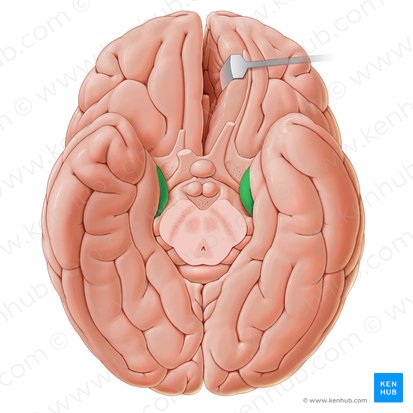
Parahippocampal Place Area (PPA)
gray matter cortical area that surrounds hippocampus and apart of the limbic system. Important for memory encoding and retrieval
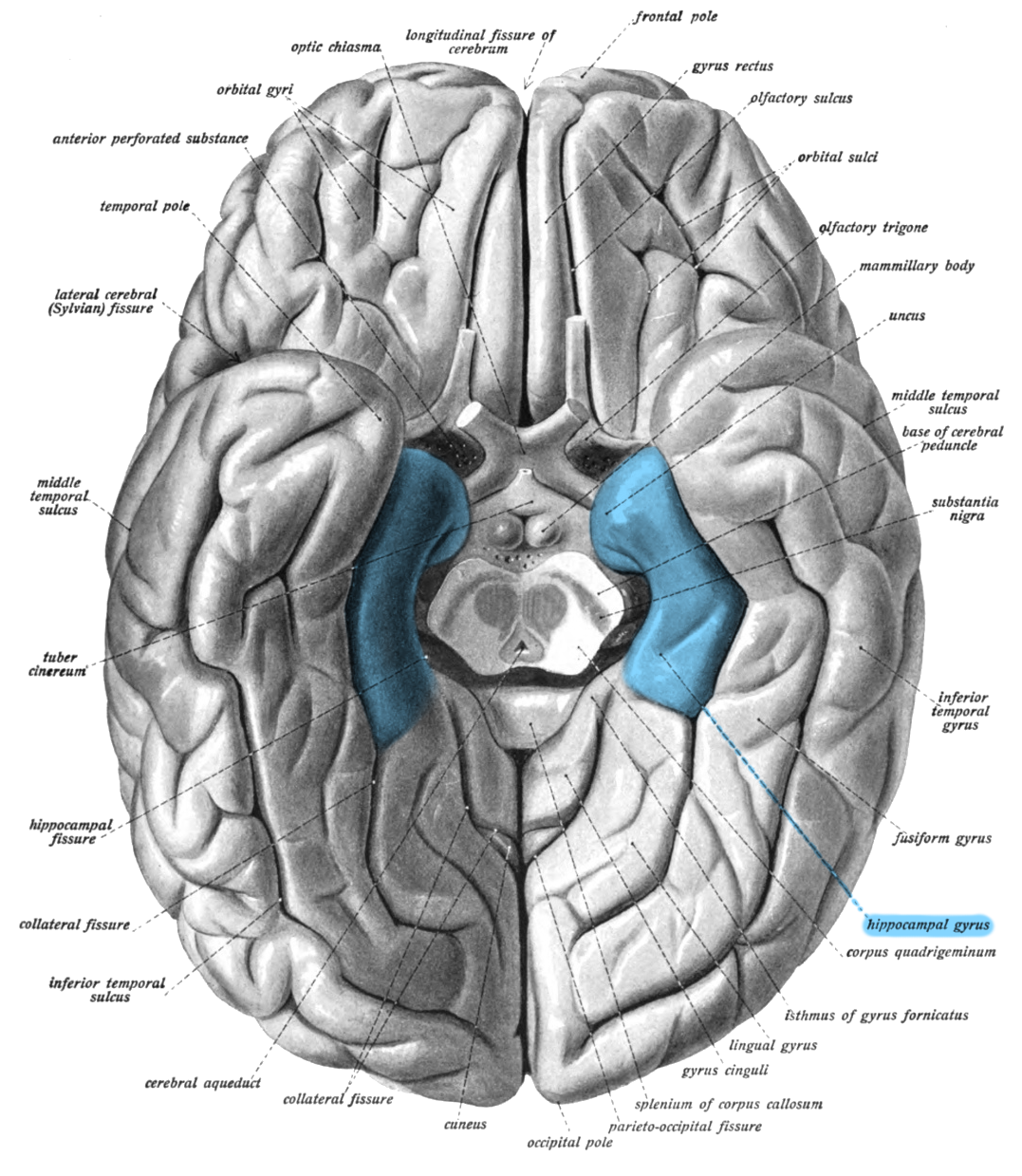
Fusiform Face Area (FFA)
area of the brain located in the inferior temporal lobe of the brain, in the fusiform gyrus. Important for detecting faces
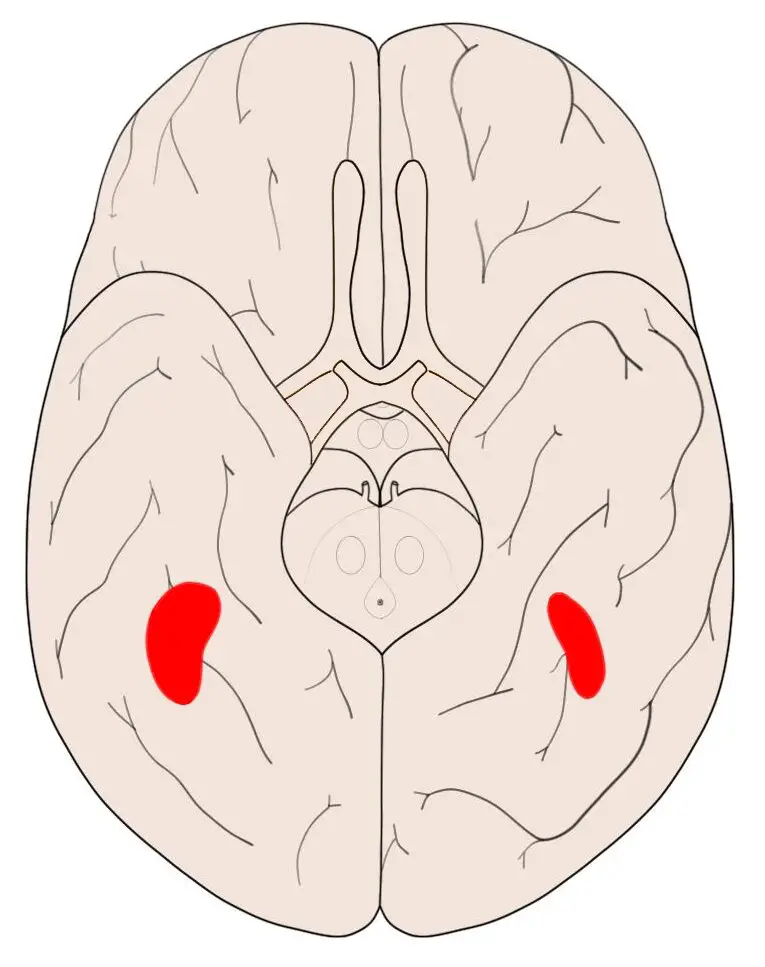
Claustrum
thin sheet of gray matter in the brain that's involved in many functions, including attention, memory, and consciousness. It's highly connected to other parts of the brain, including the limbic, cortical, and subcortical structures.
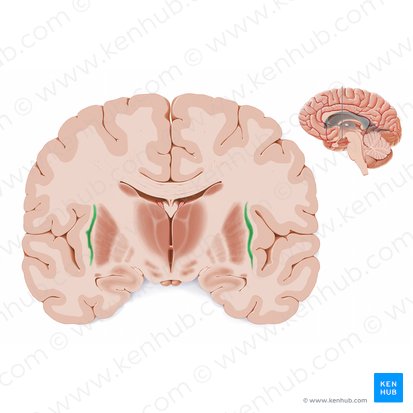
Dentate Nucleus
Deep cerebellar nucleus located in the posterior cerebellum. Plays a crucial role in motor coordination and control
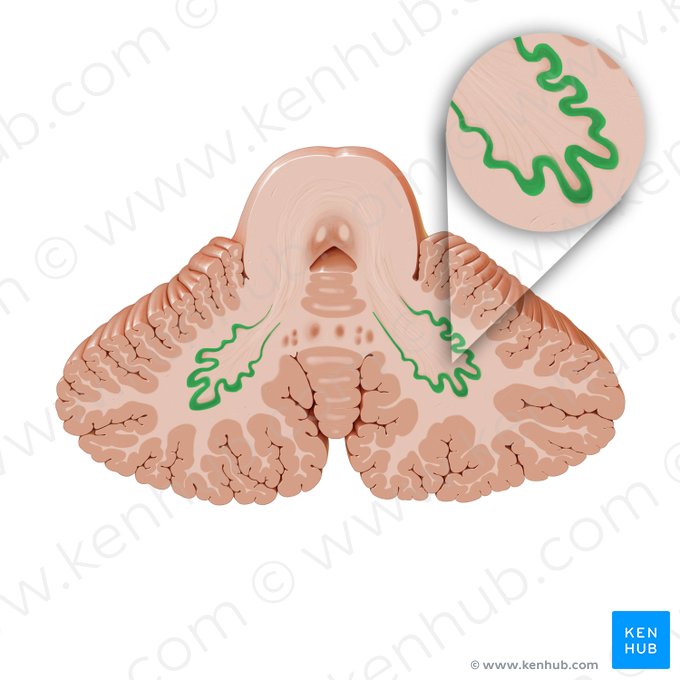
Striatum
Cluster of nuclei in basal ganglia. Made up of caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus
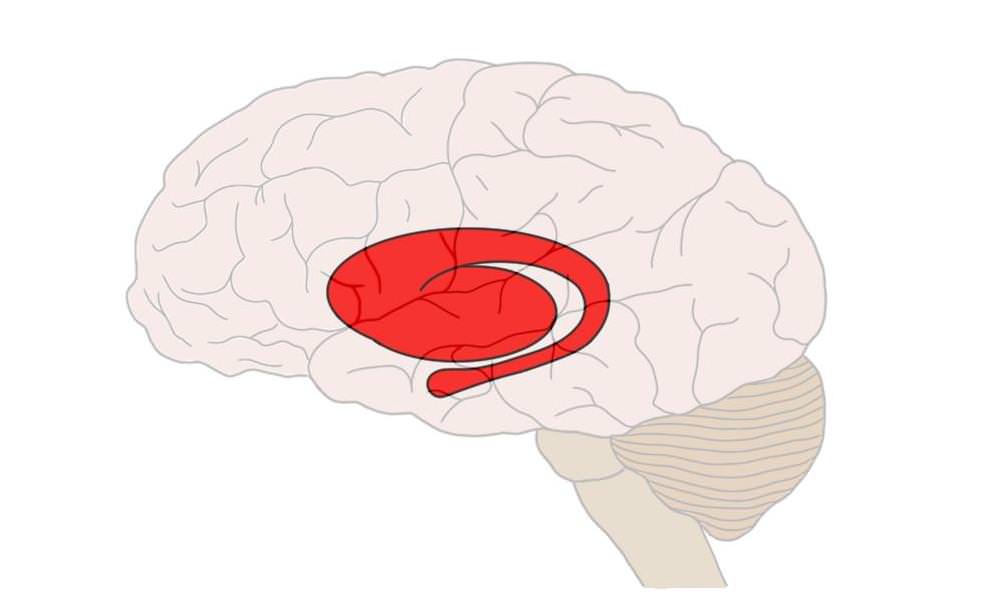
Internal Capsule
white matter structure of the brain lateral to the thalamus and caudate nucleus. Important for connecting cortical regions to sub-cortical regions and the brainstem.
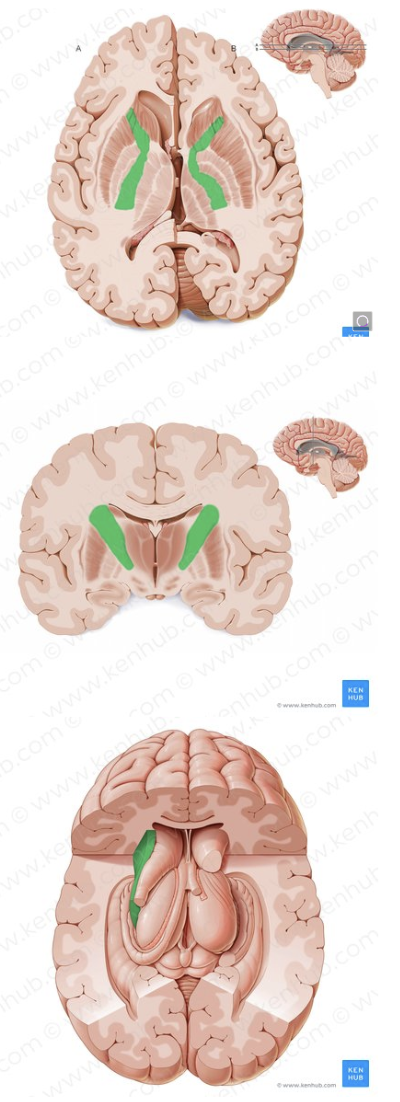
External Capsule
Network of nerve fibers medial to claustrum and lateral to putamen. Thought to be important for processing sensory information and coordinating movement
Extreme Capsule
Nerve fibers medial to insula and lateral to claustrum.