BIOA01 chapter 7 and 8
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
1
New cards
Cellular Respiration
The process that releases energy (ATP) by breaking down glucose. (converts food molecules (glucose) into a form usable (ATP) by the organism)
2
New cards
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Energy. Main energy source that cells use for most of their work.
3
New cards
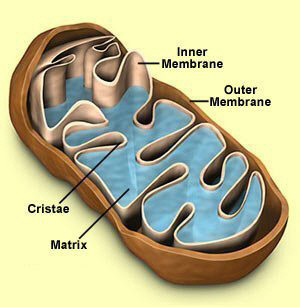
Mitochondria
Organelle found in all organisms that is the site of cellular respiration
4
New cards
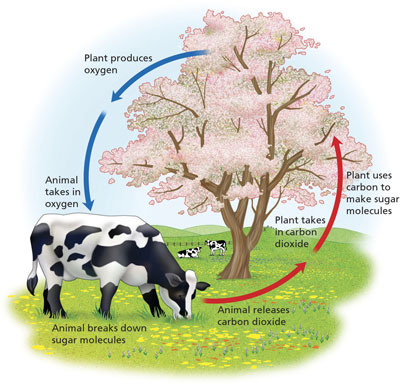
Definition of Cellular Respiration
The process of breaking the chemical bonds of glucose into energy.
5
New cards
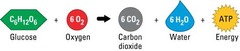
Cellular Respiration Chemical Equation
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)
6
New cards
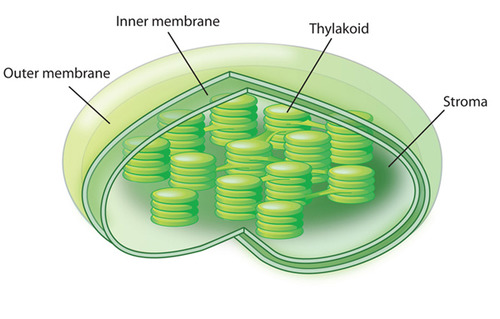
Location of Photosynthesis
Chloroplast
7
New cards
Reactants of Photosynthesis
6H20 + 6CO2
8
New cards
Products of Photosynthesis
C6H12O6 + 6O2

9
New cards
Plants need these to survive
Water, carbon dioxide, and light
10
New cards
Animals need these to survive
Food, oxygen, and water
11
New cards
Gas released by plants during photosynthesis
oxygen
12
New cards
autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
13
New cards
heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.
14
New cards
reactants
The starting material in a chemical reaction
15
New cards
chlorophyll
Absorbs light energy.
Pigment that gives a plant its green color. Found in the chloroplast
Pigment that gives a plant its green color. Found in the chloroplast

16
New cards
chloroplast
organelle where photosynthesis takes place.
17
New cards
oxygen
product of photosynthesis
18
New cards
carbon dioxide
Gas taken in and used during photosynthesis.
19
New cards
leaf
the part of the plant where most photosynthesis takes place

20
New cards
light energy
energy from the sun that is used by plants to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis

21
New cards
Photosynthesis
converting light energy to the chemical energy of food, in plants
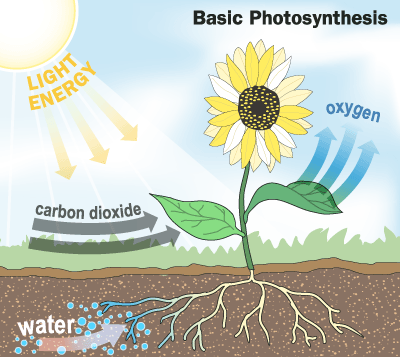
22
New cards
Glucose
the type of sugar made during photosynthesis

23
New cards
product
a substance that is formed by a chemical reaction
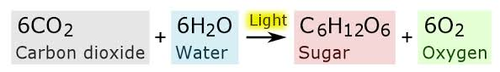
24
New cards
water formula
H2O
25
New cards
carbon dioxide formula
CO2
26
New cards
glucose formula
C₆H₁₂O₆
27
New cards
oxygen
O2
28
New cards
reactants of cellular respiration
glucose and oxygen
29
New cards
products of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
30
New cards
organisms that make their own food
What's an autotroph?
31
New cards
Organisms that obtain food by consuming other living things
What's a heterotroph?
32
New cards
A chemical compound cells use to store and release energy
What's ATP?
33
New cards
active transport
Energy provided by ATP is used in what kind of transport?
34
New cards
Saclike photosynthetic membranes that contain chlorophyll and other pigments and are rearranged in stacks called grana
What's a thylakoid?
35
New cards
The fluid potion outside of the thylakoids
What's a stroma?
36
New cards
No
Does the light-independent reaction use energy?
37
New cards
Yes
Does the light-dependent reaction use light energy?
38
New cards
Wavelength
What determines color?
39
New cards
Saclike photosynthetic membranes called thylakoids
What do chloroplasts contain and abundance of?
40
New cards
Increase the energy level of the chlorophyll's electrons
What does the visible light absorbed by chlorophyll do?
41
New cards
Water molecules that are split into O2 H+, and high energy electrons
Where do the high-energy electrons carried by NADPH come from?
42
New cards
carbon dioxide and water
What are the reactants of the photosynthesis reaction?
43
New cards
Oxygen and ATP
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions?
44
New cards
Stroma
Where do light independent reactions occur?
45
New cards
A series of electron carrier proteins
What's an electron transport chain?
46
New cards
Temperature, light intensity, and availability of water affect photosynthesis
What factors influence the rate of photosynthesis?
47
New cards
Photosytem I
NADP is the product of which photosystem?
48
New cards
ATP and NADPH
What are two types of energy carriers
49
New cards
Photosystem I
The light dependent reactions begin when which photosystem absorbs light?
50
New cards
Thylakoid membrane
Where do the light dependent reactions take place?
51
New cards
Light's absorbed increasing the energy of the electrons. The electrons are passed down the electron transport chain
What happens in photosystem II
52
New cards
Electrons are passed from protein to protein to protein releasing energy. The energy is used to pump H+ ions from the stroma into the thylakoid space.
What happens in electron transport chain?
53
New cards
Electron is reenergized by light, then picked up by NADP+ and H+ forming NADPH
What happens in photosystem I
54
New cards
glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain
Cellular respiration captures the energy from food in three main stages which are?
55
New cards
No
Does glycolysis require oxygen?
56
New cards
Yes
Does the Krebs cycle require oxygen?
57
New cards
Yes
Does the electron transport chain require oxygen?
58
New cards
processes that require oxygen
What does aerobic mean?
59
New cards
Processes that occur without oxygen
What's anaerobic?
60
New cards
Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back
What does photosynthesis remove?
61
New cards
Oxygen into the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back
What does photosynthesis release?
62
New cards
Glycolysis
Cellular respiration begins with a pathway called?
63
New cards
Cytoplasm of the cell
Where does glycolysis take place?
64
New cards
Energy storage
What's the function of photosynthesis?
65
New cards
Energy release
What's the function of cellular respiration?
66
New cards
Chloroplasts
Where does photosynthesis take place?
67
New cards
Mitochondria
Where does cellular respiration take place?
68
New cards
CO2 and H20
What are the reactants of photosynthesis?
69
New cards
C6H12O6 and O2
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
70
New cards
C6H12O6 and O2
What are the products of photosynthesis?
71
New cards
CO2 and H2O
What are the reactants of cellular respiration
72
New cards
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
73
New cards
C6H12O6 + 602 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
What is the equation of cellular respiration?
74
New cards
2 ATP
What is used at the start of glycolysis to get cellular respiration started?
75
New cards
4 ATP
How much ATP synthesized during glycolysis for a net gain of 2 ATP?
76
New cards
Krebs cycle
What's the second stage of cellular respiration?
77
New cards
When oxygen is available
When does Krebs cycle operate?
78
New cards
A series of energy- extracting reactions
What's the Krebs cycle?
79
New cards
NAD+
What's the electron carrier?
80
New cards
The innermost compartment of a mitochondrion
What's the matrix?
81
New cards
Carbon dioxide and acetyl-CoA molecules
What are pyruvic acid molecules broken down into? (Cellular respiration)
82
New cards
ATP, NADH, FADH2
Energy released by the breaking and rearranging of carbon bonds is captured in the forms of ___________,__________ and ______________
83
New cards
H+ ions
The charge difference across the membrane forces what through channels in enzymes?
84
New cards
A phosphate group is added to ADP, generating ATP
What happens as the atp synthase spins?
85
New cards
Lactic acid
What does lactic acid fermentation produce?
86
New cards
Produces ATP w/o oxygen
Whats the function of fermentation?
87
New cards
Long-term, large product of ATP
Whats the function of cellular respiration?
88
New cards
Cellular Respiration
The process that releases energy (ATP) by breaking down glucose. (converts food molecules (glucose) into a form usable (ATP) by the organism)
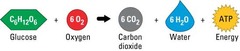
89
New cards
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Energy. Main energy source that cells use for most of their work.
90
New cards
Mitochondria
Organelle found in all organisms that is the site of cellular respiration
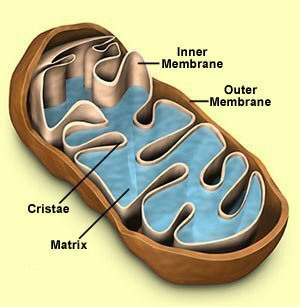
91
New cards
Definition of Cellular Respiration
The process of breaking the chemical bonds of glucose into energy.
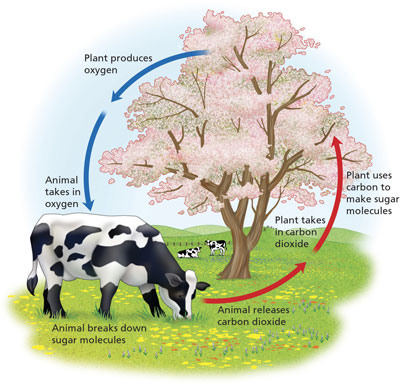
92
New cards
Cellular Respiration Chemical Equation
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)
93
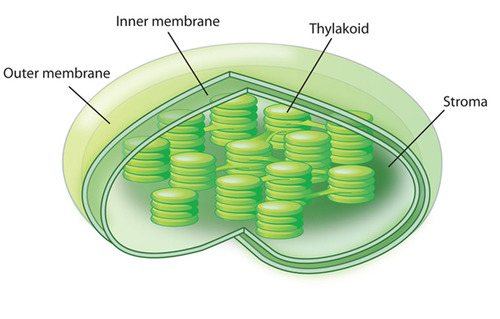
New cards
Location of Photosynthesis
Chloroplast
94
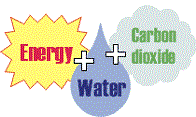
New cards
Reactants of Photosynthesis
6H20 + 6CO2
95
New cards
Products of Photosynthesis
C6H12O6 + 6O2

96
New cards
Plants need these to survive
Water, carbon dioxide, and light
97
New cards
Animals need these to survive
Food, oxygen, and water
98
New cards
Gas released by plants during photosynthesis
oxygen
99
New cards
autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
100
New cards
heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.