AP Biology unit 1
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Hypothesis
A prediction that can be tested by recording observations or experiments.
Control Group
Groups that hep eliminate experimental errors and biases of researchers.
Experimental Group
The group in an experiment that receives the variable being tested
Independent Variable
The factor that you are changing during the experiment.
Dependent Variable
The factor that is measured during the experiment.
Null Hypothesis
Hypothesis that the researchers are testing.
Alternate Hypothesis
An opposing theory to the null hypothesis.
Constants
Something that stays the same throughout the whole experiment.
Mean
Average
Median
Middle number of a data set.
Mode
Number that appears most often in a data set.
Variability
How much the data in the set vary from the mean/central tendancy.
Standard Deviation
Average distance from the mean.
Range
Difference between highest and lowest number in the data set.
Standard Error of the Mean
The standard deviation of a sampling distribution
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Capillary Action
The attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
Chemical Bonds
An attraction between two atoms resulting from a sharing of outer-shell electrons or the presence of opposite charges on the atoms. The bonded atoms gain complete outer electron shells.
Hydrogen Bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule.
Covalent Bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms.
Ionic Bonds
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance.
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances.
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances.
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together.
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Base
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
Functional Groups
The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain carbon
Hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Macromolecule
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
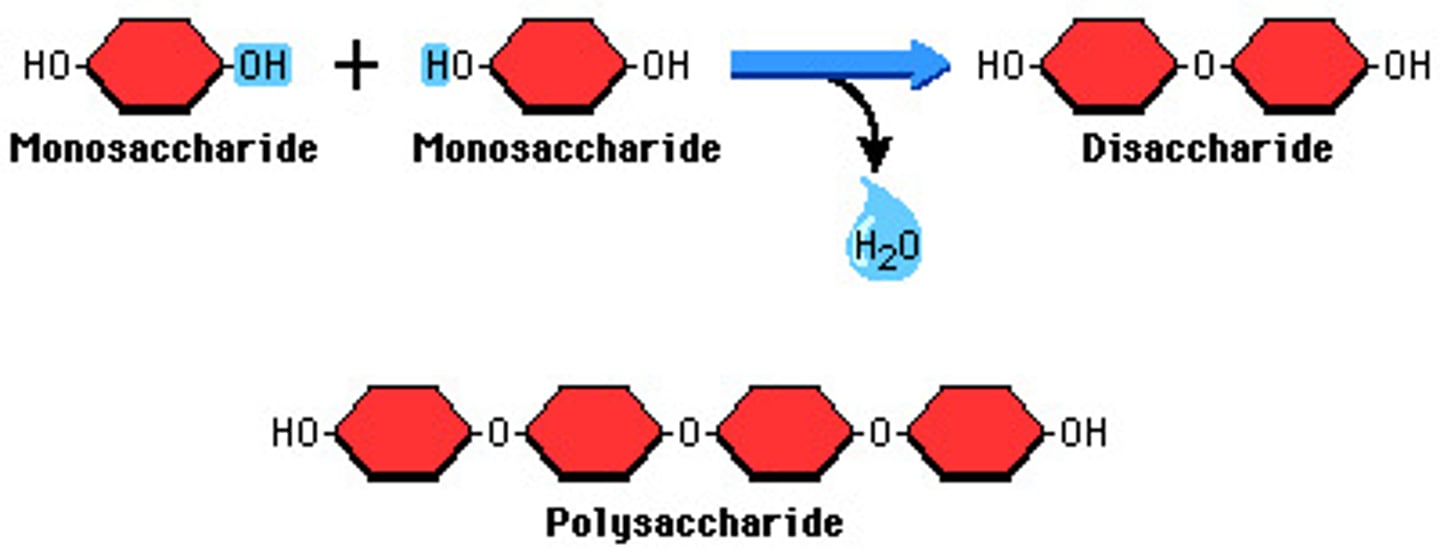
Dehydration Reaction
A chemical reaction in which molecules combine by removing water
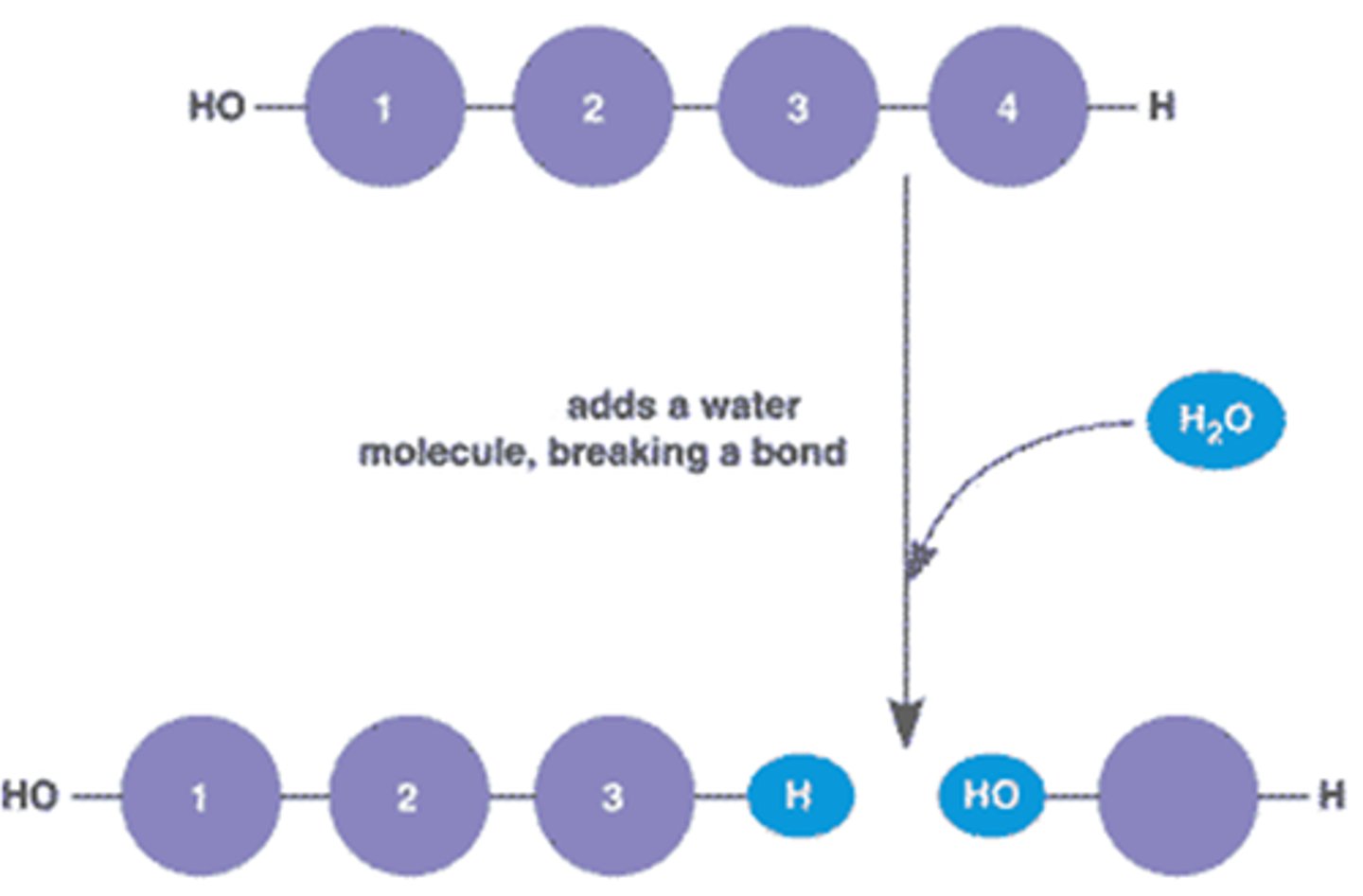
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
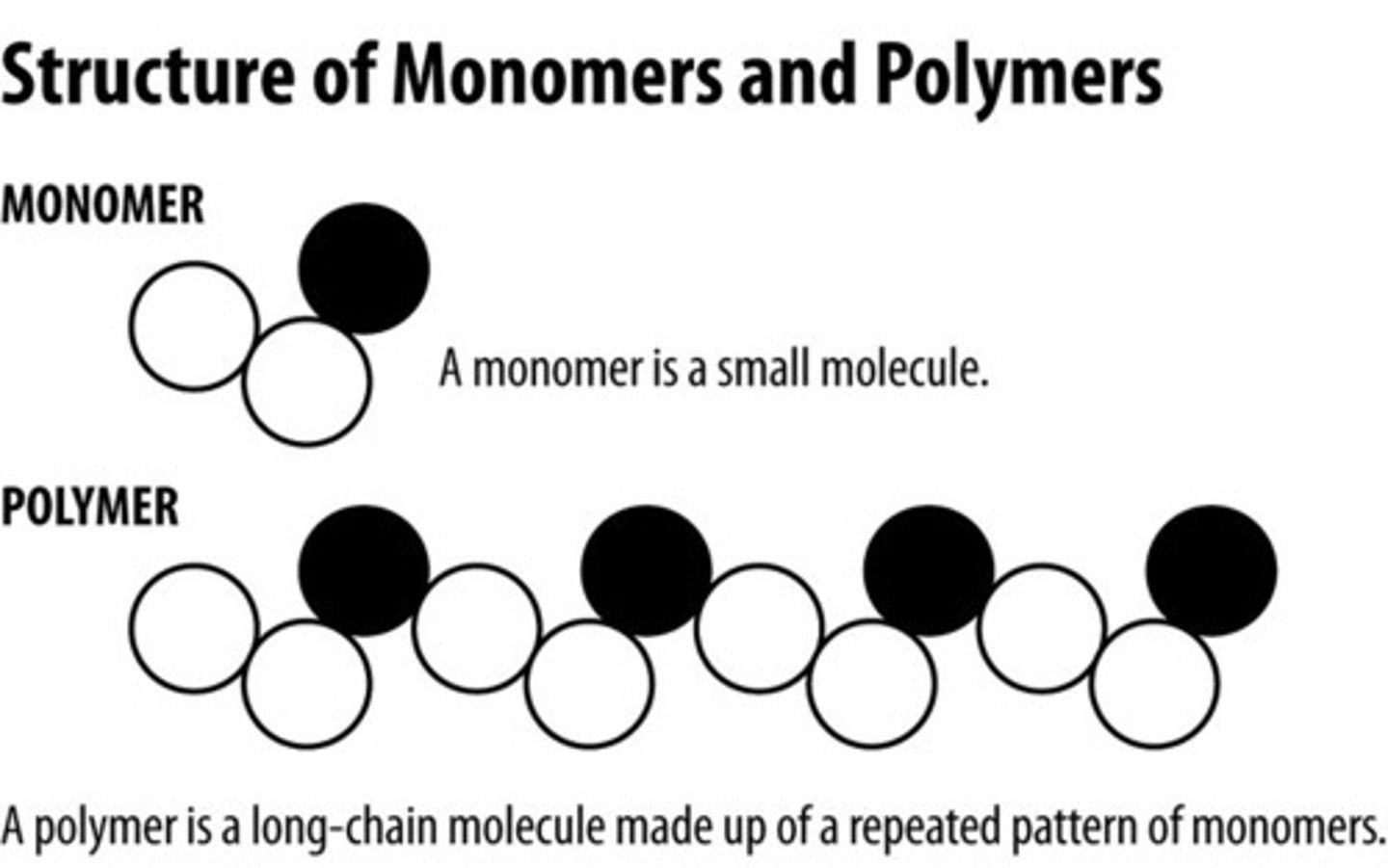
Polymers
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Monomers
small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers
Diasaccharides
A sugar molecule consisting of two monosaccharides linked by dehydration synthesis. Maltose, Lactose, Sucrose and Fructose.
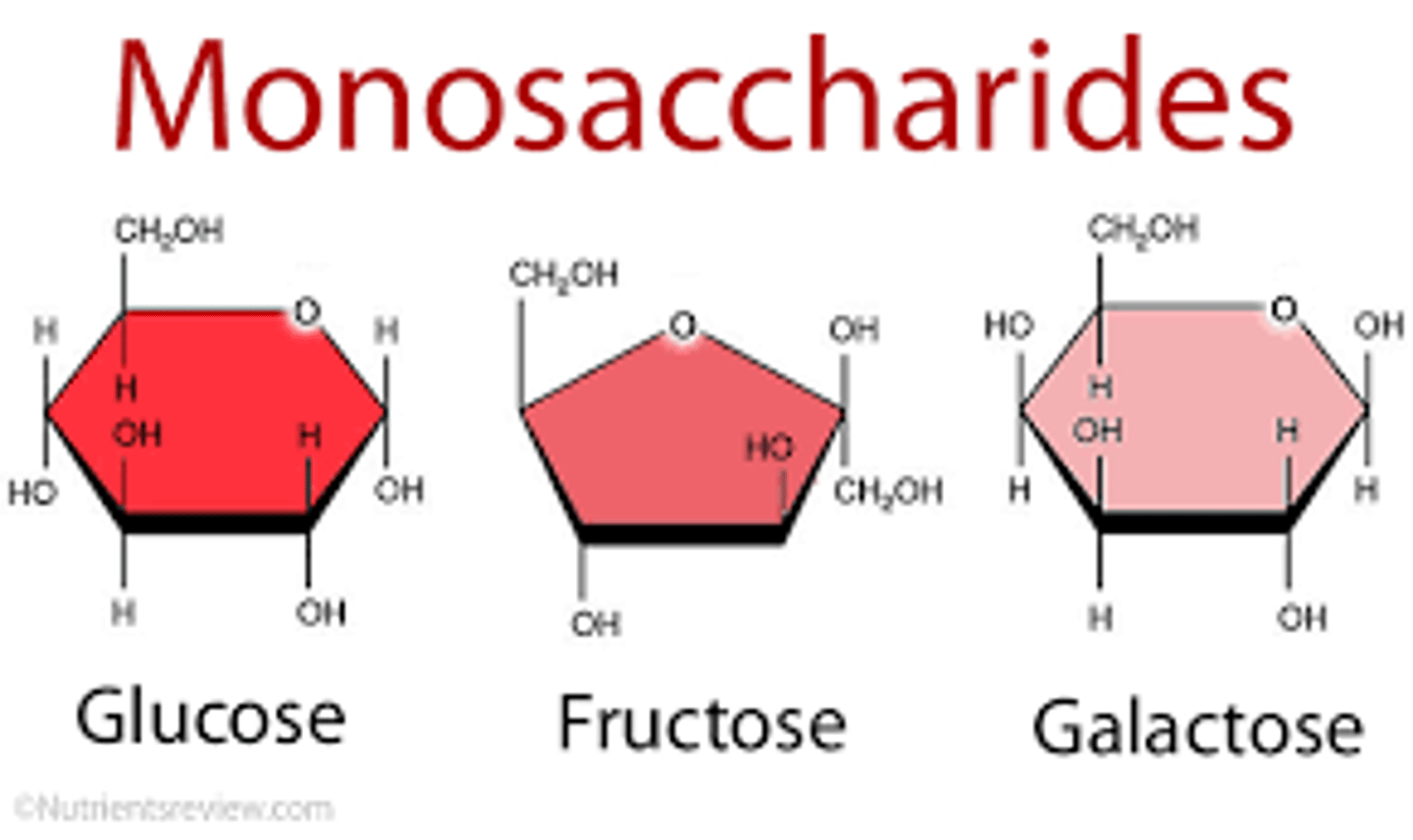
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules.
glucose, fructose, galactose
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
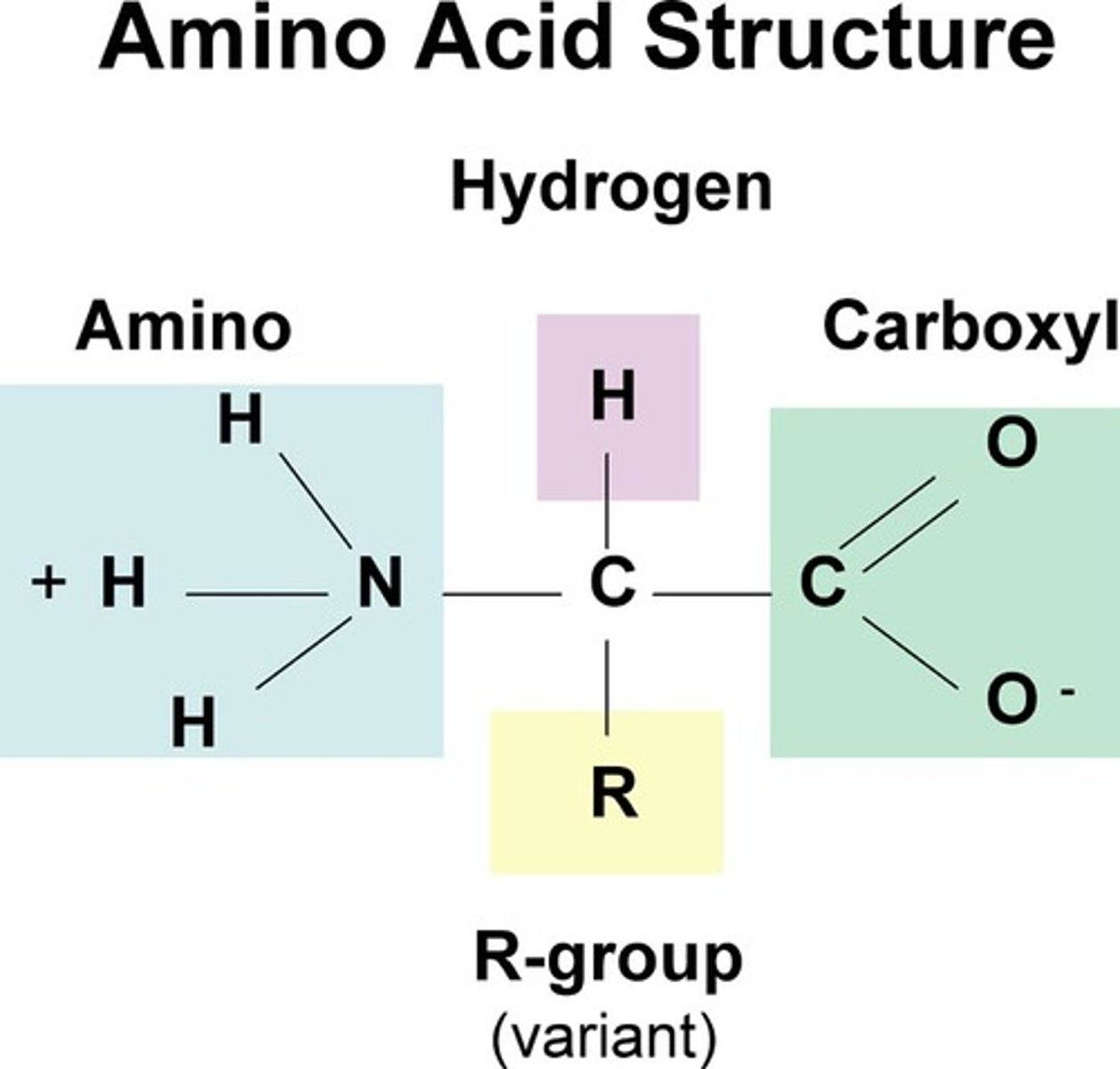
Amino Acids
a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group.
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Cellulose
polysaccharide consisting of glucose monomers that reinforces plant-cell walls
Glycogen
Storage form of glucose
Hydrophobic
Non Polar molecules that repel water.
Hydrophilic
molecules that are attracted to water.
Glycocidic Linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
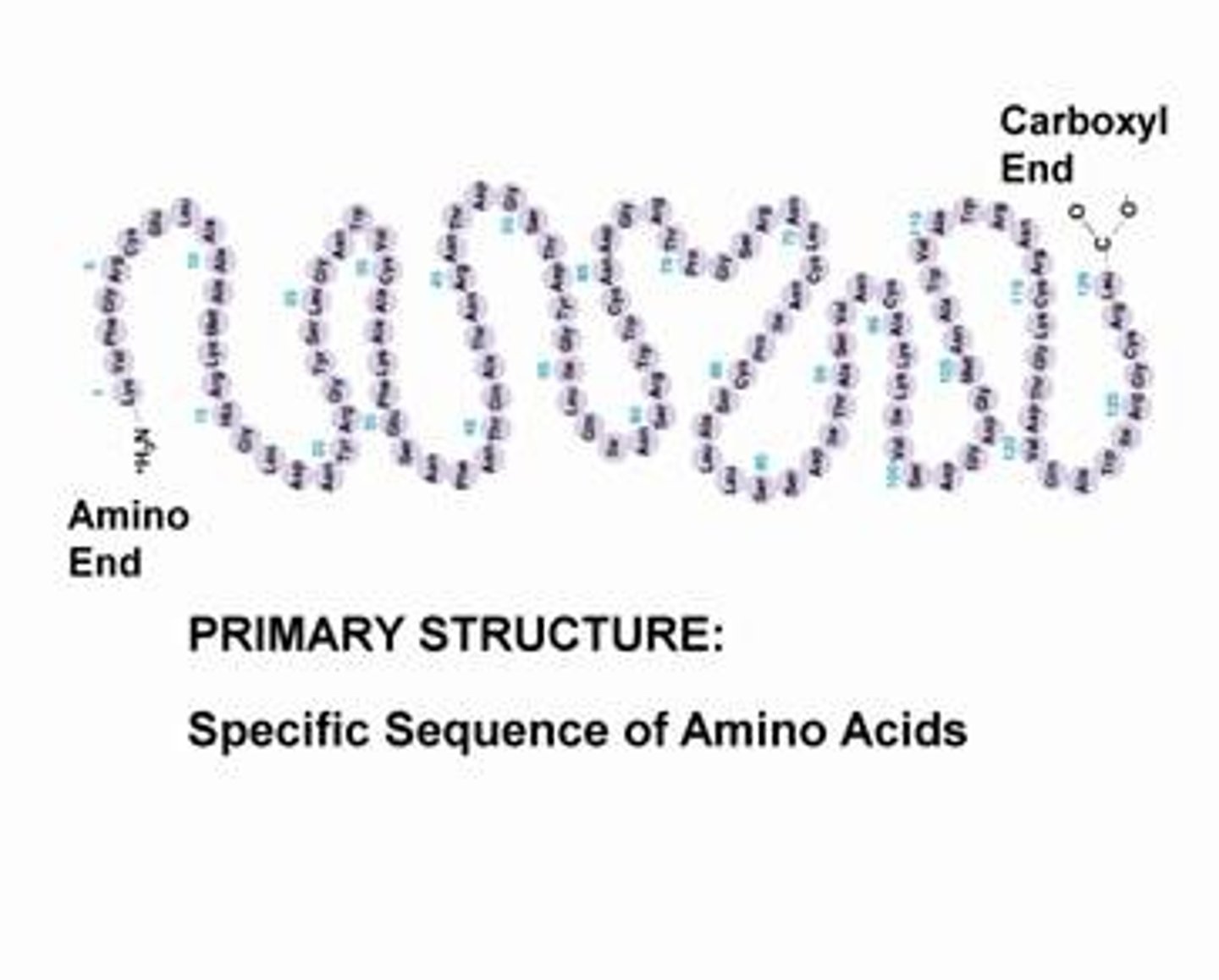
Primary Structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.
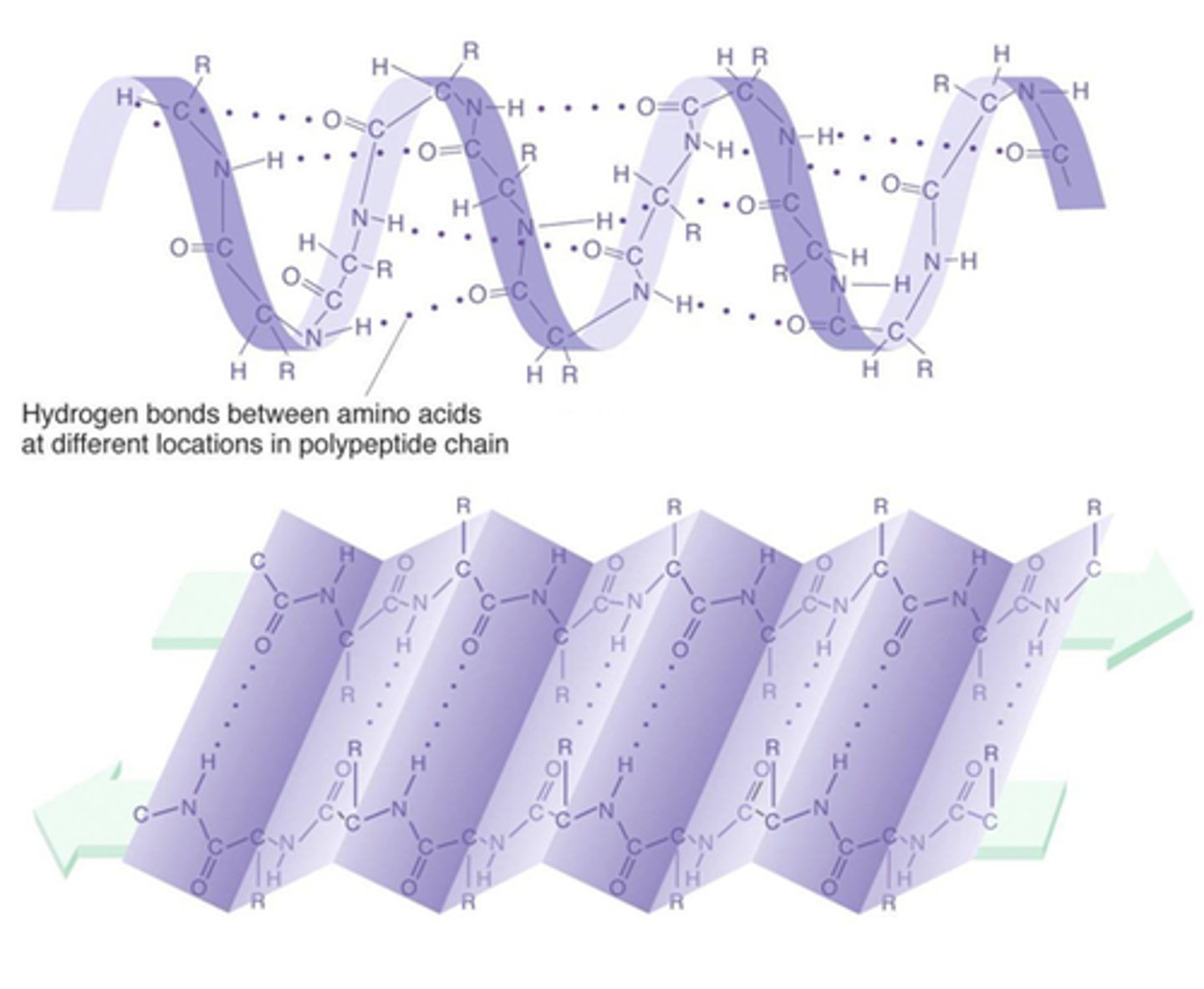
Secondary Structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
Tertiary Structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
Quaternary Structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
Lipid
Class of molecules that do not include true polymers.
Fat
A large lipid molecule made from an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids; a triglyceride. Most fats function as energy-storage molecules.
Fatty acid
Building Blocks of Lipids
Amino Acid
compound with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end. Building block of protein.
Phospholipid
a lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things).
Protein
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
Steroid
lipid molecule with four fused carbon rings
What is the relationship between monomers and polymers?
Monomers build polymers
Polymers are composed of monomers
dehydration synthesis
This is when water is removed between two monomers to JOIN them together
Hydrolysis
The breaking of a bond using water
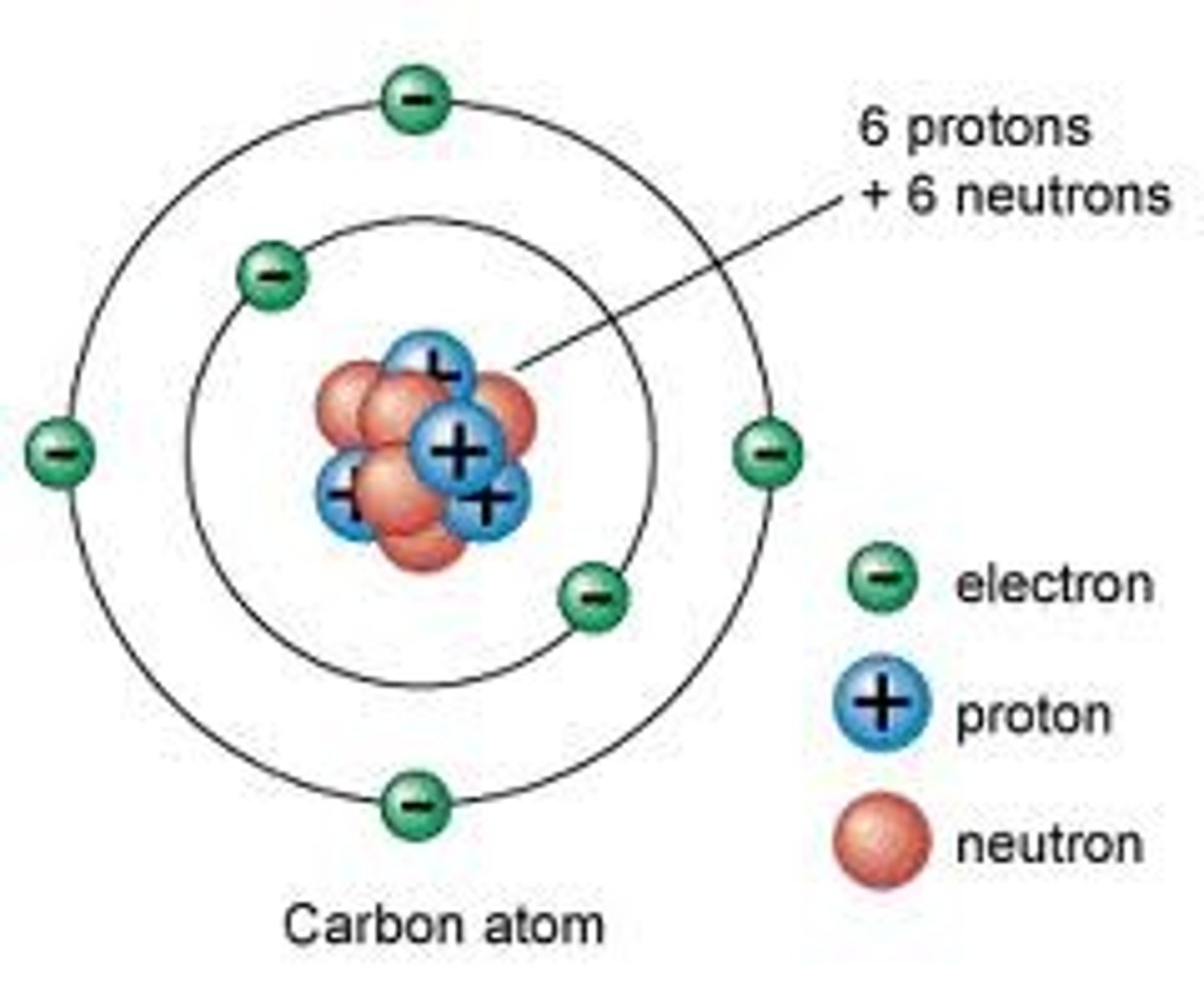
Why is Carbon important?
Found in ALL organic compounds, is a versatile element since it can make 4 bonds
Can create carbon chain or carbon ring structures
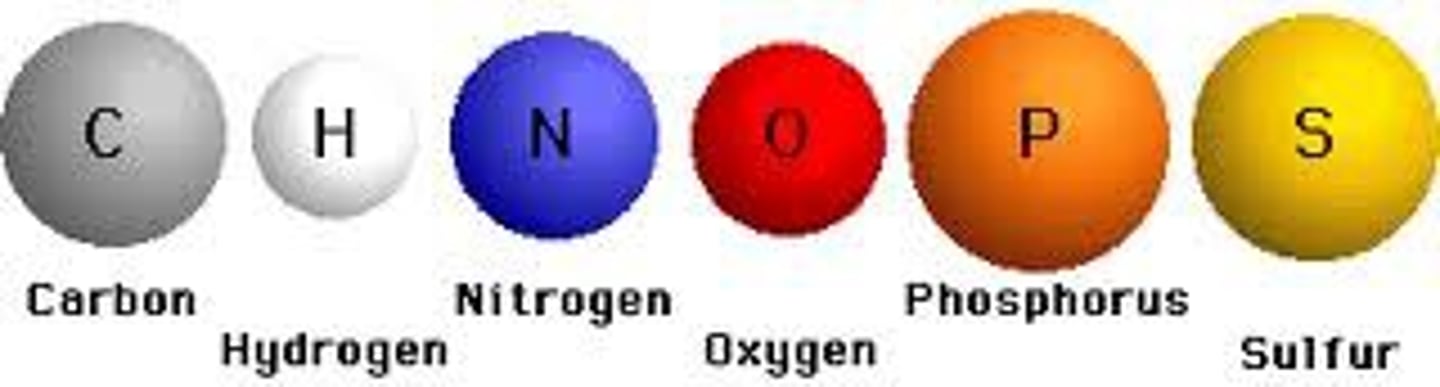
What are the main elements found in organic compounds?
C, H, O, N, P, (S)
Carbohydrates include what?
Sugars and polymers of sugars
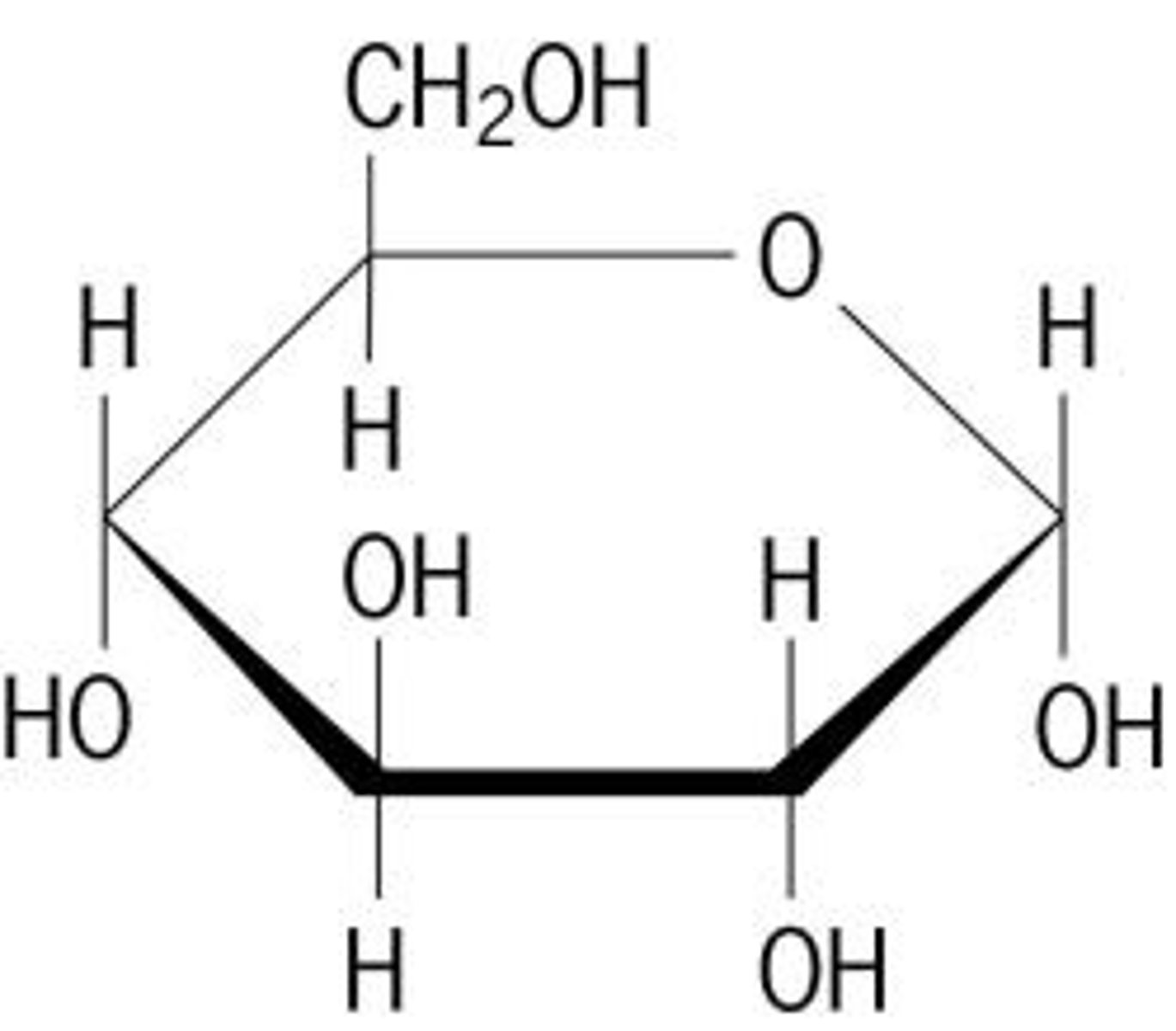
What is the basic structural formula for a carbohydrate?
Basic structural formula = (CH2O)N
Example: Glucose = C6H12O6 = (CH2O)6
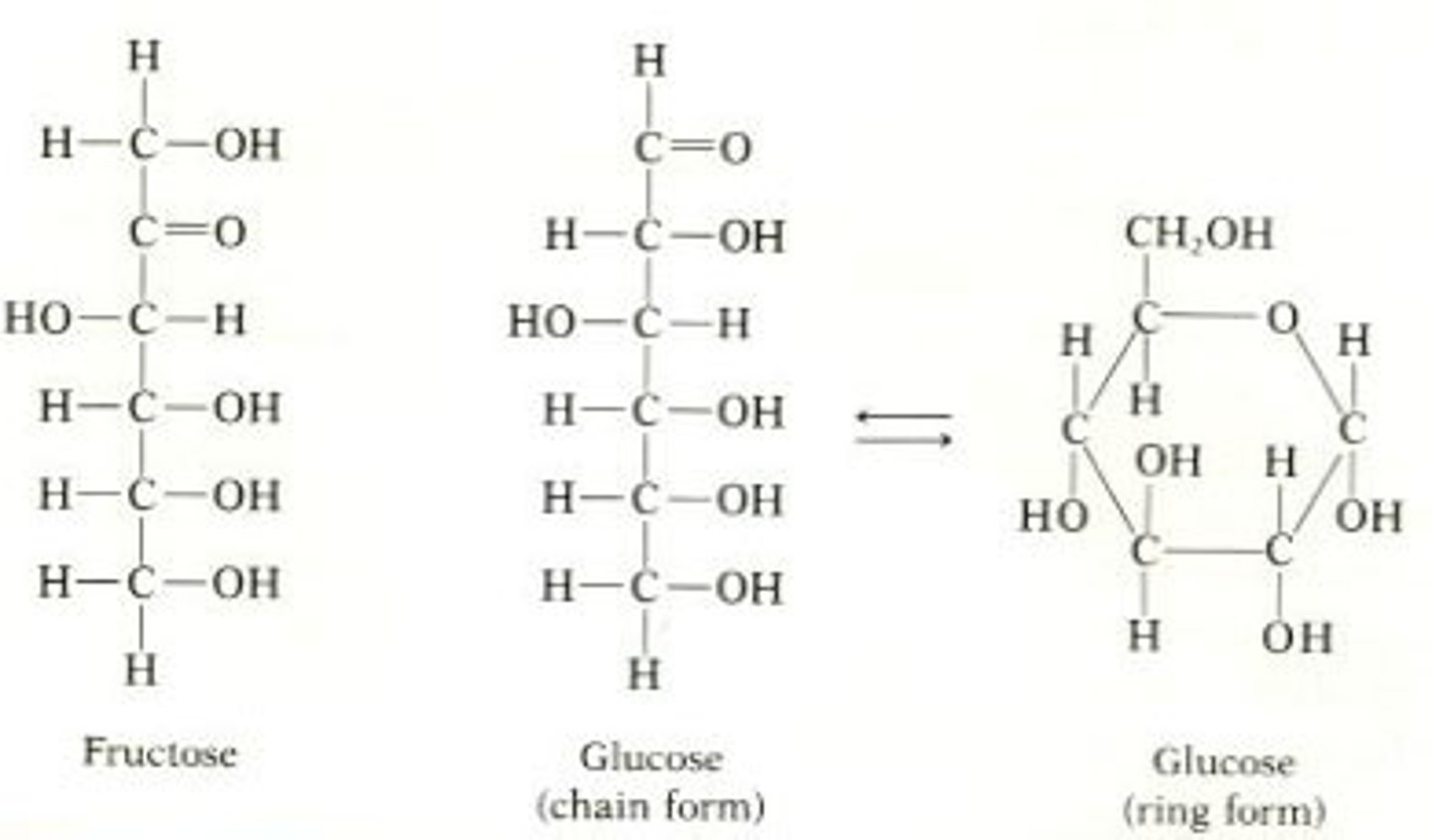
How are carbohydrates made?
Made by monosaccharides joined through glycosidic linkage (creates polysaccharides)
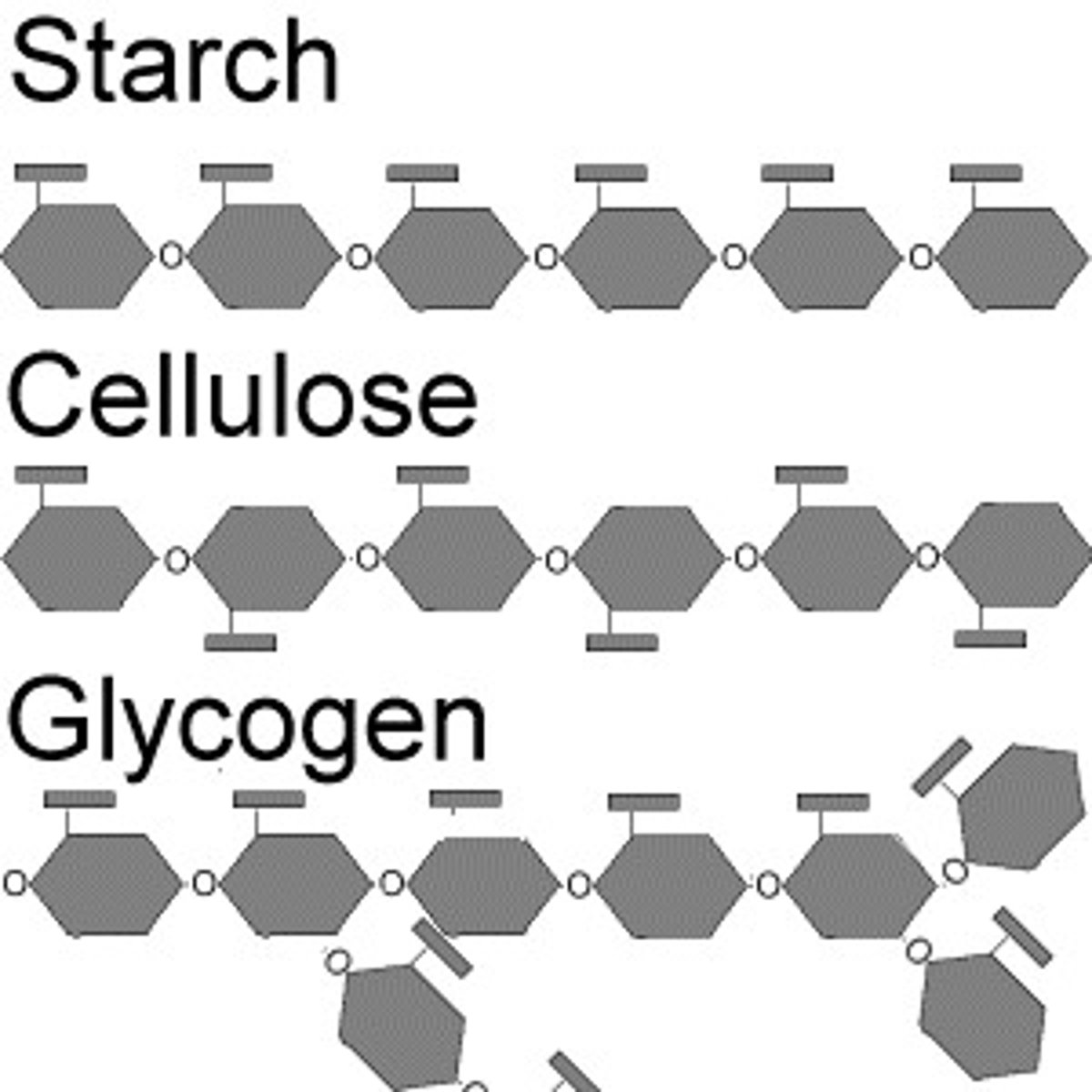
Examples of carbohydrates include
sugars and starches

The names of many carbohydrates tend to end in
-ose
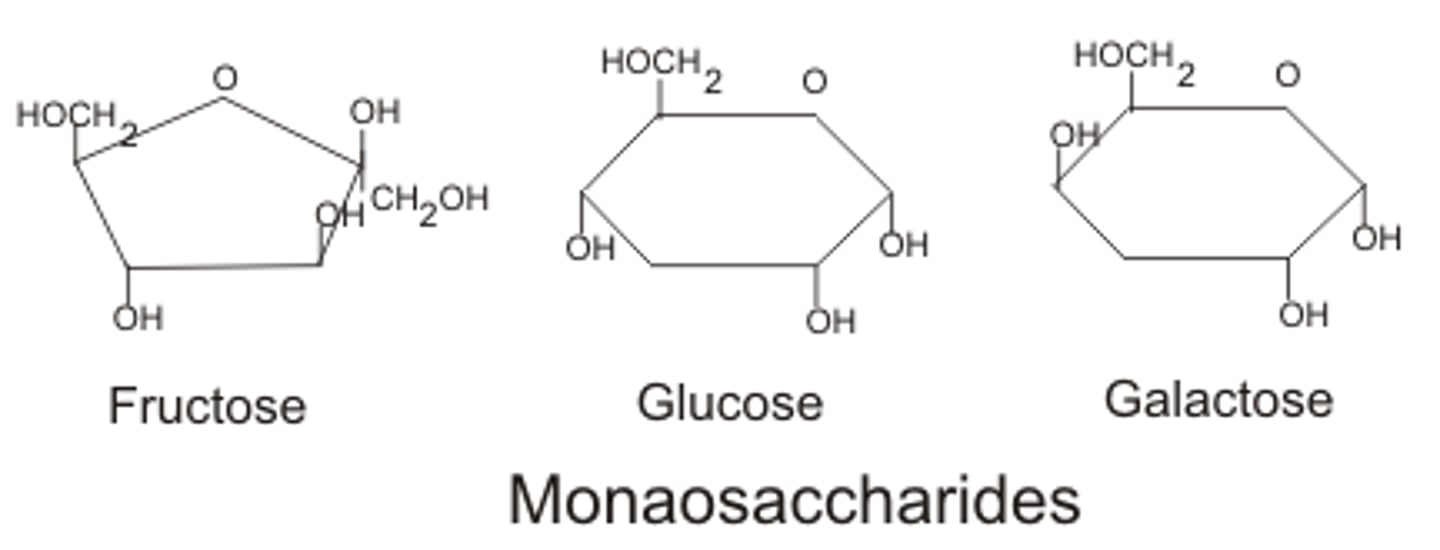
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharide (Glucose, fructose, galactose)
What is the function of a carbohydrate?
Short Term Energy Source
Plants use starch as an energy-storage polysaccharide
Animals use glycogen as an energy-storage polysaccharide
. Structural Support
Plants have cellulose as a major component of their cell walls
Arthropods have chitin in their exoskeletons and fungi have this in their cell walls.
Lipids are primarily made from
Carbon and hydrogen (hydrocarbons)
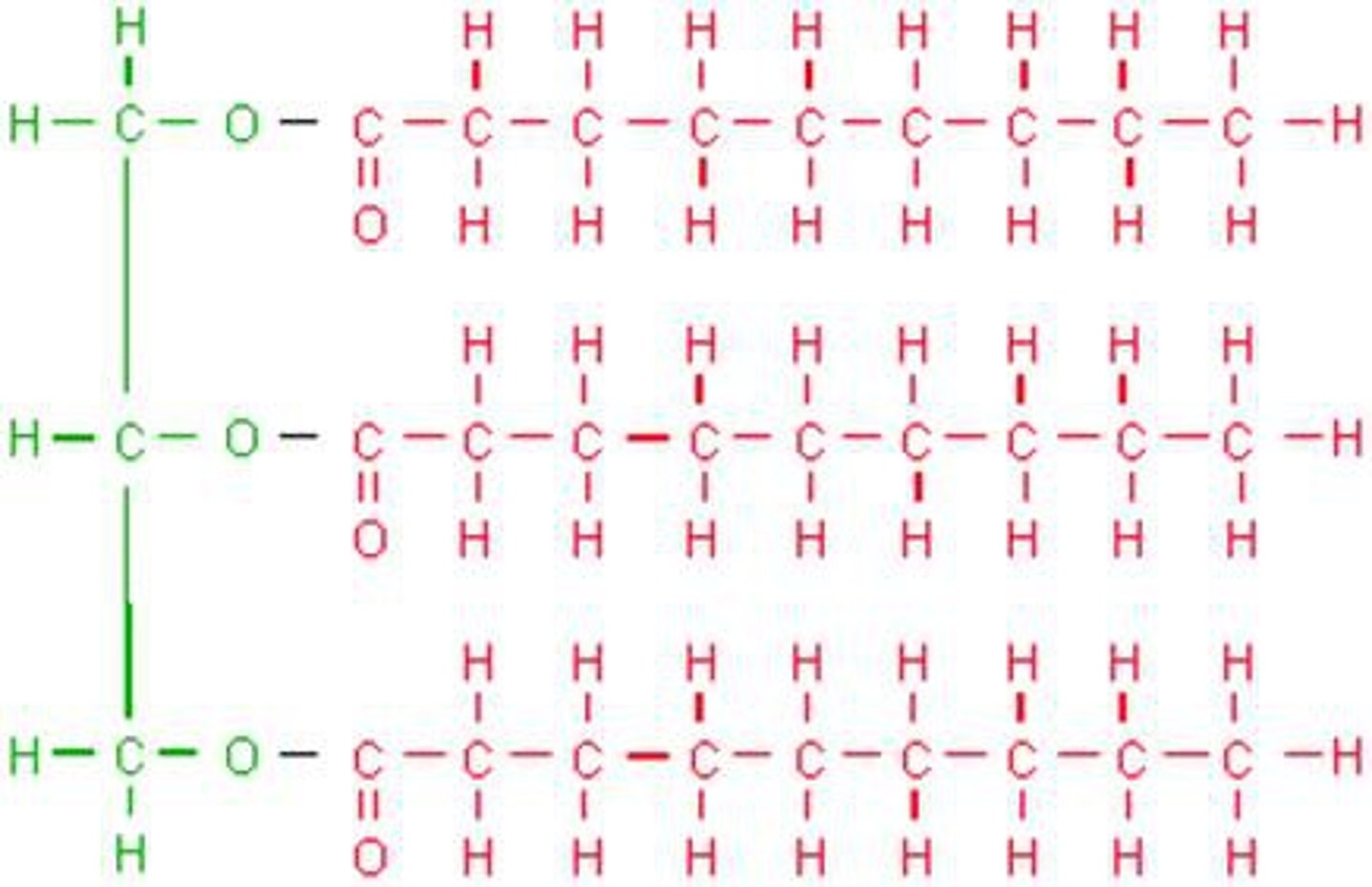
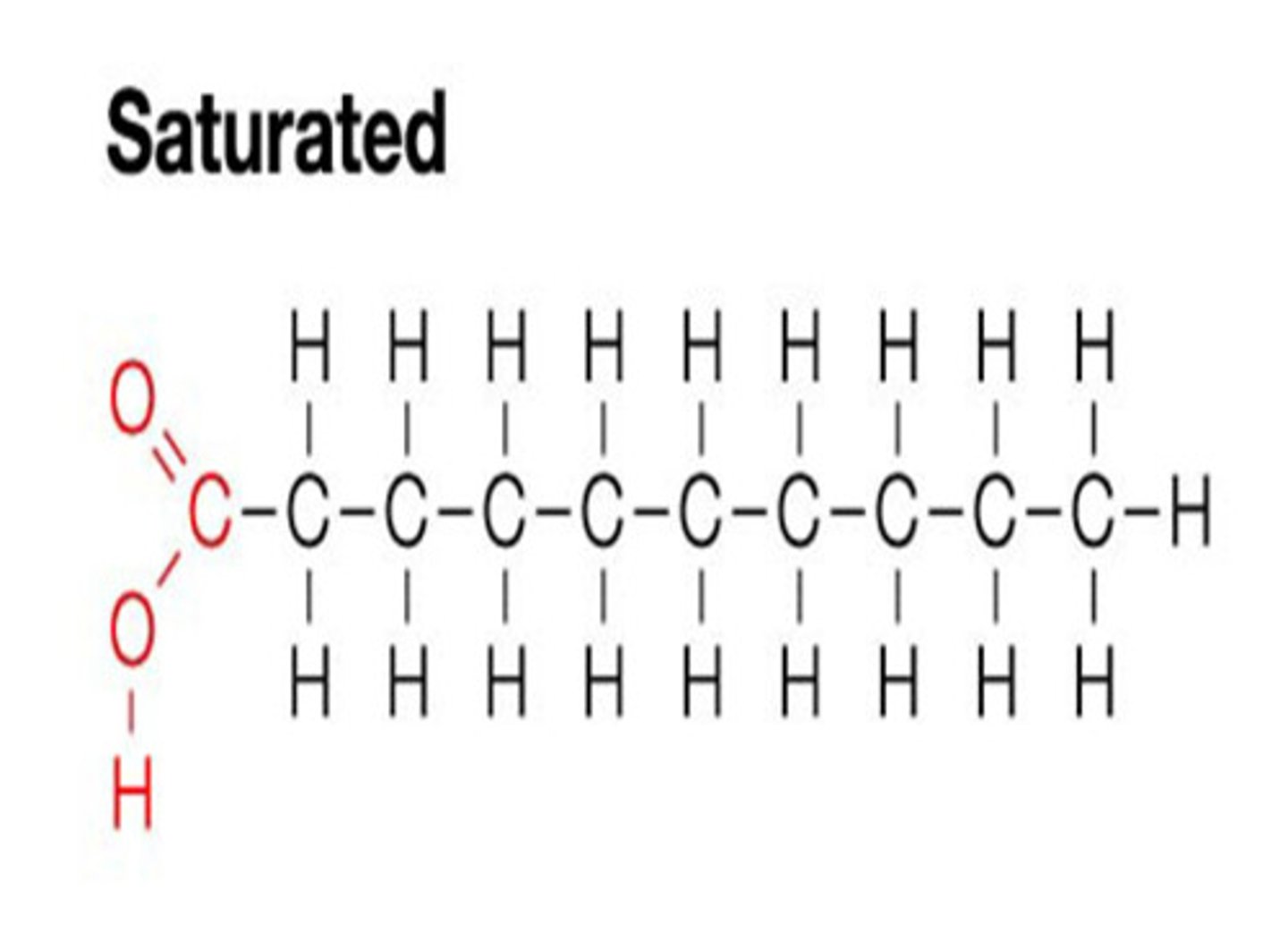
Type of fat with no double bonds between carbons, tends to be solids at room temp. and is produced by animals
Saturated fat
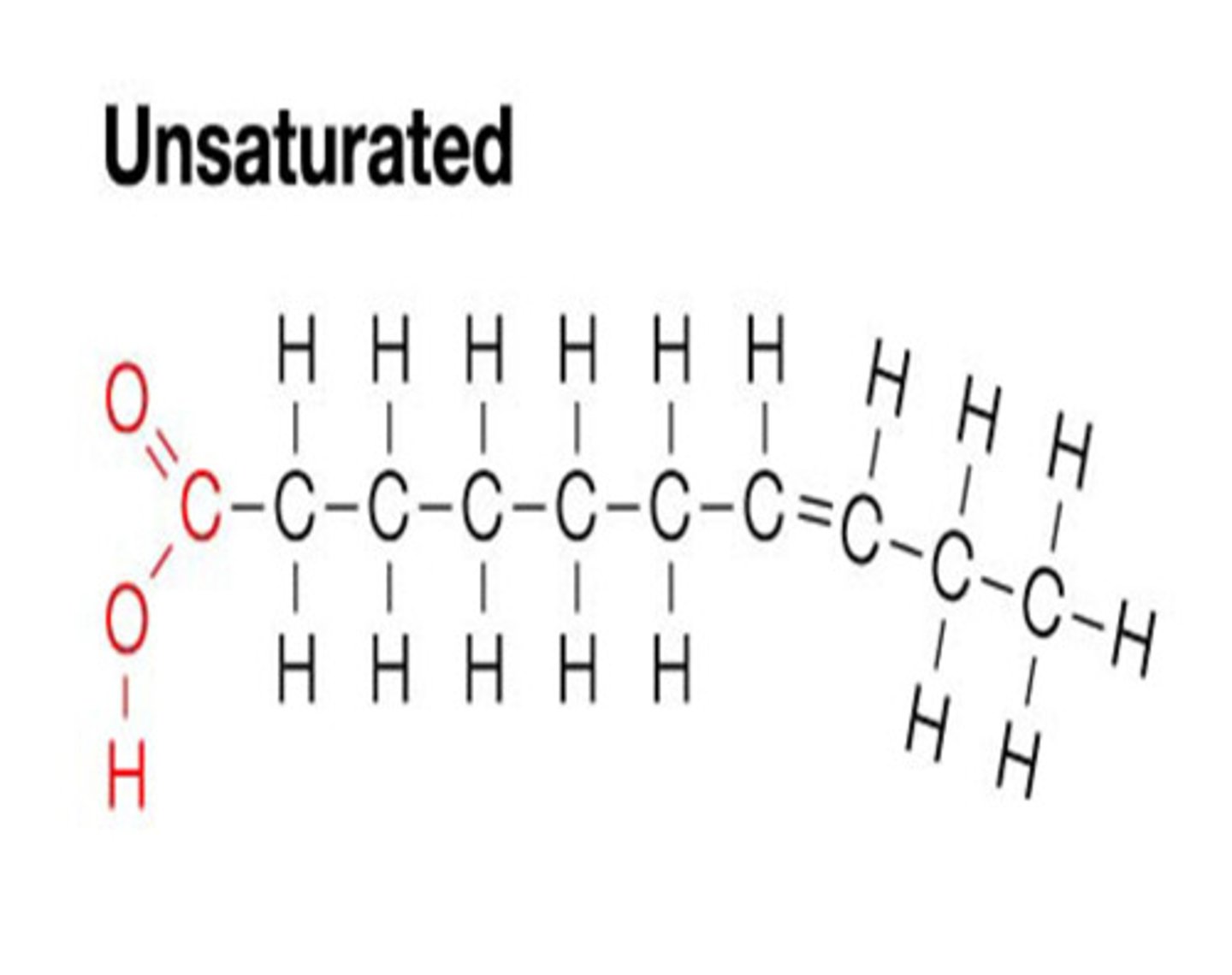
Type of fat with some double bonds between carbon. Creates a kink in the fatty acid chain. Tends to be liquid at room temp. and is produced by plants
Unsaturated Fat
What atoms are found in lipids?
C, H, O

Is there a monomer for Lipids?
technically no
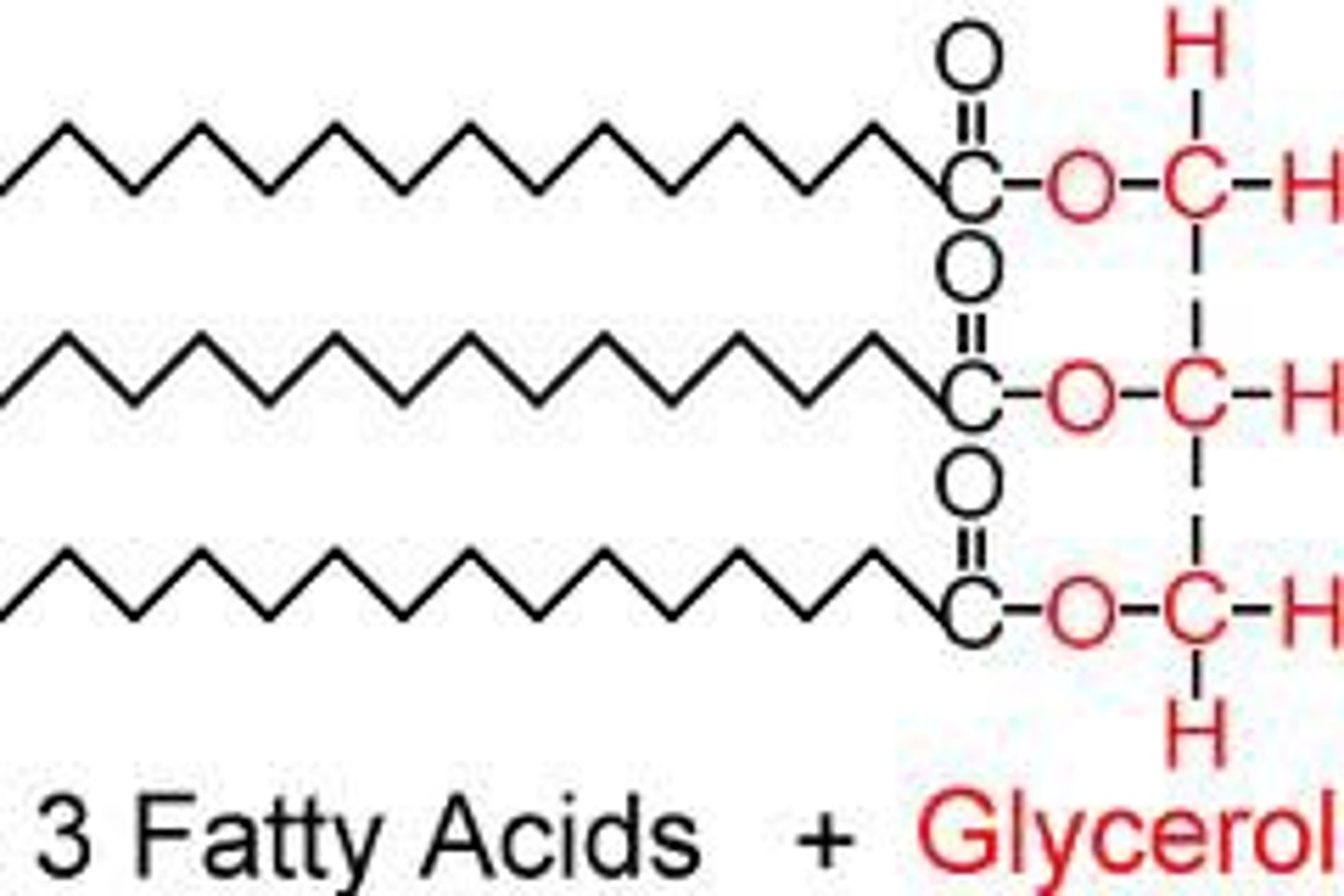
If there was a monomer for lipids what we it be considered as?
Fatty acid chains and glycerol are considered to be the building blocks for lipids
What are the functions of lipids?
1. Long-term Energy Storage
Stores twice as many calories per gram as carbohydrates
2. Protection and Insulation
Protects vital organs
Keeps animals warm
3. Chemical Messengers
Many hormones are lipids
Steroids are made of 4 fused carbon rings
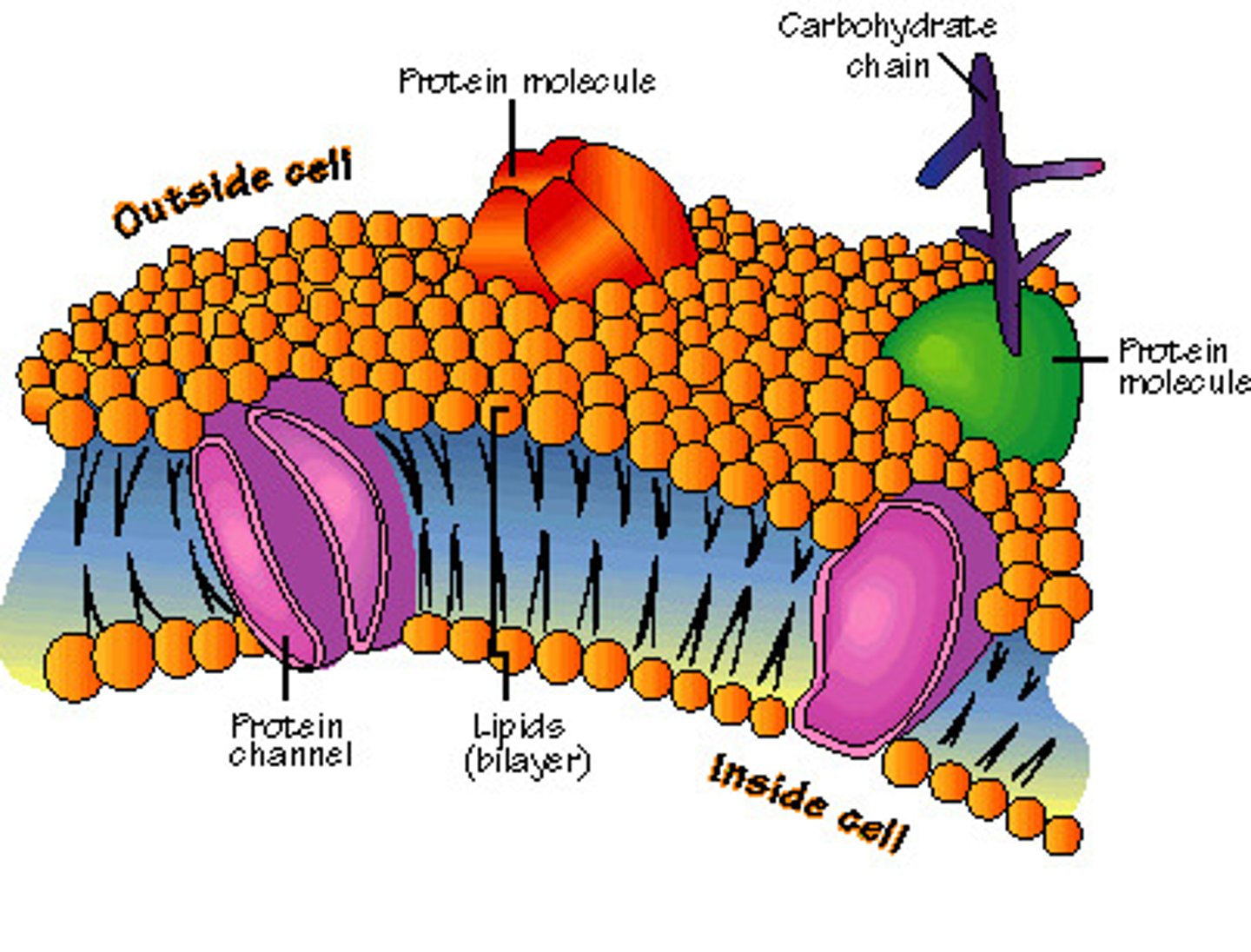
4. Cell Membrane Structure
Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes.
What is the monomer of Proteins
Amino acids
The primary structure of a protein
Unique sequence in which amino acids are joined together through peptide bonds (chain of amino acids)
The secondary structure of a protein
Due to TWO different 3-dimensional shapes that result from hydrogen bonding
α-helix - coiled shape
β-pleated sheet - accordion shape
The tertiary structure of a protein
Results in a globular structure due to interactions between R-groups
hydrophobic interactions
hydrogen bonds
van der Waals forces
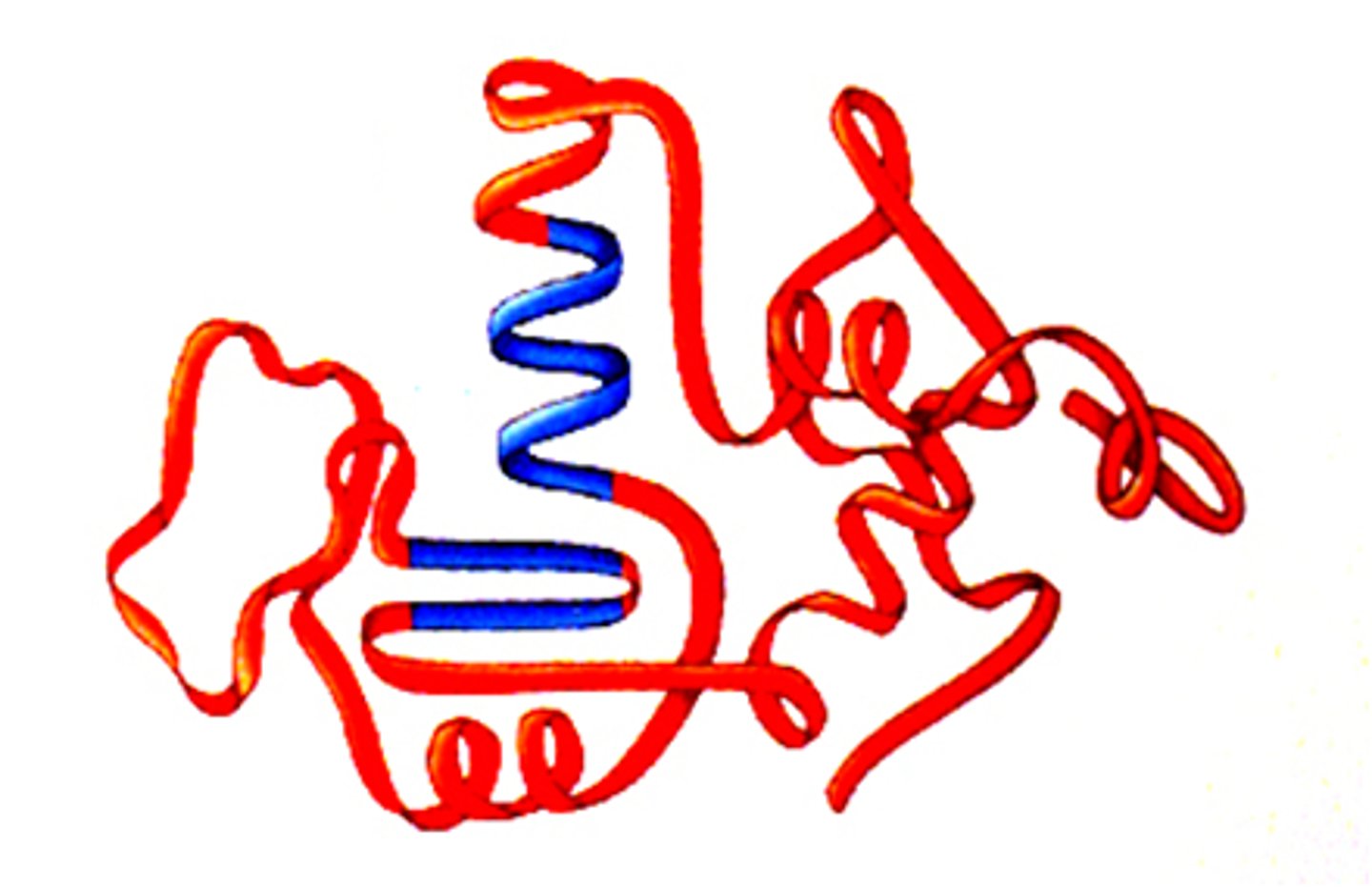
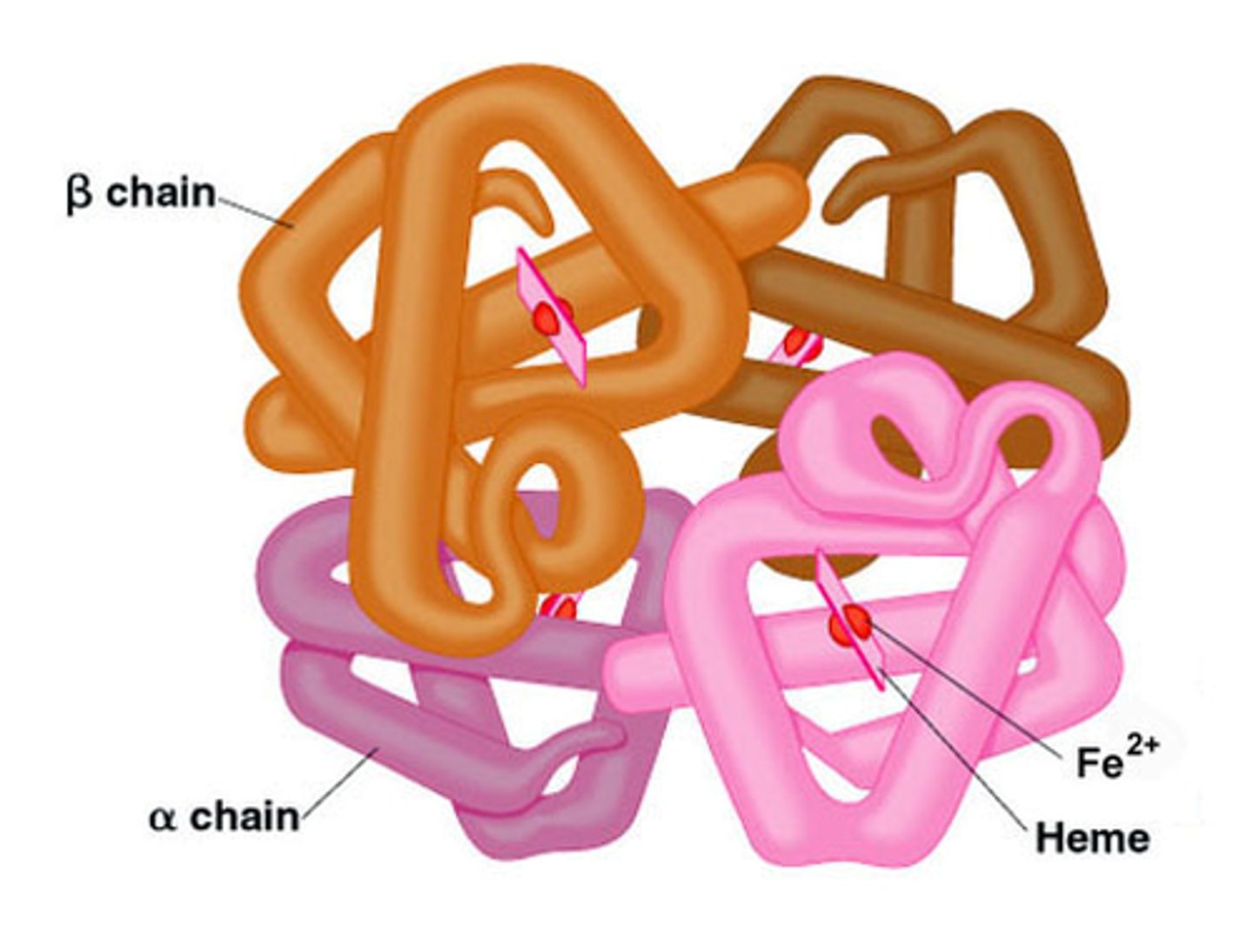
The Quaternary structure of a protein
Not all proteins have this structure!
The association of 2 or more polypeptide chains into one large protein.
Each chain has it's own primary, secondary, and tertiary structure
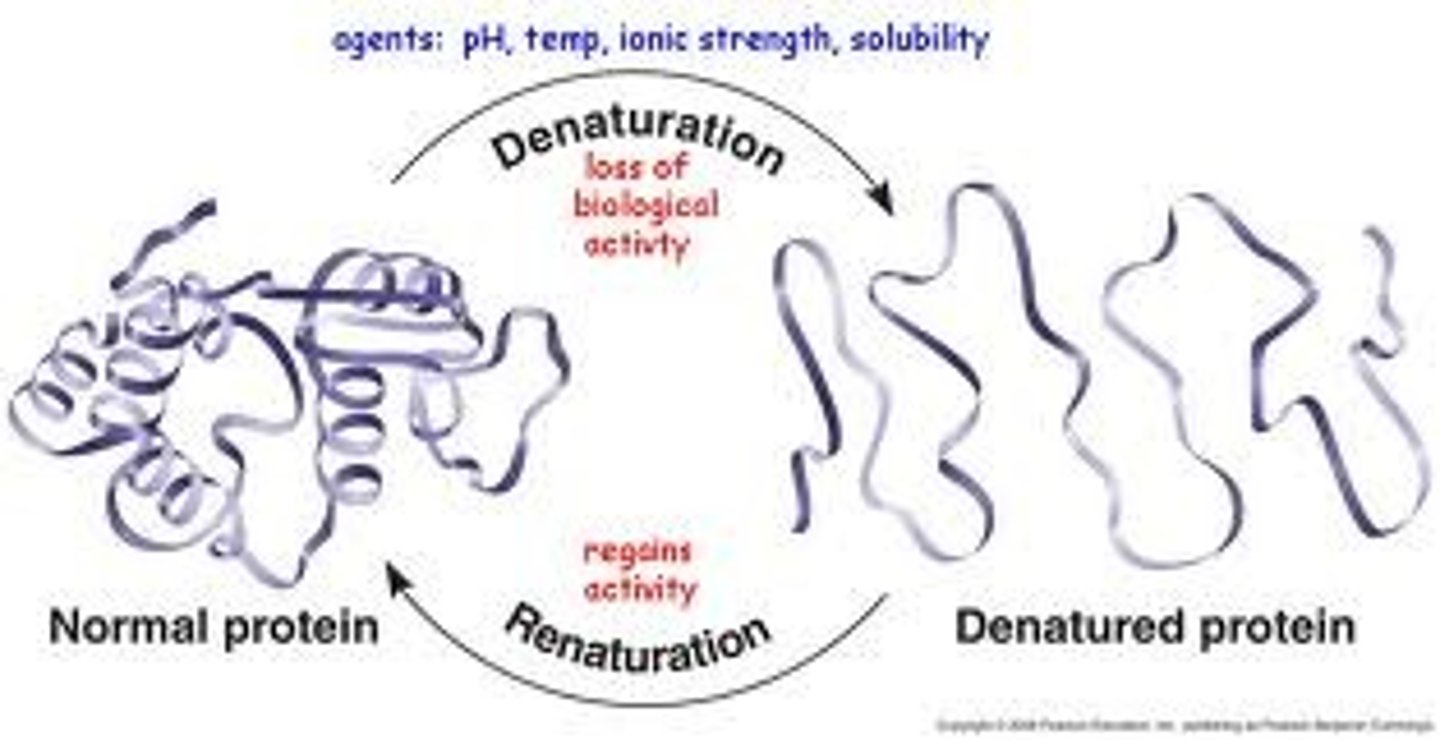
How can a protein be denatured?
Proteins can be denatured (loss of shape) due to changes in pH, temperature, or extreme salt concentration (salinity).
Causes protein to lose its ability to function!
Carries genetic information that codes for the sequence of amino acids in proteins.
Two major types include DNA and RNA.
ATP is also a nucleic acid used for energy transfer in cells.
Nucleic acids
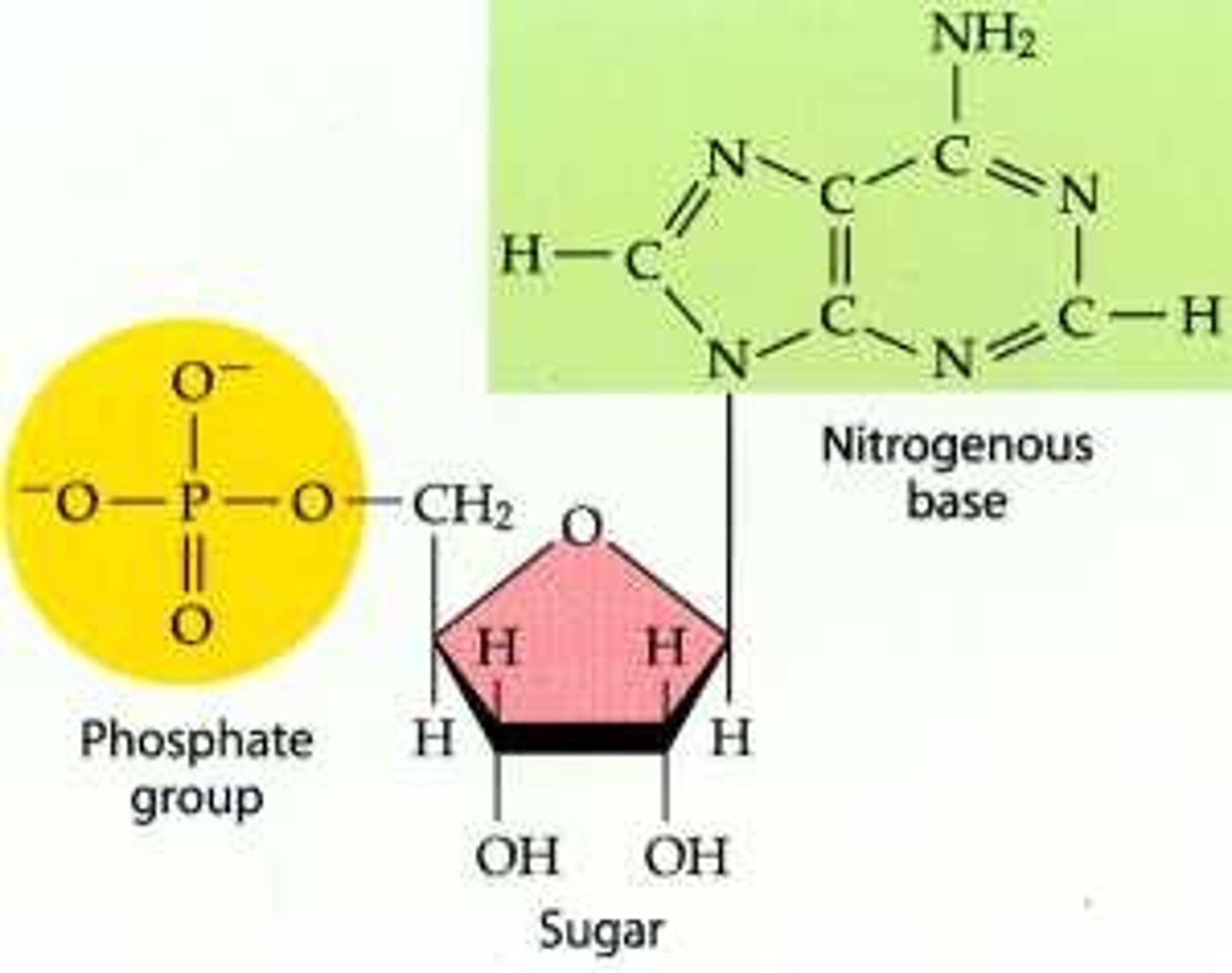
Contains CHONP and it's monomer is a nucleotide which contains three parts
Nucleic acids
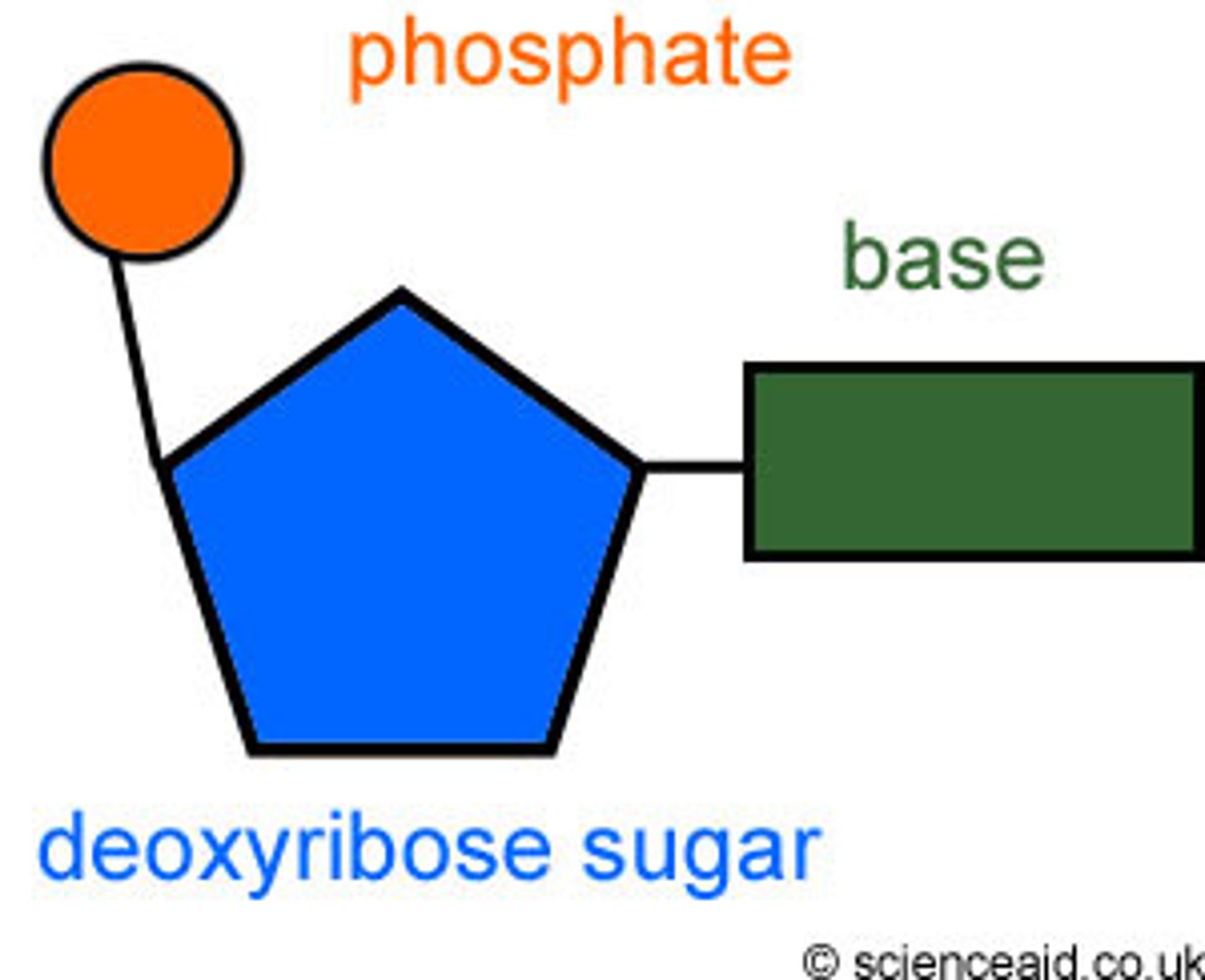
The three parts of a nucleotide include
Three phosphate groups, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base
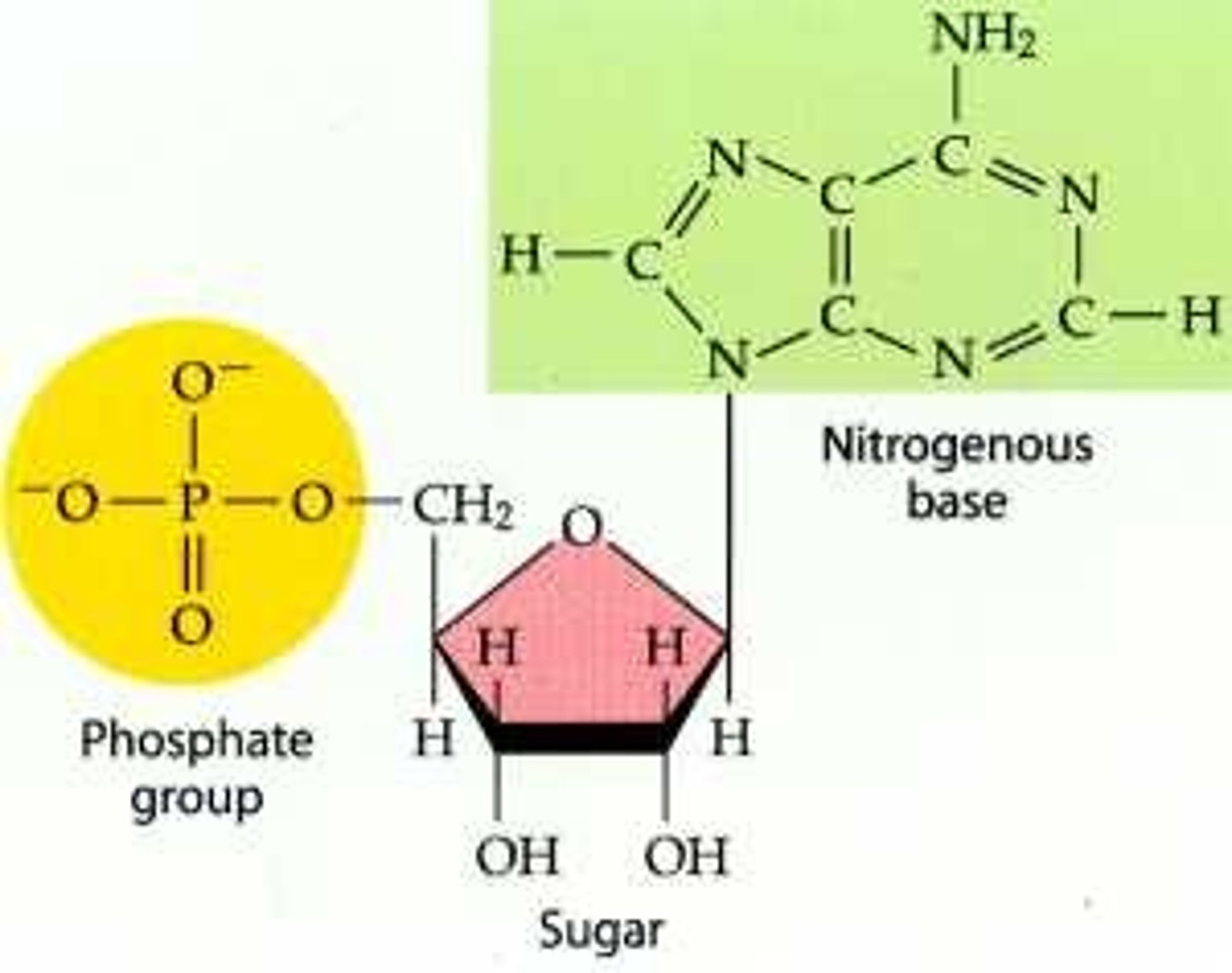
The function of a nucleic acid is to
Function
Store and transmit genetic information!
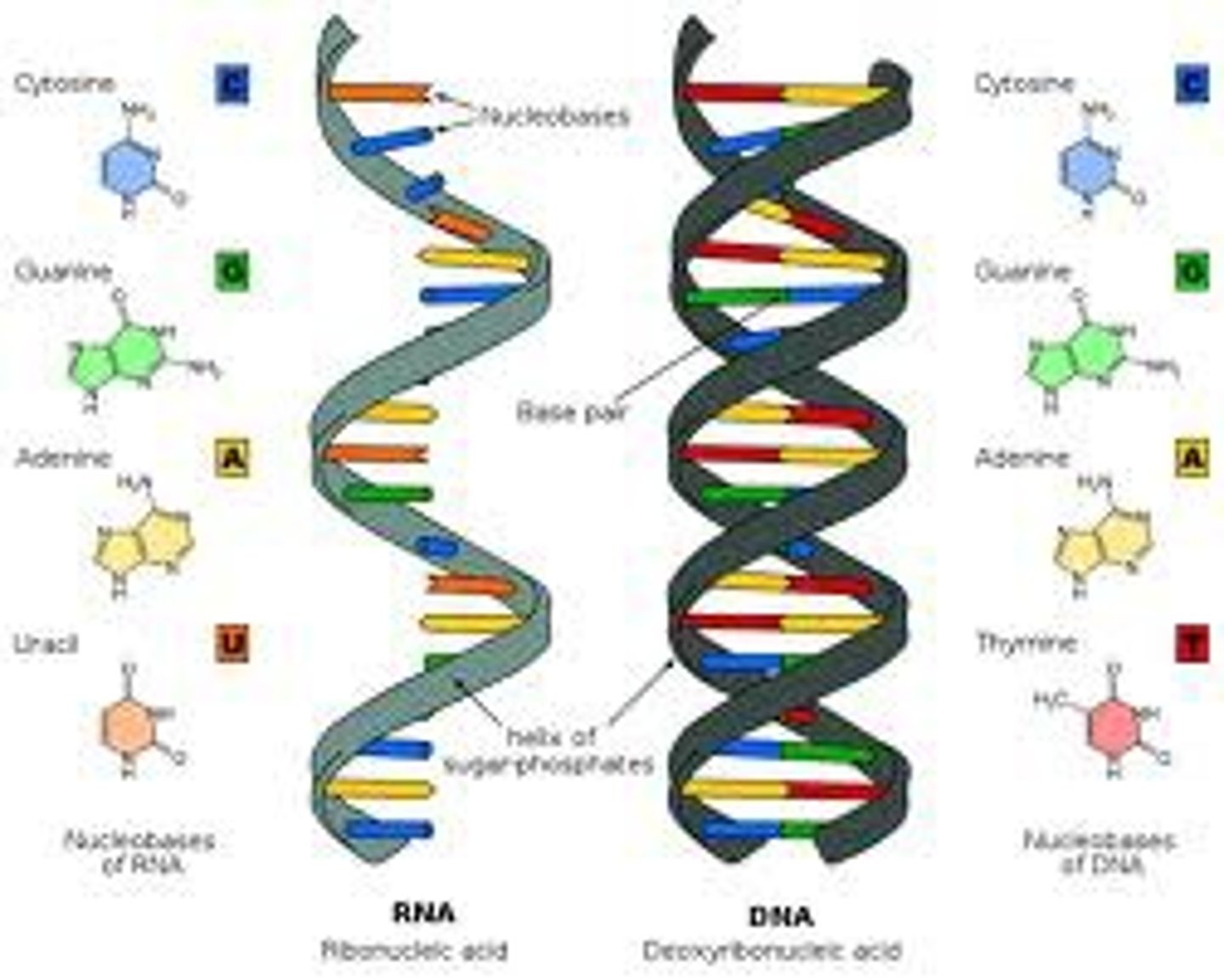
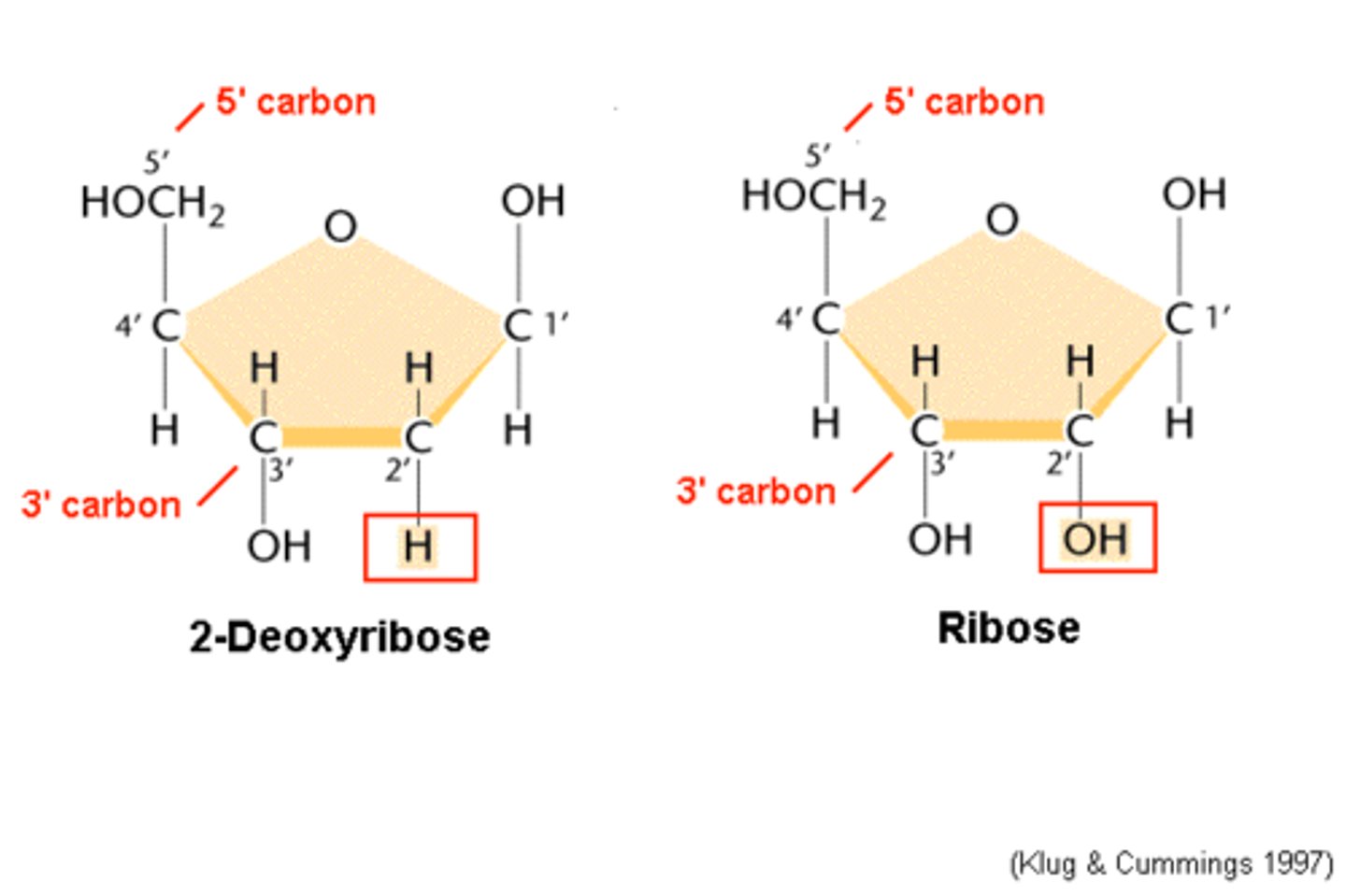
The difference between DNA and RNA is
The sugar; DNA is a deoxyribose sugar, RNA is a Ribose sugar
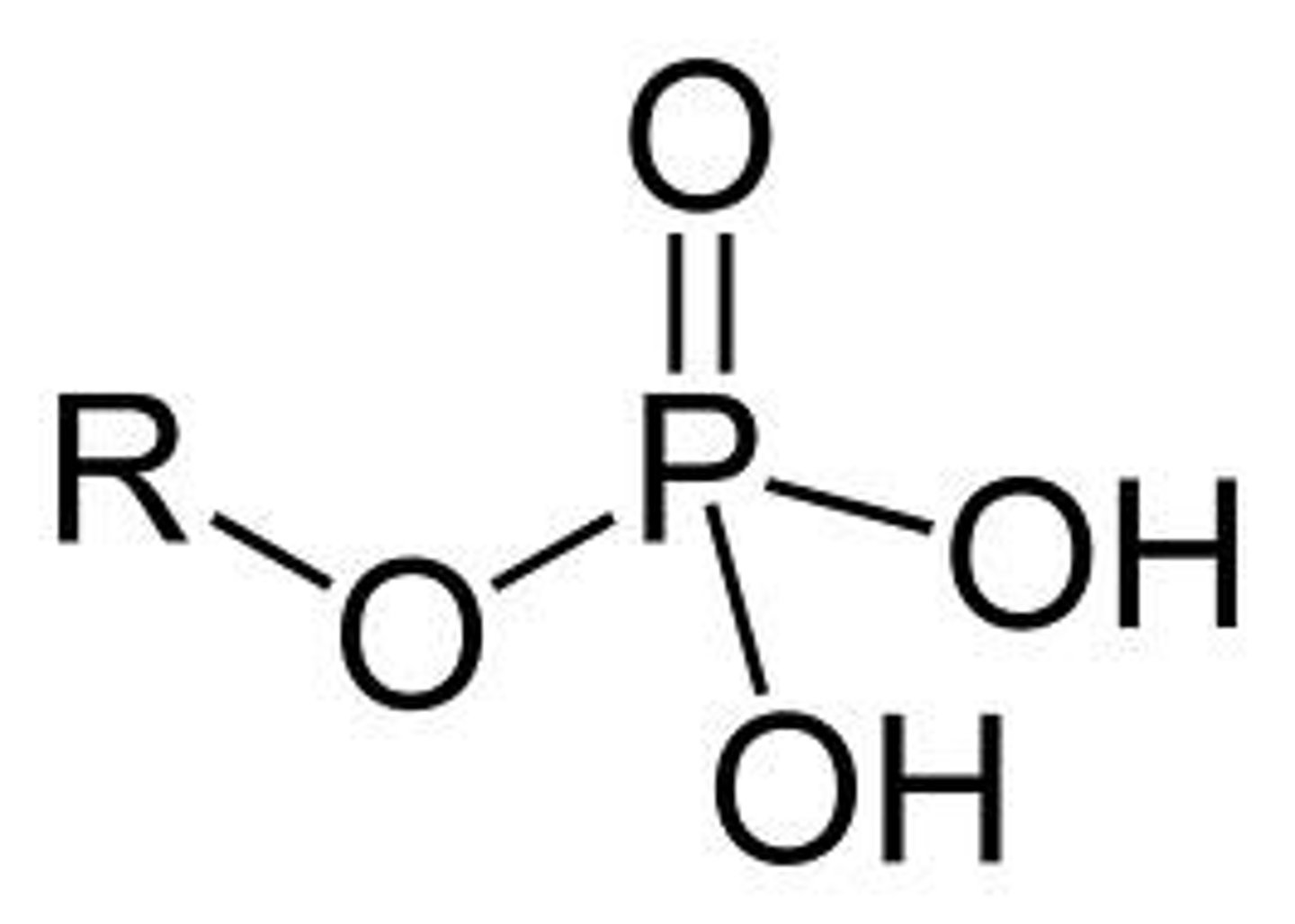
Phosphate group
R-PO4
double helix
The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent polynucleotide strands wound into a spiral shape
RNA
A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses
DNA
A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule capable of replicating and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins
starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose
glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch
nucleotide
The building block of a nucleic acid, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous bas and a phosphate group
monosaccharide
The simplest carbohydrate, active alone or serving as a monomer for disaccharides and polysaccharides. Also known as simple sugars, the molecular formulas of monosaccharides are generally some multiple of CH20