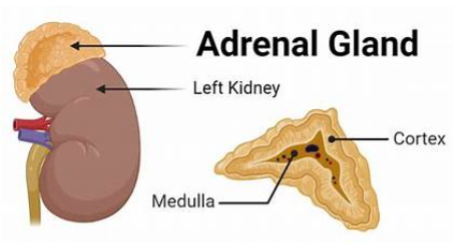
The Adrenal Glands
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 312
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
location of adrenal glands
two bilaterally symmetrical endocrine organs located just anterior to the kidneys
what are the two sections of the adrenal gland?
cortex and medulla
what are adrenal hormones important for?
for adaptation to adverse environmental conditions
stress
extreme temperatures
anxiety, fear, excitement
injury/illness
adrenal gland depicted in textbook
adrenal gland depicted on radiograph
adrenal gland depicted on abdominal ultrasound
function of cortex zone of adrenal gland
produces steroid hormones
corticosteroid hormones
cortisol
aldosterone
function of medulla zone of adrenal gland
produces amine hormones
norepinephrine
epinephrine
what are the 3 adrenal cortex layers?
zona glomerulosa (outermost)
zona fasciculata (middle)
zona reticularis (innermost)
adrenocortical cells have intracellular features characteristic of steroid hormone synthesis. what are these features?
abundance of lipid droplets (containing cholesterol)
mitochondria
smooth ER
the adrenal cortex produces 2 major types of corticosteroid hormones. what are they?
glucocorticoids
mineralocorticoids
glucocorticoids are produced by…
Zona Fasciculata (MOST PRODUCTION)
Zona Reticularis
function of glucocorticoids
regulation of all aspects of metabolism
major hormone produced by glucocorticoids
cortisol
mineralocorticoids are produced by…
Zona Glomerulosa
function of mineralocorticoids
important role in electrolyte balance and blood pressure
major hormone produced by mineralocorticoids
aldosterone
how are corticosteroid hormones transported in the blood
remember they’re steroid hormones
carried in blood through specific binding globulins called Corticosteroid-Binding Globulins (CBG)
List the ways that the Glucocorticoid hormone, cortisol, is transported in the blood
Transcortin (75%)
albumin (15%)
unbound cortisol (10%)
list the ways that the mineralocorticoid hormone, aldosterone, is transported in the blood
transcortin (10%)
albumin (50%)
unbound aldosterone (40%)
while there are distinct differences between corticosteroids and the effects they have on the body, it’s important to realize that there is some overlap in _________ _______
biological activity
glucocorticoids are important mediators of ___________
metabolism
function of glucocorticoids in relation to metabolism
stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis → increases blood glucose
inhibits glucose uptake and metabolism → increases blood glucose
the ability to store excess blood glucose in tissues is inhibited
effect is referred to as Anti-Insulin Effect
clinical significance = iatrogenic diabetes mellitus
stimulates lipolysis/fat redistribution to liver and abdomen
inhibits protein synthesis and stimulates protein catabolism
stimulates water excretion (diuresis)
regulation of glucocorticoid synthesis follows a negative-feedback system. Thus, glucocorticoids will inhibit the release of hormones. What hormones does it inhibit the release of?
hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
results in decreased ACTH secretion by the pituitary gland
anterior pituitary ACTH
results in decreased cortisol release from adrenal gland
the glucocorticoid response to stress is __________
immediate
(the glucocorticoid response is proportional to the severity of the stress)
clinical symptoms of chronic excess glucocorticoids includes…
tendency for high blood glucose
due to gluconeogenesis and anti-insulin effect
larger liver and abdomen
due to increased fat storage in liver and abdomen
muscle wasting
due to muscle break down and hindered repair
excessive drinking and urinating
due to hindered water retention by kidneys
clinical significance of Glucocorticoids
suppresses inflammation
injuries
allergic reactions
arthritis
itching
pain
what are the primary physiologic effects of mineralocorticoids
electrolyte balance
blood pressure homeostasis
mineralocorticoids promote electrolyte balance by acting on kidneys and promoting…
retention of
sodium (Na+)
excretion of
potassium (K+)
hydrogen (H+)
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) corticotropin stimulates secretion of glucocorticoids by the _______ __________ and Zona Reticularis is by the tropic hormone
Zona Fasciculata
the regulation of mineralocorticoid secretion is controlled by factors produced in the ______
kidney
(regulation of mineralocorticoids) in response to decreases in blood pressure, cells in the kidney produce and enzyme called ____________
renin
renin acts on _____________, an alpha2 globulin produced by the liver and is already present in the circulation
Angiotensinogen
the combination of renin with angiotensinogen results in…
a substance called Angiotensin I.
Angiotensin I is further hydrolyzed by an enzyme resulting in a substance called _____________
Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II stimulates the ________ _________ to produce mineralocorticoids (such as Aldosterone)
Zona Glomerulosa
Aldosterone acts on Kidneys to stimulate ____________ of Na+ and H2O, and ___________ of K+ and H+
retention; excretion
this results in electrolyte balance and blood pressure regulation
what is the central portion of the adrenal gland?
medulla
what does the adrenal medulla produce?
amine hormones called Catecholamines
what are the 2 types of catecholamines produced by the adrenal medulla?
norepinephrine
epinephrine
when are both norepinephrine and epinephrine released?
when nerve fibers to the adrenal medulla are stimulated during times of stress
what is epinephrine commonly referred to as?
adrenaline or “epi”
what is the major catecholamine secreted by the adrenal medulla of most mammals?
epinephrine
(synthesis of catecholamines within chromaffin cells) the synthesis of the catecholamines begins with either one of these amino acids…
Phenylalanine or Tyrosine
most catecholamines are derived from __________
tyrosine
chromaffin cells
the cells of the adrenal medulla which synthesize catecholamines
what is contained within chromaffin cells?
granules which contain the synthesized catecholamines (norepinephrine and epinephrine)
acetylcholine
release from the nerve fibers initiates the synthesis and release of the catecholamines by the medullary cells
the stimulation of release of catecholamines from chromaffin granules, a phenomenon called…
stimulus-secretion coupling
catecholamines are important mediators of
metabolism
acute stress response
a major metabolic change from catecholamine release is…
increased blood glucose
what is the primary catecholamine responsible for increased blood glucose?
epinephrine — inhibition of insulin secretion from pancreas
what happens during acute stress response?
stimulate cardiac function (fast HR)
relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle
relaxation of smooth muscle of GI tract
urine retention
excitation of the CNS
awake and aware
sweating
piloerection
the main factors that stimulate catecholamine secretion are…
acute stress response
hypoglycemia