Anatomy Lab Quiz #3 Terms and Stuff (2)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Auscultation
the method of listening to and studying heart sounds during heart activity
Stethoscope
a medical instrument with ear pieces connected to tubes attached to a small, disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the chest
Heart Murmurs
one of the heart valves does not function correctly
1st Heart Sound (S1)
the “lub” sound of the heart, heard during systole, and caused by the closing of the atrioventricular (AV) valves, the mitral (bicuspid) valve, and the tricuspid valve; longer and louder than S2
2nd Heart Sound (S2)
the “dub” sound of the heart, heard during systole, and caused by the closure of the semilunar (SL) valves, the aortic semilunar valve, and the pulmonary semilunar valve; higher-pitched sound than S1
3rd Heart Sound (S3)
occurs during diastole, and is a lower-pitched sound produced by vibrations of the ventricle walls as the ventricles rapidly fill with blood
4th Heart Sound (S4)
occurs during diastole, and is a low-intensity sound heart as the atria contract to push blood down into the ventricles
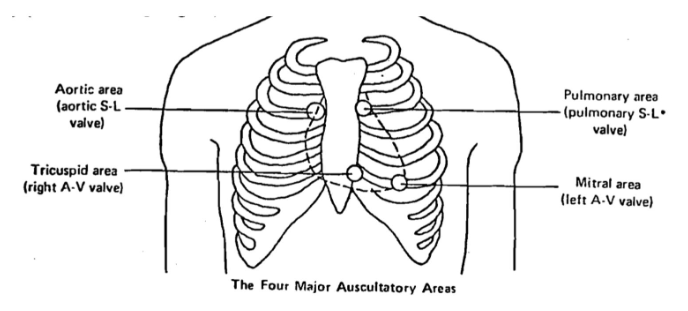
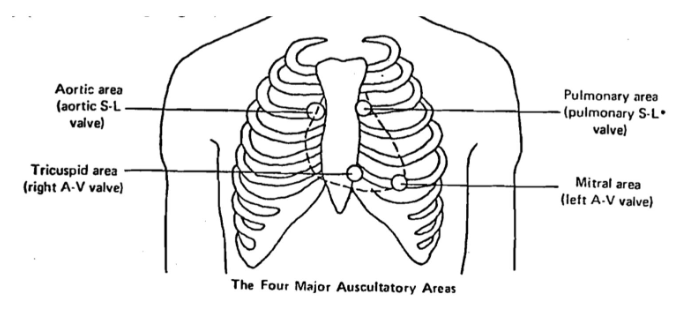
Auscultatory Areas
represent where sounds from each valve can be heart most clearly
Blood Pressure
pressure created by the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as your heart pumps blood into the blood vessels (mm Hg)
Systolic Pressure
pressure in the arteries when the ventricles are contracting (i.e., ventricular systole); important indicator of the force of contraction of the heart; highest pressure
90-120 mm Hg
Diastolic Pressure
pressure in the arteries when the ventricles are relaxed (i.e., ventricular diastole); an important indicator of systemic blood vessels; lower pressure
60-80 mm Hg
Pulse Pressure
the difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure indicating the force of blood pushing through the vessels
average = ~40 mm Hg
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
average blood pressure during a cardiac cycle; a normal MAP is 70-100 mm Hg
combination of cardiac output (CO) and total peripheral resistance (TPR)
Perfusion
blood flow
MAP equations
MAP = diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure
OR
MAP = cardiac output (ml blood/min) * total peripheral resistance (TPR units)
Cardiac Output (CO) Equation
Cardiac Output = stroke volume (ml blood/beat) * heart rate (beats/min)
What happens to peripheral resistance as vessel diameter decreases?
peripheral resistance increases
What happens to peripheral resistance as blood viscosity increases?
peripheral resistance increases
What happens to blood pressure as either cardiac output or resistance increase?
blood pressure increases
Sphygmomanometer (pressure cuff)
indirect measurement of blood pressure; determined by listening to sounds of the artery by use of a stethoscope
Palpatory Method
indirect measurement of blood pressure; involves palpating the pulse as pressure is applied to an artery with a sphygmomanometer
What artery is most typically used for application of pressure in for the sphygmomanometer and palpatory method?
brachial artery
What artery is most typically used to determine systolic pressure for the palpatory method?
radial artery → diastolic pressure cannot be measured
What is the time limit for leaving the cuff on a person's arm for?
no more than 1 minute and don’t overtighten the valve
What is the stethoscope used for during the auscultatory method?
used to hear changes in sounds in the brachial artery
What happens to the artery as pressure is released during the auscultatory method?
as pressure is released, the artery collapses and reopens with each heartbeat and blood flow through the artery returns
this pattern or collapsing and reopening results in turbulence through the vessel
Korotkoff Sounds
5 phases of these sounds with 1, 4, and 5 being easier to ausculate
Phase 1 Korotkoff Sounds
a sharp tapping or thudding sound which may increase in intensity over the next 10 mm Hg drop in pressure; this phase indicates the systolic pressure
Phase 4 Korotkoff Sounds
the distinct abrupt muffling of the sounds; they will become soft and reduced in intensity → usually called the “first diastolic reading”
Phase 5 Korotkoff Sounds
all sounds disappear → absence of sound is considered the “second diastolic reading.”
doctor’s usually use this pressure as the recorded diastolic pressure
Where should the pulse rate be taken if the blood pressure is being taken on one arm?
should be taken on the OPPOSITE arm
Total Peripheral Resistance (TPR)
the amount of force affecting resistance to blood flow through the circulatory system
What does vasoconstriction of blood vessels do to TPR? Vasodilation?
vasoconstriction causes an increase in TPR and vasodilation causes a decrease in TPR
TPR Equation
Mean Arterial Pressure / Cardiac Output (CO)
TPRest Equation
\frac{\frac{\left\lbrack systolicpressure+\left(2\cdot diastolicpressure\right)\right\rbrack}{3}}{pulsepressure\cdot heartrate}
The Auscultatory Method
this method utilizes the sphygmomanometer, but also requires the use of a stethoscope to hear changes in sounds in the brachial artery
The Cold Pressor Test
a normal reflex response to a decrease in temperature is an increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure
Hypertension
a chronic condition where blood force against artery walls is consistently high
pressure will rise as high as 40 mm Hg during cold pressor test
Venous Insufficiency
a problem where blood is not effectively returned to the heart at a desireable rate
The Diving Reflex
most marine mammals experience a decrease in metabolic rate while underwater such that cells require less oxygen with time
Diving Bradycardia & Peripheral Vasoconstriction (diving reflex)
a noticeable slowing of the heart rate while submerged underwater and a decrease in blood vessel diameter to non-vital parts of the body
results in an overall reduction of circulation to all parts of body except vital organs/tissues
Where is the receptor responsible for the response for diving bradycardia found? What nerve do these receptors trigger?
in the nose; trigger the trigeminal nerve
The Harvard Step Test
a measure of cardiovascular health and endurance, testing the general capacity of the body to cope with increased physical work, and the ability to recover from it
Index of Physical Fitness (Index) Equation
Index=\frac{duractionexercise\left(s\right)\cdot100}{2\cdot\left(\sum^{}3pulsecountsinrecovery\right)}
duration of exercise (seconds)
3 pulse counts in recover
YMCA 3 Minute Step Test
popular test that estimates the subject’s cardiovascular fitness based on how the body responds to physical work
accounts for heart rate immediately after exercise; a measure of submaximal cardiovascular fitness