Immunology Antibodies, T cells, & Interactions
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:33 AM on 4/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
1
New cards
Extra CH domain
What part of IgE do mast cells bind to?
2
New cards
3
Papain can split the Ig molecule into ___ different fragments of about equal size.
3
New cards
1. Shingrex
2. Zostavax
What are 2 vaccination options for Herpes Zoster infections?
4
New cards
Zostavax
What herpes zoster vaccine contains a live, weakened form of the chickenpox (varicella) virus?
5
New cards
Shingrix
What herpes zoster vaccine is NOT a whole weakened form of the virus but instead, contains a surface-sitting protein and 2 adjuvants?
6
New cards
Shingrix
Which herpes zoster vaccine has a higher protective effect after 4 years?
7
New cards
72
Shingles symptoms can be eradicated if treated within _____ hours.
8
New cards
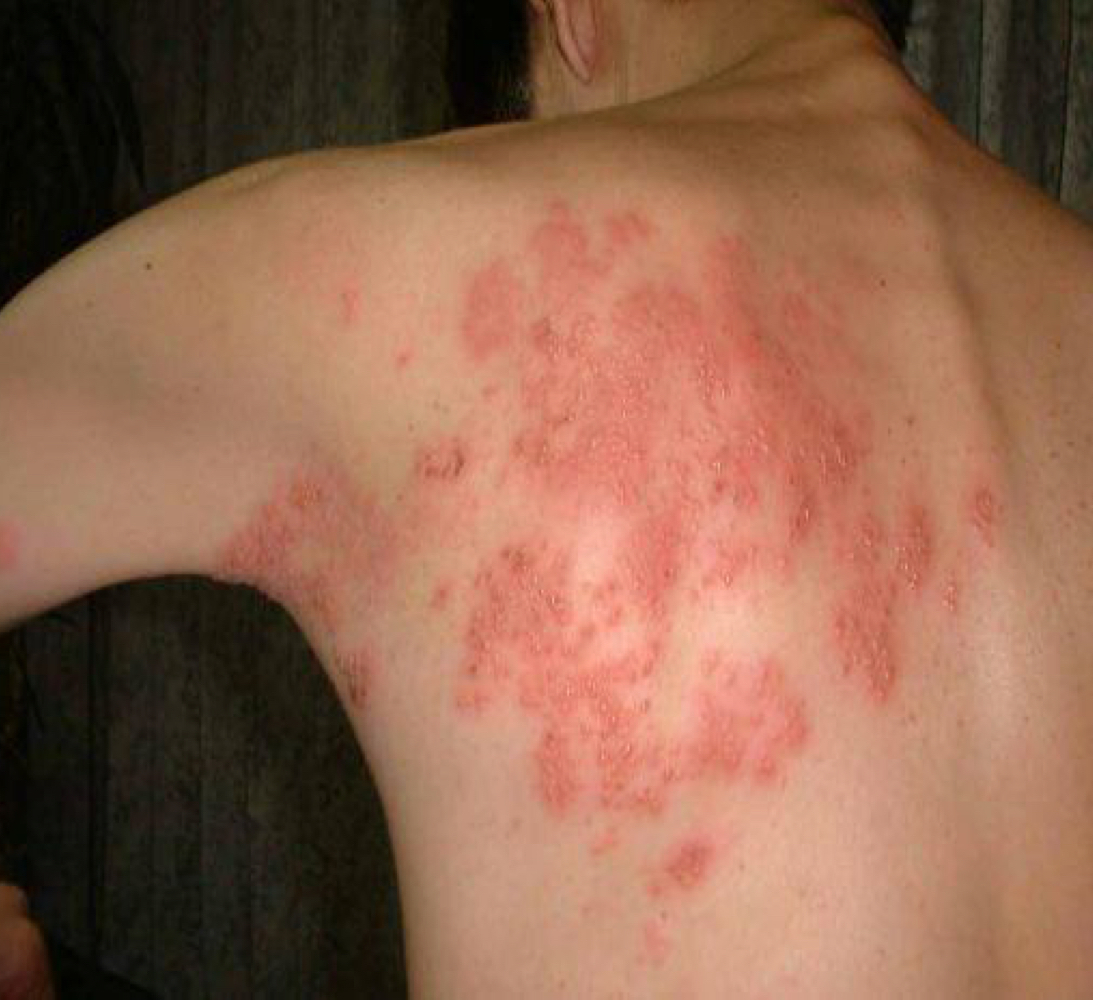
shingles
What infection is shown in the image?
9
New cards
50 & older
At what age can the shingrix vaccine be given?
10
New cards
2 doses
How many doses make up the shingrix vaccine?
11
New cards
Shingrix
Which shingles vaccine is preferred by doctors--Shingrix or Zostavax?
12
New cards
2
If you have already had Zostavas, you should receive ____ doses of Shingrix.
13
New cards
True
True/False: You will not need Zostavax or Shingrix if you have had the chicken pox vaccine.
14
New cards
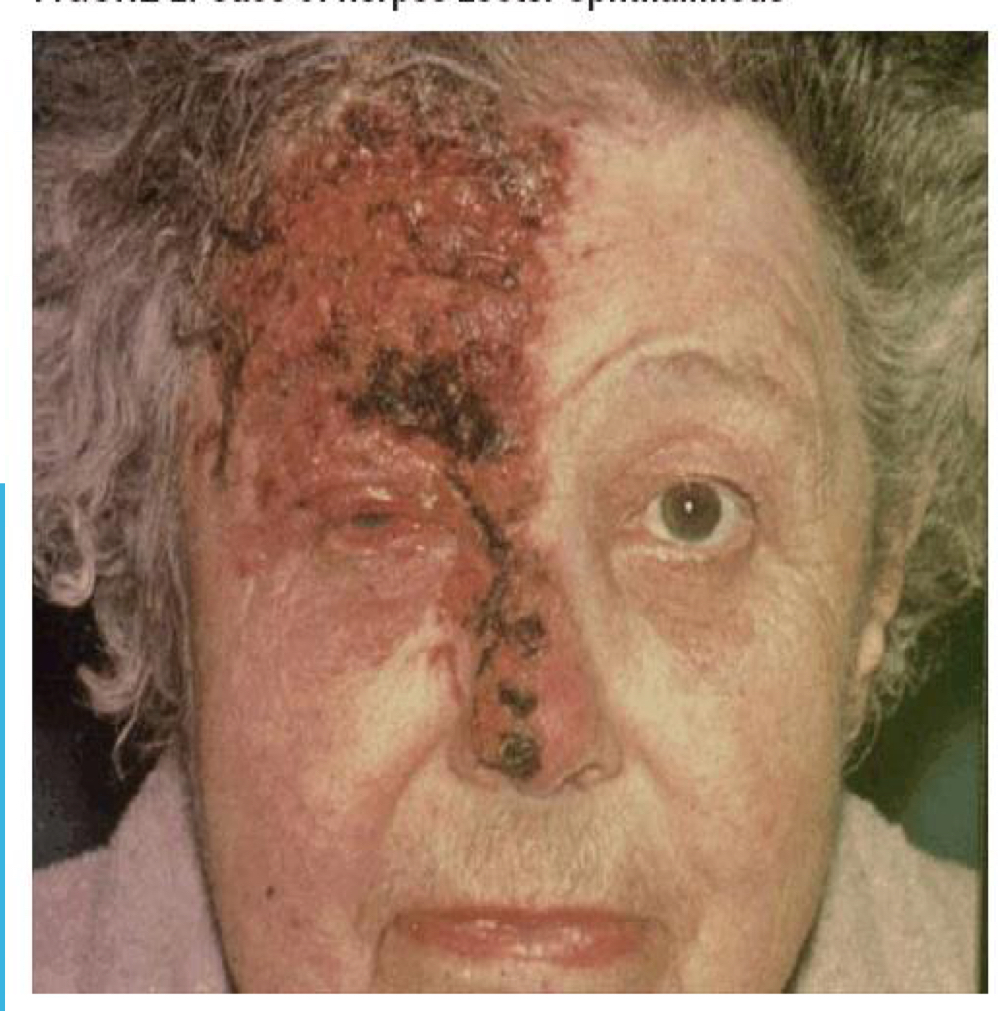
herpes zoster ophthalmicus
What condition is shown in the image?
15
New cards
1. Fever
2. Myalgia
3. Chills
Yes
What are the 3 main side effects of Shingrix? Is this worse than the Zostavax side effects?
16
New cards
NSAIDs
What medication can be taken to alleviate side effects associated with the Shingrix vaccine?
17
New cards
Fc portion
What portion of the antibody determines the biological activity of the antibody?
18
New cards
soluble; globulins; adaptive
Antibodies are (insoluble/soluble) proteins made of amino acids that circulate freely and contribute to immunity. They belong to a class of proteins called __________ and are important to the (innate/adaptive) immune response.
19
New cards
True
True/False: Antibodies can be either membrane bound or secreted.
20
New cards
plasma cells
What type of cells secrete antibodies?
21
New cards
Fragment Antigen Binding
What does the “Fab” portion of the antibody mean?
22
New cards
Fab portion
What portion of the antibody is specific to a particular antigen?
23
New cards
Fragment Crystallizable
What does “Fc” portion mean?
24
New cards
constant; hypervariable
The Fc portion of an antibody is also known as the _____ region. The Fab portion of an antibody is also known as the ___________ region.
25
New cards
1. Neutralization of toxins (i.e. animal bite)
2. Immobilization of microorganisms
3. Precipitation followed by phagocytosis
4. Activation of complement
5. Placental cross (i.e fetal protection)
What are the 5 main functions of the Fc portion of an antibody?
26
New cards
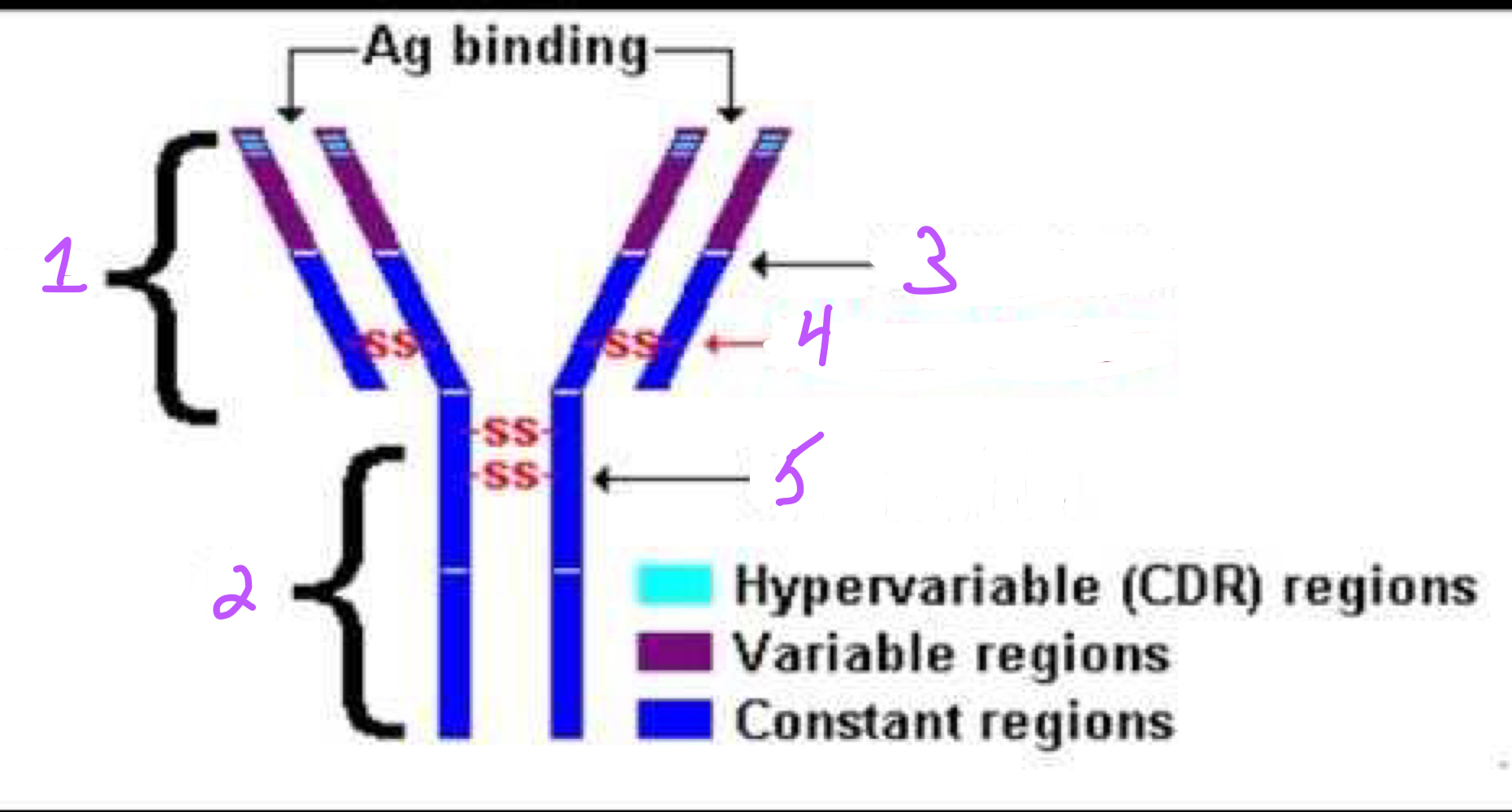
1. Fab portion
2. Fc portion
3. Light chain
4. Disulfide chain
5. Heavy chain
Identify regions 1-5 in the image of the antibody structure.
27
New cards
1. Serum electrophoresis
2. Bence Jones proteins
3. Papain
What are the 3 ways in which the structure of antibodies were figured out?
28
New cards
serum electrophoresis
What form of solving antibody structure used electric field to separate the different parts of the antibody?
29
New cards
urine
Homogenous proteins produced by patients with multiple myeloma during Bence Jones proteins testing
30
New cards
Bence Jones proteins
What test is useful for the determination of antibody light chain structures?
31
New cards
Papain
Proteolytic enzyme discovered to split Ig molecule at the hinge region
32
New cards
1. Fab portion
2. Fab portion
3. Fc portion
What are the 3 fragments produced from papain enzyme?
33
New cards
Fc
During the use of papain, the _____ portion cannot bind the antigen and is responsible for biological activity post-antigen binding.
34
New cards
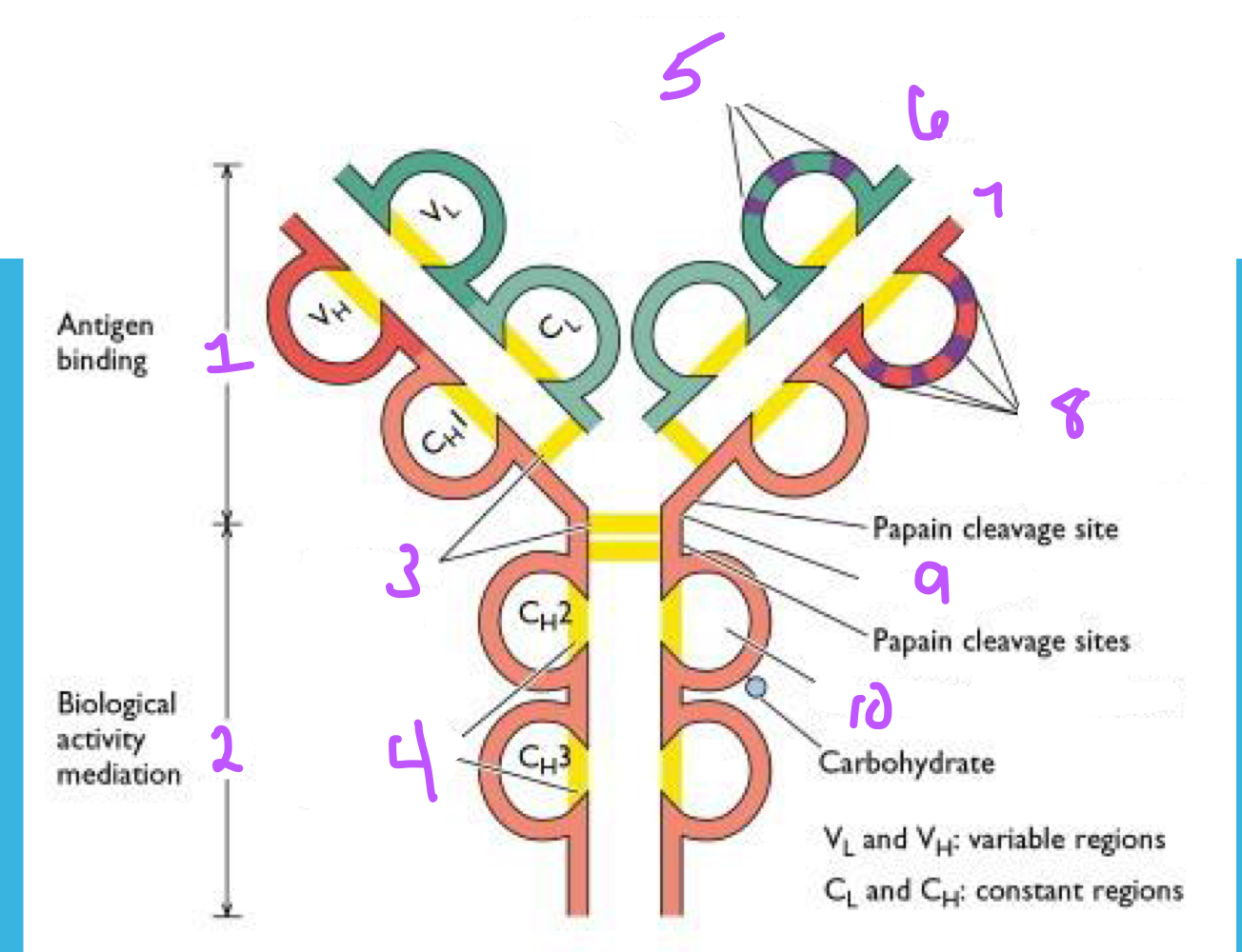
1. Fab portion
2. Fc portion
3. Interchain disulfide bonds
4. Intrachain disulfide bonds
5. Light chain hypervariable region
6. Light chain
7. Heavy chain
8. Heavy chain hypervariable region
9. hinge region
10. Complement binding region
Identify the following structures of the antibody.
35
New cards
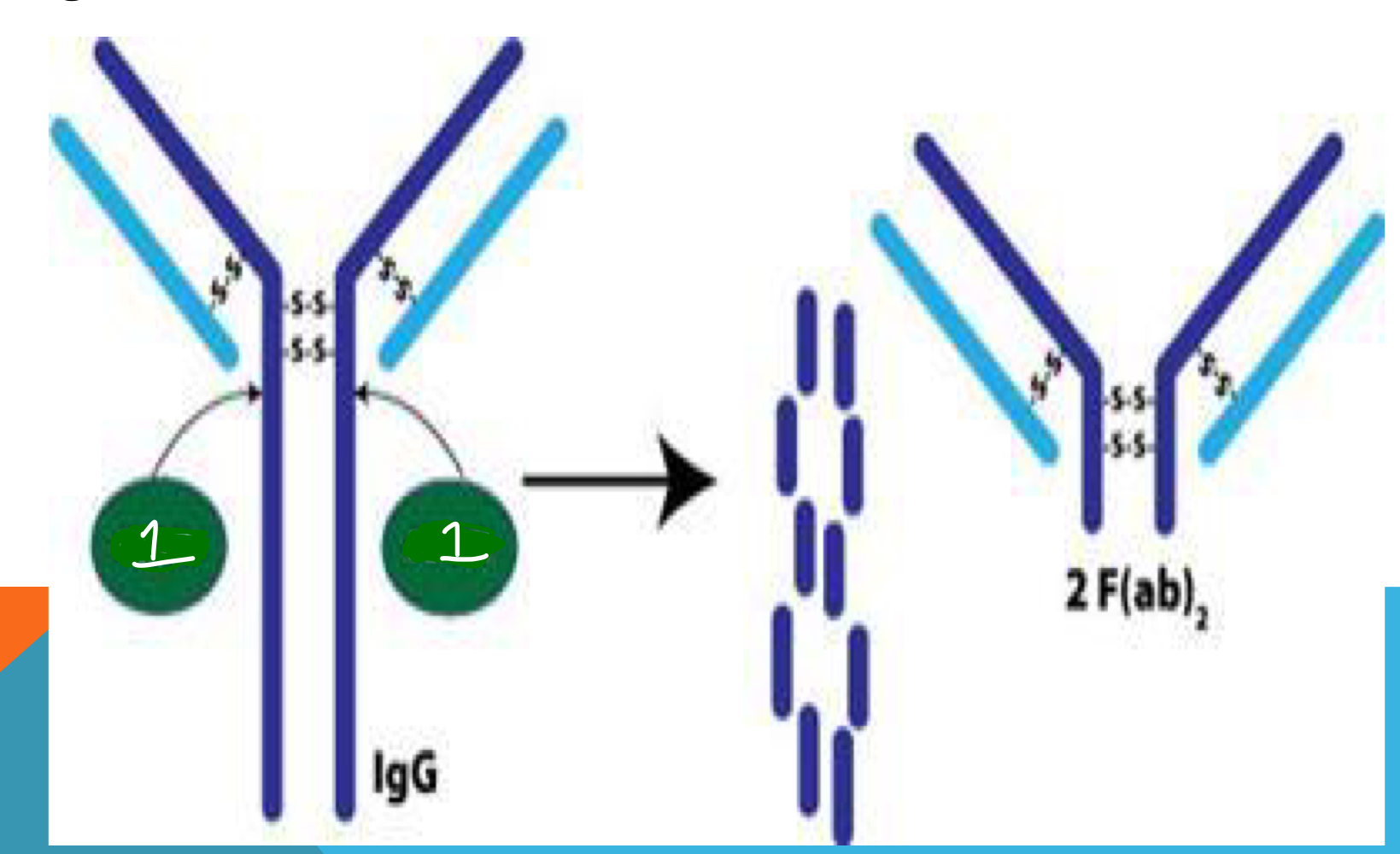
pepsin
The use of ____ enzyme resulted in 2 Fab connected structure and the dissolving of the Fc portion into smaller fragments.
36
New cards
pepsin
What enzyme is indicated by number 1 in the image and results in the fragments presented on the right side?
37
New cards
mercaptoethanol
In figuring out antibody structure, what was used as a disulfide bond breaker that splits Ig into 4 chains?
38
New cards
2 identical light chains & 2 identical heavy chains
What 4 chains does Ig split into when using mercaptoethanol?
39
New cards
disulfide bond
What type of bond holds together the light chains and heavy chains?
40
New cards
hinge region
At what part of the antibody does papain split the immunoglobulin?
41
New cards
1. Kappa
2. Gamma
What are the 2 classes of light chains that are present in antibodies of most species?
42
New cards
1. Protein sequence
2. Carbohydrate content
3. Size
4. Constant regions of heavy chains
What are the 4 distinguishing features of heavy chains?
43
New cards
1. IgG
2. IgA
3. IgM
4. IgE
5. IgD
What are the 5 different isotopes/classes of antibodies?
44
New cards
nature of the heavy chains
What determines the difference between the 4 different isotopes of antibodies?
45
New cards
1. IgA
2. IgG
Which 2 antibody types have subclasses?
46
New cards
Interchain disulfide bonds
What type of disulfide bonds occur between heavy and light chains?
47
New cards
Intrachain disulfide bonds
What type of disulfide chains occur within heavy and light chains, causing loops?
48
New cards
IgG
_____ field domains form interchain disulfide bonds.
49
New cards
Fab chain
What type of chain is considered to be a variable chain?
50
New cards
Fc chain
What type of chain is also known as a constant chain?
51
New cards
Between CH1& CH2
Between what chains is the hinge region formed?
52
New cards
heavy
The hinge region is located on (heavy/light) chains`.`
53
New cards
1. Cysteine
2. Proline
What amino acid residues are present at the hinge region?
54
New cards
Ig flexibility
What does the hinge region permit?
55
New cards
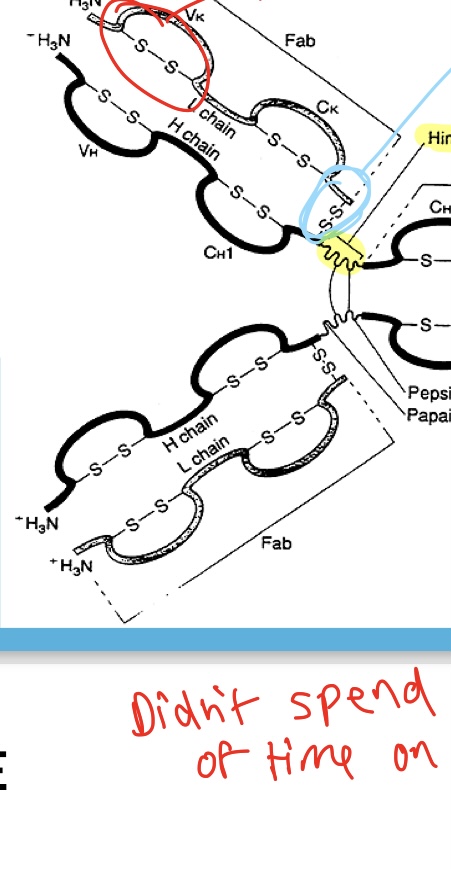
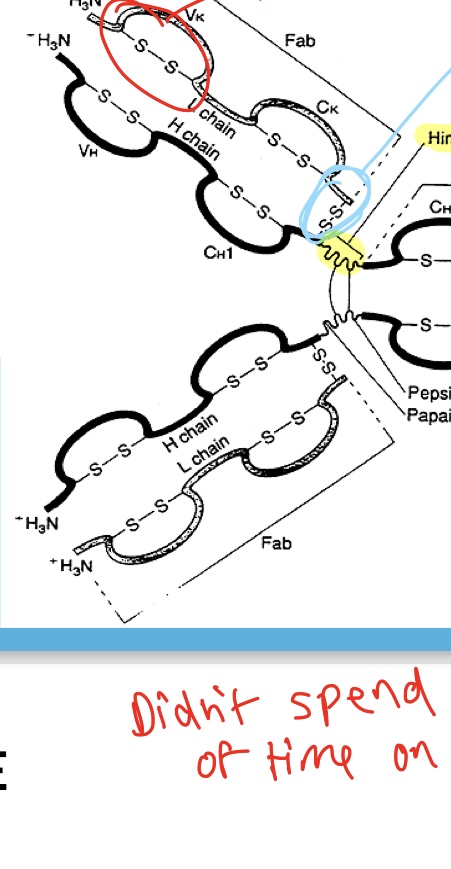
Interchain disulfide bond
What type of chain is indicated by the blue circle?
56
New cards
Intrachain disulfide bond
What chain is indicated by the red circle?
57
New cards
Isotypes
\-Immunoglobulin variant that allows for different biological responses due to differences in constant regions
\-IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM
\-IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM
58
New cards
Alloptypes
\-Immunoglobulin variant that is based on genetic differences of members of the same species
\-differences due to different alleles of same constant region gene
\-differences due to different alleles of same constant region gene
59
New cards
Idiotypes
Immunoglobulin variant that has differences due to rearrangement of VH and VL encoding genes within a given isotype
60
New cards
1. Membrane-bound antigen receptor on B cells
2. Secreted proteins
In what 2 form do antibodies exist?
61
New cards
Membrane-bound antigen receptors
What form of antibodies recognize antigens to start B cell activation?
62
New cards
Secreted proteins
What form of antibody is present in the blood and mucosal secretions and eliminates microbes and other toxins in humoral immunity?
63
New cards
IgG
Most common Ig in blood, lymph fluid, CSF, peritoneal fluid
64
New cards
15
IgG makes up _____% of total body protein.
65
New cards
2; 2
How many heavy chains does IgG contain? Light chains?
66
New cards
4
How many subclasses does IgG contain?
67
New cards
IgG
Which antibody is the workhorse and is the most versatile Ig?
68
New cards
IgG
What Ig had the longest half life?
69
New cards
IgG
What antibody isotype is the best for passive immunization?
70
New cards
precipitated
Phagocytes can rid antigens easier once __________.
71
New cards
precipitate; agglutinate
Soluble antigens (agglutinate/precipitate) while insoluble antigens (agglutinate/precipitate).
72
New cards
IgG
What antibody passes through the placenta to transfer immunity from mom to fetus?
73
New cards
IgG
What antibody is responsible for hemolytic disease of the newborn?
74
New cards
Fc portion
On what part of the IgG antibody do phagocytes attach to?
75
New cards
opsonization
Preparation of antigen before being “eaten” by macrophages
76
New cards
Fc portion
Natural killer cells interact with what part of the antibody of IgG?
77
New cards
IgG
What immunoglobulin is responsible for activation of complement, neutralization of toxins, immobilization of bacteria, and neutralization of viruses?
78
New cards
anti-toxin
To neutralize toxins, injection of an _______ can be used to block the active sites of the toxin.
79
New cards
passive
The injection of anti-toxin is a form of (passive/active) immunization.
80
New cards
IgG
What immunoglobulin reacts with flagella and cilia causing them to clump and immobilize the bacteria?
81
New cards
IgM
What immunoglobulin has the highest molecular weight of all Ig’s?
82
New cards
5; J; 5; 10
IgM has ____ basic Ig units. The __ chain is the connector. IgM has __ binding sites for the antigen but has _____ Fab segments.
83
New cards
antigen-specific
IgM is an ______________ B cell receptor.
84
New cards
IgM
What immunoglobulin is present on the surface of mature B cells along with IgD?
85
New cards
IgM
What is the first Ig produced following immunization or infections?
86
New cards
IgM
What Ig the first line of humoral defense against bacteria?
87
New cards
IgM
Elevated levels of what immunoglobulin indicates recent infection or exposure to an antigen?
88
New cards
IgM
Which immunoglobulin is the best at activating complement?
89
New cards
membrane attack complex
Activation of complement leads to activation of what cell that can attack bacteria?
90
New cards
IgG
Comparing IgM and IgG, what immunoglobulin is highest in the secondary response against T-dependent antigens?
91
New cards
IgM
Comparing IgM and IgG, what immunoglobulin is highest in the primary response against T-dependent antigens?
92
New cards
IgM; congenital or perinatal infection
What immunoglobulin is synthesized by the fetus at about 5 months? Elevated levels of this Ig indicate what?
93
New cards
IgM
What immunoglobulin is an efficient agglutinator and involves isohemagllutinins?
94
New cards
Isohemagglutinins
Naturally occurring antibodies against the RBC antigens of the ABO blood groups
95
New cards
Type O
What blood type has antibodies to A and B antigens?
96
New cards
1. Serum
2. Secretions
What are the 2 structural forms of IgA?
97
New cards
IgA
What antibody has no known biologic function?
98
New cards
dimer
Secratory IgA is mainly in the structural form of a _______.
99
New cards
monomer
The serum form of IgA is in the structure form of a ________.
100
New cards
J chain
What chain joins the 2 four-chained units of IgA?