community and population ecology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
native
from the ecosystem
nonnative
die off
naturalized- become established, reproduce, but don’t become invasive
invasive- aggressively displace native spaces
why and how do nonnative species become invasive
no predator
better able access resources
another limiting factor is not present
indicator species
their presence or by their absence indicates an environment condition
moss= bad soil
algal bloom= presence of excess nutrients
keystone species
niche has a major impact on an ecosystem by impacting many other niches
ex; otter
foundation species
habitat creating species
coral reef
Law of competitive exclusion
no two species can occupy the same niche
resource portioning
dividing up resource to reduce competition
predation
predator and prey
predators and prey adaptations
speed, eyesight, smell, size, armor, agility, camouflage, chemicals, and mimicry
parasitism
one organism benefits other is harmed
commensalism
one organism benefits and other is neither hurt nor helped
mutualism
both benefit
what influences the diversity in an ecosystem
latitude: higher latitude= less diversity
Pollution
NPP
habitat availability and conditions
time
climax community
one in which population remains stable in balance with each other and their environment
primary succession
long time starts on bare rock, typically linches and mosses (pioneer species), make soil, then early successional plant species, grasses, then mid-successional plant species shrubs, late successional plant species trees; first pines, then hardwoods
secondary succession
begins in a disturbed area
catastrophic natural
fire, landslides, storm damage, volcanic eruptions
catastrophic human caused
fire, deforestation
gradual natural
climate change
gradual human caused
climate change, invasive species, salt on crops over grazing
inertia/ persistence
resistance to disturbance
consistency
ability to remain unchanged
resilience
ability to recover from disturbance
clumping and what are reasons for clumping
staying together in groups
safety and resource
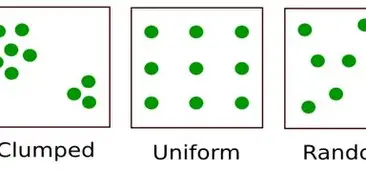
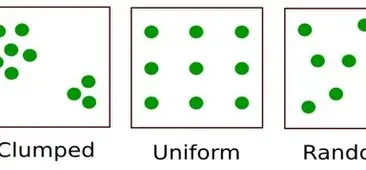
uniform
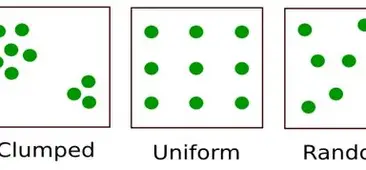
random
species richness
number of difference species per unit area
species evenness
relative abundance of the different species per unit area
population change
Population Change=(Births−Deaths)+(Immigration−Emigration)
new population
New Population=Initial Population+Births−Deaths+Immigration−Emigration
population density
Population Density=Total Population/Land Area
carrying capacity
the maximum population an ecosystem can sustain
biotic potential
reproductive capacity of a species
intrinsic rate of increase
capacity for growth with no limits
minimum viable population
lower limit of species population that will survive in the wild
environmental resistance
factors that limit r
what are variable K and r
K: carrying capacity
r: rate of increase
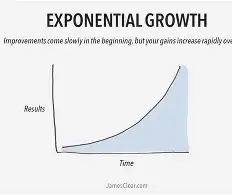
exponential growth
logistic growth
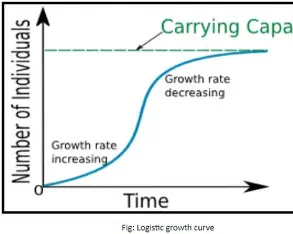
what happens when N>K?
it means the population size (N) has exceeded the carrying capacity (K) of the environment.
population cycles
stable
cyclic
Irruptive
Irregular
predator prey population cycles
one is high other is high
one is low other is low
what is the purpose of reproduction?
is to leave your genes for the future
r strategies
lots of offsprings
independent early
reproduce early
little parental care
small
don’t live long at birth
K strategies
large
reproduce late
lots of parental care
live a long time at birth
few offsprings
independent late
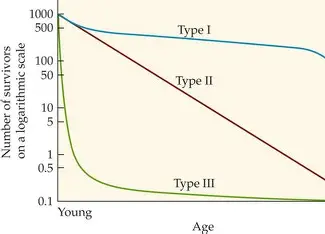
Type 1
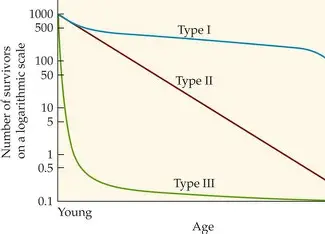
Type 2
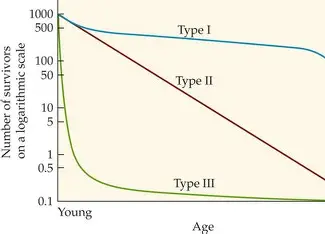
type 3