Linear Algebra New Material
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
A vector x is in W Perp if?
1.if and only if x is orthogonal to every vector in a set that
spans W.
W perp is a subspace of Rn
What is the orthogonal complement of Row(A) and Col(A)

What is the connection between their inner dot product and the angle # between the two line segments from the origin to the points identified with u and v?

Suppose y is a linear combination of an orthogonal basis. How to compute c1 without row reduction
y dot u1 / u1 dot u1 = c1
an orthogonal projection is a sum of what two components
y hat: scalar * vector u
z: vector orthogonal to u

orthogonal set of unit vectors
orthonormal set
An m n matrix U has orthonormal columns if
U^Transpose * U = I
Define v1 and v2 and v3 in the Gram-Schmidt Process

How to construct an orthonormal basis given vectors v1 and v2

Define an nxn orthogonal matrix and a least squares solution to Ax=b
(a) Least-squares solution to Ax=b
Let A be an m×n matrix and b∈Rm. A least-squares solution to Ax=b is a vector x^∈Rn that minimizes the sum of squared errors
|b-Ax^| <= |b-Ax| for any x existing in R^n
(b) n×n orthogonal matrix
An n×n matrix Q is orthogonal if its columns are orthonormal vectors and Q = Q^-1 and Q*Q^T = I
y^, y and z formulas

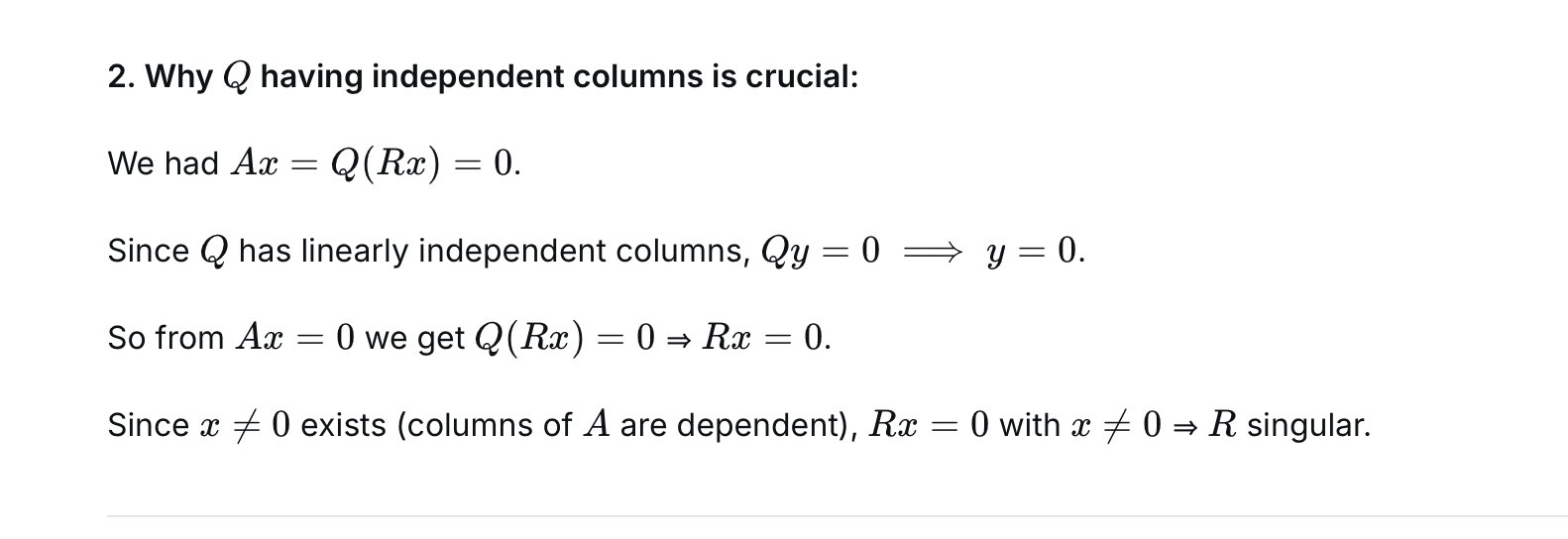
Suppose A= QR, where Q is an m x n matrix with orthogonal columns and R is
an n x n matrix. Show that if the columns of A are linearly dependent, then R cannot be invertible.
what 3 statements are logically equivalent from least squares chapter?

least squares solution formula
A^T*Ax = A^T*b
Even if you have the number of linearly independent vectors, under what condition could the matrix not be a basis for R^_?
If it contains the zero vector
row operations and linear dependence relations between the columns and the rows facts
row operations don't preserve linear dependence relationships across the columns but they do preserve the linear dependence relation of the rows
determinant of cA
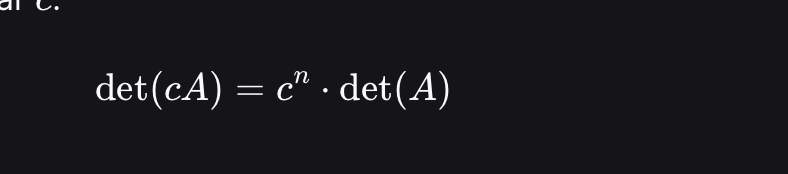
det(A^-1)
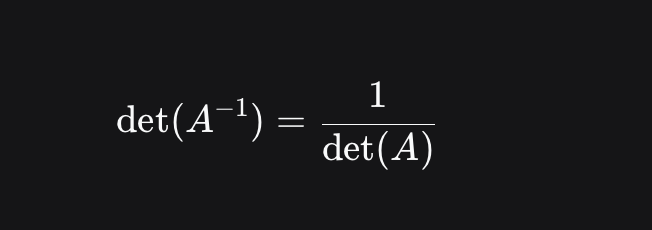
{u1 up through up} is an orthogonal basis for W, and y is in the span of W, the span{u1.up} then,
The projection of y onto W = y
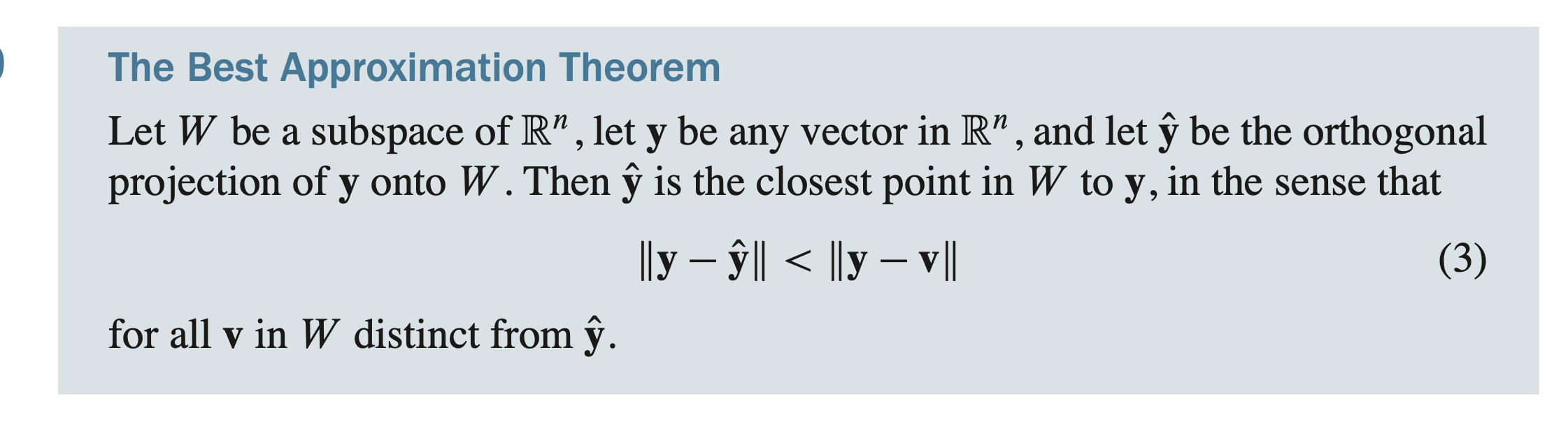
The best approximation theorem
y^ is then called
the best approximation to y by elements of W.
Description of what it means for the error to be minimized
||y-v|| becomes ||y-y^||
By the Best Approximation Theorem, the distance from y to W is
||y-y^||
Relationship of orthogonally diagonalizable matrix to symmetric matrix
A is orthogonally diagonalizable if and only if it symmetric
Spectral theorem
The set of eigenvalues of a matrix A is called the spectrum of A.
-Let A be an nxn symmetric matrix.
1. A has n eigenvalues
The dimension of the eigenspace is equal to the multiplicity of the root of the characteristic polynomial
Eigenspaces are mutually orthogonal
A is orthogonally diagonalizable
An orthonormal basis of eigenvectors for Rn
If u1 up through up is an orthonormal basis for a subspace W of Rn, then the projection of y onto W is equal to
U*U^T*y for all y in R^n
condition for A being factored into QR
A is m x n and has linearly independent columns
define linear transformation
In linear algebra, a transformation (often specifically a linear transformation) is a mapping between two vector spaces that preserves vector addition and scalar multiplication.
One-to-one injective transformation
A linear transformation T:Rn→Rm is one-to-one if each vector in the codomain (Rm) is the image of at most one vector in the domain (Rn)
Onto surjective transformation
A linear transformation T:Rn→Rm is one-to-one if each vector in the codomain (Rm) is the image of at least one vector in the domain (Rn)
Standard Matrix of a Linear Transformation
The matrix A such that T(x)=Ax. Its columns are T(e1),T(e2),...