Psychology paper 1 practice
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All key terms you need to know for Paper 1 SL and HL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
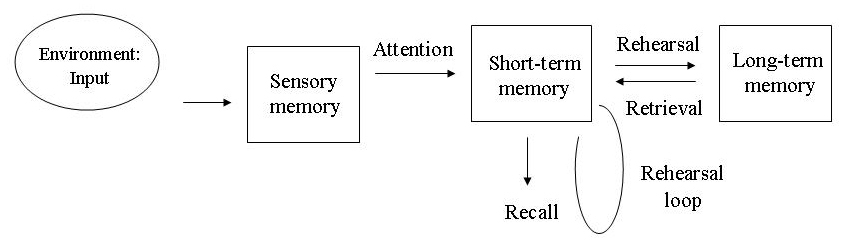
Multi-Store Model (MSM)
By Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)
Argues that memory consists of separate locations
Each memory store operate in a single uniform way
Multi-Store Model (MSM)
Strengths & Limitations
Strengths:
Experimental research and biological case studies to support model
Has historical importance and more research was based on this model
Limitations:
Oversimplified and assumes each store works independently
Several times where STM doesn’t enter LTM
Doesn’t explain memory distortions
Schema theory
Suggests that all knowledge is stored in _______ and influence process/remember new information.
Schema
Mental representations derived from prior experiences
Schema theory
Limitations & Strengths
Strengths:
Strong empirical evidence
Explains memory distortion
Has wide applicability
Limitations:
Low construct validity: Cannot directly be observed/difficult to measure
Limited predictive power: cannot predict what an individual will remember
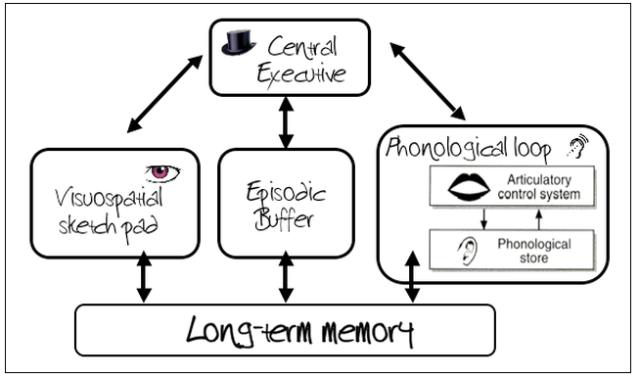
Working Memory Model (WMM)
Suggested by Baddeley & Hitch (1974)
Suggests that STM is not a single store but consists of a number of different stores
Assimilation
Fitting new processes into existing mental schemas
Accommodation
Modifying existing schemas/creating new ones to fit new contradictory information
Dual Process Model
A cognitive psychological framework proposing that human thinking, decision making and reasoning function through 2 different systems. (System I and System II)
System I
An automatic, intuitive, and effortless way of thinking. Often employs heuristics. This “fast” mode of thinking allows for efficient processing but is prone to errors.
System II
Slower, conscious, & rational mode of thinking. Requires more effort and thinks carefully about all possible ways we could interpret a situation and eliminates possibilities based on sensory information until we arrive at a solution. Allows us to analyze the world around us carefully.
Heuristics
Mental shortcuts that involve focusing on 1 aspect of a complex problem and ignoring others.
Reconstructive memory
A theory that memory isn’t a passive recording of events, but an active process of rebuilding memories using schemas, beliefs, and expectations.
The misinformation effect
The phenomenon where a persons recall of episodic memories become less accurate because of exposure to incorrect information post-event.
Flashbulb memory
Proposed by Brown and Kulik (1977).
A highly detailed vivid “snapshot” of a moment when a surprising and emotionally arousing event happens.
Cultural norms
A set of behaviors/beliefs shared by members of a society/group of people
Individualism vs Collectivism
the degree at which people integrate into groups.
Individualistic cultures are more likely to focus on individual achievements and experiences unlike collectivistic cultures where they focus on the group.
Long vs short term orientation
A cultures attitude towards the future or connection to the past
cultural dimensions
the values of a society that affect behavior
Enculturation
Maintaining and learning of the behaviors and norms in our own culture
Acculturation
adapting and adjusting to a new culture
Salience
Becoming more aware about a part of 1s identity
Acculturative stress
A battle between acculturation and enculturation causing stress
social categorization
process of categorising people into groups based on similar characteristics (ingroups and outgroups)
Social comparison
Comparing your ingroups to your outgroups
Social Identity theory
A person not just a personal self but multiple that corresponds to group membership
Social Cognitive Theory
Assumes that we learn behaviors through observational learning
4 components of social cognitive theory
Attention: learning a behavior through attention
Retention: remembering behavior to reproduce
Motivation: must want to replicate behavior
Potential: must be physically and mentally able to carry out behavior
Self-efficacy
Ones belief in ones ability to successfully carry out a task
Stereotyping
a social perception of an individual in terms of group membership or physical attributes
Illusory correlation
Seeing a correlation in 2 variables when there is none
Stereotype threat
When 1 is in a situation where there is a threat of being judged or fear of doing something that aligns with a stereotype
Localisation
Theory that specific parts of the brain are responsible for specific behaviors
lateralization
How specific mental processes are more dominant in 1 hemisphere of the brain
Plasticity
The brains ability to reogranize its structure and function based on its environmental demands
Neural networks
Interconnected group of neurons that form complex pathways
Neural pruning
when the brain removes unused synaptic connections between neurons to optimize cognitive efficiency
Memory consolidation
how the brain changes STM to LTM
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter that regulates memory, muscle movement, learning and attention.
Antagonist (scopolamine)
A substance binding to receptors, blocking the effects of the neurotransmitters by inhibiting receptor sites
Inheritance
transmission of genetic, behavioural, and physical traits from parent to offspring
Family studies
Incidence of behavior over a number of generations
Concordance
The presence of same traits between a twin pair