(ACS) Acute Coronary Syndrome (nSTEMI, STEMI, UNSTABLE ANGINA)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Unstable Angina (UA)
new in onset
Occurs ________or during sleep
Occurs with increasing frequency, duration, or less effort than the patients usual chronic stable angina
Usually lasts at least _________
UNPREDICTABLE
At rest, 10 min
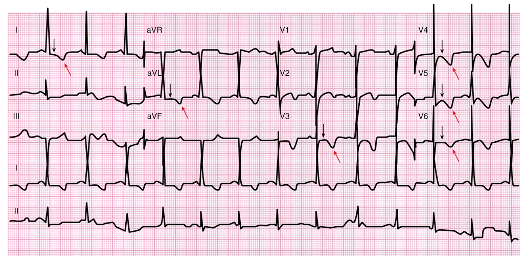
Non-ST-Elevation MI (NSTEMI)
Caused by- ________________
does NOT cause ST segment elevation
ECG may show ST depression &/or T wave inversion
Pts will usually undergo cardiac Catherization within ________
Thrombolytic therapy is ___________________
Nonocclusive thrombus, 12-72 hrs, not a treatment option
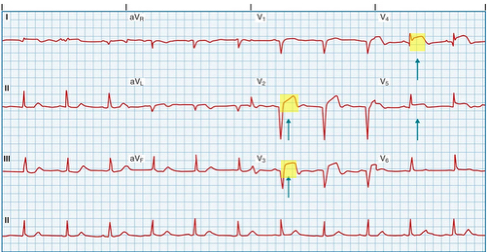
ST-Elevation MI (STEMI)
Caused by- ________________
Myocardial cell death occurs
ST segment elevation
Occlusive thrombus
First line STEMI treatment : ________________
if available, must occur within _______ of arrival to ED
Percutaneous coronary intervention, 90 min
STEMI treatment (if PCI not available)
______________ : must occur within ________ of arrival to ED
Thrombolytic therapy, 30 min
MI chest pain: persistent
Heavy, pressure, tight, burning, constricted, or crushing
Common locations: _____________or _________
May radiate to neck, lower jaw, arms, or back
Often occurs in early morning
Substernal, epigastric
MI chest pain usually lasts
20 min or longer
MI chest pain:
Atypical symptoms:____________
Discomfort, weakness, nausea, indigestion, SOB
patients with ______ may have silent (asymptomatic) MIs
Diabetes
MI clinical manifestations for Older patients:
_____________
SOB
_____________
_____________
Dysrhythmia
Change in mental status, pulmonary edema, dizziness
Clinical manifestations of MI:
SNS stimulation:
__________
Increased HR & BP
vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels (Skin may be ______, ________, or cool)
Diaphoresis, ashen, clammy
Clinical manifestations of MI:
Nausea & vomiting:
Severe pain causes reflex stimulation of the vomiting center
___________ in area of infarcted heart muscle
Vasovagal reflex
Clinical manifestations of MI: Fever
May last ____________
Death of heart cells cause systemic inflammatory process
4-5 days
Often given to limit remodeling after Mi
ACE inhibitors
Complications of MI: Dysrhythmias
Occurs in 80-90% of pts after MI
_____ & ______ are the most common cause of death in prehospital period
Bradycardia
________
VT, VF, PVCs
Complications of MI: dysrhythmias, _______, _________
Heart failure, Cardiogenic shock
Complications of MI: Papillary muscle dysfunction or rupture
treatment: reduce afterload with __________ &/or ______
Immediate surgery to repair or replace mitral valve
Nitroprussidd, IABP
Complications of MI: Ventricular Septal Wall Rupture & LV free wall rupture
may cause HF, Cardiogenic shock
Treatment→ _________
Emergency surgical repair
mild to severe chest pain that increases with inspiration, coughing, and movement of upper body
May occur 2-3 days after MI
Pericarditis
pericarditis & fever that develops 1-8 weeks after MI
may be autoimmune reaction to necrotic heart muscle
May have pericardial friction rub & pericardial effusion
Dressler syndrome
Dressler syndrome treatment
High dose aspirin
Diagnostics of ACS:
ECG, AND ________
Echocardiogram
Worsening myocardial contractility
Hypokinesis
Standard to identify MI: Cardiac-Specific Troponin
serial sets are drawn over _______
24 hrs
MI: cardiac biomarker- less sensitive than Troponin
Creatine Kinase MB
Patients w/ STEMI must have cardiac cath w/ PCI within ____ mins of arrival at ED
90
Patients w/ UA or NSTEMI usually have cardiac cath during hospitalization to diagnose & evaluate extent of disease; they do NOT need emergent cath
usually within _____-_____hrs after arrival to hospital
PCI may be done during diagnostic cath if appropriate
12-72
Management of ACS:
• Always assess & monitor ABCs.
• Position patient _______ unless contraindicated.
• Give O2 by __________ or __________ mask.
• Obtain baseline vital signs, including O2 saturation.
• Auscultate heart & breath sounds.
• Obtain 12-lead ECG.
• Insert 2 IV catheters.
• Assess pain using PQRST mnemonic (Table 37.8).
• Medicate for pain as ordered (e.g., nitroglycerin, morphine).
Upright, nasal cannula, nonrebreather
Management of ACS:
Start continuous ECG monitoring.
• Obtain baseline blood work.
• Obtain portable chest x-ray.
• Assess for contraindications for antiplatelet, anticoagulant, or thrombolytic therapy, as appropriate.
• Give _______ for heart-related chest pain unless contraindicated.
• Give a high-dose _______.
• Give antidysrhythmic drugs for life-threatening dysrhythmias.
Aspirin, statin
ACS: Ongoing monitoring
Assess & record response to drugs (e.g., decrease in chest pain) & re-medicate or titrate drugs (e.g., _________) as needed.
nitroglycerin
ACS: ongoing monitoring
Anticipate need for intubation if ___________ is evident.
• Prepare for CPR & defibrillation if cardiac arrest is evident.
• Anticipate need for transcutaneous pacing for symptomatic bradycardia or _________.
Respiratory distress, heart block
Management of ACS: cardiac catheterization
Diagnostic functions:
_________ blockage
Assess _________ of blockage
Determine presence of ____________
Evaluate LV function
Locate, severity, collateral circulation
Management of ACS: cardiac catheterization
Therapeutic functions:
Balloon angioplasty
Insert ______ or ______ into blocked coronary artery
Bare metal stent, DES
Post-Op care after CABG
ICU for first ____-____ hrs
Hemodynamic monitoring
__________ for continuous BP monitoring
Pleural & mediastinal _____________ for chest drainage
Continuous ECG monitoring
Mechanical ventilation
24-48, arterial line, chest tubes
Post-Op care after CABG
Epicardial pacing wires for emergency pacing of the heart is for _________
Urinary cath
NGT for gastric decompression
Temp pacemaker
Potential complications after CABG
Systemic inflammation
Bleeding & anemia
F&E imbalances
Infection
Hypothermia
Dysrhythmias (A. Fib)
_____________should be started at least 24 hrs. before surgery & restarted ASAP
__________________________
Beta blockers, postoperative cognitive dysfunction
Management of ACS: thrombolytic therapy
Indicated only for pts with _______ who cannot have an emergent cardiac cath
STEMI
Management of ACS: Thrombolytic Therapy
Inclusion criteria:
Chest pain <______ & ECG findings show a STEMI
Must have NO absolute contraindications
12 hrs
Management of ACS: Thrombolytic Therapy:
What are the most important Absolute contraindications?
Bleeding, uncontrolled HTN
Management of ACS: Thrombolytic Considerations:
BEFORE starting:
- draw blood for baseline lab values
- start _________IV lines_
- Perform all other _______________
Regularly assess _____________ for changes that could indicate cerebral bleeding
MAIN COMPLICATION —> ___________
2-3, invasive procedures, neuro, bleeding
ACS: drug therapy
quickly reduces cardiac workload & ischemia
Titrate infusion to chest pain
IV nitroglycerin
ACS: drug therapy
Reduces cardiac O2 demand
Treats acute chest pain
Morphine
ACS: drug therapy: Antidysrhythmics (if needed)
CCB, Beta blockers
ACS: drug therapy
T or F ?
Stool softeners used
T