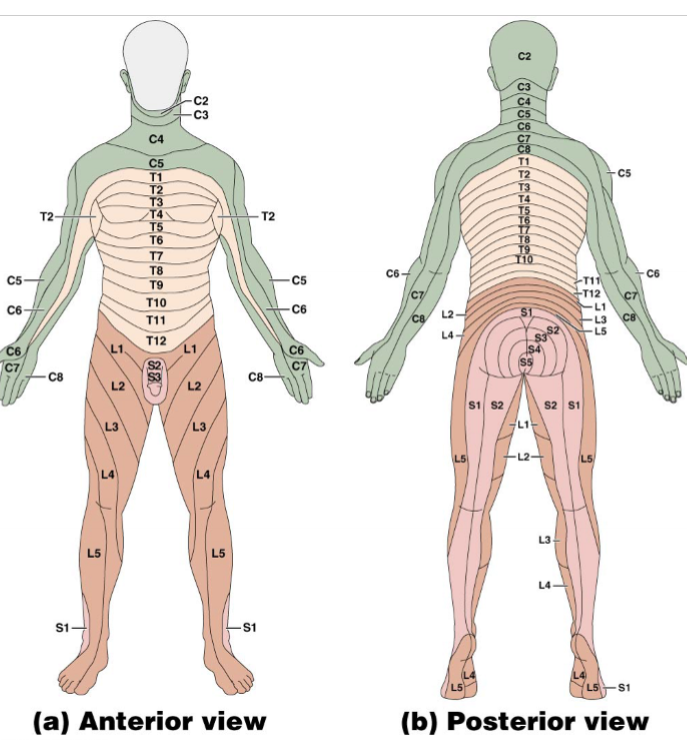
Spinal Cord and PNS
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
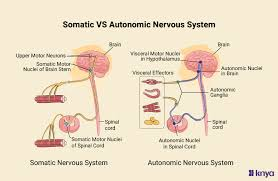
What are the somatic and autonomic nervous system?
part of the motor division of the PNS
somatic = voluntary
autonomic = automatic
What is gray matter in the PNS called?
ganglia
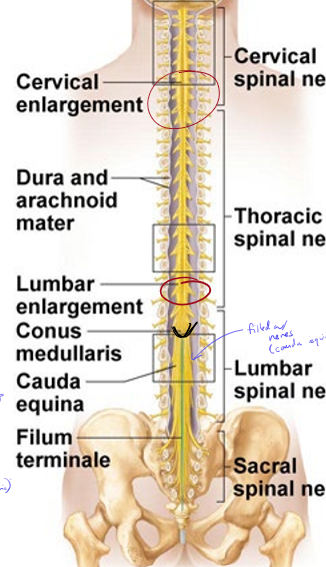
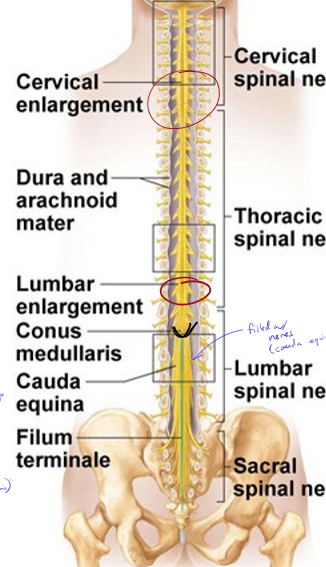
Why are there enlargements in the cervical and lumbar regions of the spinal cord?
arms and legs are very innervated, so more cell bodies are stored in the enlargements
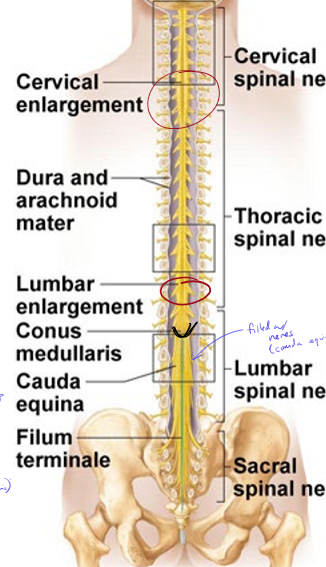
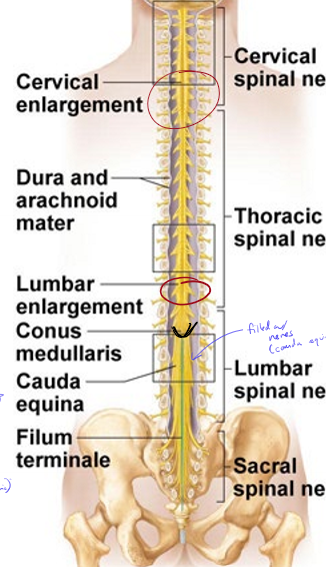
Where does the spinal cord end?
near the L1 vertebrae
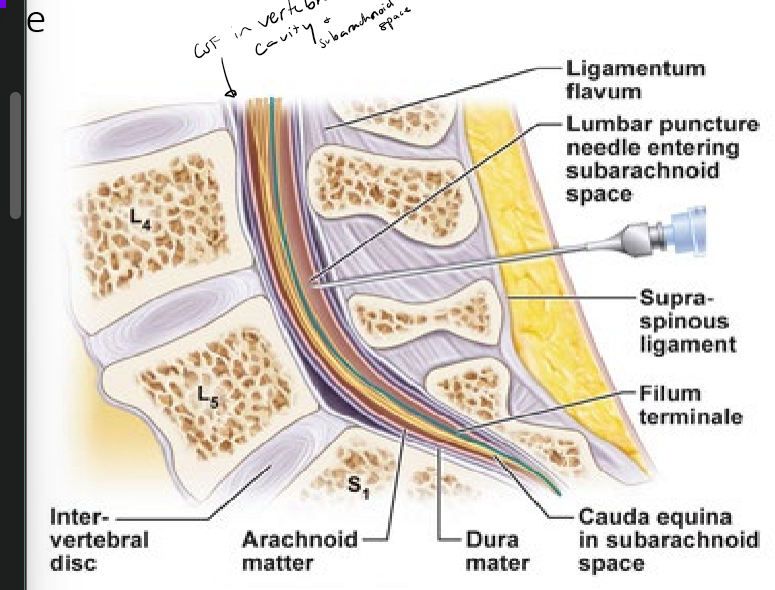
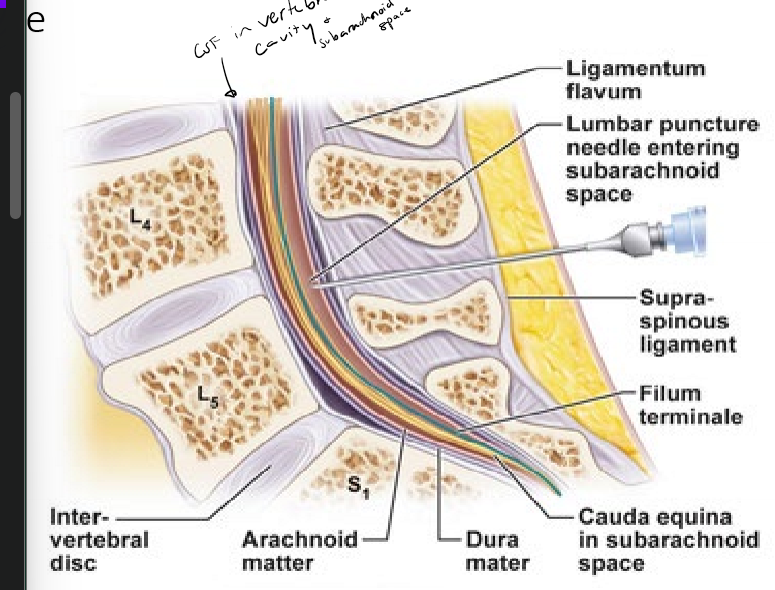
What is a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) and why is it performed?
done below spinal cord to avoid hitting spinal cord
done to get CSF from the subarachnoid space to look for bacteria
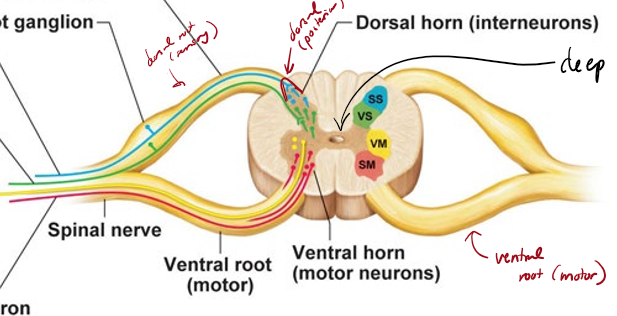
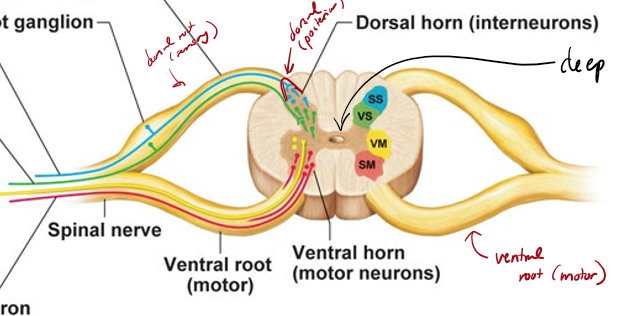
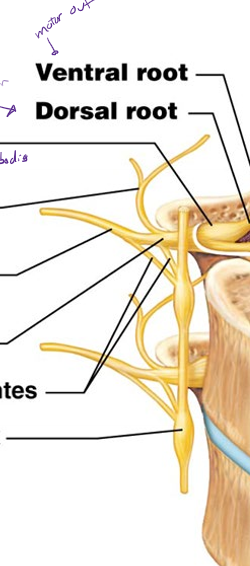
What are the parts of he spinal cord and what does each do?
dorsal horn - gray matter, interneurons
ventral horn - gray matter, motor neurons
ventral root - carries motor neurons away from spinal cord
dorsal root - carries sensory neurons towards spinal cord
dorsal root ganglion - contains sensory cell bodies
spinal nerve - carries both sensory and motor nerves
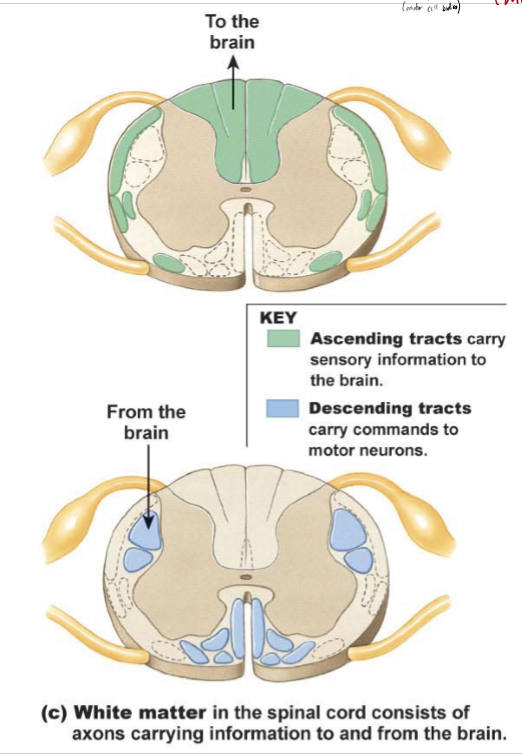
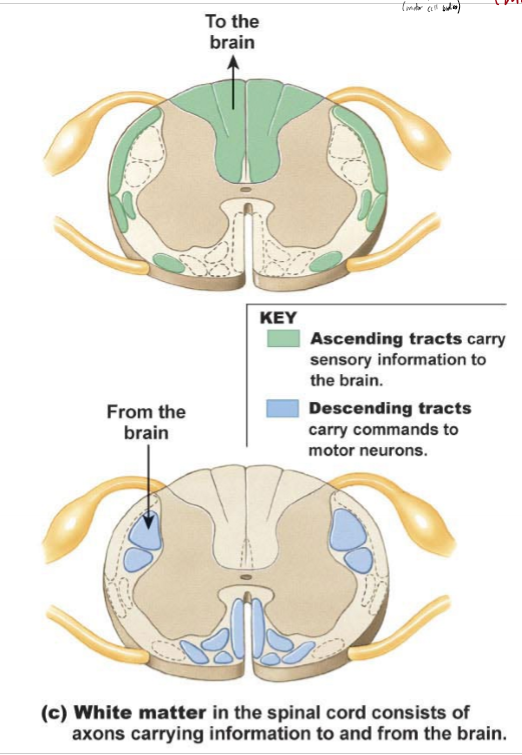
What are ascending and descending tracts?
white matter (axons) in the spinal cord traveling to/from the brain
ascending - info to the brain up spinal columns, decussation occurs in brainstem or spinal cord, 3 neuron circuits from receptor to primary somatosensory cortex (parietal lobe)
descending - info to motor neurons from CNS, dessucation in brainstem/spinal cord, 2 or 3 neuron circuits from primary motor cortex to muscle
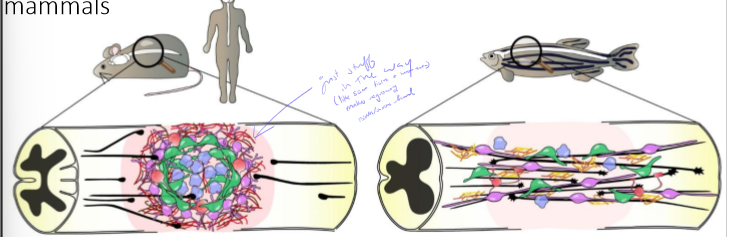
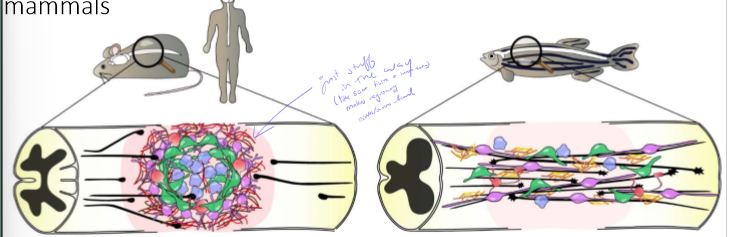
Why don’t spinal cords regenerate very well?
immune system puts fibroblasts, scar tissue, etc. in way of where axons need to grow
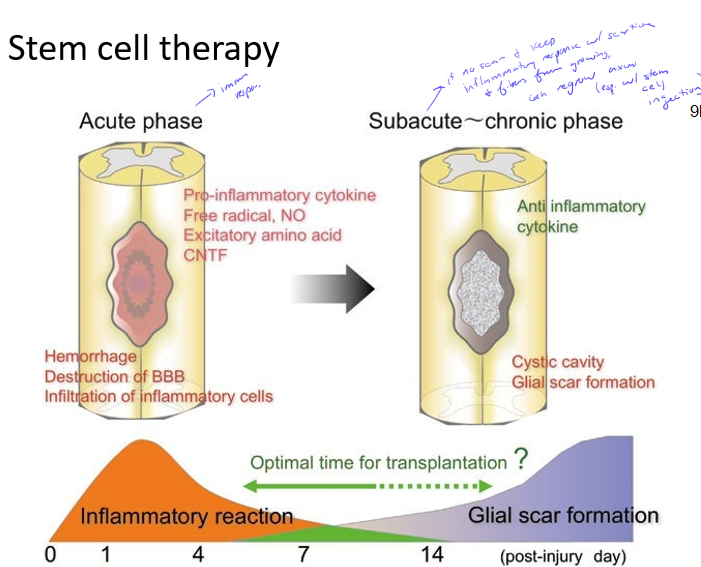
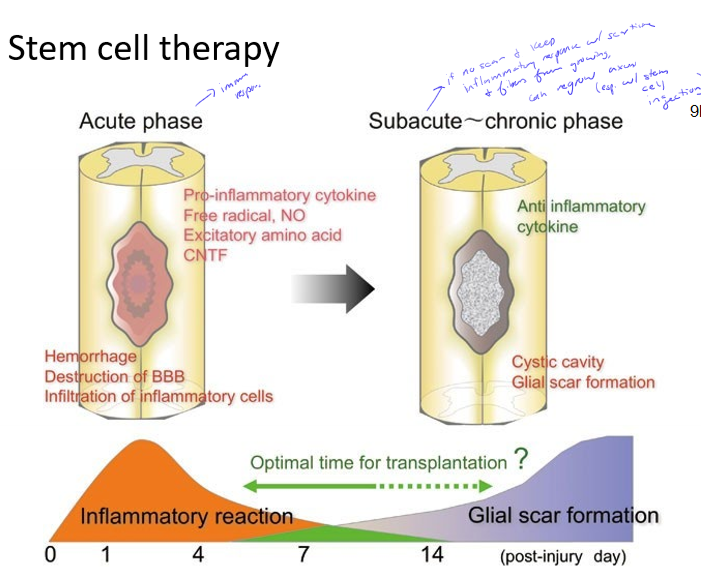
Describe the stem cell therapy treatment for spinal cord injuries and why they work
occur between acute and subacute phase
after inflammatory response but before scar forms, axons can regenerate before stuff gets in the way, especially if stem cells are injected
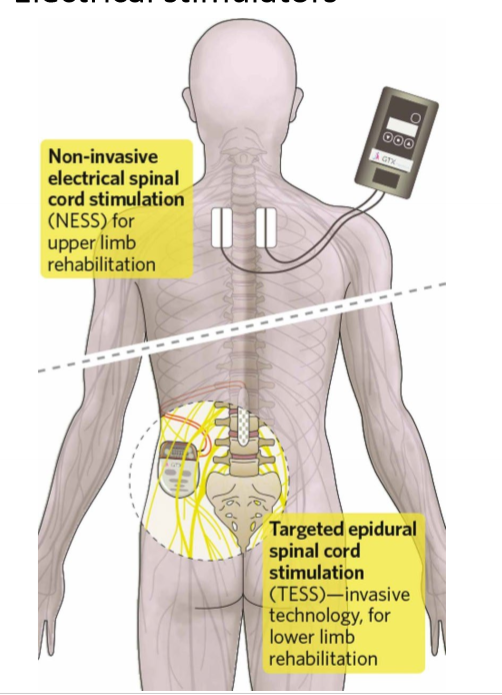
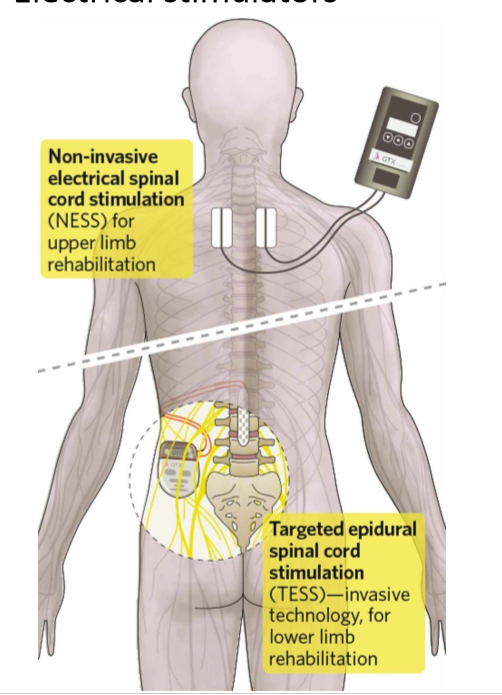
Describe electrical stimulators after spinal cord damage and why this can help
even if axons are cute, many neurons below point of damage still function
can stimulate nerves despite damage to other parts of the body
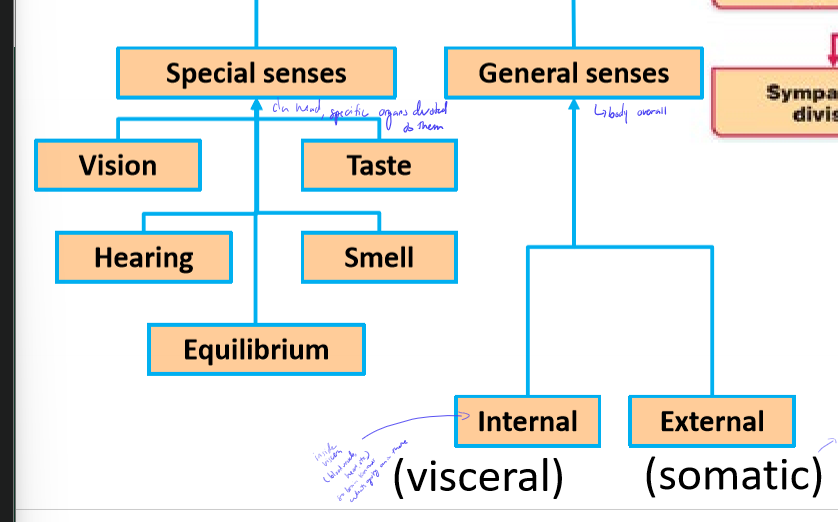
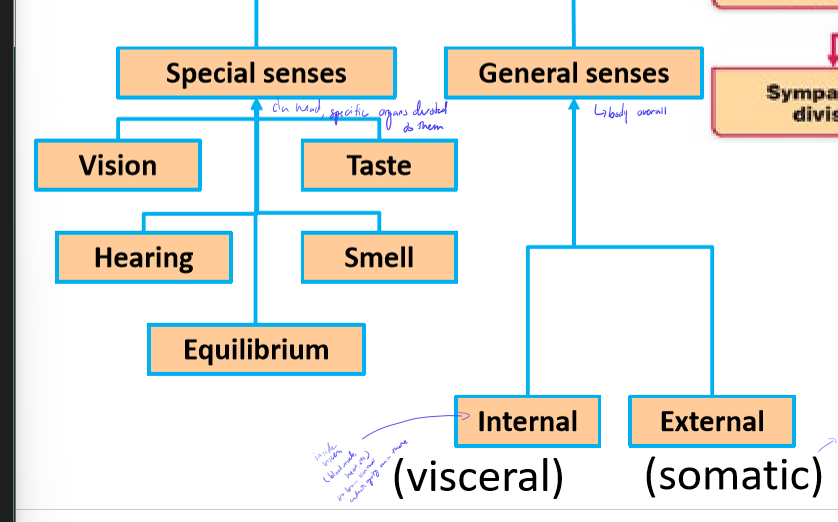
What are internal (visceral) and external (somatic) afferent inputs?
visceral - signals from inside viscera, ex. blood vessel, heart
somatic - signals associated with skin ex. touch, temperature, pain
What is white matter in the CNS?
nerve, root, ramus
What are rami? Describe the dorsal and ventral ramus
branch like bundles of motor and sensory nerves after it exits the spinal cord
dorsal - to back
ventral - to front of body
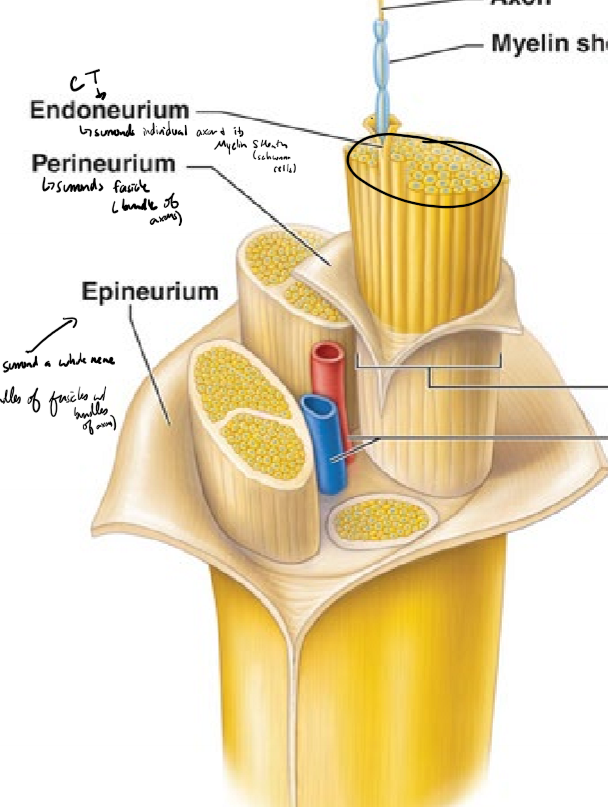
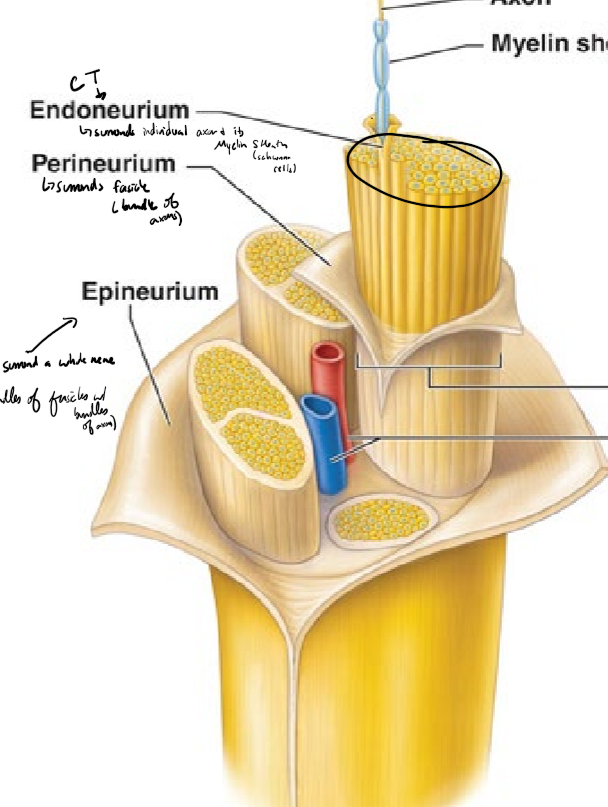
Describe the structure of a nerve from deepest to most superficial
axon surrounded by a myelin sheath (schwann cells)
endoneurium surrounds individual axons and their myelin sheath
perineurium surrounds fascicles (bundles of axons)
epineurium surrounds a whole nerve (bundles of fasicles)
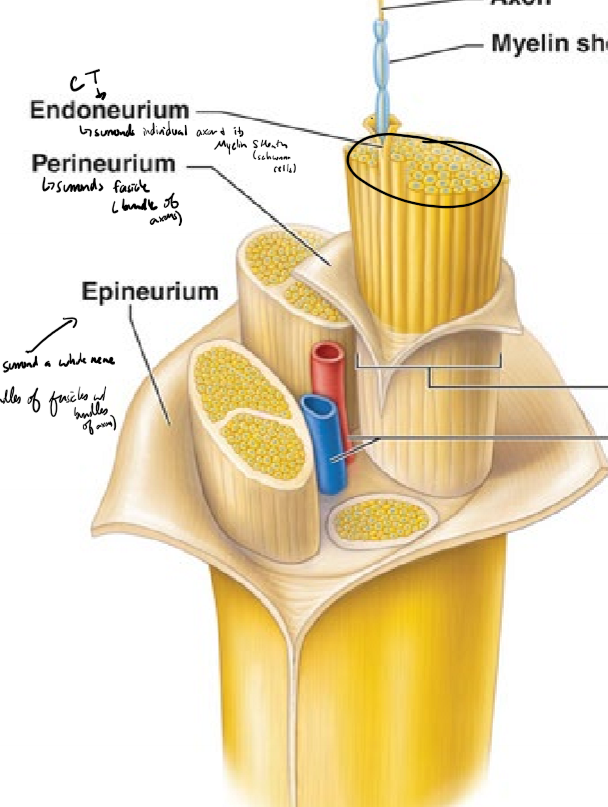
What is a fasicle?
group of axons bundled together
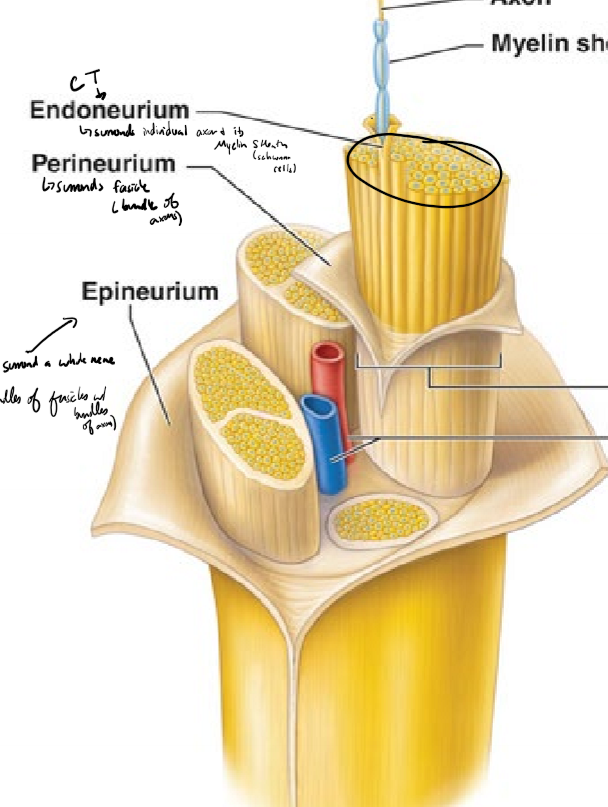
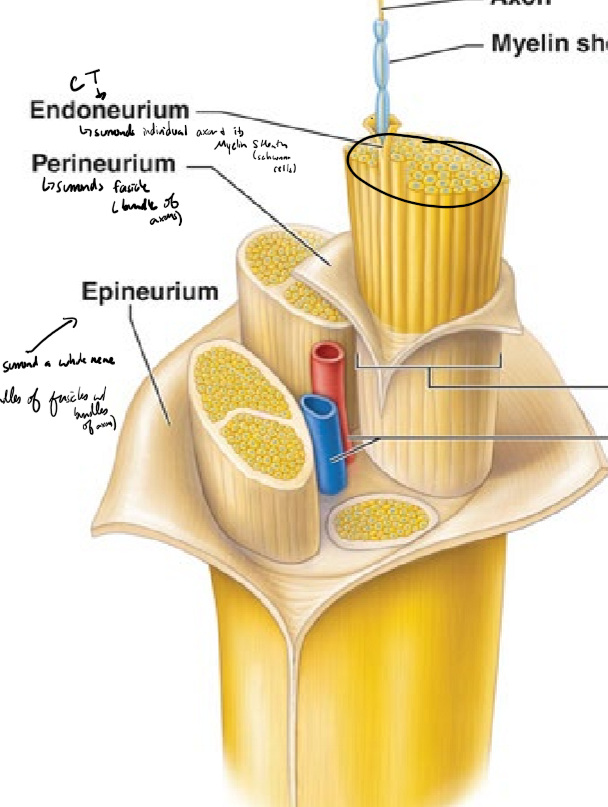
What do the endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium surround? What kind of tissue are they?
endonerium surronds an individual axon and its myelin sheath
perineurium surrounds a fascicle (bundle of axons)
epineurium surrounds a whole nerve
connective tissue
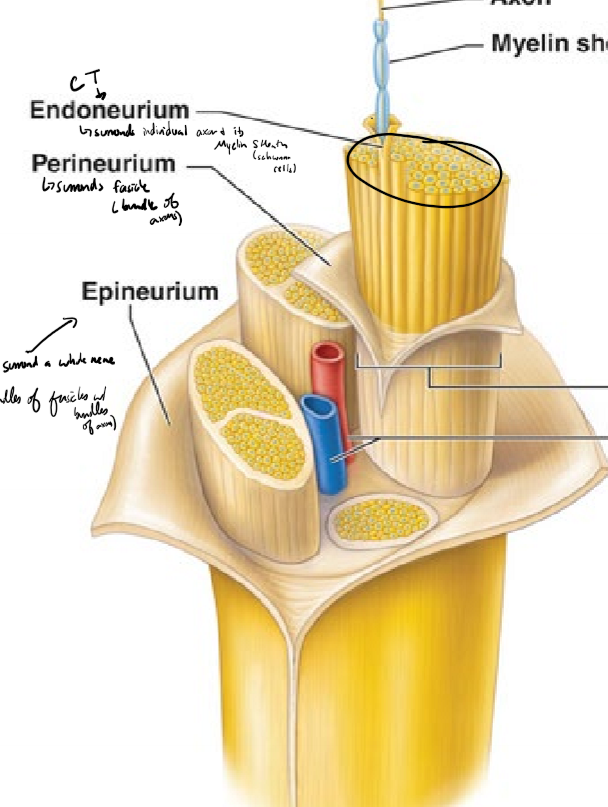
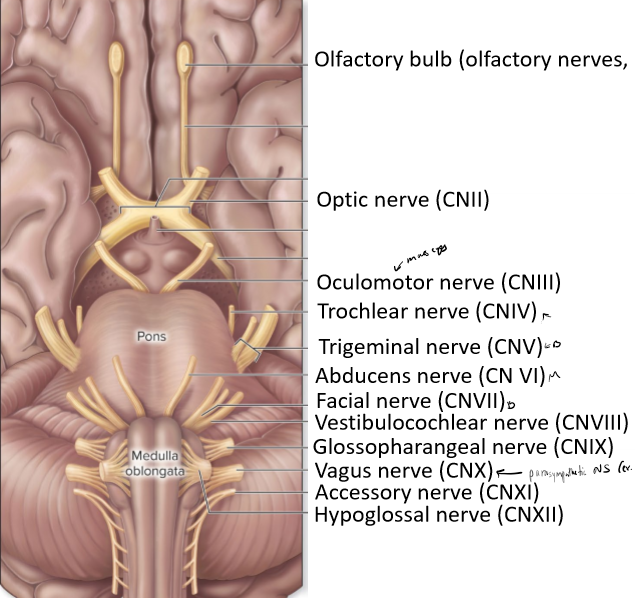
Describe cranial nerves
nerves coming off the brain
can be only sensory, only motor, or both
most connect to the brain stem
most are involved with structures in the head and neck
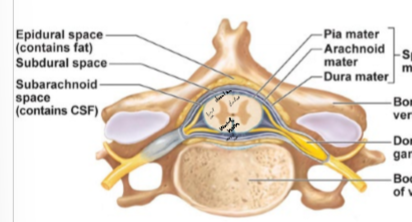
Describe spinal nerves
nerves coming off spinal cord
mixed nerves, both sensory and motor fibers
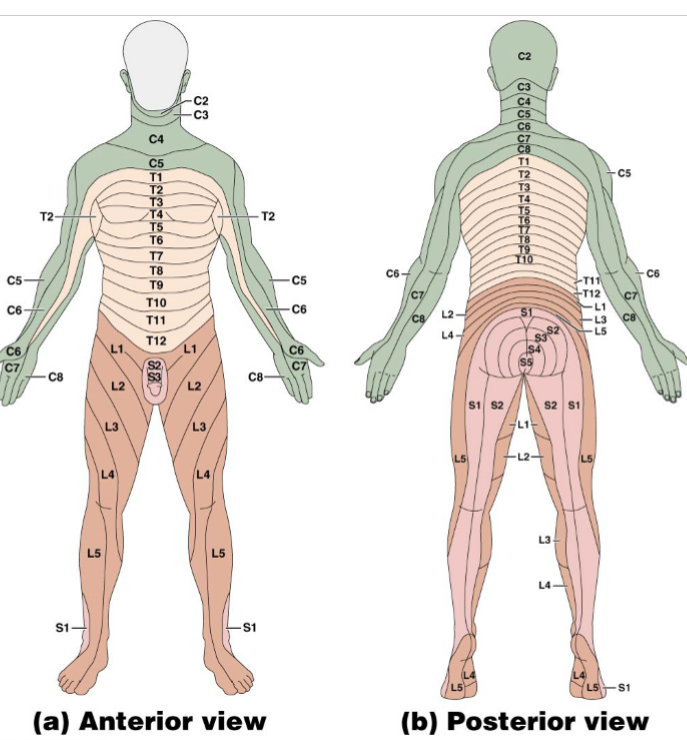
What are nerve plexuses?
branching and unbranching of axons (not necessarily synapses)
branch to get specific nerves at a specific spot to innervate
nerve roots generally map to parts of the body from superior to inferior