Naplex: Infectious Disease II: Bacterial Infections
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
What are the two common organisms on the surface of the skin?
Staphylococci and Streptococci
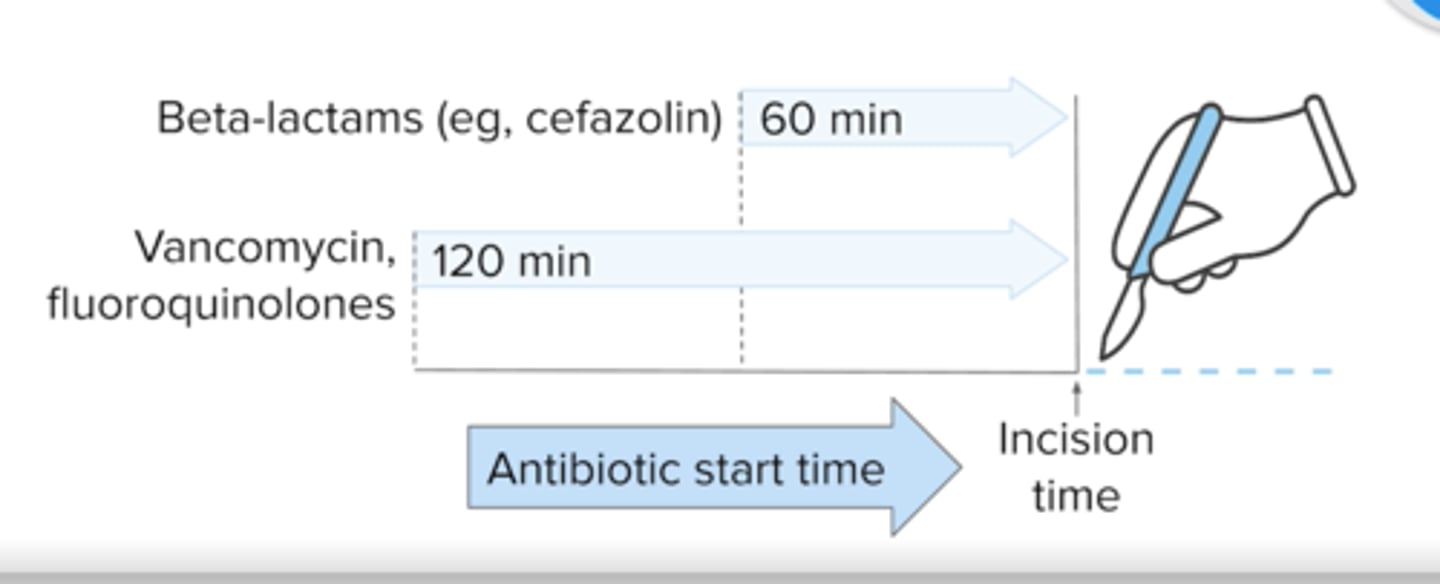
What two antibiotics are used commonly used prior to surgery (pre-operative) and when are they given?
beta-lactam: Cefazolin or Cefuroxime -- 60 minute before incision
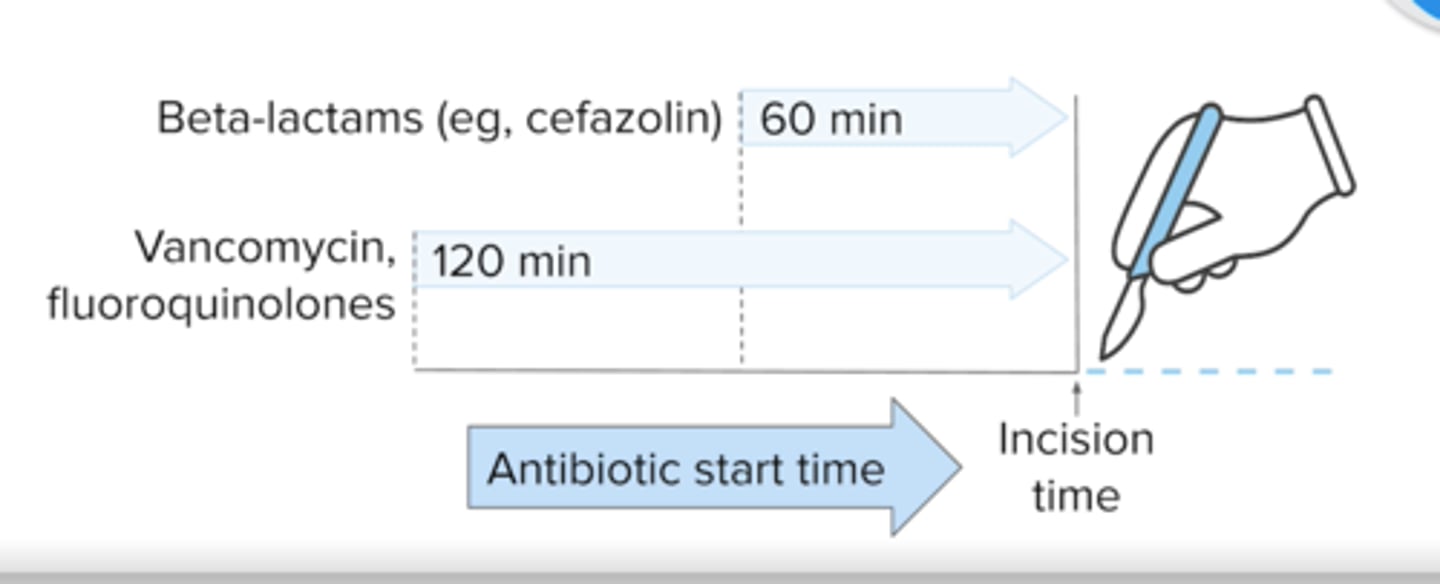
If patient has a beta-lactam allergy, what other two antibiotics can be used prior to surgery and when are they given?
Quinolone or Vancomycin or Clindamycin -- 120 minute before incision
How many hours to discontinue the antibiotics in surgery?
24 hours
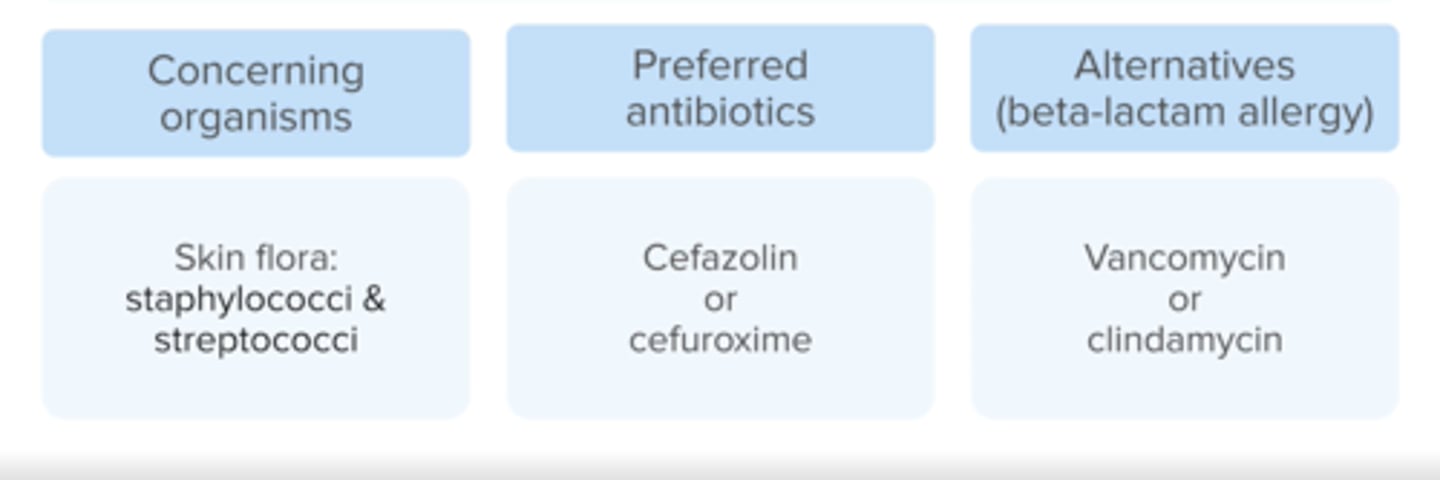
what abx are used in cardiac, orthopedic, and vascular surgeries? + alt s
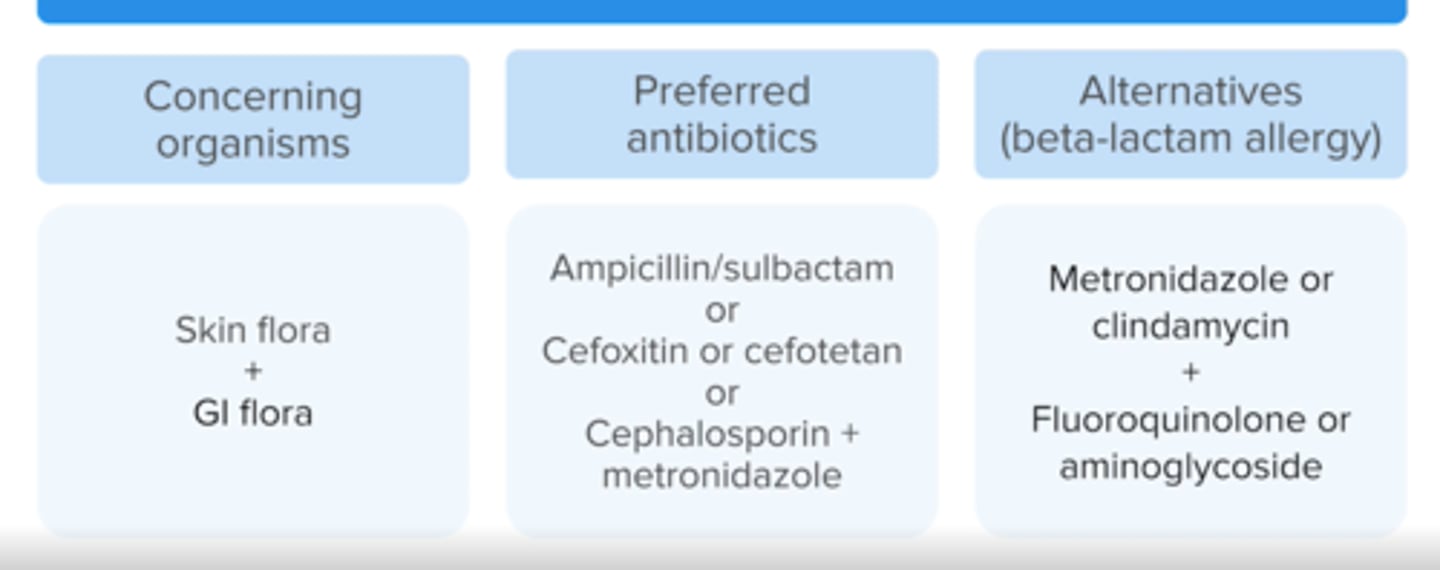
what abx are used in GI surgeries?
What antibiotics are used in Hip fracture repairs/total joint replacements?
Cefazolin
What is meningitis?
inflammation of the meninges that cover the brain and spinal cord
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
headache, fever, nuchal rigidity (stiff neck) and altered mental status
Other symptoms: chills, vomiting, seizures, rash and photophobia
How is meningitis diagnosed?
lumbar puncture
What are common bacterias in Meningitis?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Neisseria meningitidis
Haemophilus influenzae
(Listeria monocytogenese in neonate, >50, immunocomp'd)
Antibiotics duration for N. meningitidis and H. influenzae meningitis?
7 days
Not underlined
Antibiotics duration for S. pneumoniae meningitis?
10 - 14 days
Antibiotics duration for Listeria monocytogenes meningitis?
21 days
Not underlined
Why is dexamethasone given prior to the Antibiotic in meningitis>
To help prevent neurological complications (EG. hearing loss)
What steroid can be given in meningitis treatment to prevent neurological compications?
Dexamethasone 15 -- 20 minutes prior or with first antibiotic dose

What drug is given for Listeria coverage in meningitis?
Ampicilliin
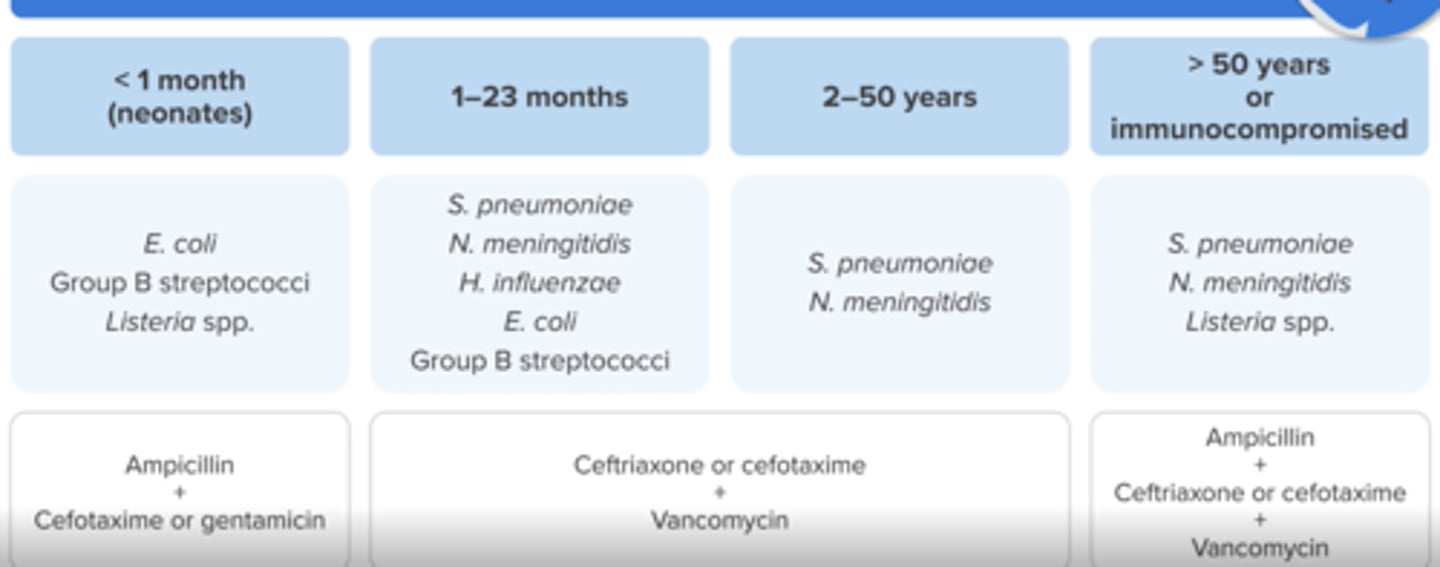
Empiric treatment for bacterial meningitis in Age < 1 month (neonates)?
Ampicillin (for Listeria coverage) + Cefotaxime (no ceftriaxone) or gentamicin
do not use ceftriaxone!!
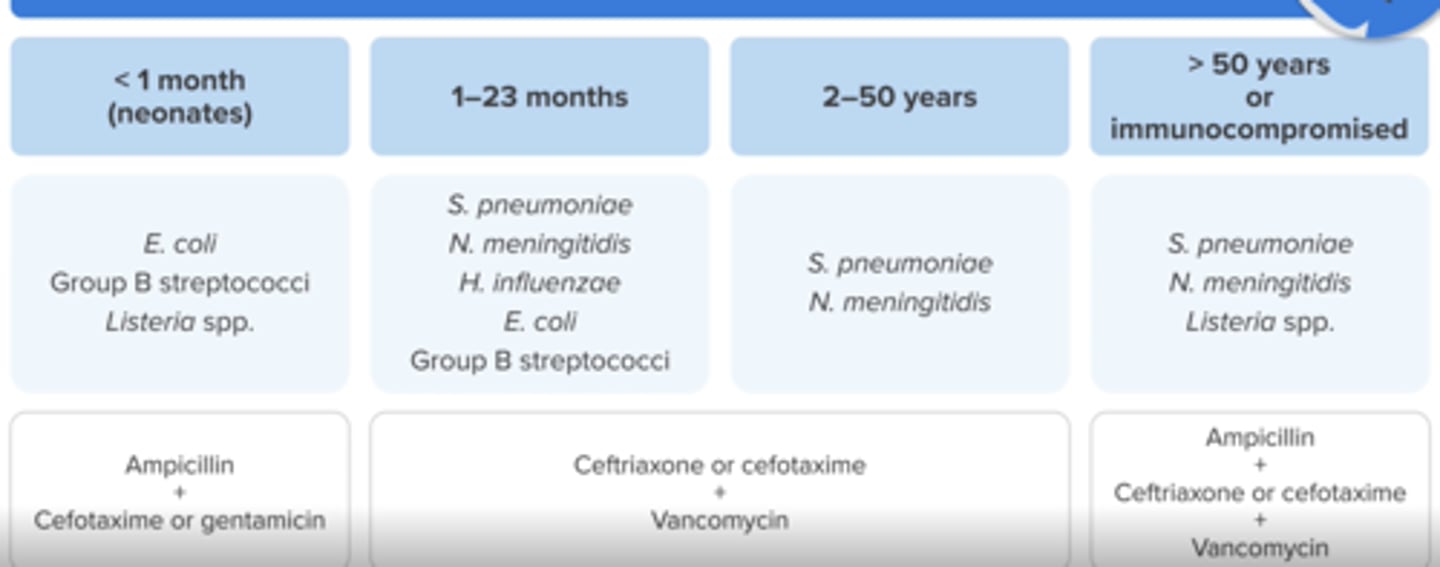
Empiric treatment for bacterial meningitis in Ages 1 month to 50 years
Ceftriaxone or cefotaxime + Vancomycin
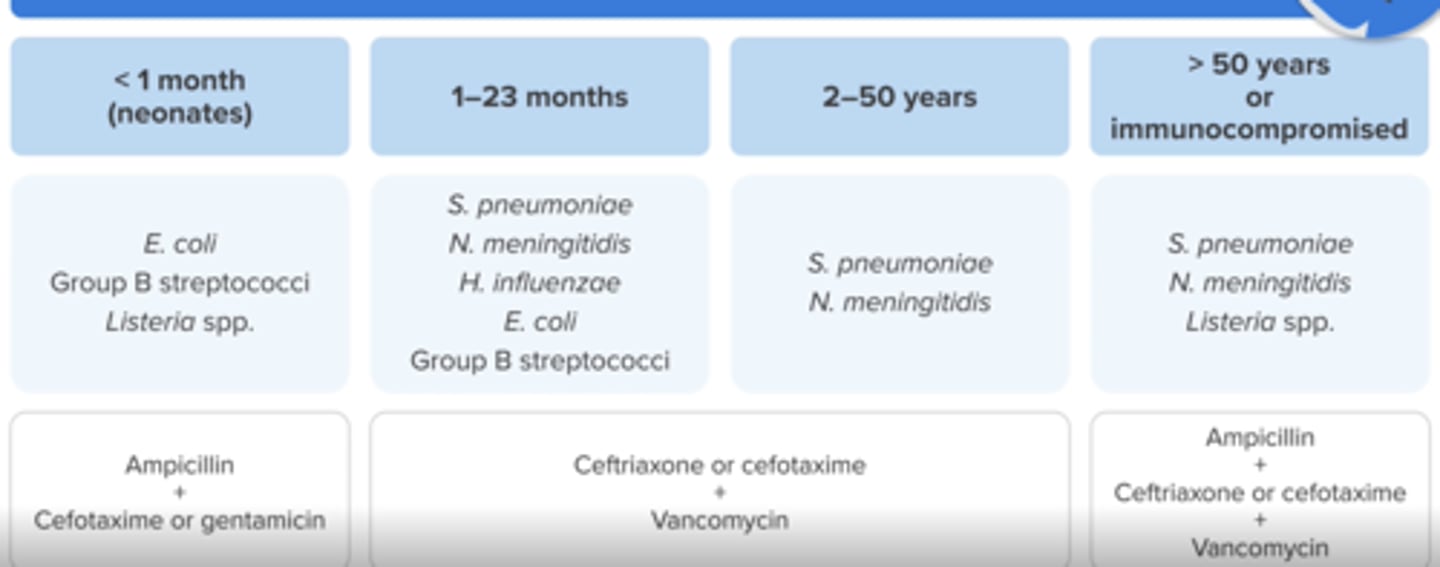
Empiric treatment for bacterial meningitis in ages > 50 or Immunocompromised patients
Ampicillin (for Listeria) + Ceftriaxone or cefotaxime + Vancomycin
What are symptoms of acute otitis media?
bulging tympanic (eardrum), otorrhea (middle ear effusion/fluid), otalgia (ear pain), tugging or rubbing ears, fever and crying
What is an option for non-severe acute otitis media?
Observation without antibioitics for 48 - 72 hours
know when not to observe
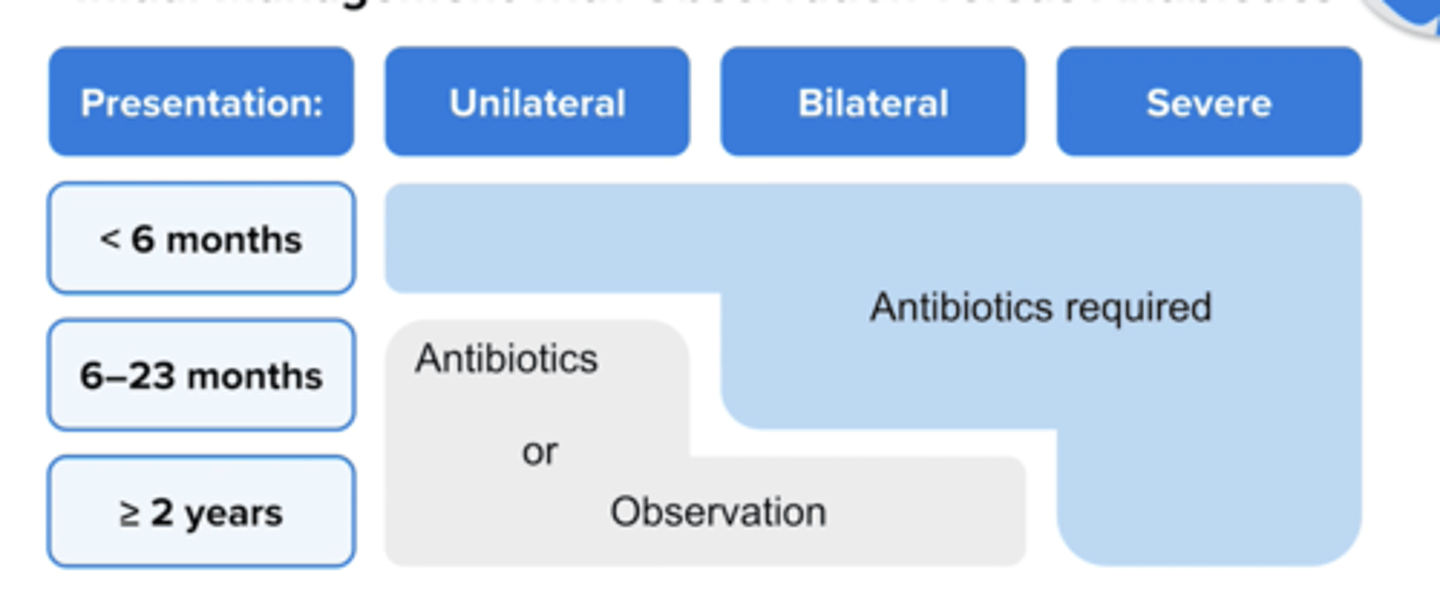
when should you NOT observe (when are abx required) in AOM in kids?
know when not to observe
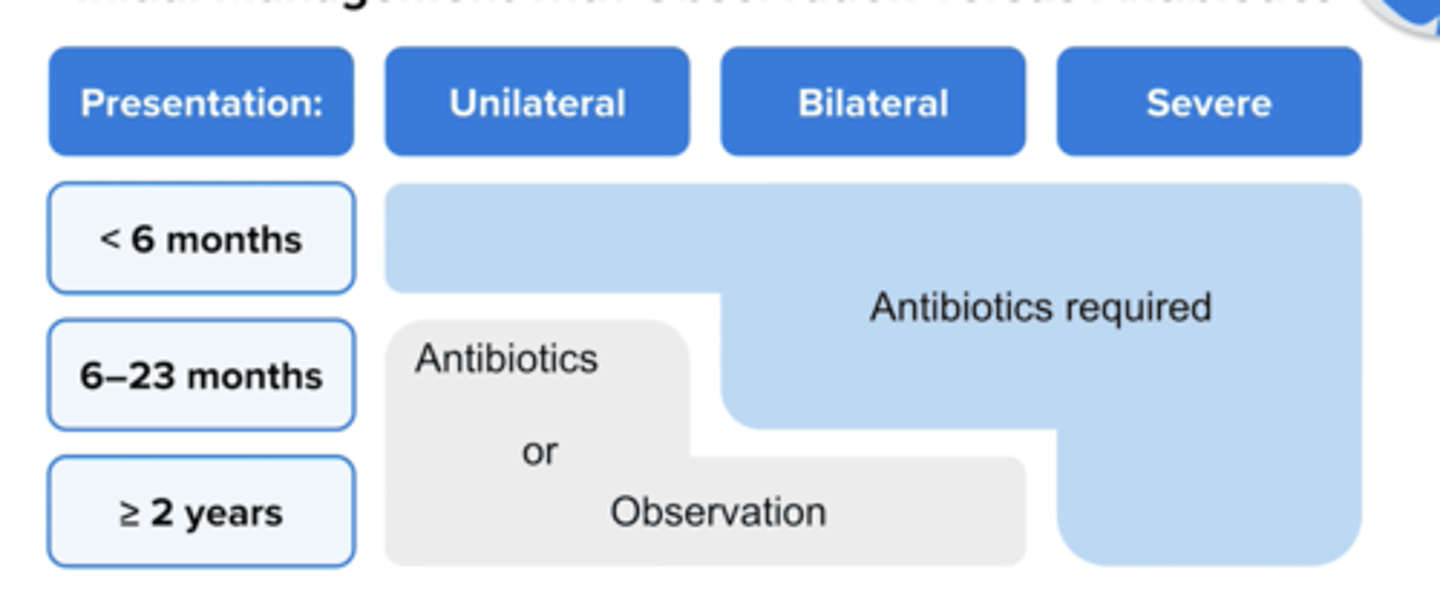
When should you try observation for AOM in children age 6 -- 23 months?
Try for 2 - 3 days if symptoms are non severe (mild otalgia < 48 hours or temperature < 102.2 * F and symptom in one ear only
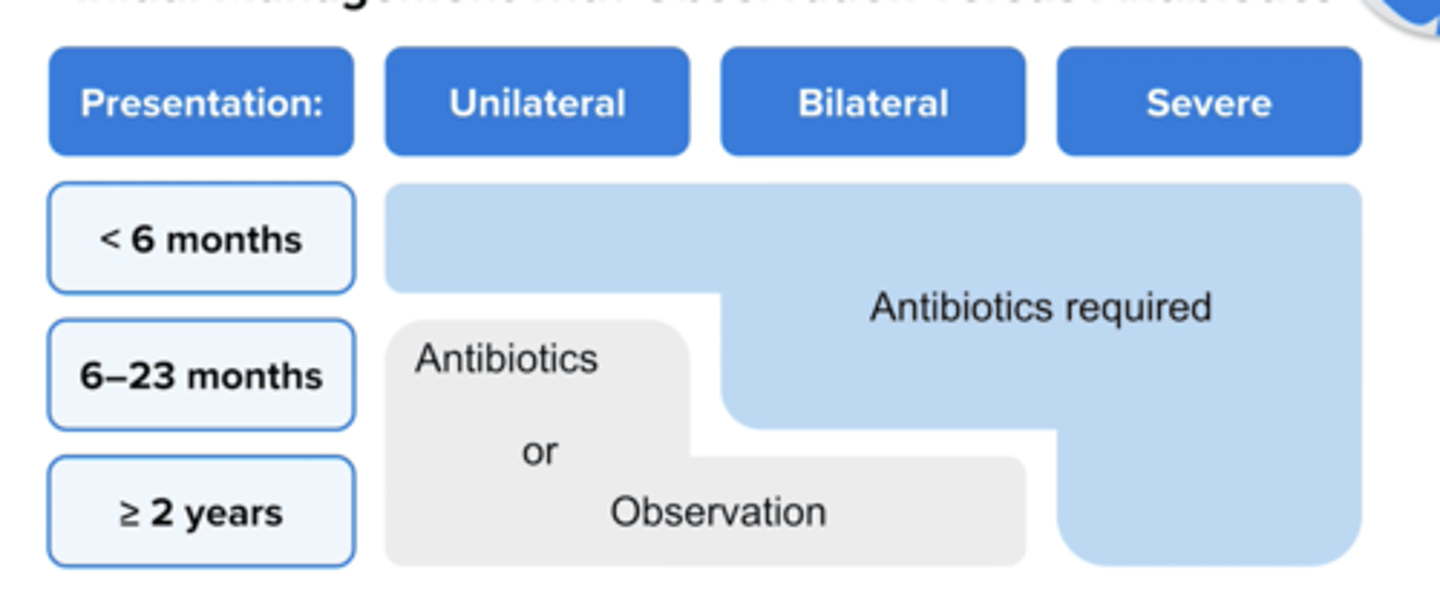
When should you try observation for AOM in children age > 2 years?
Try for 2 - 3 days if symptoms are non severe (mild otalgia < 48 hours or temperature < 102.2 * F and symptom in one or both ears
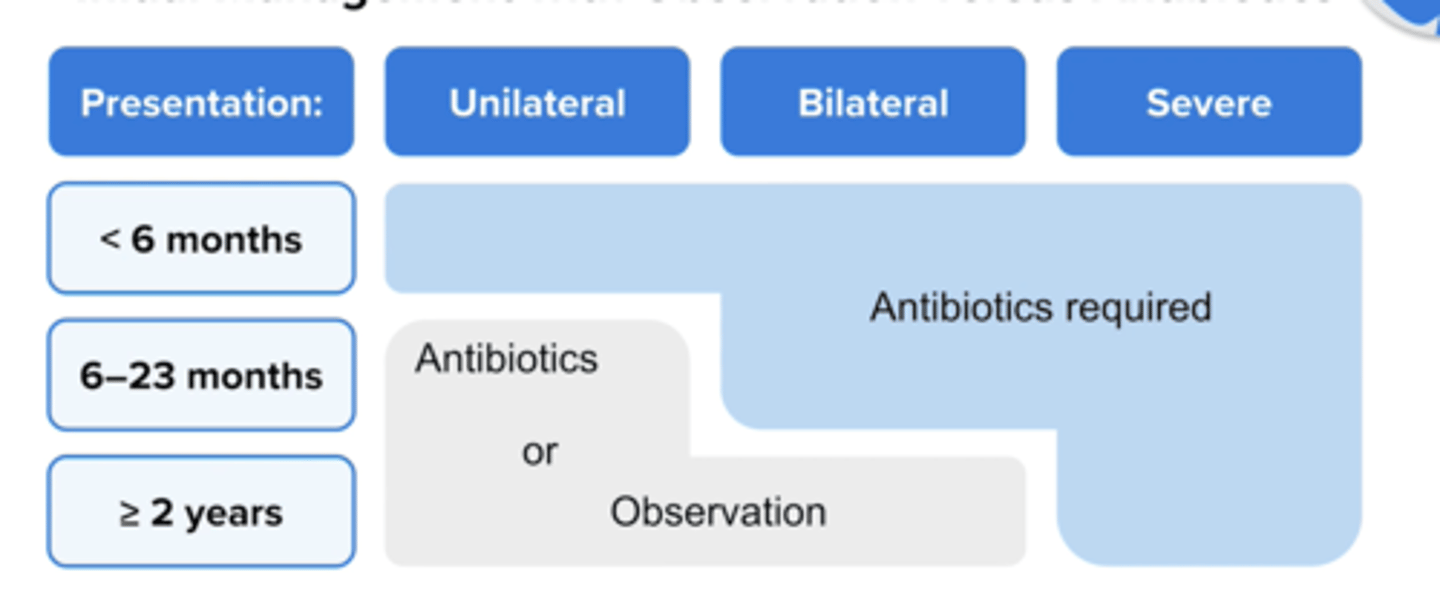
What is First line treatment for Acute Otitis Media in?
Amoxicillin 90 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses or
Amoxicillin/clavulanate 90 mg/kg/day of amoxicillin with 6.4 mg/kg/day of clavulanate in 2 divided doses
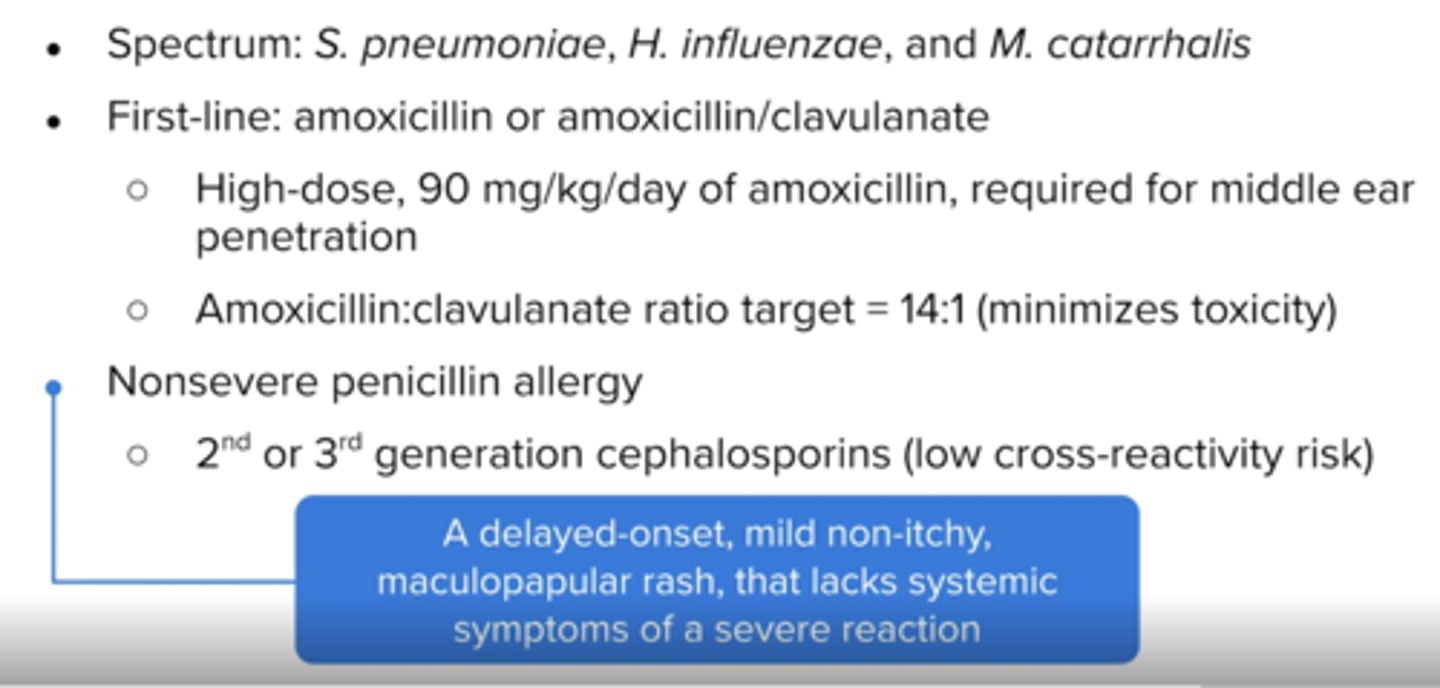
How should amox/clauv be dosed (ratio) for AOM? why?
14:1
minimizes toxicity and diarrhea
What is an alternate treatment for AOM if child has a mild penicillin allergy?
Cefdinir 14 mg/kg/day in 1 or 2 doses
Cefuroxime 30 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses
Cefpodoxime 10 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses
Ceftriazone 50 mg/kg IM/IV daily for 1 or 3 days
not underlined
What is recommended if child fails the first treatment for AOM?
ceftriaxone IM
Clinical presentation of the common cold
sneezing, runny nose, cough, mucus production, sore throat and mild (low-grade) fever
Generally clears up in a few days
tx: symptomatic, no abx/anti viral
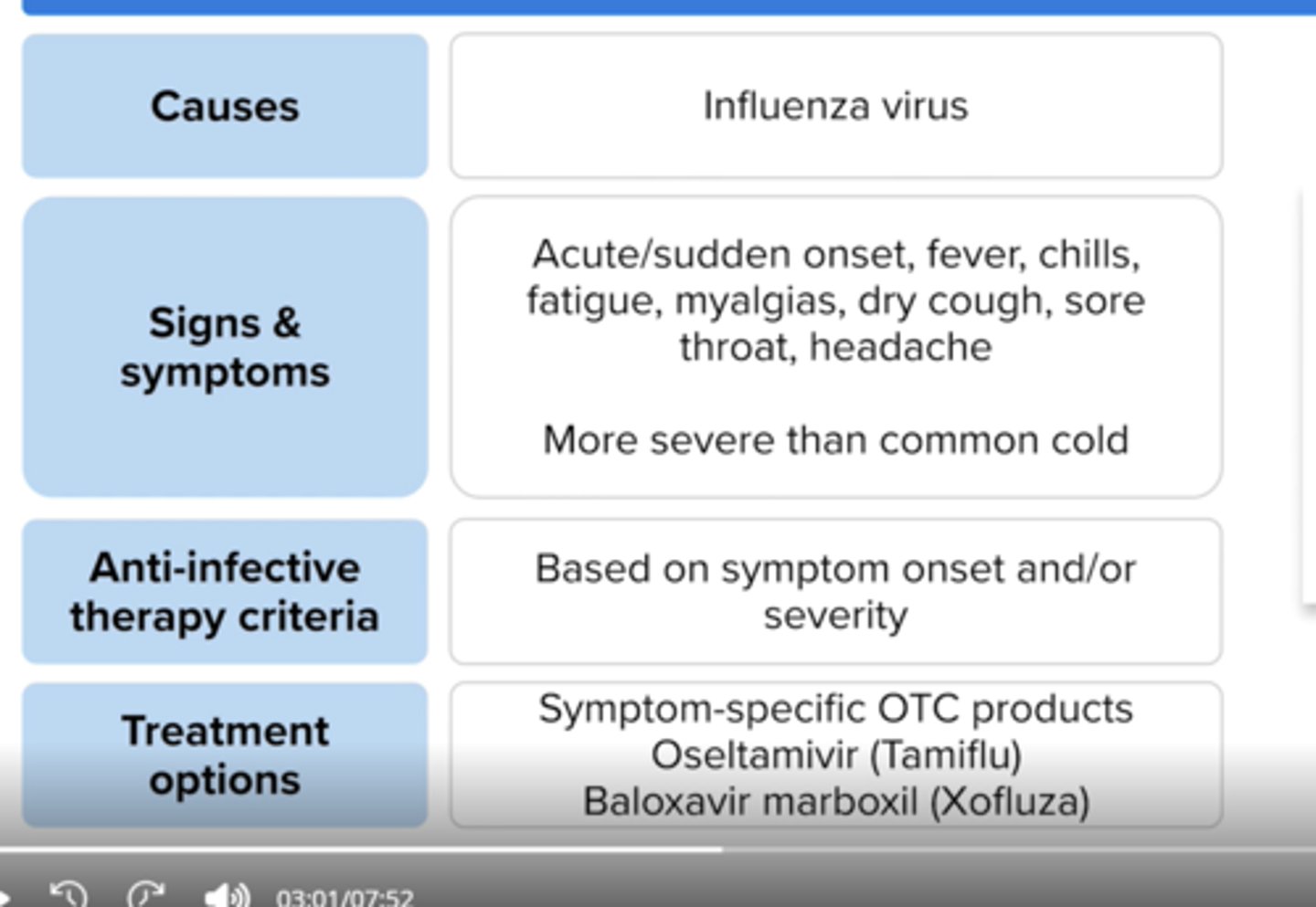
Clinical presentation of influenza
sudden onset fever, chills, fatigue, body aches, dry cough, sore throat and headache
What is the criteria for anti-infective treatment in influenza?
< 48 hours since symptom onset, severe illness (hospitalized), symptoms plus risk factors for influenza complications
Prophylaxis (if high risk for influenza complications or during outbreak scenario)
Treatment options for influenza?
Oseltamivir x 5 days
Baloxavir marboxil x 1 dose
Zanamivir inhalation x 5 days
Peramivir (IV)x 1 dose
Common pathogens in pharyngitis?
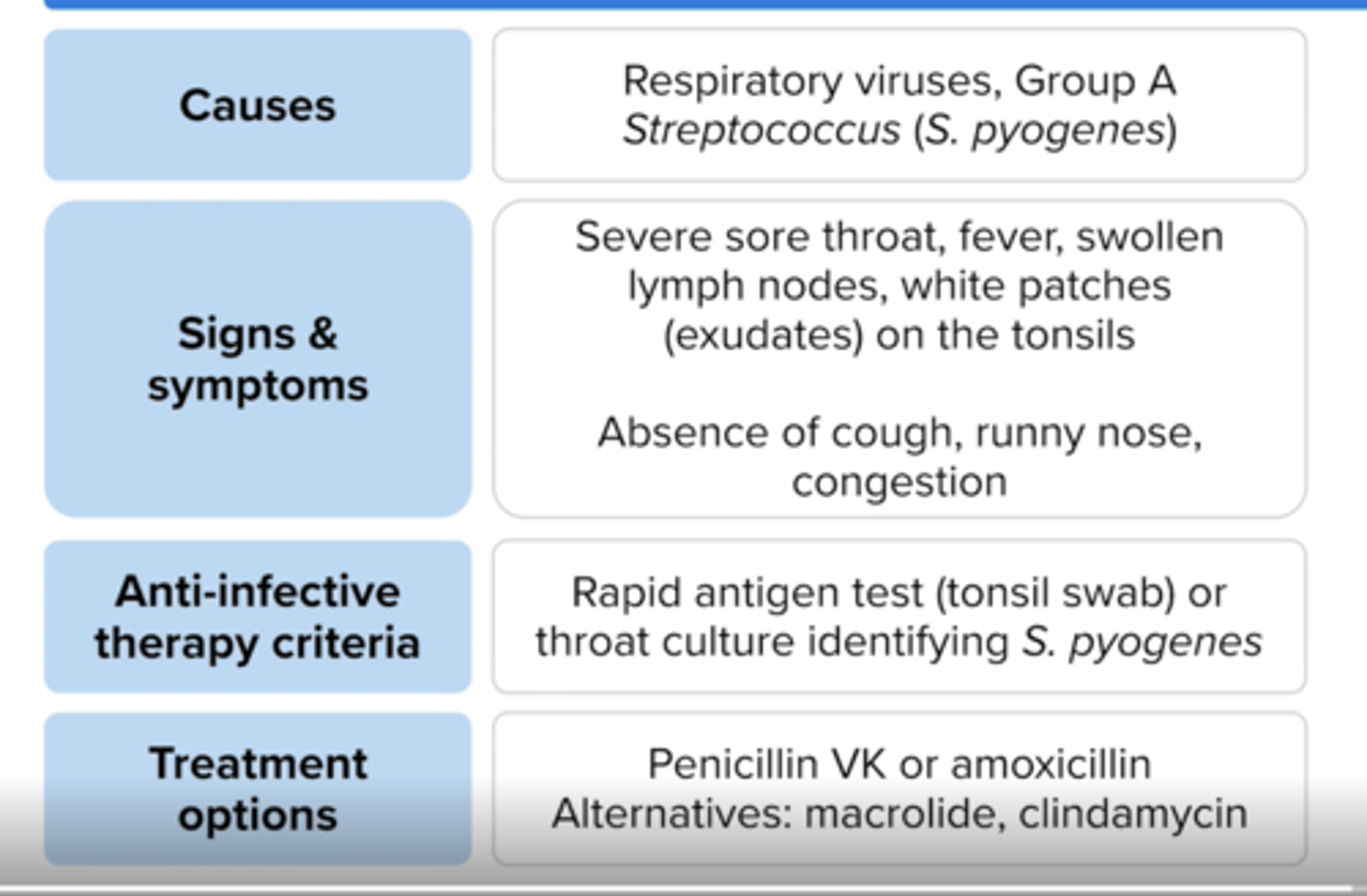
Respiratory viruses
S. pyogenes
aka strep throat
Clinical presentation of pharyngitis?
"Strep throat" often presents with sore throat, swollen lymph nodes and white patches on the tonsils, fever, headache
no cough, runny nose, congestion
Criteria for anti-infective treatment for pharyngitis?
Positive rapid antigen diagnostic test (tonsil swab) or positive S. pyogenes culture
Treatment options for pharyngitis
penicillin VK, amoxicillin or cephalosporin (1st/2nd gen),
if for beta-lactam allergy: clarithromycin, azithromycin, clindamycin
Treat for 10 days, except with azithromycin (5 days)
Common pathogens for sinusitis
Respiratory viruses, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis;
Staphylococci, anaerobes and gram-negative rods can be present in chronic sinusitis
Clinical presentation of sinusitis
nasal congestion, purulent nasal discharge, facial/ear/dental pain or pressure, headache, fever and fatigue
Criteria for anti-infective treatment for sinusitis
> 10 days of symptoms
or
> 3 days of severe symptoms (fever > 102*F, face pain, purulent nasal discharge)
or
Worsening symptoms after initial improvement
Treatment options for sinusitis
First line-- Amoxicillin/clavulanate
Second line- oral 2nd/3rd gen cephalosporing + clindamycin, doxycycline or a respiratory quinolone (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)
what are symptoms of acute bronchitis?
treatment?
non productive cough for 1-3 weeks
chest xray normal, usually virus
abx NOT rec'd -> supportive care
What bacteria cause whooping cough?
Bordetella pertussis
What antibiotic is used for Bordetella pertussis bronchitis?
Macrolide (azithromycin, clarithromycin) or SMX/TMP
What type of bronchitis often requires an antibiotic?
Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (ABECB) aka copd exacerbation
What requirements must be met for Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (ABECB) for antibiotic treatment? (COPD exacerbation)
↑ dyspnea, ↑ sputum volume and ↑ sputum purulence
↑ sputum purulence + 1 additional symptom
Mechanically ventilated
any of the following
Preferred antibiotics for ABECB?
Amoxicillin/Clavulanate, azithromycin, doxycycline, or respiratory quinolone (moxi, levo)
Common symptoms of pneumonia?
fever, cough with purulent sputum, chest pain, rales (cracling noises in the lungs, tachypnea (increased respiratory rate) and decreased breath sounds
What is the gold standard diagnosis for pneumonia?
Chest x-ray and showing "infiltrates", "opacities" or "consolidations" to indicate pneumonia
Common bacteria that cause community acquired pneumonia?
S.pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. pneumoniae and possibly C.pneumoniae
What is the treatment duration for CAP?
5 - 7 days
What comorbities require broader coverage in pneumonia?
Comorbidities like chronic heart, lung, liver or renal disease; diabetes; alcoholism; malignancy or asplenia
What risks require coverage for Pseudomonas or MRSA in pneumonia?
Prior respiratory infection of either patogen or hospitilazation with receipt of parenteral antibiotics in the past 90 days
Treatment recommendation for outpatient CAP in patients with no comorbidities?
Amoxicillin high dose (1 gram TID), or
Doxycycline, or
Macrolide (azithromycin or clarithromycin) if resistance is < 25 %

Treatment recommendation for outpatient CAP in patients with comorbidities?
Beta lactam + macrolide or doxycycline (amoxicillin/clavulanate or cephalosporin (e.g., cefpodozime, cefuroxime) plus macrolide or doxycyline
or
Respiratory quinolone monotherapy (moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin or levofloxacin)

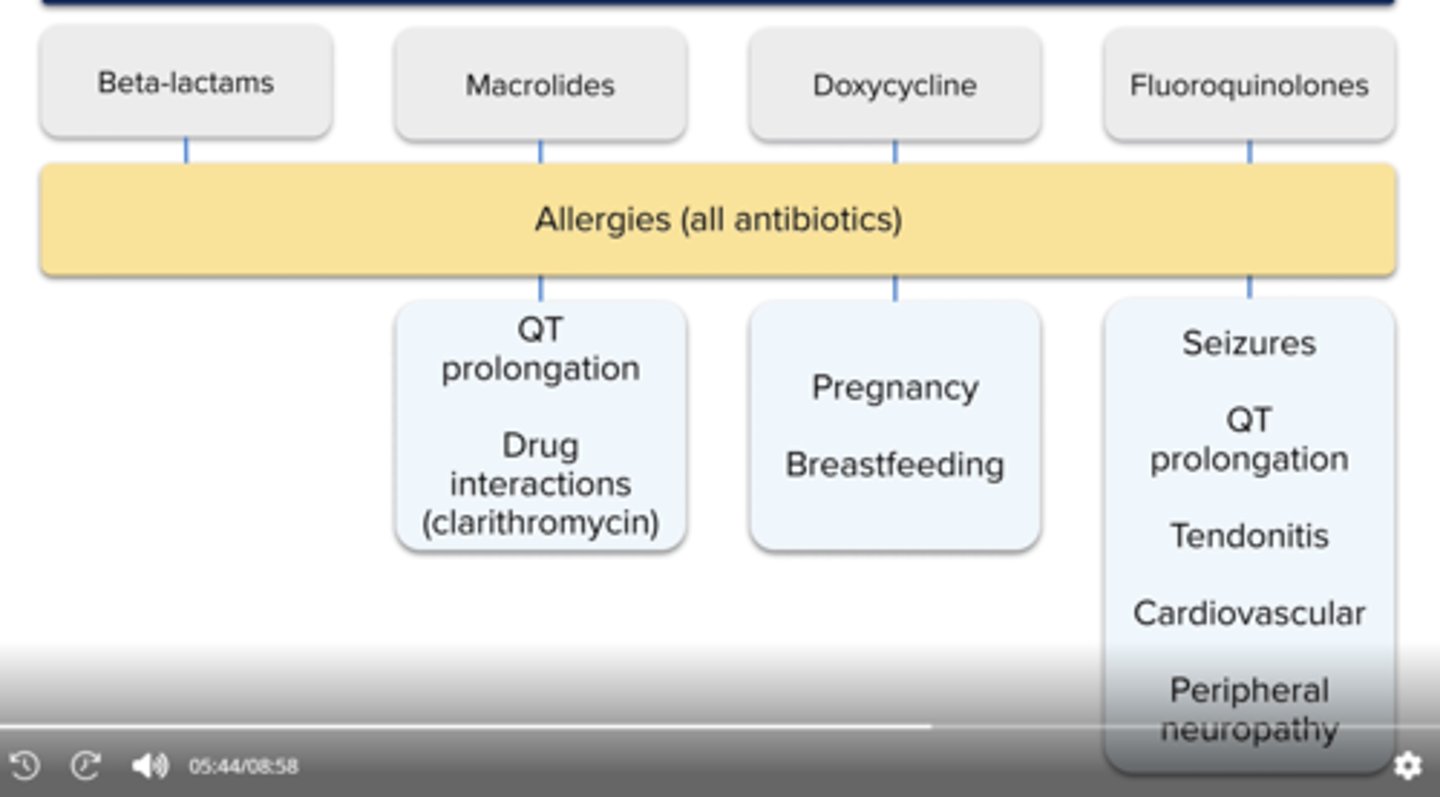
Drug specific risks when evaluating CAP therapy
macrolides
doxy
fqs
all: allergies
macorlides (eg. azith): qt prolong, drug interactions (clarith mainly)
doxy: good for risk of qt prolon pts. dont use in preg, breastfeeding
fqs: szs, qt prolong, tendonitis, cardiovascular, peripheral neuropathy, avoid also in preg
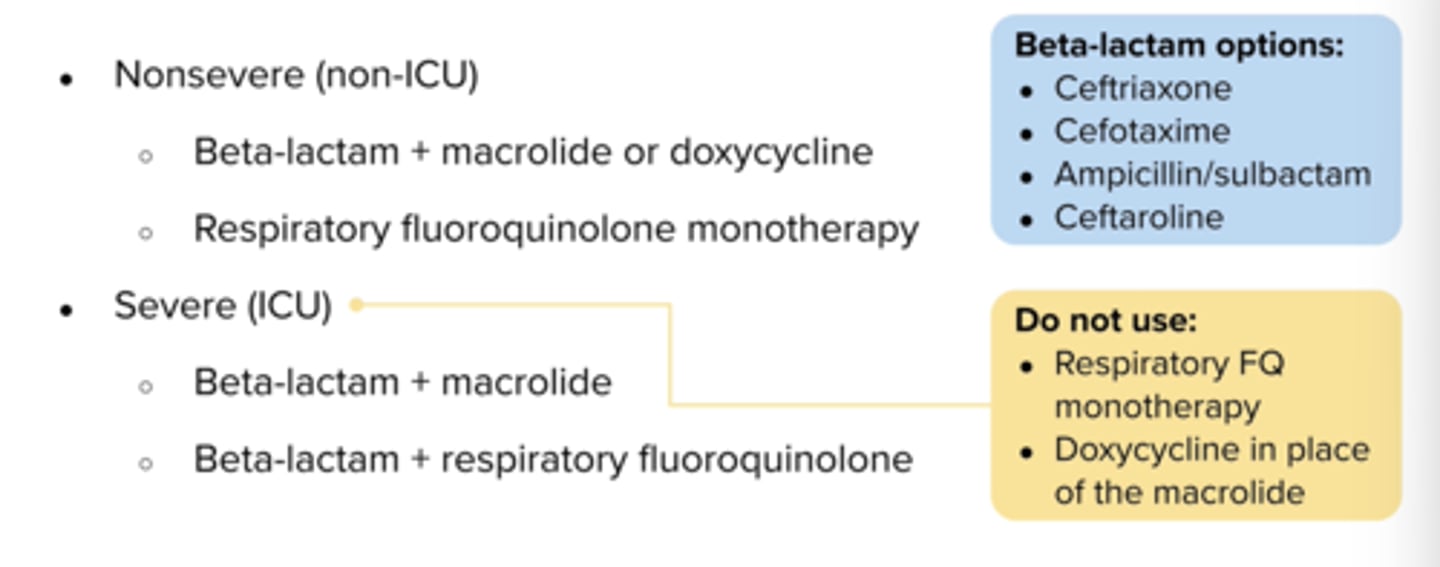
What are treatment options for Non-severe Inpatient CAP (gem med unit)?
Beta-lactam + macrolide or doxycycline (beta-lactams: ceftriaxone, ceftaroline or ampicillin/sulbactam)
or respiratory quinolone monotherapy
What are treatment options for Severe (ICU) Inpatient CAP?
Beta lactam + macrolide or
Beta lactam + respiratory quinolone
do not use quinolone monotherapy!!in
RP is a 46 year old female who presents to the urgent care clinic with shortness of breath productive cough and a temperature of 100.8. A chest X ray reveals a left lower lobe infiltrate. Her path metal history includes back pain and schizophrenia. She has a penicillin allergy (hives). Her scheduled medications include GEODON 40, Trazodone 50.
Which empiric antibiotic regimen should RP receive for cap?
No comorbidities (heart,lung, liver, renal dx, dm, alcohol use) - not at risk so s.pneumo - > healthy category
pencillin allergy -> avoid amoxicillin
macrolides can prolong wt -> avoid d/t use of geodon, trazodone (both can qt prolong)
which leaves doxycyline as the correct choice
inpatient CAP treatment:
risk factors for mrsa
pseudomonas
if hopsitalization and use of IV abx in past 90 days
MRSA: add vanc or linezolid
pseudomonas: add pip/tazo, cefepime, meropenem
if hopsitalization, use of parenteral abx in past 90 days: cover both mrsa and pseudomonas
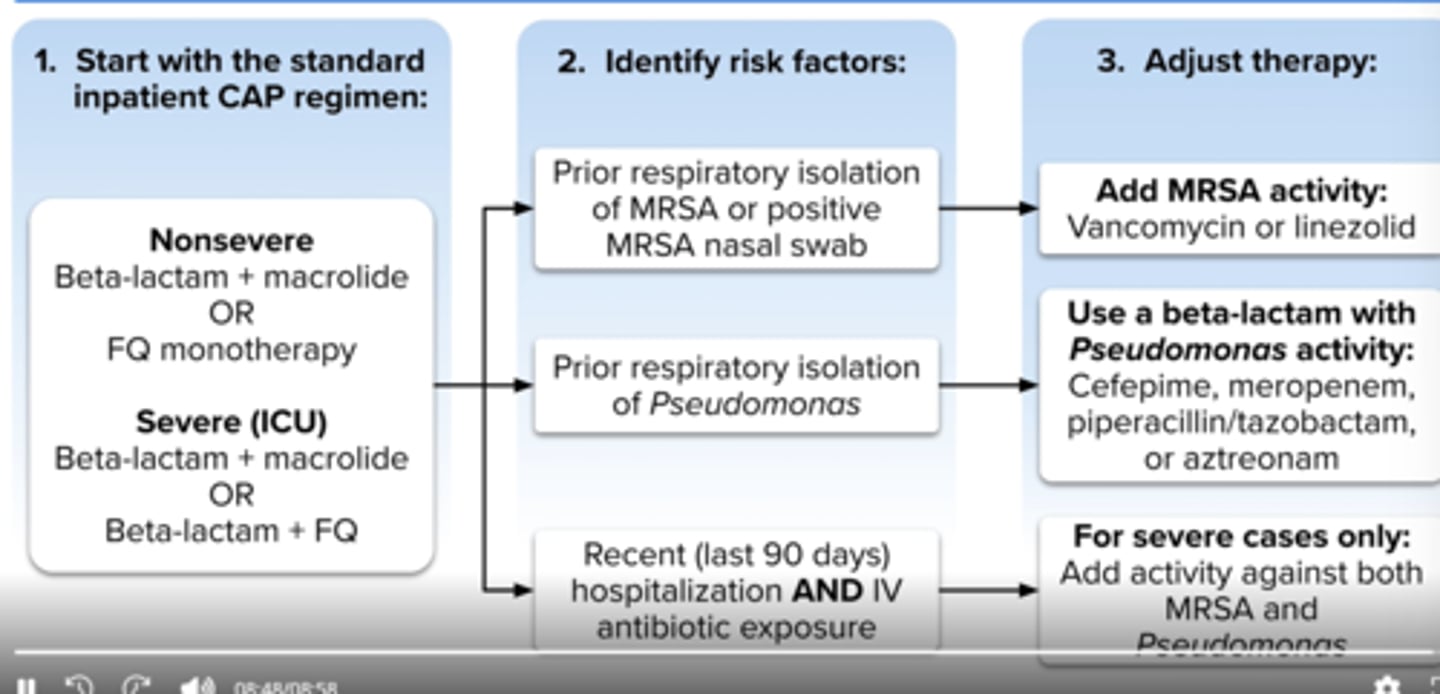
What is hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP)?
pneumonia occurring 48 hours or longer after hospital admission
What is ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP)?
pneumonia that occurs at least 48 hours after the start of mechanical ventilation
Common pathogens in HAP and VAP
Nosocomial pathogens (increase risk for MRSA and MDR pathogens including P.aeruginosa, Acinetobacter, Enterobacter, E. coli and Klebsiella
What should not be used done when picking Pseudomonas treatment in HAP/VAP?
Do not use two beta-lactams together
HAP/VAP treatment:
all pts
risk for mrsa
risk for pseudomonas
abx for pseudomonas/mssa
-cefepime, pip/tazo, levofloxacin (BL allergy)
mrsa: add vanc or linezolid
Pseudomonas: use two abx (not two beta lactams)
-BLs (piptazo, cefepime, ceftazidime, merrem)
-levo/ciprofloxacin
-aztreonam
-aminoglycosides (tobramycin,gentamicin)

What bacteria causes tuberculosis?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
What are the symptoms in latent tuberculosis?
TB is latent so patient lacks symptoms
What are symptoms of active TB?
cough/hemoptysis
purulent sputum
fever/night sweats
unintentional weight loss
How is TB spread?
transmitted by aerolized droplets
How is latent TB diagnosed?
tuberculin skin test or PPD test
What is a PPD test?
purified protein derivative is injected intradermally and then the area is inspected for induration 48 -- 72 hours later
What can cause a false positive TB test?
If the patient received a BCG vaccine
in which populations is > 5 mm induration a positive result?
Close contacts of recent TB cases
Significant immunosuppression (e.g., HIV, taking transplant medications)

in which populations is > 10 mm induration a positive result?
Recent immigrants
IV drug users
Moderate immunosuppression
Residents/employees of "high risk" congregate settings (e.g., prison inmates, healthcare workers)

in which populations is > 15mm induration a positive result?
Patients that have no risk factors

What is preferred for Latent TB treatment?
Short regimens (3 or 4 months) are preferred for Latent TB due to higher completion rates and less hepatotoxicity risk
which medications are treatment for latent TB? + duration of therapy
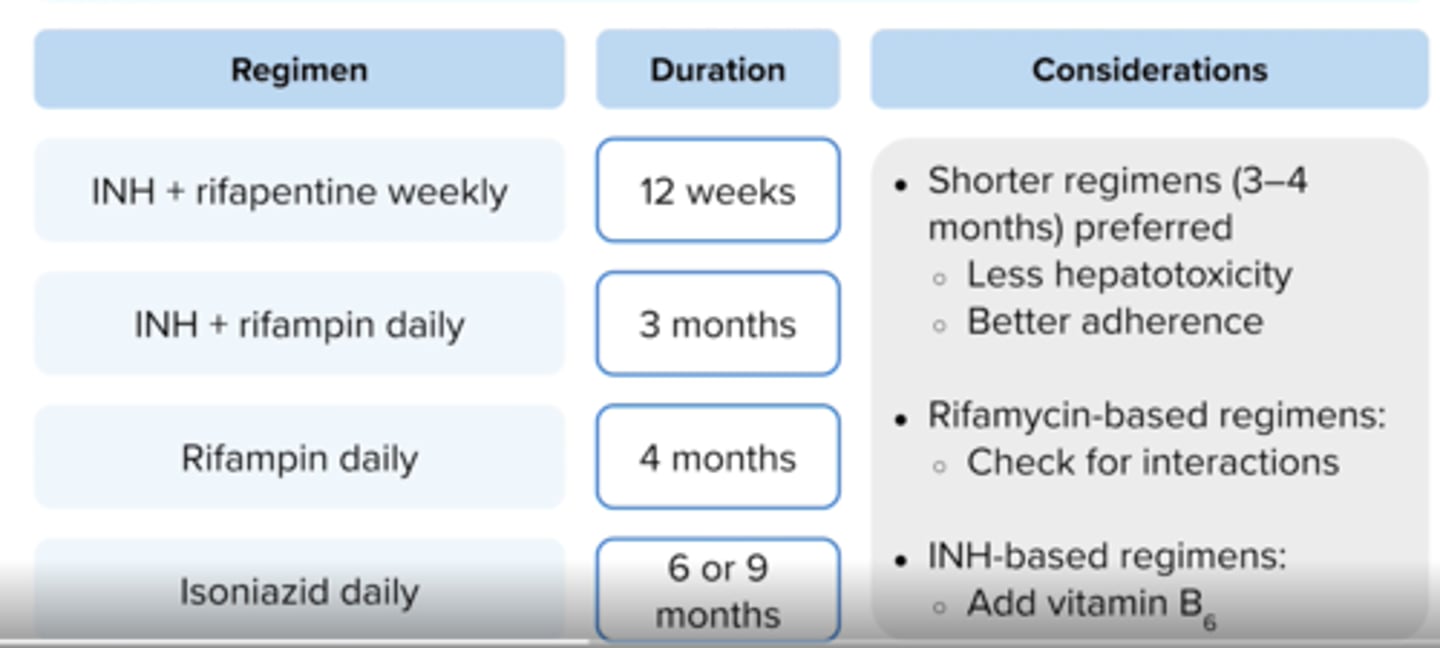
Which latent TB treatment should NOT be used in pregnancy?
inh + rifapentine
what should be added to treatment in latent tb patient is taking and INH regimen?
add vit b6 to reduce risk for peripheral neuropathy
which duration of treatment regimen is preferred in latent tb?
shorter (3-4 months) decreases risk for hepatotoxicity and increases completion rates
which latent TB treatment is preferred in HIV+ pts taking art?
INH qd for 6-9 months
What is a preferred treatment for Laten TB in pregnant patients?
INH for 9 months
How is active TB diagnosed?
postive TST and confirmed with AFB stain in the lab
What therapy is used for initial phase of active TB?w
RIPE therapy- (rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for 2 months
What is the continuation phase for Active TB treatment?
2 drugs (commonly rifampin and isoniazid for 4 months)
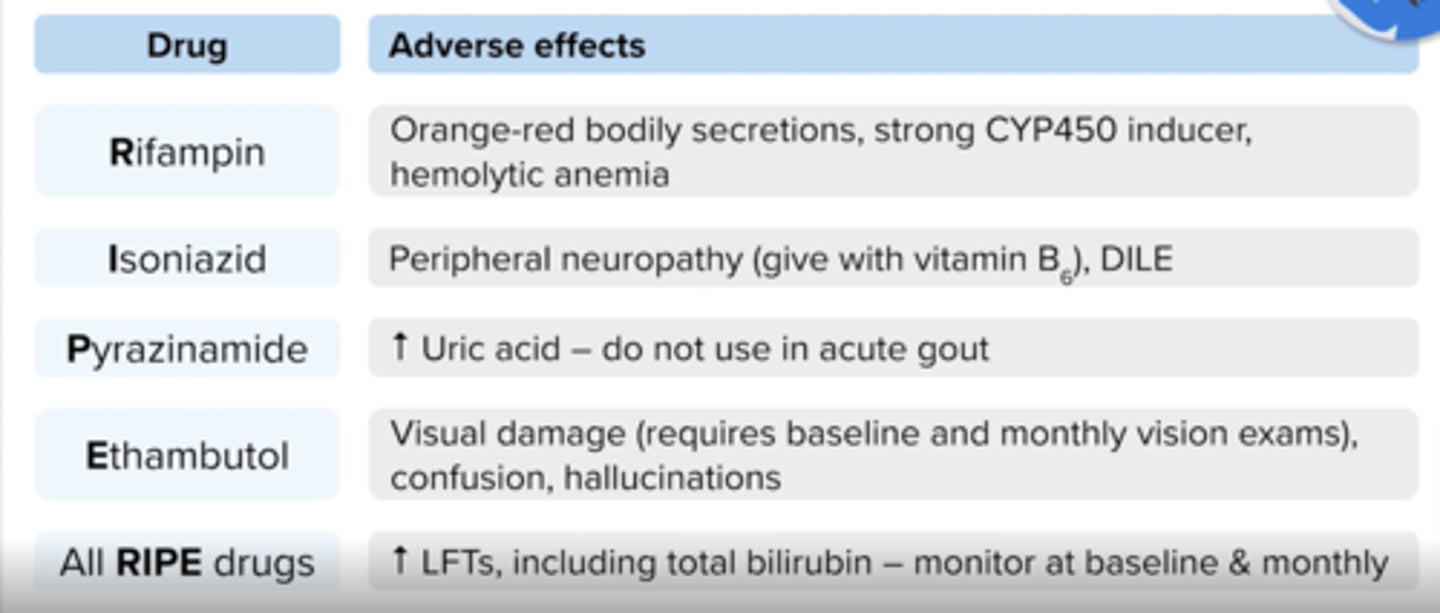
What are side effects of Rifampin?
↑ LFTs, hemolytic anemia (detected with a positive Coombs test), flu-like syndrome, GI upset, rash pruritus
Orange-red discoloration of body secretions (sputum, urine, sweat, tears, teeth); can stain contact lenses, clothing and bedsheets
what is the issue with using rifampin in treatment of TB?
many drug interactionsv-> can use rifabutin (eg. pt using protease inh)
What is used to prevent peripheral neuropathy in Isoniazid?
Pyridoxine (vitamin b6) 25 - 50 mg
Boxed warning for isoniazid
severe and fatal hepatitis
Side effects of Isoniazid (INH)?
↑ LFTs, drug-induced lupus erythematosus (DILE), hemolytic anemia (detected with a positive Coombs test), agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hyperglycemia, headache, GI upset, pancreatitis, severe skin reactions (SJS/DRESS), optic neuritis
What are contraindications for Pyrazinamide?
Acute gout, severe hepatic damage
side effects of pyrazinamide
↑ LFTs, hyperuricemia/gout, GI upset, malaise, arthralgias, myalgias, rash
Side effects for Ethambutol (Myambutol)?
↑ LFTs, optic neuritis (dose related), ↓ visual acuity, partial loss of vision/blind spot and/or color blindness (usually reversible), rash, headache, confusion, hallucinations, N/V
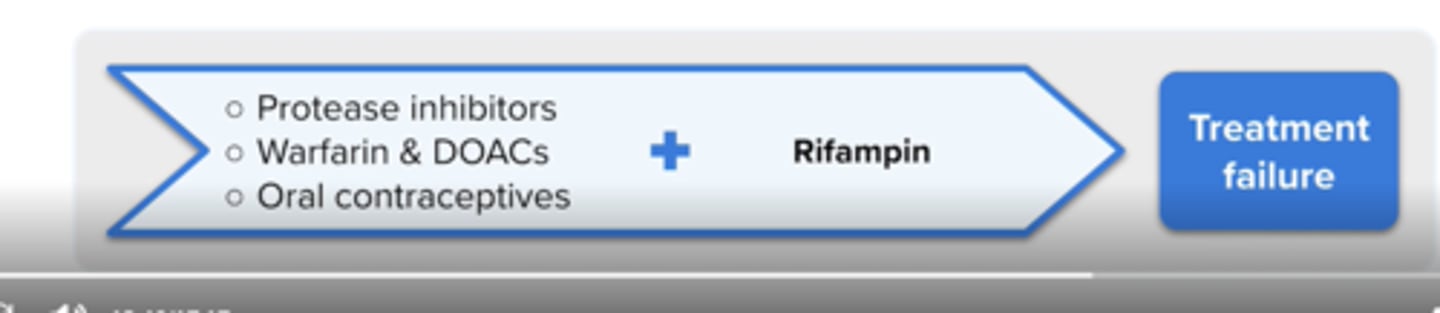
Why does Rifampin have many drug interactions?
It is a potent inducer of CYP450,1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 3A4 and P-glycoprotein
Rifampin can decrease the effects of?
Protease Inhibitors
Warfarin
Oral Contraceptives
Don't use with apixaban, rivaroxaban, edoxaban, or dabigatran
RIPE key safety features (side effects)
What is endocarditis?
inflammation of the inner lining of the heart and valves
Who is at greater risk for endocarditis?
Patients who have prosthetic heart valves, chronic IV access, IV drug abuse or frequent and chronic healthcare exposure
The common organisms in endocarditis are?
Staphylocci, Streptococci and Enterococci
What drug is added for synergy in endocariditis?
Gentamicin is added when infection is more difficult to eradicate