ID Lecture 5: Clinical Microbiology Lab Data | Quizlet
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Colonization
occurs when organisms inhabit a specific site but do NOT cause signs and symptoms of infection
Contamination
occurs when bacteria are accidentally introduced into a specimen during collection, transport, or processing
Infection
occurs when an organism invades a specific site and evokes a host immune reponse
What are some reasons to run cultures?
Identify infection
Source control
Confirm coverage of antimicrobials
Refine therapy based on susceptibility
What are some reasons NOT to run cultures?
Illnes is predictive of infectious source and the pathogen is readily predictable
Getting a good culture is painful/difficult
What are some limitations of microbiological lab tests?
May not identify pathogens
Organisms identified may not be causing the illness
What are the various microbiology lab tests?
Gram stain
Culture
Susceptibility testing
What does a gram stain tell us about a bacteria?
Morphology
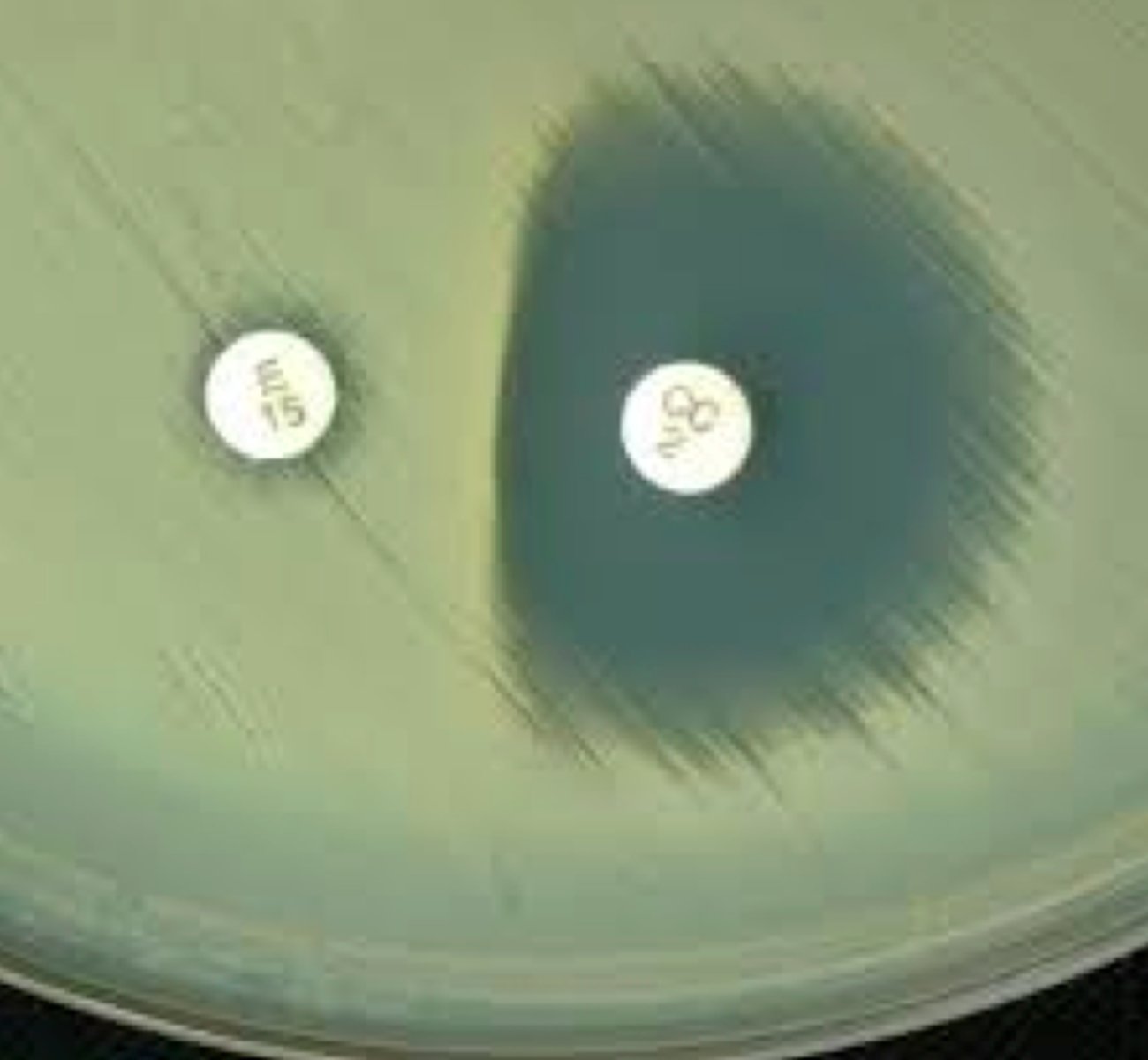
What is the D-test?
detects if S. aureus is resistant to Clindamycin if it is alredy resistant to Macrolides
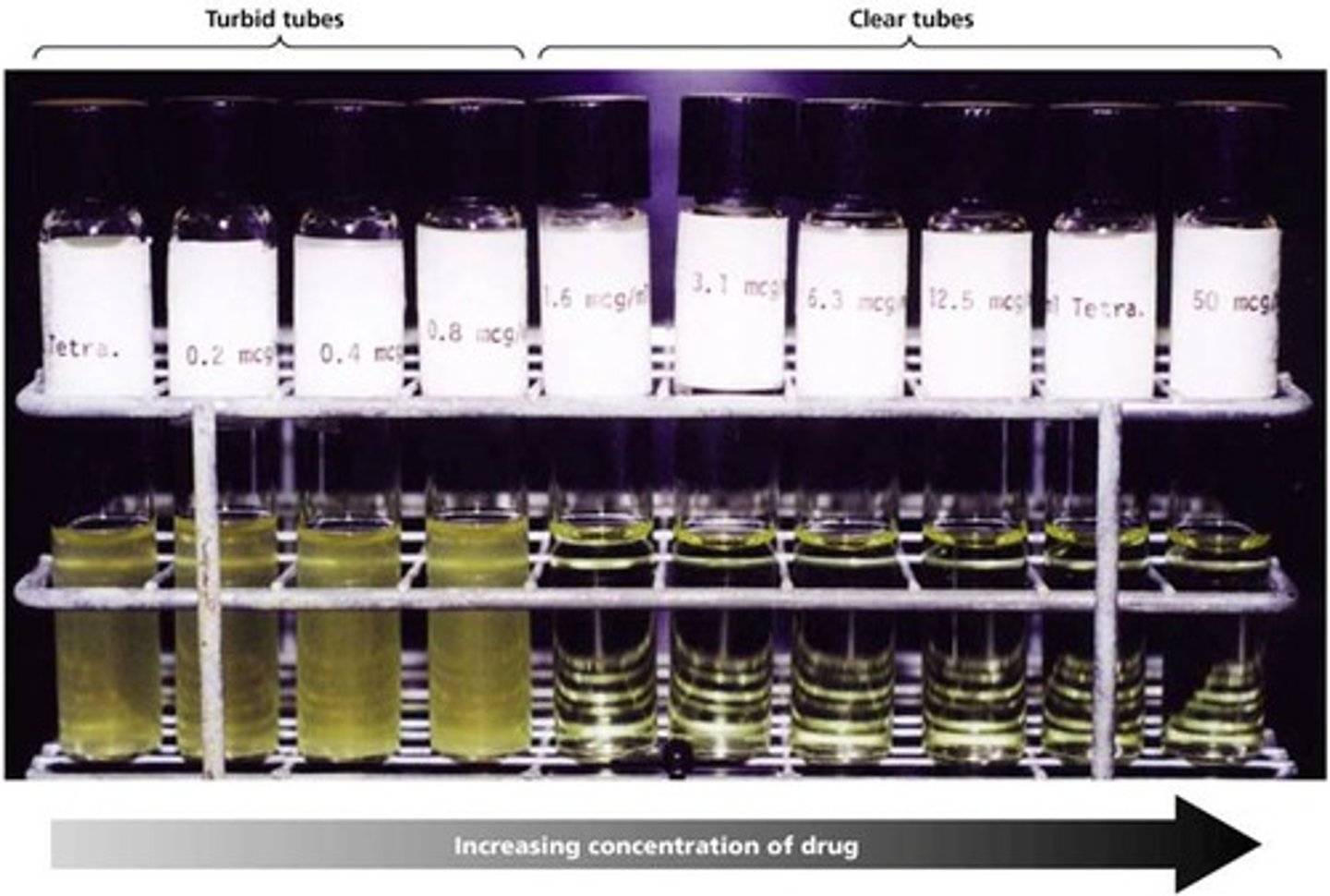
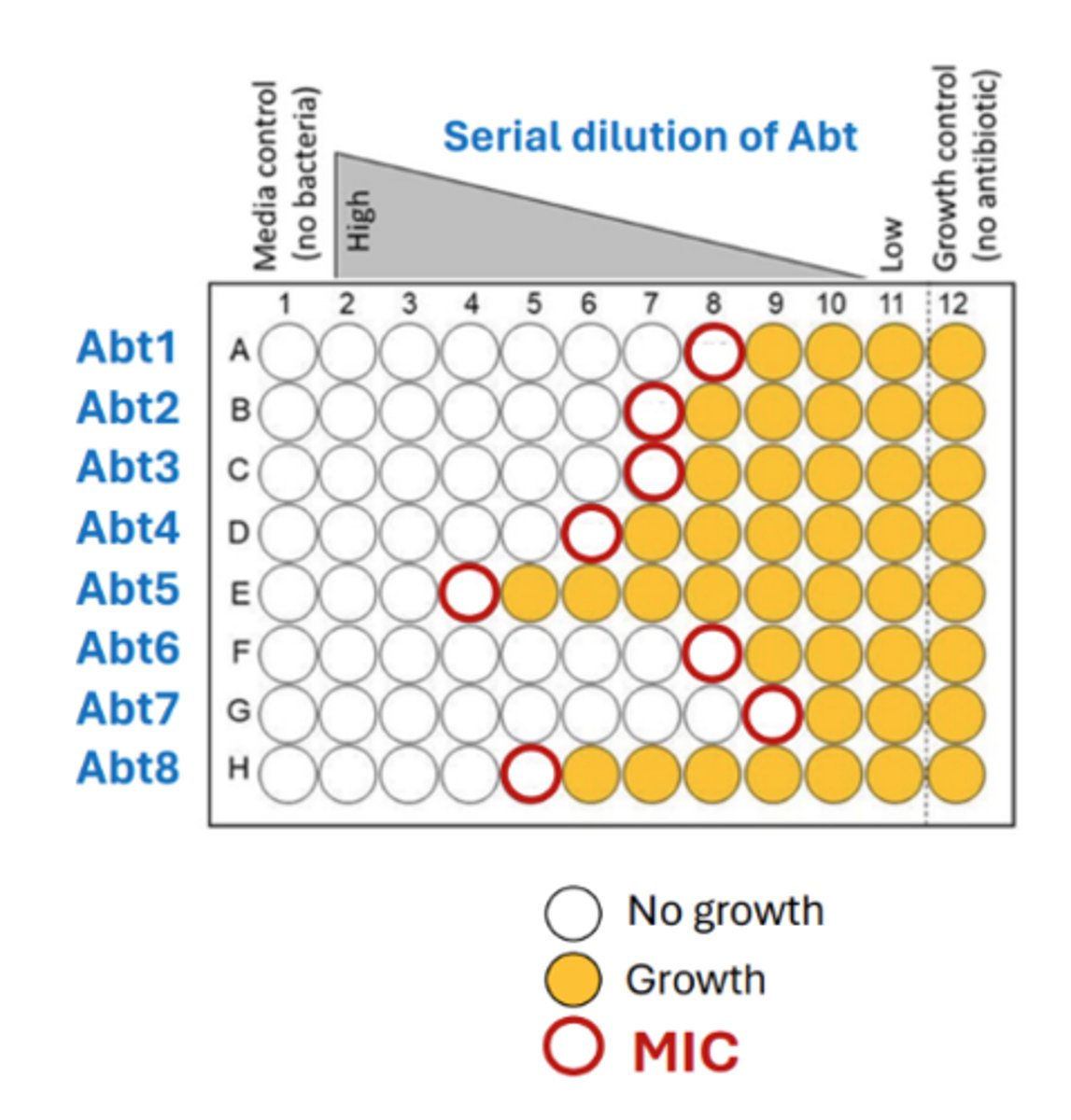
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
the smallest concentration (highest dilution) of drug that visibly inhibits growth

What are the broth dilution methods used to determine an MIC?
Macro and Microdilution
What is Macrodilution?
broth dilution where serial twofold dilutions of an antibiotic are placed in a liquid growth media
What are the pros and cons of a macrodilution MIC?
Pros - provides an EXACT MIC
Cons - resource and labor-intensive
What is Microdilution?
like macrodilution, but in a smaller volume of broth on smaller trays
What are the pros and cons of microdilution?
Pros
- can test susceptibility to multiple antibiotics
- easy to use
- quicker results
- decreased labor and costs
Cons
- limited number of antibiotics and concentrations in trays
- abx concentrations are limited
- MIC a range instead of being exact
Breakpoint
concentration of drug that is readily achievable in SERUM using standard doses of antibiotic
used with MIC to determine susceptibility
MIC < BP
Susceptible
MIC = BP
Intermediate
MIC > BP
Resistant
Antibiogram
cumulative report of the most commonly isolated pathogens in an institution along with their susceptibilities
What are the limitations to antibiograms?
Duplicate isolates reported
Number of isolates reported
Collection bias (inpt vs outpt)
Whole hospital antibiogram may not reflect unit specific patterns