Barriers and compartments
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What does connective tissue consist of?
cells(Fibroblast, adipocytes,macrophages, mast cells ) +
extracellular matrix (collagen, elastin)
What type of collagen are reticular fibres made up of?
Type III
What is the point at which the trachea bifurcates called?
Carina T4/5
What is the difference between regular and irregular dense connective tissue?
Regular dense CT - collagen fibers are arranged parallel to each other with fibroblasts and strength is in 1 direction
Irregular dense CT - collagen fibers are arranged randomly and strength is in multiple directions
Difference between loose and dense connective tissue?
Loose is widely spaced with collagen and elastin and dense is tightly packed by collagen fibres
Skeletal muscle
striated and voluntary
Location: muscle attached to bone
cardiac muscle
involuntary, striated
Location: heart
smooth muscle
involuntary, non-striated
Controls movement of hollow organs
Why does the trachea have c shaped cartilage?
Support and to allow it to move
Structure of tube in digestive tract (from the outside)
Adventitia
Smooth muscle
Submucosa
Mucosa
Lumen
What cells are found in the stomach?
Patietal (oxynitic) cells: produces HCl
Chief (Zymogenic) cells: produces enzymes
Endocrine cells: produces hormones
Where is the appendix located?
Outgrowth of the caecum
What cells make up cartilage?
Chondocytes
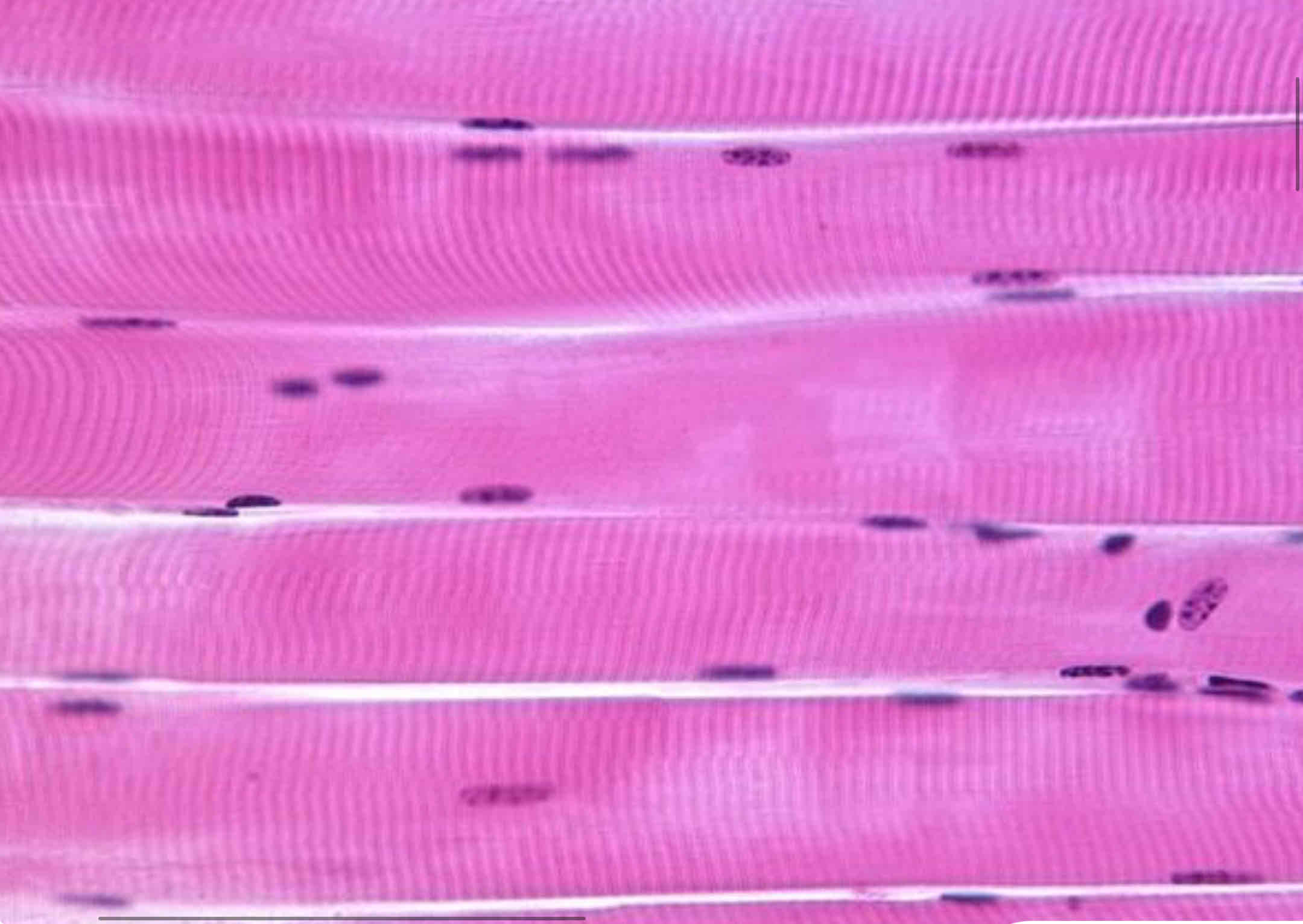
Skeletal muscle
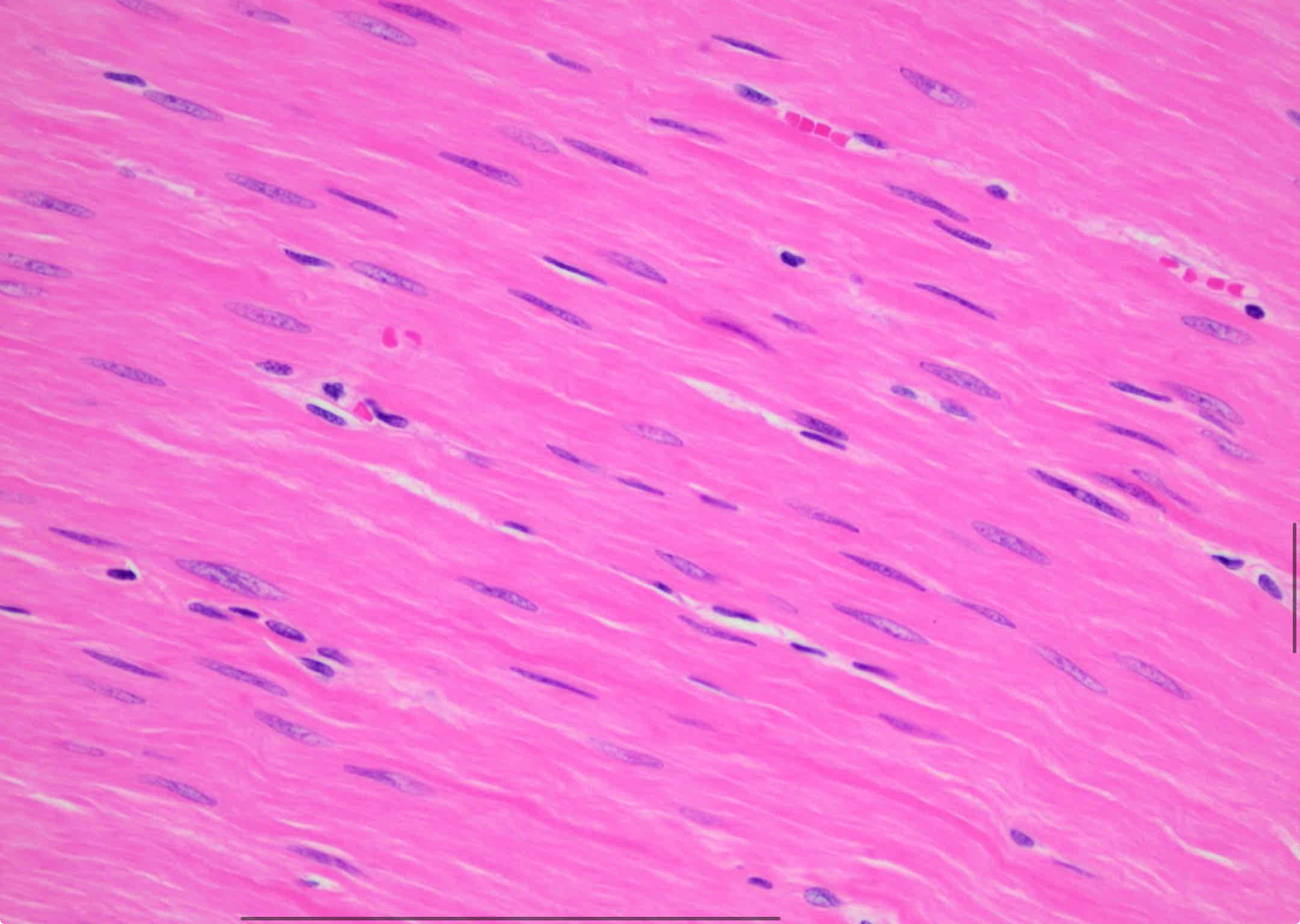
Smooth muscle
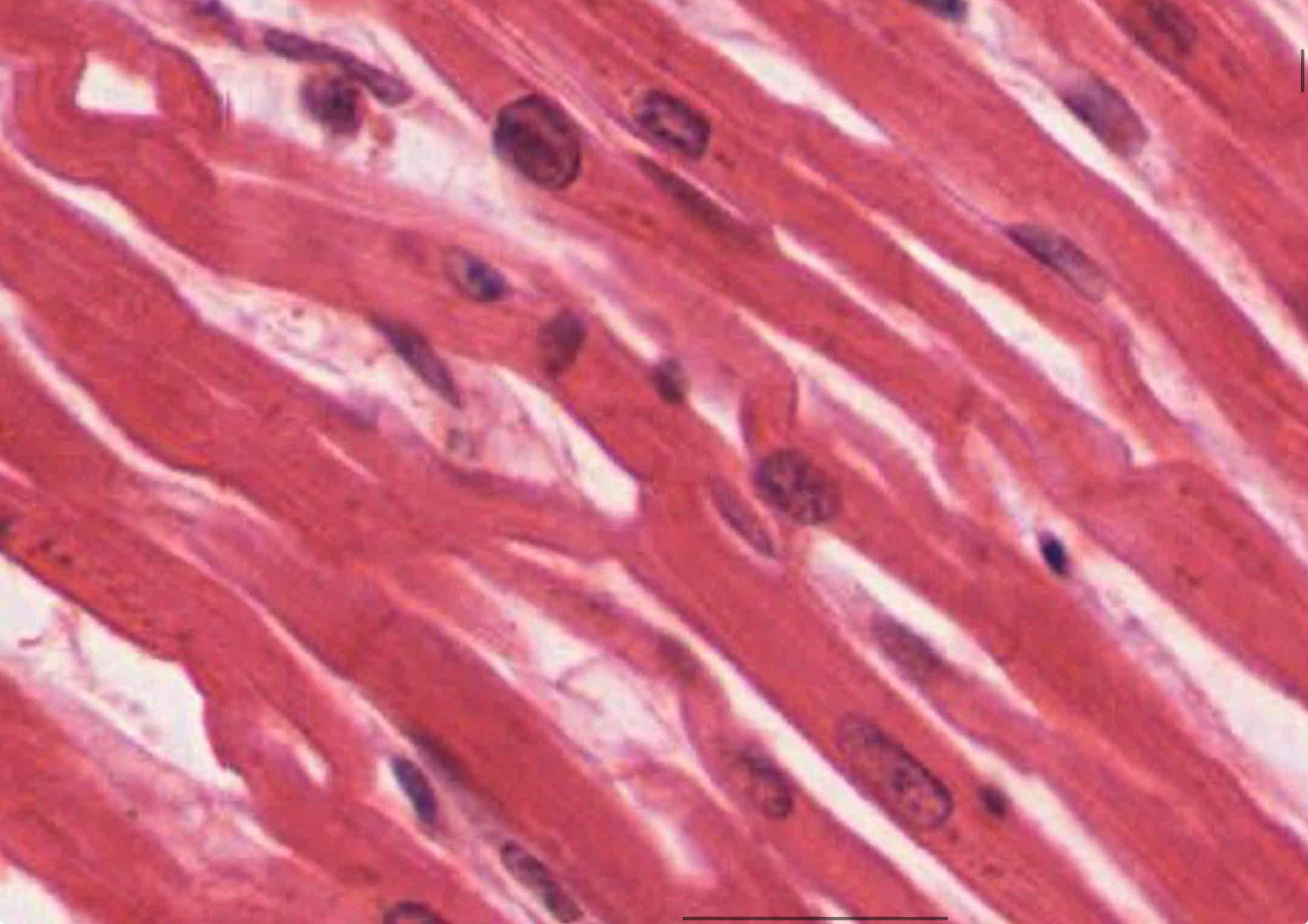
Cardiac muscle
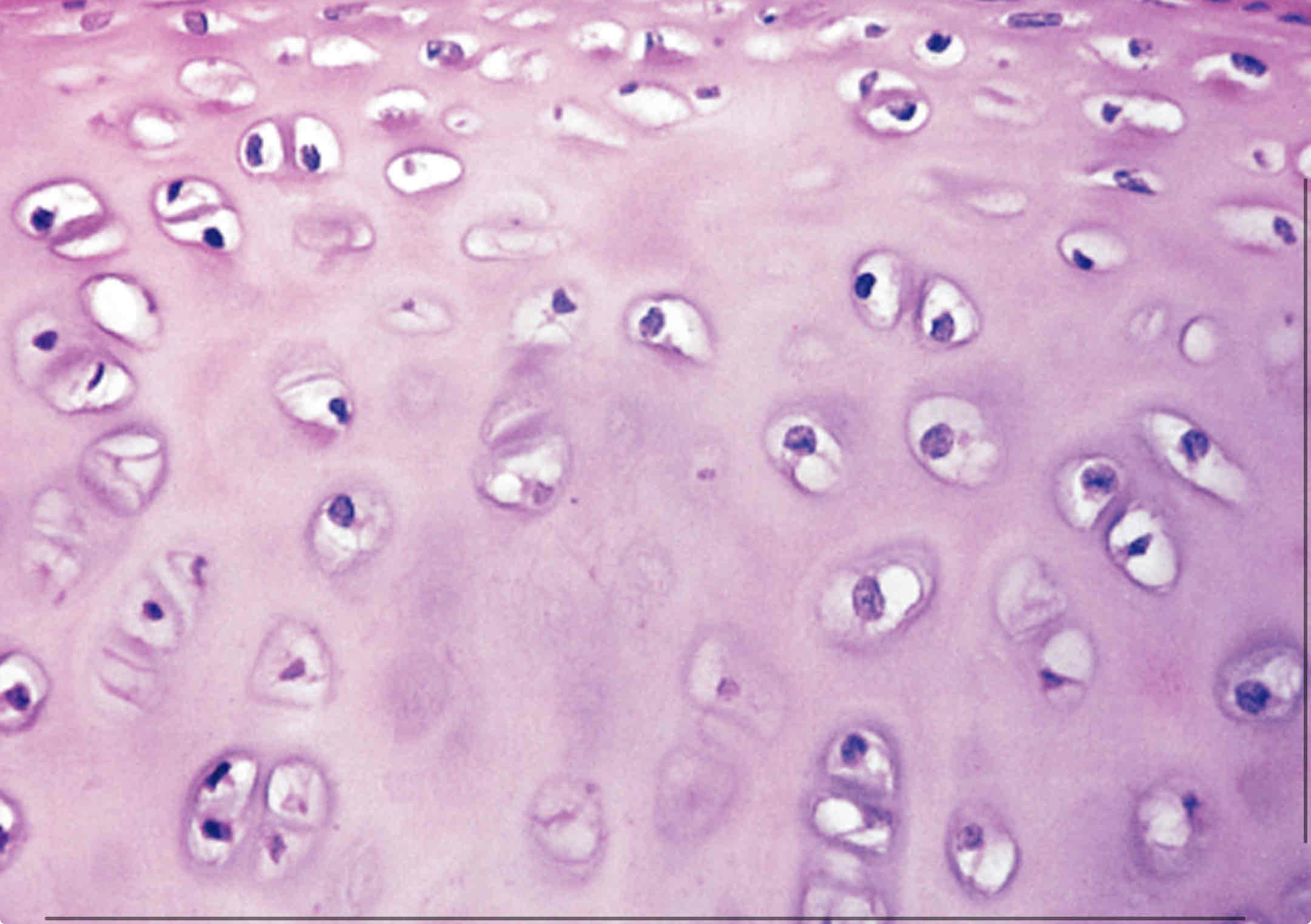
Hyaline cartilage
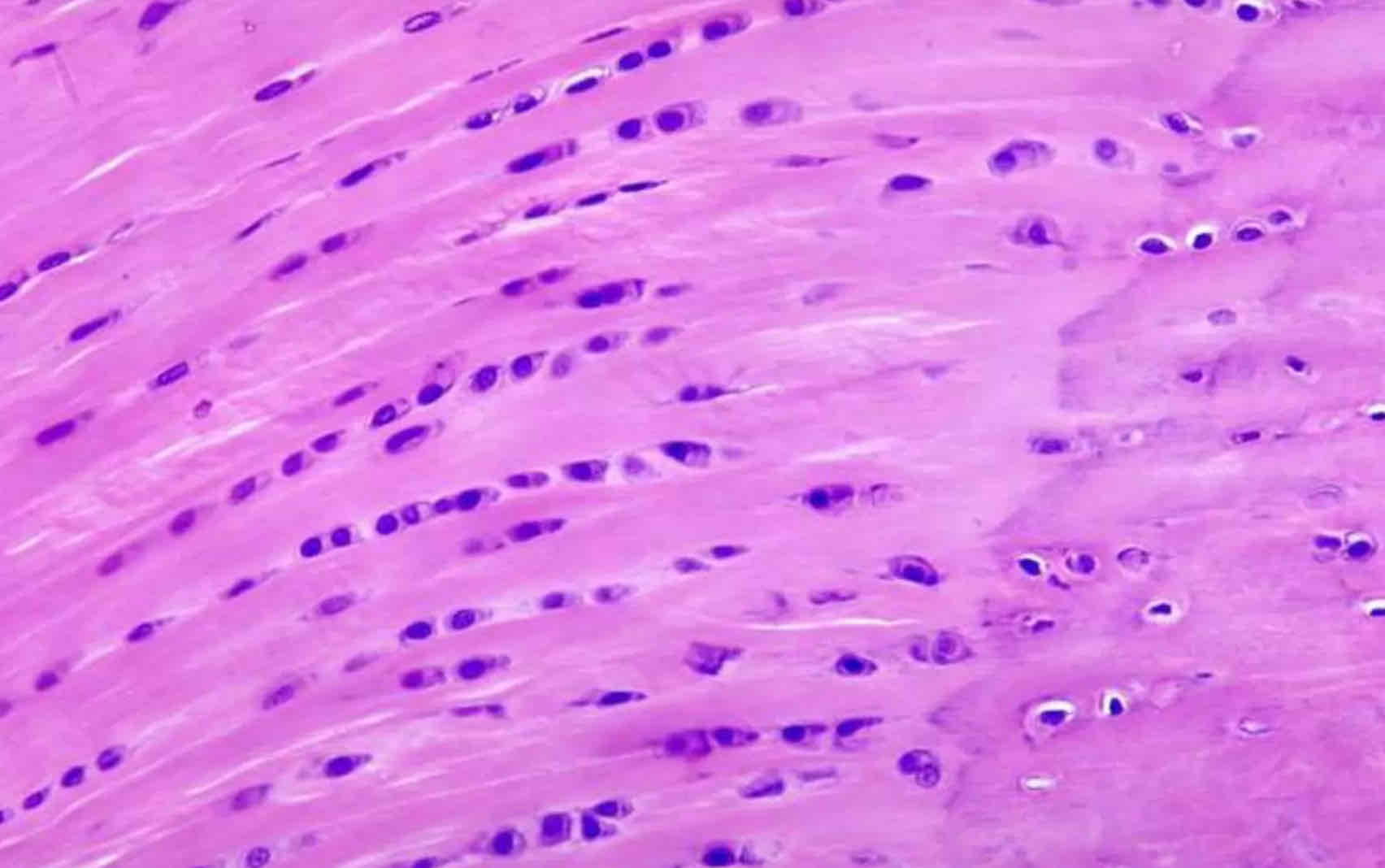
Fibrocartilage
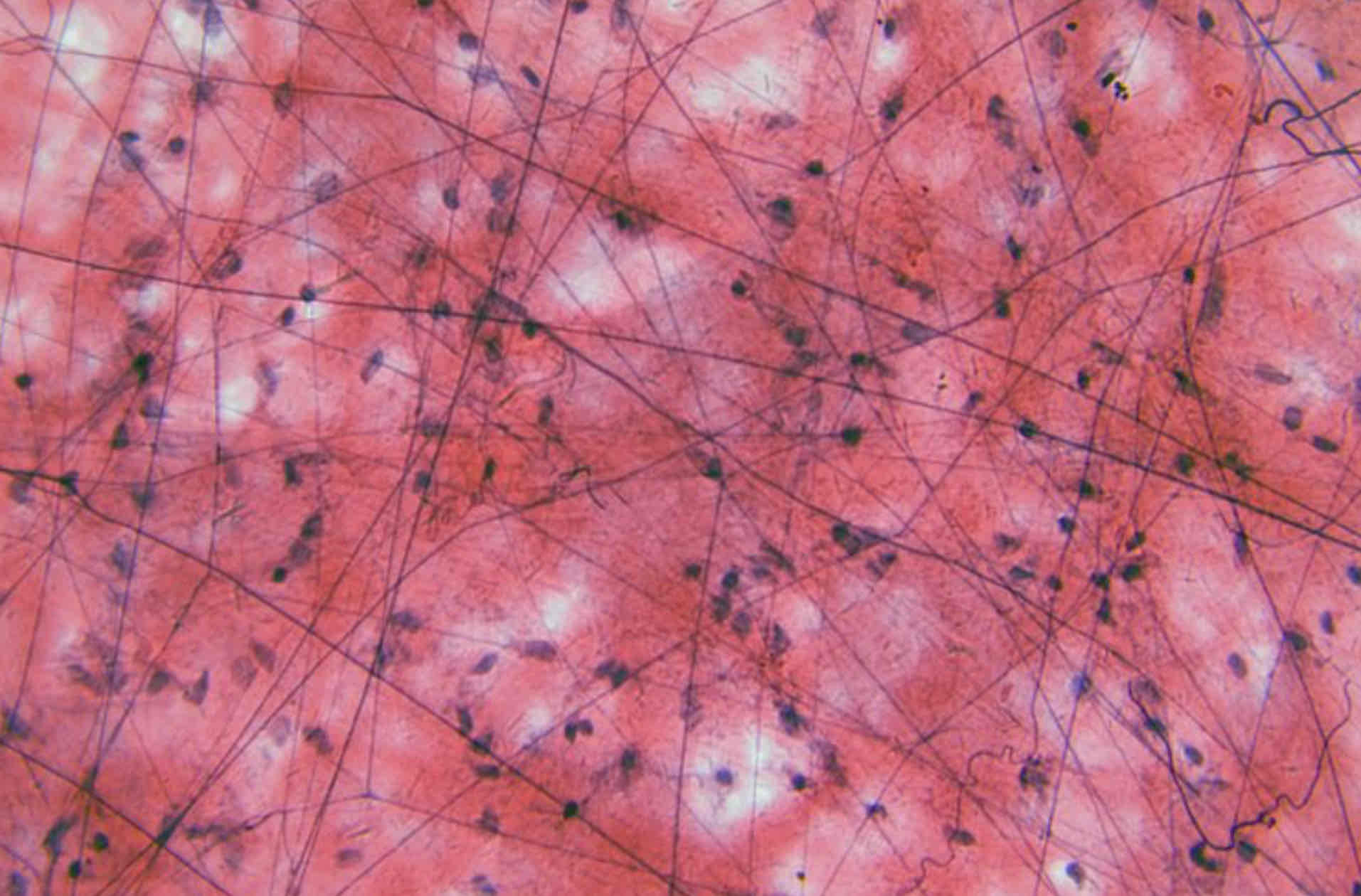
Loose connective tissue
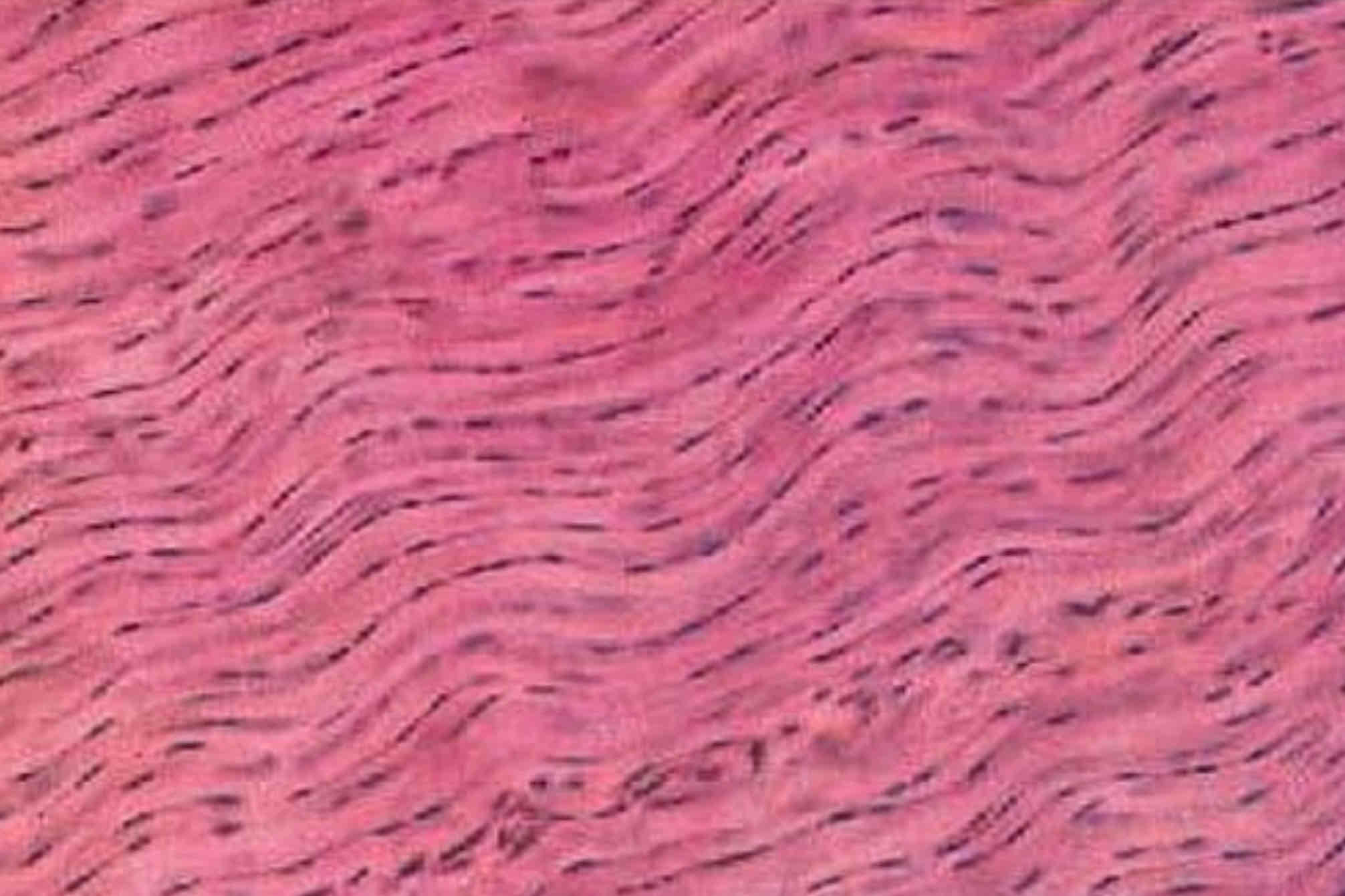
Dense regular connective tissue
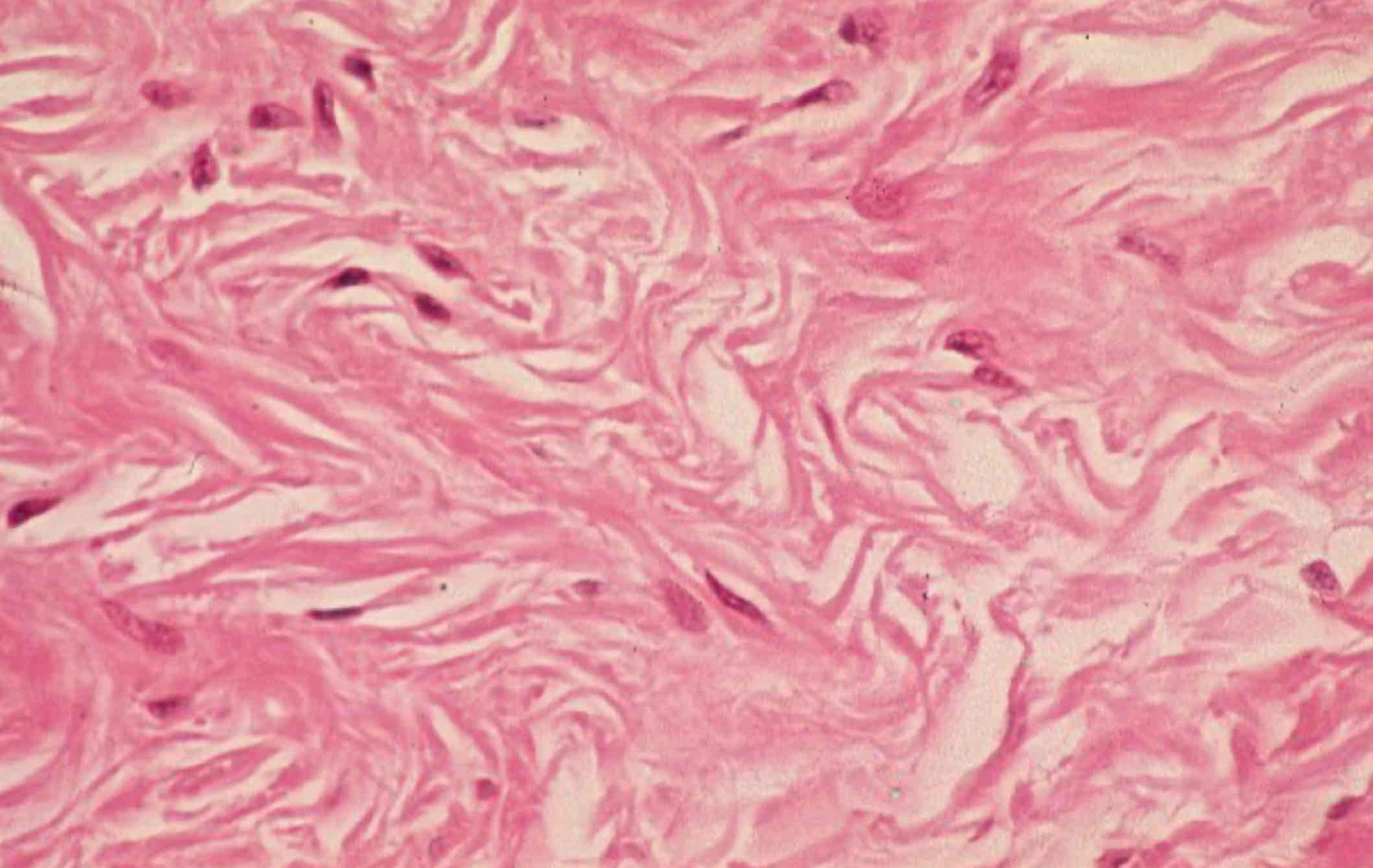
Dense irregular connective tissue
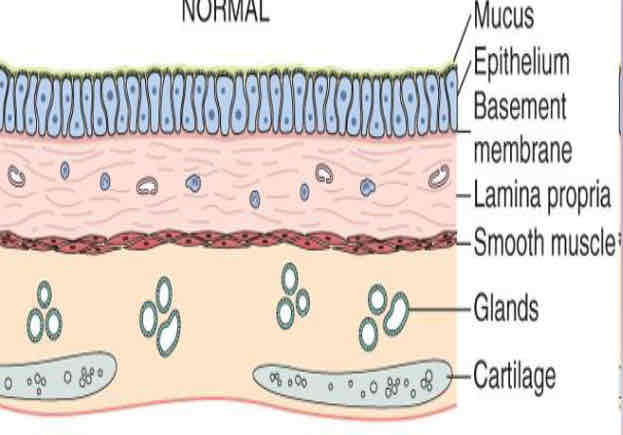
What are the airway layers?
Respiratory epithelium: pseudostratified columnar, ciliated + BM. Also contain goblet cells which form mucus.
Lamina propria: contain connective tissue, blood and lymph - give nutrients and structural support.
Submucosa: seromucus glands, smooth muscle/elastin fibres.
Cartilage: hyaline cartilage - C-shaped in trachea, but less prominent as tubes get smaller.
What vessels make up the portal triad?
the hepatic artery, the hepatic portal vein and the bile duct
Describe the lovers dual blood supply
The hepatic artery delivers oxygenated blood from the general circulation.
the hepatic portal vein delivering deoxygenated blood from the small intestine containing nutrients
Which muscle that controls the diameter of the trachea
Trachealis muscle