Bug Final Lecture Exam (all combined content)
1/794
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
795 Terms
Classification of Insects from Domain to Class
Domain: Eukaryota (organelle surrounded by membrane)
Kingdom: Animalia
Bilateria (bilaterally symmetrically animals)
Ecdysozoa (animals that molt between development stages)
Phylum: Arthropoda
Hexapoda (with six legs)
Class: Insecta
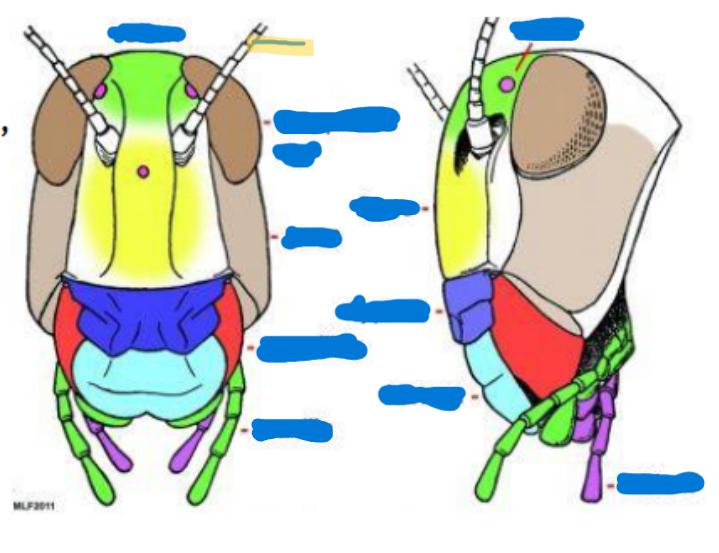
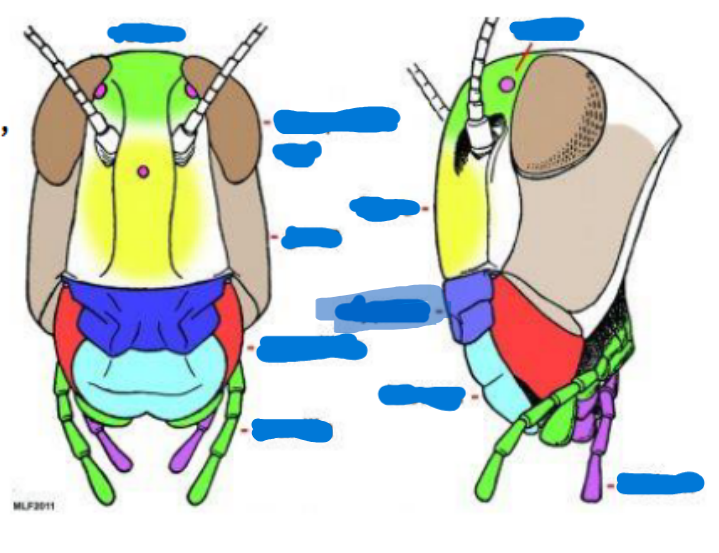
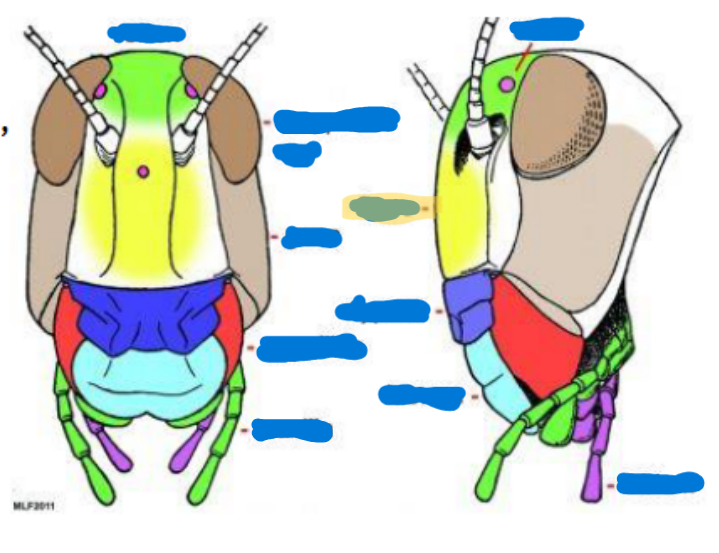
Arthropod
bilaterally symmetrical; exoskeleton; 2-3 body regions; paired; jointed appendages; hemocoele with dorsal heart; ventral nervous system
Exoskeleton
external skeleton aka hardened integument
Cuticle
non-living; more than 50% proteins
Epicuticle
waxy, waterproofing, outermost layer
Procuticle
25-50% chitin linked with proteins to form glycoprotein complex; made up of the exocuticle and endocuticle
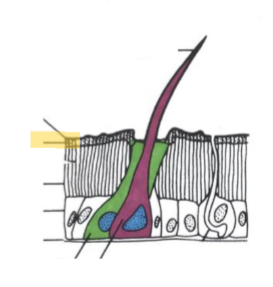
Exocuticle
sclerotizes, hard and rigid
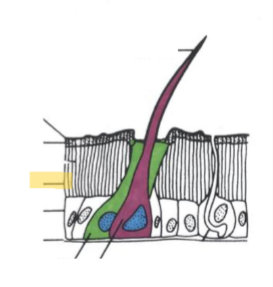
Endocuticle
thickest layer, soft and flexible
Epidermis
living cellular layer; one cell thick; produces the cuticle and assists in creating the basement membrane
Basement membrane
Supportive layer that separated exoskeleton from hemolymph
Sclerite
hard, sclerotized (process of getting hardened) plate on insect exoskeleton
Suture
inward folding of the exoskeleton
Endoskeleton
Apodemes-inflection in exoskeleton
Apophysis-peg or finger-like apodeme
Phragma-extensive, flange-like, especially in the thorax, deeper
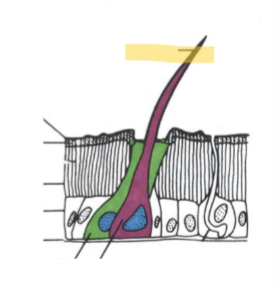
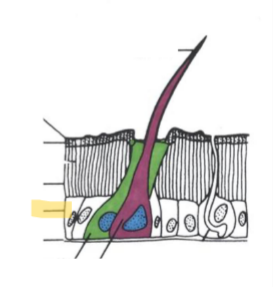
Setae
“hairs” consisting of three cells
Trichogen cell (hair)
Tormogren cell (socket)
Nerve cell (usually included)
Spine
rigid, multicellular outgrowth of cuticle
Spur
movable, multicellular outgrowths of cuticle
Apodemes
inflection in exoskeleton
Made up of apophysis and phragma
Apophysis
peg or finger-like apodeme
Phragma
extensive, flange-like, especially in the thorax, deeper
Setae

Epicuticle
Exocuticle
Endocuticle
Epidermis
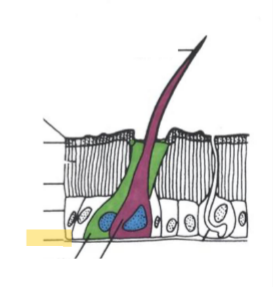
Basement Membrane

Procuticle
Sclerite

Suture
Spine

Spur
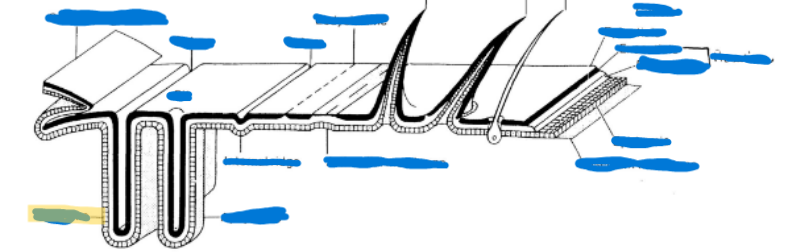
Phragma
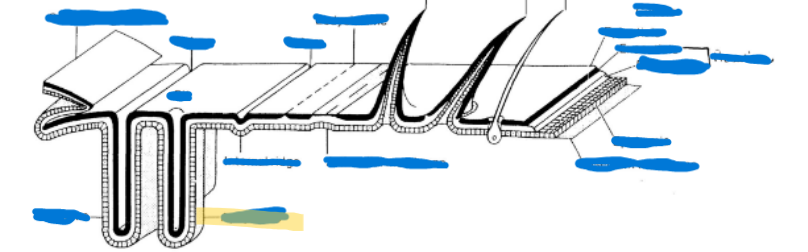
Apophysis
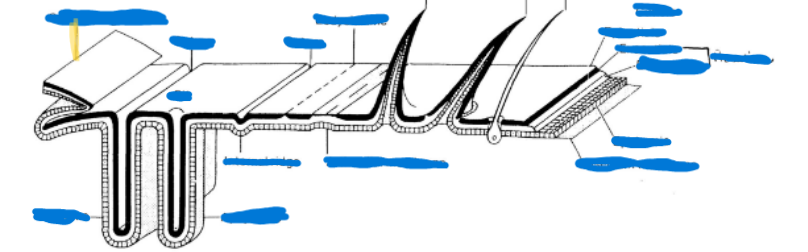
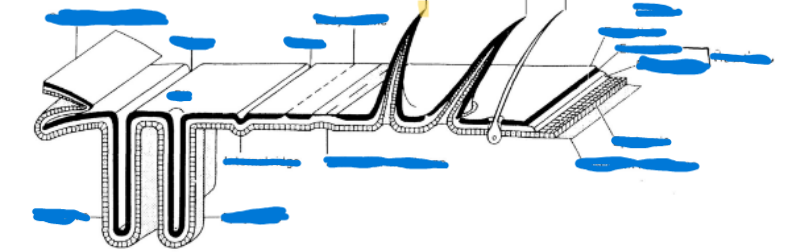
Primary segmentation
visible as grooves
Found in embryonic, some insect larvae
muscles attached within a given metamere (basic building block of a body segment)
Secondary segmentation
allows for rigidity without loss of movement
Found in many immature insects, most adults
Antecosta = primary intersegmental fold, ridge where muscles attach
Muscles now attached between “secondary” segements
Antecosta (antecostal suture)
primary intersegmental fold, ridge where muscles attach
Intersegmental fold
ridge where muscles attach
Tagmosis
evolutionary process of grouping
Tagma = a division
Homology (=similarity of structure due to commonality of origin)
Serial homology (= homologous structures on different segments of an individual)
Metamere
primitive body segment
Bear a single bear of outgrowths (= podites; pod-foot, ie-little)
Podite
bear a single bear of outgrowths
Rempel & Others’ Head Formation Theory
6 metameres
-Prostomium (=acron)
-Metamere 1 (Labral segment)
-Metamere 2 (Antennal segment)
-Metamere 3 (Intercalary segment)
-Metamere 4 (Mandibles)
-Metamere 5 (Maxillae)
-Metamere 6 (Labium)
Snodgrass’ Head Formation Theory
4 metameres
-Prostomium (already w/ antennae)
-Metamere 1 (2nd antennae of Crustacea)
-Metamere 2 (Mandibles)
-Metamere 3 (Maxillae)
-Metamere 4 (Labium)
Compound eye (2)
Obvious eyes; used for typical seeing and perception
Ocelli
(0-3) used to sense light, found on top of the head, relative location to the moon/sun
Antenna
(0-2 pairs)
Scape (with intrinsic musculature)
Pedicel (usually with Johnston’s organ) (with intrinsic musculature)
Flagellum (w/o intrinsic musculature except for Collembola and Diplura)
Mandible
primarily used for biting, chewing, and manipulating food
Maxilla
keeps food in, sensory organs, taste, chemical perception, helps them to know if what they’re eating is good
Labium
bottom jaw
Maxillary palps
serve primarily as sensory organs for touch and taste
Labial palps
serves primarily as sensory and feeding organs
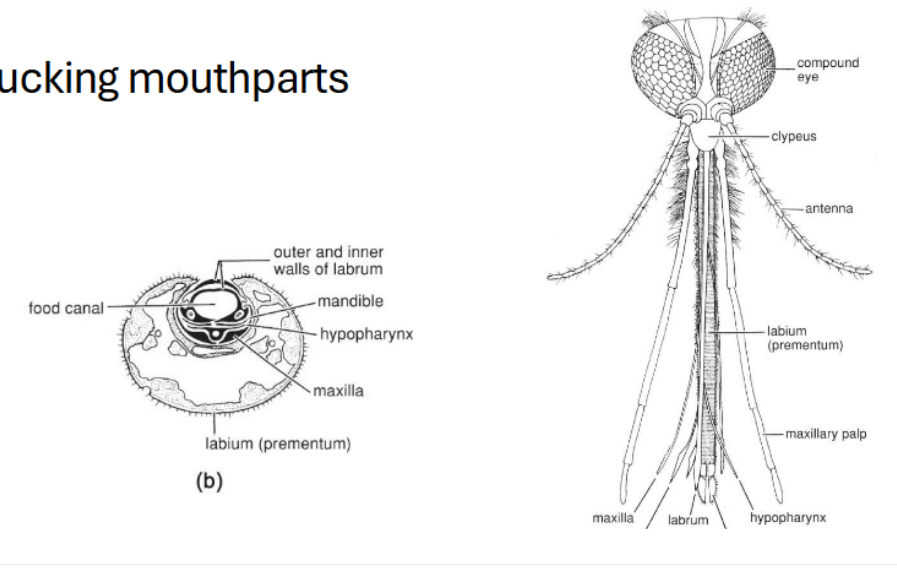
Hypopharynx
tongue, manipulates food
Salivarium
saliva
Labrum
top lip
Anterior tentorial pit
provides a point of attachment for muscles and supports the mouthparts
Cervical sclerites
two hardened patches on the side of the neck for protection/flexibility
Cervix
neck; softer and more flexible
Clypeus
sits above the labrum, secondary top lip
Frons
sits above Clypeus (forehead), front of the face
Gena
cheek, sits above the mandible and below the eyes
Subgena
above mandible and below gena
Vertex
on top of the head
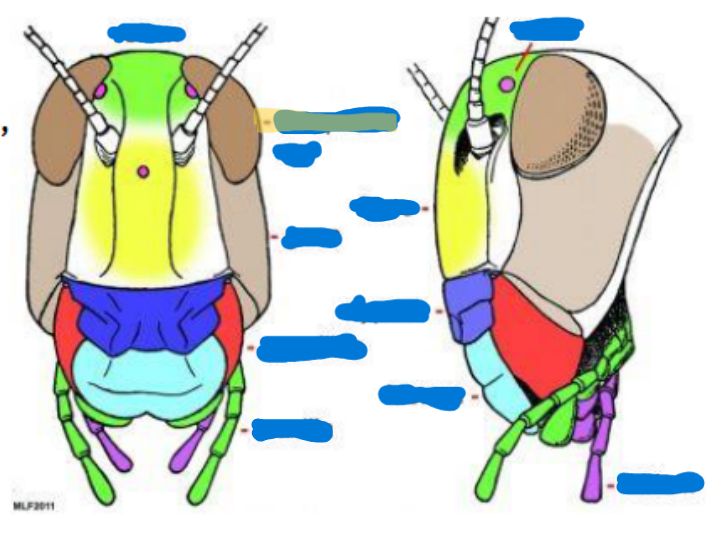
Compound eye
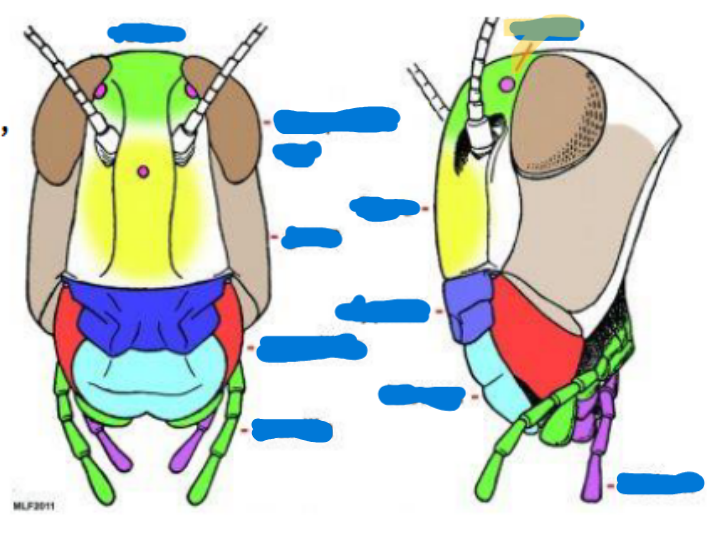
ocelli
antenna
scape
pedicel
flagellum
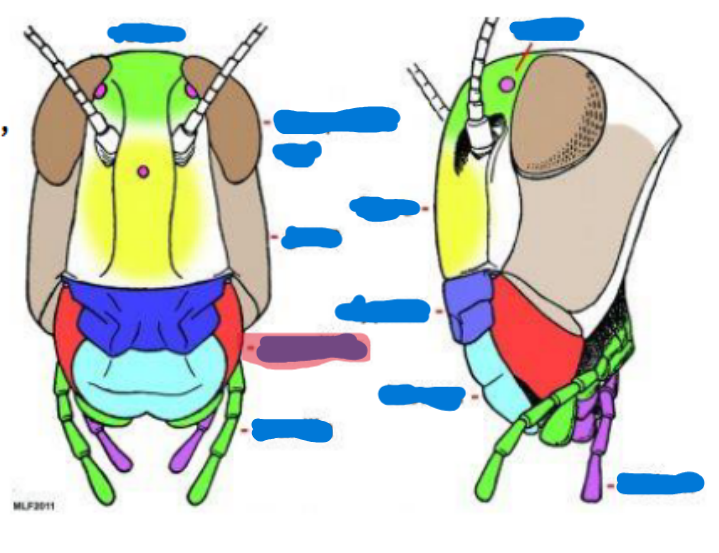
Mandible

maxilla and maxillary palps
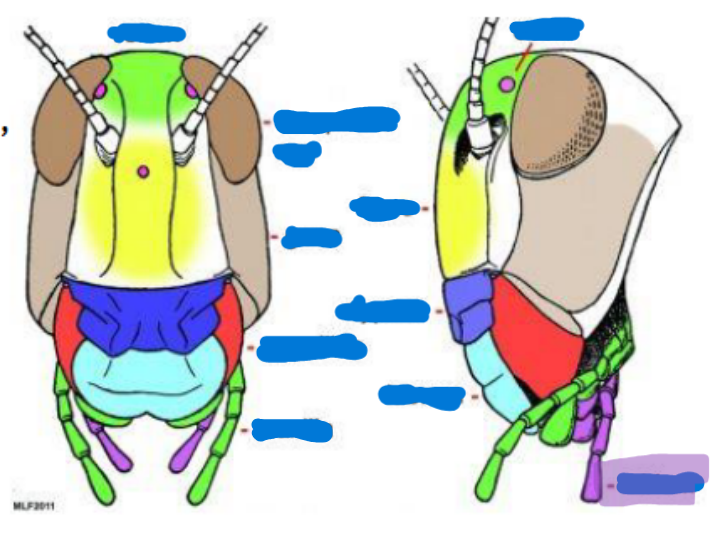
Labium and Labial palps
hypopharynx
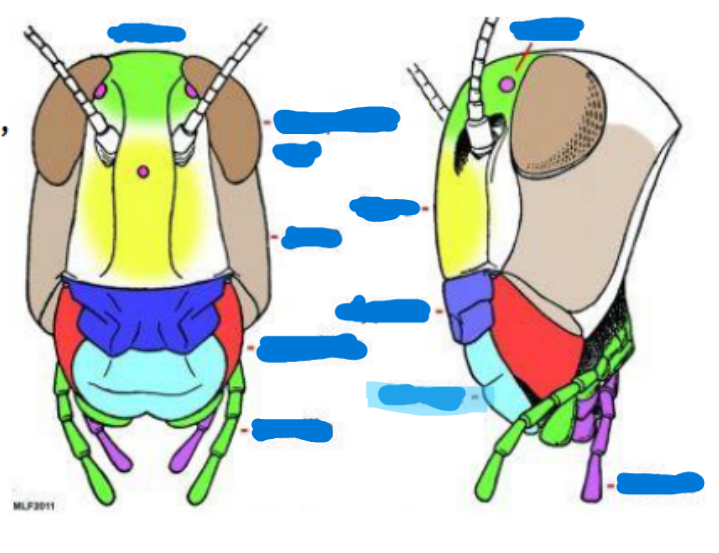
labrum
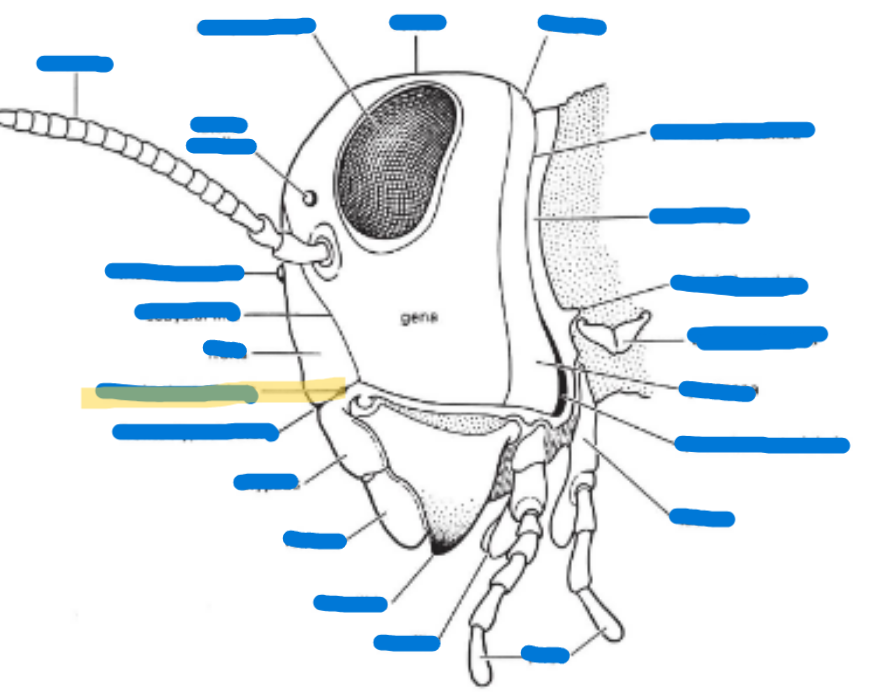
anterior tentorial pit
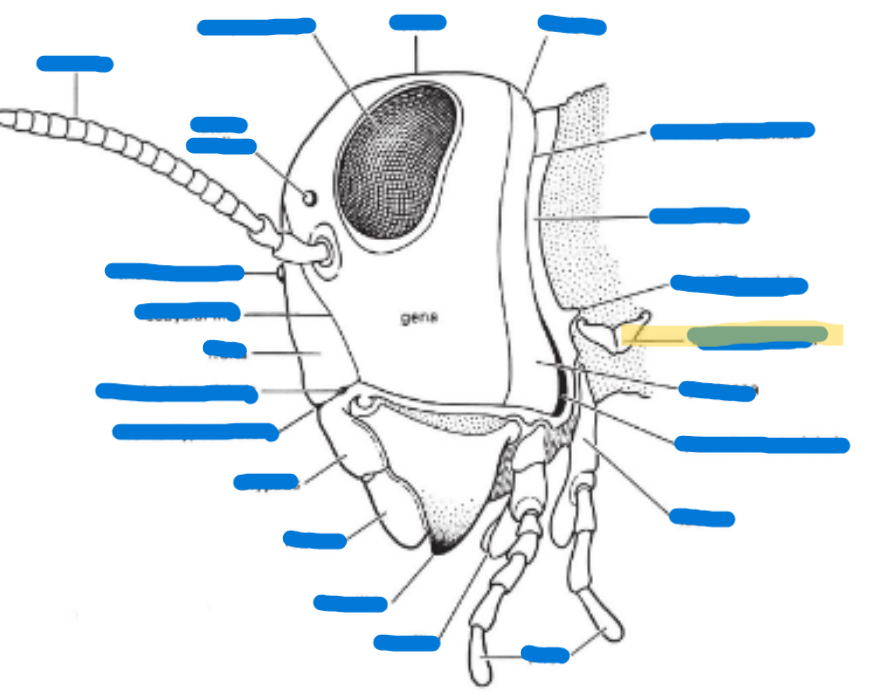
cervical sclerites
Clypeus
frons
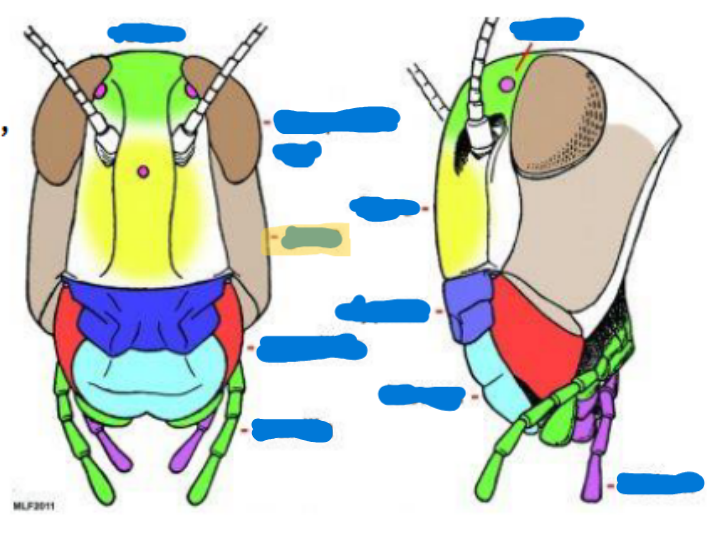
gena
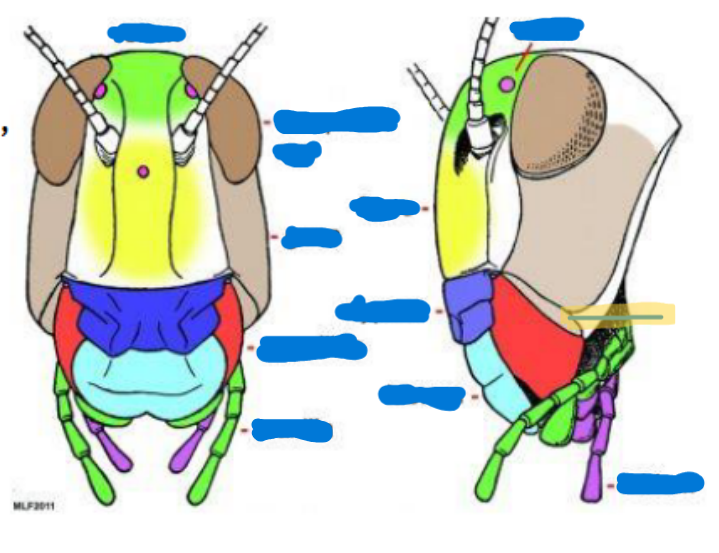
subgena
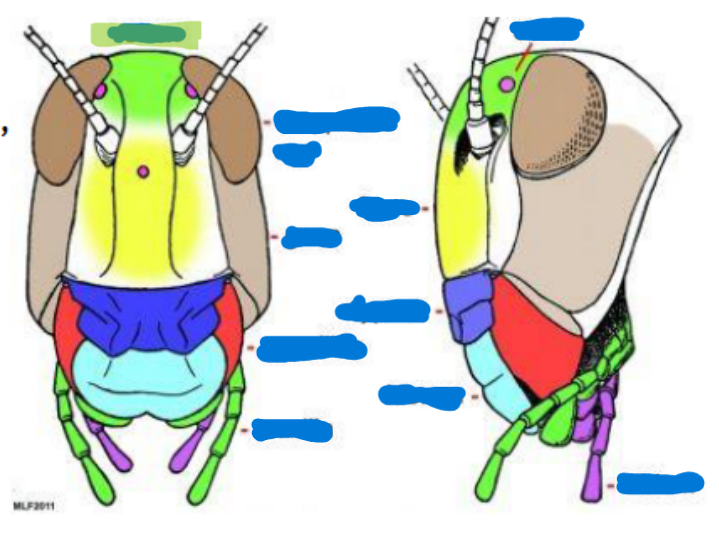
vertex
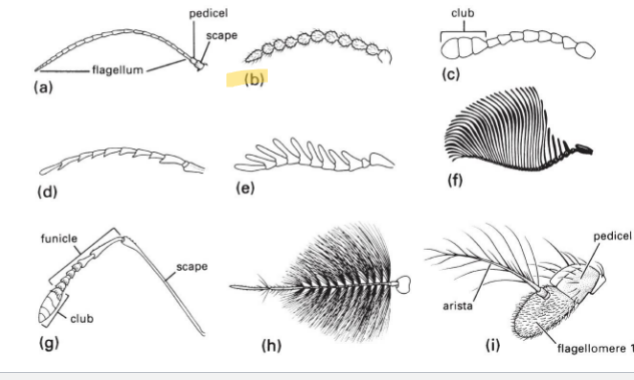
Filiform Antenna Type
Basic type; tubes
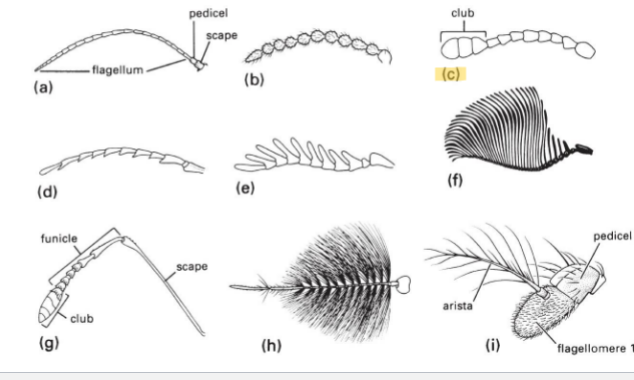
Moniloform Antenna Type
string of beads
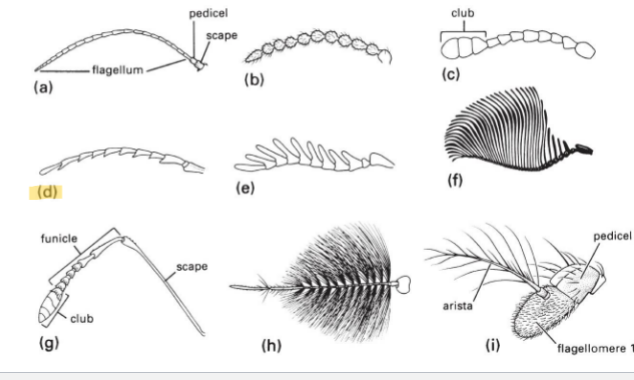
Clavate or Capitate Antenna Type
have a club on the end (termites, butterfly)
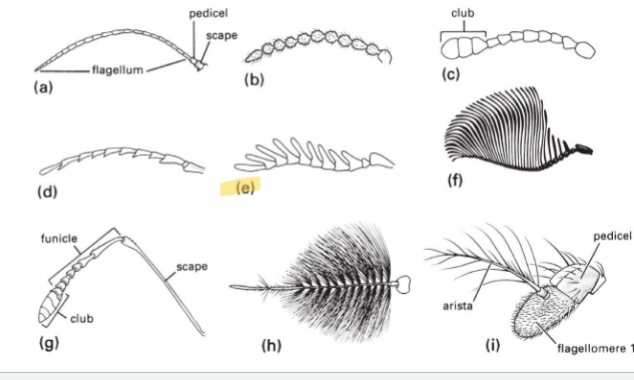
Serrate Antenna Type
little teeth on antennae
Pectinate Antenna Type
fingers
Flabellate Antenna Type
long feathery, fin
Geniculate Antenna Type
has an elbow on it (ants, wasps)
Plumose Antenna Type
plums, fluffy
Aristate
have one large flagellomere with one feather coming off of it
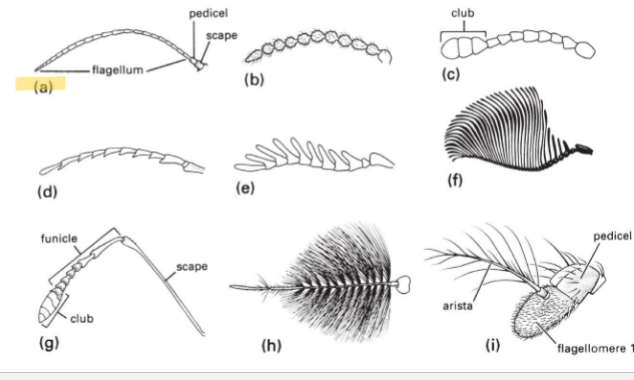
Filiform
Moniloform
Clavate or Capitate
serrate
pectinate
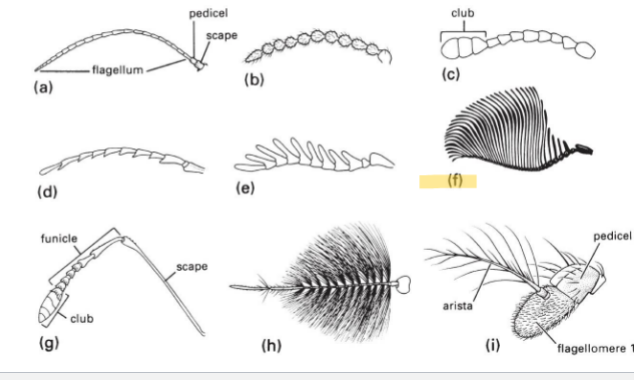
Flabellate

Geniculate
Plumose
Aristate
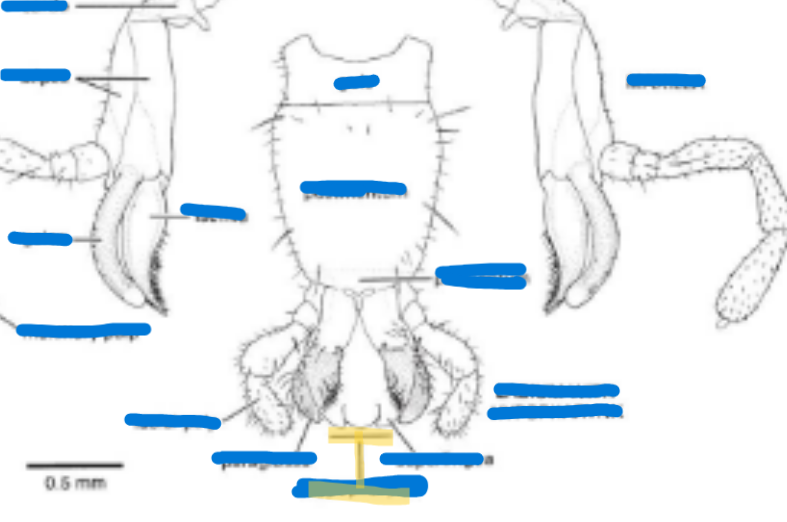
Sucking mouthpart modifications
Labrum: flat piece on the top
Mandible, hypopharynx, maxilla, etc. come together to create a strawlike, sucking mouthpart
Combination mouthpart modifications
highly modified hypopharynx → used to suck up liquid
Galea-unqiue to bees, see it when their tongue is out
Mandible-unmodified
Maxilla and palps are highly modified
Lapping mouthpart modifications
Labellum-goes around the labrum, labium, and hypopharynx
(Flies are able to sponge up their food and the food canal is made up of the hypopharynx)
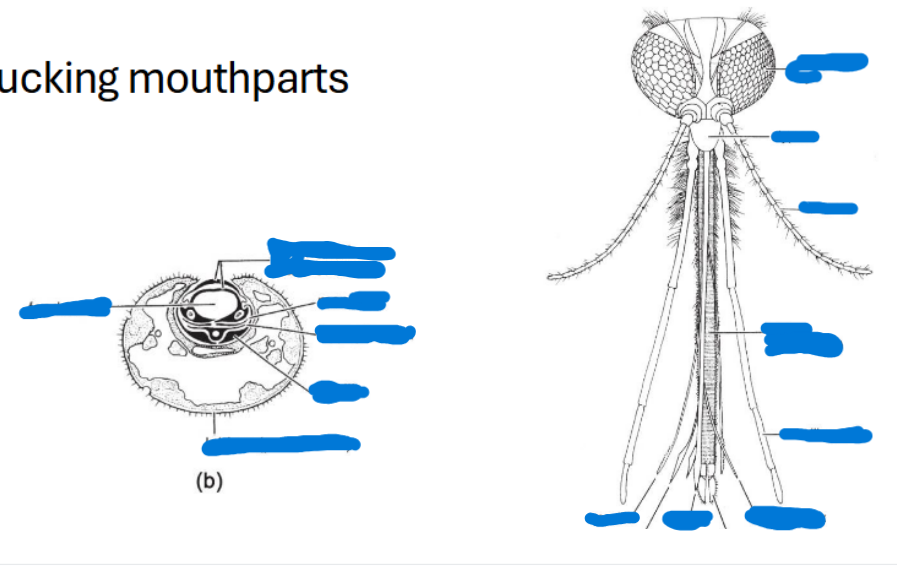
Label all of the sucking mouthparts