Physical assessment Quiz 2 WCU
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
CN I
Olfactory (sensory)
smell
CN II
Optic(sensory)
vision
CN III
Oculomotor (motor)
eye movement, pupil constriction
CN IV
Trochlear (Motor)
Down and inward movement of eye
CN V
Trigeminal Nerve;
Both
Sensory--cutaneous sensations from face and mouth
Motor--opening jaw, chewing from maxillary and mandibular (mastication)
CN VI
abducens(motor)
lateral eye movement
CN VII
Facial (motor and sensory)
facial expression, taste
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear(sensory)
hearing and balance
CN IX
glossopharyngeal (motor)
gag reflex, swallowing and speech
CN X
Vagus(Sensory and motor)
autonomic functions of viscera (glands, digestion, heart rate)
CN XI
Accessory Nerve(Motor)
Moving head and swallowing
CN XII
Hypoglossal(Motor)
Tongue movement
What does it mean when using the Snellen chart, the pt's vision is 20/30.
The patient can see at 20 ft what a person with normal vision can see at 30
Which CN is responsible for Vision (Snellen chart)?
CN II (optic) Vision
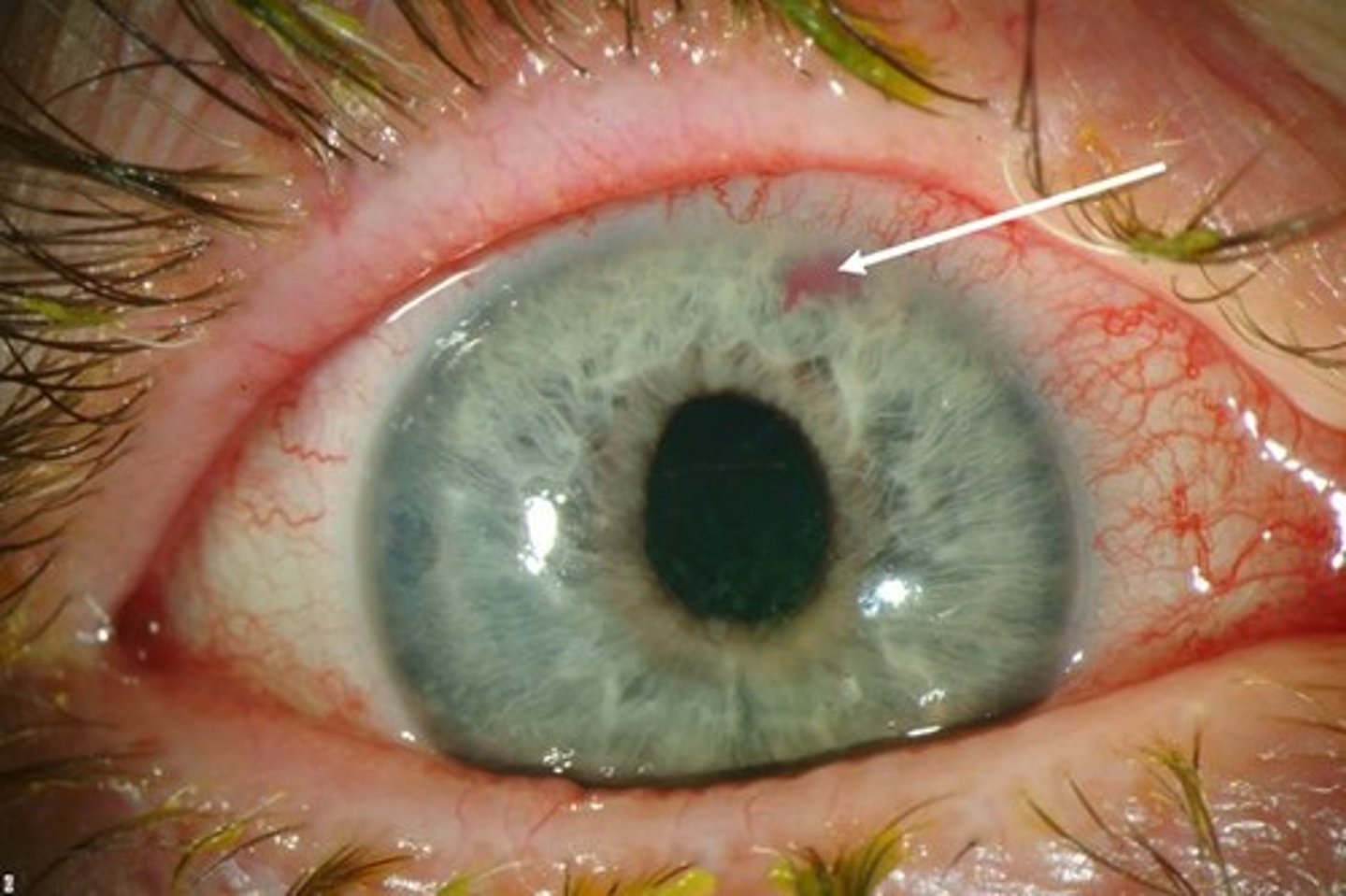
Glaucoma
Pt describes a change in vision, the loss of peripheral vision
presbyopia
impaired vision as a result of aging
(farsightedness)

Astigmatism
a condition in which the eye does not focus properly because of uneven curvatures of the cornea; Pt will see floaters
hyperopia
Condition in which a person can see things in the distance but has trouble seeing at close range.
myopia
nearsightedness
patient sees faraway objects as blurry

PERRLA
pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation
What condition could be occurring if pt's intraocular pressure is 26?
Glaucoma
What should the tympanic membrane look like?
pearly gray color
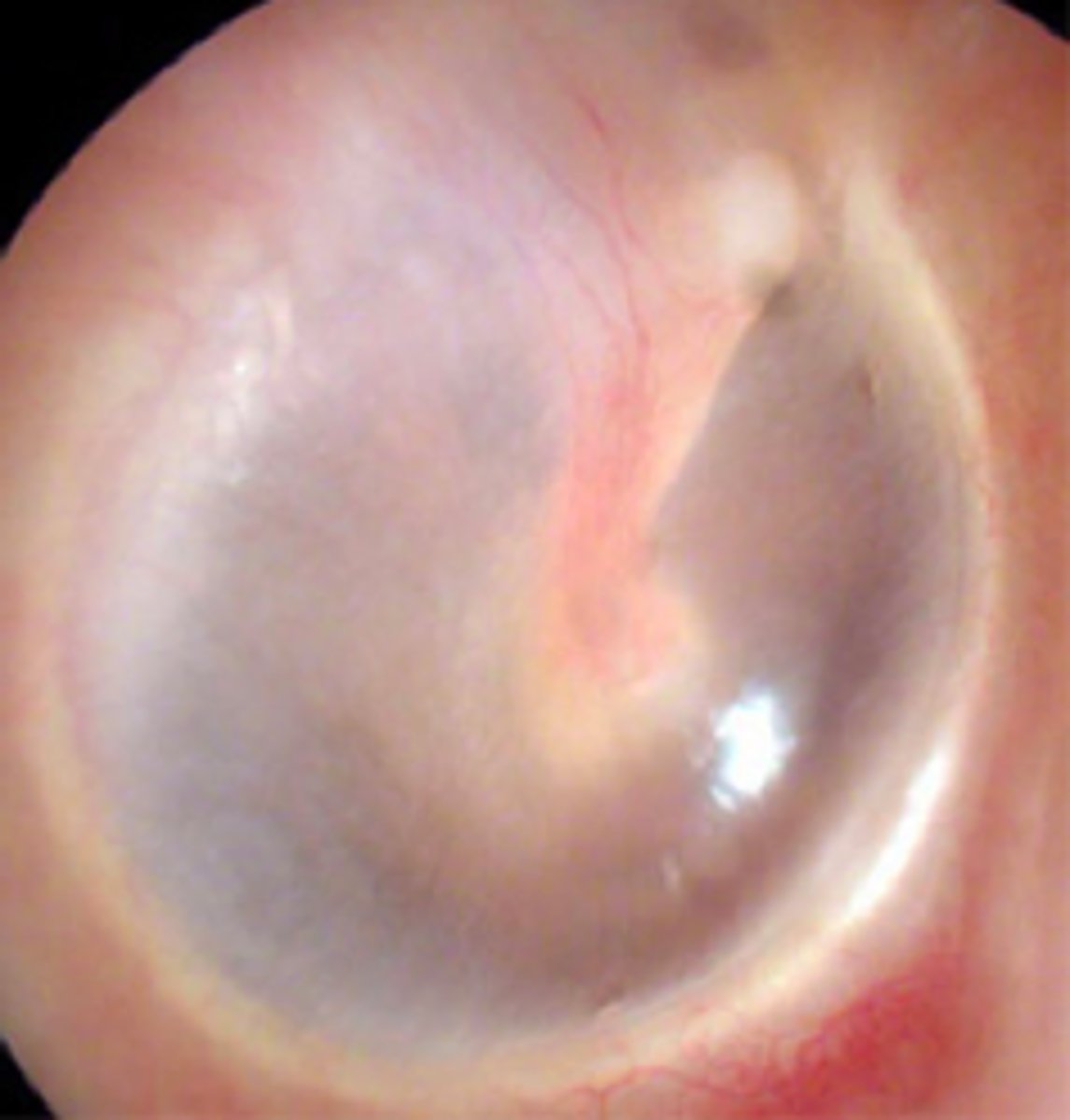
normal finding on the Rinne test
AC>BC
air conduction is greater than bone conduction
Questions nurses should ask during ear assessment
Do you use hearing devices?
Are you taking any medications for the ears?
Are there any changes to your hearing?
Do you suffer from frequent ear infections?
Proper way to use the otoscope
pull pinna up and back
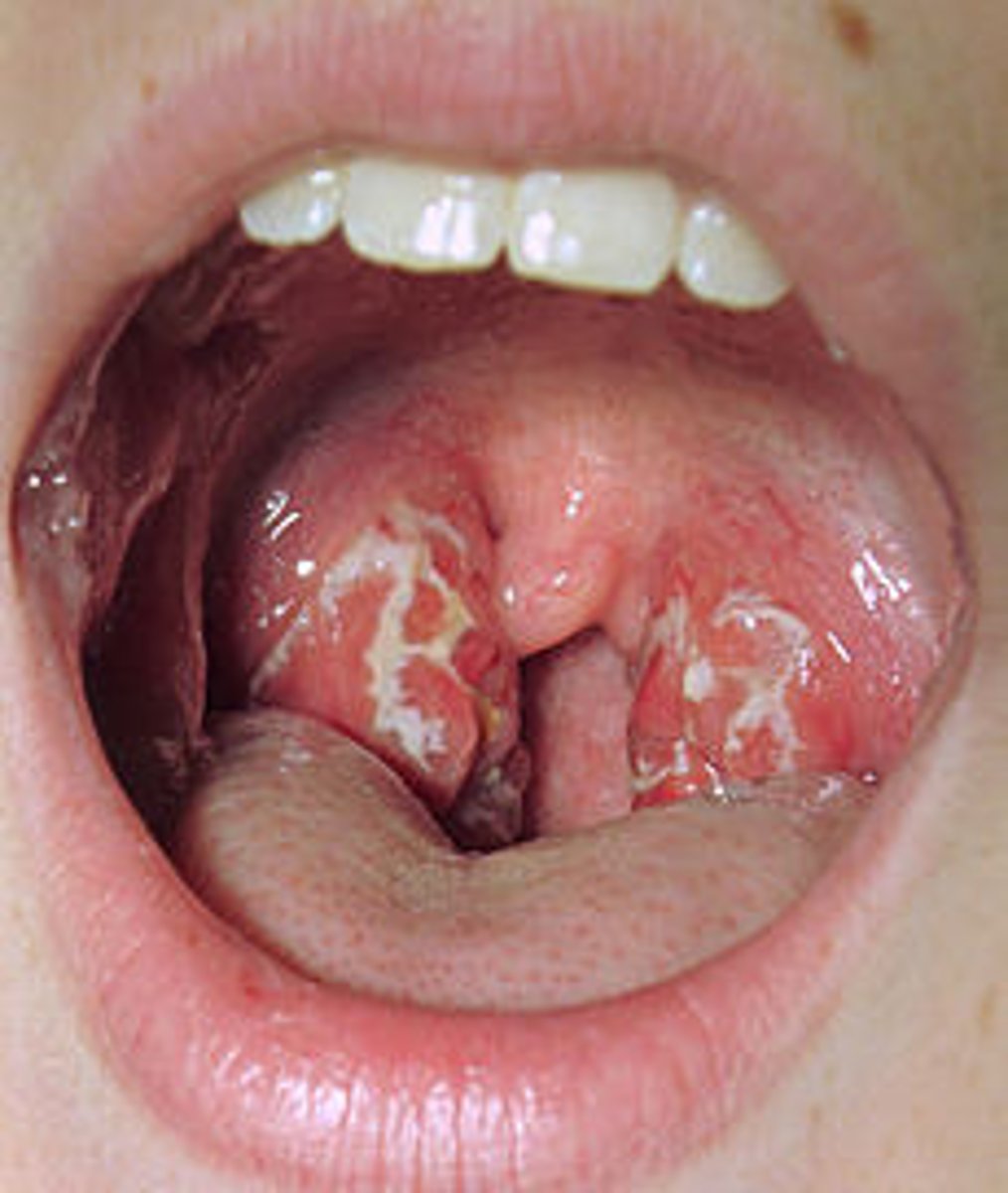
Tonsillitis
inflammation of the tonsils
Red, swollen tonsils. White or yellow coating or patches on the tonsils
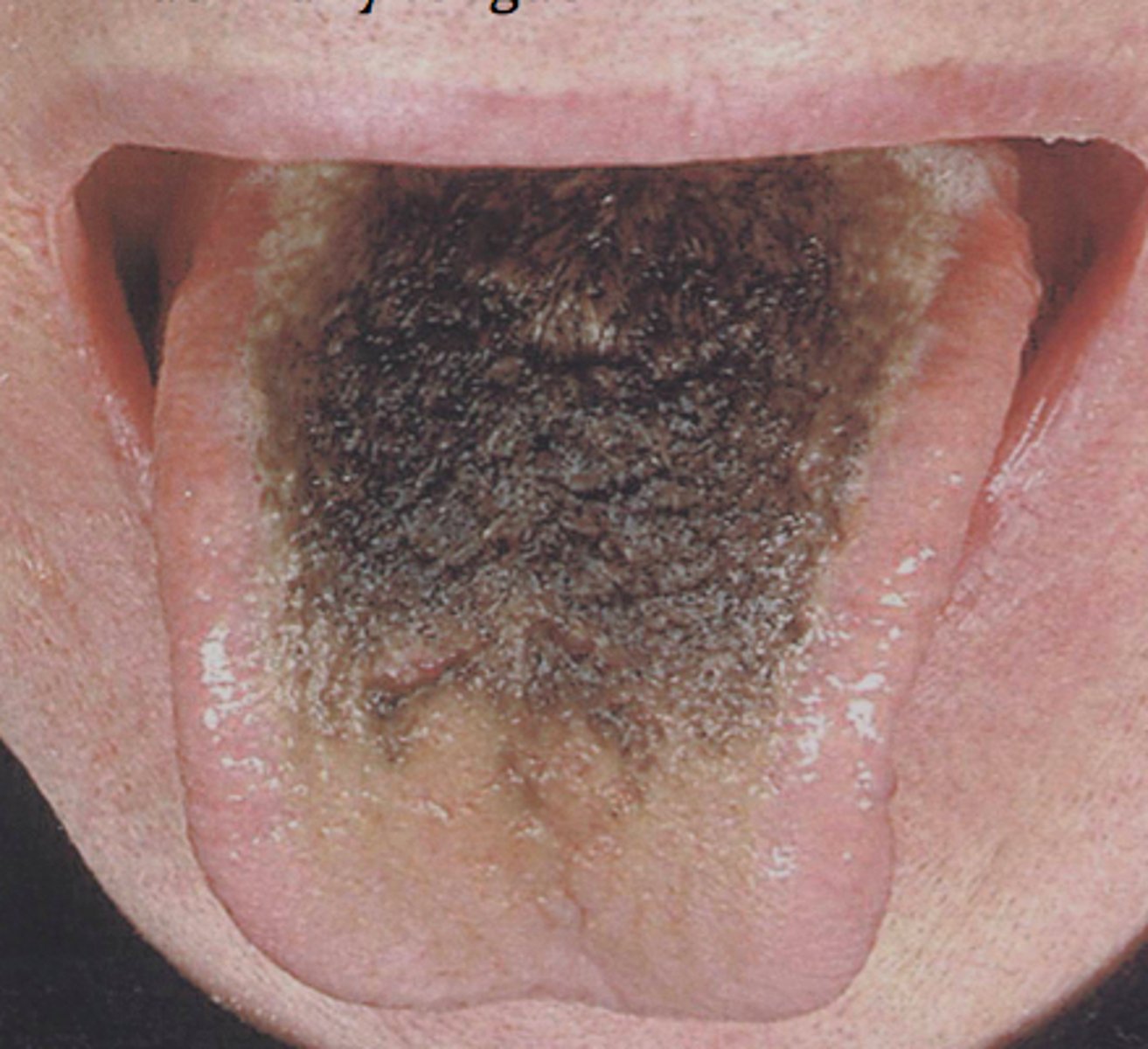
black hairy tongue
fungal infection of the tongue
tongue has black on it
direct percussion
percussion technique is used for the sinuses
Transilluminating the sinuses looks for what in the sinus cavity?
Reddish glow indicating normal air filled sinus
2 ways to test for CN8
Romberg Test
Whisper test
macular degeneration
deterioration of macula lutea of retina; patient notices loss of vision in center of visual field
Symptoms include blind spots and loss of central vision - can lead to visual disability
Glaucoma Symptoms & Treatment
Symptom: loss of peripheral vision, blurred vision, vision loss
treatment: lower intraocular pressure and possibly surgery
Cataracts
clouding of the lens of the eye that effects vision. Usually related to aging
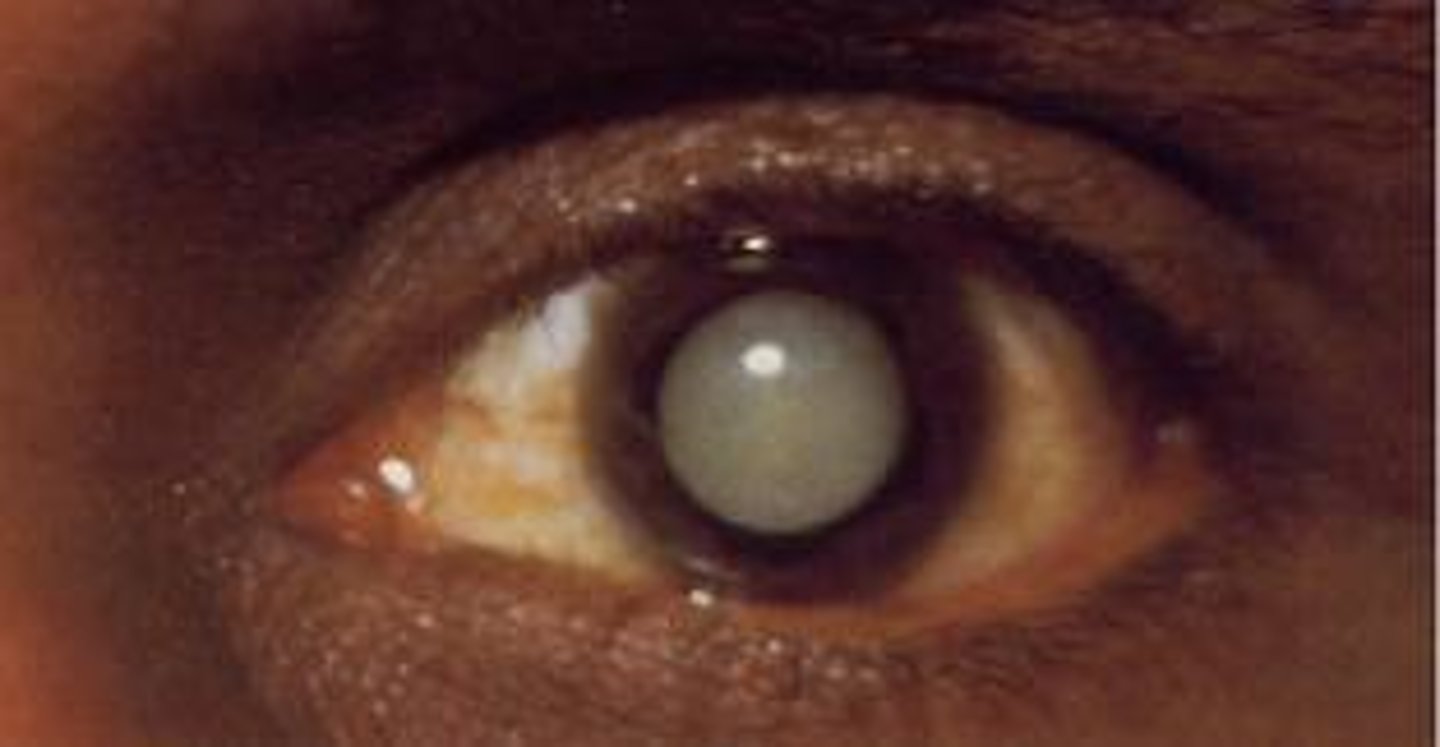
Blepharitis
inflammation of the eyelid; Staphylococcal infection leads to red, scaly, and crusted lids. The eye burns, itches, and tears
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Most common and least severe type of skin cancer; often characterized by light or pearly nodules. Usually seen on the lower lid and medial canthus. It has a popular appearance

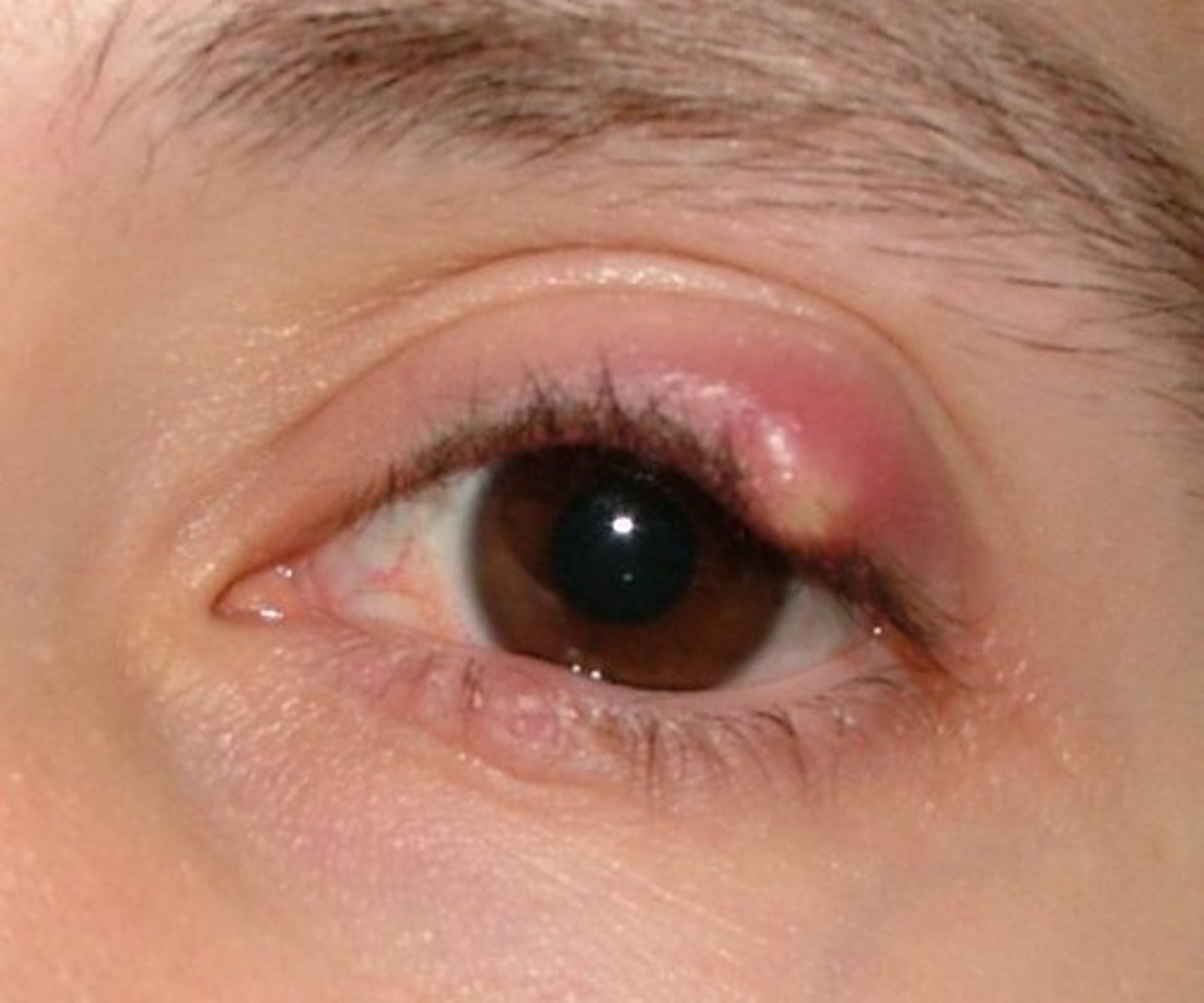
chalazion
small, hard, cystic mass (granuloma) on the eyelid

hordeolum (stye)
staph infection of a sebaceous gland in the eyelid
entropion
The inversion of the edge of an eyelid, turning inward

Ectropion
The eversion of the edge of an eyelid, turning outward.

Ptosis
Drooping of the eyelid; occurs with cranial nerve damage or systemic neuromuscular weakness

periorbital edema
swelling of the tissues surrounding the eye or eyes;
occurs with crying, infection, trauma, and systemic problems including kidney failure, heart failure, and allergy

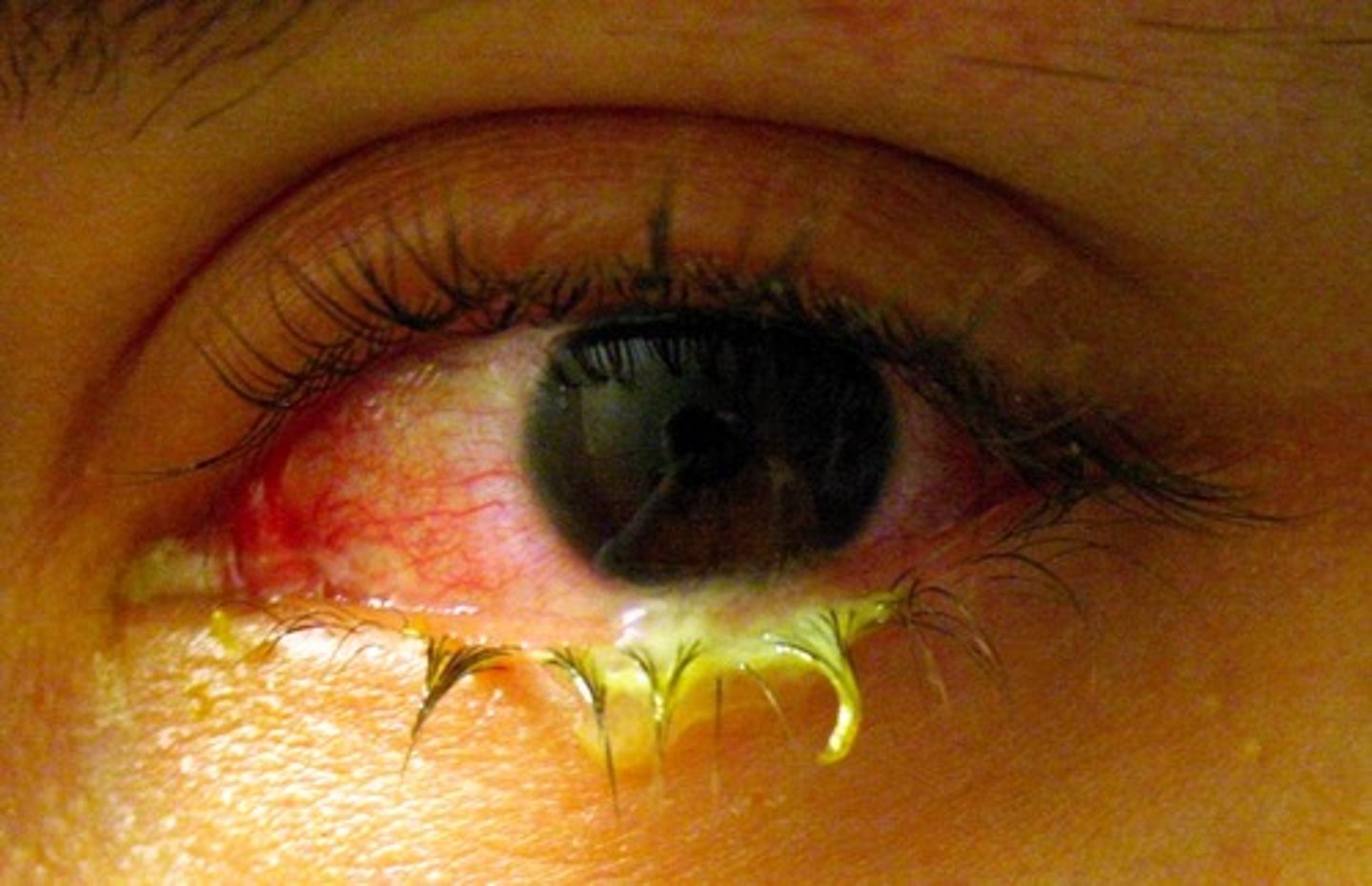
conjuctivitis
inflammation of the conjunctiva (pink eye); Infection of the conjunctiva usually due to bacteria or virus but which may result from chemical exposure.
the eye will have liquid coming out
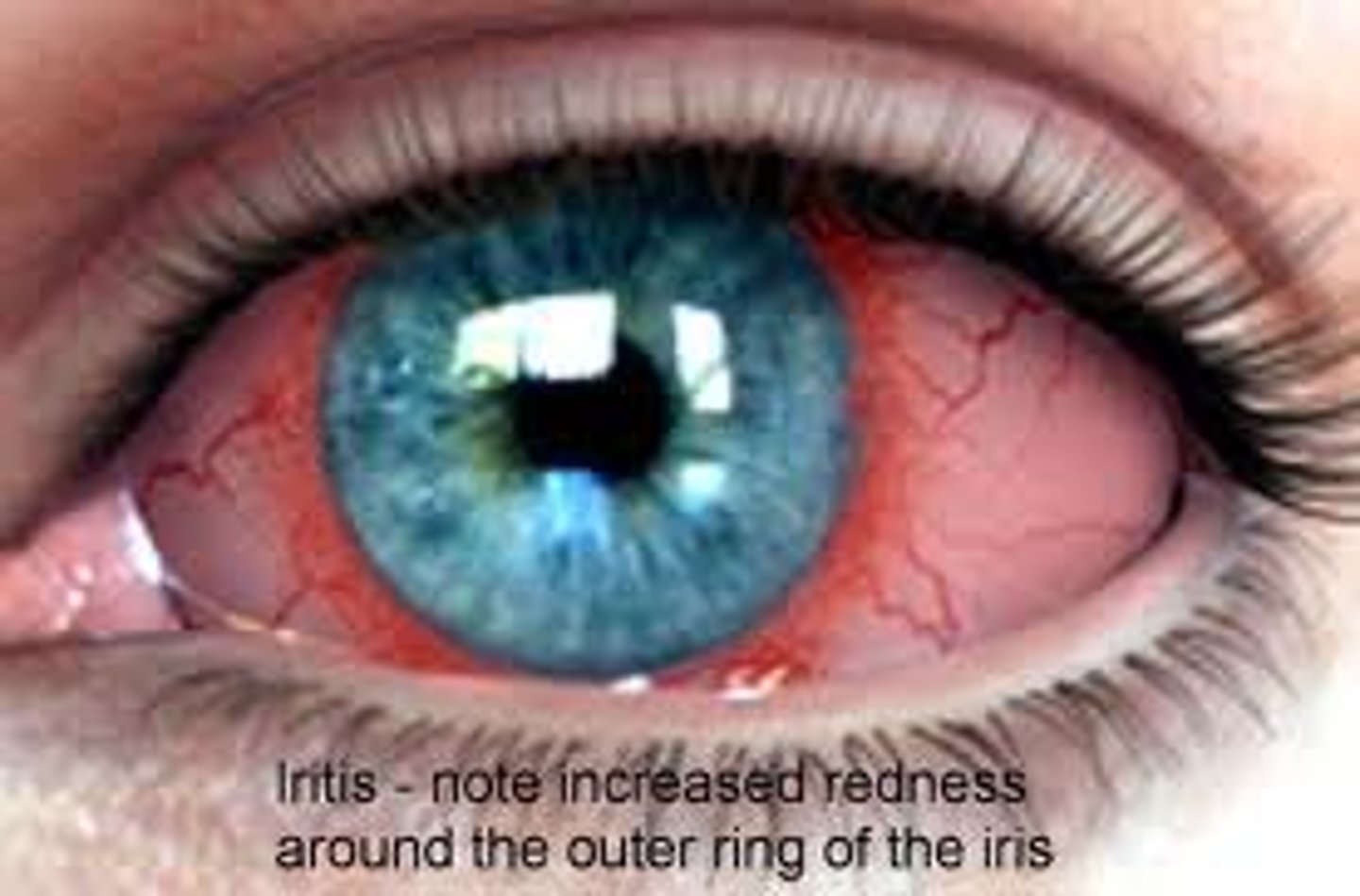
Iritis
inflammation of the iris, usually marked by pain,
pupil is often irregular
arcus senilis
gray-white arc or circle around the limbus of the iris that is common with aging
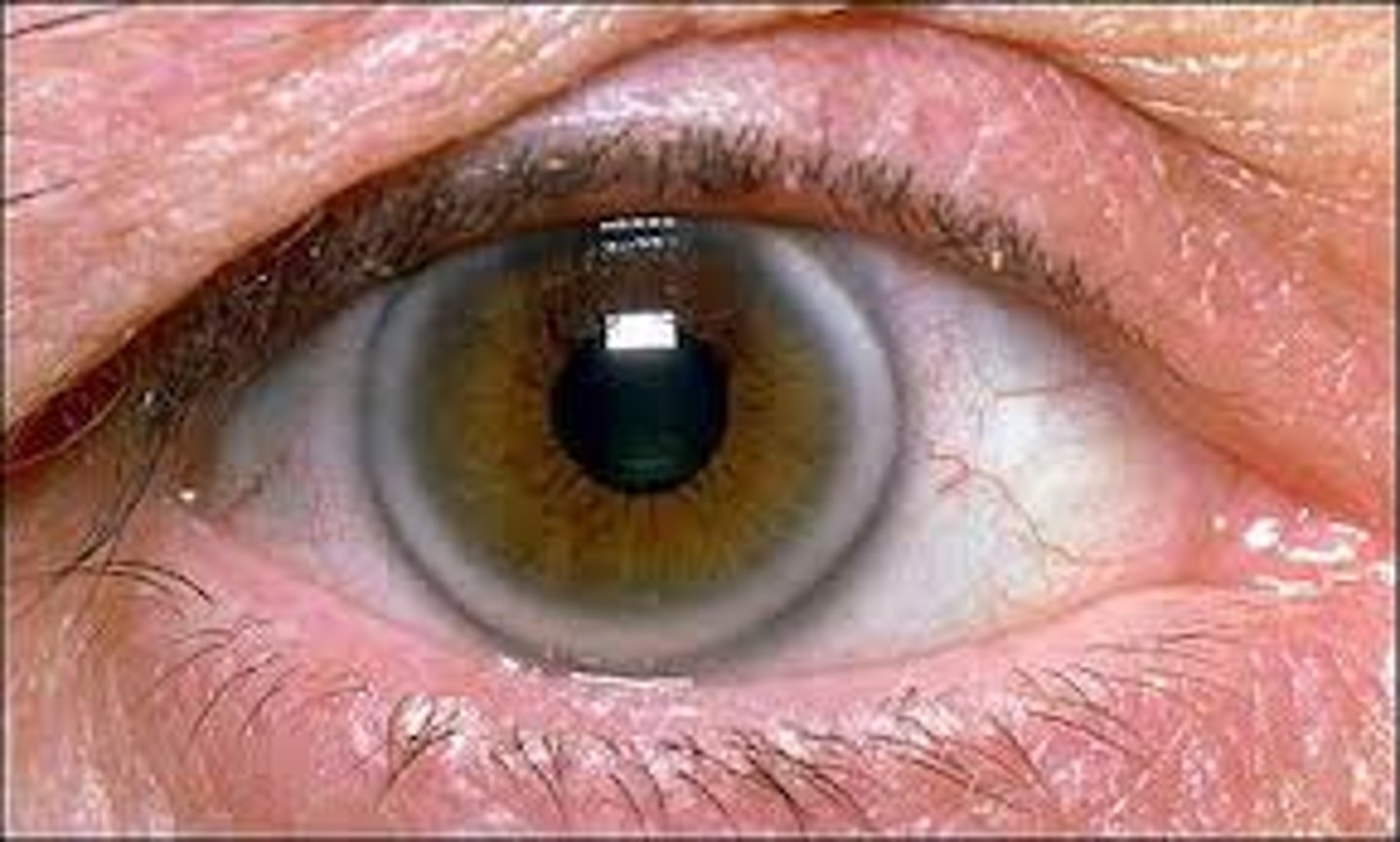
Pingueculae
Yellowish nodules that are thickened areas of the bulbar conjunctiva. Caused by prolonged exposure to sun, wind, and dust.
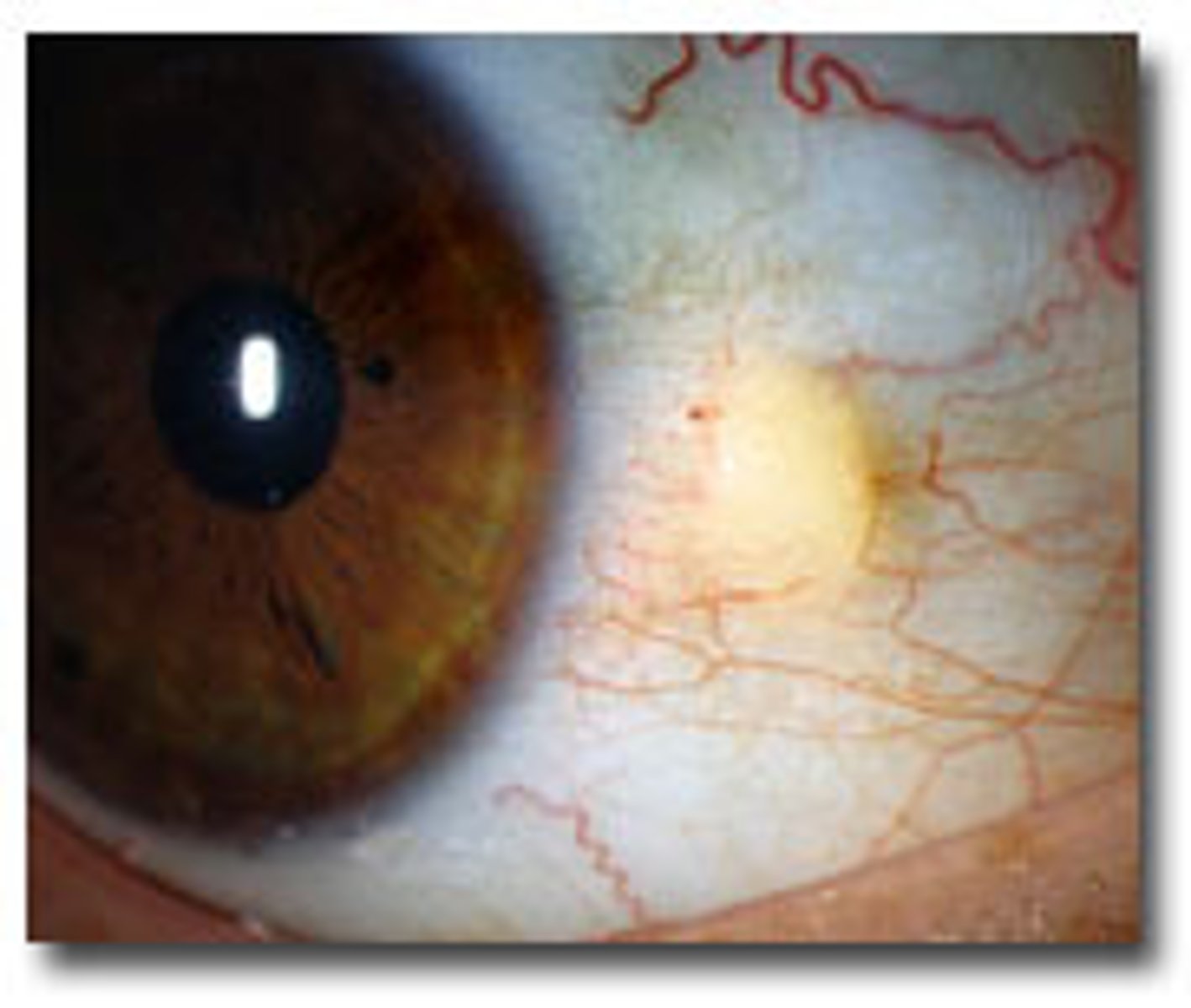
Xanthelasma
raised yellowish plaque on eyelid caused by lipid disorder

Lifespan Considerations for Infant
The red reflex should be elicited from birth
Binocular vision develops at 6 weeks of age
Lateral deviations are normal until 4 months of age
Lifespan Considerations with Pregnancy
Dryness of the eyes
Vision changes - due to shifting fluid in cornea, blurriness, distorted vision, and can happen up to 6 weeks postpartum
Cranial Nerve III damage
Unilateral dilated pupil has no reaction to light or accommodation and occurs with oculomotor nerve damage. Ptosis with eye deviating down and laterally may be present.

Argyll Robertson pupils
Non-Reactive to light. Occurs with CNS disorders, including tumor, syphilis and narcotic use

Miosis
Fixed and constricted pupils. May occur with use of narcotics, damage to pons, or result of treatment for glaucoma

anisocoria
a condition in which the pupils are unequal in size
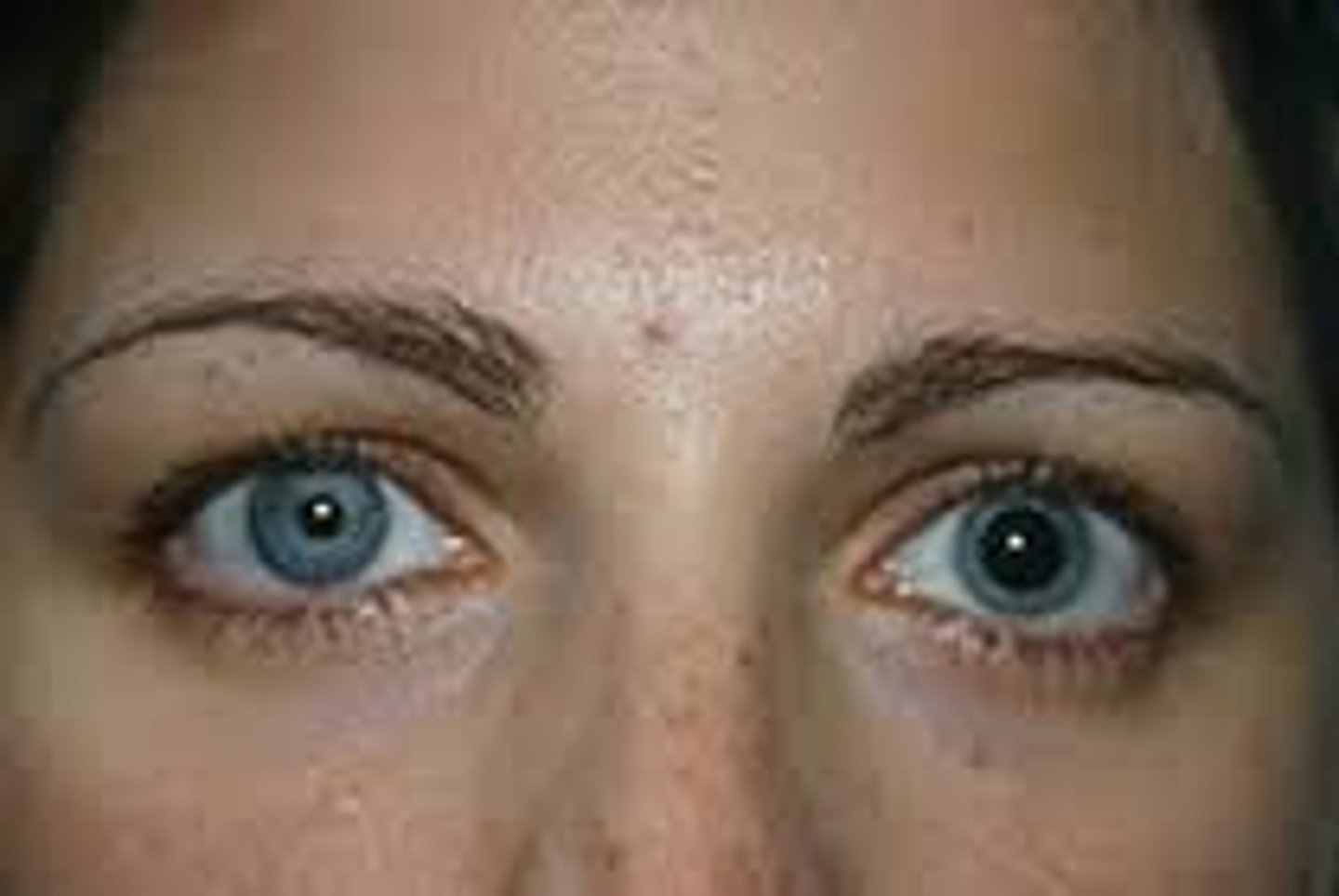
Mydriasis
Fixed and dilated pupils. May occur with sympathetic nerve stimulation, glaucoma, CNS damage or deep anesthesia.

Focus Assessment: Extraocular muscle
Movement of the eyes - follow finger 6-12 inches in front of the eyes - 6 cardinal fields of gaze
Visual fields - tests the peripheral vision fields
Focus Assessment: Visual acuity
The degree of detail the eye can discern in an image
Near vision = newspaper print - Rosenbaum
Snellen Chart = 20 ft in front of the patient
Eye assessment questions to ask
"When was the last eye exam and findings?" (2 years is recommended)
"Any medications for eye disorders?"
"Do you wear corrective glasses or contact lenses?"
"Have you ever been diagnosed with a disease of the eye?"
"Do you have any family history of eye disorders?"
Assessment of nose questions to ask
"Are you experiencing any problems with your nose or sinuses?"
"Any discharge, frequent nose bleeds?"
"Have you had any nasal surgeries or injuries?"
"Any recreational drug use?"
Any medications including OTC for nasal decongestion?"
Romberg Test
-ask client to stand with feet at comfortable distance apart, arms at sides, and eyes closed
-expected finding: client should be able to stand with minimal swaying for at least 5 seconds
Weber test
Test done by placing the stem of a vibrating tuning fork on the midline of the head and having the patient indicate in which ear the tone can be heard.
NORMAL findings: the sound is heard in the center of the head, or equally on both ears
Rhine test
Compares Air conduction (AC) with bone conduction (BC). Place fork on mastoid process, then quickly place next to ear canal comparing how long pt could hear the tuning fork in each location.
If the AC (air conduction) is greater than BC (bone conduction) then its normal; If BC is greater than AC this is conductive deafness. A negative test indicates a minimum air-bone gap of 15-20