Enzymes lectures 5-6
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
lineweaver burk plot
easier to define exact Km and Vmax
takes the inverse of the axes (makes the plot linear)
slope on a lineweaver-burk plot
Km/Vmax
X intercept on Lineweaver-Burk plot
-1/Km
Is Km ideally supposed to be big or small?
small so we can reach Vmax quickly
Why does changing pH affect reaction rates?
change the charge of substrate—> changing how the substrates cant fit can interact with the active site
k_{cat}
number of subunits converted to product by an enzyme at max velocity
what determines the k_{cat} ?
how long it takes to get to transition state
ternary complex
all the substrates are present at once before product is made
either ordered or random
ping-pong reaction
one substrate comes in—> modify the enzyme —> leaves —> another substrate comes in —> product is formed —> leaves
how does ordered binding to a ternary structure work?
each substrate binders one at a time then the products leave one at a time
how does substrate binding randomly to a ternary complex work?
either substrate binds first then the other binds —> either product leaves first then the other
substrates in Cleland nomenclature
A, B, C, D (first being A)
products in Cleland nomenclature
P, Q, S, T
bi bi reaction
two substrates come in and two products leave (ternary structure)
Cleland nomenclature of successive enzymes in a ping pong reaction
1st- E —> F —> G (always has to go back to original E)
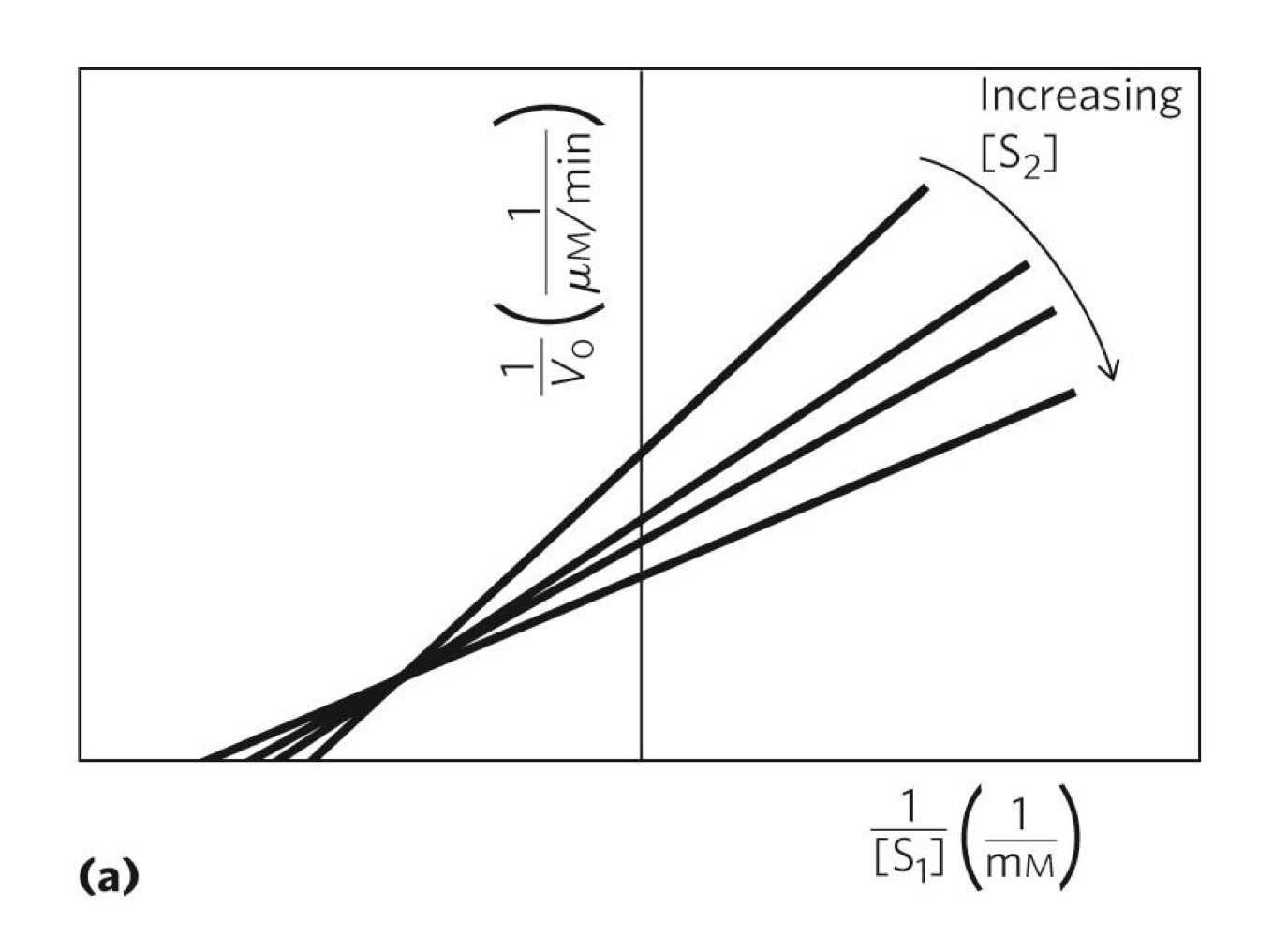
what does this graph indicate and what type of graph is it?
the pathway includes a ternary complex
lineweaver-burk plot
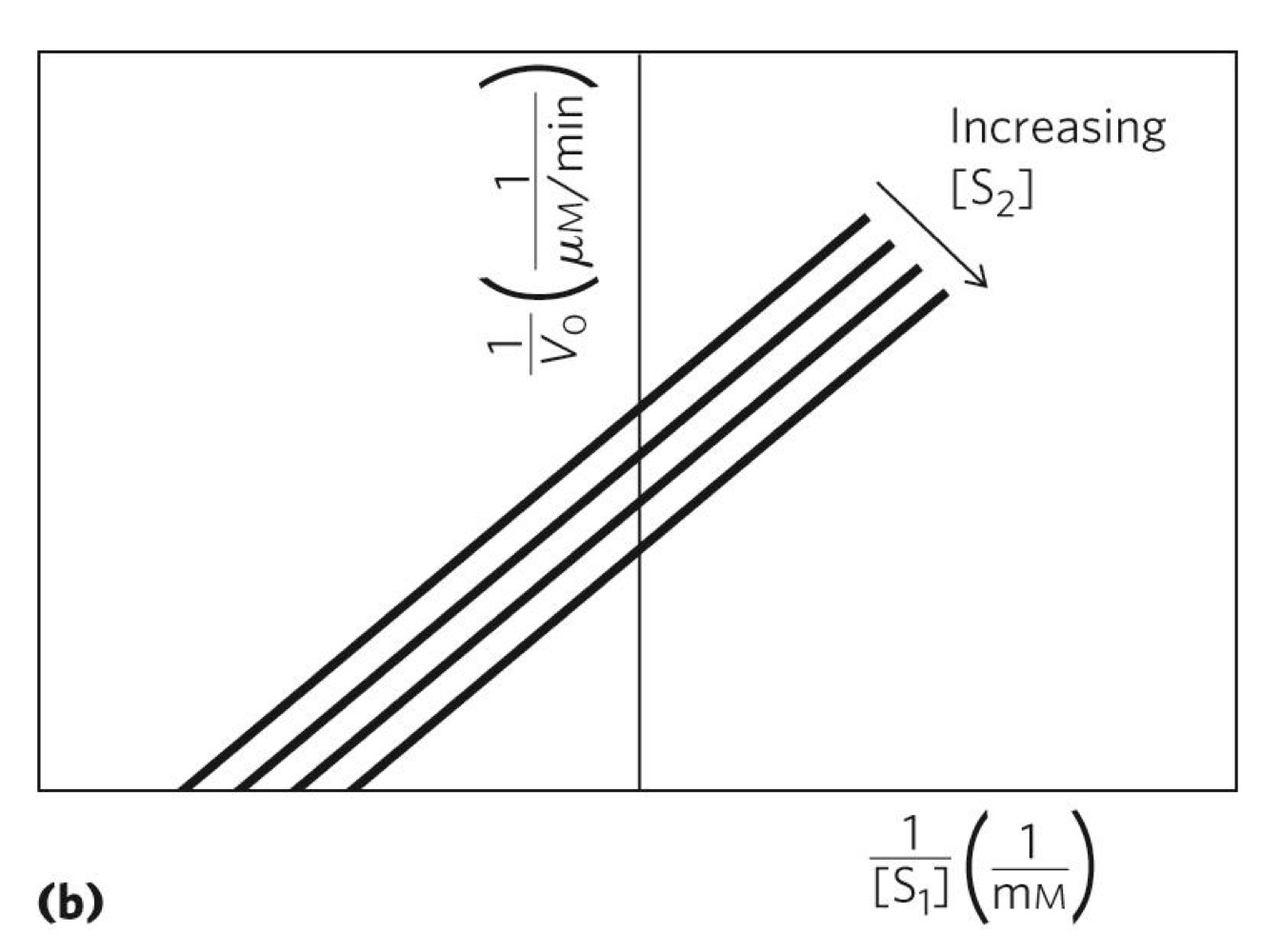
What does this graph indicate
ping pong reaction
why do we need to regulate enzymes
to conserve energy in the body
enzyme inhibitors
show or stop enzyme catalysis
irreversible inhibitors
permanently inactivate enzymes
usually on active site
what’s irreversible inhibitors work (4)
covalently bind to a functional group needed
destroy functional group
target protein for degradation
cause enzymes to fall apart
suicide inhibitors
type of permanent inhibitor
bind to active site and start doing the chemical reaction
hold enzyme in a permanent intermediate
transition state analogs
look like a substrate in its transition state but its in its ground state —> bind most tightly to enzyme
makes really stable bonds (not covalent) with enzyme —> no reason to leave so stays permanently
reversible inhibitors
like protein ligands have an on/off rate (bind—> release)
K_{I}
reversible inhibitor binding rate
competitive inhibitors
looks like substrate and competes with the substrate
enzyme bind —> [EI] complex—> inhibitor falls off
when are competitive inhibitors useful in medicine?
when they have a large \frac{1}{K_{I}} (Ki is small) —> means inhibitor rate is beating regular rate
how do competitive inhibitors change Km and Vmax?
change Km but not Vmax
because changes how often E binds to S but not how many E
(apparent) \alpha K_{m}
how much the inhibitor is affecting K_{m}
no inhibitor \alpha=1
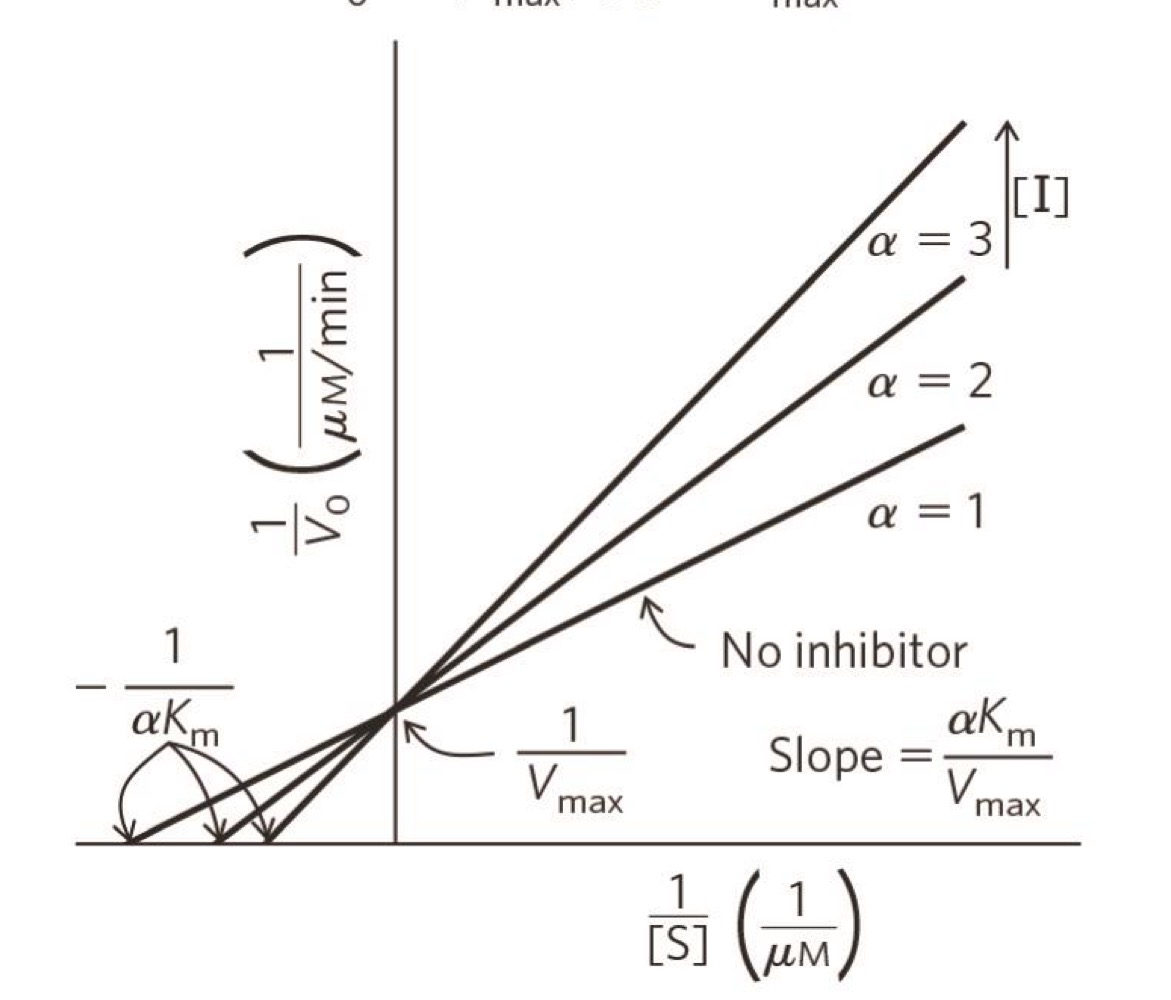
what type of inhibition?
competitive inhibition
types of inhibition that happens at the active site
competitive and some irreversible
types of inhibitors that alter active site structure
mixed, noncompetitive, and uncompetitive
mixed inhibitor
reversible
binds to the allosteric site on either the E or ES
mixed inhibition on a Lineweaver-burk plot
different y-intercepts and different X-intercepts
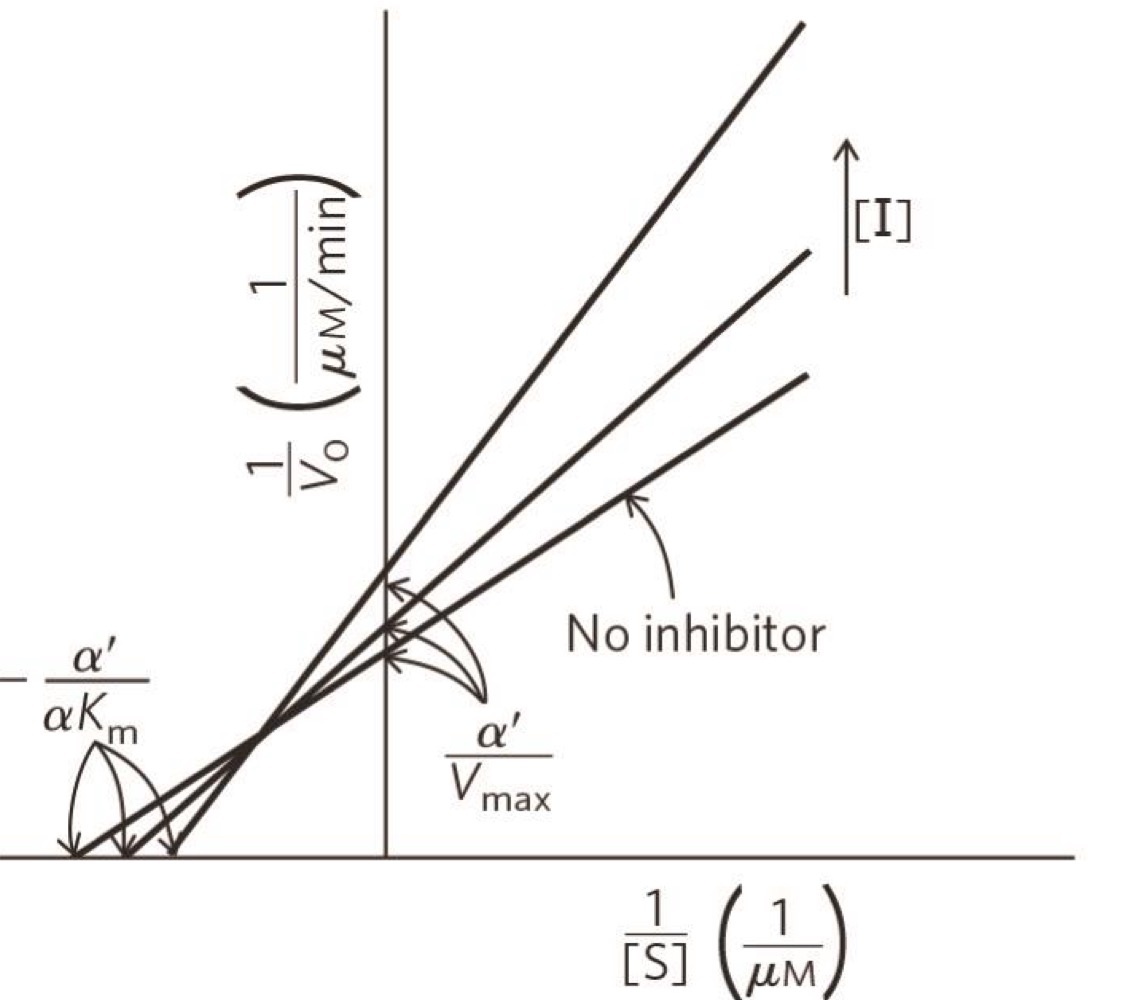
what type of inhibition
mixed inhibition
noncompetitive inhibition
type of mixed inhibitor where I binds to E and ES equally
noncompetitive inhibition on Km and Vmax
affects Vmax but Km of unbound enzymes
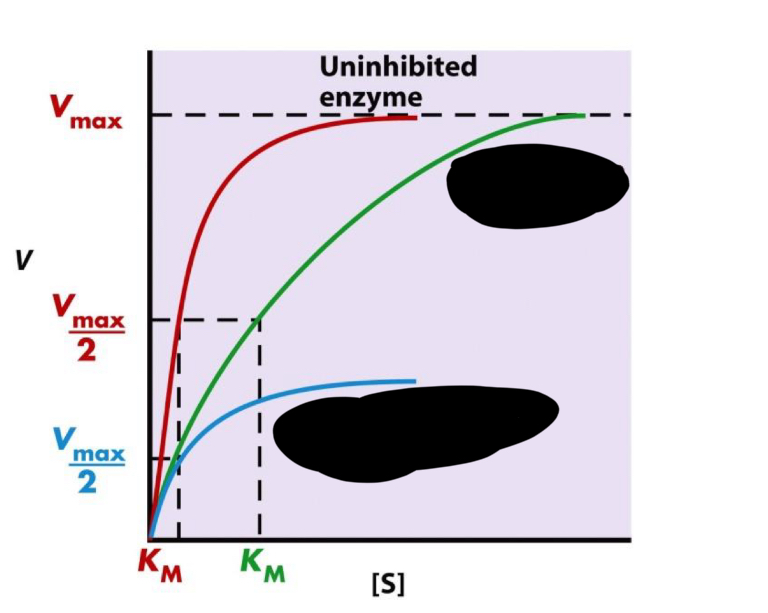
blue
noncompetitive inhibition
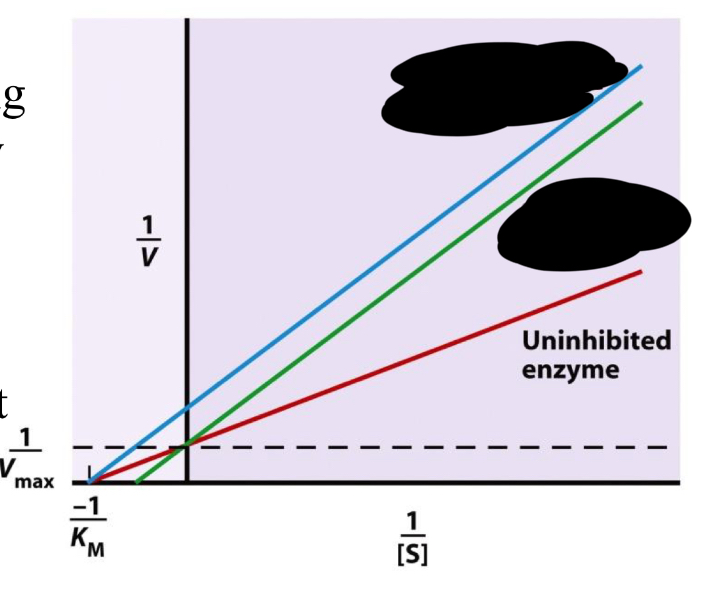
blue
noncompetitive inhibition
uncompetitive inhibition
binds to ES on allosteric site and makes it so the ES can’t get to transition state
uncompetitive inhibition on Km and Vmax
Vmax decreases
Km decreases- takes smaller amounts of substrate to reach Vmax
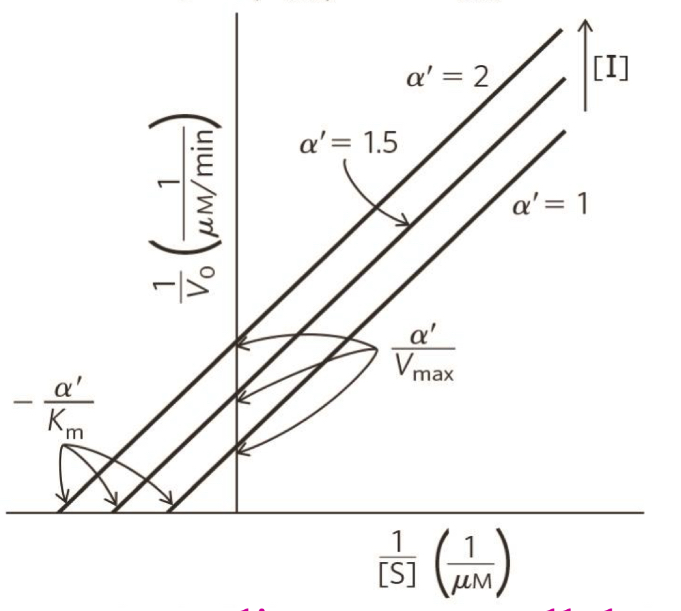
what type of inhibition is this?
uncompetitive inhibition
how to alter activation site without inhibitors?
covalent modification of enzyme
how to covalently modify an enzyme?
adding a phosphate by protein kinase
taking away a phosphoryl group with phosphatases
adding methyl or acetyl groups
what does adding and taking away phosphorly groups do to the active site?
change active site and whether a substrate can get into it and do its work
why is phosphorylation important in enzyme control?
it can fine tune the activation of an enzyme base on the specific processes in which enzymes can be phosphorylation (complex long cascade or one step)
proteolytic cleavages
permanently removes a part of the protein
zymogen
precursor to proteases that need their inhibitory part cut off
proproteins/proenzymes
the protein that need to have an inhibitory part cleaved off
feedback inhibition
when end product binds to allosteric site and creates a conformational change to stop the S for binding to the E
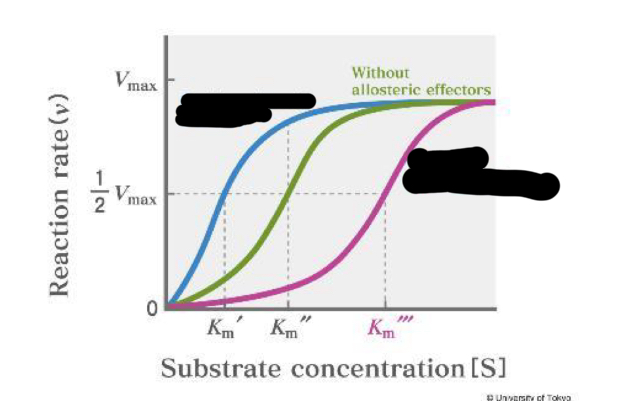
blue
positive allosteric effectors
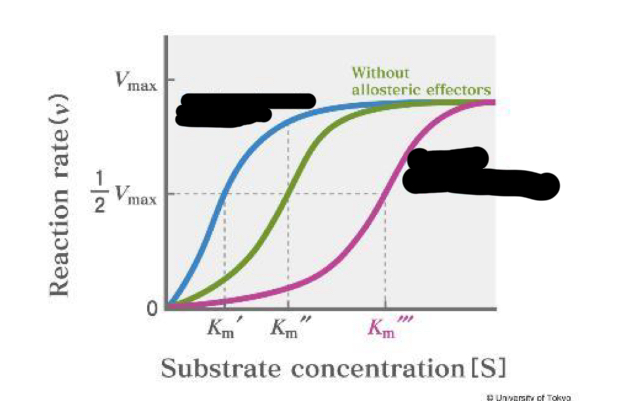
pink
negative allosteric effectors