2.2 - Set Operations
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
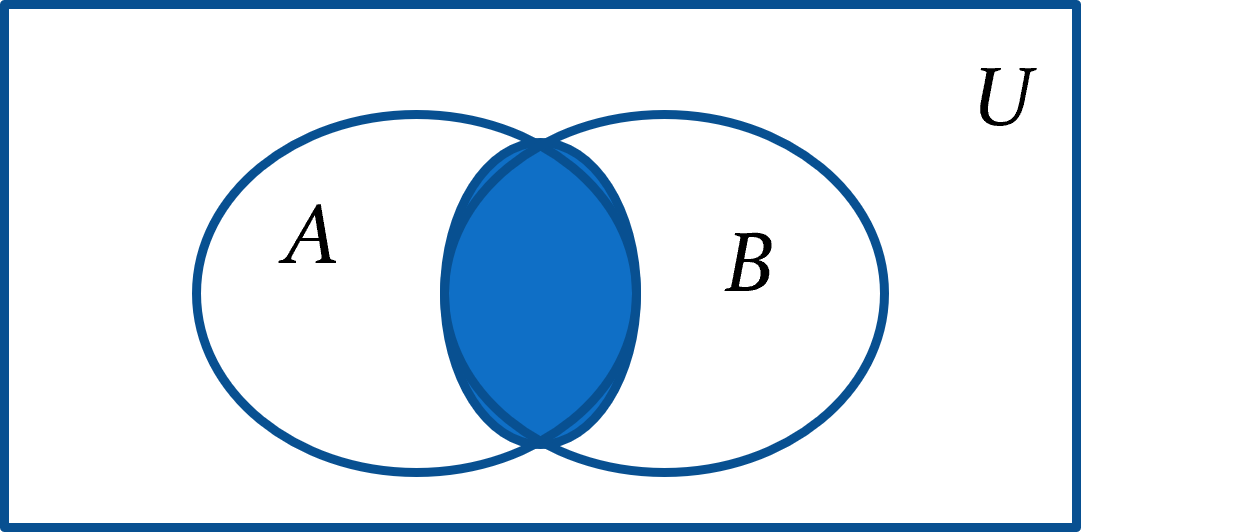
union
A ∪ B
all the combined elements in sets
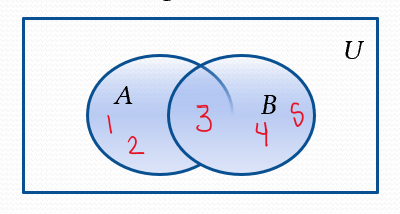
intersection
A ∩ B
the elements that the sets have in common
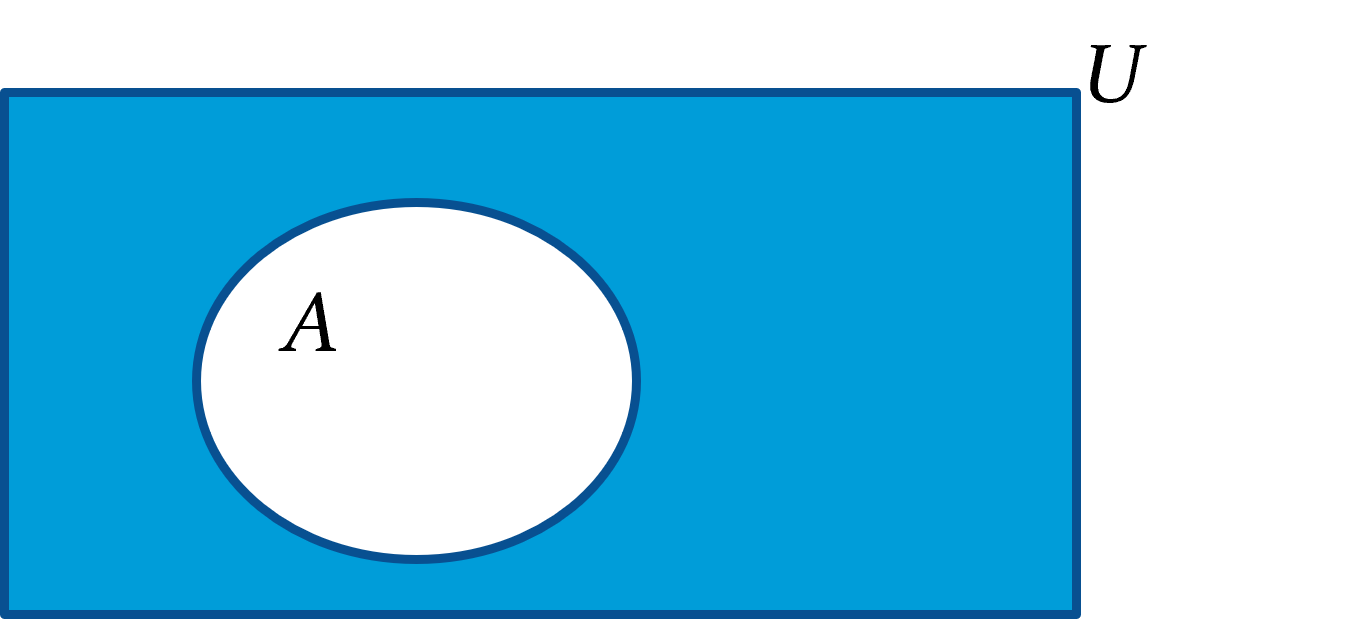
complement
Ā
all the elements not in A
difference
A - B
elements in A but not B
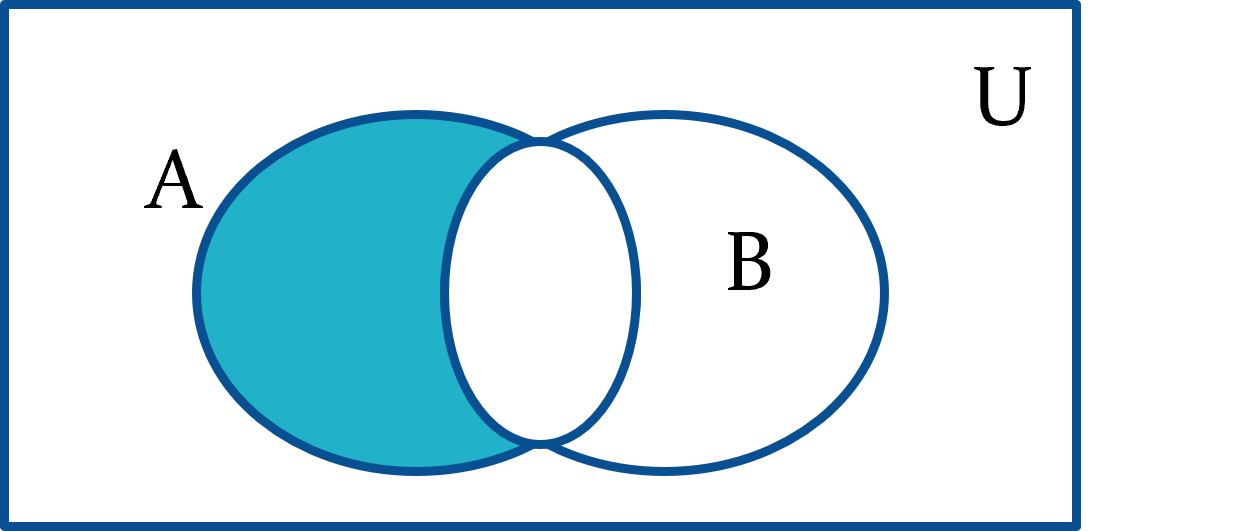
identity law
A union empty set = A | A intersection U = A
A union empty set = A | A intersection U = A
identity law
domination law
A union U = U | A intersection empty set = empty set
A union U = U | A intersection empty set = empty set
domination law
idempotent law
A union A = A | A intersection A = A
A union A = A | A intersection A = A
idempotent law
complementation law
complement (complement A) = A
complement (complement A) = A
complementation law
commutative law
A union B = B union A | A intersection B = B intersection A
A union B = B union A | A intersection B = B intersection A
commutative law
associative law
A union (B union C) = (A union B) union C | A intersection (B intersection C) = (A intersection B) intersection C
A union (B union C) = (A union B) union C | A intersection (B intersection C) = (A intersection B) intersection C
associative law
distributive law
A intersection (B union C) = (A intersection B) union (A intersection C) | A union (B intersection C) = (A union B) intersection (A union C)
A intersection (B union C) = (A intersection B) union (A intersection C) | A union (B intersection C) = (A union B) intersection (A union C)
distributive law
de morgan’s law
complement (A union B) = complement A intersection complement B | complement (A intersection B) = complement A union complement B
complement (A union B) = complement A intersection complement B | complement (A intersection B) = complement A union complement B
de morgan;s law
absorption law
A union (A intersection B) = A | A intersection (A union B) = A
A union (A intersection B) = A | A intersection (A union B) = A
absorption law
complement law
A union complement A = U | A intersection complement A = empty set
union
{x | x is an element of A or x is an element of B}
intersection
{x | x is an element A and a is an element B}
complement
{x is an element U | x is not an element A}
difference
{x | x is an element A and x is not an element B}
cartesian product
the set of ordered pairs (a, b) where a is an element of A and b is an element of B
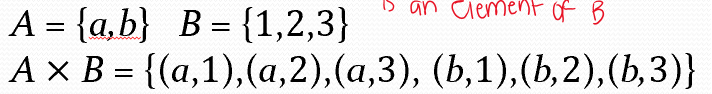
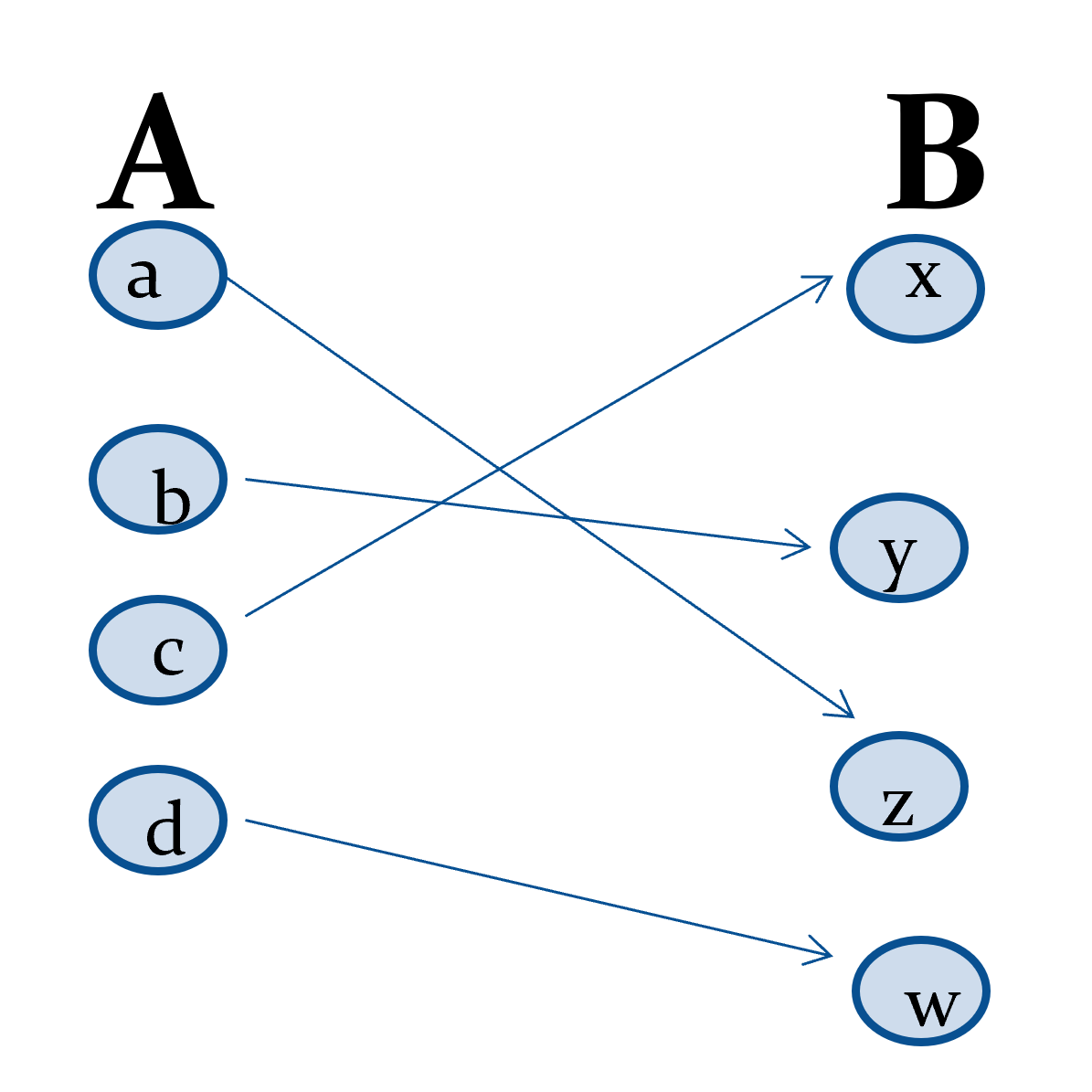
functions
a relation from A to B in which for each element a in A there is exactly one element in b in B
f: A → B
A = domain B = codomain
range
f(A)
codomain
B
domain
A
image
if f(a) = b;
b is called the of a under f
preimage
if f(a) = b;
a is called the of b
injection/one-to-one
each element of y is mapped to at most one element of X
each element in B has 0 or one preimage(s)
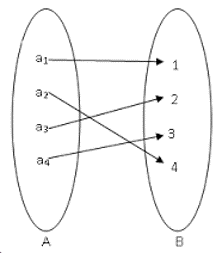
surjection/onto function
each element of Y is mapped to at least one element of x
each element in B has 1 or more preimage(s)
if the range and codomain are equal, then the function is onto
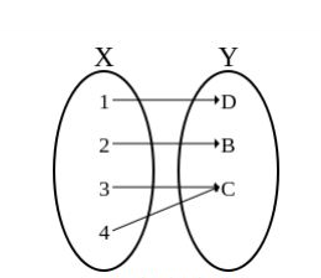
bijection
if a function is one-to-one (injection) and onto (surjection)
each element of Y is mapped to exactly 1 element of