A&P lecture ch 3. pt 1.
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cell structure and function
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
non membranous organelles
SIX TYPES
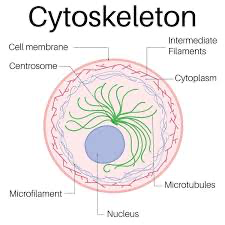
cytoskeleton
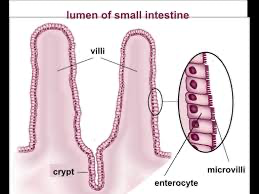
microvilii
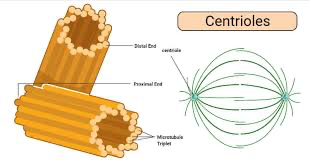
centrioles
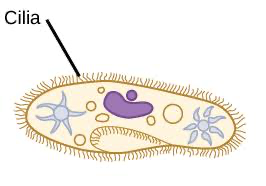
cilla
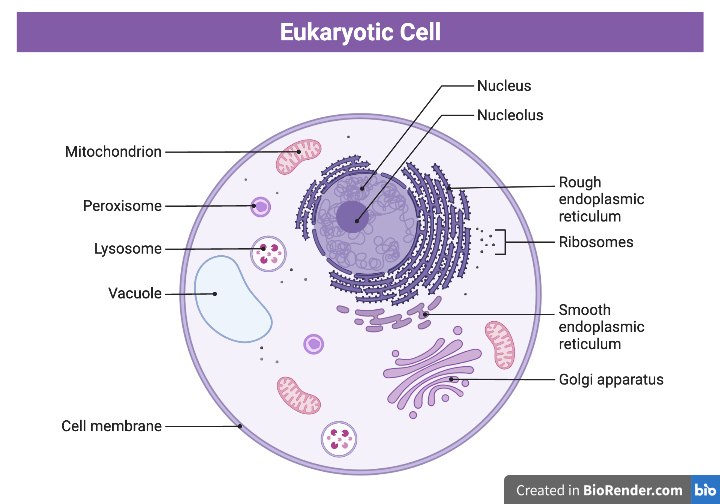
ribosomes
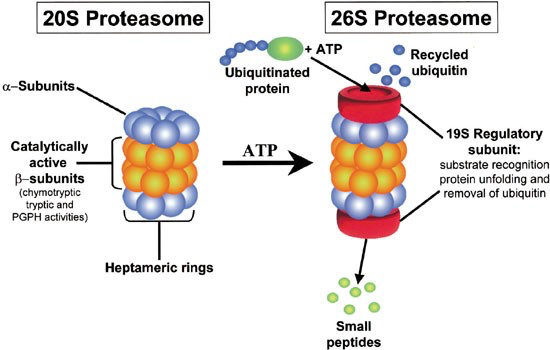
proteasome
cytoskeleton
microvilli
centrioles
cilia
ribosomes
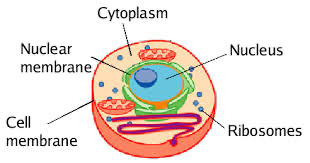
two types:
-free ribosomes in cytoplasm (inside cell)
-fixed ribosomes attached to ER (outside cell)
proteasome
membranous organelles
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
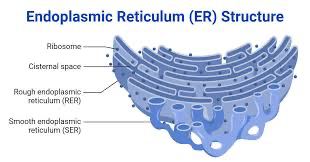
-cisternae are storage chambers within membranes
-endo=withn, plasm=cytoplasm, reticulum=network
smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
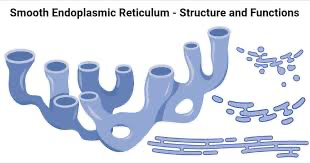
-no ribosomes
-sythnesizes lipids and carbohydrates
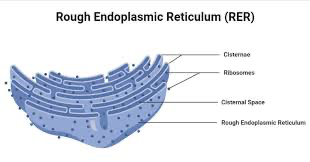
rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
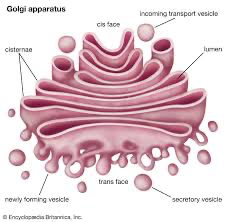
golgi apparatus
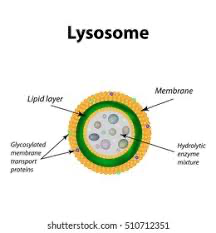
lysomes
peroxisomes
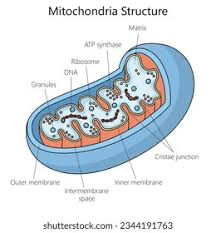
mitochondria
sex cells (germ cells)
reproductive cells, male sperm, female oocyte (egg)
somatic cells
“soma=body”
all body cells, except sex cells
extracellular fluid (interstitial fluid) EFC
-watery medium that surrounds a cell
-plasma membrane, separates cytoplasm from the extracellular fluid
cytoplasm
jelly like substance that fills the cell
cytosol
the “jelly like substance”
anchoring proteins (membrane protein)
-stabilizers
-attach to inside or outside structures
recognition proteins (membrane protein)
-identifiers
-these label cells as normal or abnormal
-often glycoproteins
enzymatic protiens (membrane proteins)
-catalyst reactions either in cytosol or in ECF, depending on location of active site
receptor protiens (membrane proteins)
binds and respond to ligands (ions and hormones)
carrier protiens (membrane proteins)
-transport specific solutes through membrane
-may require ATP
channel protiens (membrane proteins)
regulate water flow and small solutes through membrane
proteoglycans (membrane carbohydrates)-