OPT 323 Healthcare Delivery in the US
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is a health care provider?
individual (MD, OD, NP, OT, etc) or institution who provides preventative, curative, or rehabilitative health care services for individuals, families, communities
What are the 2 different classes of hospitals?
private = for-profit or non-profit (note that non-profits still make a profit)
government = federal (VA, IHS, military), state, county, city

What are the 3 modes of practice?
private = solo, group
direct employment = for-profit, non-profit
government = military, VA, IHS, state/local

What are the 3 categories of preventative health care?
primary = stop initiation of disease
secondary = early diagnosis of disease
tertiary = control the impact of disease
What are the 3 categories of curative health care?
primary = initial approach to a PCP for treatment
secondary = specialist treatment
tertiary = specialized consultative care
What is the single-payer national health service form of health care systems?
"Beveridge model" = government is a single payer and provider; gov owns mostly all hospitals and clinics = universal participation

What is an example of a single-payer national health service form of health care systems?
UK's NHS

What is the single-payer national health insurance form of health care systems?
all individuals receive government-funded health insurance which is then billed to by private providers

What is an example of a single-payer national health insurance form of health care systems?
Canada = Medicare
Taiwan
South Korea

What is the social insurance model of health care systems?
"Bismark model" = government plays central role in setting costs by private providers = insurance companies cover basic services as non-profit = universal participation

What are some examples of the social insurance model of health care systems?
Germany
Japan
France
Belgium
Netherlands
Switzerland

What is the out-of-pocket model of health care systems?
no widespread public or private system of health insurance = access to care is determined by ability to pay private providers = most expensive form of healthcare

What are some examples of the out-of-pocket model of health care systems?
developing countries:
Afghanistan
Bangladesh
Guatemala
Nigeria

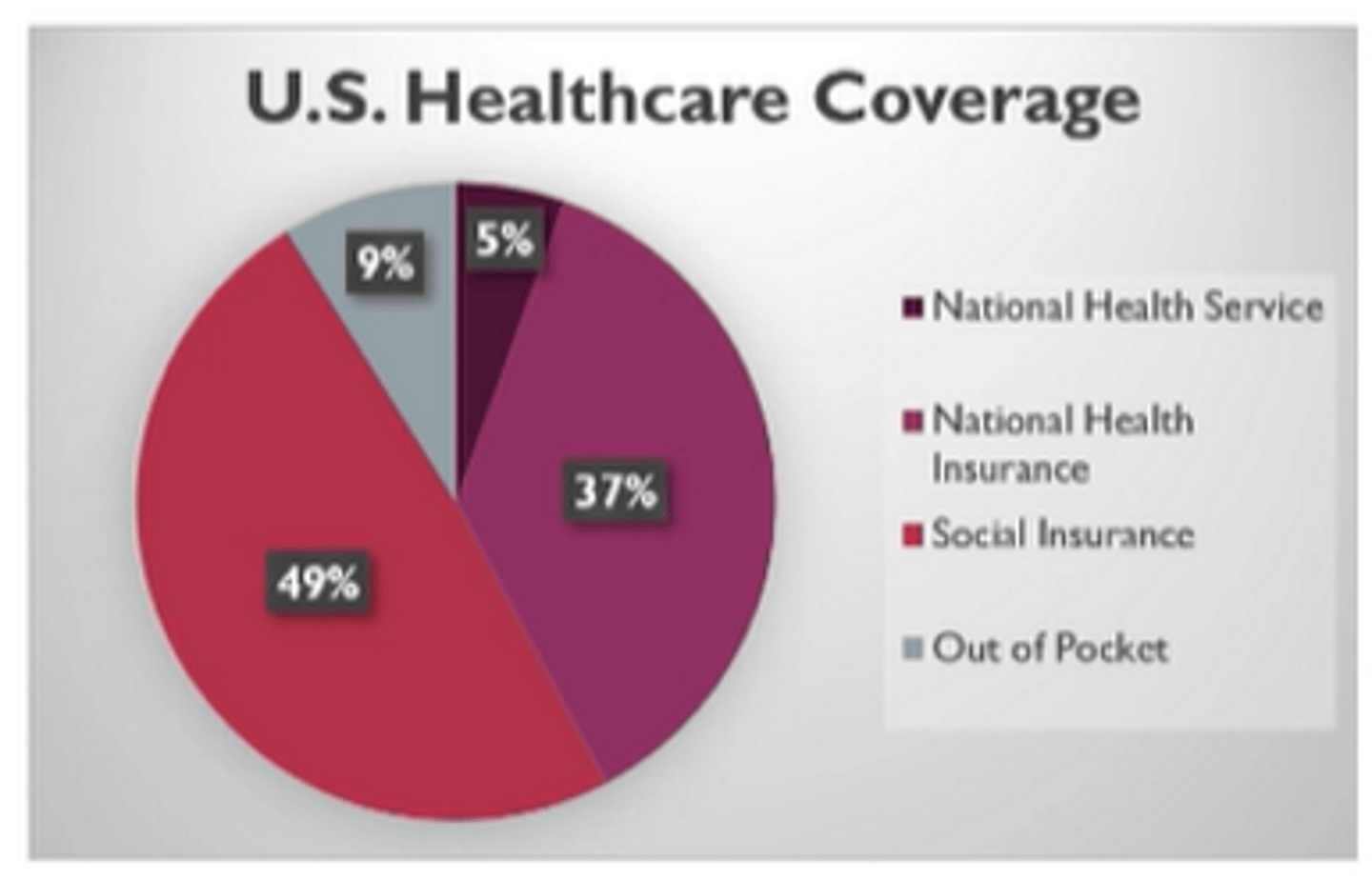
The US's health care system is most similar to which country?
Germany = social insurance model
BUT has a combo of all 4 really:
single-payer national health service = VA, military, IHS, federal prisons
single-payer national health insurance = Medicare, Medicaid
social insurance = BCBS, UHC, VSP
out-of-pocket = uninsured, underinsured
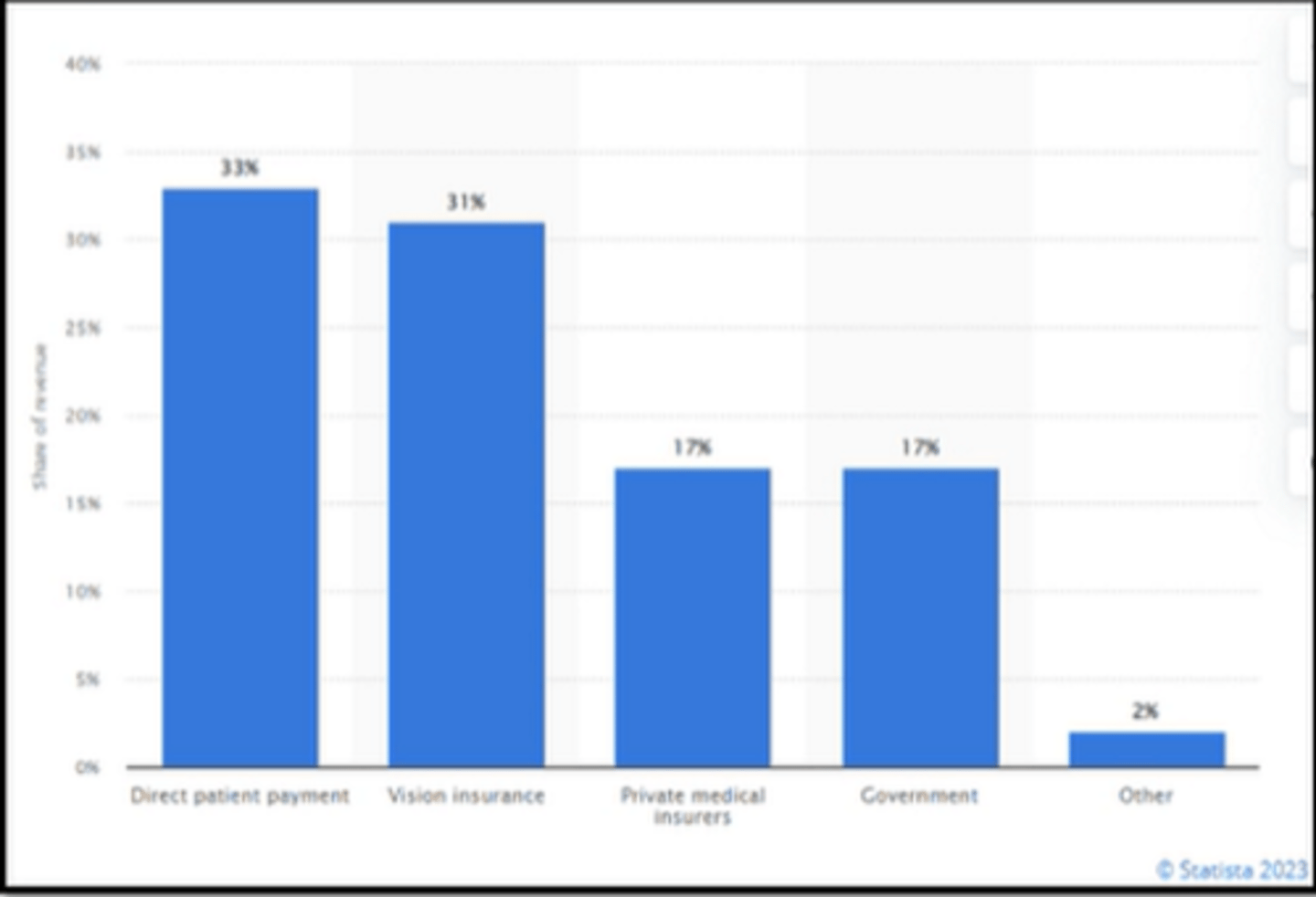
What are the top 2 ways that OD's get paid?
direct pt payment
vision insurance
private medical insurers
gov
other
What are some pros of the US health care system?
tech advanced
responsive
access = lots of providers
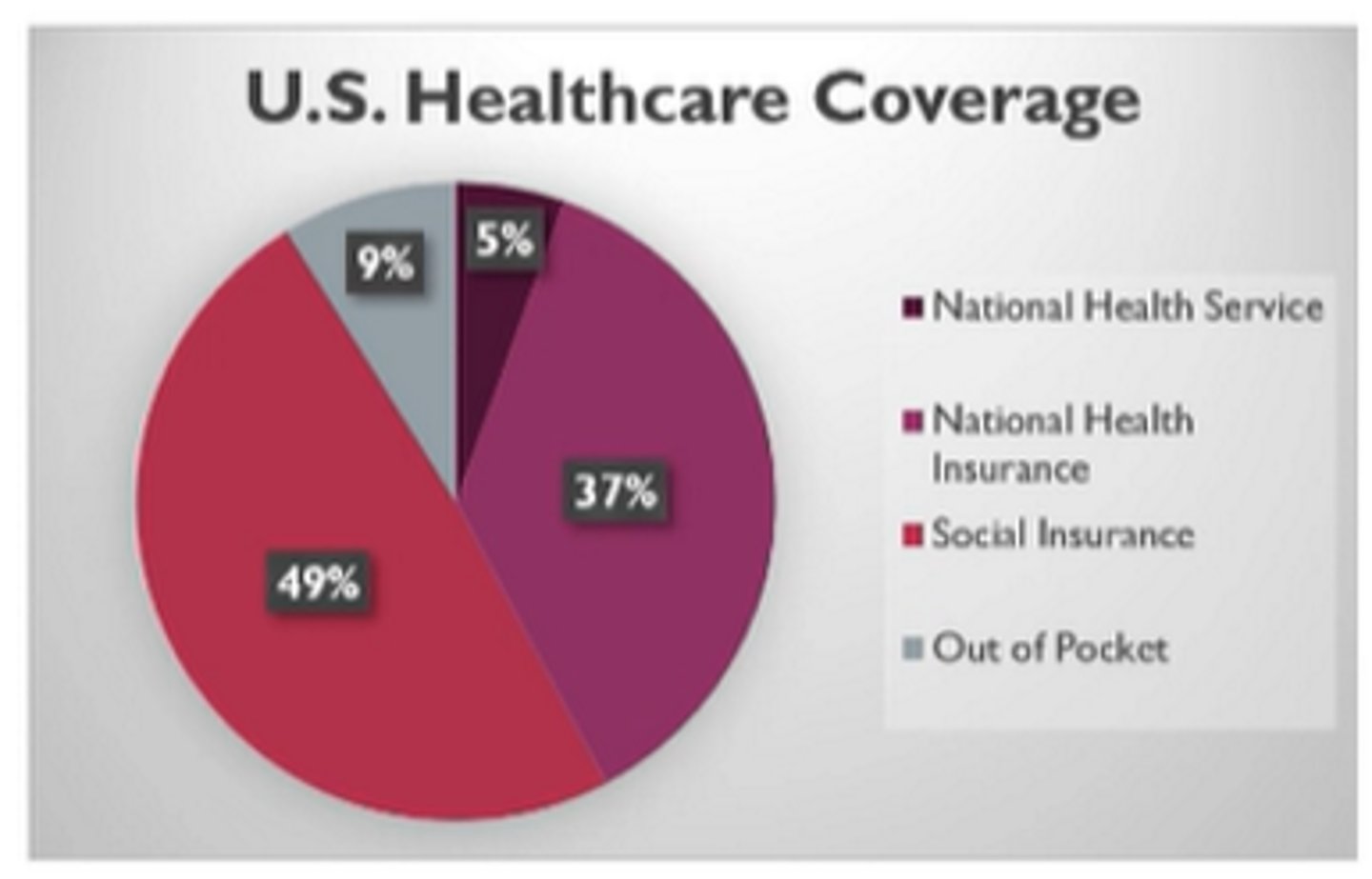
What are some cons of the US health care system?
cost
coverage
outcomes = very low ranking in the world for infant mortality, adult mortality, life expentancy
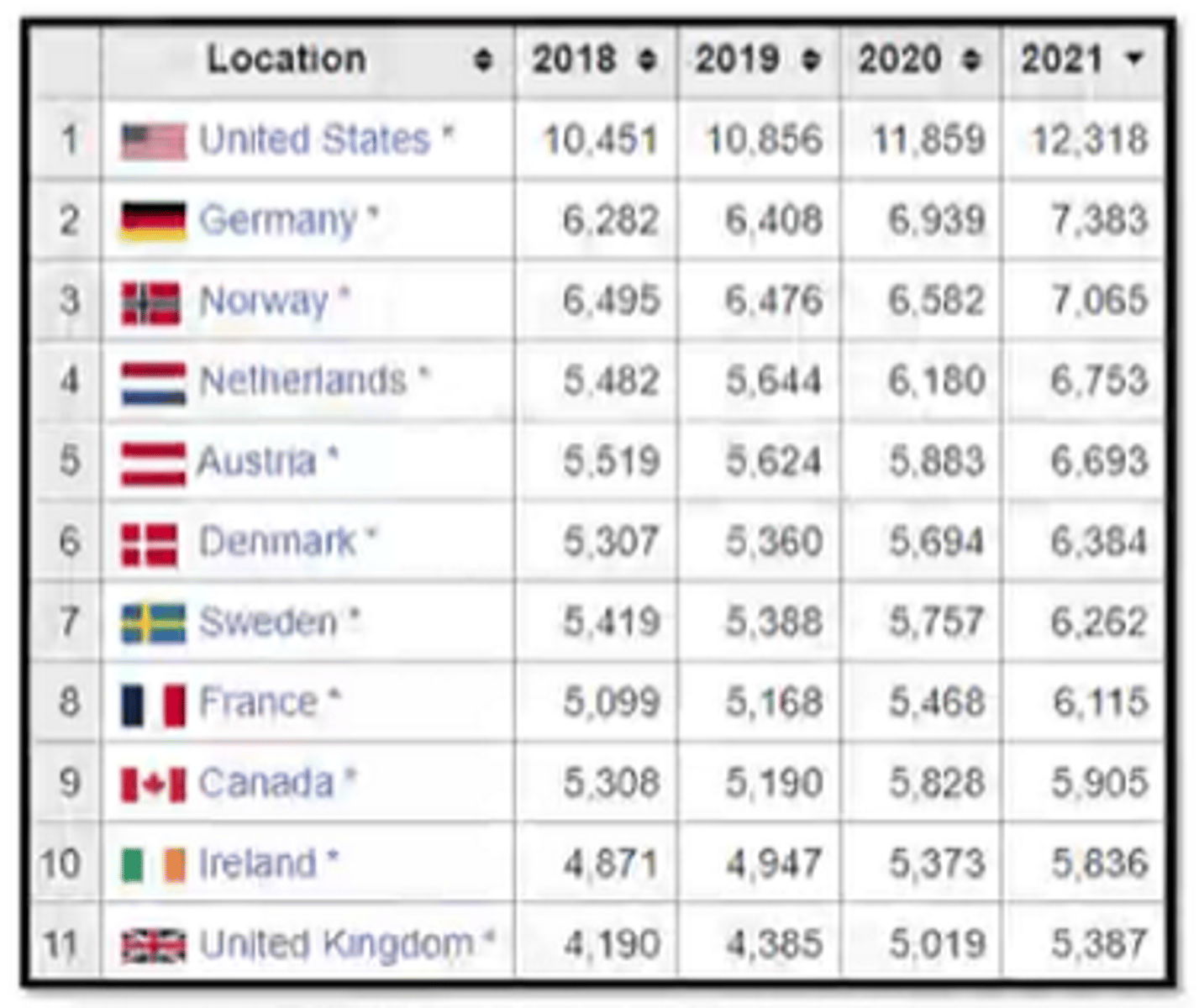
The US has the highest _______________ health care costs in the world.
per capita
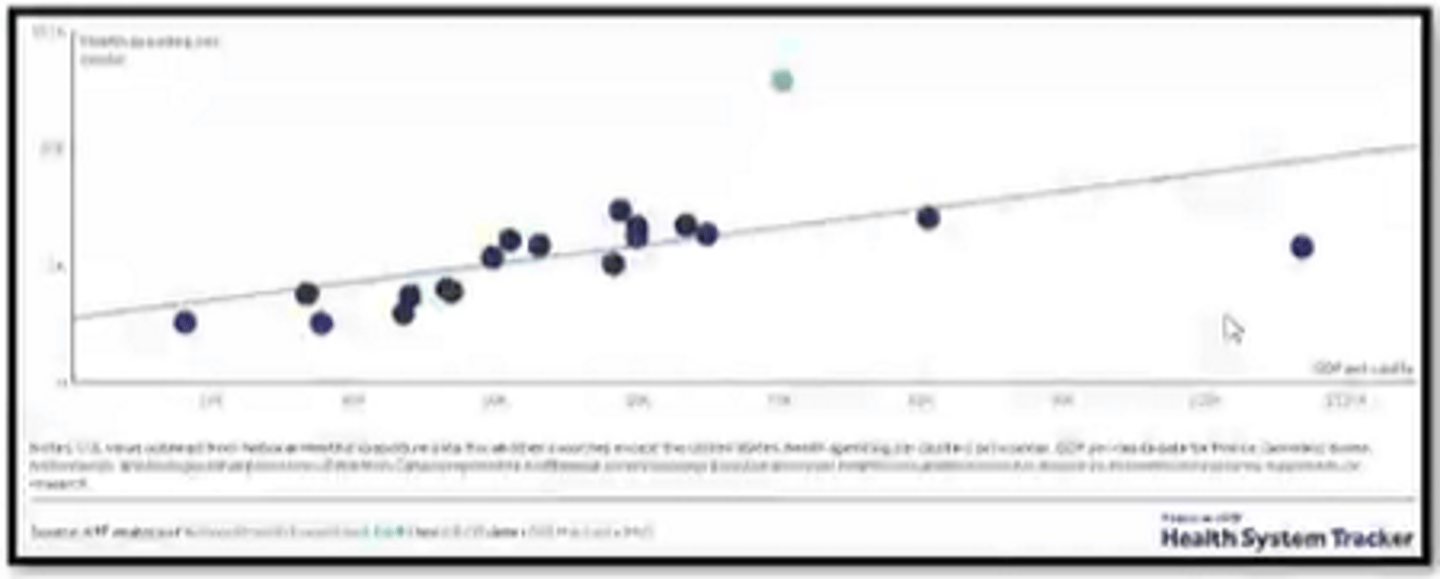
The US has the highest % of ___________ spent on health care in the Western world.
GDP
What are some reasons that health care is so expensive?
chronic disease = obesity, HTN, CVD, DM, AMD
technology = over testing
prescription drugs = brand vs generic, pharma
utilization = ED visits vs PCP, etc
administrative costs = managers, insurance, etc.
provider salaries
What are some possible cost control measures that could be utilized?
utilization controls
EHR = prevent repeat testing/redudancies
EBM recommendations
reward preventation that costs less than future tx
control fees/provider incomes
decrease price of drugs/products
increases taxes for health care
increase public health funding