Comprehensive Guide to Preterm Labor, Birth Complications, and Obstetric Procedures
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What defines preterm labor (PTL)?
Regular contractions with a change in cervical effacement or dilation, or cervical dilation of at least 2 cm.
What is considered preterm birth?
Any birth that occurs between 20 0/7 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation.
What are the three sub-categories of preterm birth?
Very preterm (<32 weeks), moderately preterm (32 to 34 weeks), and late preterm (34 0/7 to 36 6/7 weeks).
Why is preterm birth more dangerous than low birth weight?
Less time in the uterus correlates with immaturity of body systems.
What is the definition of low birth weight?
A birth weight of ≤ 2500 grams.
What percentage of preterm births are spontaneous?
75% of preterm births.
What is the only definitive factor causing spontaneous preterm labor?
Infection.
What role does cervical length play in predicting preterm labor?
A cervical length >30 mm is unlikely to result in premature birth.
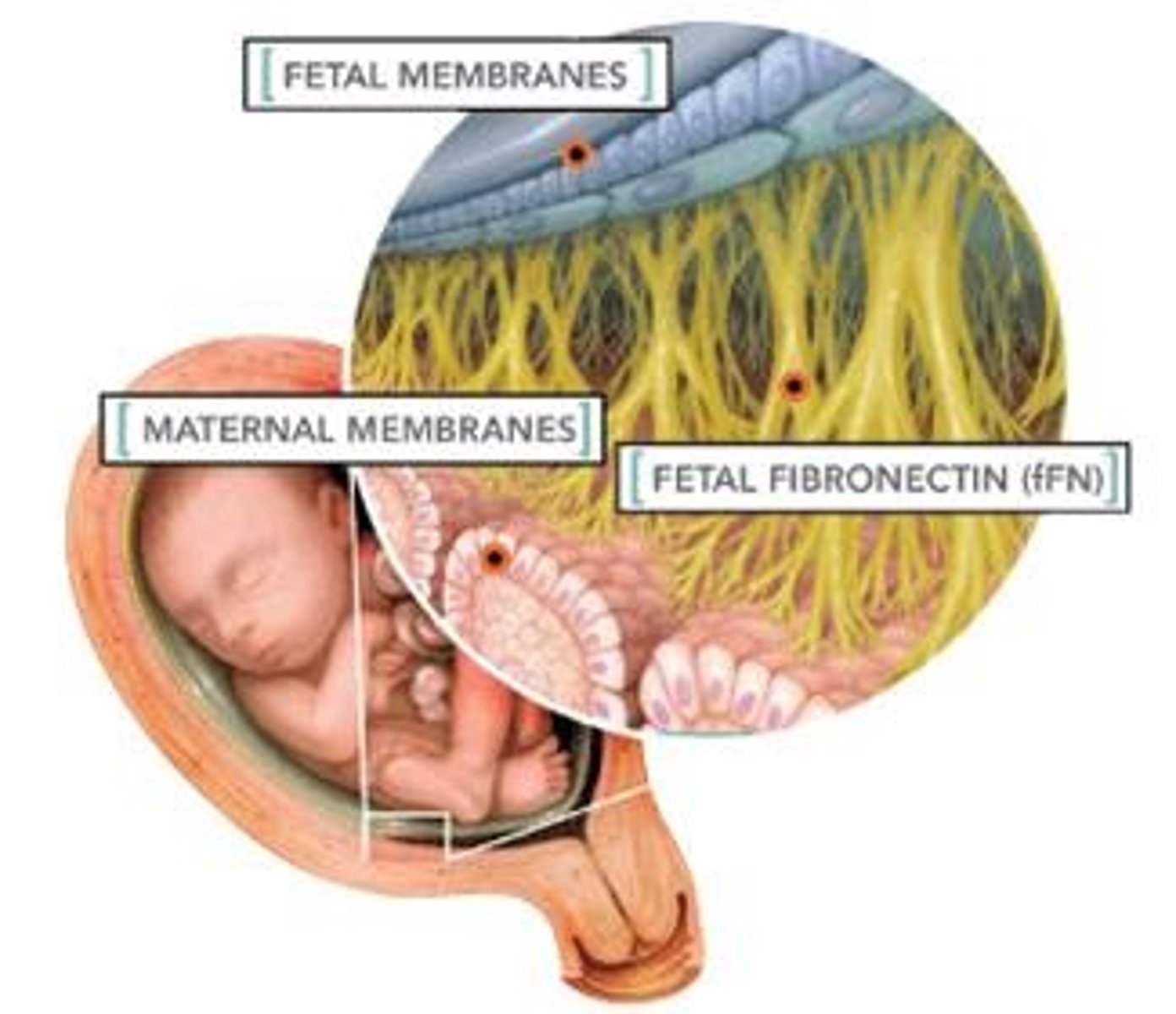
What is the purpose of the Fetal Fibronectin Test (fFn)?
To indicate the likelihood of going into labor; a negative result suggests a 1% chance of giving birth within 2 weeks.
What are some prevention strategies for preterm labor?
Addressing risk factors, preconception counseling, and progesterone supplementation.
What is the purpose of antenatal glucocorticoids?
To promote fetal lung maturity and reduce the incidence of respiratory distress syndrome.
What are the common medications used in the management of preterm labor?
Magnesium sulfate, terbutaline, nifedipine, and betamethasone.
What is PROM?
Spontaneous rupture of the amniotic sac and leakage of fluid prior to the onset of labor.
What is PPROM?
Premature rupture of membranes occurring before 37 0/7 weeks of gestation.
What is chorioamnionitis?
A bacterial infection of the amniotic cavity, a major cause of complications for mothers and newborns.
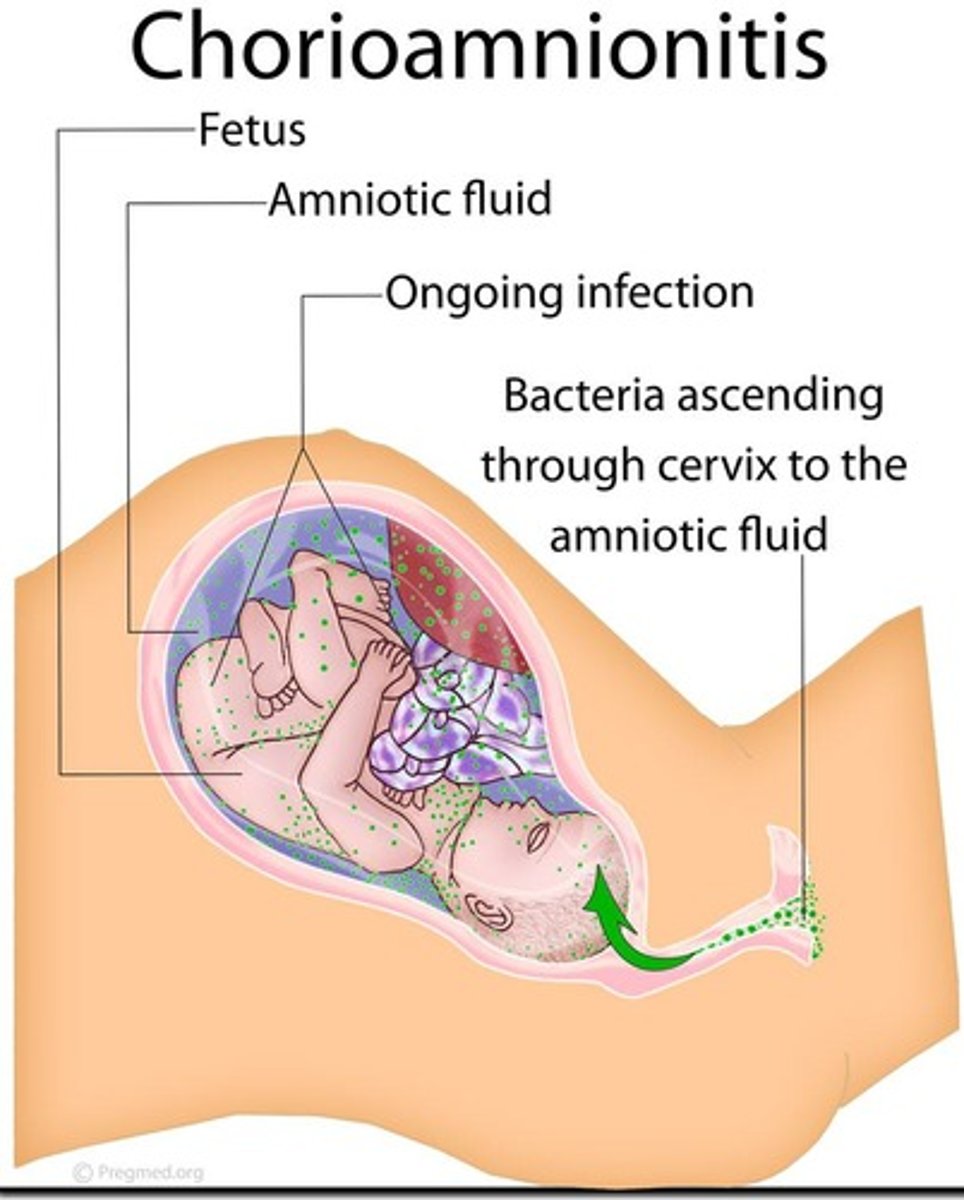
What are the signs of chorioamnionitis?
Maternal fever, maternal and fetal tachycardia, uterine tenderness, and foul odor of amniotic fluid.
What defines postterm pregnancy?
Pregnancy greater than or equal to 42 weeks of gestation.
What are the maternal risks associated with postterm pregnancy?
Increased maternal morbidity, dysfunctional labor, and birth canal trauma.
What is the recommended management for postterm pregnancy?
More frequent fetal assessments and monitoring for signs of labor.
What is the risk of perinatal morbidity and mortality in postterm pregnancies?
It increases greatly beginning at 41 0/7 weeks of gestation.
What is macrosomia in fetal growth?
Abnormal fetal growth characterized by excessive weight.
What is shoulder dystocia?
A condition where the anterior shoulder cannot pass under the pubic arch after the head is born.
What is dysfunctional labor?
Labor that is long, difficult, or abnormal, often leading to cesarean births.
What are the five factors that affect labor?
The powers, the passage, the passenger, maternal position, and psychological responses.
What is precipitous labor?
Labor that lasts less than 3 hours from the onset of contractions to the time of birth.
What complications can arise from precipitous labor?
Maternal lacerations and fetal hypoxia or trauma.
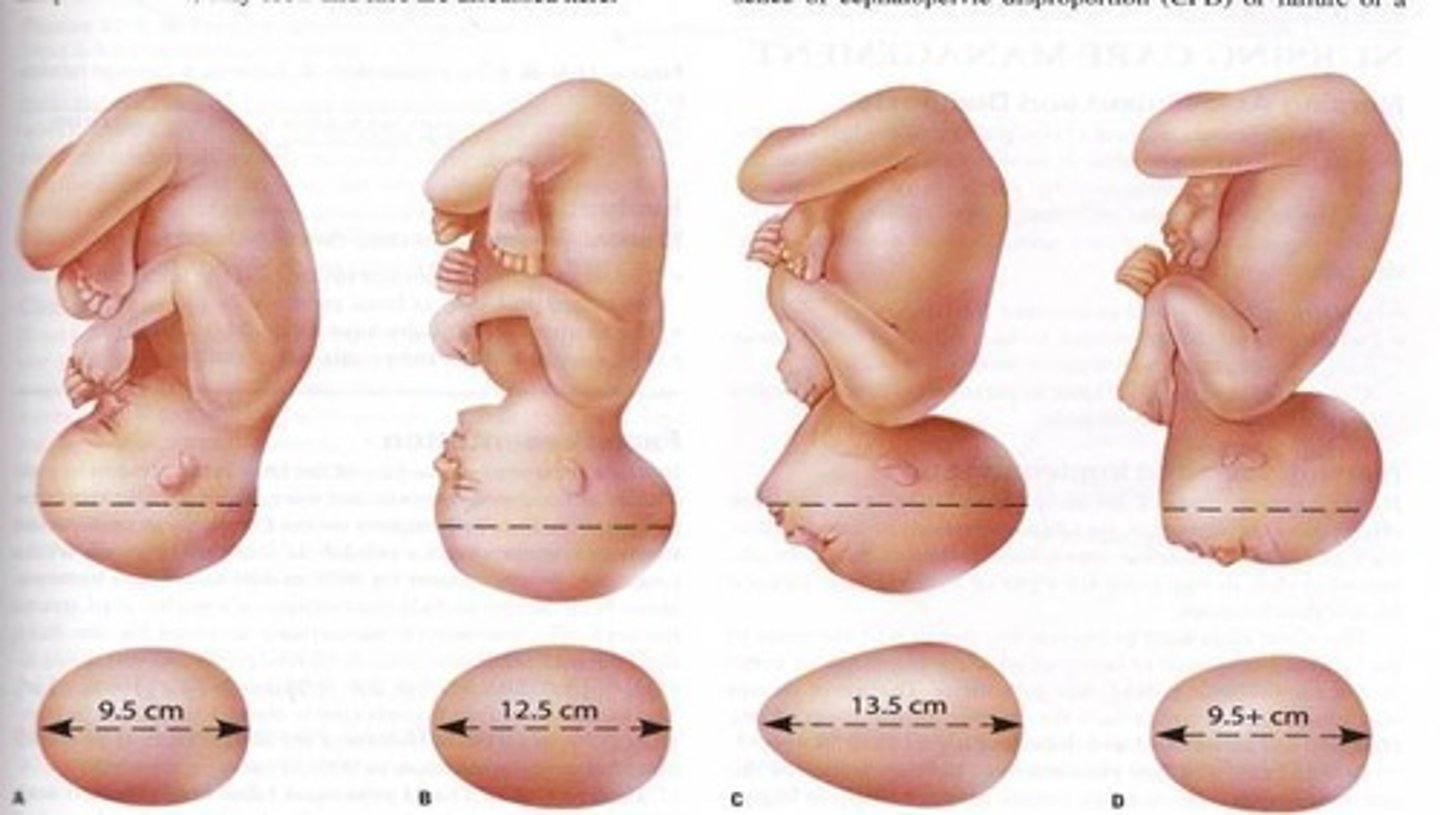
What is the definition of cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD)?
A condition where the fetal head is too large to pass through the mother's pelvis.
What is the body mass index (BMI) range for obesity?
A BMI of 30 or greater.
What are some risks associated with obesity during pregnancy?
Increased risk for spontaneous abortion, gestational diabetes, and cesarean birth.
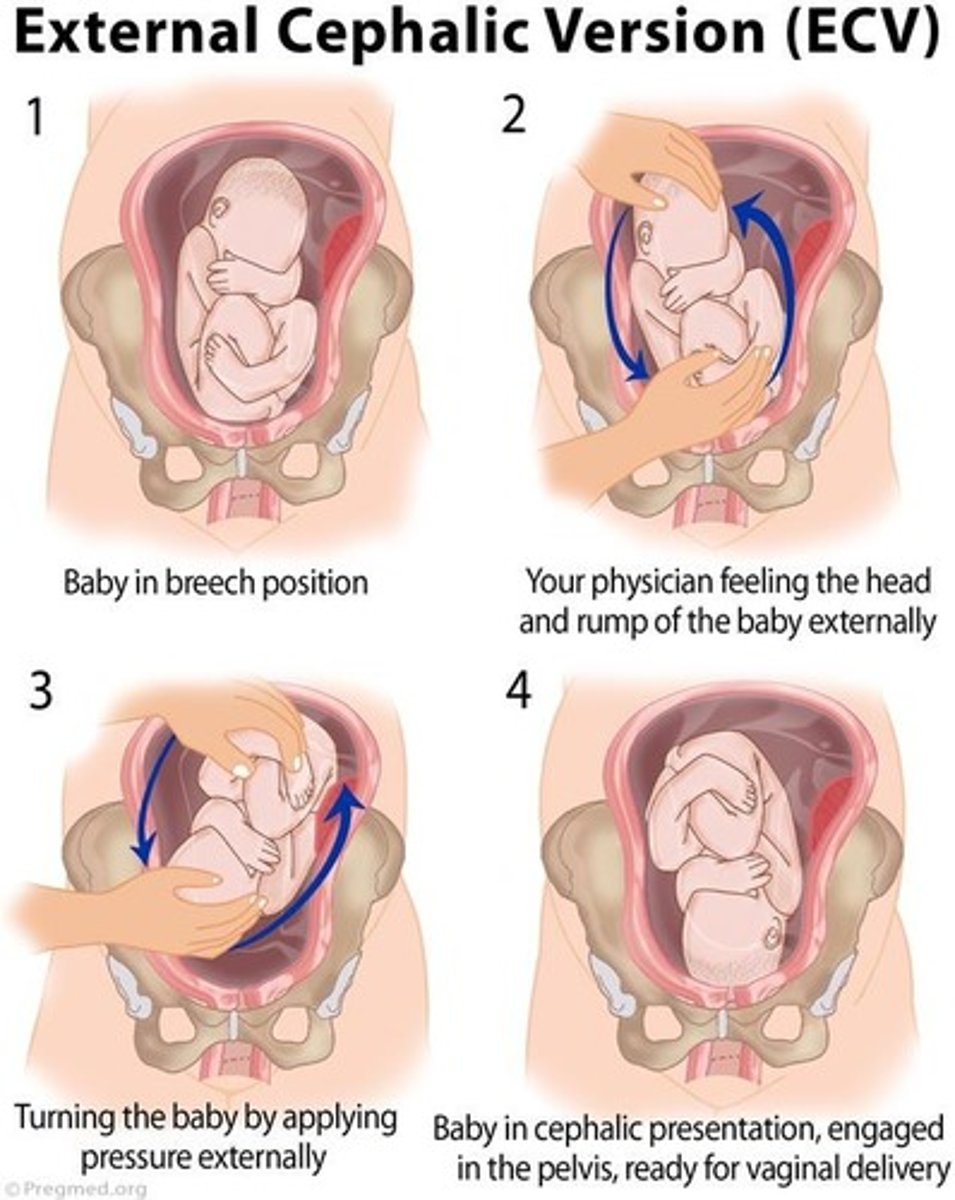
What is external cephalic version (ECV)?
A procedure to turn a fetus from a breech or shoulder presentation to a vertex presentation.
What is the purpose of inducing labor?
To chemically or mechanically initiate uterine contractions before spontaneous labor.
What are the risks of elective induction of labor?
Increased rates of cesarean birth and neonatal morbidity.
What is the role of oxytocin in labor?
It stimulates uterine contractions and aids in milk let-down.
What is operative vaginal birth?
Birth performed using forceps or a vacuum extractor.
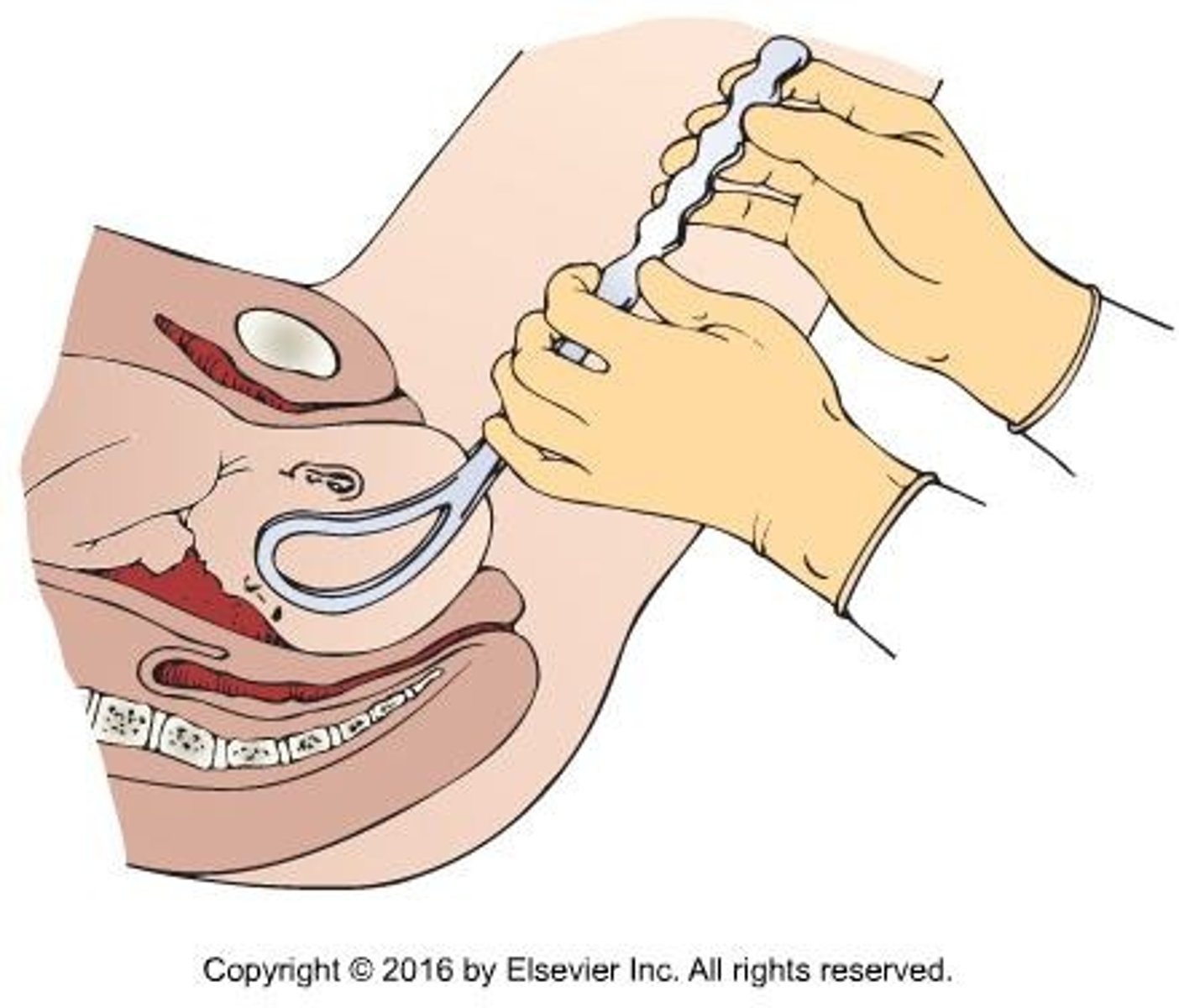
What is the cesarean birth rate in the United States?
Over 32% since the early 2000s.
What does VBAC stand for?
Vaginal birth after cesarean.
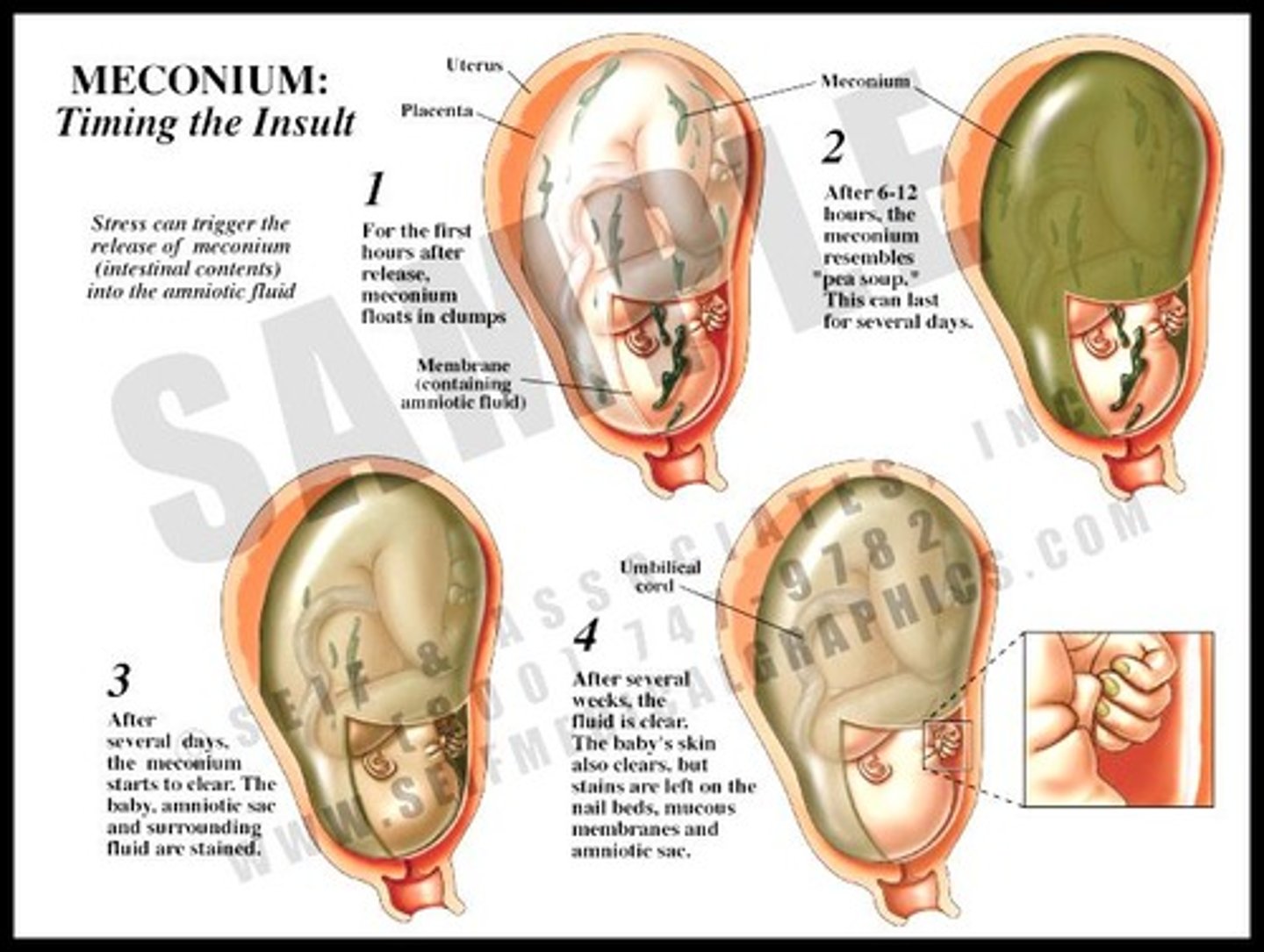
What is meconium-stained amniotic fluid?
Indicates that the fetus has passed stool prior to birth.
What is a prolapsed umbilical cord?
Occurs when the cord lies below the presenting part of the fetus.
What is the primary risk associated with shoulder dystocia for the mother?
Excessive blood loss from uterine atony or rupture.
What is an amniotic fluid embolus (AFE)?
A rare but serious complication characterized by sudden hypotension and hypoxia due to debris entering maternal circulation.
What is the purpose of an episiotomy?
To enlarge the vaginal opening during childbirth.
What are the two types of episiotomy?
Midline and mediolateral.
What is the significance of the McRoberts maneuver?
A technique used to resolve shoulder dystocia.
What are common causes of uterine rupture?
Separation of a previous cesarean scar, trauma, or intense contractions.
What is the management for a prolapsed cord?
Prompt recognition and relieving pressure off the cord.
What is the role of interprofessional care management in obstetrics?
To ensure coordinated care and address complications effectively.