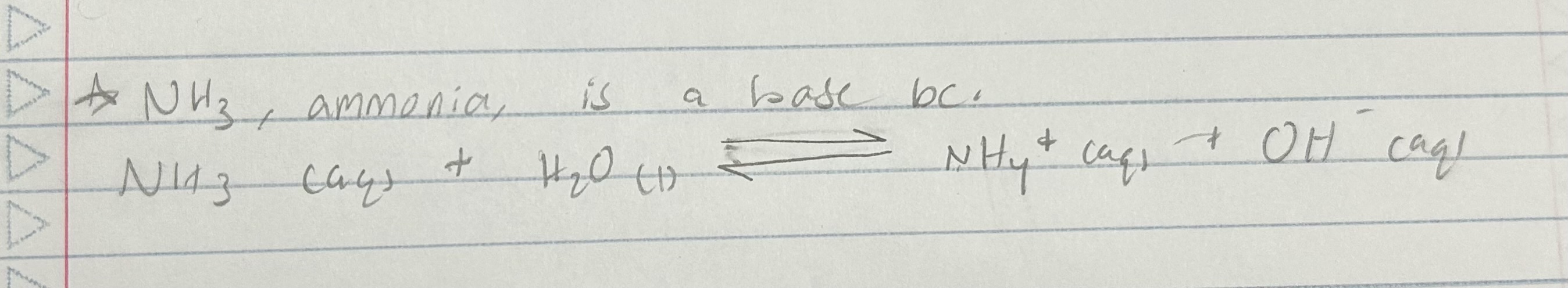10. 1, arrhenius acids and bases + pH, 12/5/25
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Simplest and most limited definition of acid
Acid is a substance that dissolves and dissociates in water to form aqueous hydrogen ions, H+ (aq)
Simplest and most limited definition of base
Base is a substance that dissolves and dissociates in water to form aqueous hydroxide ions, OH- (aq)
do acids have be ionic?
no, ie. HCl is not ionic but instead highly polarized which allows it to form ions in water. Water tears apart different elements in HCl to form ions.
strong acid
Completely dissociates (ionizes: forma ions) in water
Strong base
Completely dissociates in water
Weak acid
does not ionize completely
Weak base
Does not dissociate completely
Electrolyte
Ahh substance that dissolves in water and can conduct electrical through ions
Types of electrolytes
Strong and weak electrolytes
pH scale is calculated based on
Based on hydrogen ion concentration, p is a function of H+
pH scale 0
[H+] = 1 M (concentration of H+ is one molar)
Most acidic
pH 14
[OH-] = 1 M (concentration of hydroxide ions is one molar)
Most basic
can you have negative pH or greater than 14?
Yes
Square brackets in chemistry [H+ (aq)]
square brackets means molar concentration or molarity
[H+][OH-] = constant
Concentration of hydrogen ions times the concentration of hydroxide ions equals a constant number that cannot be zero
Properties of [H+] and [OH-]
cannot be zero
If one increases, the other must decrease
pH of 7 is where they are neutral, so [H+] = [OH-], they are balanced but always present
Ionization
Process of forming ions
Dissociation
Process in which ions break apart when dissociate in solution
Concentration of H+ in dilute solution of a strong acid =
Concentration of the acid
Concentration of OH- in dilute solution of a strong base =
Concentration of the base
Why is ammonia a base?
NH3 (aq) + H2O (l) ←> NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq)