Chapter 3.1 Vocab
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From principles of life second edition for AP Course
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Nucliec Acids
Store, transmit & express genetic info, Made of monomers
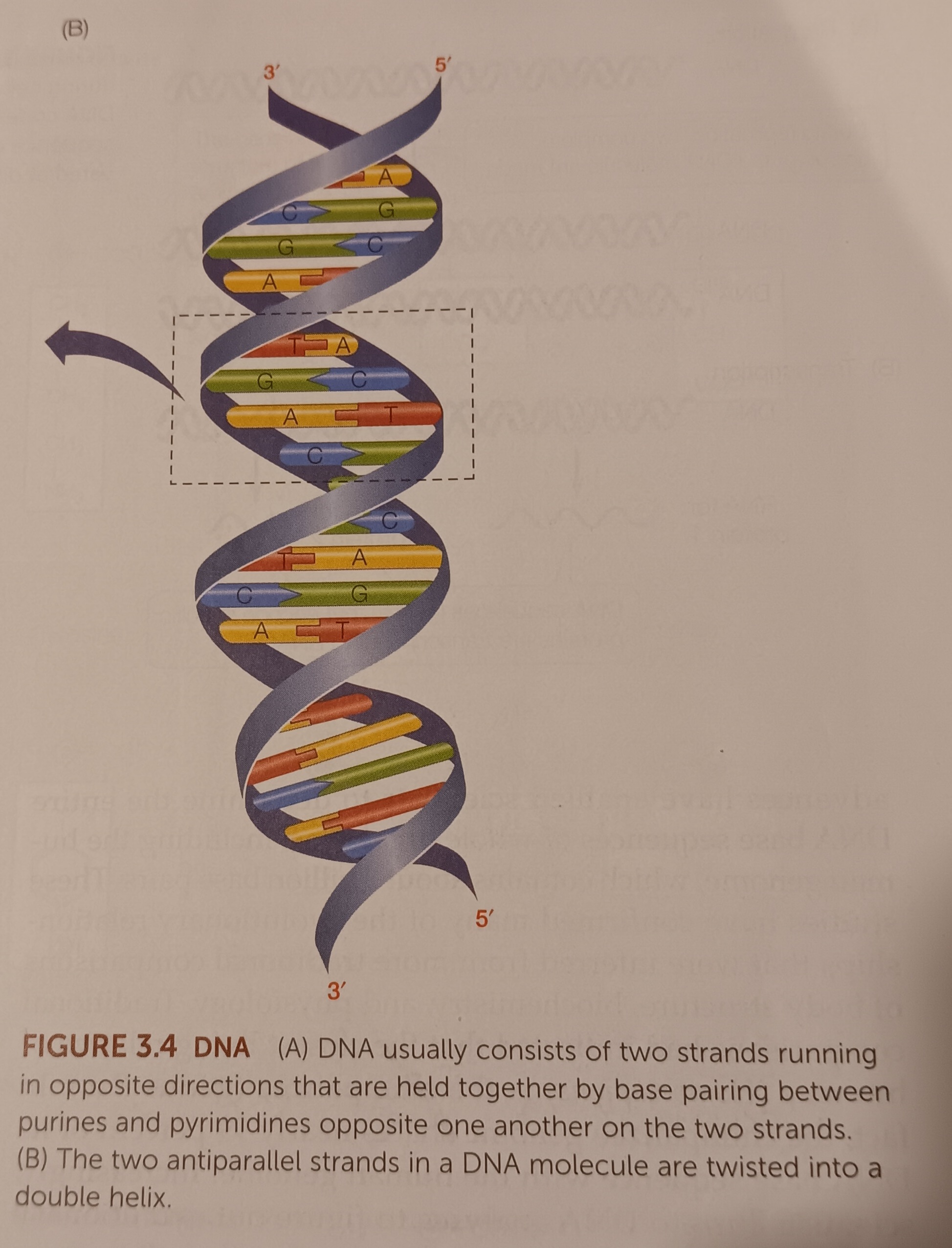
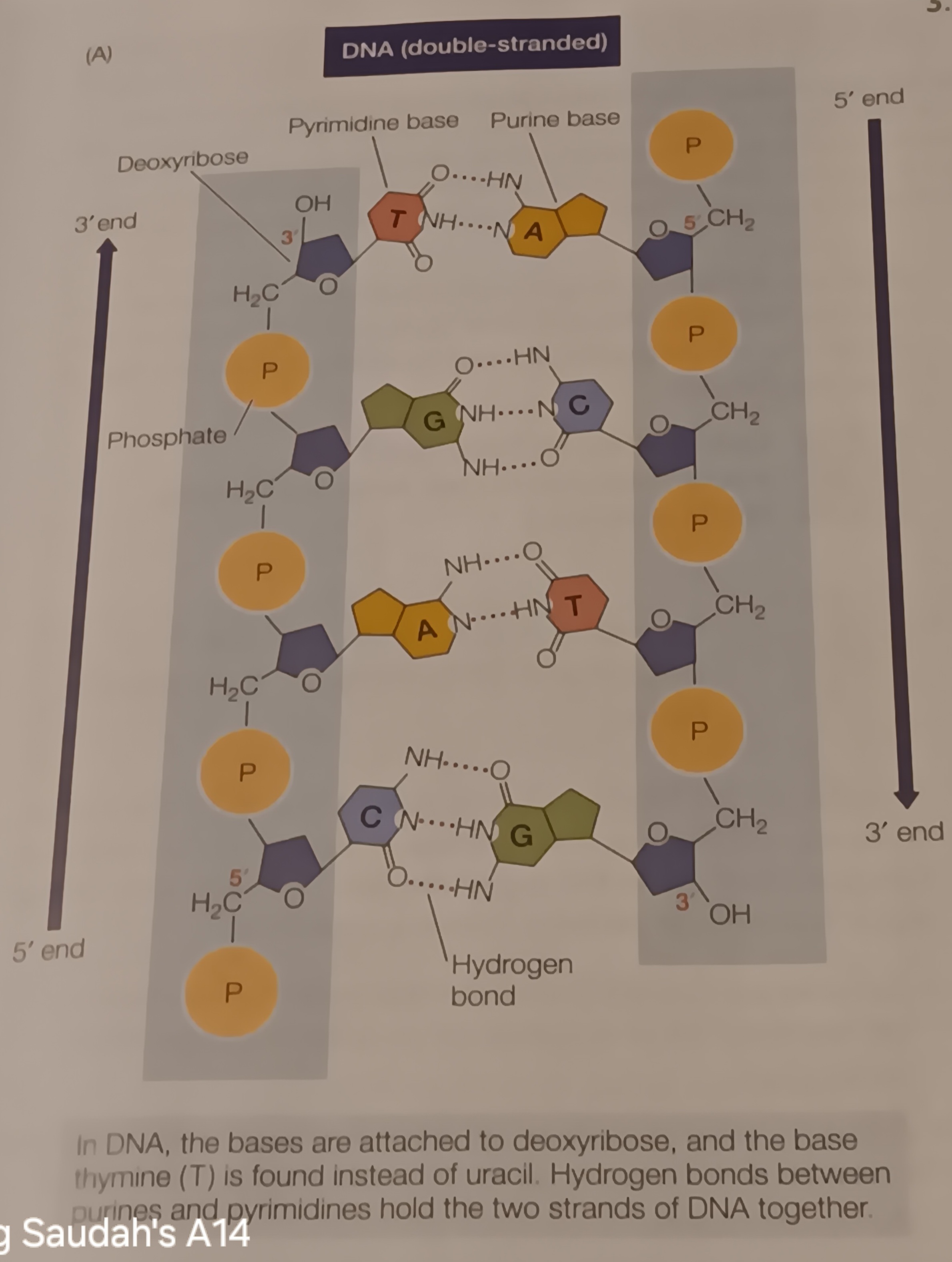
DNA
Type of nucleic acid. Deoxyribonucleic acid
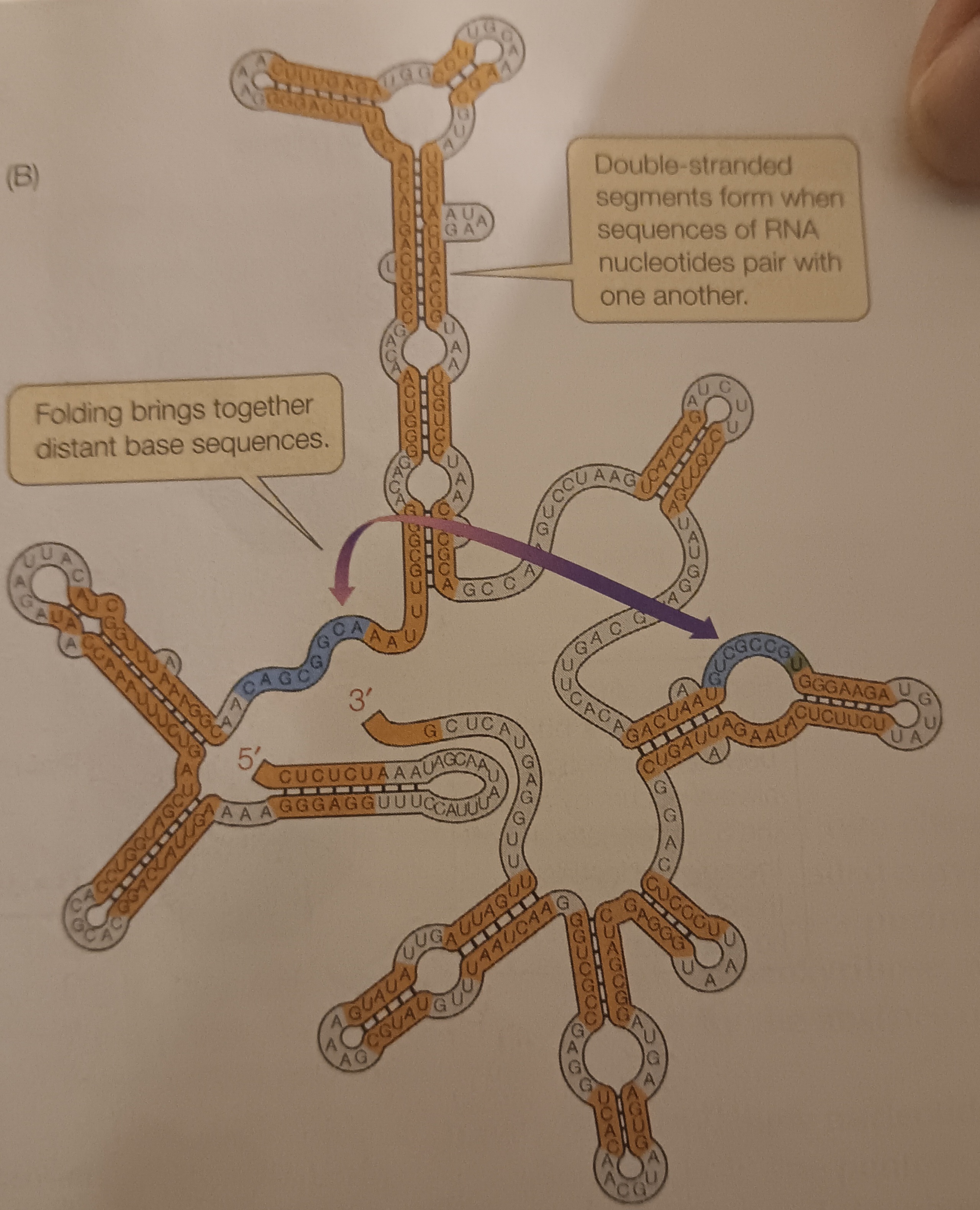
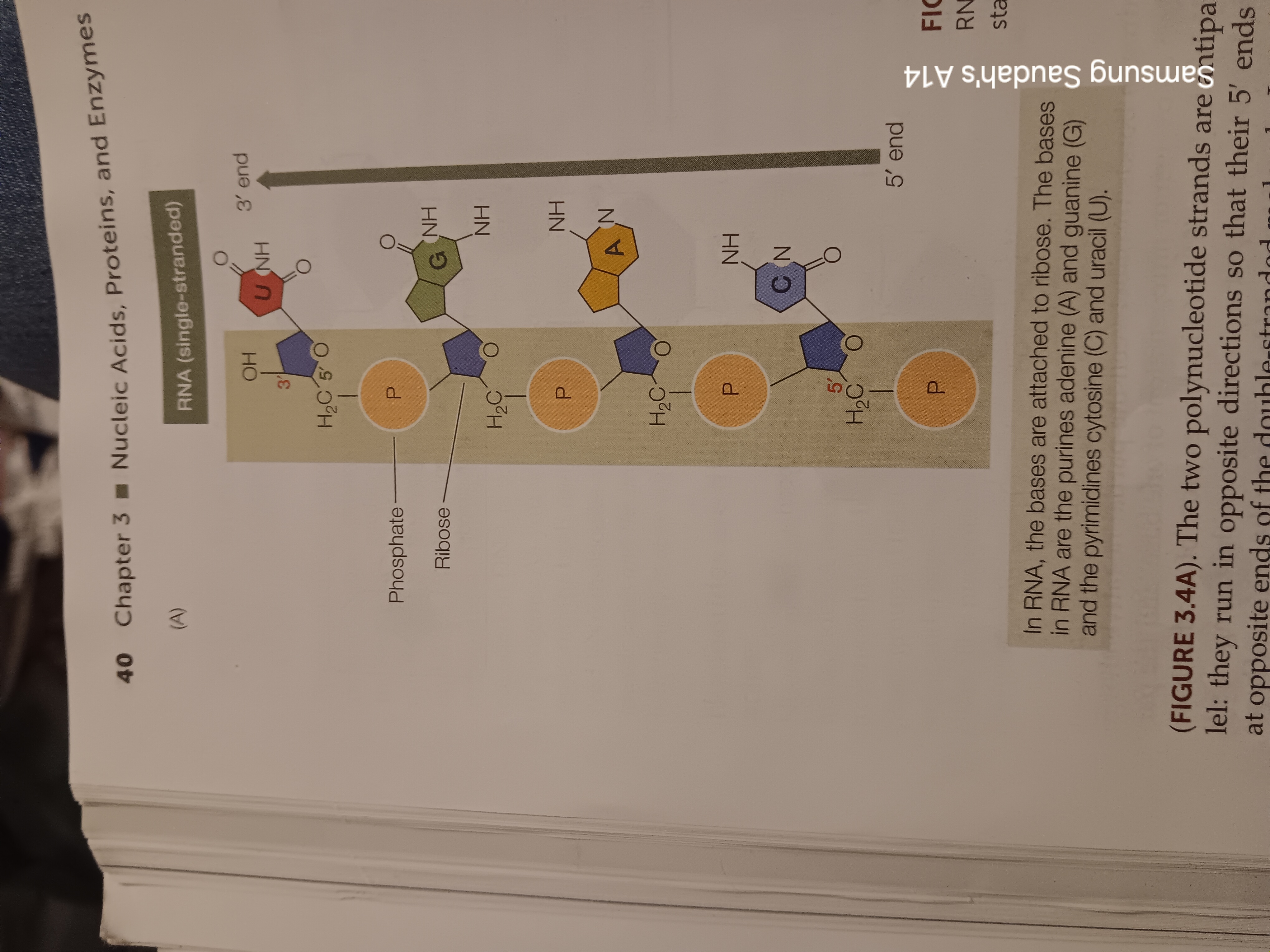
RNA
Type of nucleic acid. Ribonucleic acid
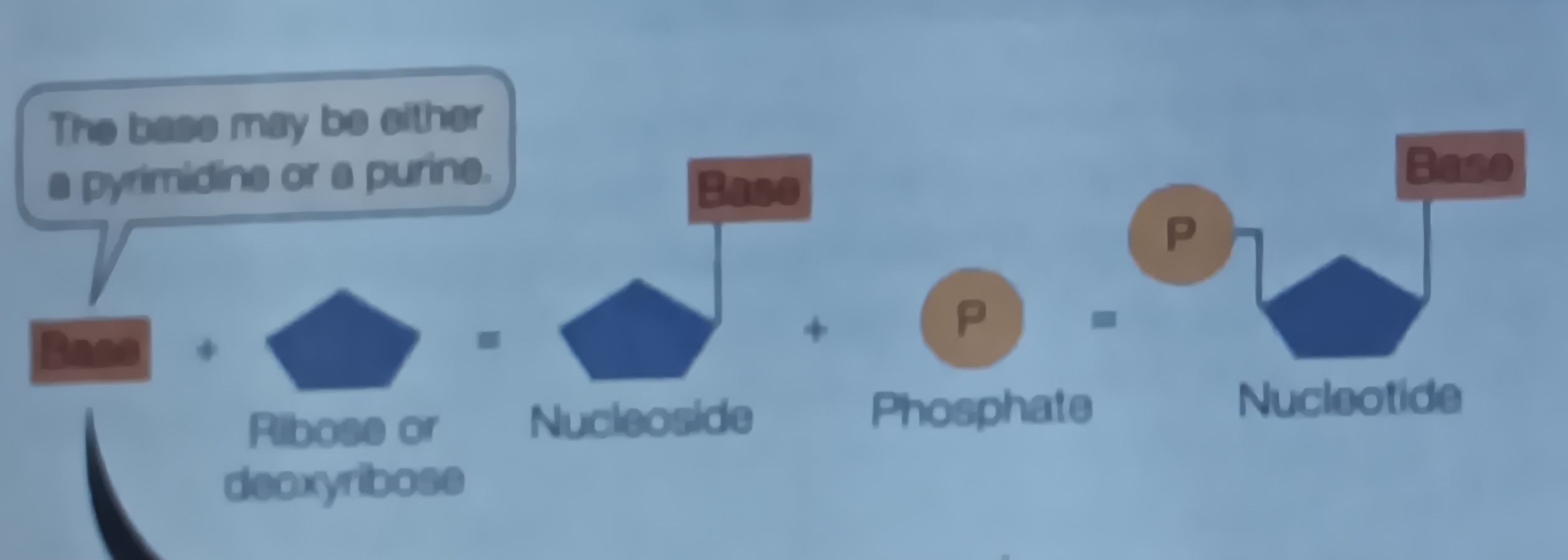
Nucleotide
Has (nitrogen having) base, Penrose sugar and 1-3 phosphate groups
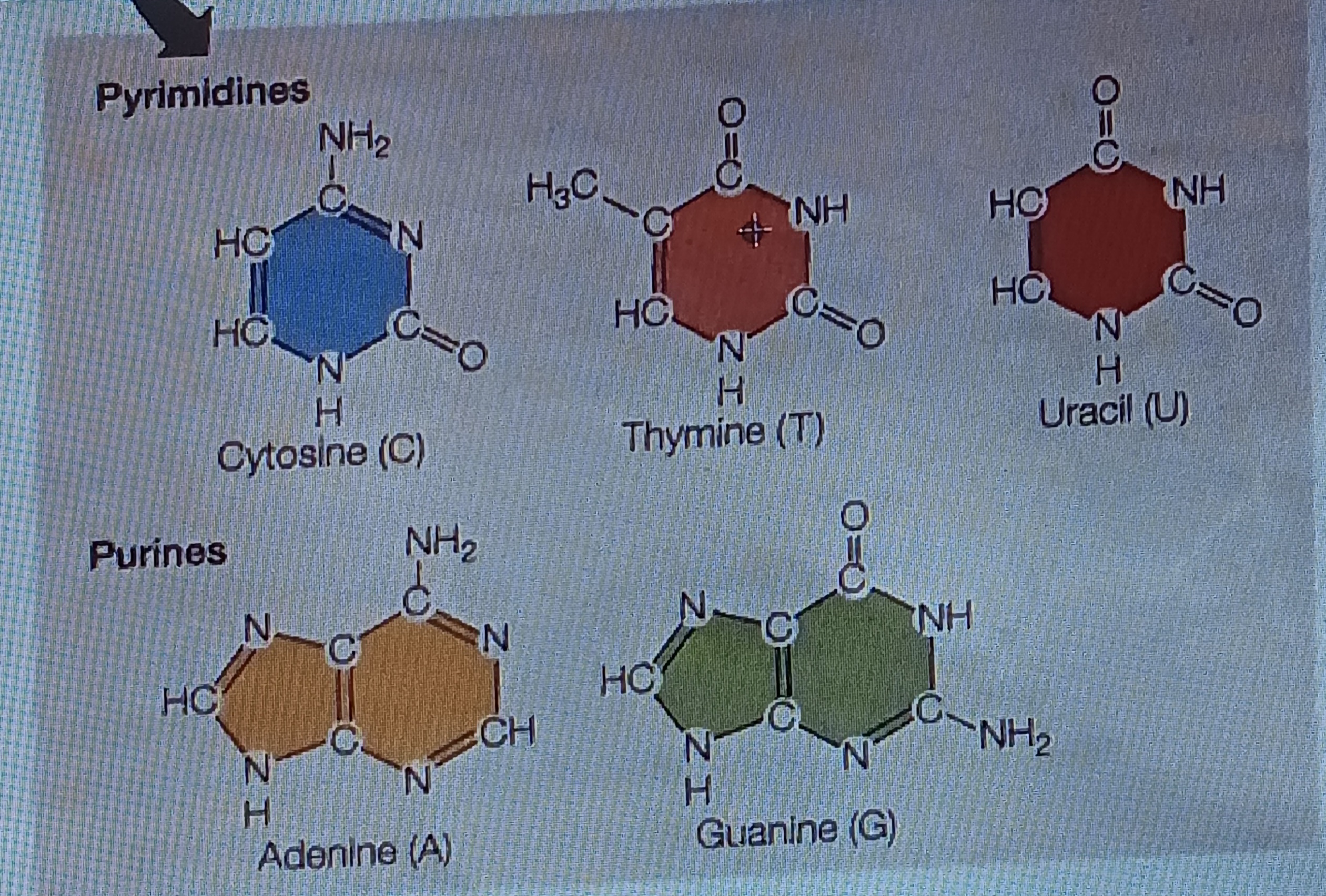
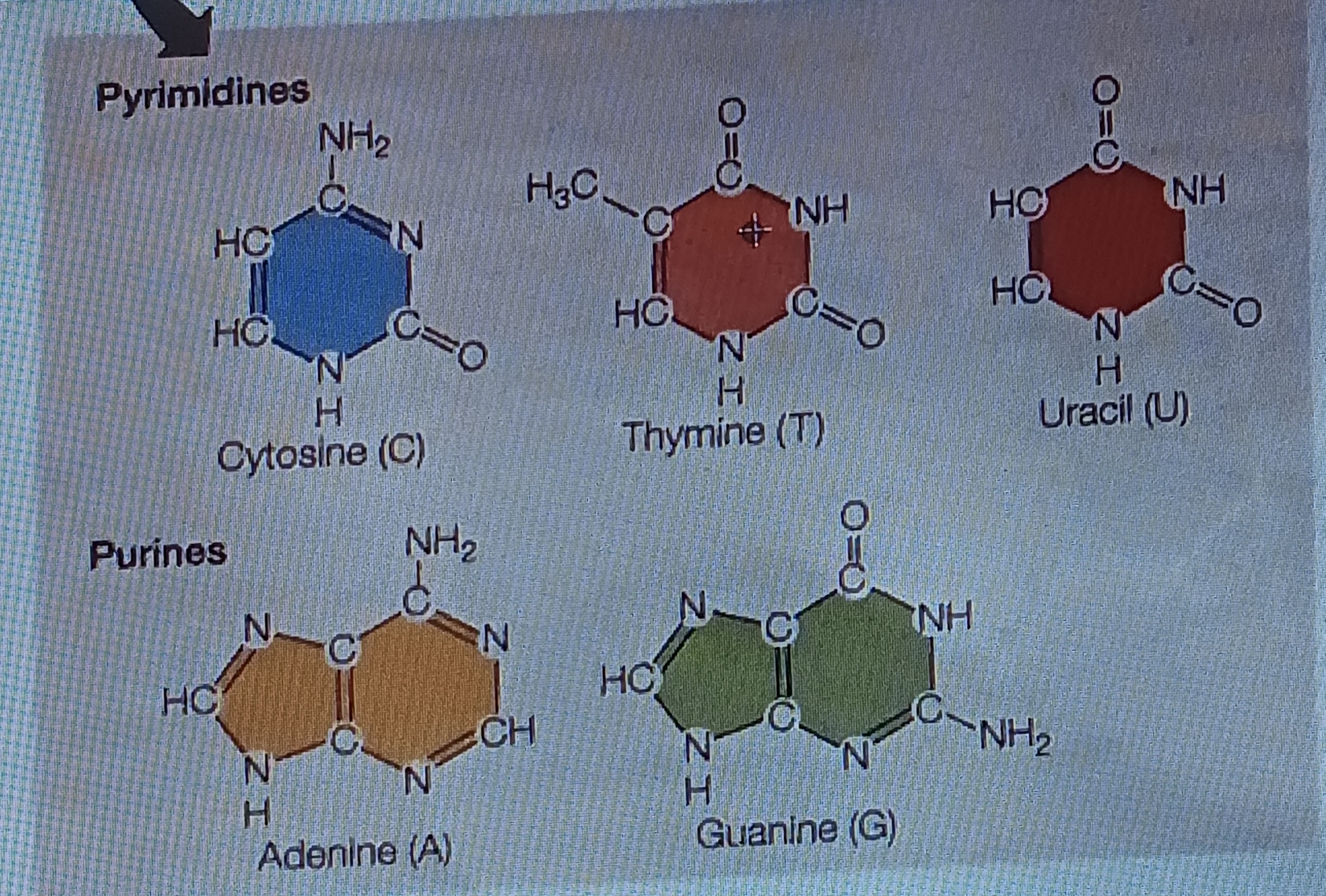
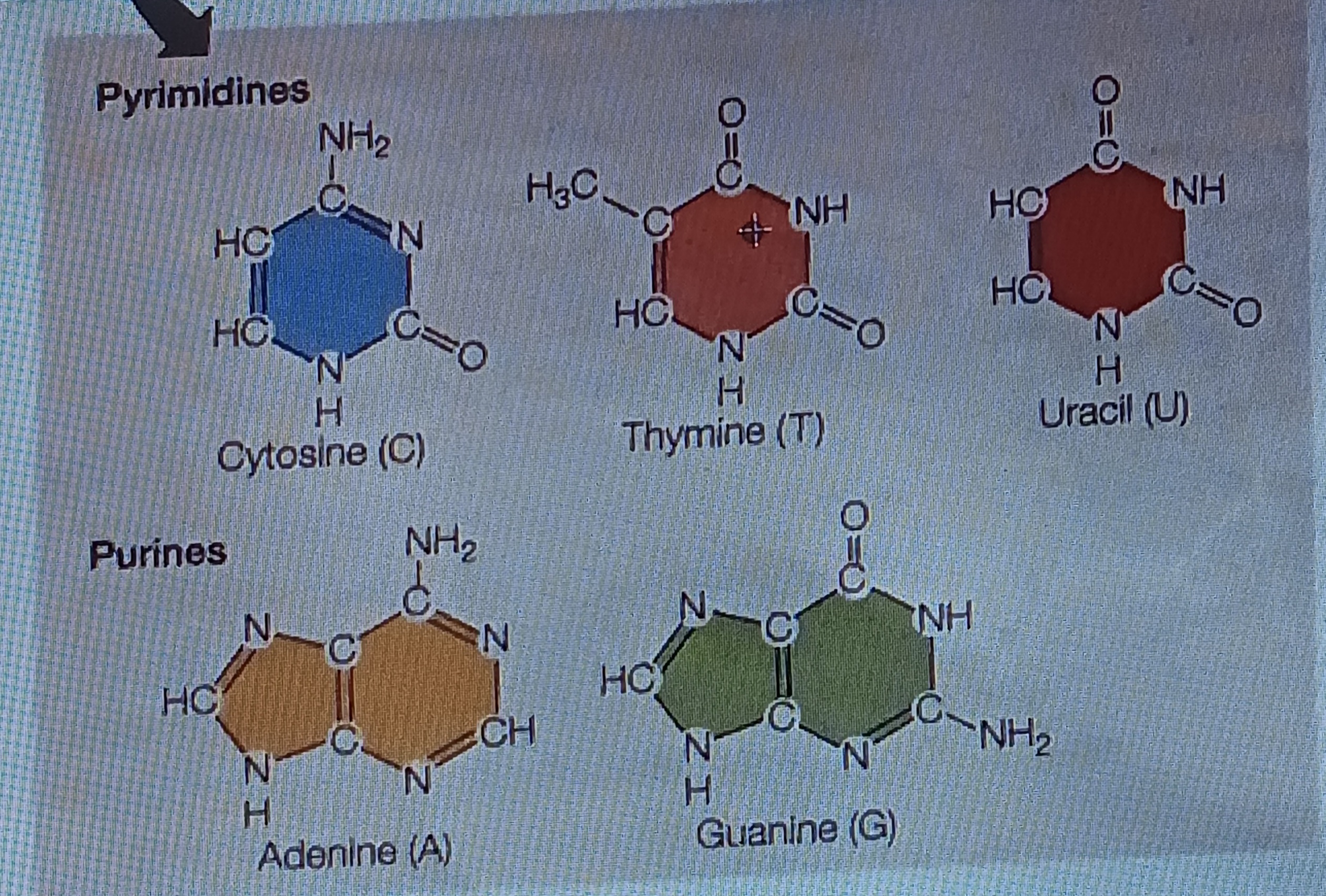
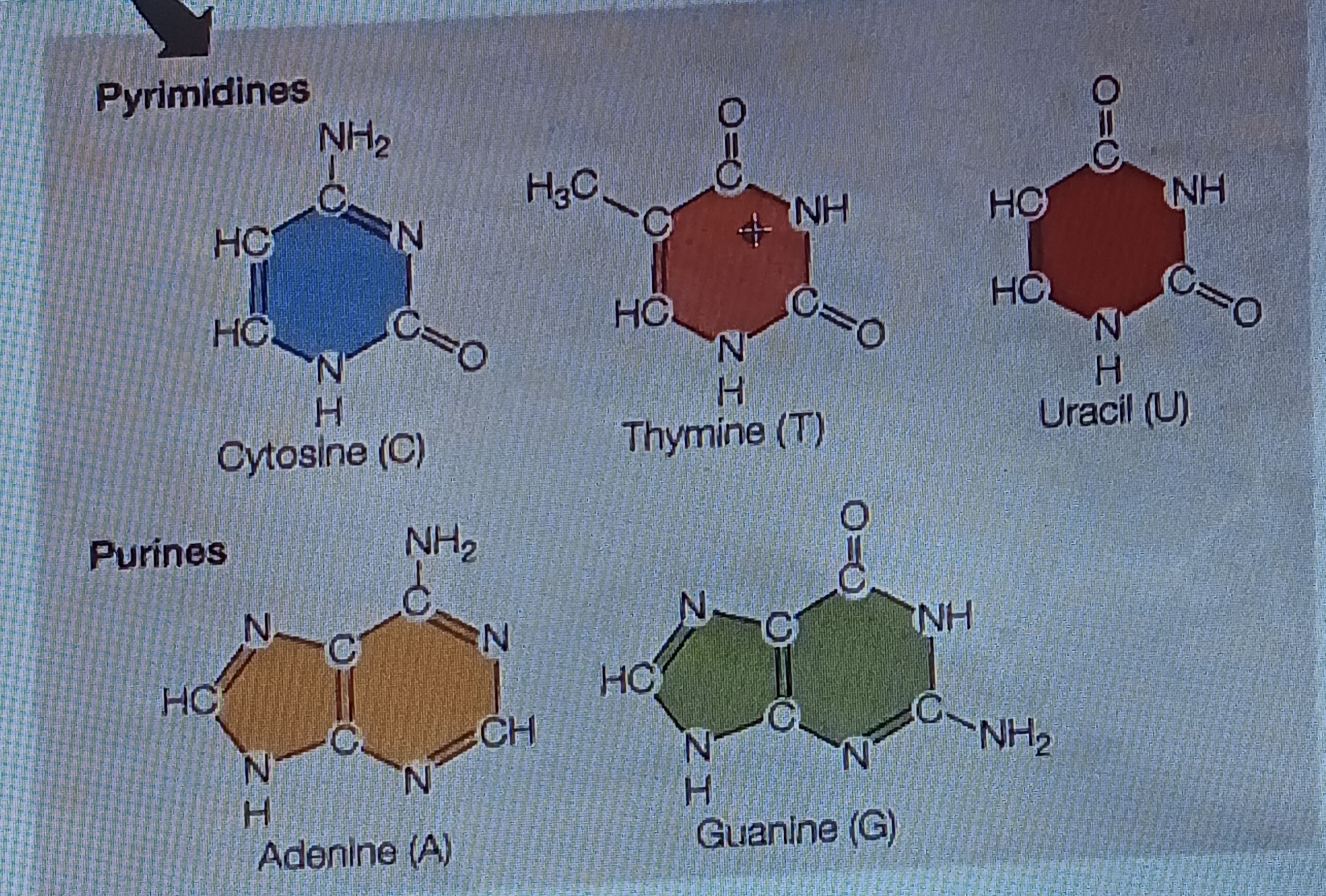
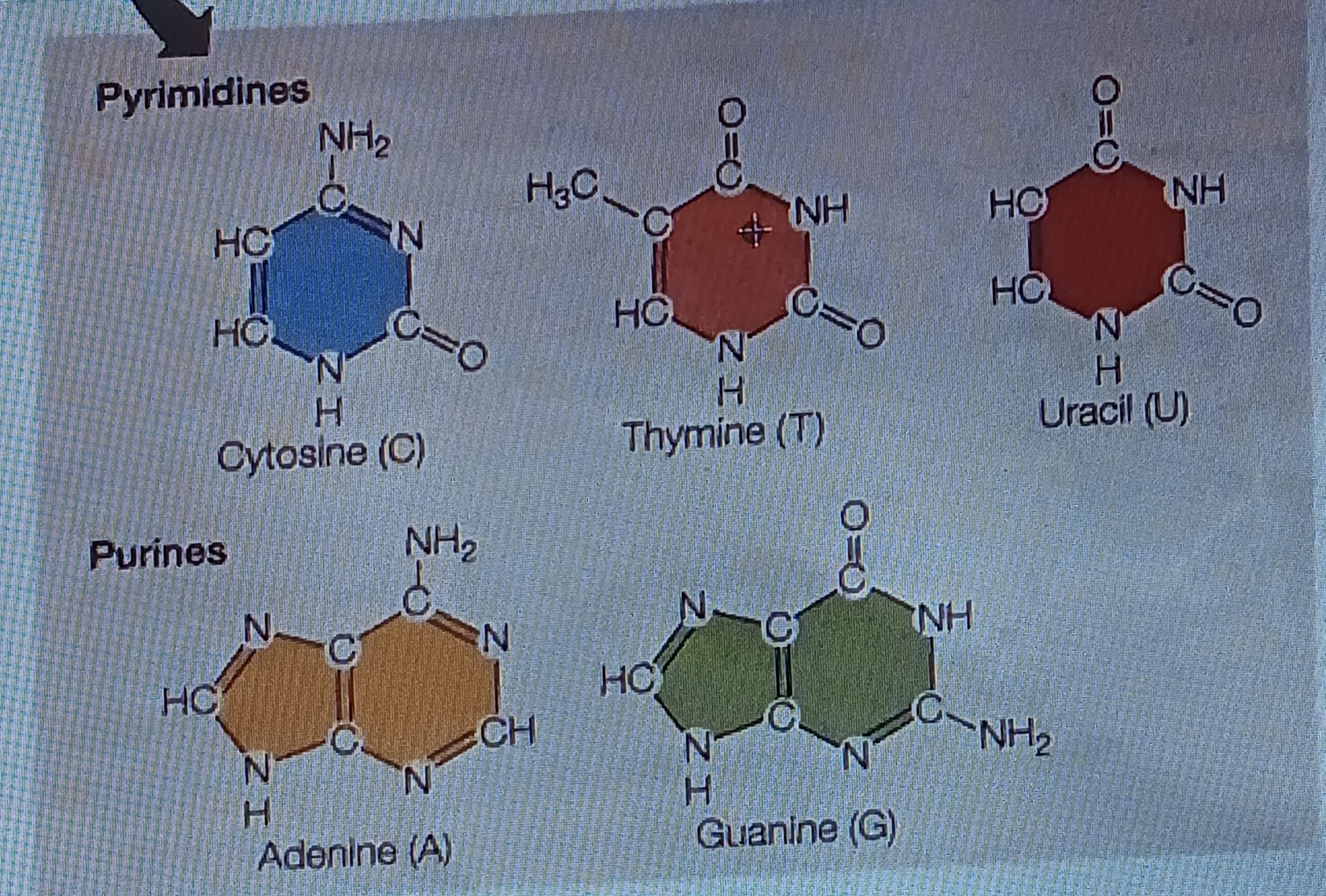
pyrimidine
Six membered single ring structure, chem form
purine
Fused double ring structure, chem form
deoxyribose
Pentose sugar with one less oxygen than ribose, in dna
ribose
Pentose sugar, in RNA
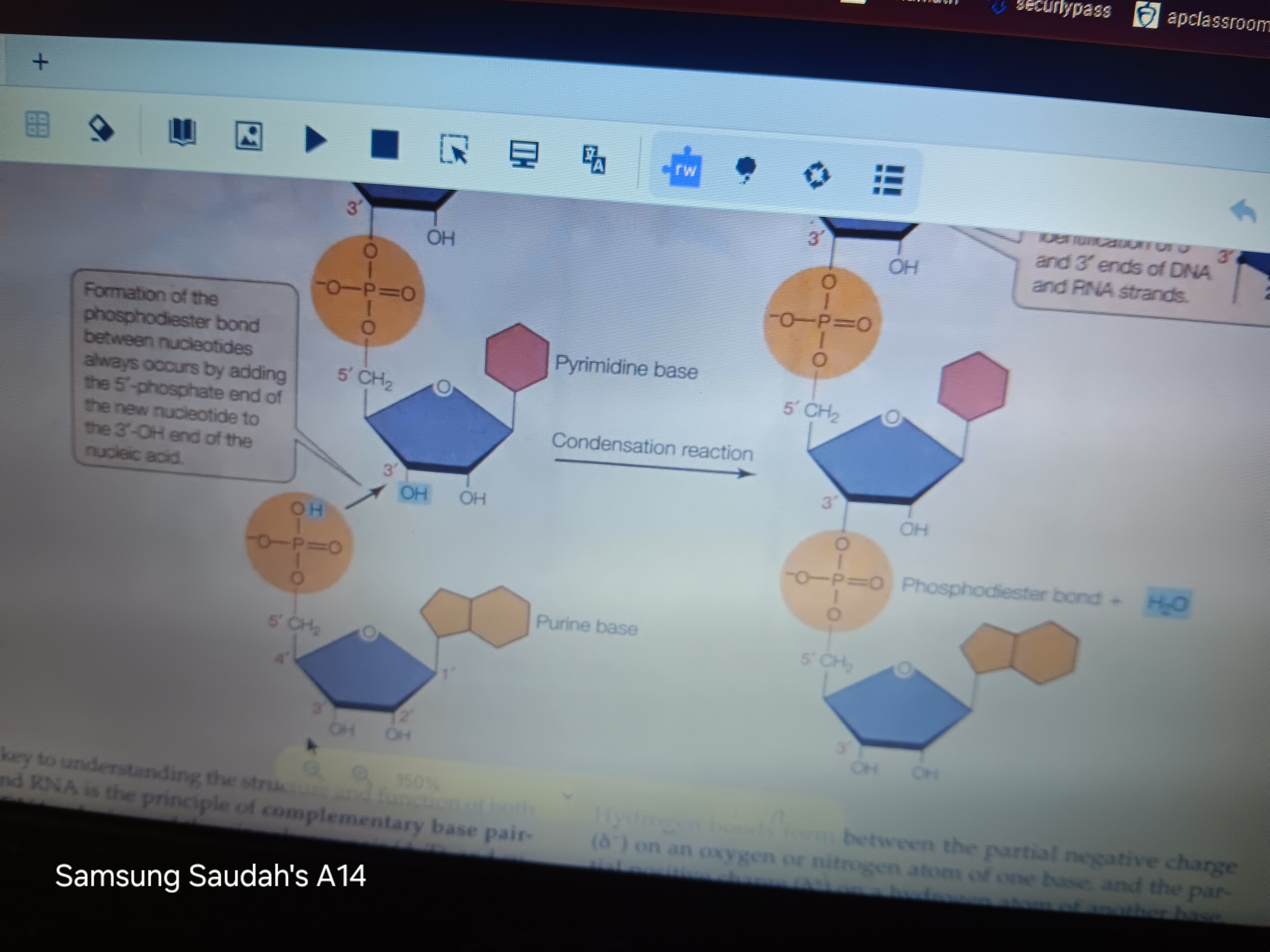
phosphodiester bond
Condensation reaction/linkage between pentose sugar and phosphate
Adenine (A)
Base, purine
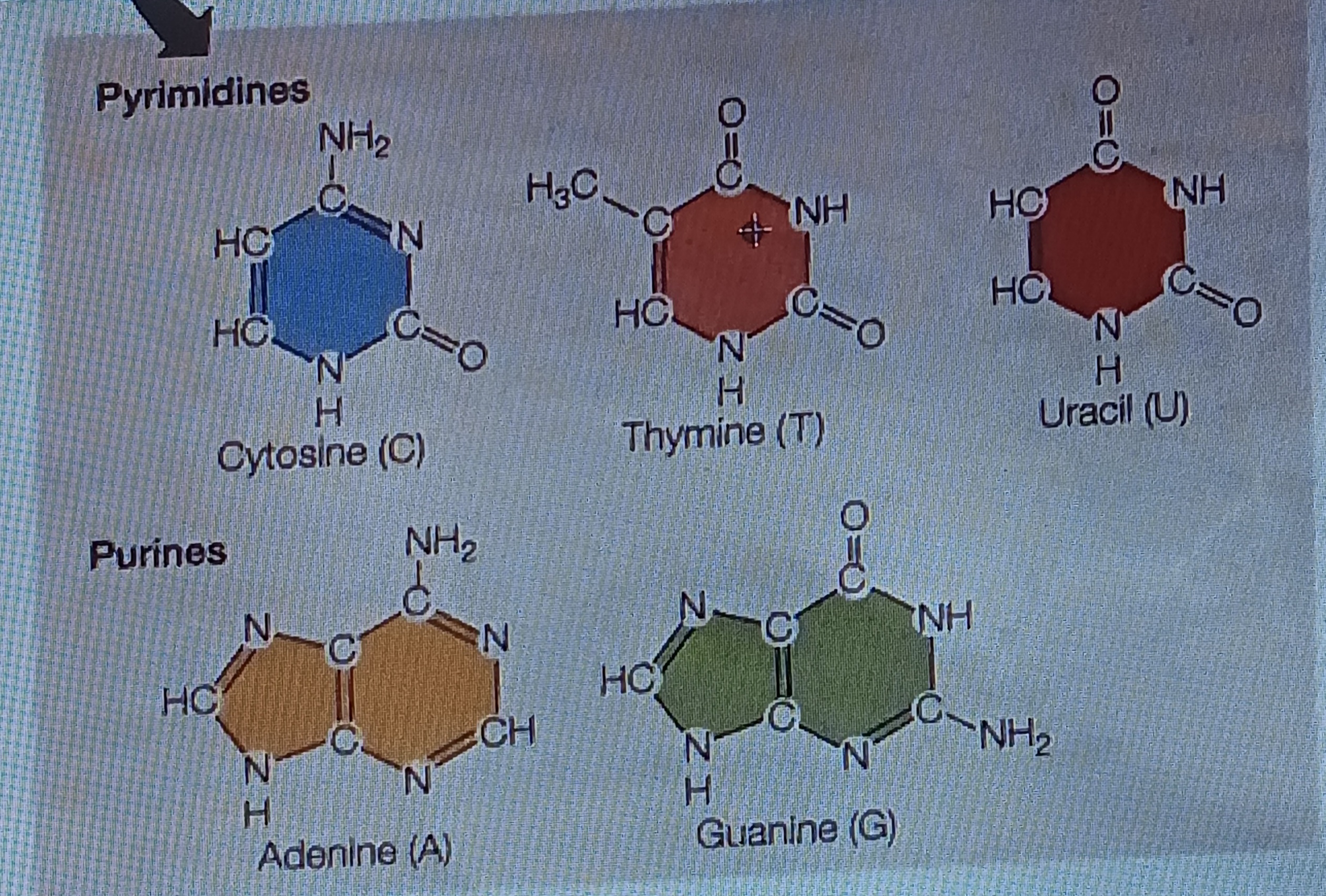
Cytosine (C)
Base, pyrimidine
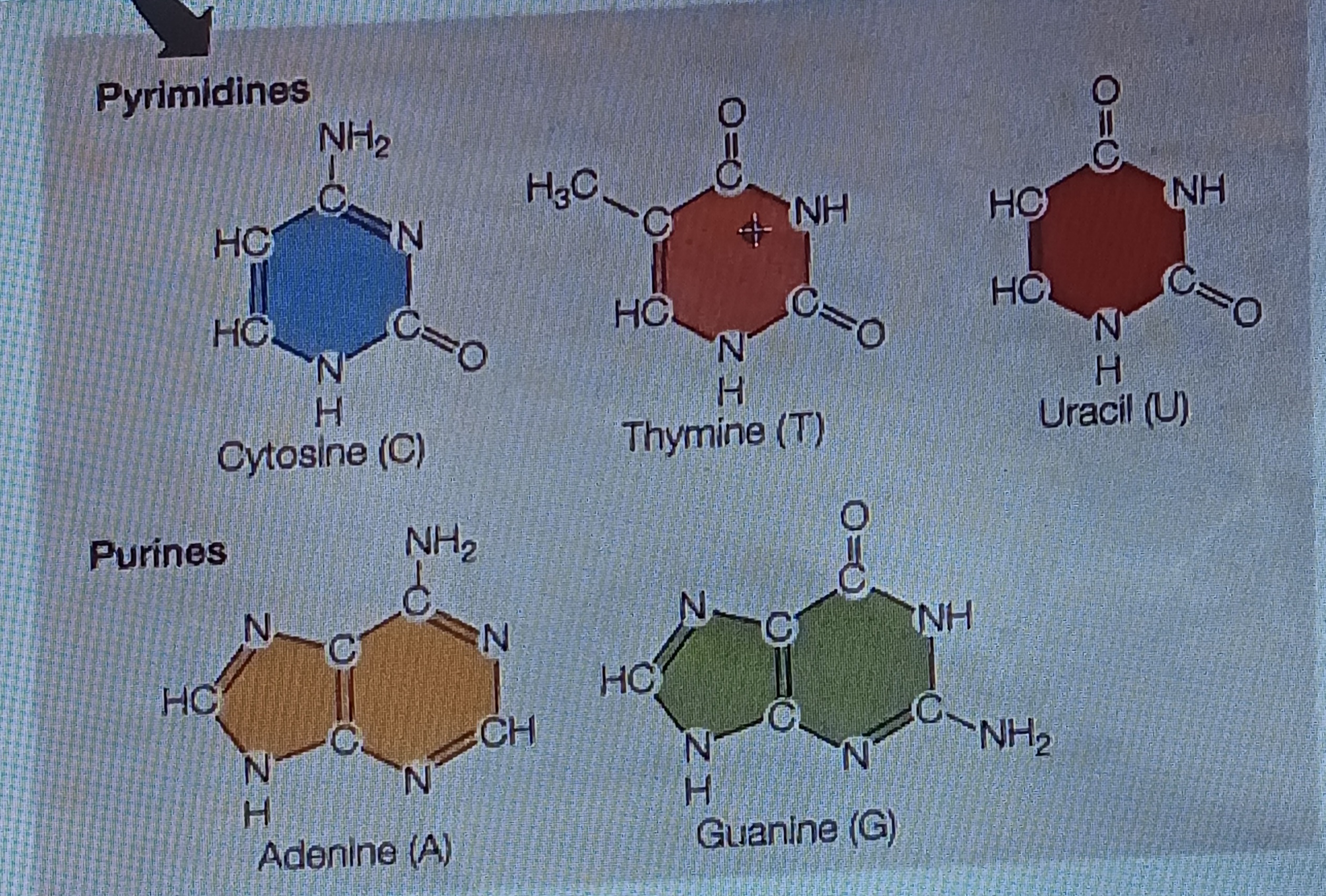
Guanine (G)
Base, purine
Thymine (T)
Base, pyrimidine
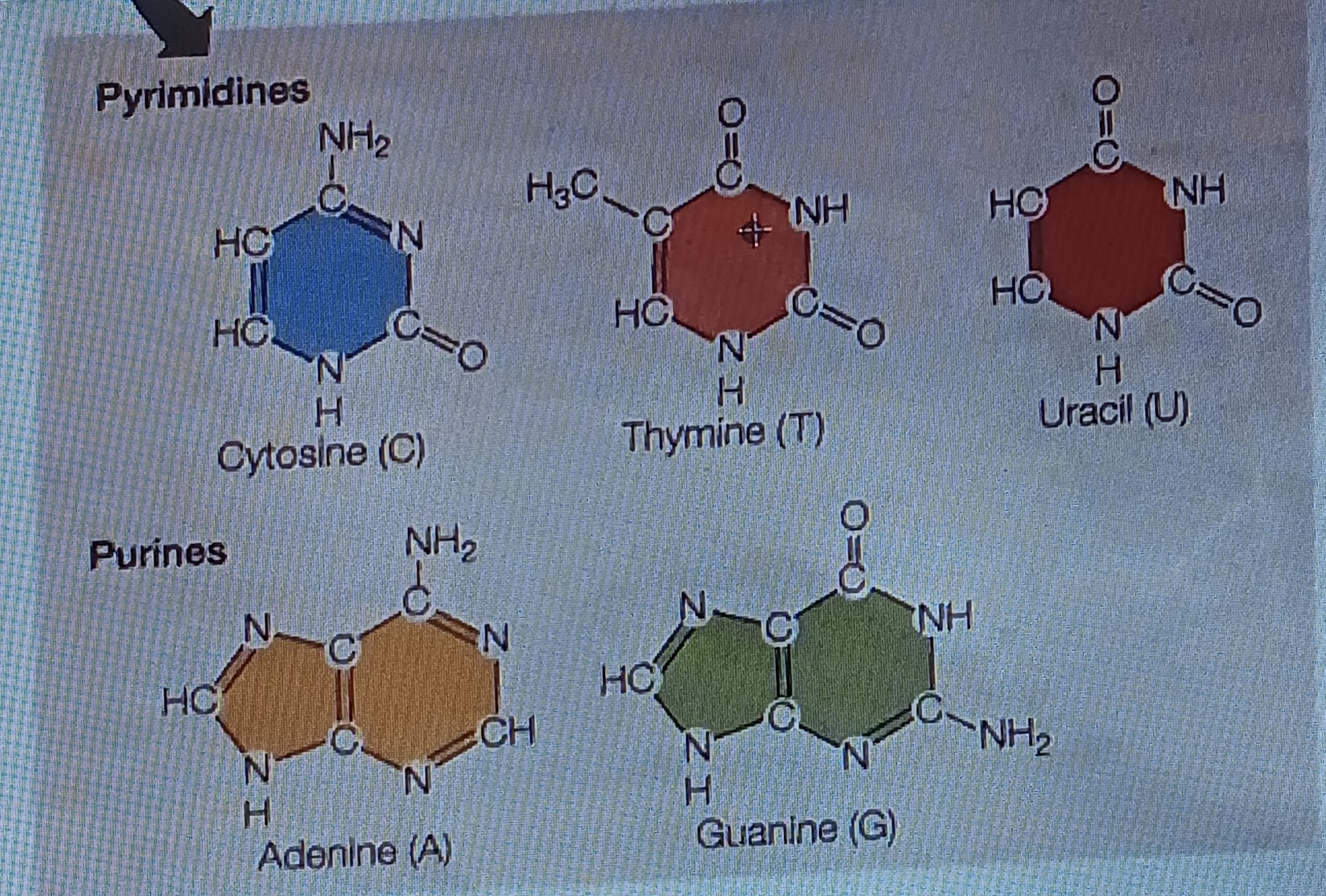
Uracil (U)
Base, pyrimidine
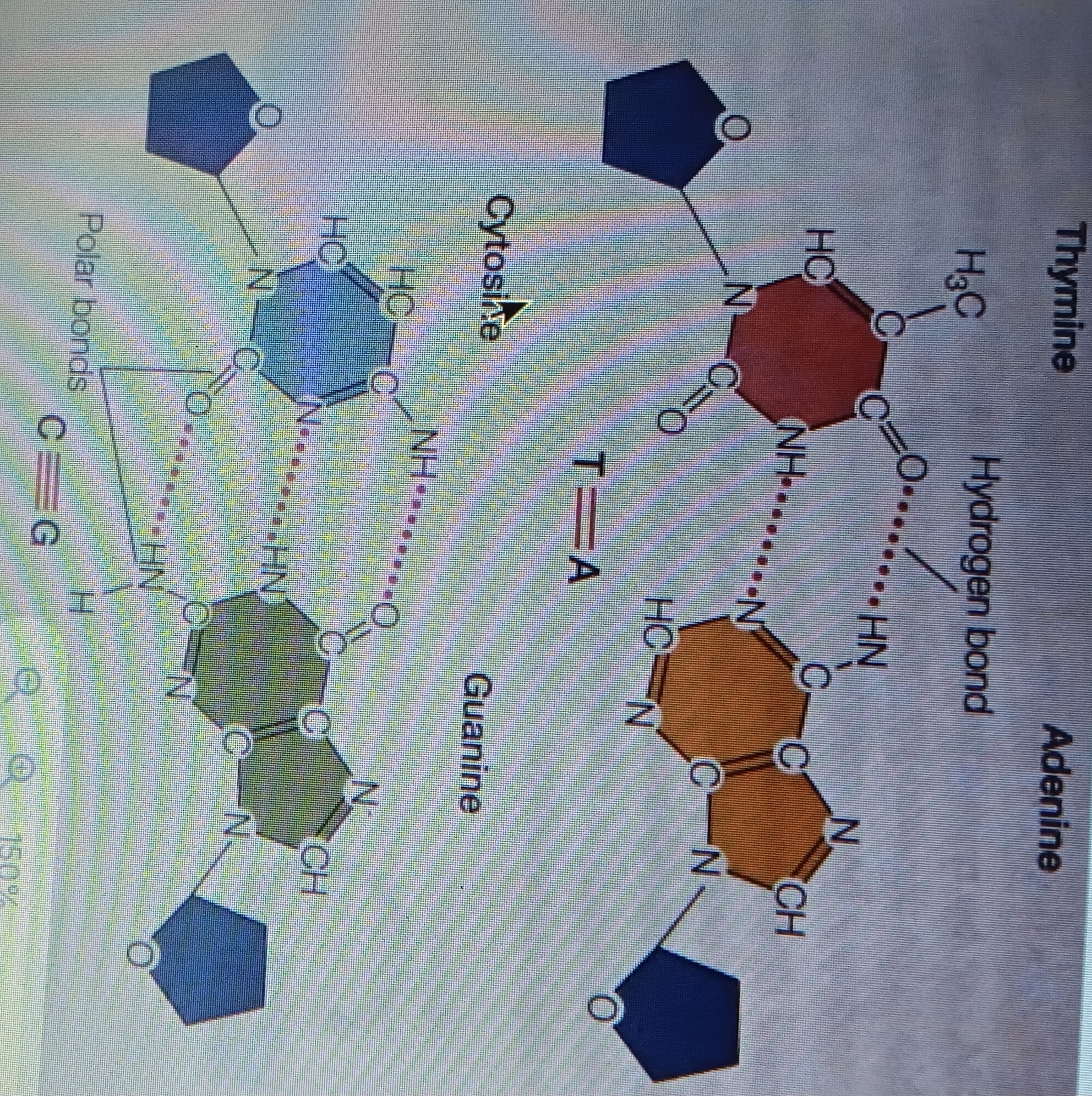
Complementary base pairing
Hydrogen bonds between bases
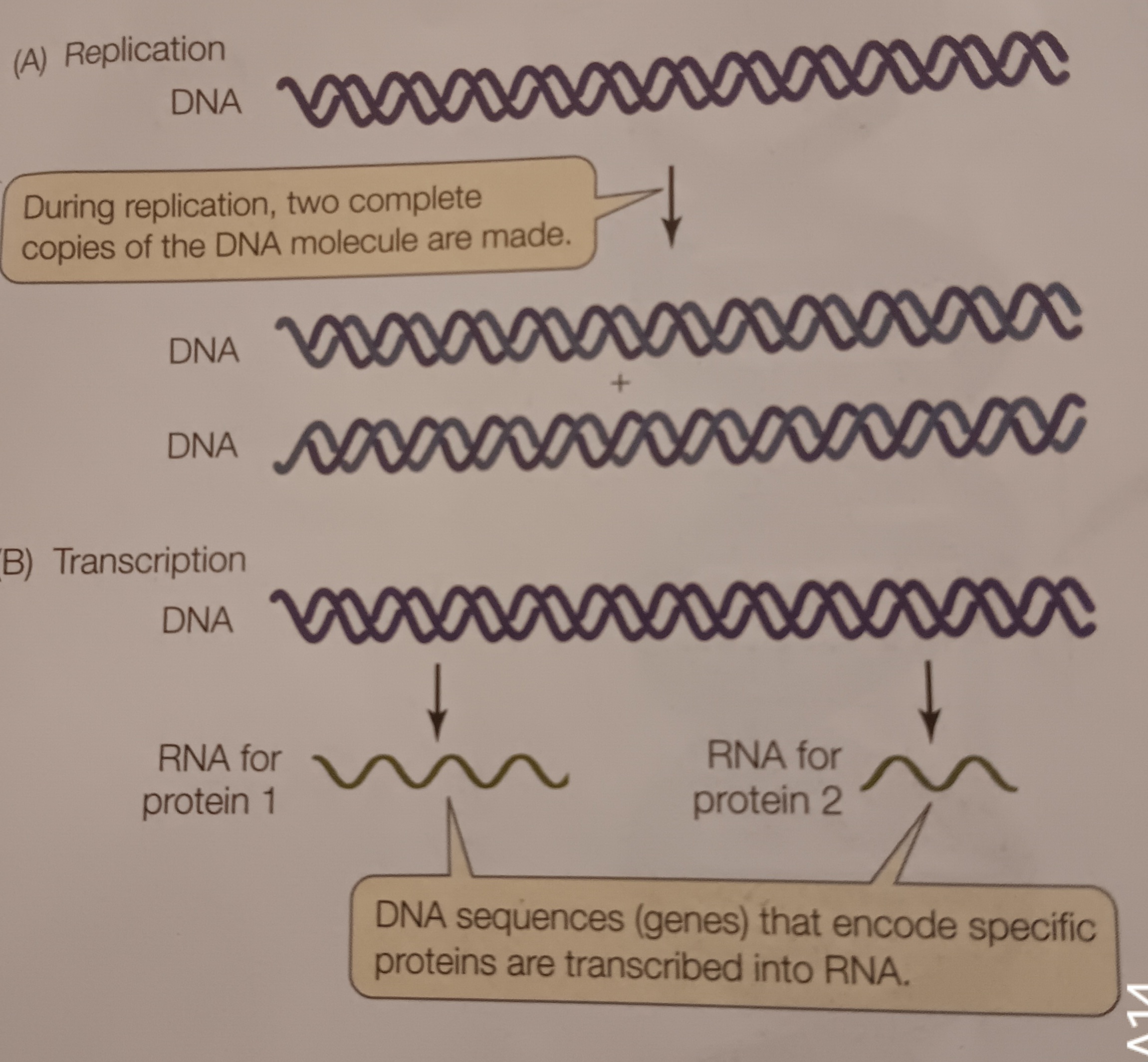
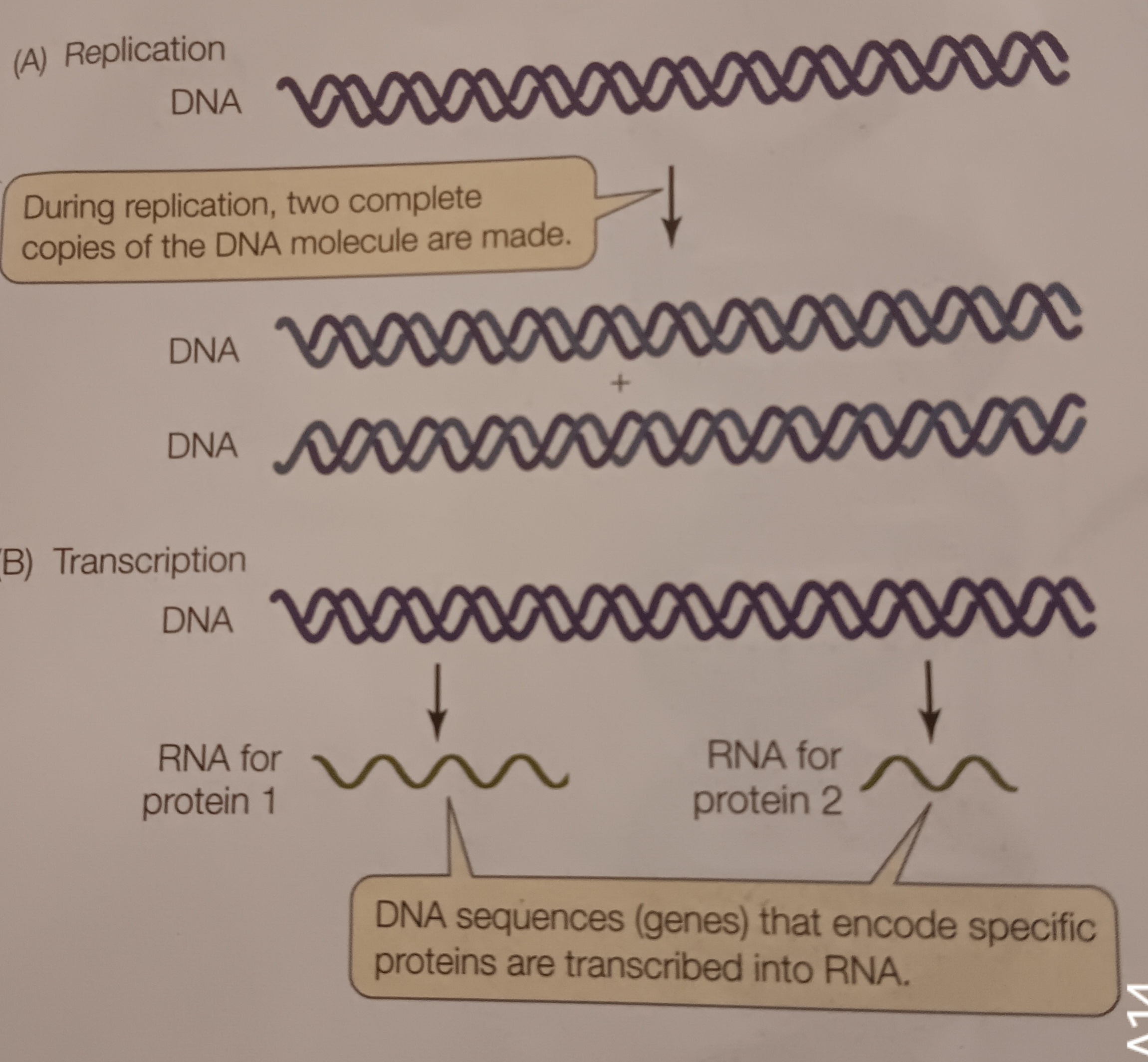
DNA replication
When a DNA is replicated. Polymerization existing strand as template. Involves entire molecule
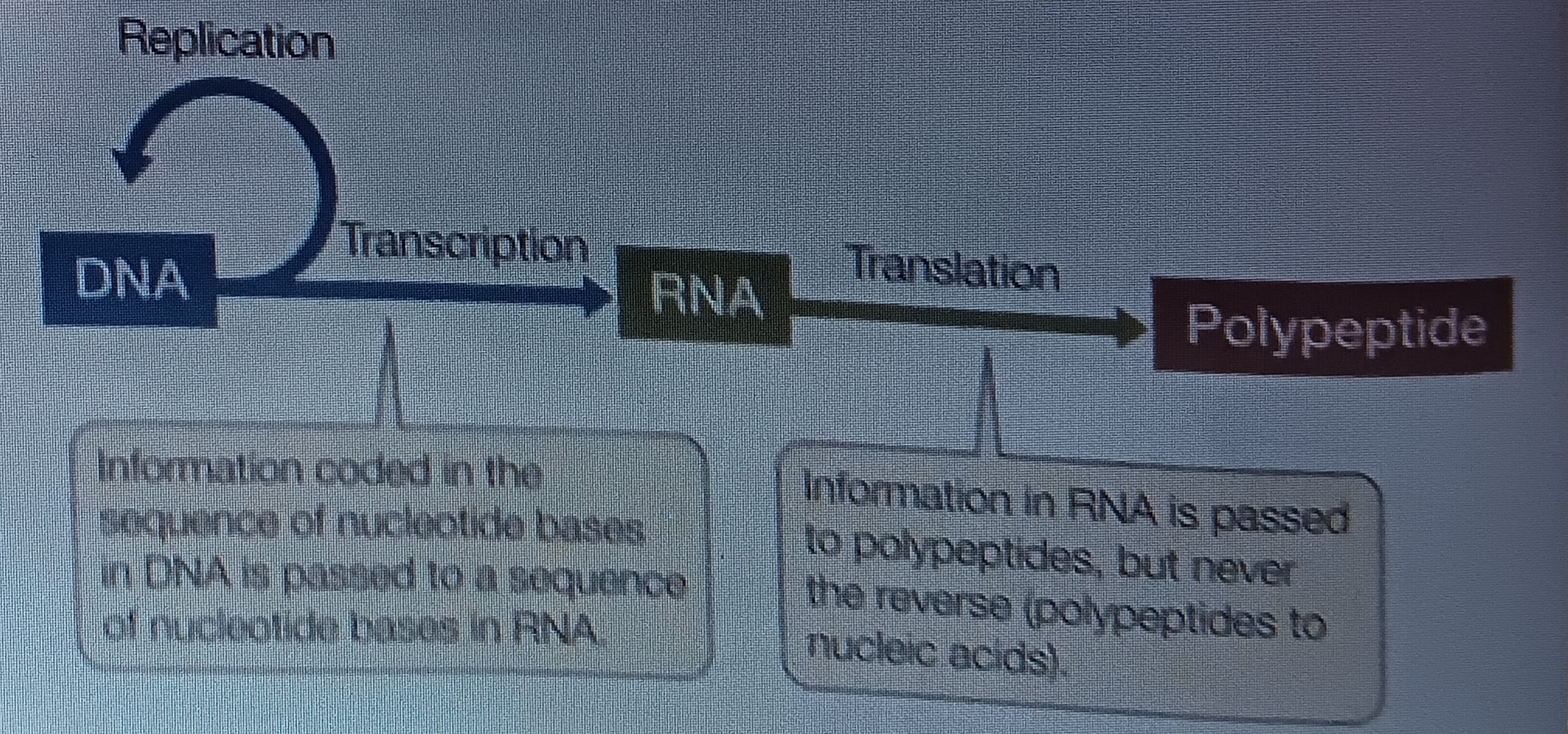
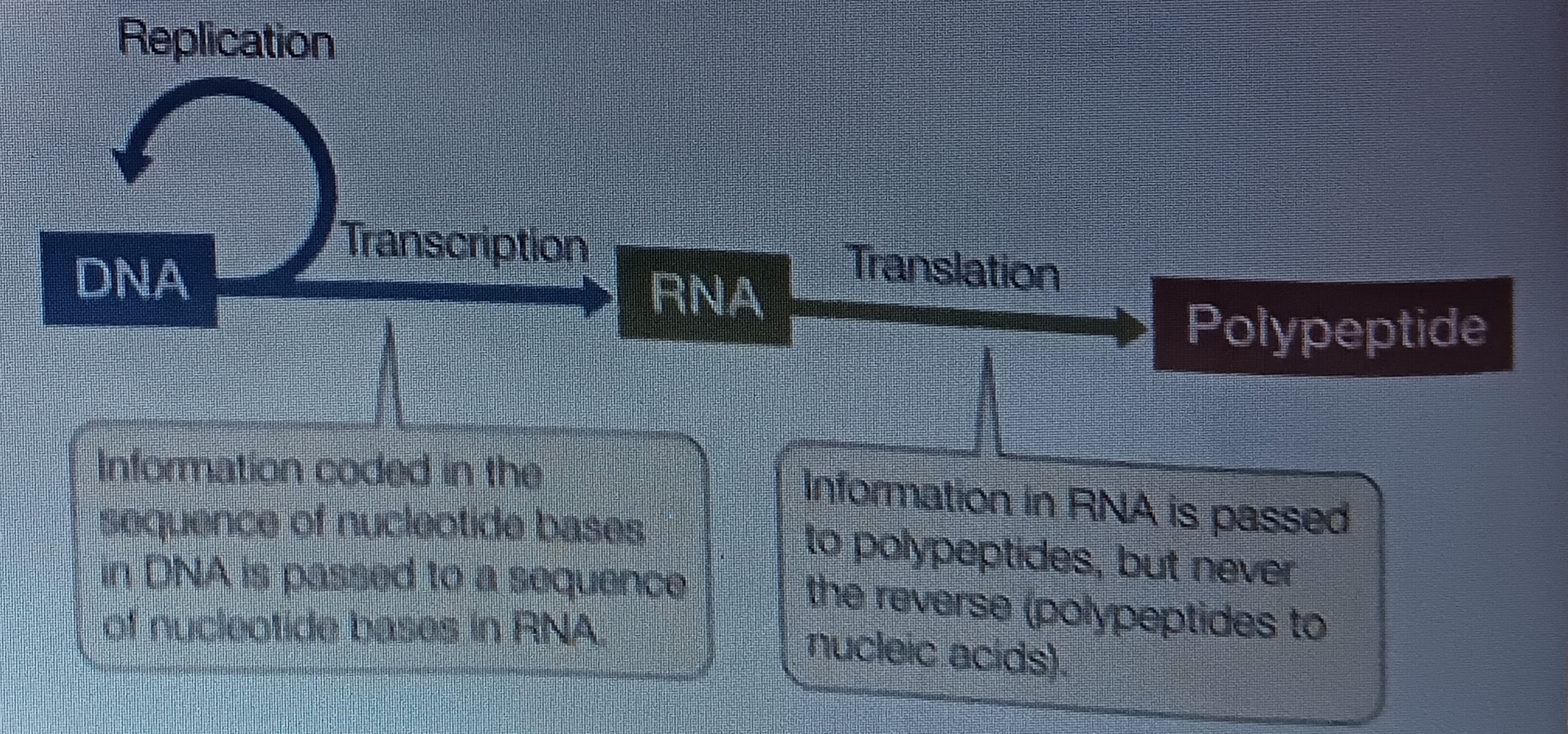
transcription
When DNA is copied into RNA,
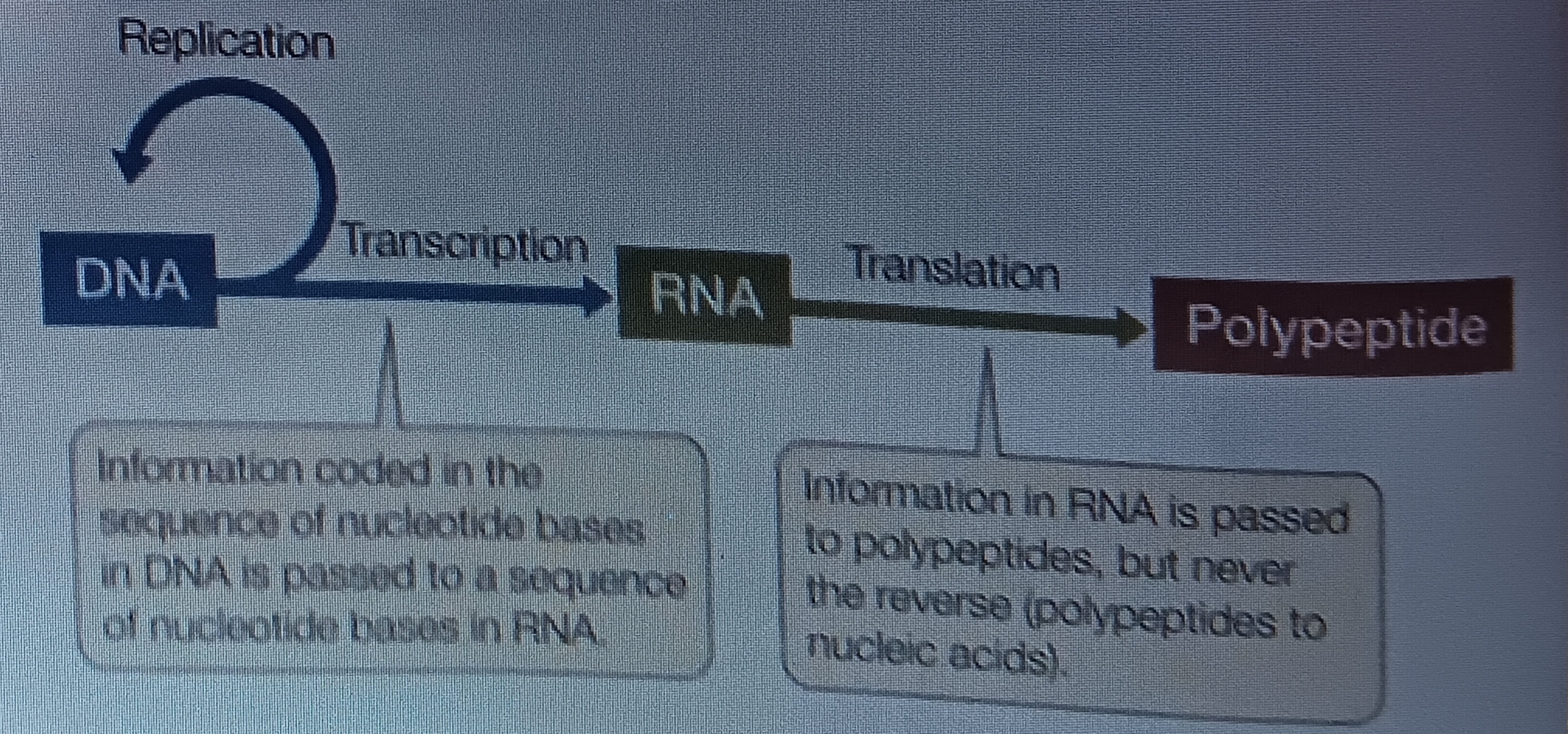
translation
RNA used to specify sequences of amino acids in proteins
genome
Complete set of DNA in a living organism
Base
Pyrimidine or purine
Genes
Sequences of DNA that encode specific proteins and are transcribed into RNA