ex 11 tannins
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lagyan mo pa structures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
tannins
Are complex substances usually occurs as mixtures of polyphenols that are difficult to separate because they do not crystallize
TANNINS & POLYPHENOLS
•first applied to plant constituents capable of transforming raw animal skin into leather
non-crystallization
tannins & polyphenols are ___ compounds that with water form colloidal solutions possessing an acid reaction and a sharp puckering taste
TANNINS & POLYPHENOLS
•they are non-crystallizable compounds that with water form colloidal solutions possessing an acid reaction and a sharp puckering taste
polyphenols
include a wide range of plant substances that possess in common, an aromatic ring bearing two or more hydroxyl groups
water-soluble
polyphenols (water or lipid-soluble?)
additives
•because of polyphenols’ similarity to tannins in terms of structure, they are used as __ in tanning agents
non-hydrolyzable
condensed tannins
hydrolyzable tannins
structure related to pyrogallol
non-hydrolyzable tannins
structure related to cathecol
hydrolyzable tannins
+HCL = phenolic acid + sugars
hydrolyzable tannins
+FeCl3 = bluish black
hydrolyzable tannins
+BrH2O = do not ppt
hydrolyzable tannins
Leather type: bloom
non-hydrolyzable tannins
+HCl = phlobaphenes (red dye)
non-hydrolyzable tannins
+FeCl3 = brownish green
non-hydrolyzable tannins
+BrH2O = forms ppt
non-hydrolyzable tannins
Leather Type: tanner’s red
Hydrolysable Tannins
Condensed Tannins
Pseudotannins
classification of tannins
hydrolysable tannins
Esters that are easily hydrolysable to yield:
◦Phenolic acid and sugar
◦Phenolic acids: Gallic acid OR Ellagic acid; Hexahydroxydiphenic
phenolic acid and sugar
phenolic acids: gallic acid or hexahydroxydiphenic
+FeCl3 - Bluish black
hydrolysable tannins yield
Cathecol, Phlobatannins or Proanthocyanidin
examples of condensed tannins
pseudotannins
false tannins
pseudotannins
•Does not precipitate proteins thus do not form leather yet it reacts with Fe salts
polyhydric phenols
tannins, when hydrolysed, yield relatively __
pyrogallol
Gallic acid → (hydrolysed)
cathecol
Protocatechuic acid → (hydrolysed)
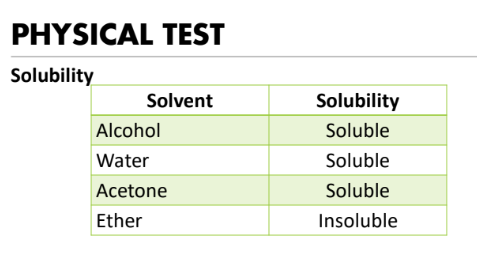
•soluble in water, dilute alcohol, alkalis, and acetone; sparingly soluble in organic solvents
•causes precipitation of gelatin as well as alkaloids
•precipitated by salts of Cu, Pb, Sn, and aqueous solution of potassium dichromate
•precipitate proteins from solution and can combine with it which renders the protein resistant to proteolytic enzymes
PROPERTIES OF TANNINS
•soluble in water, dilute alcohol, alkalis, and acetone; sparingly soluble in organic solvents
•causes precipitation of gelatin as well as alkaloids
•precipitated by salts of Cu, Pb, Sn, and aqueous solution of potassium dichromate
•precipitate proteins from solution and can combine with it which renders the protein resistant to proteolytic enzymes
PROPERTIES OF TANNINS
•soluble in __; sparingly soluble in __
•causes precipitation of __ as well as alkaloids
•precipitated by salts of __, and aqueous solution of __
•precipitate proteins from solution and can combine with it which renders the protein resistant to proteolytic enzymes
•Non-crystallizable
•With water forms colloidal solution
•Sharp puckering taste
•Causes precipitation of gelatin and alkaloids
•Their ability to precipitate proteins makes them an antiseptic and astringent
•Utilized in the process of vegetable tannins thus converting animal hides to leather
PROPERTIES OF TANNINS
•Non-crystallizable
•With _____ forms colloidal solution
•Sharp puckering taste
•Causes precipitation of ______ and alkaloids
•Their ability to __________ proteins makes them an ______ and ________
•Utilized in the process of vegetable tannins thus converting animal hides to _____
•produced by a plant as a feeding deterrent, as their binding to protein may reduce the dietary value of the plant as a food
•astringent in both GIT and skin abrasions
•used in tanning leather because of their ability to combine with proteins of animal hides
•used as an antidote for alkaloidal poisoning because of their ability to precipitate alkaloids from solutions of their salt forming an insoluble tannate
•used in the manufacture of inks/dyes because they form deeply colored compounds with iron salts
•solutions of tannins are used in the laboratory as reagents for the detection of gelatin, proteins and alkaloids
USES OF TANNINS
•Astringent
•Antiseptic
•Anti-diarrhea
•diuretics
•Anti-tumor (stomach and duodenal)
•Anti-inflammatory
•Anti-oxidant
•Hemostatic agent
medical used of tannins
•Maceration
Soaking
•Decoction
Soaking with the application of heat or with boiling
•Maceration – Soaking
•Decoction – Soaking with the application of heat or with boiling
•Solvent alcohol or water
EXTRACTION OF TANNINS
◦ Color: Brownish color
◦ Odor: Pungent odor
◦ Sharp, puckering taste
◦ State: Amorphous, non-crystalline
IDENTIFICATION TEST of tannin extract
color:
odor:
taste:
state:
-
Reagent | Theoretical Result | Interpretation |
gelatin solution | Ppt | Presence of Tannins |
No ppt- negative | polyphenolic compound |
10% GELATIN
Reagent | Theoretic Result | Interpretation |
Reagent | Theoretical Result | Interpretation |
Br2 | do not precipitate | Hydrolysable tannin |
precipitate | Condensed Tannins |
Br2 Test
Reagent | Theoretical Result | Interpretation |
Br2 | ||

brown or black
positive result of goldbeater’s skin test
gelatin salt solution
reagent of gelatin test
jelly-like precipitate
positive result of gelatin test
bluish black (hydrolysable tannins), brownish green and (+) in gelatin (condensed tannins), brownish green but (–) in gelatin (polyphenolic compounds)
positive result of ferric chloride test
formation of precipitate with condensed tannins only
Bromine Water Test result
formation of precipitate
Lime Water Test result
Brown solution and formation of precipitate
Iodine test result
matchstick test
test for catechin
Catechin in the presence of acid produces phloroglucinol which stains the lignified wood pink or red.
matchstick test result
A dilute solution of chlorogenic acid containing extract, slowly turns green indicating the presence of chlorogenic acid.
test for chlorogenic acid
Drug shows pink or red color, reaction produces phloroglucinol which along with vanillin gives pink or red color.
VANILLIN-HYDROCHLORIC ACID TEST result
Flavonoids
(What type of polyphenol?) Quercetin
Phenolic acids
(What type of polyphenol?) Caffeic acid
Stillbenes
(What type of polyphenol?) Resveratrol
Lignans
(What type of polyphenol?) Flaxseed