Optics Flashcards UNIT TEST! TUESDAY!!
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 11.1 - What is light Ch 11.2 - How is light produced? Ch 11.4 - Ray Model of Light Ch 11.6 - Laws of Reflection Ch 11.7 - Images in Plane Mirrors Ch 11.9 - Images in Curved Mirrors
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
electromagnetic spectrum
radio waves
microwaves
infrared light
visible light
ultraviolet light
X rays
gamma rays
What’s are some uses for radio waves?
• AM/FM radio
• TV signals
• cellphone communication
• radar
• astronomy (for example, discovery of pulsars)
What’s are some uses for microwaves?
• telecommunications
• microwave ovens
• astronomy (for example, background radiation associated
with the Big Bang)
What’s are some uses for infrared light?
• remote controls (for example, DVD players and
game controllers)
• lasers
• heat detection (for example, leakage from windows, roofs)
and remote sensing
• keeps food warm (in fast-food restaurants)
• astronomy (for example, discovering the chemical
composition of celestial bodies)
• physical therapy
What’s are some uses for visible light?
• human vision
• theatre/concert lighting
• rainbows
• visible lasers
• astronomy (for example, optical telescopes, discovering
the chemical composition of celestial bodies)
What’s are some uses for ultraviolet light?
• causes skin to tan and sunburn
• increases risk of developing skin cancer
• stimulates production of vitamin D
• kills bacteria in food and water (sterilization)
• “black” lights
• ultraviolet lasers
• astronomy (for example, discovering the chemical
composition of celestial bodies)
What are some uses for X-rays
• medical imaging (for example, of teeth and broken bones)
• security equipment (for example, scanning of luggage at
airports)
• cancer treatment
• astronomy (for example, study of binary star systems,
black holes, the centres of galaxies)
What are some uses for gamma rays
• cancer treatment
• astronomy (for example, study of nuclear processes
in the universe)
• product of some nuclear decay
Light from Incandescence
The production of light as a result of high temperature
Light from Electric Discharge
The process of producing light by passing an electric current through a gas
Light from Phosphorescence
The process of producing light by the absorption of UV light results in the emission of visible light over extended periods of time
Light from Fluorescence
The absorption of ultraviolet light, causing visible light to be emitted immediately
Light from Chemiluminescence
Chemiluminescence is the direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction with little or no heat produced
Light from Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production of light in living organisms as the result of a chemical reaction with little or no heat produced
Light from Triboluminescence
Triboluminescence is the production of light from friction as a result of scratching, crushing, or rubbing certain crystals
Light from a Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in semiconductors
Semiconductor
A material that allows an electric current to flow only in 1 direction
LAWS OF REFLECTION?
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
Specular Reflection?
Diffuse Reflection?
Specular Reflection: reflection of light off a flat smooth surface
Diffuse Reflection: reflection of light off a rough surface
Lower density to higher density = what happens to the speed of light?
The speed of light decreases
Higher density to lower density = what happens to the speed of light?
The speed of light increases
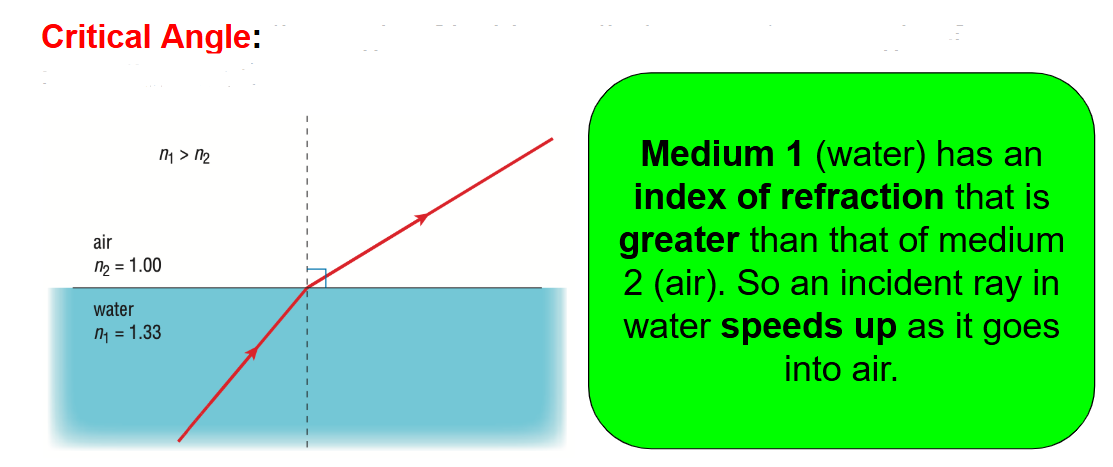
What is a Critical Angle?
When the angle of incidence results to an angle of refraction of 90 degrees.
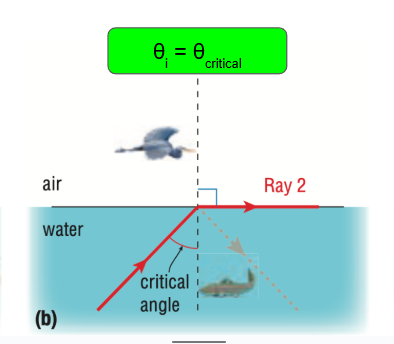
What is total internal reflection
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle (90 degrees angle of refraction)

What is apparent depth
what the depth of an object that “appears” to be due to the refraction of light in a transparent medium
What is a Mirage
Formed by refractions and the total internal reflection caused by the earth’s atmosphere. (Ex: When the road appears to look like it has a pool of water)
What is Shimmering
When light gets refracted as it passes through different temperatures
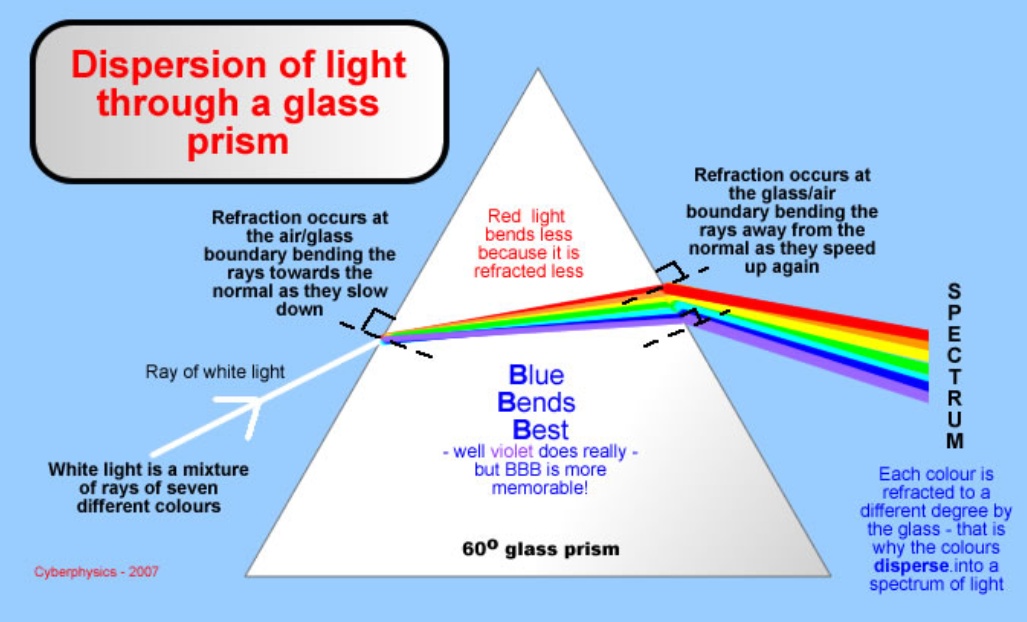
What is Dispersion
When a ray of light splits of into its constituent colors
How does Dispersion work?
Each colour of visible light travels at a different speed of light when it goes through a glass prism
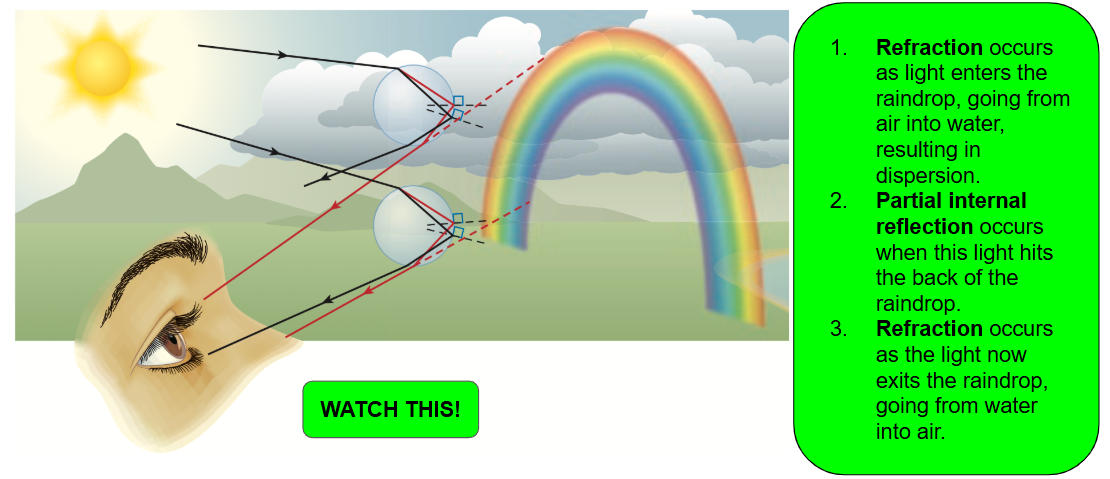
How is a rainbow formed
You can only see a rainbow when the Sun is behind you.
Refraction: Light enters a raindrop, causing dispersion from water to air.
Partial Internal Reflection: occurs when this light hits the back of the raindrop.
Refraction: Light exits the raindrop, going from water to air.
This is the light the human eye sees, which we perceive as a rainbow. Your brain projects these light rays backwards and forms a virtual image of the spectrum: a rainbow.