Orgo CH1-12 all HW Problems & Explanations
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What is the approximate bond angle shown in the structure below? (Approximate bond angles are according to your understanding of the hybridization of the atom. Also, only include the number, as the answer is assumed to be in the unit of "degrees").
120
(The bond angle is approximately 120° because the central atom is sp² hybridized, which forms a trigonal planar geometry with 120° angles between the bonds.)
Identify whether the following structures may act as only a Lewis acid, only a Lewis base, both a Lewis acid or a Lewis base, or neither.
a) BF3
b) NBr3
c) Ethane (C2H6)
d) NH3
a) Lewis acid only
b) Lewis base only
c) neither Lewis acid nor base
d) Lewis Acid and Lewis Base
(a) BF₃ is a Lewis acid only because it has an incomplete octet and can accept a lone pair.
b) NBr₃ is a Lewis base only because nitrogen has a lone pair it can donate.
c) Ethane is neither because it has no available lone pairs or empty orbitals for donation or acceptance.
d) NH₃ is both because it can donate its lone pair (base) and accept a proton (acid) depending on the reaction.)
Of the following bonds, which bond is most polar? (HINT: Use your knowledge of the trend of electronegativity to answer this question).
a. C-O
b. C-H
c. C-F
d. H-F
e. C-N
H-F
(H–F is the most polar because fluorine is the most electronegative element, creating the largest difference in electronegativity between it and hydrogen.)
What is the approximate bond angle shown in the structure below? (Approximate bond angles are according to your understanding of the hybridization of the atom. Also, only include the number, as the answer is assumed to be in the unit of "degrees").
180
(The bond angle is 180° because the central atom is sp hybridized, resulting in a linear geometry.)
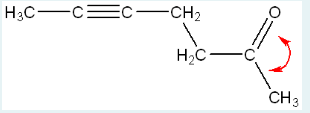
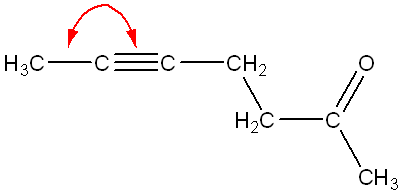
Using the structure below, indicate how many carbon atoms are sp2 hybridized. (HINT: type the number, do not spell out the word of the number).
8
(Count all the carbons with sp2 hybridization, or with double bonds between them and another atom.)
For the following compound, draw a Lewis structure where all non-hydrogen atoms obey the octet rule, all hydrogens obey the duet rule and all formal charges are zero. (HINT: This structure contains at least one multiple bond, where a multiple bond is either a double bond or a triple bond.)
C5H6 (condensed formula: CH3CCCHCH2)
How many pi bonds are in this structure?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 3
e. 5
d. 3
(There are 3 pi bonds because the structure includes two triple bonds (each with 2 pi bonds, but one overlaps) or one triple bond and one double bond, totaling three pi bonds in the molecule.)
How many sigma bonds are in the structure of buta-1,3-diene? (Condensed formula is CH2CHCHCH2). (HINT: type the number, do not spell out the word of the number).
9
(There are 9 sigma bonds: each single bond counts as one sigma, and each double bond contributes one sigma (the other is a pi bond), totaling 9 sigma bonds in the whole structure.)
Consider the structure of the medication below. This medication can treat fever, pain, inflammation, headaches, and reduce the risk of heart attack.
What is the total number of hydrogens in this structure? Make sure you count all the hydrogens, even those that might be hidden or understood if you are using a line structure.
8
(Keep in mind carbons with 1 single bond will need 3 more bonds with hydrogens to satisfy the tetravalent nature of carbon, contributing to the total count of hydrogens. From there, look at carbons with multiple single bonds, or double bonds, etc, to ensure all 8 electrons are used up.)
Rank the following acids from most to least acidic. (Most = 1, Least = 4)
a) acetic acid (pKa = 4.76)
b) acetone (pKa = 19.3)
c) ammonia (pKa = 38)
d) isopropanol (pKa = 16.5)
a) acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) → 1
b) acetone (pKa = 19.3) → 3
c) ammonia (pKa = 38) → 4
d) isopropanol (pKa = 16.5) → 2
(Acidity increases as pKa decreases, so acetic acid is most acidic (lowest pKa), followed by isopropanol, then acetone, and ammonia is least acidic (highest pKa).)
Label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base in the following acid-base reaction.
H2S + CN- --> HS- + HCN
a) CN-
b) HCN
c) HS-
d) H2S
a) CN⁻ → base (accepts proton)
b) HCN → conjugate acid (formed after proton donation)
c) HS⁻ → conjugate base (formed after proton loss)
d) H₂S → acid (donates proton)
Draw trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. You may opt to build the model as well. If the methyl substituent on carbon 1 is equatorial, then what what is true about the methyl group on carbon 3?
It must be axial.
(If the methyl group on carbon 1 is equatorial in trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane, the methyl group on carbon 3 must be axial to maintain the trans relationship, where the substituents are on opposite sides of the ring and to minimize steric strain.)
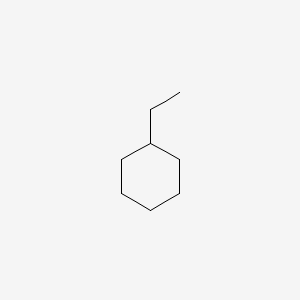
From among the constitutional isomers of C8H16, give the IUPAC name for the one that contains only one substituent, of which is an ethyl group, and does not contain a double bond.
ethylcyclohexane
(The IUPAC name is ethylcyclohexane because it is a cyclohexane ring with a single ethyl group attached, and no double bonds are present, fitting the formula C₈H₁₆.)
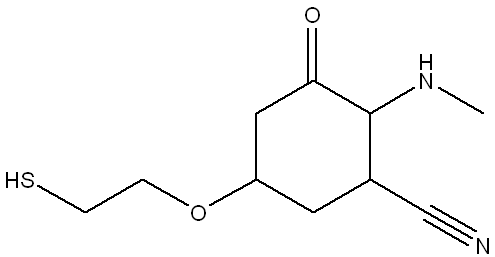
There are multiple functional groups present in the structure below. Select all functional groups that are present in the given structure.
a.
amine
b.
nitro
c.
alcohol
d.
imine
e.
aldehyde
f.
amide
g.
nitrile
h.
ester
i.
ketone
j.
ether
k.
alkene
l.
sulfide
m.
thiol
The correct answers are:
thiol,
ketone,
nitrile,
amine,
ether
(Thiol: Contains a -SH group (sulfur-hydrogen bond).
Ketone: Contains a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms.
Nitrile: Contains a -C≡N group (triple bond between carbon and nitrogen).
Amine: Contains a nitrogen atom bonded to hydrogen or carbon.
Ether: Contains an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms.)
Give the IUPAC name for the following compound:
(CH3CH2)3CCH2CH2C(CH3)3
5,5-diethyl-2,2-dimethylheptane
(The longest carbon chain has 7 carbons (heptane), with two methyl groups at position 2 and two ethyl groups at position 5, following IUPAC rules for numbering the chain to give the lowest possible numbers to the substituents.)
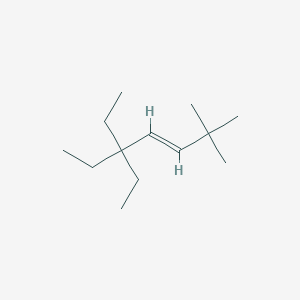
The following compound was named incorrectly. Draw the molecule that fits this description and then name it correctly, using IUPAC nomenclature rules.
2-ethyl-4-propylhexane
5-ethyl-3-methyloctane
(Start by finding the longest continuous carbon chain, which has 8 carbons, making it octane. Number the chain from the end closest to the first branch to give the substituents the lowest possible numbers—this puts a methyl on carbon 3 and an ethyl on carbon 5.)
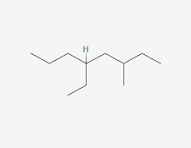
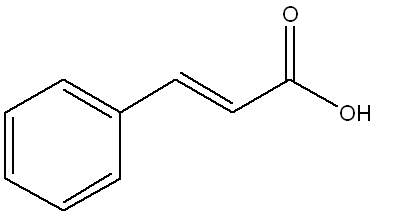
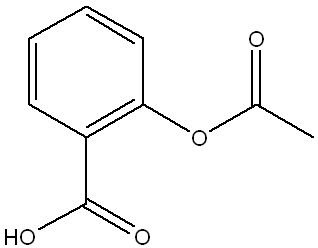
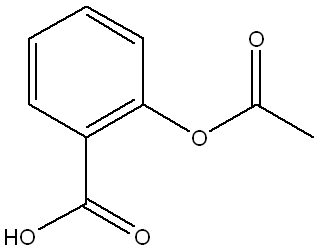
Below is the structure of trans-cinnamic acid. Which functional groups are present in the structure?
a.
arene, alkene, carboxylic acid
b.
carbonyl, arene, alcohol
c.
alkene, ketone, alcohol
d.
alkene, arene, ester
e.
alkyne, aldehyde, arene
a.
arene, alkene, carboxylic acid
(This structure contains a benzene ring (arene), a double bond (alkene) between two carbons, and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH), making option a the correct set of functional groups.)
The following compound was named incorrectly. Draw the molecule that fits this description and then name it correctly.
2-tert-butyl-4-ethyl-5-propylhexane
5-ethyl-2,2,3,6-tetramethylnonane
(Start by identifying the longest continuous carbon chain, which has 9 carbons (nonane). Number the chain from the end nearest the first branch to assign the lowest possible numbers to substituents. The original name misidentified the substituents, which are actually four methyl groups at positions 2, 2, 3, and 6, and one ethyl group at position 5, leading to the corrected name.)
Which of the following would you expect to have the lowest boiling point?
a.
C40H82
b.
C11H24
c.
C30H62
d.
dodecane
e.
C20H42
C11H24
(Boiling point generally increases with molecular weight and surface area, so C₁₁H₂₄ has the lowest boiling point because it is the smallest and least massive molecule among the options.)
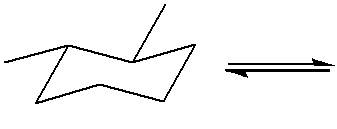
Which of the following answer choices is the correct ring inversion for the following structure? (HINT: build a model! You may also want to practice this on paper to get to the right answer.)
(To get the correct ring inversion, flip all axial groups to equatorial and all equatorial groups to axial, keeping each substituent on the same carbon. This helps compare the stability of chair conformations, as bulky groups prefer the equatorial position to reduce 1,3-diaxial interactions.)
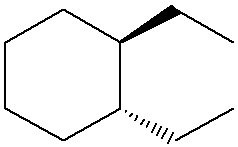
Name the following structure using IUPAC naming rules. (HINT: Include stereochemistry.)
trans-1,2-diethylcyclohexane
(Start by identifying the cyclohexane ring with ethyl groups on carbons 1 and 2, then note that they are on opposite sides of the ring, which makes the configuration trans. Include the position numbers and stereochemistry, resulting in the name trans-1,2-diethylcyclohexane.)
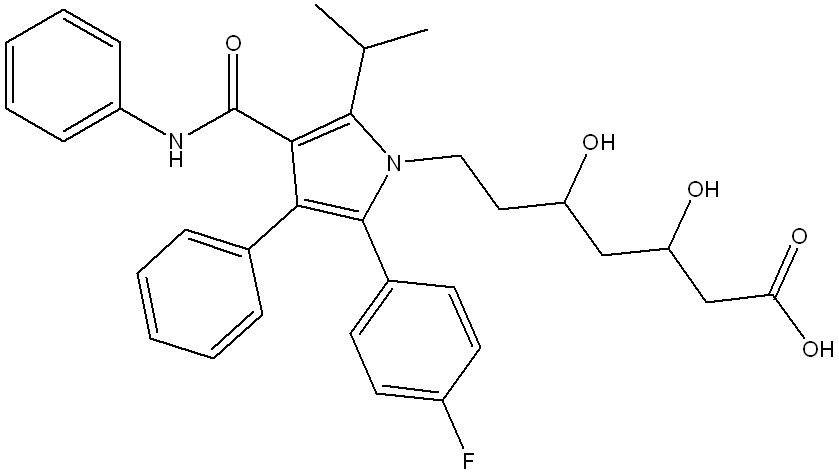
Atorvastatin is a medication used to lower cholesterol. How many chirality centers are in its structure?
2 (at the 2 OH’s)
(To find a chiral center, look for a carbon atom bonded to four different groups—these can be atoms or chains that differ in connectivity or composition. The carbon must be sp³ hybridized (tetrahedral) and not have any plane of symmetry.)
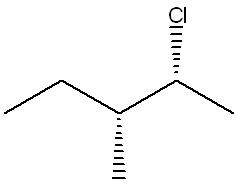
The following structure is named (2R,3R)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane. Give the name of its enantiomer.
(2S,3S)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane
(To name the enantiomer, reverse the stereochemistry at all chiral centers—so both the R configurations at carbons 2 and 3 become S, giving (2S,3S)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane.)
Which of the following is capable of existing as a pair of enantiomers? Select all that apply. (5% penalty for incorrect choices).
a.
3-ethyl-2-iodopentane
b.
2-chloro-2-iodopentane
c.
2,2-dichloropentane
d.
2-bromopentane
e.
3-chloropentane
f.
methylcyclopentane
a.
3-ethyl-2-iodopentane
b.
2-chloro-2-iodopentane
d.
2-bromopentane
(To identify enantiomers, look for chiral centers, which are carbons attached to four different groups. 3-ethyl-2-iodopentane, 2-chloro-2-iodopentane, and 2-bromopentane each have a chiral center at carbon 2, making them capable of existing as enantiomers, while the others do not have chiral centers or have symmetry.)
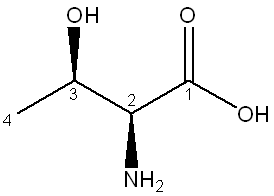
Below is the structure of threonine. Determine the configuration of each numbered chiral center.
2=S, 3=R
(To determine the configuration of the chiral centers in threonine, assign priorities to the substituents based on atomic number using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system. At carbon 2, the highest priority group (the amino group) is on the left, making it S configuration, and at carbon 3, the highest priority group (the hydroxyl group) is on the right, making it R configuration.)
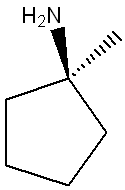
What is true of the following structure?
It is achiral.
(It is not symmetrical because its substituents are trans.)
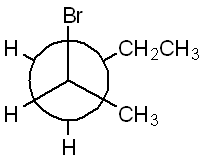
Name the following molecule, including any stereochemistry, using IUPAC naming rules. (Hint: Newman projections are from Chapter 2). As a reminder, the prefix for a bromine atom is "bromo."
(R)-2-bromopentane
(To name the molecule, first identify the longest carbon chain, which has five carbons, making it pentane. The bromine atom is attached to carbon 2, and the configuration at this chiral center is R, so the correct name is (R)-2-bromopentane.)
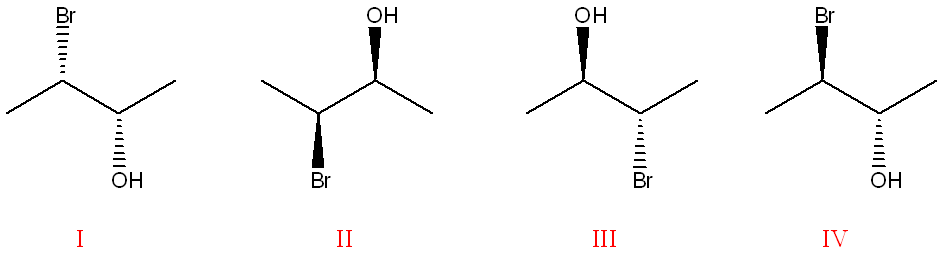
Select all of the following statements that are true pertaining to the structures given below. (5% penalty for incorrect selections).
a.
Structures II and III are diastereomers.
b.
Structures III and IV are the same molecule.
c.
Structures I and II are the same molecule.
d.
Structures II and III are enantiomers.
e.
Structures III and IV are enantiomers.
f.
Structures I and II are enantiomers.
a.
Structures II and III are diastereomers.
c.
Structures I and II are the same molecule.
e.
Structures III and IV are enantiomers.
(To compare stereoisomers, check if the molecules have the same connectivity and then compare the configurations at each chiral center. Structures I and II have identical configurations at all chiral centers, so they are the same. Structures II and III differ at only one chiral center, making them diastereomers. Structures III and IV differ at both chiral centers, making them non-superimposable mirror images, or enantiomers.)
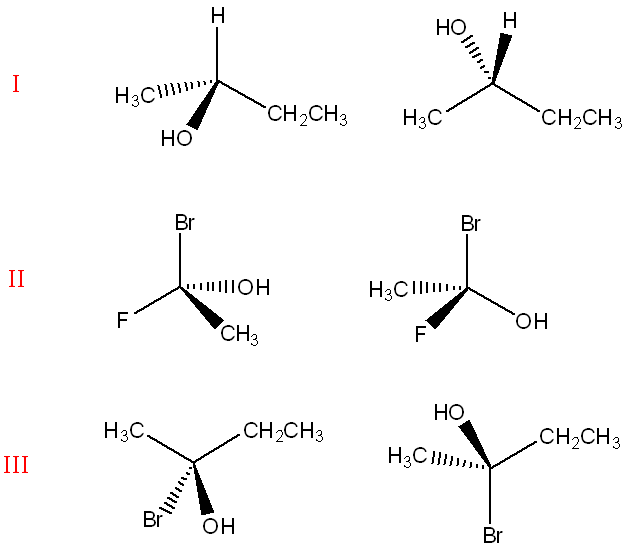
Which of the following pairs are pairs of enantiomers?
I, II
(Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images with opposite configurations at all chiral centers. Structures I and II have the same connectivity but opposite configurations at every chiral center, confirming they are enantiomers.)

The following reaction is an example of which reaction type?
substitution
(This is a substitution reaction because one atom or group (usually a leaving group, Br) is replaced by another atom or group (typically a nucleophile, N3) without changing the carbon skeleton.)
Identify whether the following structures are considered to act as an electrophile or as a nucleophile.
NH2-
Ag+
H+
H-
(attached image)
nucleophile
electrophile
electrophile
nucleophile
electrophile
(NH₂⁻ and H⁻ are nucleophiles because they have lone pairs or negative charges that can donate electrons. H⁺ and Ag⁺ are electrophiles because they are positively charged and seek electrons. The attached molecule likely has an electron-deficient site (+ charge), making it an electrophile.)
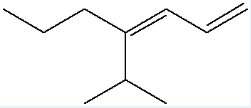
Name the following molecule using IUPAC naming rules. Include E/Z in your naming.
(Z)-4-isopropyl-1,3-heptadiene
(To name this molecule, identify the longest carbon chain (heptane) and number it so the double bonds are at positions 1 and 3, making it a 1,3-heptadiene. The isopropyl group is on carbon 4, and since the higher priority groups on the first double bond are on the same side, the configuration is Z, giving (Z)-4-isopropyl-1,3-heptadiene.)
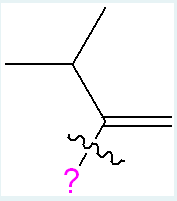
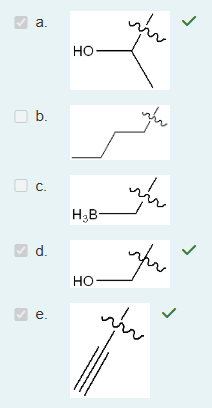
Which of the substitutions, when replacing the pink question mark (see below), would be ranked as the higher priority group on the left carbon of the alkene? Choose all that apply. (5% penalty for each incorrect answer).
(To rank priority on the alkene carbon, look at the atoms directly bonded to the alkene carbon and assign higher priority to the one with the higher atomic number. If the first atoms are the same, compare the atoms bonded to them step by step until a difference is found. In this case, C > B, O > C, and a triple bond > double bond.)
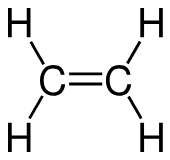
Which of the following is true pertaining to alkene structure and bonding (considering a carbon that is only participating in one double bond)? Select all that apply. (5% penalty for each incorrect answer).
a. The molecular shape of the alkene carbon is linear.
b. The bond angle around an alkene carbon is approximately 180 degrees.
c. The bond angle around an alkene carbon is approximately 120 degrees.
d. The alkene carbon is sp2 hybridized.
e. The alkene carbon is sp hybridized.
f. The bond angle around an alkene carbon is approximately 109 degrees.
g. The molecular shape of the alkene carbon is trigonal planar.
h. The alkene carbon is sp3 hybridized.
i. The molecular shape of the alkene carbon is tetrahedral.
c. The bond angle around an alkene carbon is approximately 120 degrees.
d. The alkene carbon is sp2 hybridized.
g. The molecular shape of the alkene carbon is trigonal planar.
(Alkene carbons are sp² hybridized, which results in a trigonal planar shape and bond angles of about 120°, due to the arrangement of three electron domains around each carbon in the double bond.)
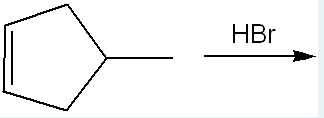
Give the name of the product of the following reaction.
1-bromo-3-methylcyclopentane
(This is an addition reaction with Br being added to the molecule. The cyclopentene → cyclopentane, when the H+ from HBr breaks the double bond, and the bromine is attached to where the double bond used to be and gets the 1st position. The methyl is still there in the 3rd position)
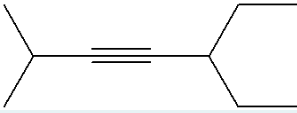
Give the IUPAC name for the molecule given below.
5-ethyl-2-methylhept-3-yne
(-yne because triple bond, hept- because 7 is longest chain, methyl group at 2, ethyl group at 5, triple bond at 3)
How many different structures can be drawn with the formula C4H8? (HINT: consider stereochemistry).
6
(First, for straight-chain alkenes: you can have but-1-ene and but-2-ene (which can also be cis or trans, so that's 2 more). Next, branched alkenes: isobutene is a possibility. Then, for cycloalkanes, you can have cyclobutane. So, counting all unique combinations and isomers, you end up with 6 structures.)
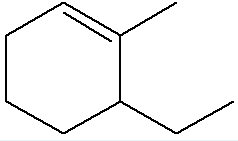
What is the IUPAC name of the structure given below?
6-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexene
(cyclohexene because it’s a hexane ring but with a double bond, the direction of numbering goes counterclockwise because if we give position 1 to methyl we have to reach the other side of the double bond on 2 before going to ethyl, so ethyl would be at position 6)
Select all of the following statements that are true about catalysts in chemical reactions. (5% penalty for each incorrect answer).
a. Catalysts increase the rate of a reaction.
b. Catalysts provide an alternate pathway in a chemical reaction.
c. Catalysts lower the activation energy for the step(s) in the reaction.
d. Catalysts are regenerated over the course of the reaction.
e. Using a catalyst will result in producing different final product(s) compared to the the uncatalyzed reaction.
f. Catalysts lower the energy of the products.
g. Catalysts generate different intermediates than the uncatalyzed reaction.
h. Catalysts lower the energy of the reactants.
a. Catalysts increase the rate of a reaction.
b. Catalysts provide an alternate pathway in a chemical reaction.
c. Catalysts lower the activation energy for the step(s) in the reaction.
d. Catalysts are regenerated over the course of the reaction.
g. Catalysts generate different intermediates than the uncatalyzed reaction.
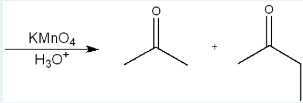
Give the IUPAC name of the starting material that will react in the given conditions to produce the products below.
2,3-dimethylpent-2-ene
(The products suggest that the original compound was an alkene that, when cleaved at the double bond, produced these ketones. One ketone has 3 carbons and the other has 4 carbons, but we subtract one from each because it’s part of the ketone bond, so we get a total of 5 extra carbons, meaning the original structure was a pentene. Reconstructing the alkene, we place a double bond between the two central carbons that originally connected the ketone fragments. Since there are 7 carbons total in the products and only a 5 parent chain, there are 2 extra carbons somewhere and so those are the methyl groups. One goes on each sp2 carbon. This results in the structure 2,3-dimethylpent-2-ene.)
What product would you expect to obtain from the addition of Cl2 to 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene? Please include cis- or trans- as appropriate.
trans-1,2-dichloro-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
(One Cl goes to one sp2 carbon, the second Cl goes to the other sp2 carbon. That gives us 1,2-dichloro… It is trans because of the specific reaction, halogenation, which always gives us trans products.)
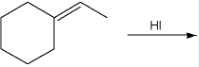
Give the IUPAC name of the major organic product of the following reaction.
1-ethyl-1-iodocyclohexane
(This is hydrohalogenation, with a strong nucleophile and weak base. The H+ attacks the double bond, breaking it, and the I adds to the most substituted carbon (where the double bond is attached to the hexane ring.) So at position one, we have an ethyl group and iodo- attached to the cyclohexane, which is no longer a cyclohexane.)
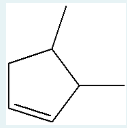
What product would you expect to obtain from catalytic hydrogenation of this alkene?
1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
(In catalytic hydrogenation of an ALKENE, H2 is added, resulting in an ALKANE. So we know the cyclopentene turns into a cyclopentane. The methyl groups remain in the same places (1 and 2), giving us the product.)
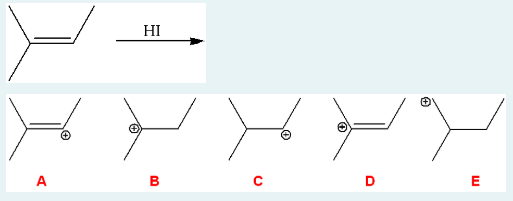
Identify the carbocation intermediate that is formed in the mechanism for the following reaction.
B
(In the intermediate, the H+ from the HI attacks the double bond. Before the I attaches to the most substituted place, we are left with a + charge where the double bond used to be. It is on the most substituted (tertiary) carbon, not the other side of the bond.)
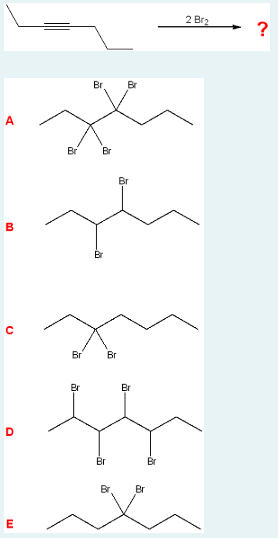
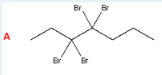
Identify the major product of the following reaction.
A
(Bromination. 2 Br2’s (so 4 bromines) are added to a 7-carbon chain that is an alkyne at carbon 3. After the triple bond breaks, 2 bromines each go on the most substituted carbocations, on either side of where the bond used to be.)
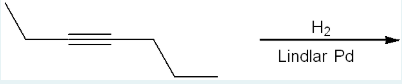
Give the IUPAC name of the product formed in the following reaction, including any relevant stereochemistry.
cis-hept-3-ene
(We only have 1 H2 reacting with the reactant, so that will be hydrogenation of an alkyne, where it turns into an alkene—it still has a double bond, not fully being reduced to an alkane because Lindlar’s catalyst is poisoned, not fully reducing bonds. There is a 7-carbon parent chain. It is cis because Lindlar always gives cis alkenes.
Give the name of the most substituted alkene starting material that will generate the following product upon a hydration reaction. Be sure to include stereochemistry in your name.
(E)-3-methyl-2-pentene
(A hydration reaction happens when H2O is added, forming an alcohol. The methyl group should be in its original position—carbon 3. We see an OH at carbon 3 and know the H2O must have been added there. We also know that it used to be a pentene chain, which was broken by the hydration reaction. The double bond would’ve been located where the OH group is now, making it go from position 2—3, and the OH must’ve added to carbon 3 because it is the most substituted (with the methyl group being there), thus having a tertiary position. It is E stereochemistry because, when the double bond was there, the more powerful groups were on opposite sides (double bond > single bond.)
Which of the following reactions experience Markovnikov regioselectivity? Select all that apply.
a. reduction of alkene
b. addition of water (acid-catalyzed) to alkene
c. addition of HX to alkyne
d. addition of water (acid-catalyzed) to alkyne
e. addition of HX to alkene
b. addition of water (acid-catalyzed) to alkene
c. addition of HX to alkyne
d. addition of water (acid-catalyzed) to alkyne
e. addition of HX to alkene
(Markovnikov addition happens when H adds to the less substituted carbon and the other group to the more substituted one. This applies to acid-catalyzed hydration and HX additions to alkenes and alkynes.)
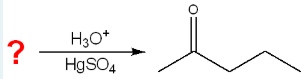
Give the IUPAC name of the starting material that would produce the following product in the given set of conditions.
pent-1-yne
(We know we must’ve had a pentane chain because of 5 carbons in the parent chain, and it should have been a pentyne, because the catalyst had to have broken a bond. This bond must’ve been at carbon 1—2 because it is where the ketone formed.)
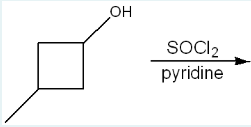
Give the IUPAC name of the product of the following reaction.
1-chloro-3-methylcyclobutane
(SOCl₂ (thionyl chloride) reacts with alcohols to replace the –OH group with a –Cl, and pyridine is used to neutralize the HCl byproduct. Since the starting material is a cyclobutane ring with an –OH on carbon 1 and a methyl on carbon 3, the product becomes 1-chloro-3-methylcyclobutane.)
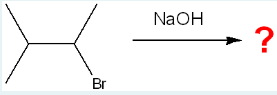
What is/are the major organic product(s) of the following reaction?
D
(When NaOH reacts with a molecule containing a Br, it often acts as a base and removes a hydrogen from a β-carbon (a carbon adjacent to the one bonded to Br). This causes the Br to leave and a double bond to form between the α- and β-carbons — a process called E2 elimination.)
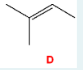
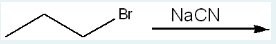
What is the product of the following reaction?
(When NaCN reacts with an organic molecule containing a halide, such as bromine (Br), the bromine is substituted by the cyanide ion (CN-). This reaction is a nucleophilic substitution where NaCN serves as the nucleophile. The bromine atom is removed, allowing the cyanide to attach to the carbon atom, resulting in the formation of a nitrile compound. This type of reaction typically occurs via an SN2 mechanism, which involves a single concerted step where the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom from the opposite side, leading to the inversion of configuration.

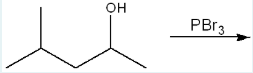
Give the IUPAC name of the major product formed in the following reaction.
2-bromo-4-methylpentane
(We are reacting PBr3 with the molecule. Br gets substituted where OH used to be, and the remaining carbon chain is adjusted accordingly, resulting in 2-bromo-4-methylpentane.)
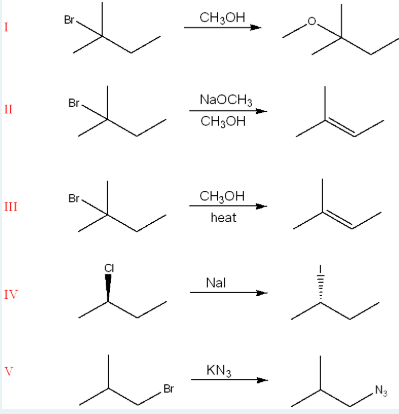
Identify the mechanism responsible for forming the products in the following reactions. Each mechanism may be more than once or not at all.
I. SN1
II. E2
III. E1
IV. SN2
V. SN2
(SN2= substitution, 1 step, no rearrangement. SN1: substitution, 2 steps, carbocation formation. E2: elimination, 1 step and formation of double bond. E1: elimination, 2 steps, double bond after carbocation.
Give the IUPAC name of the major organic product formed when 2-methylbutan-2-ol reacts with hydrogen chloride.
2-chloro-2-methylbutane
(The OH group is on a tertiary carbon, so when reacting with HCl, it undergoes an SN1 reaction where the OH is replaced by Cl, forming 2-chloro-2-methylbutane as the major product. Chloro comes before methyl alphabetically.)
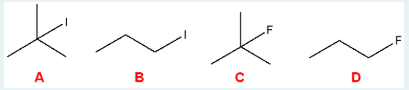
Which of the following would be most reactive towards an SN1 reaction?
A
(Tertiary alkyl halides are most reactive in SN1 reactions because they form the most stable carbocations after the leaving group departs. Primary carbocations are unstable and don’t readily form, so primary halides are very poor at SN1.)
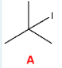
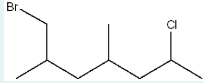
Give the IUPAC name of the following molecule.
1-bromo-6-chloro-2,4-dimethylheptane
(remember priority is given alphabetically. Find the longest parent chain: 7, or heptane. Label substituents. We have a Br on C1, methyl groups on C2 and C4, and a Cl on C6.)
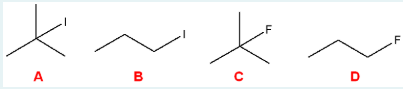
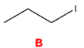
Which of the following would be the most reactive towards an SN2 reaction?
B
(Primary alkyl halides are most reactive in SN2 reactions because they have minimal steric hindrance, allowing the nucleophile to attack the carbon easily from the backside. Tertiary halides are the least reactive due to bulky groups blocking access to the electrophilic center.)
Substitution reactions require the presence of a good leaving group. However, the hydroxide group (-OH) is a poor leaving group. What can be done to complete a substitution reaction on a starting material containing an alcohol?
An alcohol group should be converted to a better water leaving group by using reagents like H+, SOCl2 or PBr3.
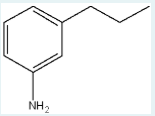
Use the prefixes o-, m-, p- and the common parent name (when appropriate) to name the following compound (using IUPAC naming rules).
m-propylaniline
(First, identify the amino group (-NH₂) as the main group, making the molecule based on "aniline." Then, find where the propyl group is attached: if it’s two carbons away from the amino group (with one carbon between them), it’s in the meta (m-) position, leading to the name m-propylaniline.)
Which of the following reactions would you use to prepare acetophenone from benzene?
a.
Halogenation
b.
Friedel-Crafts alkylation
c.
Nitration
d.
Sulfonation
e.
Friedel-Crafts acylation
e. Friedel-Crafts acylation
(Friedel-Crafts acylation adds an acyl group (RCO–) to an aromatic ring using an acid chloride and AlCl₃. To make acetophenone, you react benzene with acetyl chloride (CH₃COCl) and AlCl₃ to attach the carbonyl group directly to the ring.)
Identify the following atoms or groups as either an o/p-activator, o/p-deactivator, or m-deactivator in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
aldehyde group
methoxy group (--OCH3)
iodo group
nitrile group
ethyl group
aldehyde group → m-deactivator
methoxy group (--OCH3) → o/p-activator
iodo group → o/p-deactivator
nitrile group → m-deactivator
ethyl group → o/p-activator
What is/are the major product(s) in the bromination of benzenesulfonic acid? (5% penalty for each incorrect answer).
a.
The meta product
b.
The ortho product
c.
The para product
The meta product
(The sulfonic acid group (-SO₃H) is a strong electron-withdrawing group, which deactivates the benzene ring and directs incoming electrophiles to the meta position. So bromination of benzenesulfonic acid gives the meta product as the major one.)
What is the role of FeBr3 in the bromination of benzene?
It is a catalyst.
(FeBr₃ acts as a Lewis acid catalyst by polarizing the Br-Br bond, generating a more reactive electrophile (Br⁺) that can attack the benzene ring during the electrophilic aromatic substitution.)
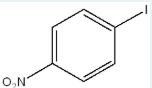
Use the prefixes o-, m-, p- and the common parent name (when appropriate) to name the following compound (using IUPAC naming rules).
p-iodonitrobenzene
(p= 1,4 position. benzene = aromatic ring. O2N and I are 1,4 positions but specified by p.
Give the IUPAC name (using o-, m- and p- where necessary) of the product of the reaction between 1-butyl-4-chlorobenzene with potassium permanganate in water.
p-chlorobenzoic acid
(KMnO₄ oxidizes any benzylic alkyl group to a carboxylic acid; the butyl chain becomes –COOH, and since the Cl is para to the original side chain, the product is p-chlorobenzoic acid (IUPAC: 4-chlorobenzoic acid).)
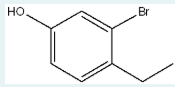
Use IUPAC naming rules to name the following molecule. Use the common name as the parent if necessary.
3-bromo-4-ethylphenol
(The parent is phenol, and substituents are numbered to give the hydroxyl group position 1; bromine is at position 3 and ethyl at 4, so the name is 3-bromo-4-ethylphenol.)
Which one of the following compounds will react faster in a nitration reaction?
a.
nitrobenzene
b.
benzaldehyde
c.
chlorobenzene
d.
aniline
aniline
(Aniline has an electron-donating –NH₂ group that activates the benzene ring toward electrophilic substitution like nitration, making it react faster than the other electron-withdrawing groups.)
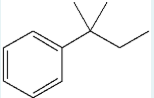
Upon reacting with benzene and aluminum trichloride, what reagent (which contains a chlorine) is used to produce the following product? Give the IUPAC name of this reagent.
2‑chloro‑2-methylbutane
(In a Friedel–Crafts alkylation, the alkyl halide used becomes the substituent on the benzene; since the product is tert-pentylbenzene, the starting reagent must be 2-chloro-2-methylbutane, which provides the tert-pentyl group.)

What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
(We are adding 1. K2Cr2O7 and 2. H+, H2O to a secondary alcohol, resulting in the formation of a ketone. The secondary alcohol is oxidized to form the corresponding ketone compound.)
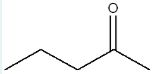
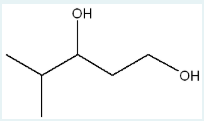
Give the IUPAC name of the following molecule.
4-methyl-1,3-pentanediol
(Longest parent chain: 5= pentane. The molecule contains two –OH groups at carbons 1 and 3, with a methyl group on carbon 4.)
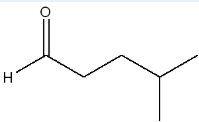
What is the IUPAC name of the product obtained when the following compound is treated with sodium borohydride followed by water and acid?
4-methylpentan-1-ol
(We are treating the compound with sodium borohydride followed by water and acid. This process reduces the ketone to a primary alcohol, resulting in 4-methylpentan-1-ol.
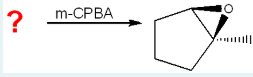
Which starting material will produce the product below with the given reagent?
1-methylcyclopent-1-ene
(mCPBA forms epoxides by reacting with alkenes; the product shows an epoxide across C1–C2 and a methyl on C1, which matches the structure of 1-methylcyclopent-1-ene as the correct starting alkene.)
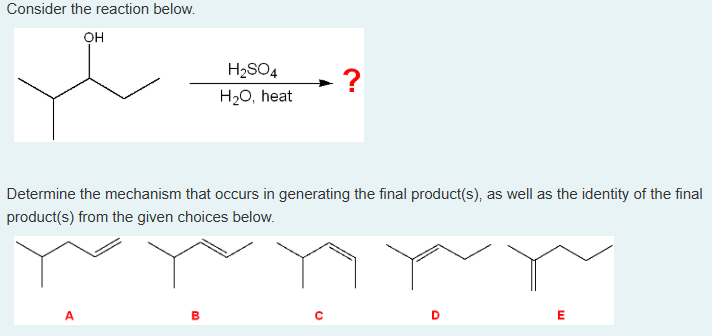
Consider the reaction below.
Determine the mechanism that occurs in generating the final product(s), as well as the identity of the final product(s) from the given choices below.
What is/are the major product(s) of this reaction?
What mechanism occurs in this reaction?
What is/are the major product(s) of this reaction? → product D
What mechanism occurs in this reaction? → E1 mechanism
(1. We need to find the product. In the reaction, we’re adding 1. H2SO4 and 2. H2O, heat. This is an elimination reaction. We will eliminate OH via dehydration (the H2O, heat) and instead form a double bond with the H2. The double bond will be between where the OH was eliminated and the most substituted carbon.
It is an E1 mechanism because it is a 2-step elimination, with a carbonation formed in the process.)
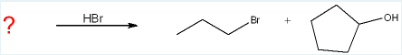
Give the name for the ether starting material that will produce the products in the following reaction.
cyclopentyl propyl ether
(In the reaction, we see HBr is the catalyst, making bromopropane and cyclopentanol. We can conclude that the Br wasn’t in the original molecule since it is a catalyst, but there was a propyl and cyclopentyl. Also, there must’ve been an ether that split. The ether starting material is a compound formed by the etherification of cyclopentanol and propyl alcohol, which produces cyclopentyl propyl ether.)
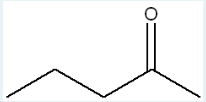
What is the IUPAC name of the product obtained when the following molecule reacts with propylmagnesium bromide (CH3CH2CH2MgBr) in the presence of ether, followed by addition of acid and water?
4-methylheptan-4-ol
(A Grignard reagent adds to a ketone or aldehyde to form an alcohol; in this case, the original compound was likely 4-methylheptan-4-one, and adding propylmagnesium bromide forms a tertiary alcohol, 4-methylheptan-4-ol.)

In the following reaction, identify (i) the type of reaction that is occurring and (ii) the reagents needed to complete the given reaction.
(i) reduction; (ii) 1. LiAlH4 in ether followed by 2. H3O+
(We know it is a reduction because the ketone is removed entirely without another bond forming.The reagents must be 1. LiAlH4 in ether followed by 2. H3O+ because they are commonly used for reducing ketones to alcohols in organic synthesis.)

Give the name of the following molecule.
ethyl propyl sulfide
(The sulfide is enclosed by 2 substituents, an ethyl and a propyl group. We put ethyl first because e>p alphabetically and sulfide comes last.)
What is the name of the product obtained when the isobutanol reacts with sodium hydride (NaH, a base), followed by addition 1-bromopropane?
isobutyl propyl ether
(NaH deprotonates isobutanol to form an alkoxide, which then performs an SN2 reaction with 1-bromopropane to form an ether—specifically, isobutyl propyl ether.)
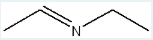
Which carbonyl-containing starting material will react with ethylamine (CH3CH2NH2) to form the product shown below?
acetaldehyde
(or ethanal?)
(A primary amine like ethylamine reacts with an aldehyde to form an imine; the simple structure of the product suggests the aldehyde must be acetaldehyde)
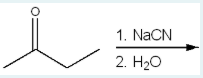
Which of the following structures is the major organic product of the following reaction?
(We are reacting 1. NaCN, 2. H2O with a 4-carbon chain with a ketone on carbon 2. The OH from H2O is added to where the ketone double bond splits (2), and the CN is added to the same carbon (2).)
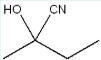
Give the IUPAC name of the following molecule.
2-propylhexanal
(The longest parent chain is 6, or hex-. On C2, there is a propyl group (3). On carbon 1 is a ketone and an H, or an aldehyde. The molecule is a hexanal with a propyl group at the second carbon. This gives us the answer.)
Give the IUPAC name of the product formed when 3-methylbutanal reacts with sodium borohydride in ethanol.
3-methylbutan-1-ol (or 3-methylbutanol?)
(Sodium borohydride (NaBH₄) reduces aldehydes to primary alcohols; reducing 3-methylbutanal gives 3-methylbutan-1-ol, where the aldehyde group becomes a –CH₂OH.)
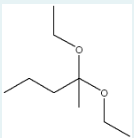
Which carbonyl structure and which alcohol will react in acid to form the following structure?
ethanol and pentan-2-one
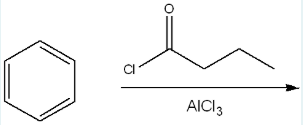
Give the IUPAC name of the product of the following reaction.
1-phenylbutan-1-one
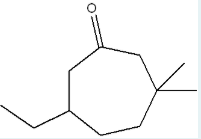
Give the IUPAC name of the following molecule.
6-ethyl-3,3-dimethylcycloheptan-1-one
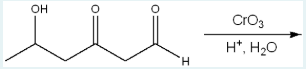
What is the product of the following reaction?
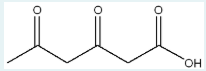
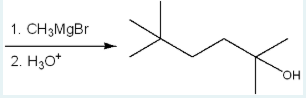
Give the IUPAC name of the starting material that will react in the given conditions below to generate the product below.
5,5-dimethyl-2-hexanone
(or 5,5-dimethylhexan-2-one?)
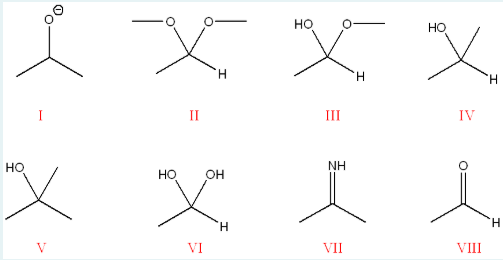
Correctly identify the name of the groups given in the figure below.
I:
II:
III:
IV:
V:
VI:
VII:
VIII:
I: alkoxide (RO-)
II: acetal (RO, OR, R, H)
III: hemiacetal (C(OH)(OR)
IV: secondary alcohol (OH attached to 2 carbons)
V: tertiary alcohol (OH attached to 3 carbons)
VI: hydrate (OH(OH)(H))
VII: imine (C=N)
VIII: aldehyde (O=C-R-H)
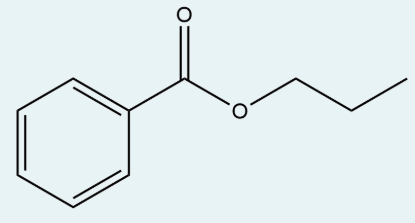
Give the IUPAC name of the starting material that will react with propanol and acid catalyst in order to generate propyl benzoate (structure below).
benzoic acid
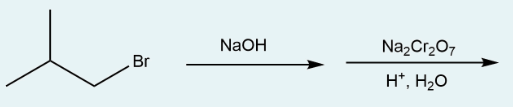
Give the IUPAC name of the product formed in the multi-step synthesis reaction below. The first step is treatment of sodium hydroxide to an alkyl halide. The product of the first reaction is treated with sodium dichromate in acidic conditions to form the product.
2-methylpropanoic acid
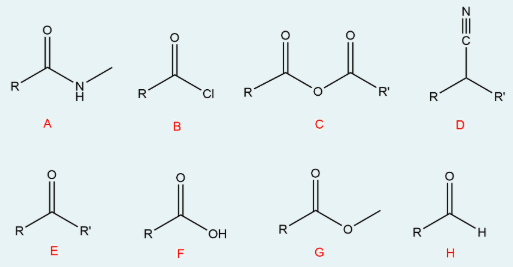
Correctly identify the name of the groups given in the figure below.
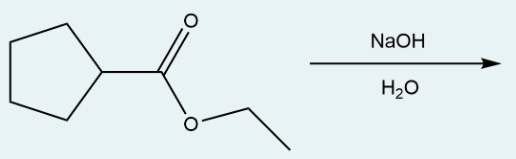
Give the IUPAC name of the product formed in the following reaction of ethyl cyclopentanecarboxylate with sodium hydroxide.
cyclopentanecarboxylic acid
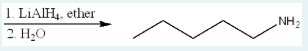
Give the IUPAC name of the starting material that, given the following reagents, will produce the product below.
pentanenitrile
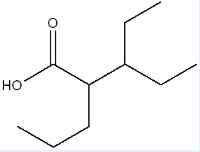
Give the IUPAC name for the following molecule.
3-ethyl-2-propylpentanoic acid
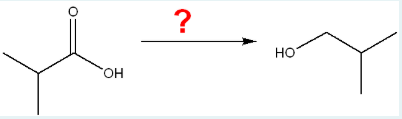
What is the correct set of reagents needed to complete the following reaction?
a.
periodinane
b.
1. LiAlH4, ether; 2. H3O+
c.
NaBH4, CH3OH
d.
NaCr2O7, H3O+
e.
KMnO4, H3O+
1. LiAlH4, ether; 2. H3O+
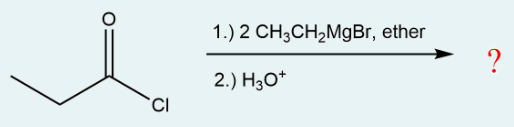
Give the IUPAC name for the major organic product that is produced in the following reaction.
3-ethylpentan-3-ol
Identify the compound with the highest boiling point.
a.
pentanol
b.
pentanal
c.
pentanoic acid
d.
pentane
e.
pentan-2-one
c.
pentanoic acid
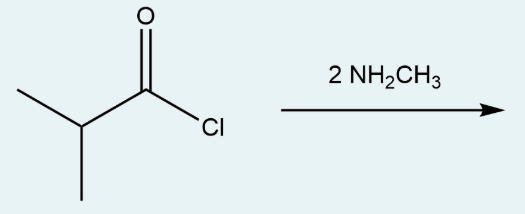
The following reaction produces a compound that contains which type of functional group?
a.
amine
b.
amide
c.
nitrile
d.
carboxylic acid
e.
ester
b.
amide
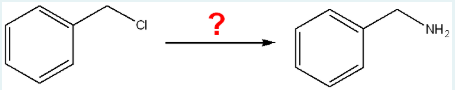
Determine the sequence and sets of reagents required in order to complete the following synthesis. (Note that extra reagents have been included).
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 1: → sodium azide
Step 2: → lithium aluminum hydride in ether
Step 3: → acid workup step
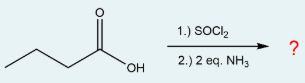
What is the name of the product that is produced in the following reaction?
butanamide