Tooth Morphology Terminology
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
maxillary
refers to the upper jaw (maxilla)
mandibular
refers to the lower jaw (mandible)
primary dentition
deciduous teeth, baby teeth
permanent dentition
secondary teeth, succedaneous teeth
what are the four quadrants that divide the teeth and mouth?
upper right, upper left, lower left, lower right
diphyodont
having two sets of teeth during a lifetime
primary or deciduous teeth begin form prenatally around
14 weeks in utero
the primary dentition consists of __ teeth in the maxilla and __ in the mandible
10, 10
each quadrant of the primary teeth consist of
two incisors, one canine, and two molars (five teeth total)
generally, the first primary teeth that emerge in the oral cavity at the mean of
8 months (6-12 months)
the first primary teeth are typically __ centered
mandibular
the last primary teeth emerge in the oral cavity at the mean age of
28 ± 4 months
the last primary teeth to emerge are typically the
maxillary second molars
around what age do the first permanent teeth begin erupting
6 years
generally, what are the first permanent teeth to emerge?
mandibular first molars (aka six-year molars)
note: sometimes mandibular incisors
mixed dentition period
period of time where the oral cavity contains primary and permanent teeth
aka the transition period
when does the permanent dentition period begin?
generally, when the permanent second molars start to erupt
primary molars are replaced by
permanent premolars
what age is the eruption of the permanent dentition usually completed?
14-15 years old
what age are third molars usually completed?
18-25 years old
what is the dental formula for the primary/deciduous teeth in humans?
I2 C1 M2 = 10
what is the dental formula for the permanent/secondary teeth in humans?
I2 C1 P2 M3 = 16
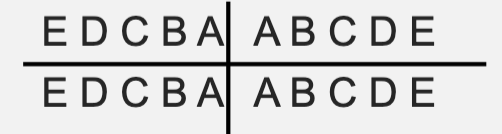
symbolic or zsigmondy/palmer system for permanent teeth
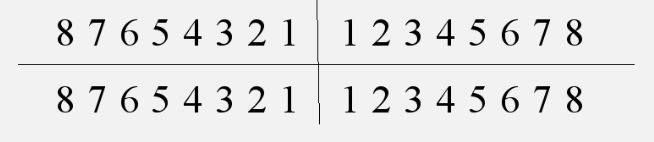
symbolic or zsigmondy/palmer system for primary teeth
two digit system for permanent teeth
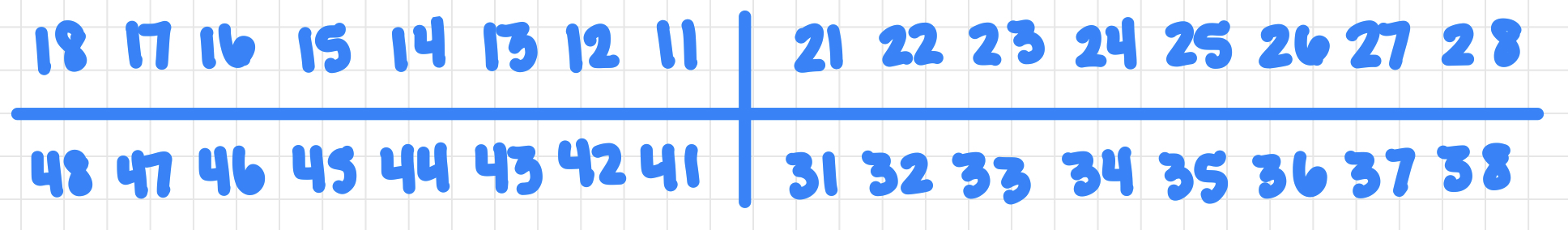
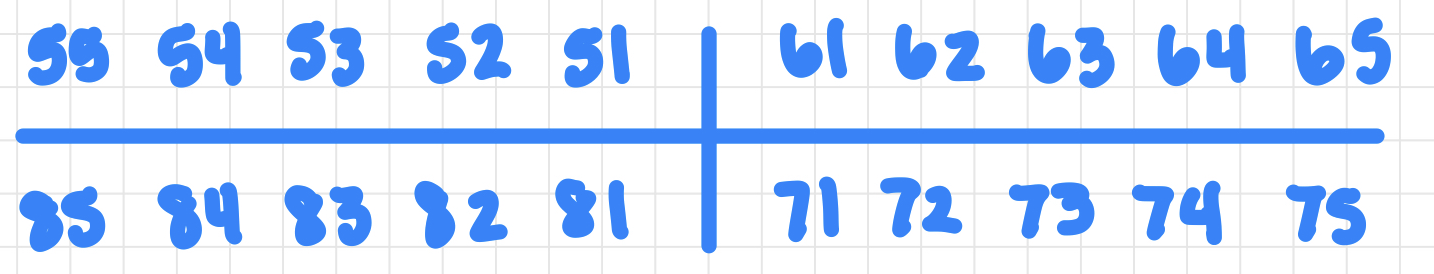
two digit system for primary teeth
universal system for permanent dentition
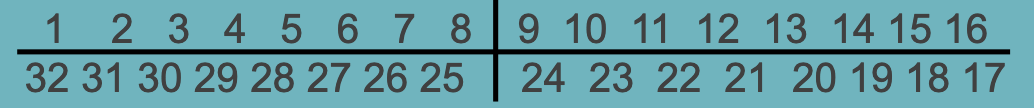
universal system for primary dentition

clinical crown
the part of the tooth that can be seen in the oral cavity
clinical root
the part of the tooth that is covered by the gingiva (gum)
anatomical crown
the part of the crown that is covered with the enamel
anatomical root
the part of the tooth that is covered with cementum
what divides the anatomical crown and root?
cervical line or the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
tip of the root
apex
apical foramen
opening at the root apex
what are the four tooth tissues?
enamel, dentin, cementum, pulp
out of the four tooth tissues, which is not a soft tissue?
pulp
what is the primary function of the pulp?
form the dentin of the tooth
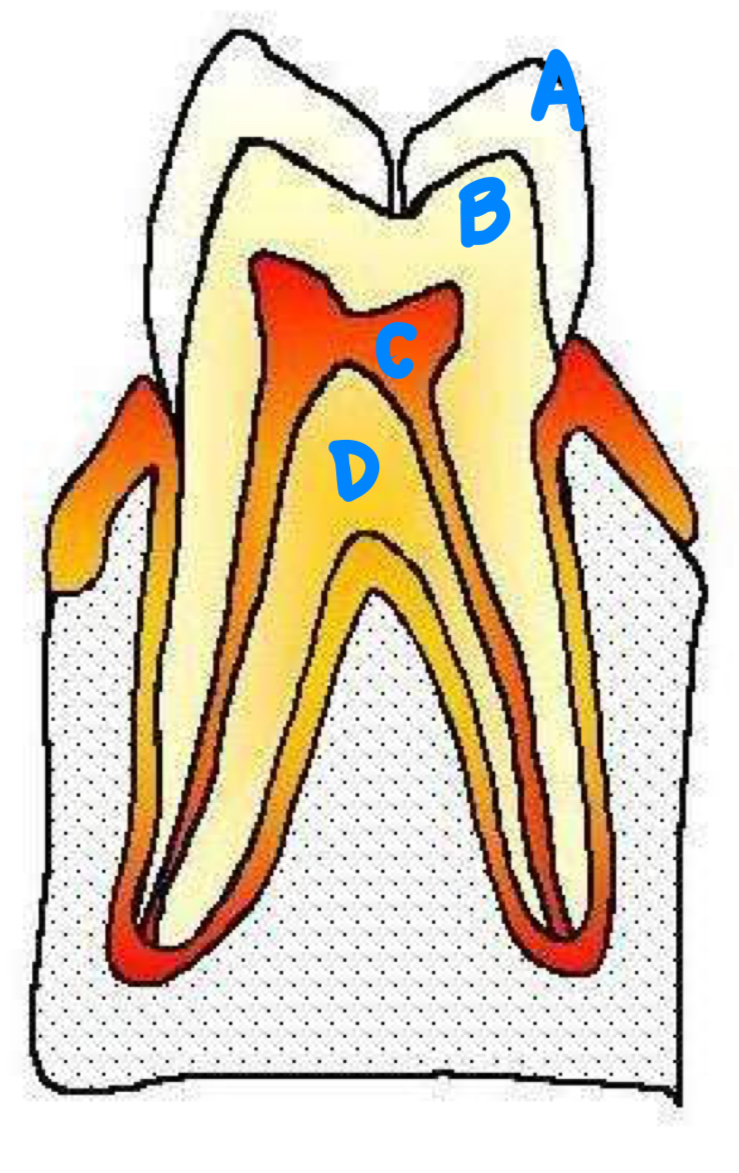
A:
B:
C:
D:
A: enamel
B: dentin
C: cementum
D: pulp
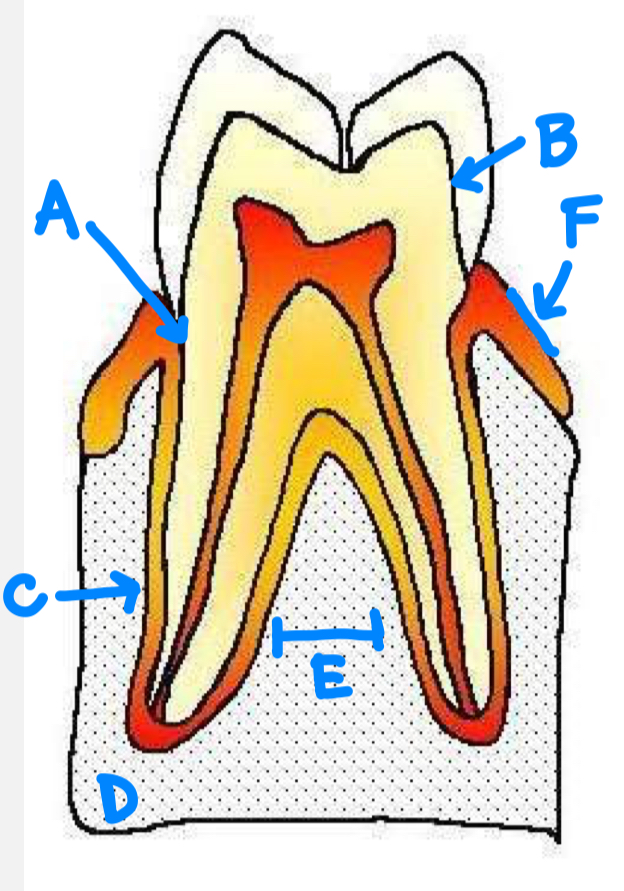
A:
B:
C:
D:
E:
F:
A: CEJ
B: DEJ
C: periodontal ligament
D: bone
E: bony septum
F: gingiva
pulp horn
projections in the roof of the pulp chamber corresponds to the major cusps or lobes
pulp chamber
crown portion of a tooth that contains the pulp tissues
root canal
root portion of the tooth that contains the pulp tissue
furcation
the area of the multi-rooted tooth where the root divides
root trunk
the area of the root between the CEJ and the furcation
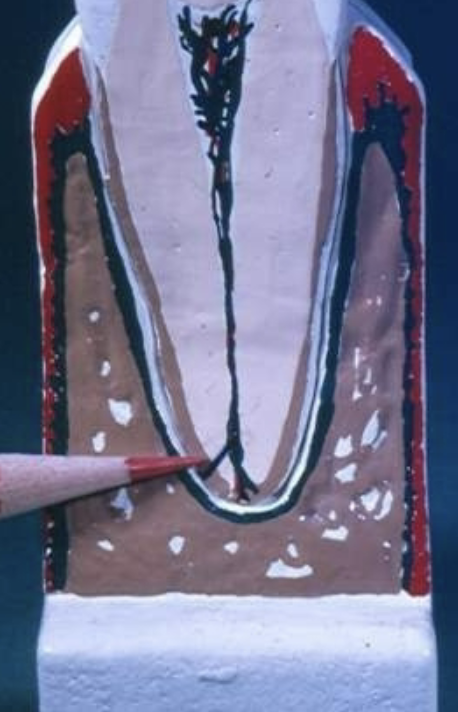

supplemental canal
bifurcation
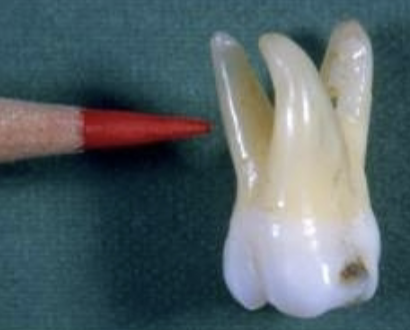
trifurcation
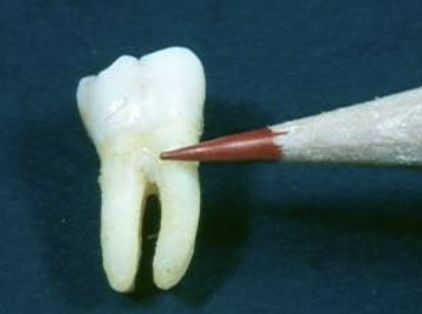
root trunk
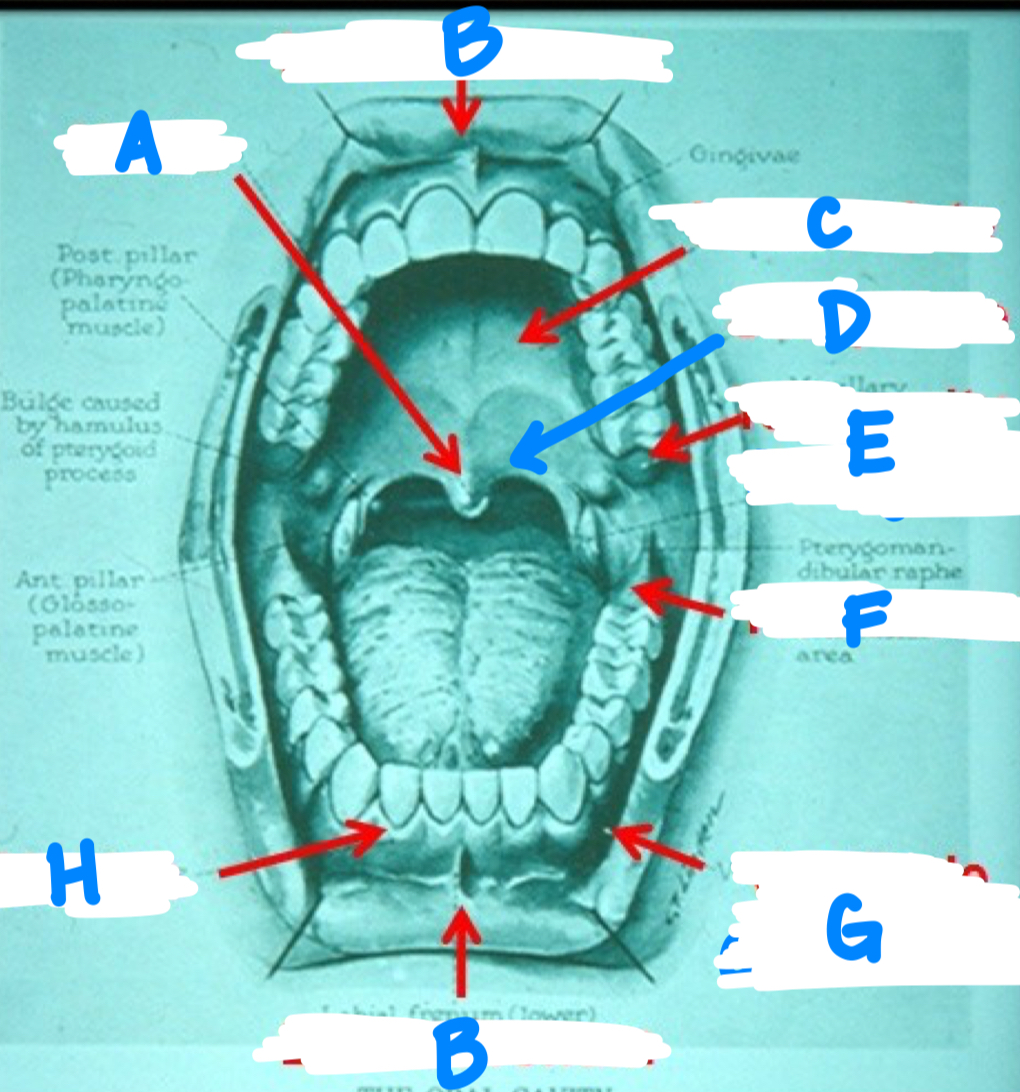
A: uvula
B: labial foramen
C: hard palate
D: soft palate
E: tuberosity
F: retromolar
G: vestibule
H: gingiva
alveolar process
portion of the jaw serving as support for the tooth
alveolus
bone of the tooth socket
proximal
towards the adjacent teeth
mesial
towards the midline
distal
away from the midline
facial
towards the face
labial
towards the lip
buccal
towards the cheek
lingual
towards the tongue
palatal
towards the palate
occlusal
the chewing surface/the surface that comes in contact with the opposing tooth
incisal
the cutting surface
radicular
of, relating to, or occuring at the root of a tooth
coronal
of, relating to, or occuring at the crown of a tooth
height of contour
concept used in aspects of restorative dentistry and means the most prominent part of the tooth
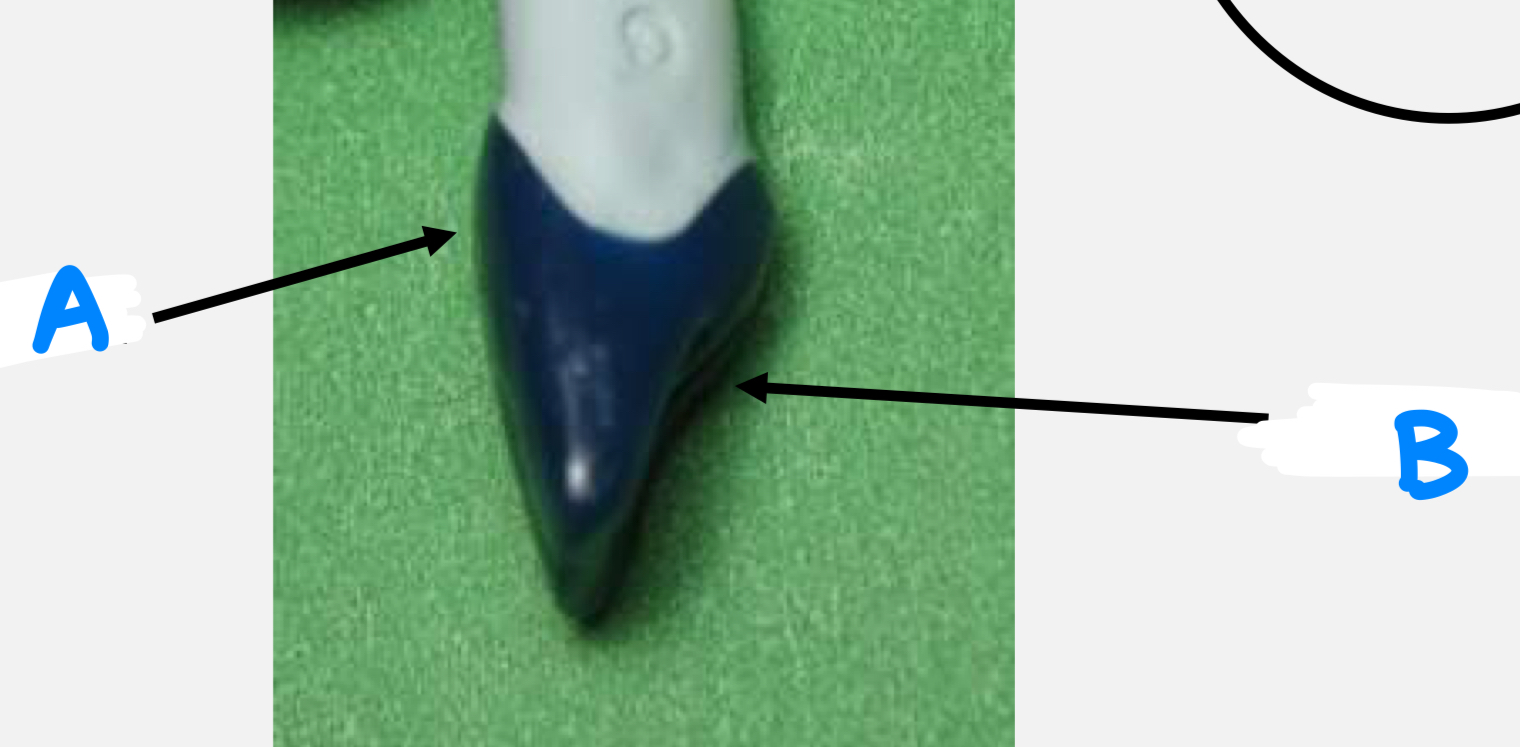
A: convex
B: concave
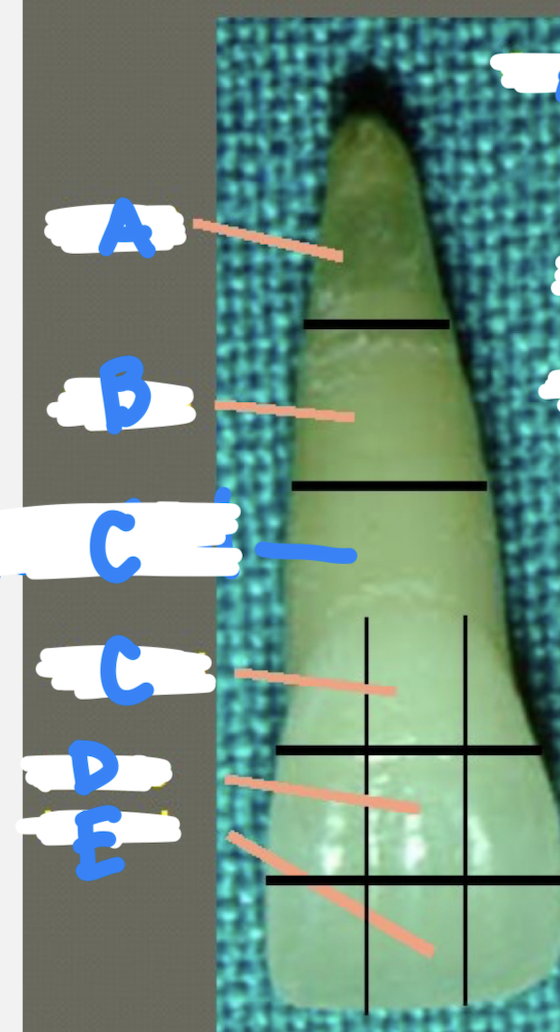
A: apical
B: middle
C: cervical
D: middle
E: incisal
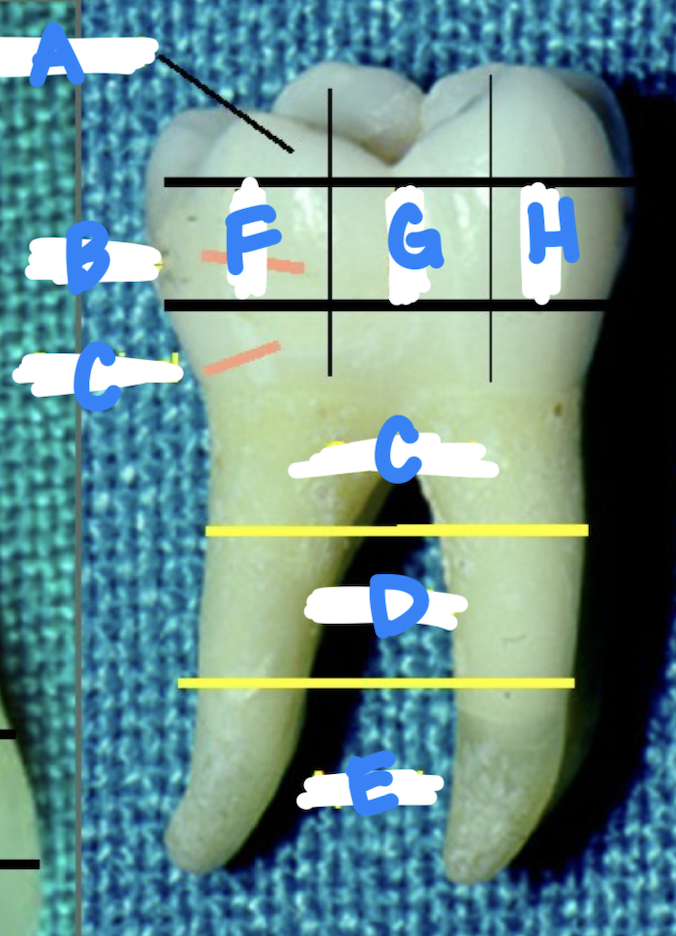
A: occlusal
B: middle
C: cervical
D: middle
E: apical
F: distal
G: middle
H: mesial
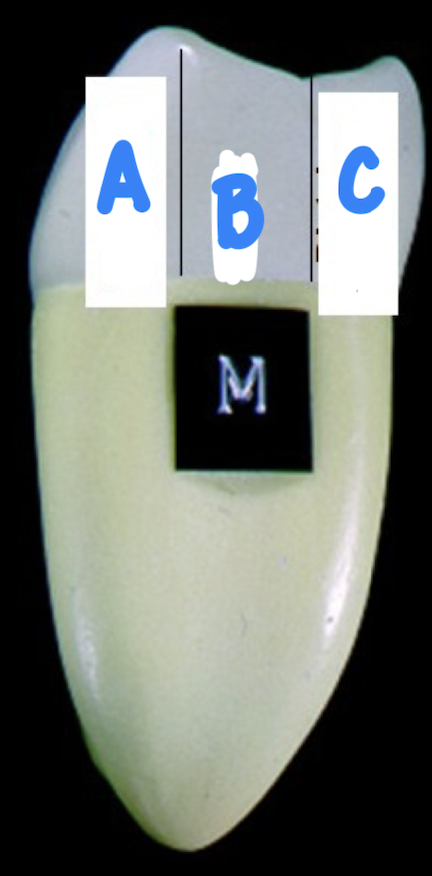
A: buccal
B: middle
C: lingual
lobe
one of the primary sections of formation in the development of the crown
representative of lobes
cusps, cingulum, mamelons
tubercle
an elevation on the crown produced by an extra formation of enamel
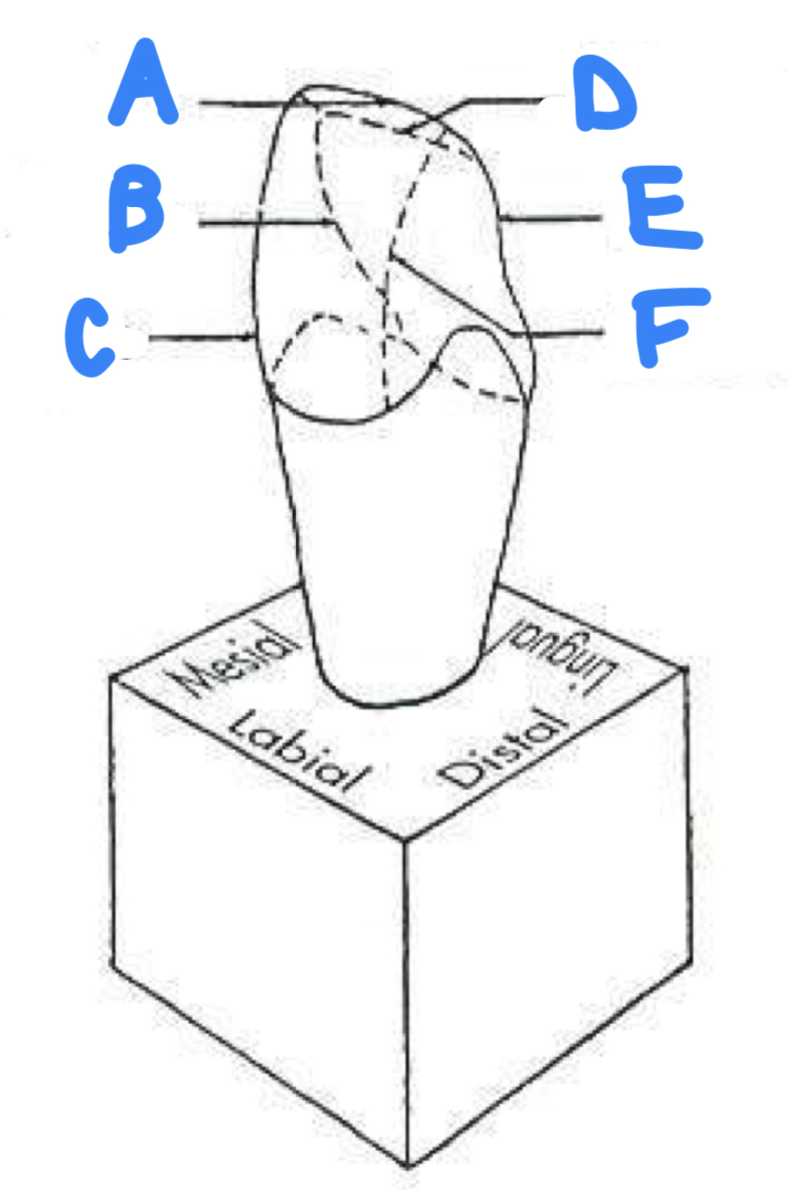
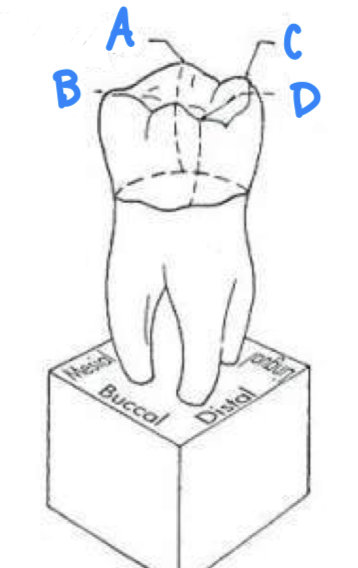
A: labioincisal line angle
B: mesioincisal line angle
C: mesiolabial line angle
D: linguoincisal line angle
E: distolingual line angle
F: distolabial line angle
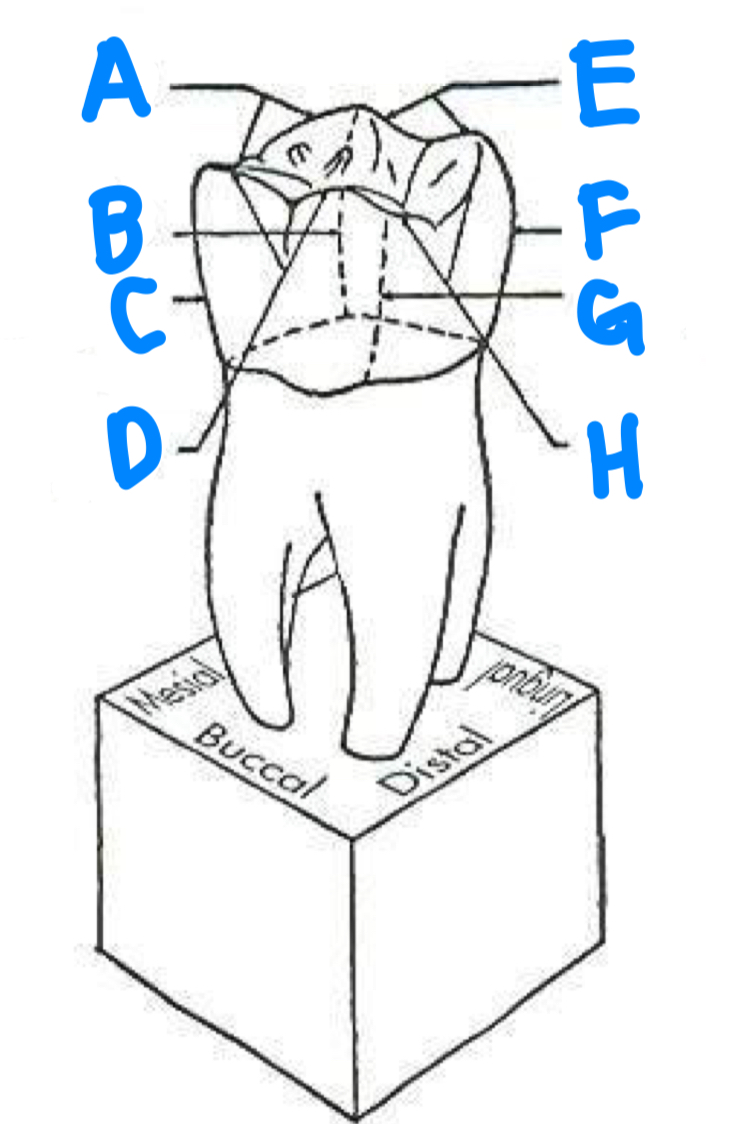
A: mesio-occlusal line angle
B: mesiolingual line angle
C: mesiobuccal line angle
D: bucco-occlusal line angle
E: linguo-occlusal line angle
F: distolingual line angle
G: distobuccal line angle
H: disto-occlusal line angle
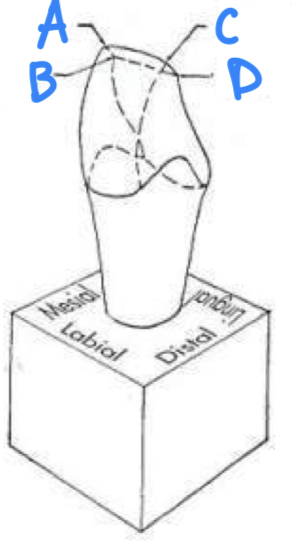
A: mesiolabioincisal point angle
B: mesiolingualincisal point angle
C: distolabialincisal point angle
D: distolinguoincisal point angle
A: mesiolinguo-occlusal point angle
B: mesiobucco-occlusal point angle
C: distolinguo-occlusal point angle
D: distobucco-occlusal point angle
how many line angles are there in the anterior teeth?
6
how many line angles are there in the posterior teeth?
8
how many point angles are there in all teeth?
4
embrasures
spillways that are found between two adjacent teeth
interdental papilla (IDP)
part of the gingiva that cervical or gingival embrasures contain
purposes of embrasures?
provide a spillway for food
prevent food from being forced into the contact areas