Physics III Exam
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
true
true or false: at the atomic level— SN poles still exist?
Force on a moving charge in the magnetic field
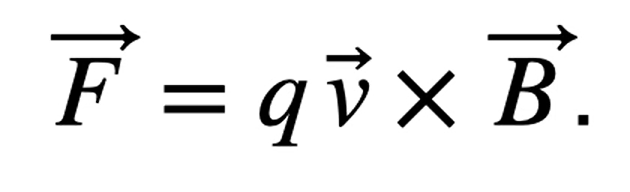
velocity selector equation
m/s
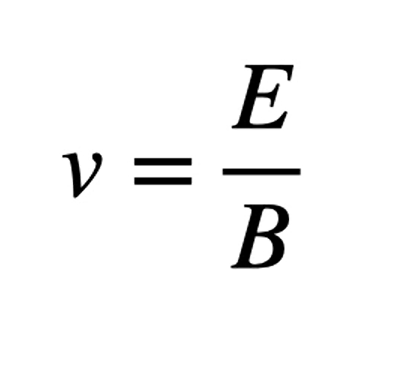
velocity selector
the particles do not dip or rise bc the electro + mag forces balance
true
0.5 T is strongish
true or false: 1 tesla is a strong magnet

1 T =
equate centripetal to magnetic force equation
mv²/r = qvB
charge
mass
speed
strength of mag field
what does radius depend on?
relationship between the radius of a charged particles trajecotry in a mag field
r=mv/qB
mass spectrometer
method used to identify samples of unknown origin
magnitude formula
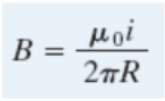
permeability of free space
μ0
ture
true or false: two wires can repeal or attract
true
true or flase: magnetic field is not r² dependent
force per unit length of wire
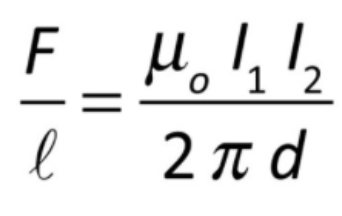
they will attract each other
currents flowing in the same direction will attract or repel each other?
repel
currents flowing in opposite directions will attract or repel each other?
flux
the amount of magnetic field lines going through a patricular area
Tm²
unit of flux is___
true
true or false: when you gain flux then a current is generated in the opposite direction
charge
mass
speed
strength of the mag field
what does radius depend on?
bc it is harder to move/accelerate
m2>m1
why does a bigger mass = a bigger circle/trajectory?
to fix v so that the radius of the path is proportional to mass
what does a veloctiy selector do in a calutron?
the number of circuits and intensity of current
what does the magnetic field of a solenoid depnd on?
the field outside is weaker and divergent
what area of the field is weaker in a solenoid?
stronger, uniform
long solenoid = ____ and ___ magnetic field
dipole magnet, not as uniform
short solenoid magnetic field looks like a ___ and is not as ___
Faraday’s law of induction
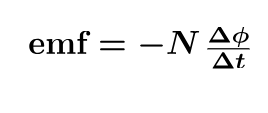
Lenz’s Law
the minus sing of faraday’s law of induction means
lenz’s Law
the emf creates a current I and magnetic field B that oppose the change in flux ΔΦ
lose flux to the right and the new current and other loop will generate magnetic field lines of its own in opposite direction
N pushed towards the current = gaining positive flux → current creates negative flux to conserve energy (counter current)
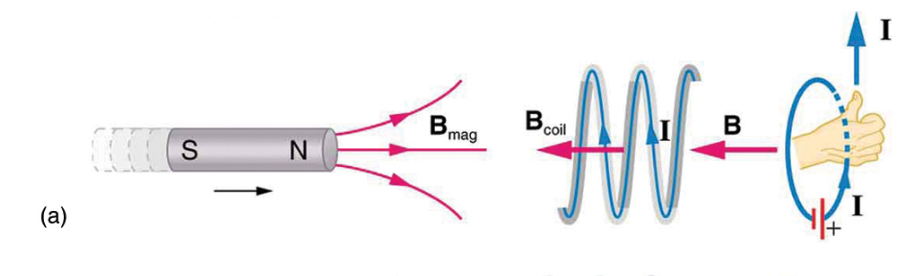
N side is pulled away (to the left) = loop loses pos flux → the current generates more positive counter flux = moves to the right
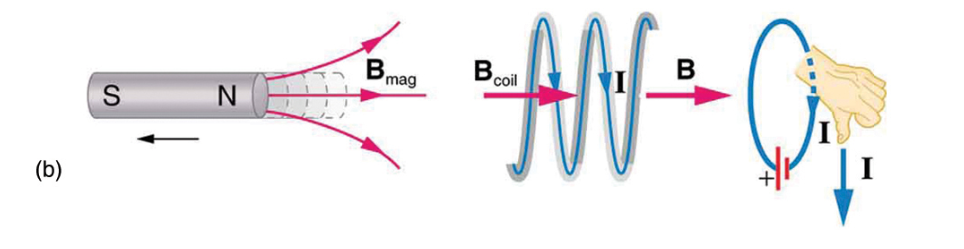
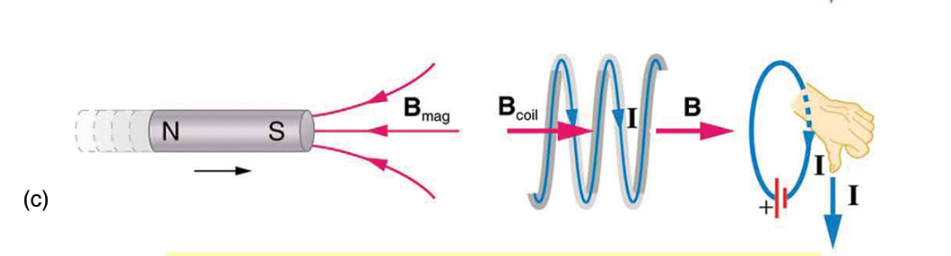
S is pulled toward the current = gaining negative flux (moves leftward)→ coil makes positive counter flux to the right
n̂
indicates whether flux can be positive or negative
Inductance (L)
generates counter current + depends on the current changing
not stable
volts x seconds/ amperes
units of inductance (L)
capacitor
potential energy
½ x 1/c x Q²(t)
inductor
kinetic energy
½ x LI²
(ΔQ/Δt)²
kinetic energy of oscillating system
Q(t)=Q(0)cos(ωt)
the charge on a capacitor in an LC circuit equation
Capacitor
stores E in electric field
Inductor (L)
stores E in magnetic field
v(t)= -ωx0sin(ωt)
x(t)= x0cos(ωt) is complimentary to
v(t)=ωtx0cos(ωt)
x(t)= x0sin(ωt) is complimentary to
v(t)= ωx0sin(ωt)
x(t)= -x0cos(ωt) is complimentary to
v(t)= -ωx0cos(ωt)
x(t)= -x0sin(ωt) is complimentary to
E and B
radiation is the motion of ____ and ____
c= λf
wave equation
red
orange
yellow
green
blue
indigo
purple
low to high frequency (colors)
gamma rays
x-rays
ultraviolet wave
infrared waves
radio waves
high to low frequneices of rays
faraday’s Law of induction describes the emf or potential difference produced by a changing mag field
a potential difference can be related to an electric field = changing a mag field produces an electric field
vice versa
what did maxwell discover?
maxwell’s equation spatial variations

maxwell’s equation temporal variations

square of the fields B + E
on a volume basis; u
how momentum + energy are transported across spacetime
energy in a field is ____
energy density equation
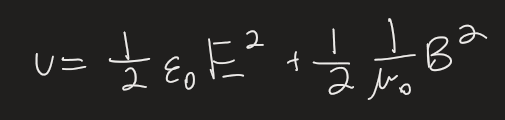
electromagnetic waves move like ocean waves
maxwell
luminiferous ether
E always ⊥ B
E can be oriented in any direction in the y-z plane
B oriented with it
3 aspects of the polarization of light
polarized light
Restricting the E field to being parallel to a given axis (polarization axis)
B field is polarized too + 90 degrees away
incoming light polarized vertically
light pass thru his sample
came out polarized a few degrees out of vertical
tldr optical roation
pasteur studied tartaric acid’s effect on polarized light and found that
the theoretical black body
the perfect absorber and emitter of radiation
the quantum of energy and his constant h
explained why those sepctra peak
began the quantum science revolution
Max Planck’s new theory of black body radiation introduced ___
circular shape
slope angle can vary from steep to very gradual
they are like a stack of circles of steadily increasing radius
for a “right cone” the symmetry axis for the stack of circles is perpendicular to the plan of each circle
what do you know about cones?
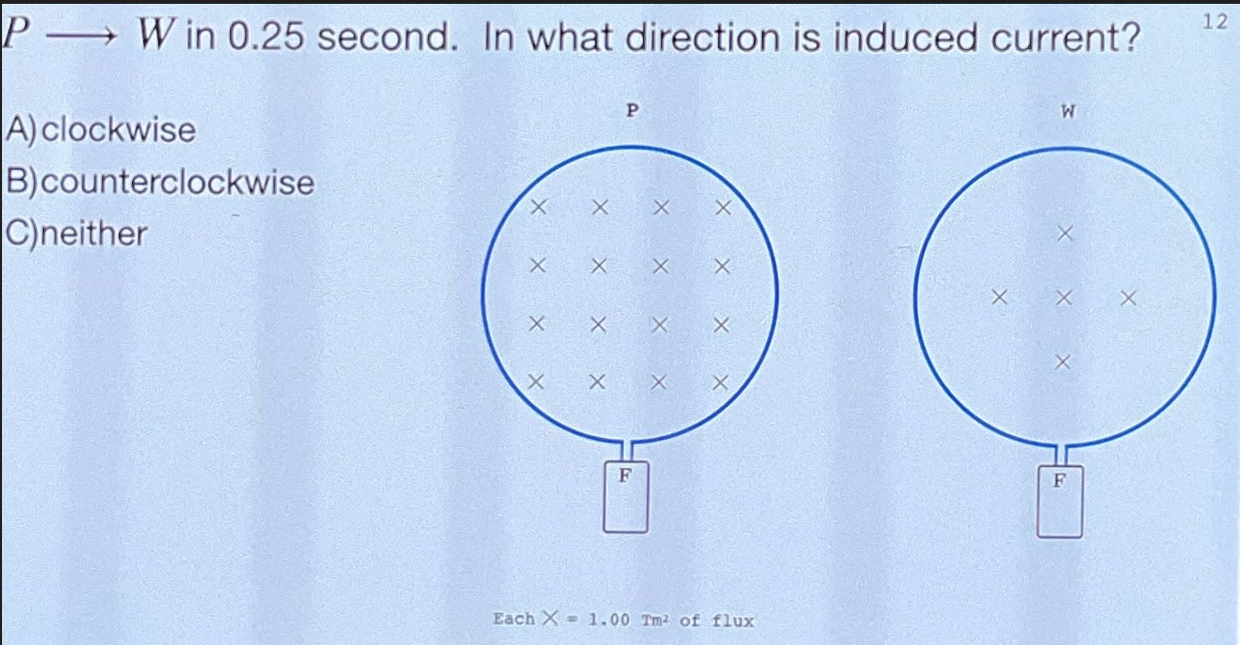
clockwise
it is losing inward flux → needs more = thumb points inward = clockwise current
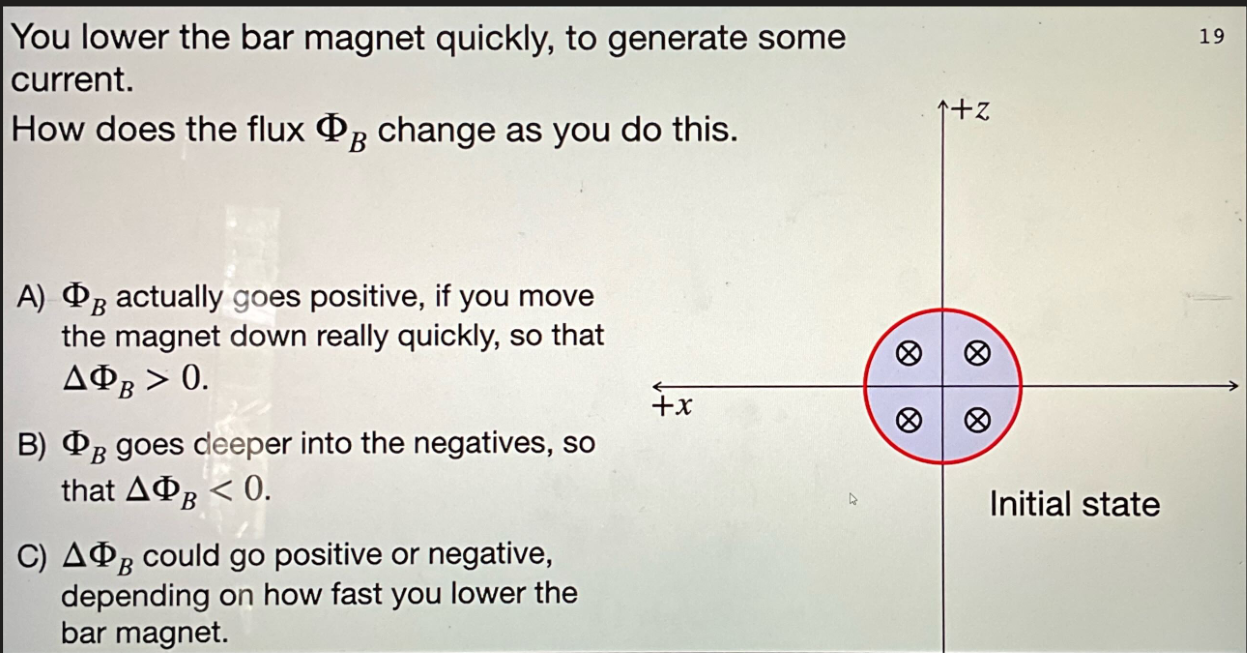
flux goes deeper into the neg so that change in flux is < 0
room temp: 295 K
sun temp: 5800 K
room temp and the temp of the sun in Kelvin
emf induced by an inductor
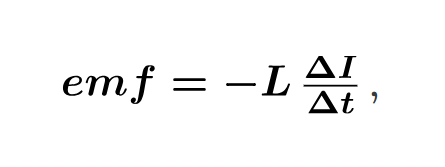
ground state: n=1
excited states: n = 2,3,4
ground state vs excited state
quantum theory
only a few orbital levels of hydrogen are allowed
electrons only live at certain specific “altitudes” & no others
H-alpha photon
when the electron de-orbits from n=3 to n=2 it loses energy which goes into a photon
Quantum theory of hydrogen
as an electron drops to lower EPE orbit, it emits a photon w/ missing energy
E=ħω
false
true or false: an electron can drop lower than it’s ground state
only the assumption of specific quantized oscillation would fit the data
E=hf for an oscillator of frequency f
einstein said ditto for photons
Planck’s quantum of energy proposed
only certain orbits and ħ allowed = why the f and λ are quantized
Planck’s quantum of energy concluded
smallish atom: constructive interference and diffraction is observable
realllyyyy small atom: diffraction effecrs will not be observable as you pull it out of your pocket
smallish atom vs realllyyyy small atom
you get small inerference which is not observable
if the opening is much much larger than the wavelenth then ____
ħ
each quantum leap is a jump between ellipses in a phase diagram for the electron and the area decrease or increases by a multiple of ___
orbital size
ħ and λ → selects the ____
hf
orbital size controls ΔEPE which = __